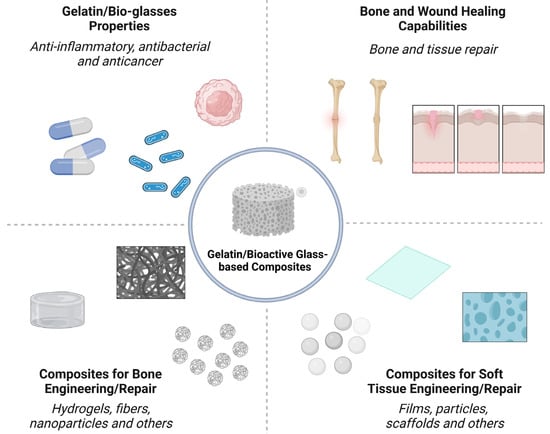
Nano-/micron-sized bioactive glass (BG) particles are attractive candidates for both soft and hard tissue engineering. They can chemically bond to the host tissues, enhance new tissue formation, activate cell proliferation, stimulate the genetic expression of proteins, and trigger unique anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer functionalities. Composites based on biopolymers and BG particles have been developed with various state-of-the-art techniques for tissue engineering. Gelatin, a semi-synthetic biopolymer, has attracted the attention of researchers because it is derived from the most abundant protein in the body, viz., collagen. It is a polymer that can be dissolved in water and processed to acquire different configurations, such as hydrogels, fibers, films, and scaffolds.
Nano-/micron-sized bioactive glass (BG) particles are attractive candidates for both soft and hard tissue engineering. They can chemically bond to the host tissues, enhance new tissue formation, activate cell proliferation, stimulate the genetic expression of proteins, and trigger unique anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer functionalities. Composites based on biopolymers and BG particles have been developed with various state-of-the-art techniques for tissue engineering. Gelatin, a semi-synthetic biopolymer, has attracted the attention of researchers because it is derived from the most abundant protein in the body, viz., collagen. It is a polymer that can be dissolved in water and processed to acquire different configurations, such as hydrogels, fibers, films, and scaffolds.
- bioactive glass
- gelatin
- tissue engineering
- bone
1. Introduction
2. Bone Engineering
Bone tissue is one of the largest systems present in living organisms [37]. It differs from other tissues in that it is in a constant process of reconstruction, as some parts of the bone are absorbed, others are excreted and/or remodeled as a result of the dynamics of osteoblastic, osteolytic, and osteoclastic cells [7][11][37][7,11,37]. Bone is a natural composite, with about 70% of its composition consisting of inorganic phases based on calcium and phosphate salts. The other fraction is organic, predominately composed of type I collagen, but proteins such as proteoglycans and glycoproteins are also present. The tissue morphology is also heterogenous as it consists of some compact/dense regions (cortical bone) and other porous/spongy (trabecular bone) regions [1][38][39][1,38,39].2.1. Bone Healing Mechanisms
When bone is damaged, whether as a result of bone loss, fractures, disease, or any other type of injury, phenomena such as hemorrhage, matrix destruction and cell death occur. From this, the regeneration process can be summarized in three continuous and simultaneous phases: inflammation, regeneration, and remodeling [5][11][5,11]. Initially, macrophages eliminate cellular and tissue debris. Then, new osteoprogenitor cells begin to proliferate, forming connective tissue, “glue”, between the ends of the injured region [7]. Gradually, a “bone callus” is formed at the site (Figure 2), which is replaced by a secondary structure similar in shape to the one that previously existed [37].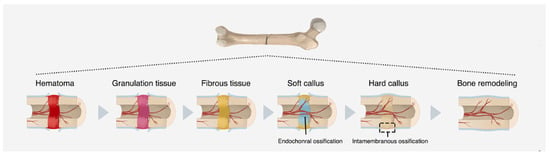
2.2. Orthopedic Clinical Challenges
For hundreds of years, prosthetic implants utilized metals and their alloys with a primary emphasis on titanium, cobalt-chromium, and stainless steel. These metals had good mechanical performance but were subject to corrosion and lacked osteointegration [10][14][43][44][10,14,43,44]. From the end of the 20th century, with the creation of the tissue engineering concept, studies were directed towards the search for materials that exhibit chemical similarity with the tissue, maintain the mechanical stability of the host and lead the tissue regeneration process [43][45][43,45]. However, orthopedic problems still represent an emerging and global issue. In the 2019 World Health Organization report, injuries caused by trauma occupy the second position in the ranking of the main causes of death in the world [46]. Critical-sized bone defect healing represents one of the most significant unmet obstacles in bone regeneration. Originally, bone grafting was used to repair defects caused by tumors, traumatic fractures, and other types of injuries [41]. However, the technique has limitations associated with prohibitive costs and potential damage to health, resulting from infection, inflammation, or immunological rejection at the implant site [5][47][5,47]. Biomaterials are used to repair these defects and restore structure and function, often by acting as a substitute for the missing bone. The optimal characteristics for such biomaterials may differ significantly depending on the location of the bone defect and the kind of bone loss (cortical versus cancellous). If a soft biomaterial (e.g., gelatin/BGs composites) is used to fill the cortical lesion instead, a stable plate fixation is necessary to provide mechanical stability. In such a circumstance, the patient will need to be able to move around freely, which requires a rapid change of the softer biomaterial into cortical bone. In most cases, implant loosening or fatigue failure should not occur until after bone growth and consolidation have occurred. If this race is lost, incomplete osteosynthesis leads to nonunion and implant failure [48][49][50][48,49,50]. Bone loss or resection due to a tumor or infection can also result in critical-sized defects. Bone replacement is an integral aspect of treatment in these scenarios. It would be beneficial if a biomaterial could deliver substances that cure the underlying disease that causes bone loss. This functionalization of biomaterials may become one of the most important progresses in biomaterials research. Treatment for bone abnormalities following infection typically entails two or more phases of revision surgery, with antibiotic-loaded bone cement spacers used between procedures. In this case, a vascularized fibular graft is used to bypass the donor site morbidity of the autologous bone graft by using a biomaterial with bone regeneration capabilities for large defects and the elution of antibiotics [51][52][53][51,52,53]. Another problem is bone abnormalities in seniors because of low-impact fractures. Significant deformities sometimes result from several fractures in these people, with the underlying cause often being an osteopenic bone weakness. A commuted fracture most often occurs in the proximal femur, proximal humerus, or vertebral body. Limited bone quality in the remaining bone makes rigid fracture fixation by standard instrumentation difficult. Bone grafting, either autologous or allogeneic, is frequently used to repair these types of abnormalities, which can lead to arthroplasty in the future. Methods of enhancing bone regeneration are desperately needed considering the aging of the population and the rise in late-life activity. Given this, it is easy to appreciate the pressing need for novel therapies that give surgeons the tools they need to facilitate rapid and reliable bone regeneration in their patients [54][55][56][54,55,56].3. Soft Tissues Engineering
Soft tissues are present in all organs that make up the body, being distinguished into four types: epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous. The epithelial tissue (or epithelium) lines the surfaces and body cavities and has the function of secreting substances. Connective tissue is located below the others, acting to support and sustain them. Muscle tissue, in turn, is responsible for body movements induced by cells capable of contracting. Nervous tissue establishes the connection between external and internal stimuli to the organism, enabling the performance of activities with different levels of complexity [37][40][37,40]. In this section, skin lesions, which predominantly consider the epithelial and connective tissues, will be discussed in greater depth. The skin is considered the largest organ in the body. It plays an immunological role, as it acts as a mechanical, physical and chemical barrier, protecting internal structures against infections and injuries of different nature, such as cuts, traumas, burns and ulcers [57]. In addition to functioning as an “envelope” for the body, the skin regulates moisture loss and changes in body temperature while also acting as natural mechanism to promote the reconstitution of its structure when damaged, which makes up the wound healing cascade [6][58][6,58]. The skin’s immune mechanism can be subdivided into two parts that are connected to each other and synchronized with the body’s immune system as a whole: the epidermal region and the dermal region. Both generate a favorable environment for the performance of immune cells, but also coexist cells responsible for continuous tissue maintenance and regeneration. Fibroblasts stand out as a predominant lineage in connective tissues in general, whose functions include locomotion capacity, collagen fiber production and extracellular matrix (ECM) renewal [59].3.1. Wound Healing Mechanisms
The wound healing process occurs in well-defined phases, involving different cell types and metabolisms. Three overlapping steps are known: inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling [8][60][8,60]. Some classifications consider separately a hemostasis stage, totaling four, briefly described below and illustrated in Figure 3. The initial stage precedes inflammation and results in bleeding interruption from clot formation (hemostasis). In this scenario, activated platelets secrete cytokines that attract inflammatory cells and other populations to the wound site [58].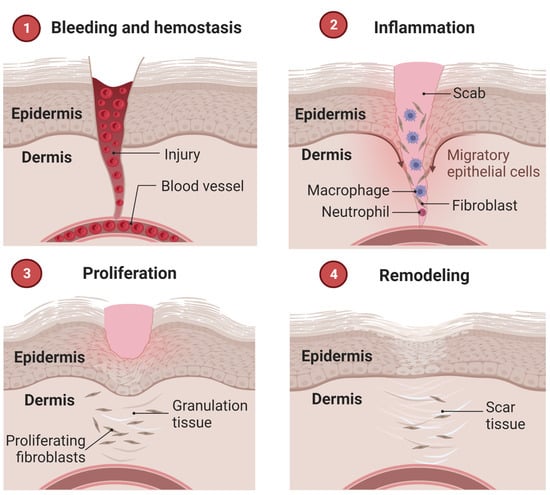
3.2. Therapeutic Approaches in Wound Repair: A Brief Introduction
To repair injuries caused to soft tissues (Figure 4a) as a result of trauma, diseases and/or accidents, one of the most used practices over time is grafting, as for hard tissue. For wound care, costs exceed $50 billion annually to serve more than 5.7 million people in the United States alone [13]. When the wound does not heal on its own, standard therapy includes debridement and skin grafting once the granulation tissue has formed [65].