Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Giovanni Nicola Roviello and Version 2 by Amina Yu.
Willardiine was first identified by Rolf Gimelin in 1959 from the extracts of seeds of Acacia willardiana. Structurally it corresponds to (2S)-2-amino-3-(2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)propanoic acid (1) and carrying an uracil moiety it can be ascribed to the category of nucleoamino acids. Willardiine is synthesized by the single specific enzyme uracilylalanine synthase, and the N–heterocyclic moiety uracil obtained by the orotate pathway proved to be an effective bioisostere for the distal carboxyl group of L-glutamate. Different aspects on both chemistry and biotechnological applications of willardine/willardine-analogues and nucleopeptides will be reviewed in therein.is work
- willardiine
- kainate receptor
- nucleopeptide
- peptide
- nucleobase
1. Introduction
Willardiine was first identified by Rolf Gimelin in 1959 from the extracts of seeds of Acacia willardiana [1]. Structurally it corresponds to (2S)-2-amino-3-(2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)propanoic acid (1, Figure 1) and carrying an uracil moiety it can be ascribed to the category of nucleoamino acids [2][3][4][2,3,4]. Willardiine is synthesized by the single specific enzyme uracilylalanine synthase, and the N–heterocyclic moiety uracil obtained by the orotate pathway [5] proved to be an effective bioisostere for the distal carboxyl group of L-glutamate [6].
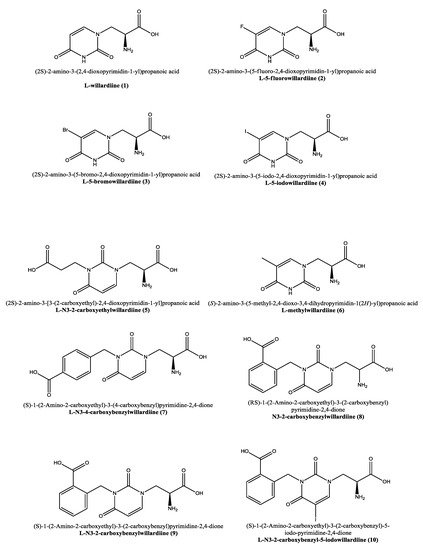
Figure 1. Molecular representation of the structures of willardiine and some of its analogues. IUPAC and use names are reported alongside with the numbering used in thereinis manuscript.
This is the main excitatory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) and mediates its actions through a variety of metabotropic (G-protein coupled) and ionotropic (ligand-gated cation channels) receptors [7]. Among the others, ionotropic glutamate receptors are proteins present in almost all mammalian brain structures at the excitatory synapses that facilitate signal transmission in the central nervous system mediating the fast excitatory neurotransmission, and are involved in human nervous system development and function, with their dysfunction being correlated with several CNS disorders [8][9][10][11][12][13][8,9,10,11,12,13]. Mechanistically, antagonists of ionotropic glutamate receptors prevent the closure of the bilobed ligand-binding domain while full agonists close it. In fact, extracellular cleft closure of ionotropic glutamate receptors is associated with receptor activation; however, the mechanism underlying partial agonism is not necessarily linked to the blockade of the full receptor cleft closure; instead, partial agonists more likely destabilize the cleft closure as suggested by in silico studies [14]. There are three types of ionotropic glutamate receptors: the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, a glutamate receptor and ion channel present in neurons, and the α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid (AMPA) [15] and kainate receptors [16][17][18][16,17,18]. It was demonstrated that in mammalians 1 agonizes non-NMDA glutamate receptors acting as a partial agonist of ionotropic glutamate receptors [19] and in particular activates the AMPA receptors [20][21][22][20,21,22].
Similar to willardiine, its analogues (Figure 1) often act as agonists of AMPA and kainate receptors, but due to their different binding affinities for each receptor, they have been employed not only to investigate the structural and functional consequences of activation of AMPA/kainate receptors, but also to determine the structural modifications required in order to convert 1 into an antagonist at AMPA and kainate receptors [23].
2. Disease Relevance and Potential Pharmaceutical Role
Willardiine analogues may bind specifically to kainate and AMPA receptors, which are implicated in a variety of neurological disorders characterized by alterations in glutamate signaling. For example, the selective antagonists for glutamate receptor subtypes disclose therapeutic importance for a variety of neurological disorders characterized by aberrant activation of kainate or AMPA receptors. Though far from being exhaustive, in the following section we report on some neurological disorders characterized by dysregulation in either AMPA or kainate receptor activation will be reported.
2.1. AMPA Receptors in Neurological Disorders
AMPA receptors are particularly implied in neurodegenerative disorders through their connection with synaptic plasticity, which plays a fundamental role in many physiological aspects of cognitive abilities but also in neural development [24][26]. Many neuropathies are associated with the cognitive decline, which in turn is linked to changes in AMPA-mediated plasticity [25][26][27,28]. In animal models of Parkinson’s disease, enhanced levels of AMPA receptors have been revealed in affected regions, while AMPA antagonists have been proposed as potential therapeutics. However, the benefits of inhibiting AMPA receptors with respect to curing the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease do not always justify the use of this strategy that can cause severe off-target effects [27][28][29,30]. On the other hand, AMPA receptor deficits have been correlated with Huntington’s disease, that causes the progressive degeneration of neural cells in the brain [29][31], as demonstrated in studies conducted in human postmortem tissues and animal models. In particular, modulating AMPA receptors in animal models led to a decrease of degeneration in both the striatum and memory deficits [27][29]. Moreover, genetic alterations leading to AMPA receptor GluA2 subunit defects were correlated with autism spectrum disorders [30][32]. The role of AMPA receptors in autism is also supported by the effectiveness of the pharmacological modulation of this type of receptors which rescued social impairments in animal models [31][33]. Among the many hypotheses about the biological basis of the major depressive disorder, the glutamate hypothesis was corroborated by the evidence that NMDA receptor antagonists blocking the activation of NMDA receptors, and thus causing the AMPA receptor activation to compensate for the decrease in glutamate signaling, have antidepressant effects in animal models [32][34]. Interestingly, AMPA receptors mediate also the dysregulated sleep, that is a major symptom of major depressive disorder [33][35].
2.2. Kainate Receptors in Neurological Disorders
Recent biochemical and behavioral studies suggest a key role for the kainate receptor GluK2 in controlling abnormalities related to the behavioral symptoms of mania, such as psychomotor agitation, aggressiveness and hyperactivity [34][36], while the kainate receptor GluK3 was associated with recurrent major depressive disorder [35][37]. Kainate receptors are expressed in regions of spinal cord implied in the transmission of sensory stimulation and pain, and their functional dysregulation was linked to pain [36][37][38,39]. Several studies led to a variety of linkages between epilepsy and kainate receptors including different and sometimes contradictory mechanisms that clearly demonstrate the difficulty in studying kainate receptors in this respect [37][38][39][39,40,41].
3. Molecular Insights on Bioactivity of Willardiine analogues
As anticipated, willardiine is a partial agonist of ionotropic glutamate receptors [14] and specifically, agonizes non-NMDA glutamate receptors in particular activating the AMPA receptors [15][16][17][15,16,17]. In analogy to willardiine, its most common analogues are also agonists of kainate/AMPA receptors. The addition of a halogen to the uracil moiety affects the binding affinities and stability of the analogues that are generally more stable than 1 and show higher binding affinity for AMPA receptors. Extensive research has been conducted on the 5-fluorowillardiine (2, Figure 1) that showed limited effects at the kainate receptor but acted as a selective agonist of the AMPA receptor and is widely employed in vitro to selectively stimulate AMPA receptors [40][41][42][43][44][45][46][42,43,44,45,46,47,48]. The activity of the halogen-based analogues 2–4 (Figure 1) at AMPA/kainate receptors was also assayed using mouse embryonic hippocampal neurons [40][42]. In particular, 5-bromowillardiine (3) acted as a potent agonist, and led to rapid but incomplete desensitizing responses. As for the 5-iodowillardiine (4) it resulted a selective kainate receptor agonist [47][49]. On the other hand, 2 with an 1.5 µM EC50 was seven times more potent than AMPA (EC50 = 11 µM) and 30 times more potent than 1 (EC50 = 45 µM); as for the potency sequence within the explored halogen derivatives the observed trend was F(2) > Br(3) > I(4) > willardiine (1, Table 1) [40][42].
Table 1.
Steady-state EC
50
1
for AMPA/kainate receptor activation by willardiines.
| Compound | EC50 (μM) | ±SD |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 44.8 | 15.0 |
| 2 | 1.47 | 0.39 |
| 3 | 8.82 | 1.29 |
| 4 | 19.2 | 1.92 |
Moreover, cross-desensitization experiments revealed that halogen-bearing willardiines bind with different affinity to desensitized receptors that are the same receptors activated by kainate and AMPA, and the rapidly desensitizing and equilibrium responses to the analogues under investigation were mediated by the same receptors. However, they produced different degrees of desensitization with the desensitization sequence being F(2) > willardiine (1) > Br(3) > I(4). More in detail, the Iodine-containing derivative (4) blocked the activation of the desensitizing response elicited by 1 and 2, while 1 and 2 blocked the equilibrium response to 4. It was possible to conclude that simple changes in the molecular structure of willardiine can lead to marked differences in the ability of agonists to produce desensitization of AMPA/kainate receptors [40][42].
The thermodynamics connected with the interaction of willardiine and its analogues with the ionotropic receptors was studied in order to obtain useful insights exploitable for new drug design [36][38]. For example, analogues of willardiine modified at position 5 with F, Cl, I, H and NO2 led to deeper insights on the thermodynamics of the interaction of willardiine with AMPA receptors [48][50]. The binding of willardiine analogues to subtypes of the AMPA receptor was, in some cases, driven by increases in entropy. The major part of the studied analogues were partial agonists whose charged state was found in direct connection with the enthalpic contribution to the interaction [36][38]. In particular, the binding of the charged forms to AMPA receptor is driven essentially by enthalpy, while the interaction of the uncharged form is largely dominated by the entropic contribution due to changes in the hydrogen-bonding network within the binding site, with these findings providing clues for further neurodrug development [36][38].
Interestingly, the carboxyethyl derivative of willardiine (5) was found to act as antagonist of the AMPA receptor and more in detail, the crystal structure of the GluR2 binding domain of this receptor, which is crucial for mediating its calcium permeability, in complex with 5 was described in the literature (Figure 2a,b) [49][51].
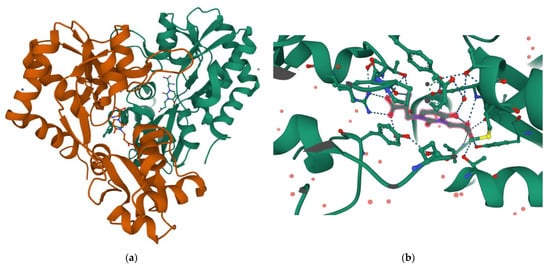
Figure 2. (a) 3D view of the crystal structure of the complex between the binding domain of the AMPA subunit GluR2 and 5 (PDB DOI: 10.2210/pdb3H03/pdb PDB ID: 3H03 https://www.rcsb.org/3d-sequence/3H03?assemblyId=1, accessed on 29 August 2022); (b) Detailed view of the ligand interaction in the same complex (for more details on protein residues involved in the binding see the link https://www.rcsb.org/3d-view/3H03?preset=ligandInteraction&label_asym_id=E, accessed on 29 August 2022). Note how the amino acid COOH forms a double H-bond with Arg93, while the ethyl COOH forms H-bonds with Tyr187 and Thr171.
This compound binds to one lobe of the protein with interactions similar to agonists, while the binding with the second lobe produces a stable lobe orientation that is similar to the apo state. The carboxyethyl substituent in the N(3) position of 5 keeps the protein lobes separated and the internal dynamics are minimal compared to the protein bound to the reference antagonist 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione, which minimizes the contacts with one of the two lobes. This latter complex is less stable than that observed with 5 despite a 100-fold higher affinity [43][45]. Overall, the study with 5 suggests that the antagonism of willardiine analogues is associated with the overall orientation of the lobes of the AMPA receptor rather than with specific interactions [43][45]. Another study [23] conducted on a range of novel willardiine analogues as antagonists acting at AMPA and kainate receptors suggested that for a derivative to act as AMPA/kainate receptor antagonist, an N3-substituent bearing a carboxylic acid (like in 5) side-chain is needed, the S-stereochemistry should be present in the derivative and a iodine added to the 5-position of the uracil moiety enhances antagonism at kainate receptors. Moreover, in the same study the 3-methyl analogue 6 (Figure 1), was found to be a weak agonist, indicating that merely blocking ionisation of the uracil ring of willardiine even though decreases the agonist activity is not sufficient to convert the analogue into an antagonist [23]. Aiming at developing new antagonists of kainate/AMPA receptors also N3-carboxybenzyl substituted willardiine analogues were synthesized [47][49]. The N3-4-carboxybenzyl derivative (7) proved to be equipotent at AMPA and kainate receptors in the rat spinal cord. The racemic N3-2-carboxybenzyl analogue (8) was found to be a potent and selective kainate receptor antagonist in experiments conducted on native rat and human recombinant kainate and AMPA receptors. More in detail, the kainate receptor antagonist activity was de[1]monstrated to reside essentially in the S enantiomer (9). 5-Iodo substitution of the uracil ring of 9 gave 10, which proved to have enhanced selectivity and potency for the kainate receptor [47][49].
References
- Gmelin, R. Die freien Aminosäuren der Samen von Acacia Willardiana (Mimosaceae). Isolierung von Willardiin, Einer Neuen Pflanzlichen Aminosäure, Vermutlich L-Uracil--(3). Hoppe-Seyler’s Zeitschrift für Physiol. Chem. 1959, 316, 164–169. Rosanna Palumbo; Daniela Omodei; Caterina Vicidomini; Giovanni N. Roviello; Willardiine and Its Synthetic Analogues: Biological Aspects and Implications in Peptide Chemistry of This Nucleobase Amino Acid. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1243, 10.3390/ph15101243.
- Lorenz, K.B.; Diederichsen, U. Nucleo amino acids as arginine mimetics in cyclic peptides. Lett. Pept. Sci. 2003, 10, 111–117.
- Cheikh, A.B.; Orgel, L.E. Polymerization of amino acids containing nucleotide bases. J. Mol. Evol. 1990, 30, 315–321.
- Musumeci, D.; Ullah, S.; Ikram, A.; Roviello, G.N. Novel insights on nucleopeptide binding: A spectroscopic and In Silico investigation on the interaction of a thymine-bearing tetrapeptide with a homoadenine DNA. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 347, 117975.
- Negi, V.S.; Pal, A.; Borthakur, D. Biochemistry of plants N–heterocyclic non-protein amino acids. Amino Acids 2021, 53, 801–812.
- Stensbol, T.; Madsen, U.; Krogsgaard-Larsen, P. The AMPA receptor binding site: Focus on agonists and competitive antagonists. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2002, 8, 857–872.
- Kew, J.N.; Kemp, J.A. Ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptor structure and pharmacology. Psychopharmacology 2005, 179, 4–29.
- Yelshanskaya, M.; Sobolevsky, A. Structural Insights into Function of Ionotropic Glutamate Receptors. Biochem. Suppl. Ser. A Membr. Cell Biol. 2022, 16, 190–206.
- Bowie, D. The Many Faces of the AMPA-Type Ionotropic Glutamate Receptor; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; p. 108975.
- Pinzón-Parra, C.A.; Coatl-Cuaya, H.; Díaz, A.; Guevara, J.; Rodríguez-Moreno, A.; Flores, G. Long-term effect of neonatal antagonism of ionotropic glutamate receptors on dendritic spines and cognitive function in rats. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2022, 119, 102054.
- Hu, T.-M.; Wu, C.-L.; Hsu, S.-H.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Cheng, F.-Y.; Cheng, M.-C. Ultrarare Loss-of-Function Mutations in the Genes Encoding the Ionotropic Glutamate Receptors of Kainate Subtypes Associated with Schizophrenia Disrupt the Interaction with PSD95. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 783.
- Bowie, D. Ionotropic glutamate receptors & CNS disorders. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2008, 7, 129–143.
- Negrete-Díaz, J.V.; Falcón-Moya, R.; Rodríguez-Moreno, A. Kainate receptors: From synaptic activity to disease. FEBS J. 2021, 289, 5074–5088.
- Postila, P.A.; Ylilauri, M.; Pentikäinen, O.T. Full and partial agonism of ionotropic glutamate receptors indicated by molecular dynamics simulations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 1037–1047.
- Henley, J.M.; Wilkinson, K.A. Synaptic AMPA receptor composition in development, plasticity and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 337–350.
- Sihra, T.S.; Rodríguez-Moreno, A. Presynaptic kainate receptor-mediated bidirectional modulatory actions: Mechanisms. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 982–987.
- Rodríguez-Moreno, A.; Sihra, T.S. Metabotropic actions of kainate receptors in the control of glutamate release in the hippocampus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 717, 39–48.
- Sihra, T.S.; Rodríguez-Moreno, A. Metabotropic actions of kainate receptors in the control of GABA release. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 717, 1–10.
- Neto, J.X.L.; Fulco, U.L.; Albuquerque, E.L.; Corso, G.; Bezerra, E.M.; Caetano, E.W.; Da Costa, R.F.; Freire, V.N. A quantum biochemistry investigation of willardiine partial agonism in AMPA receptors. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 13092–13103.
- Pasternack, A.; Coleman, S.K.; Jouppila, A.; Mottershead, D.G.; Lindfors, M.; Pasternack, M.; Keinänen, K. α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptor channels lacking the N-terminal domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 49662–49667.
- Kato, A.S.; Gill, M.B.; Yu, H.; Nisenbaum, E.S.; Bredt, D.S. TARPs differentially decorate AMPA receptors to specify neuropharmacology. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 241–248.
- Traynelis, S.F.; Wollmuth, L.P.; McBain, C.J.; Menniti, F.S.; Vance, K.M.; Ogden, K.K.; Hansen, K.B.; Yuan, H.; Myers, S.J.; Dingledine, R. Glutamate receptor ion channels: Structure, regulation, and function. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 405–496.
- More, J.C.; Troop, H.M.; Dolman, N.P.; Jane, D.E. Structural requirements for novel willardiine derivatives acting as AMPA and kainate receptor antagonists. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 138, 1093–1100.
- Huganir, R.L.; Nicoll, R.A. AMPARs and synaptic plasticity: The last 25 years. Neuron 2013, 80, 704–717.
- Kessels, H.W.; Malinow, R. Synaptic AMPA receptor plasticity and behavior. Neuron 2009, 61, 340–350.
- Cheng, G.-R.; Li, X.-Y.; Xiang, Y.-D.; Liu, D.; McClintock, S.M.; Zeng, Y. The implication of AMPA receptor in synaptic plasticity impairment and intellectual disability in fragile X syndrome. Physiol. Res. 2017, 66, 715–727.
- Lee, K.; Goodman, L.; Fourie, C.; Schenk, S.; Leitch, B.; Montgomery, J.M. AMPA receptors as therapeutic targets for neurological disorders. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2016, 103, 203–261.
- Lees, A.; Fahn, S.; Eggert, K.M.; Jankovic, J.; Lang, A.; Micheli, F.; Maral Mouradian, M.; Oertel, W.H.; Olanow, C.W.; Poewe, W. Perampanel, an AMPA antagonist, found to have no benefit in reducing “off” time in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 284–288.
- Walker, F.O. Huntington’s disease. Lancet 2007, 369, 218–228.
- Salpietro, V.; Dixon, C.L.; Guo, H.; Bello, O.D.; Vandrovcova, J.; Efthymiou, S.; Maroofian, R.; Heimer, G.; Burglen, L.; Valence, S. AMPA receptor GluA2 subunit defects are a cause of neurodevelopmental disorders. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3094.
- Kim, J.-W.; Park, K.; Kang, R.J.; Gonzales, E.L.T.; Kim, D.G.; Oh, H.A.; Seung, H.; Ko, M.J.; Kwon, K.J.; Kim, K.C. Pharmacological modulation of AMPA receptor rescues social impairments in animal models of autism. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 314–323.
- Jaso, B.A.; Niciu, M.J.; Iadarola, N.D.; Lally, N.; Richards, E.M.; Park, M.; Ballard, E.D.; Nugent, A.C.; Machado-Vieira, R.; Zarate, C.A. Therapeutic modulation of glutamate receptors in major depressive disorder. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 57–70.
- Shepherd, J.D. Memory, plasticity and sleep-A role for calcium permeable AMPA receptors? Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 5, 49.
- Shaltiel, G.; Maeng, S.; Malkesman, O.; Pearson, B.; Schloesser, R.; Tragon, T.; Rogawski, M.; Gasior, M.; Luckenbaugh, D.; Chen, G. Evidence for the involvement of the kainate receptor subunit GluR6 (GRIK2) in mediating behavioral displays related to behavioral symptoms of mania. Mol. Psychiatry 2008, 13, 858–872.
- Schiffer, H.; Heinemann, S. Association of the human kainate receptor GluR7 gene (GRIK3) with recurrent major depressive disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2007, 144, 20–26.
- Nair, J.D.; Wilkinson, K.A.; Henley, J.M.; Mellor, J.R. Kainate receptors and synaptic plasticity. Neuropharmacology 2021, 196, 108540.
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Guan, Y.; Wang, Y. The emerging role of kainate receptor functional dysregulation in pain. Mol. Pain 2021, 17, 1744806921990944.
- Henley, J.M.; Nair, J.D.; Seager, R.; Yucel, B.P.; Woodhall, G.; Henley, B.S.; Talandyte, K.; Needs, H.I.; Wilkinson, K.A. Kainate and AMPA receptors in epilepsy: Cell biology, signalling pathways and possible crosstalk. Neuropharmacology 2021, 195, 108569.
- Crépel, V.; Mulle, C. Physiopathology of kainate receptors in epilepsy. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 20, 83–88.
- Patneau, D.K.; Mayer, M.L.; Jane, D.E.; Watkins, J.C. Activation and desensitization of AMPA/kainate receptors by novel derivatives of willardiine. J. Neurosci. 1992, 12, 595–606.
- Hawkins, L.; Beaver, K.; Jane, D.; Taylor, P.; Sunter, D.; Roberts, P. Characterization of the pharmacology and regional distribution of (S)--5-fluorowillardiine binding in rat brain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 116, 2033–2039.
- Lunn, M.; Ganakas, A.; Mercer, L.; Lawrence, A.; Beart, P. Localisation and properties of AMPA-insensitive kainate sites: Receptor autoradiography and gene expression in rat brain. Neurosci. Lett. 1996, 204, 121–124.
- Larm, J.A.; Cheung, N.S.; Beart, P.M. (S)-5-fluorowillardiine-mediated neurotoxicity in cultured murine cortical neurones occurs via AMPA and kainate receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 314, 249–254.
- JENSEN, R.J. Responses of directionally selective retinal ganglion cells to activation of AMPA glutamate receptors. Vis. Neurosci. 1999, 16, 205–219.
- Olivera, S.; Rodriguez-Ithurralde, D.; Henley, J.M. Regional localization and developmental profile of acetylcholinesterase-evoked increases in -5-fluorowillardiine binding to AMPA receptors in rat brain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 133, 1055–1062.
- Kessler, M.; Arai, A.C. Use of fluorowillardiine to study properties of AMPA receptor allosteric modulators. Brain Res. 2006, 1076, 25–41.
- Dolman, N.P.; Troop, H.M.; More, J.C.; Alt, A.; Knauss, J.L.; Nistico, R.; Jack, S.; Morley, R.M.; Bortolotto, Z.A.; Roberts, P.J. Synthesis and pharmacology of willardiine derivatives acting as antagonists of kainate receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 7867–7881.
- Martinez, M.; Ahmed, A.H.; Loh, A.P.; Oswald, R.E. Thermodynamics and Mechanism of the Interaction of Willardiine Partial Agonists with a Glutamate Receptor: Implications for Drug Development. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 3790–3795.
- Ahmed, A.H.; Thompson, M.D.; Fenwick, M.K.; Romero, B.; Loh, A.P.; Jane, D.E.; Sondermann, H.; Oswald, R.E. Mechanisms of antagonism of the GluR2 AMPA receptor: Structure and dynamics of the complex of two willardiine antagonists with the glutamate binding domain. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 3894–3903.
More
