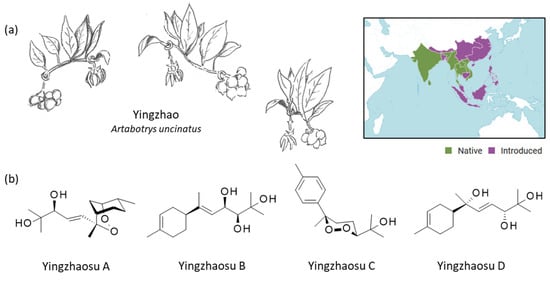
Figure 1. Yingzhao plant and yingzhaosu compounds. (
a) The plant yingzhao (
Artabotrys uncinatus (L.) Meer.) with a view of the young fruits, the leaves and the flower (drawing: Prof. J.-P. Hénichart). The plant is largely distributed in Southeast Asia. The plant is native to countries such as India, Thailand, Vietnam, and Sri Lanka (and other counties in green) and has been introduced in Indonesoia, China, Japan (and other countries in purple) (
https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:72395-1, accessed on 14 September 2022). (
b) Structure of the four yingzhaosu compounds, all isolated from yingzhao.
2. The Plant Yingzhao
The Chinese medicine yingzhao is usually associated with the plant name
Artabotrys uncinatus (L.) Meer. (Annonaceae), from which yingzhaosu compounds have been isolated, as discussed above (
Figure 1). However, and in fact,
A. unciatus is one of the synonyms for the plant
Artabotrys hexapetalus (L.f.) Bhandari, which is the accepted botanical name
[8][13]. Other synonyms are used, such as
A. odoratissimus R.Brown. (
Table 1). This plant, commonly called tail grape or climbing ylang-ylang, can be found in China, India, Malaysia, Indonesia, Vietnam and other countries of Southeast Asia. It is native to Sri Lanka and Southern India and can be grown in many places
[9][14]. For example, two established plants of
A. hexapetalus (L.f.) Bhand. growing at the Fairchild Tropical Garden in Miami (US) have been used to study plant architecture during growth
[10][15]. It can also be found in some tropical African countries, like Tanzania
[11][16].
Table 1.
The plant yingzhao, accepted botanical names and synonyms.
Yingzhao behaves as a woody climber, possibly growing up to 10 m in height. It should not be confused with
Cananga odorata (ylang-ylang) used in perfumery.
A. hexapetalus is a woody scandent climbing shrub. The leaves are oblong to broadly lanceolate in shape and the flowers are fragrant, with yellow petals (
Figure 1). The plant is recognizable from the flower stalks, which are shaped like hooks. With beautiful and aromatic flowers, it is an ornamental plant now cultivated and also used in the perfume industry. The seeds are used for propagation, but the germination process is complex and long, taking as long as 238 days
[12][17]. The plant is appreciated for its pleasant-smelling yellow flowers, from which a delicate essential oil, rich in sesquiterpenoids (such as β-caryophyllene and caryophyllene oxide), can be prepared
[13][18]. Essential oils can also be obtained from the stem bark or leaves of the plant to be used as a mosquito repellent
[11][16].
3. Traditional Medicinal Uses of Yingzhao
For a long time, yingzhao-based preparations have been used to treat human diseases. Different parts of the plant have been used. The symptoms and pathologies treated with plant extracts vary from one country to another. In Malaysia, leaf decoctions were given for curing cholera, whereas the roots and fruits have been used for the treatment of malaria and scrofula (tuberculous lymphadenitis). There is also mention of the use of the plant to treat fever, diarrhea, dysentery, cuts, sprains, ulcers, and asthma.
Recently, Kousalya and Doss
[14][19] have inventoried the diverse ethnomedicinal uses of
A. hexapetalus extracts. These can range from antibacterial and antifungal effects to hepato-protective and anti-ulcer activities (
Table 2). In general, the pharmacological effects were obtained with organic extracts prepared from the plant’s leaves, bark, or roots. For example, methanolic leave extracts were found to display antifungal and antibacterial effects
[15][16][17][20,21,22]. The essential oil of
A. odoratissimus R.Br. (synonym) has shown a broad-spectrum activity against 14 different storage fungi, and interestingly, it was reported to arrest aflatoxin B1 secretion by a toxic strain of
Aspergillus flavus [18][23]. Flower extracts of
A. hexapetalus also revealed antifungal effects
[19][24].
Table 2.
Pharmacological properties of
A. hexapetalus
extracts.
Alcoholic leave extracts display cytoprotective effects in vitro and in vivo. An ethanolic extract orally administered (100–200 mg/k for seven days) to mice with drug-induced liver injury was found to reduce the oxidative damages at least at the biochemical level and to alleviate the sign of cellular degeneration and necrosis. The extract was well tolerated in mice
[35][40]. The observed effects were attributed to the presence of antioxidant natural products, including flavonoids and alkaloids. Similar antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects have been reported in other studies with
A. hexapetalus extracts
[24][32][33][29,37,38].
The hydroalcoholic leave extracts of
A. hexapetalus have been found to reduce sperm count and mobility in rats, reducing the diameter of seminiferous tubules. The extract lowered the testosterone level and significantly reduced fertility in rats
[28][33]. The observation was consistent with the reported antifertility activity of various leaf extracts of
A. odoratissimus Roxb. (synonym). In this case, the extracts (obtained with benzene, ethanol and water) were found to disturb the oestrus cycle and reduce implantation and thus fertility
[26][31]. Antifertility activity has been confirmed in a recent study performed with extracts from the leaves and stem of
A. odoratissimus Roxb. in female rats. The extracts altered the level of cholesterol and steroidal hormones (estradiol and progesterone) and caused polycystic ovaries in rats
[28][29][33,34]. In India, antifertility activity of
A. odoratissimus plant extracts is known for several decades
[36][37][41,42] and remains considered today for the regulation of fertility
[30][35].
The main bioactivity of
A. hexapetalus refers to antiparasitic effects. For a long time, yingzhao (roots and fruits) has been used to combat parasites such as
Plasmodium falciparum and
Leishmania donovani. A petroleum ether extract of
A. hexapetalus was shown to moderately reduce the growth of the promastigote forms of cultured
L. donovani. The effect was attributed to the presence of flavonoids such as quercetin and apigenin
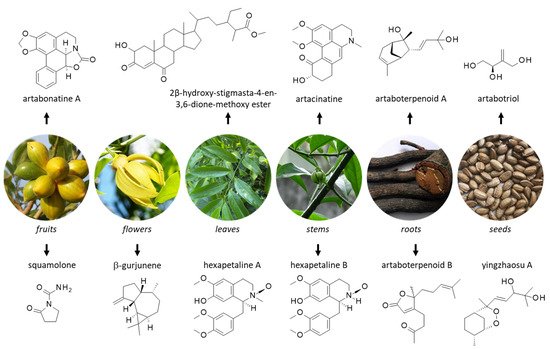
[23][28]. Notwithstanding, there are many other flavonoids in the plant extracts, such as taxifolin, apigenin glycosides, glucoluteolin, arabotrysides A and B (
Figure 2), and the flavonol glycosides called arapetalosides A and B
[38][39][43,44]. Hydroalcoholic leaf extracts of
A. hexapetalus display activities against
Plasmodium and
Leishmania, but not against the African earthworm
Eudrilus eugeniae (African nightcrawler)
[22][23][27,28]. It should be noted that there is not many published information about the antiplasmodial activity of
A. hexapetalus. Solid data have been reported with other species, such as
A. crassifolius [40][45], but not for yingzhao extracts despite the traditional use.
Figure 2. Structure of selected natural products isolated from different parts of yingzhao. Detailed botanical information on yingzhao can be found at
http://www.instituteofayurveda.org/plants/plants_detail.php?i=75&s=Local_name (accessed on 14 September 2022).
Occasionally, other pharmacological effects have been reported. For example, a recent study underlined the antiproliferative activity of
A. odoratissimus fruit extract against MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cells. The organic (ethyl acetate) extract reduced cell growth, revealed an antioxidant effect, and induced apoptotic cell death associated with DNA damage
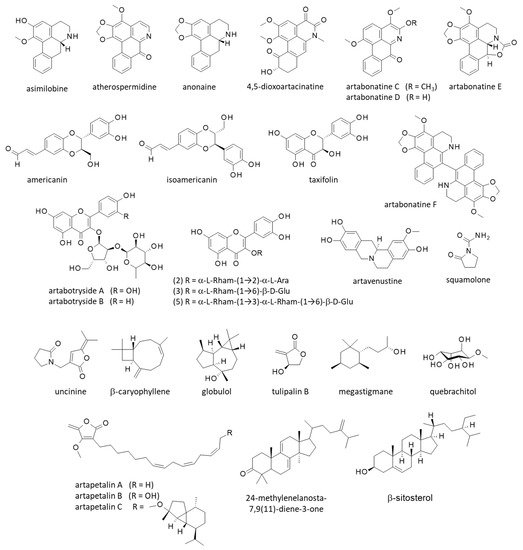
[31][36]. The phytochemicals at the origin of the anticancer action were not specified, but it could be linked to the presence of cytotoxic alkaloids. More than 25 alkaloids have been isolated from
A. uncinatus (synonym), including cytotoxic oxoaporphines and other alkaloids endowed with cytotoxic effects such as atherospermidine and squamolone (
Figure 3)
[41][42][46,47].
Figure 3.
Structure of other natural products isolated from yingzhao.
The multiple bioactive properties evidenced by extracts of the plants stimulate research and the elaboration of novel bioinspired products. For example, silver nanoparticles have been made using an aqueous extract of
A. hexapetalus with the objective to propose new bactericide products
[25][30]. There are also non-medicinal usages of the plant extracts. For example, the plant leaf extract has shown anticorrosion activity. It could be used as an eco-friendly green inhibitor for acidic-induced corrosion of mild steel
[43][44][48,49].