Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Hugo Albrecht and Version 2 by Camila Xu.
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest family of membrane receptors, and many are overexpressed in solid tumors, including ovarian cancer.
- ovarian cancer
- G protein-coupled receptor
- GPCR
- nanoparticle
- drug delivery
- active targeting
1. Introduction
The symptoms of ovarian cancer are non-specific, and due to a lack of effective screening strategies, it is generally not detected at an early stage when the tumor is still confined to the organ of origin. Resultingly, 70% of patients are diagnosed when their ovarian cancer has progressed to advanced stages (III or IV). The epidemiology of ovarian cancer is very complex and is affected by various factors, including the status of inherited and acquired somatic mutations, hormonal effects during menopause, environmental hazards, pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, and polycystic ovarian syndrome [1]. Effective disease management is extremely challenging, with an overall 5-year survival rate of less than 50%, in comparison to 91% for breast cancer. Only 25% of women with advanced stage ovarian cancer will survive for longer than 5 years.
The current frontline treatment for ovarian cancer includes debulking surgery, followed by dual carboplatin plus paclitaxel chemotherapy to kill residual tumor tissue [2]. The drugs are generally administered intravenously, or according to some treatment protocols, intraperitoneally (IP) [3]. In some patients, good results have also been achieved via a neoadjuvant approach, providing chemotherapy prior to surgical intervention. Whilst approximately 80% of patients who receive the first-line standard treatment of carboplatin plus paclitaxel will respond, often with apparent complete remission, the majority of patients relapse, and about 20% of patients do not respond to the treatment at all, meaning they possess an innate form of chemotherapy resistance [4][5][4,5]. Moreover, the currently used treatments are associated with severe and dose-limiting adverse effects.
To achieve treatments with improved therapeutic indices, several specific molecular therapies have been introduced into the clinic. Poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibition is now used as a strategy against tumors with germline or somatic BRCA1/2 and other DNA repair gene mutations [6][7][6,7]. Olaparib was the first PARP inhibitor to gain FDA approval and was followed by others, such as Rucaparib and Niraparib [8]. Administration of these inhibitors can cause severe and dose-limiting hematologic adverse effects, such as thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and anemia [8]. Grade 3/4 toxicities have been reported to force dose interruptions and reductions [9]. Apart from other mild side effects, increased frequencies of myeloblastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia have also been observed [10]. Another treatment strategy employs Bevacizumab as antibody-based, anti-angiogenic therapy, as maintenance therapy in the adjuvant setting, or in combination with other chemotherapy drugs such as liposomal doxorubicin or gemcitabine at recurrence [11]. An alternative anti-angiogenic is the kinase inhibitor Cediranib, an inhibitor of VEGFR-1, -2, -3, and c-kit. Additional novel therapies under investigation include vaccines [12], CAR-T immunotherapy, anti CA125 antibody therapy, and viral and small molecule immune checkpoint inhibitors [13][14][15][16][17][18][13,14,15,16,17,18].
2. Harnessing GPCRs to Target Ovarian Cancer Cells with Nanomedicines
Many tumors have been shown to aberrantly express GPCRs and the overwhelming complexity of an underlying signaling network has been discovered [19][20][21][22][23][174,175,176,177,178]. The clinical relevance of GPCR expression in the case of ovarian cancer is highlighted by its effects on cell growth, migration, metastasis, invasion, survival, metabolism, and secretion [24][25][26][179,180,181]. Many GPCRs are expressed in stromal, immune, and endothelial cells of ovarian cancer tissue where they play important roles in tumor growth via stimulation of angiogenesis and other mechanisms. In addition to this, β arrestin 2 expression has been associated with impaired prognosis, hence further boosting the role of GPCRs [27][182]. On one hand, small molecule-mediated modulation of GPCRs presents a potentially rewarding avenue towards novel anti-cancer solutions; whilst on the other hand, and in context with the presented resviearchw, the functional overexpression of these receptors lends itself to the targeting of cancer tissues with ligand decorated nanomedicines. Ovarian cancers are genetically unstable, most often due to mutations in DNA repair genes (e.g., BRCA1/2) and in the tumor protein P53 gene [28][183]. The latter is prevalent in ~96% of serous ovarian cancer cells, driving chromosomal instability and leading to aberrant gene expression [29][184]. Considering that GPCRs are distributed throughout the genome, it is expected that some become frequently overexpressed when healthy cells turn into neoplastic cells. As shown in Figure 13, many GPCR loci are close to copy number alterations (CNAs) or on frequently amplified chromosome arms 1q, 3q, 6p, 7q, 8q, 12p, 20p, and 20q [30][185]. Although the detailed mechanisms are poorly understood, many GPCRs are very likely to be upregulated within amplicons or as a consequence of chromosomal translocations. Alternatively, the gene expression can be triggered indirectly through upregulated signaling pathways. Whilst some genetic loci may be hotspots for gene amplification and chromosomal translocations, others may be infrequent or at random. Therefore, the basic concept to harness overexpressed GPCRs as molecular entry sites requires a personalized approach, as further discussed in Section 6.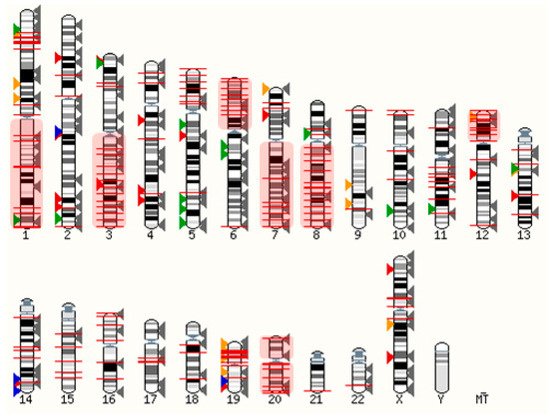
Figure 13. Distribution of GPCRs and copy number alterations (CNA on genome). All GPCRs (except olfactory receptors) are indicated with arrowheads. Overexpressed receptors are shown in color, according to Table 13. Red: Peptide and protein activated receptors; Orange: Lipid receptors; Green: Adrenergic receptors; Blue: Ionic receptors; Grey: Not frequently overexpressed in ovarian cancer (310 receptors). The red lines indicate 2902 CNAs with frequencies ranging from 5%–34% (from TCGA, Pan Cancer Atlas, 572 ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma samples; accessed via cBioportal [31][32][199,200] on 3 March 2022). Frequently amplified chromosome arms 1q, 3q, 6p, 7q, 8q, 12p, 20p, 20q are shown in red shaded boxes. The human karyotype figure was generated using Ensembl 2021 [33][201].
2.1. Ionic GPCRs
G-protein coupled receptor 4 (GPR4) is a type of GPCR that is activated by protons and is involved in cancer-related angiogenesis. GPR4 is found to be detected in a higher amount in the endothelium of vessels of EOCs compared to benign ovarian tumors [48][202]. Bai et al. reported that significant inhibition of invasion and cell growth can be induced in A2780 ovarian cancer cells with the knockdown of GPR4 and transcription factor 7 (TCF7) while promoting apoptosis [49][203]. Similarly, GPR68 also known as ovarian cancer G protein-coupled receptor 1 (OGR1) has also been identified as a proton sensing receptor [50][51][204,205]. The expression of OGR1 in human ovarian tumor HEY cells resulted in the inhibition of cell migration and proliferation [51][205]. Furthermore, G2A (or GPR132) is also known as a proton sensing receptor that regulates proliferation, immunity, and oncogenesis and exerts antitumorigenic properties via cell cycle arrest at the G2/M stage [52][53][54][206,207,208]. GPR4, GPR68, and GPR132 are recognized to be activated by lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) and sphingosylphosphorylcholine (SPC), which induces growth inhibition [48][52][55][202,206,209]. Lastly, GPR39 is frequently overexpressed in ovarian cancer tissue and mediates Zn2+ induced signaling [56][210]. GPR39 was found to be an inhibitor of cell death, hence representing a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of ovarian cancer [57][211]. Most of these receptors do not have suitable ligands to functionalize NPs. However, specific antibodies could be applied to decorate NPs to induce specific binding to the receptor. In the case of proton sensing receptors, endosomal uptake will be triggered in the acidic tumor microenvironment.2.2. Aminergic GPCRs
Aminergic GPCRs, a subset of class A rhodopsin-like GPCRs, are the targets for approximately 25% of the current clinically used drugs [58][212]. Ovarian cancer is known to be affected by receptor ligands produced by the immune and nervous systems. Receptors from the aminergic GPCR family are excellent drug targets as they are associated with memory, neurotransmission, mood and circadian cycle regulation, cognition, and vasoconstriction [59][213]. Ovarian cancer is known to be affected by receptor ligands produced by the immune and nervous systems. In line with this, histamine, acetylcholine, serotonin, dopamine, and adrenaline receptors are frequently expressed in ovarian cancer cells and have been linked to their functions including proliferation, survival, and migration [60][61][214,215]. Oppitz et al. reported that 23 out of 39 ovarian tumors tested, expressed adrenaline receptors, which was associated with reduced patient survival [62][216]. Dopamine receptor 2 (DRD2) is known to be overexpressed in ovarian cancer cells. Yong et al. studied the effect of a DRD2 antagonist, thioridazine and it was observed that it exhibited an anticancer effect in A2780 and SKOV3 cell lines as well as SKOV3 xenografts in nude mice by inducing apoptosis and oxidative stress [63][217]. Moreover, thioridazine interacted with extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and AKT signaling pathways and inhibited tumor angiogenesis. Histamine activates the histamine receptor H1 (HRH1), which stimulates the growth of ovarian tumor cells in vitro and promotes the release of extracellular vesicles (EVs) that modulate different steps of the metastatic process. Pyrilamine, a selective HRH1 antagonist can block the cell proliferating effect of histamine on OVCAR3 cells, hence acting as a therapeutic drug target for the death of tumor cells [64][218].2.3. Lipid GPCRs
Lipids can act as a signaling molecules, store energy, are involved in post-translational modifications, and, lastly, are a major constituent of cellular membranes [65][66][67][219,220,221]. These membrane lipids also play an important role in various tumorigenesis processes such as migration, proliferation, and inflammation [68][69][70][222,223,224]. They are known to directly interact with their targets or bind to extracellular or intracellular receptors. A significant number of lipid-activated GPCRs are known to be expressed in ovarian cancer tissue and their cognate ligands, such as lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), sphingosine-1-phosphate, platelet-activating factor (PAF; 1–0-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) and various free fatty acids achieve high local concentrations. Here, reswearchers discuss four classes of lipid GPCRs: fatty acid, lysophospholipid, phospholipid, and steroid GPCRs.2.3.1. Fatty Acid GPCRs
Fatty acids play a vital role in metabolic disorders and inflammation, hence contributing to tumorigenesis [71][225]. FFAR1 is a free fatty acid (FFA) receptor that has been found to be overexpressed in HGSOCs. FFA-mediated cancer cell growth has been demonstrated, and targeting this receptor is a potential future strategy [72][226]. Munkarah et al. demonstrated that the high concentration of GW1100, which is an FFAR1 antagonist was able to partially inhibit the proliferation and viability of cancer cell lines in the presence of serum [72][226]. Moreover, Hopkins et al. studied the function of FFARs in OVCAR3 and SKOV3 cell lines and examined if FFAR agonists affect their proliferation [73][227]. mRNA expression studies revealed that both the OVCAR3 and SKOV3 cell lines expressed FFAR1, and SKOV3 also expressed FFAR4 in small amounts. Furthermore, the FFAR1 agonist (GW9508) was able to inhibit the proliferation of both cell lines.2.3.2. Lysophospholipid GPCRs
Lysophospholipids are known to play an essential role in cellular processes, including migration, proliferation, and immune responses [74][75][76][228,229,230]. The most studied lysophospholipids in cancer biology are LPA and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) [77][231]. The ascitic fluid contains elevated LPA concentrations and ovarian cancer cells are known to produce high levels of LPA [78][79][80][232,233,234]. LPA has been shown to drive ovarian cancer cell migration and invasion [81][235], activate NF-kB [82][236] and AP-1 transcription factors [83][237], increase cyclooxygenase 2 production, and induce metabolic reprogramming of ovarian cancer cells inducing a glycolytic shift via hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activation [79][233]. Additional pathways to mediate or synergistically act in concert with LPA stimulation are EGFR and other RTKs, and the Hippo/YAP pathway [81][84][235,238]. LPA Receptors (LPARs) are widely expressed in normal ovaries but frequently overexpressed in benign tumors and ovarian cancer tissue [78][79][232,233]. Particularly, LPAR2 and LPAR3 have been shown to be frequently overexpressed in ovarian cancer cells and tissues [56][80][210,234]. Lysophosphatidylethanolamine has been described as an alternative ligand on some LPA receptors inducing a Ca2+ signal and boosting cell migration [85][86][239,240]. Overall, these accumulated findings make a very strong case for LPA blockage as a potential anti-cancer strategy. Similarly, S1P plays a vital role in the regulation of angiogenesis, apoptosis, cell growth, and inflammation. S1P controls the invasiveness of epithelial ovarian cancer cells through a complex mechanism involving multiple GPCR pathways, which regulate ECM-proteolysis and attachment of cells [87][241]. All five of the known S1P receptors might be involved in this complex interplay, and targeting these receptors could be relevant for some anti-cancer strategies. Visentin et al. demonstrated that the S1P-specific monoclonal antibody LT1002 can neutralize S1P by decreasing the systemic level of IL-8, hence, reducing cell survival and proliferation of tumors in a mouse model [88][242]. Moreover, S1PR antagonists such as VPC44116, VPC23019, and VPC25239 are known to inhibit the invasion and migration of OVCAR3 cells [89][243]. Hence, the role of S1P in ovarian cancer needs to be further understood to be able to discover new therapeutic strategies for the management of the disease.2.3.3. Phospholipid GPCRs
PAF binds to the PAF receptor (PTAFR) and is involved in inflammation and platelet aggregation [90][244]. PTAFR has been shown to activate the EGFR and ERK signaling pathways in ovarian cancer cells, therefore potentially contributing to cancer progression [91][147]. Yu et al. investigated the effect of WEB2086 (a PTAFR antagonist) in combination with AG1478 (an EGFR inhibitor) on CAOV3 and SKOV3 cell lines and it was observed that the combination significantly inhibited the invasion and proliferation by inducing apoptosis and arresting the cells at the G0/G1 phase [92][245]. Moreover, Gao et al. studied that PAF increases the stemness of SKOV3 and A2780 cell lines, and the application of Ginkgolide B, which is a PTAFR inhibitor successfully reduced tumor growth [93][246]. Therefore, targeting PTAFR could be a potential approach for the treatment of ovarian cancer.2.3.4. Steroid GPCRs
Steroids are typically hydrophobic polycyclic signaling molecules that elicit cellular actions by binding to intracellular nuclear receptors [94][247]. Androgens, estrogens, mineralocorticoids, progestogens, and glucocorticoids are a few examples of steroid hormones that regulate cellular interactions with nuclear receptors. Estrogen, for instance, transmits signals via G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER1) to activate the EGFR and promote proliferation [95][248]. Increased membrane estrogen receptor expression has been observed in high-grade serous samples and correlated with impaired prognosis [27][182]. However, there are controversies in the study of GPER1 and its effect on ovarian cancer. Ignatov et al. reported that the expression of GPER1 was lower in ovarian cancer tissues when compared to benign ovarian tumors [96][249]. Moreover, the selective GPER1 agonist, G1, was able to suppress the proliferation of SKOV3 and OVCAR3 cell lines. Conversely, Liu et al. demonstrated that 17β-estradiol and G1 induced proliferation of OVCAR5 cell lines [97][250]. Limited information is available on the impact and role of GPER1 on ovarian cancer, and therefore further studies are required to confirm the tumor-suppressing or proliferating effect of GPER1 before using it as a drug target.Table 13.
GPCRs expressed in ovarian cancer.
| Receptor Protein Symbol 1 | Endogenous Agonists (Signaling 2) | Antagonists | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ionic | GPR4 | Protons (Gs, Gi/o, Gq/11, G12/13) | GPR4 antagonist 3b, NE 52-QQ57 | [48][202] |
| GPR39 | Zn2+ (Gq/11) | - | [56][210] | |
| GPR68 | Protons (Gi/o, Gq/11) | Psychosine | [50][51][98][204,205,251] | |
| GPR132 | Protons (NA 3) | Lysophosphatidylcholine | [52][53][206,207] | |
| Aminergic | ADRA1B | Adrenaline, Noradrenaline (Gq/11) | AH 11110, L-765314, Rec 15/2615 | [60][214] |
| ADRB1 | Adrenaline, Noradrenaline (Gs) | Acebutolol, Atenolol, Betaxolol | ||
| ADRB2 | Adrenaline, Noradrenaline (Gs) | Sotalol, Propafenone, Nadolol | ||
| ADRB3 | Adrenaline, Noradrenaline (Gs) | L-748337, L-748328 | ||
| CHRM3 | Acetylcholine (Gq/11) | Tropicamide, Tolterodine, Oxybutynin | [60][214] | |
| DRD1 | Dopamine, 5-Hydroxytryptamine, Noradrenaline (Gs) | Ecopipam, SCH-23390, SKF-83566 | [60][214] | |
| DRD2 | Dopamine (Gi, Gi/o) | ML321, Raclopride, Domperidone | ||
| HRH1 | Histamine (Gq/11) | Astemizole, Triprolidine, Azelastine | [60][61][214,215] | |
| HTR1A | 5-Hydroxytryptamine (Gi/o) | Robalzotan, WAY-100635 | [60][214] | |
| HTR1B | 5-Hydroxytryptamine (Gi/o) | GR-55562 | ||
| HTR1D | 5-Hydroxytryptamine (Gi/o) | SB 714786 | ||
| HTR1E | 5-Hydroxytryptamine (Gi/o) | Rauwolscine, Fluspirilene, Metergoline | ||
| HTR2A | 5-Hydroxytryptamine (Gq/11) | Compund 3b, Ketanserin | ||
| HTR2B | 5-Hydroxytryptamine (Gq/11) | EGIS-7625, RS-127445, BF-1 | ||
| HTR4 | 5-Hydroxytryptamine (Gs) | RS 100235, GR 113808, SB 204070 | ||
| Lipid | FFAR1 (GPR40) | docosahexaenoic acid, α-linolenic acid, myristic acid, oleic acid, long chain carboxylic acids (Gq/11) | GW1100 | [72][226] |
| GPER1 | 17β-estradiol (Gi/o) | G15, G36 | [27][182] | |
| LPAR1 | LPA (Gi/o, Gq/11, G12/13) | AM095, ONO-7300243, AM966 | [56][78][79][80][81][82][83][84][85][86][99][100][210,232,233,234,235,236,237,238,239,240,252,253] | |
| LPAR2 | LPA, Farnesyl diphosphate, Farnesyl monophosphate (Gi/o, Gq/11, G12/13) | H2L5186303 | ||
| LPAR3 | LPA, Farnesyl diphosphate, Farnesyl monophosphate (Gi/o, Gq/11) | Dioctanoylglycerol pyrophosphate | ||
| LPAR4 | LPA, Farnesyl diphosphate (Gs, Gi/o, Gq/11, G12/13) | AM966, Farnesyl diphosphate, Farnesyl monophosphate | ||
| LPAR5 | LPA, Farnesyl diphosphate, Farnesyl monophosphate, n-arachidonoylglycine (Gq/11, G12/13) | TCLPA5, AS2717638 | ||
| LPAR6 | LPA (Gs, Gi/o, G12/13) | - | ||
| PTAFR | PAF, Methylcarbamyl PAF (Gi/o, Gq/11) | Rupatadine, Apafant, BN 50739 | [101][254] | |
| S1PR1 | S1P, Dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate, Sphingosylphosphorylcholine (Gi/o) | NIBR-0213, W146 | [87][241] | |
| S1PR2 | S1P, Dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate, Sphingosylphosphorylcholine (GS, Gq/11, G12/13) | JTE-013 | ||
| S1PR3 | S1P, Dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate, Sphingosylphosphorylcholine (Gi/o, Gq/11, G12/13) | TY-52156 | ||
| S1PR4 | S1P, Dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate, Sphingosylphosphorylcholine (Gi/o, G12/13) | CYM-50358 | ||
| S1PR5 | S1P, Dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate, Sphingosylphosphorylcholine (Gi/o, G12/13) | - | ||
| Peptide- and protein-activated receptors | AGTR1 | Angiotensin II (Gq/11, Gi/o) | Iosartan, Olmesartan, Telmisartan | [82][102][236,255] |
| AGTR2 | Angiotensin II (Gi/o) | Olodanrigan, PD123319 | ||
| BDKRB2 | Bradykinin (Gs, Gi/o, Gq/11) | Anatibant, Icatibant, FR173657 | [60][214] | |
| CCKAR | CCK-8, -33, -39, -58 (Gq/11) | Dexloxiglumide, JNJ-17156516, Devazepide | [38][39][190,191] | |
| CCKBR | CCK-4, -8, -33, gastrin-17 (Gq/11) | Lorglumide, GW-5823, tetronothiodin | ||
| CXCR1 | Interleukin 8 (Gi/o) | Navarixin, AZD5069 | [60][214] | |
| CXCR2 | Interleukin 8 (Gi/o) | SX-517, Elubirixin, SB 225002 | [103][256] | |
| CXCR4 | CXCL12 (Gi/o) | Mavorixafor, T134, Plerixafor | [104][257] | |
| EDNRA | Endothelin-1, -2 (Gq/11) | Macitentan, Ambrisentan, BQ123 | [105][106][107][108][258,259,260,261] | |
| EDNRB | Endothelin-1, -2, -3 (Gs, Gi/o, Gq/11) | K-8794, IRL 2500, BQ788 | ||
| F2R (PAR1) | Protease activated/Thrombin (Gq/11) | RWJ-56110, SCH-79797, Vorapaxar | [109][262] | |
| F2RL1 (PAR2) | Protease activated/Serine proteases (Gq/11) | GB88, I-191, AZ8838 | [110][263] | |
| FPR2 | n-formyl-methionyl peptides (FMLP) (Gi/o) | WRWWWW, t-BOC-FLFLF | [111][264] | |
| FSHR | Follicle-stimulating Hormone (Gs) | FSH deglycosylated α/β | [27][112][113][182,265,266] | |
| GHRHR | Growth Hormone-releasing Hormone (Gs) | - | [114][267] | |
| GNRHR | Type 1 gonadotropin-releasing Hormone (Gq/11) | Abarelix, Degarelix, Elagolix | [115][268] | |
| GRPR | GRP-(14–27), GRP-(18–27), Neuromedin B and C, (Gq/11) | Bantag-1, PD 168368, AM-37 | [40][41][42][192,193,194] | |
| LGR5 (GPR49) | R-spondin-1, -2, -3, -4 (Wnt) | - | [116][117][269,270] | |
| LHCGR (LHRHR) | Luteinizing hormone, Chorionic gonadotropin (Gs) | Deglycosylated chorionic gonadotropin | [27][43][44][182,195,196] | |
| NTSR1 | Neurotensin, Large neuromedin n (Gq/11) | Meclinertant, SR142948A | [45][118][197,271] | |
| NTSR2 | Neurotensin (Gq/11) | - | ||
| OXTR | Oxytocin, Vasopressin (Gq/11) | Retosiban, SSR126768A, L-372662 | [56][210] | |
| PTH2R | Parathyroid Hormone (Gs) | PTHrP-(7–34), TIP39-(7–39) | [56][210] | |
| RXFP1 | Relaxin-1, -2, -3 (Gs, Gi/o) | B-R13/17K H2 relaxin | [119][272] | |
| SSTR1 | Cortistatin-14, Somatostatin-14, -28 (Gi/o) | BIM 23454, SRA880 | [34][35][36][37][186,187,188,189] | |
| SSTR2 | Cortistatin-14, -17, Somatostatin 14, -28 (Gi/o) | BIM 23454, [D-Tyr8]CYN 154806, BIM 23627 | ||
| SSTR3 | Somatostatin-28, -14, Cortistatin-17 (Gi/o) | ACQ090, MK-4256 | ||
| SSTR4 | Somatostatin-28, -14, Cortistatin-17 (Gi/o) | PRL-2915, [L-Tyr8]CYN 154806, BIM 23454 | ||
| SSTR5 | Somatostatin-14, -28, Cortistatin-14, -17 (Gi/o) | S5A1, BIM 23056 |
1 According to the European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), the Protein Information Resource (PIR) and the Swiss Institute for Bioinformatics (SIB); 2 guidetopharmacology.org; 3 not applicable, coupling unknown.
