Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that has emerged as a powerful tool in clinical microbiology for identifying peptides and proteins, which makes it a promising tool for microbial identification. Matrix assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight MS (MALDI–TOF MS) offers a cost- and time-effective alternative to conventional methods, such as bacterial culture and even 16S rRNA gene sequencing, for identifying viruses, bacteria and fungi and detecting virulence factors and mechanisms of resistance.
- MALDI–TOF MS
- microbial identification
- proteomics
- resistome
- disease biomarkers
1. Background
Mass spectrometry (MS) was originally developed at the end of the 19th century to measure the masses of atoms, and one of its first contributions to science was demonstrating the existence of isotopes, at the beginning of the 20th century [1]. MS is an analytical approach that measures the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of chemical compounds and calculates its exact molecular weight. Laser desorption/ionization (LDI), matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) or surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization (SELDI) as well as electrospray ionization (ESI) are currently the most widely used ionization techniques for analyzing chemical structures in biological systems [2]. In the late 1980s, with the introduction of soft ionization, protein analysis developed rapidly, revolutionizing MS. In the late 1990s, the pioneering application of MS in microbiology [1] demonstrated that intact bacterial cells could be distinguished using MALDI coupled to a time of flight (TOF) analyser [3]. These achievements stimulated the fast development of MALDI–TOF MS system approaches as promising tools for the microbial characterization of bacteria [4], fungi [5], viruses [6], and even nematodes [7].
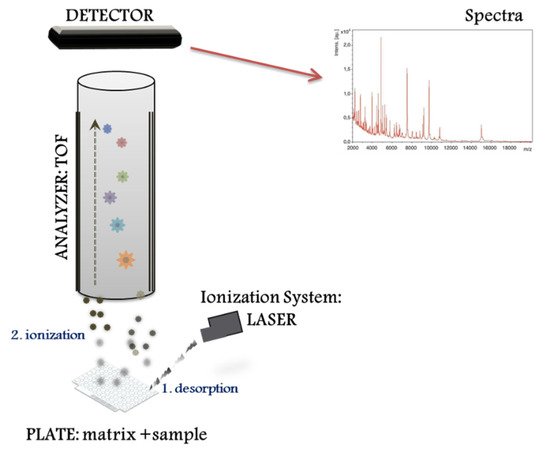
The MALDI–TOF MS system performs different proteomic strategies using intact or digested proteins. The “top down strategy” is used for direct analysis of intact proteins, proteoforms and post-translational protein modifications [8], whereas the “bottom up” is used for mixtures of peptides derived from protein digestion (i.e., peptide sequencing). MALDI–TOF MS systems represent a basic configuration workflow in a linear mode. Figure 1 presents a schematic overview divided into three compartments: (1) the ionization source system (laser), (2) the mass analyser (TOF), and (3) the ion detector. First, the sample for analysis is prepared by mixing with a matrix, an energy-absorbent, organic compound solution. Then, after the mixture (matrix and sample) crystallize upon drying, the sample is ionized using a laser beam. In the process of desorption and ionization using the ionization source system, the molecules are converted to gas-phase ions and individually charged [M+H]+, so that they can be manipulated by external electric and magnetic fields. MALDI is based on a soft ionization method that preserves the integrity of the sample without massive fragmentation [9]. Soft ionization allows the analysis of proteins and peptides and large organic molecules (i.e., polymers, dendrimers) [10], which tend to become brittle and fragmented in other ionization methods.
2. Direct Microbial Identification from Human Samples
MALDI–TOF MS has recently been used in laboratories for the rapid identification of microorganisms in emergency and inpatients, resulting in shorter hospital stays, particularly in intensive care units [22][11]. Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by an unregulated host response to infection [23][12] and is the major cause of mortality from infectious disease, according to Word Health Organization (https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/sepsis, accessed on 26 August 2020).
Commercial protocols remain the reference procedures for the extraction of bacterial proteins from direct samples [10,25][10][13]. However, more and more modified and in-house methods have emerged to address several fundamental issues related to precision and speed of identification. As discussed in the previous section, sample preparation and an adequate method of protein extraction are key steps that may influence sensitivity, resolution, and reproducibility. Poor sample preparation will lead to lower peak resolution with a consequently lower sensitivity and reproducibility, since ion generation by MALDI–TOF depends on an optimal ratio of matrix substance and analyte [10]. Therefore, it is of the utmost importance to pretreat a sample properly considering that human fluids contain proteins other than bacterial or fungal. These preliminary steps must drain and separate blood and other human cells (i.e., haemoglobin), and selectively recover bacterial proteins [24][14]; otherwise, a wrong or unknown identification will result.
3. Microbial Identification Using Reference Databases and Open Free Libraries
4. MS Big Data and Machine Learning Applied to Clinical Diagnosis
The increasing amounts of publicly available MS platforms in open access databases, mass spectrum libraries or analytical methods for visualization, standardization and validation [72,73][27][28] (Table 1), together with automated colony picking in the laboratory [24][14], are improving the typing or characterization of strains and identification of microbes.
| Platform | Statistical Analysis | Spectra Analysis | Accepted Formats | URL | Reference |
|---|
| BioNumerics | ANOVA, MANOVA, PCA, MDS, SOM and other statistical, parametric and non-parametric tests. Dendograms, cluster analysis, bioclustering, generation of phylogenetic trees. QA/QC. |
Creation, identification and classification (spectrum libraries). Pre-processing: optimization, normalization, alignment, subtraction, smoothing. Peak detection, identification and quantification. |
mzML, *.btmsp, *.txt RAW |
https://www.applied-maths.com/applications/maldi-tof-bacterial-identification | (accessed on 19 July 2021) | Bionumerics™ software (Applied Maths BVBA, Sint-Martens-Lantem, Belgium). | ||
| MaldiQUANT | Computational framework in R language: statistical analysis, dendograms, clustering, probability distributions, quality control, etc. | Pre-processing: optimization, normalization, alignment, subtraction, smoothing. Peak detection, identification, and quantification. | mzML, mzXLM, imzML *.csv, *.fid, *.tab | http://strimmerlab.org/software/maldiquant/ | (accessed on 19 July 2021) | Gibb S and Strimmer [82] | Gibb S and Strimmer [29] | |
| Mass-Up | PCA, classification analysis, biomarker discovery, clustering and bioclustering. QA/QC. |
Preprocessing: intensity transformation, optimization, alignment, subtraction, smoothing and peak analysis. Peak detection and identification. | mzML, mzXLM, *.csv, *.muc | http://www.sing-group.org/mass-up/ | (accessed on 19 July 2021) | López-Fernandez et al. [83] | López-Fernandez et al. [30] | |
| MATLAB | Regression, ANOVA, PCA, multivariate analysis, probability distributions, cluster analysis. |
Pre-processing: optimization, smoothing, alignment, signal statistics, peak analysis, envelope extraction. Spectral analysis. |
*.txt, *.xls, *.xlsx |
http://es.mathworks.com/products/matlab-online/ | (accessed on 19 July 2021) | MATLAB | ® | software (MathWorks Inc., Natick, MA, USA) |
| PEAKS | Algorithms and support for analysis. | Pre-processing: optimization, normalization, alignment, subtraction, smoothing, peak analysis. Peak detection, identification and quantification. Sequence editor. |
mzML, mzXLM, mzDATA, MGF, ASCII | http://www.bioinfor.com/ | (accessed on 19 July 2021) | Peaks | ® | software (Bioinformatics Solutions Inc., Waterloo, ON, Canada) |
Other approaches are multidimensional analysis (MDS) or principal component analysis (PCA) (Table 1). MDS and PCA are mathematical approaches that use proximity measures such as the correlation coefficient or Euclidean distance to generate a spatial configuration of points in multidimensional space where distances between points reflect the similarity among isolates. MDS and PCA analyses have been extensively used to discover discriminative peaks [78][31] and identify potential sets of biomarkers [75,79][32][33] in a statistically reliable way [80][34], as well as distinguish among different strain isolates [79][33] from a large data set or selected genes or proteins [80,81][34][35].
5. The State-of-the-Art Combining Approaches
Figure 32 presents a standard MS workflow with the exact identification of proteins and their relative quantification that provides detailed knowledge of protein expression, microorganisms and parasites, and their final integration and interaction in the human body.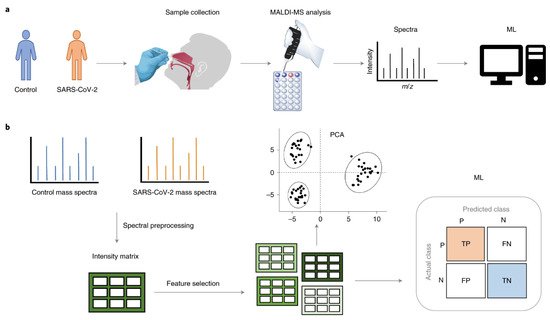
In the recent years, MS has gained importance for characterizing nanoparticles, which has expanded the possibilities of MALDI–TOF MS [84,85,86][37][38][39] in the environmental sciences to study, for example, the distribution, concentration and stability of silver and gold nanoparticles in environmental water [87][40].
Another MALDI–TOF MS combined approach currently used by few clinical microbiology laboratories is the Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIRS), uses molecular vibration fingerprints, primarily the C–O stretching of biomacromolecules, to determine the molecular composition of a wide range of sample types [92][41]. By strain-specific absorbance patterns in the infrared spectrum [93][42], FTIRS characterizes a microbial sample by reflecting its biomolecular content to correlate with its genetic information [94][43]. FTIRS has been successfully applied in many studies to discriminate among bacteria at different taxonomic levels, (e.g., serogroup or serotype) and even at the strain level, to provide simple, quick, high-throughput, cost-effective bacterial typing [95,96,97][44][45][46].
During the last decade, MALDI–TOF has found application in biological systems [98][47] with the incorporation of imaging, the so called Mass Spectrometry Imaging or MALDI imaging [99][48]. It evolved rapidly and is commonly used in the diagnosis of inflammatory and infectious diseases in human or animal tissues, [100][49], including samples such as bacterial biofilm [101][50] or mammalians [102][51].
86. Conclusions
References
- Griffiths, J. A brief history of mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 5678–5683.
- Fenn, J.B.; Mann, M.; Meng, C.K.; Wong, S.F.; Whitehouse, C.M. Electrospray ionization for mass spectrometry of large biomolecules. Science 1989, 246, 64–71.
- Holland, R.D.; Wilkes, J.G.; Rafii, F.; Sutherland, J.B.; Persons, C.C.; Voorhees, K.J.; Lay, J.O., Jr. Rapid identification of intact whole bacteria based on spectral patterns using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization with time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. RCM 1996, 10, 1227–1232.
- Dieckmann, R.; Helmuth, R.; Erhard, M.; Malorny, B. Rapid classification and identification of salmonellae at the species and subspecies levels by whole-cell matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 7767–7778.
- Valentine, N.B.; Wahl, J.H.; Kingsley, M.T.; Wahl, K.L. Direct surface analysis of fungal species by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. RCM 2002, 16, 1352–1357.
- Colquhoun, D.R.; Schwab, K.J.; Cole, R.N.; Halden, R.U. Detection of norovirus capsid protein in authentic standards and in stool extracts by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization and nanospray mass spectrometry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2749–2755.
- Perera, M.R.; Vanstone, V.A.; Jones, M.G. A novel approach to identify plant parasitic nematodes using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. RCM 2005, 19, 1454–1460.
- Gregorich, Z.R.; Ge, Y. Top-down proteomics in health and disease: Challenges and opportunities. Proteomics 2014, 14, 1195–1210.
- Altun, O.; Botero-Kleiven, S.; Carlsson, S.; Ullberg, M.; Ozenci, V. Rapid identification of bacteria from positive blood culture bottles by MALDI-TOF MS following short-term incubation on solid media. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 1346–1352.
- Clark, A.E.; Kaleta, E.J.; Arora, A.; Wolk, D.M. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry: A fundamental shift in the routine practice of clinical microbiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 547–603.
- Ge, M.-C.; Kuo, A.-J.; Liu, K.-L.; Wen, Y.-H.; Chia, J.-H.; Chang, P.-Y.; Lee, M.-H.; Wu, T.-L.; Chang, S.-C.; Lu, J.-J. Routine identification of microorganisms by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry: Success rate, economic analysis, and clinical outcome. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2017, 50, 662–668.
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810.
- Nomura, F.; Tsuchida, S.; Murata, S.; Satoh, M.; Matsushita, K. Mass spectrometry-based microbiological testing for blood stream infection. Clin. Proteom. 2020, 17, 14.
- Tsuchida, S.; Umemura, H.; Nakayama, T. Current Status of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) in Clinical Diagnostic Microbiology. Molecules 2020, 25, 4775.
- Singhal, N.; Kumar, M.; Kanaujia, P.K.; Virdi, J.S. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry: An emerging technology for microbial identification and diagnosis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 791.
- Röst, H.L.; Sachsenberg, T.; Aiche, S.; Bielow, C.; Weisser, H.; Aicheler, F.; Andreotti, S.; Ehrlich, H.-C.; Gutenbrunner, P.; Kenar, E.; et al. OpenMS: A flexible open-source software platform for mass spectrometry data analysis. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 741–748.
- Croxatto, A.; Prod’hom, G.; Greub, G. Applications of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in clinical diagnostic microbiology. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 380–407.
- Jamal, W.Y.; Ahmad, S.; Khan, Z.U.; Rotimi, V.O. Comparative evaluation of two matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) systems for the identification of clinically significant yeasts. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 26, 167–170.
- Levesque, S.; Dufresne, P.J.; Soualhine, H.; Domingo, M.C.; Bekal, S.; Lefebvre, B.; Tremblay, C. A Side by Side Comparison of Bruker Biotyper and VITEK MS: Utility of MALDI-TOF MS Technology for Microorganism Identification in a Public Health Reference Laboratory. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144878.
- Wilen, C.B.; McMullen, A.R.; Burnham, C.A. Comparison of Sample Preparation Methods, Instrumentation Platforms, and Contemporary Commercial Databases for Identification of Clinically Relevant Mycobacteria by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2308–2315.
- Brown-Elliott, B.A.; Fritsche, T.R.; Olson, B.J.; Vasireddy, S.; Vasireddy, R.; Iakhiaeva, E.; Alame, D.; Wallace, R.J.; Branda, J.A. Comparison of Two Commercial Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) Systems for Identification of Nontuberculous Mycobacteria. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 152, 527–536.
- Sun, Y.; Guo, J.; Chen, R.; Hu, L.; Xia, Q.; Wu, W.; Wang, J.; Hu, F. Multicenter evaluation of three different MALDI-TOF MS systems for identification of clinically relevant filamentous fungi. Med. Mycol. 2020, 59, 81–86.
- Camoez, M.; Sierra, J.M.; Dominguez, M.A.; Ferrer-Navarro, M.; Vila, J.; Roca, I. Automated categorization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates into different clonal complexes by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 22, 161.e1–161.e7.
- Deol, P.; Girard, V.; Hyman, J.; Miller, E.; Dussoulier, R.; Mailler, S.; Schrenzel, J.; Beni, A.M.; Ninet Bescher, B.; Walsh, J.; et al. Identification of Mycobacteria by VITEK® MS MatrixAssisted Laser Desorption Ionization—Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry; BioMerieux, Ed.; BioMerieux: Marcy-l’Étoile, France, 2013; Volume 1, p. 32. Available online: http://www.biomerieux-diagnostics.com/vitek-ms (accessed on 19 July 2021).
- Mirande, C.; Canard, I.; Perrot, N.; Welker, M.; Van Belkum, A.; Chatellier, S. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization—Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry for Rapid Antibiotic Resistance Detection; BioMerieux, Ed.; BioMerieux: Marcy-l’Étoile, France, 2013; Volume 1, p. 32. Available online: http://www.biomerieux-diagnostics.com/vitek-ms (accessed on 19 July 2021).
- Angeletti, S.; Dicuonzo, G.; Lo Presti, A.; Cella, E.; Crea, F.; Avola, A.; Vitali, M.A.; Fagioni, M.; De Florio, L. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and blakpc gene phylogenetic analysis of an outbreak of carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae strains. New Microbiol. 2015, 38, 541–550.
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Xu, Q.W.; Wang, R.; Uszkoreit, J.; Griss, J.; Sanchez, A.; Reisinger, F.; Csordas, A.; Ternent, T.; Del-Toro, N.; et al. PRIDE Inspector Toolsuite: Moving Toward a Universal Visualization Tool for Proteomics Data Standard Formats and Quality Assessment of ProteomeXchange Datasets. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2016, 15, 305–317.
- Uszkoreit, J.; Plohnke, N.; Rexroth, S.; Marcus, K.; Eisenacher, M. The bacterial proteogenomic pipeline. BMC Genom. 2014, 15 (Suppl. 9), S19.
- Gibb, S.; Strimmer, K. MALDIquant: A versatile R package for the analysis of mass spectrometry data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2270–2271.
- Lopez-Fernandez, H.; Santos, H.M.; Capelo, J.L.; Fdez-Riverola, F.; Glez-Pena, D.; Reboiro-Jato, M. Mass-Up: An all-in-one open software application for MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry knowledge discovery. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 318.
- Worley, B.; Powers, R. Multivariate Analysis in Metabolomics. Curr. Metab. 2013, 1, 92–107.
- Mantini, D.; Petrucci, F.; Pieragostino, D.; Del Boccio, P.; Sacchetta, P.; Candiano, G.; Ghiggeri, G.M.; Lugaresi, A.; Federici, G.; Di Ilio, C.; et al. A computational platform for MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry data: Application to serum and plasma samples. J. Proteom. 2010, 73, 562–570.
- Santos, T.; Capelo, J.L.; Santos, H.M.; Oliveira, I.; Marinho, C.; Goncalves, A.; Araujo, J.E.; Poeta, P.; Igrejas, G. Use of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry fingerprinting to characterize Enterococcus spp. and Escherichia coli isolates. J. Proteom. 2015, 127, 321–331.
- Landgrebe, J.; Wurst, W.; Welzl, G. Permutation-validated principal components analysis of microarray data. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, research0019.1.
- Werth, M.T.; Halouska, S.; Shortridge, M.D.; Zhang, B.; Powers, R. Analysis of metabolomic PCA data using tree diagrams. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 399, 58–63.
- Nachtigall, F.M.; Pereira, A.; Trofymchuk, O.S.; Santos, L.S. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in nasal swabs using MALDI-MS. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1168–1173.
- Montoro Bustos, A.R.; Ruiz Encinar, J.; Sanz-Medel, A. Mass spectrometry for the characterisation of nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 5637–5643.
- Torres-Sangiao, E.; Holban, A.M.; Gestal, M.C. Advanced Nanobiomaterials: Vaccines, Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases. Molecules 2016, 21, 867.
- Torres Sangiao, E.; Holban, A.M.; Gestal, M.C. Applications of Nanodiamonds in the Detection and Therapy of Infectious Diseases. Materials 2019, 12, 1639.
- Yang, Y.; Long, C.L.; Li, H.P.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Z.G. Analysis of silver and gold nanoparticles in environmental water using single particle-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563, 996–1007.
- Baker, M.J.; Trevisan, J.; Bassan, P.; Bhargava, R.; Butler, H.J.; Dorling, K.M.; Fielden, P.R.; Fogarty, S.W.; Fullwood, N.J.; Heys, K.A.; et al. Using Fourier transform IR spectroscopy to analyze biological materials. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 1771–1791.
- Vatanshenassan, M.; Boekhout, T.; Mauder, N.; Robert, V.; Maier, T.; Meis, J.F.; Berman, J.; Then, E.; Kostrzewa, M.; Hagen, F. Evaluation of Microsatellite Typing, ITS Sequencing, AFLP Fingerprinting, MALDI-TOF MS, and Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis of Candida auris. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 146.
- Naumann, D.; Helm, D.; Labischinski, H. Microbiological characterizations by FT-IR spectroscopy. Nature 1991, 351, 81–82.
- Martak, D.; Valot, B.; Sauget, M.; Cholley, P.; Thouverez, M.; Bertrand, X.; Hocquet, D. Fourier-Transform InfraRed Spectroscopy Can Quickly Type Gram-Negative Bacilli Responsible for Hospital Outbreaks. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1440.
- Burckhardt, I.; Sebastian, K.; Mauder, N.; Kostrzewa, M.; Burckhardt, F.; Zimmermann, S. Analysis of Streptococcus pneumoniae using Fourier-transformed infrared spectroscopy allows prediction of capsular serotype. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 1883–1890.
- Cordovana, M.; Mauder, N.; Kostrzewa, M.; Wille, A.; Rojak, S.; Hagen, R.M.; Ambretti, S.; Pongolini, S.; Soliani, L.; Justesen, U.S.; et al. Classification of Salmonella enterica of the (Para-)Typhoid Fever Group by Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 853.
- Alexandrov, T. MALDI imaging mass spectrometry: Statistical data analysis and current computational challenges. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13 (Suppl. 16), S11.
- Caprioli, R.M.; Farmer, T.B.; Gile, J. Molecular imaging of biological samples: Localization of peptides and proteins using MALDI-TOF MS. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 4751–4760.
- Attia, A.S.; Schroeder, K.A.; Seeley, E.H.; Wilson, K.J.; Hammer, N.D.; Colvin, D.C.; Manier, M.L.; Nicklay, J.J.; Rose, K.L.; Gore, J.C.; et al. Monitoring the inflammatory response to infection through the integration of MALDI IMS and MRI. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 11, 664–673.
- Watrous, J.D.; Dorrestein, P.C. Imaging mass spectrometry in microbiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 683–694.
- Chaurand, P.; Cornett, D.S.; Angel, P.M.; Caprioli, R.M. From whole-body sections down to cellular level, multiscale imaging of phospholipids by MALDI mass spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2011, 10, S1–S11.
