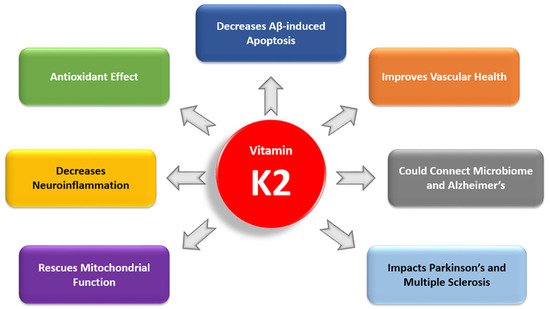
Recent studies have highlighted the importance of vitamin K2 (VK2) in human health. However, there have been no clinical studies investigating the role of VK2 in the prevention or treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), a debilitating disease for which currently there is no cure. In reviewing basic science research and clinical studies that have connected VK2 to factors involved in AD pathogenesis, we have found a growing body of evidence demonstrating that VK2 has the potential to slow the progression of AD and contribute to its prevention. In our review, we consider the antiapoptotic and antioxidant effects of VK2 and its impact on neuroinflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, cognition, cardiovascular health, and comorbidities in AD. We also examine the link between dysbiosis and VK2 in the context of the microbiome’s role in AD pathogenesis. Our review is the first to consider the physiological roles of VK2 in the context of AD, and, given the recent shift in AD research toward nonpharmacological interventions, our findings emphasize the timeliness and need for clinical studies involving VK2.
- vitamin K2
- menaquinone
- Alzheimer’s disease
- dementia
- neurodegeneration
- cognition
- neuroinflammation
- microglia
- antioxidant
- microbiome
1. Introduction
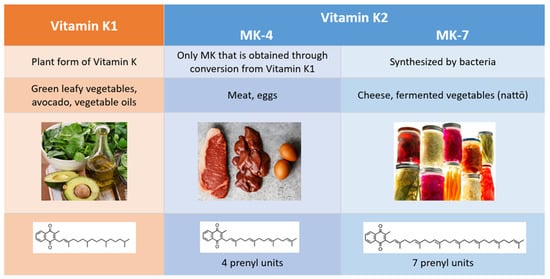
2. Comparison of Vitamins K1 and K2
References
- 2021 Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures. Available online: (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Alzheimer’s Disease International; Patterson, C. World Alzheimer Report 2018: The State of the Art of Dementia Research: New Frontiers; Alzheimer’s Disease International (ADI): London, UK, 2018.
- Serrano-Pozo, A.; Das, S.; Hyman, B.T. APOE and Alzheimer’s Disease: Advances in Genetics, Pathophysiology, and Therapeutic Approaches. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 68–80.
- Janssen, J.C.; Beck, J.A.; Campbell, T.A.; Dickinson, A.; Fox, N.C.; Harvey, R.J.; Houlden, H.; Rossor, M.N.; Collinge, J. Early Onset Familial Alzheimer’s Disease: Mutation Frequency in 31 Families. Neurology 2003, 60, 235–239.
- Edwards, G.A., III; Gamez, N.; Escobedo, G., Jr.; Calderon, O.; Moreno-Gonzalez, I. Modifiable Risk Factors for Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 146.
- Armstrong, A.R. Risk Factors for Alzheimer’s Disease. Folia Neuropathol. 2019, 57, 87–105.
- Beulens, J.W.J.; Booth, S.L.; van den Heuvel, E.G.H.M.; Stoecklin, E.; Baka, A.; Vermeer, C. The Role of Menaquinones (Vitamin K₂) in Human Health. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1357–1368.
- Kamao, M.; Suhara, Y.; Tsugawa, N.; Uwano, M.; Yamaguchi, N.; Uenishi, K.; Ishida, H.; Sasaki, S.; Okano, T. Vitamin K Content of Foods and Dietary Vitamin K Intake in Japanese Young Women. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2007, 53, 464–470.
- Shearer, M.J.; Newman, P. Metabolism and Cell Biology of Vitamin K. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 100, 530–547.
- Schurgers, L.J.; Vermeer, C. Determination of Phylloquinone and Menaquinones in Food. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2000, 30, 298–307.
- Halder, M.; Petsophonsakul, P.; Akbulut, A.C.; Pavlic, A.; Bohan, F.; Anderson, E.; Maresz, K.; Kramann, R.; Schurgers, L. Vitamin K: Double Bonds beyond Coagulation Insights into Differences between Vitamin K1 and K2 in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 896.
- Akbulut, A.C.; Pavlic, A.; Petsophonsakul, P.; Halder, M.; Maresz, K.; Kramann, R.; Schurgers, L. Vitamin K2 Needs an RDI Separate from Vitamin K1. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1852.
- Marles, R.J.; Roe, A.L.; Oketch-Rabah, H.A. US Pharmacopeial Convention Safety Evaluation of Menaquinone-7, a Form of Vitamin K. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 553–578.
- Zhong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Sagare, A.; Fernandez, J.A.; Bell, R.D.; Barrett, T.M.; Griffin, J.H.; Freeman, R.S.; Zlokovic, B.V. Protein S Protects Neurons from Excitotoxic Injury by Activating the TAM Receptor Tyro3-Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase-Akt Pathway through Its Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin-Like Region. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 15521–15534.
- Liu, D.; Guo, H.; Griffin, J.H.; Fernández, J.A.; Zlokovic, B.V. Protein S Confers Neuronal Protection during Ischemic/Hypoxic Injury in Mice. Circulation 2003, 107, 1791–1796.
- Zhu, D.; Wang, Y.; Singh, I.; Bell, R.D.; Deane, R.; Zhong, Z.; Sagare, A.; Winkler, E.A.; Zlokovic, B.V. Protein S Controls Hypoxic/Ischemic Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption through the TAM Receptor Tyro3 and Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor. Blood 2010, 115, 4963–4972.
- Kiely, A.; Ferland, G.; Ouliass, B.; O’Toole, P.W.; Purtill, H.; O’Connor, E.M. Vitamin K Status and Inflammation Are Associated with Cognition in Older Irish Adults. Nutr. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 591–599.
- Carrié, I.; Bélanger, E.; Portoukalian, J.; Rochford, J.; Ferland, G. Lifelong Low-Phylloquinone Intake Is Associated with Cognitive Impairments in Old Rats. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1495–1501.
- Ferland, G. Vitamin K, an Emerging Nutrient in Brain Function. BioFactors 2012, 38, 151–157.
- Presse, N.; Shatenstein, B.; Kergoat, M.-J.; Ferland, G. Low Vitamin K Intakes in Community-Dwelling Elders at an Early Stage of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2008, 108, 2095–2099.
- Presse, N.; Belleville, S.; Gaudreau, P.; Greenwood, C.E.; Kergoat, M.-J.; Morais, J.A.; Payette, H.; Shatenstein, B.; Ferland, G. Vitamin K Status and Cognitive Function in Healthy Older Adults. Neurobiol. Aging 2013, 34, 2777–2783.
- Soutif-Veillon, A.; Ferland, G.; Rolland, Y.; Presse, N.; Boucher, K.; Féart, C.; Annweiler, C. Increased Dietary Vitamin K Intake Is Associated with Less Severe Subjective Memory Complaint among Older Adults. Maturitas 2016, 93, 131–136.
- Chouet, J.; Ferland, G.; Féart, C.; Rolland, Y.; Presse, N.; Boucher, K.; Barberger-Gateau, P.; Beauchet, O.; Annweiler, C. Dietary Vitamin K Intake Is Associated with Cognition and Behaviour among Geriatric Patients: The CLIP Study. Nutrients 2015, 7, 6739–6750.
- Alisi, L.; Cao, R.; De Angelis, C.; Cafolla, A.; Caramia, F.; Cartocci, G.; Librando, A.; Fiorelli, M. The Relationships between Vitamin K and Cognition: A Review of Current Evidence. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 239.
- Van den Heuvel, E.G.H.M.; van Schoor, N.M.; Vermeer, C.; Zwijsen, R.M.L.; den Heijer, M.; Comijs, H.C. Vitamin K Status Is Not Associated with Cognitive Decline in Middle Aged Adults. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2015, 19, 908–912.
- Ferland, G.; Feart, C.; Presse, N.; Lorrain, S.; Bazin, F.; Helmer, C.; Berr, C.; Annweiler, C.; Rouaud, O.; Dartigues, J.-F.; et al. Vitamin K Antagonists and Cognitive Function in Older Adults: The Three-City Cohort Study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2016, 71, 1356–1362.
- Brangier, A.; Celle, S.; Roche, F.; Beauchet, O.; Ferland, G.; Annweiler, C. Use of Vitamin K Antagonists and Brain Morphological Changes in Older Adults: An Exposed/Unexposed Voxel-Based Morphometric Study. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2018, 45, 18–26.
- Alisi, L.; Cafolla, C.; Gentili, A.; Tartaglione, S.; Curini, R.; Cafolla, A. Vitamin K Concentration and Cognitive Status in Elderly Patients on Anticoagulant Therapy: A Pilot Study. J. Aging Res. 2020, 2020, 9695324.
- Annweiler, C.; Ferland, G.; Barberger-Gateau, P.; Brangier, A.; Rolland, Y.; Beauchet, O. Vitamin K Antagonists and Cognitive Impairment: Results From a Cross-Sectional Pilot Study Among Geriatric Patients. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2015, 70, 97–101.
- Brangier, A.; Ferland, G.; Rolland, Y.; Gautier, J.; Féart, C.; Annweiler, C. Vitamin K Antagonists and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults: A 24-Month Follow-Up. Nutrients 2018, 10, 666.
- Denisova, N.A.; Booth, S.L. Vitamin K and Sphingolipid Metabolism: Evidence to Date. Nutr. Rev. 2005, 63, 111–121.
- Olsen, A.S.B.; Færgeman, N.J. Sphingolipids: Membrane Microdomains in Brain Development, Function and Neurological Diseases. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 170069.
- Piccinini, M.; Scandroglio, F.; Prioni, S.; Buccinnà, B.; Loberto, N.; Aureli, M.; Chigorno, V.; Lupino, E.; DeMarco, G.; Lomartire, A.; et al. Deregulated Sphingolipid Metabolism and Membrane Organization in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 41, 314–340.
- Popescu, D.C.; Huang, H.; Singhal, N.K.; Shriver, L.; McDonough, J.; Clements, R.J.; Freeman, E.J. Vitamin K Enhances the Production of Brain Sulfatides during Remyelination. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203057.
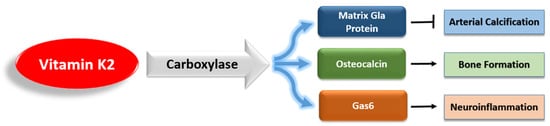
- Jaminon, A.M.G.; Dai, L.; Qureshi, A.R.; Evenepoel, P.; Ripsweden, J.; Söderberg, M.; Witasp, A.; Olauson, H.; Schurgers, L.J.; Stenvinkel, P. Matrix Gla Protein Is an Independent Predictor of Both Intimal and Medial Vascular Calcification in Chronic Kidney Disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6586.
- Guedes, J.A.C.; Esteves, J.V.; Morais, M.R.; Zorn, T.M.; Furuya, D.T. Osteocalcin Improves Insulin Resistance and Inflammation in Obese Mice: Participation of White Adipose Tissue and Bone. Bone 2018, 115, 68–82.
- Schatz, M.; Saravanan, S.; d’Adesky, N.D.; Bramlett, H.; Perez-Pinzon, M.A.; Raval, A.P. Osteocalcin, Ovarian Senescence, and Brain Health. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2020, 59, 100861.
- Shan, C.; Ghosh, A.; Guo, X.; Wang, S.; Hou, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, J. Roles for Osteocalcin in Brain Signalling: Implications in Cognition- and Motor-Related Disorders. Mol. Brain 2019, 12, 23.
- Bellan, M.; Pirisi, M.; Sainaghi, P. The Gas6/TAM System and Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1807.
- Wu, G.; Ma, Z.; Hu, W.; Wang, D.; Gong, B.; Fan, C.; Jiang, S.; Li, T.; Gao, J.; Yang, Y. Molecular Insights of Gas6/TAM in Cancer Development and Therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2700.
- Ichikawa, T.; Horie-Inoue, K.; Ikeda, K.; Blumberg, B.; Inoue, S. Vitamin K2 Induces Phosphorylation of Protein Kinase A and Expression of Novel Target Genes in Osteoblastic Cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 39, 239–247.
- Hadipour, E.; Tayarani-Najaran, Z.; Fereidoni, M. Vitamin K2 Protects PC12 Cells against Aβ (1-42) and H2O2-Induced Apoptosis via P38 MAP Kinase Pathway. Nutr. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 343–352.
- Huang, S.-H.; Fang, S.-T.; Chen, Y.-C. Molecular Mechanism of Vitamin K2 Protection against Amyloid-β-Induced Cytotoxicity. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 423.
- Kusano, J.; Tanaka, S.; Matsuda, H.; Hara, Y.; Fujii, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Sekiyama, M.; Ando, E.; Sugiyama, K.; Hirano, T. Vitamin K1 and Vitamin K2 Immunopharmacological Effects on the Peripheral Lymphocytes of Healthy Subjects and Dialysis Patients, as Estimated by the Lymphocyte Immunosuppressant Sensitivity Test. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2018, 43, 895–902.
- Meng, K.; Xu, W.; Miura, T.; Suzuki, S.; Chiyotanda, M.; Tanaka, S.; Sugiyama, K.; Kawashima, H.; Hirano, T. The Effects of Vitamin K1 and Vitamin K2 on the Proliferation, Cytokine Production and Regulatory T-Cell Frequency in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Paediatric Atopic Dermatitis Patients. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 1058–1060.
- Myneni, V.; Mezey, E. Immunomodulatory Effect of Vitamin K2: Implications for Bone Health. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 67–71.
- Saputra, W.D.; Aoyama, N.; Komai, M.; Shirakawa, H. Menaquinone-4 Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in MG6 Mouse Microglia-Derived Cells by Inhibiting the NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2317.
- Yamaguchi, M.; Weitzmann, M.N. Vitamin K2 Stimulates Osteoblastogenesis and Suppresses Osteoclastogenesis by Suppressing NF-ΚB Activation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 27, 3–14.
- Duan, F.; Mei, C.; Yang, L.; Zheng, J.; Lu, H.; Xia, Y.; Hsu, S.; Liang, H.; Hong, L. Vitamin K2 Promotes PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α-Mediated Glycolysis That Leads to AMPK-Dependent Autophagic Cell Death in Bladder Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7714.
- Enomoto, M.; Tsuchida, A.; Miyazawa, K.; Yokoyama, T.; Kawakita, H.; Tokita, H.; Naito, M.; Itoh, M.; Ohyashiki, K.; Aoki, T. Vitamin K2-Induced Cell Growth Inhibition via Autophagy Formation in Cholangiocellular Carcinoma Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 20, 801–808.
- Miyazawa, S.; Moriya, S.; Kokuba, H.; Hino, H.; Takano, N.; Miyazawa, K. Vitamin K2 Induces Non-Apoptotic Cell Death along with Autophagosome Formation in Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Breast Cancer 2020, 27, 225–235.
- Yokoyama, T.; Miyazawa, K.; Naito, M.; Toyotake, J.; Tauchi, T.; Itoh, M.; Yuo, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Georgescu, M.-M.; Kondo, Y.; et al. Vitamin K2 Induces Autophagy and Apoptosis Simultaneously in Leukemia Cells. Autophagy 2008, 4, 629–640.
- Nimptsch, K.; Rohrmann, S.; Linseisen, J. Dietary Intake of Vitamin K and Risk of Prostate Cancer in the Heidelberg Cohort of the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC-Heidelberg). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 985–992.
