The article presents some significant issues related to the fire protection infrastructure in forests. In every forest complex a sufficiently dense network of fire roads is an extremely important element of the fire protection system. The requirements to identify roads as fire roads within the forest communication network and to maintain their condition up to a certain technical standard has been briefly explained.
- fire roads,
- road network density optimization
- fire road surface
- load-bearing capacity
F
Forest fire protection is particularly important in the era of growing forest fire hazard as a consequence of the observed climate change. The forest fire protection system in Poland is complex and covers a number of activities: fire prevention, creation and maintenance of a surveillance and alarming system, specifying and implementing the organizational and technical measures enabling efficient access to the fire place and actions of the fire extinguishing forces. In Poland, forest fire protection depends on the category and degree of forest fire risk. The fire hazard category comprises forests with a similar level of susceptibility to fire, determined on the basis of the frequency of fires, climatic conditions, stand condition and anthropogenic factors. The degree of forest fire risk is determined for areas of the I and II fire hazard categories; it is carried out twice a day according to separate forecasting zones. One of the elements of improving the fire protection system in Polish forests is currently the optimization of forest communication network density and improving the load capacity parameters of forest roads acting as fire access roads.
One of the most tragic but also spectacular experiences confirming the great importance of forest road network for firefighting was the fire in the Rudy Raciborskie Forest District in 1992—the largest fire which has taken place in Poland and then in Central Europe since World War II. The fire lasted from 26 to 30 August and destroyed 9062 ha of forest area [1]. Currently, organizational units of the State Forests—National Forest Holding work on spatial optimization of road systems, also including their number, based on specially prepared forest road plans. As a result, forest districts are provided with a body of information to facilitate future operations. The main objective of these forest road plans is to precede investment processes with assessment of their economic rationale manifested, among other things, in planned management and protection operations. The road network is optimized by establishing the course of required roads, i.e., trunk roads, byways, access roads for machines, as well as matching maintenance and rehabilitation technologies adequate to the needs.
An extremely important elestment of the fire protection is particularly important in the era of growing forest fire hazard as a consequence of the observed climate change. The forestnfrastructure in every forest complex is a sufficiently dense network of fire roads. The requirement to identify roads as fire protection system in Poland is complex and covers a number of activities: fire prevention, creation and maintenance of a surveillance and alarming system,roads within the forest road network and to maintain their condition up to a certain technical standard was introduced in the State Forests organizational units by the “Instruction on fire protection in forested areas” of 1996 and 2020 [2][3]. spThecifying and implementing the organizational and technical measures enabling efficient access to the fire place and actions of the fire extinguishing forces. In Poland, forest fire protection depends on the category and degree of forest fire risk. The information and requirements included in the instruction resulted, among others, from research carried out by the authors of the current paper. It was established that the distance between any point located in the forest and the nearest public road (excluding highways and express roads) or a forest road classified as a fire road should not exceed 0.75 or 1.50 km depending on the adopted fire hazard category comprisesfor a given forests with (Figure 1) a[3][4][5][6]. sFimilar level of susceptibility to fire, determined on the basis of the frequency of fires, climatic conditions, stand condition and anthropogenic factors. The degreere roads also serve the function of the primary grid for the transportation network necessary to carry out all tasks in a given forest complex. According to data from 2015, within the area administered by the State Forests there are almost 107,000 km of forest fire risk is determinedroads, of which as much as 47% serve the function of fire roads f[7][8]. Transport areas of the I and II fire hazard categories; it is carried out twice a day according to separate forecasting zones. One of the elements of improvproblems observed in Polish forests resulted not from a lack of roads, since their density indexes were relatively high and comparable with those of other European countries, but rather from the very low percentage of paved roads [7][8]. Things the fire protection system in Polishhas facilitated a considerable investment on the forests is currently road infrastructure being made in the following years.
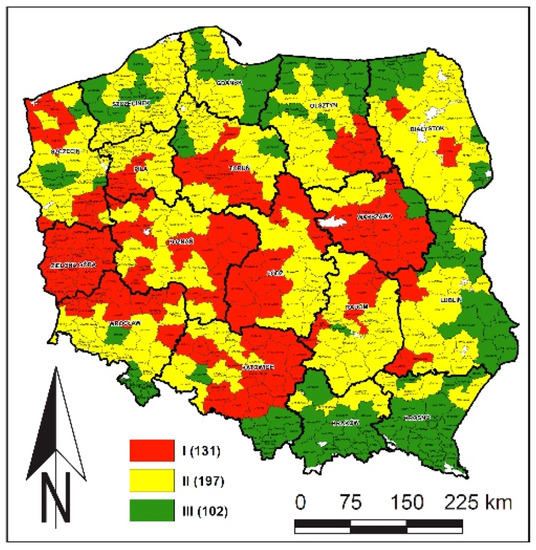
Figure 1. Assessmenthe optimization of of potential fire hazard in Polish forest communication network density and improving the load capacity parameters according to forest district (I, II, III—categories of forest roads acfire hazard, as of 31 December 2018).
Ati preseng as fire access roads.
Ont, research in the Department of Forest Engineering focuses of the most tragic but also spectacular experiencn the verification of current regulations of public law and specific professional guidelines confirming the great importance of forest road network for cerning fire roads in relation to the requirements to be met for currently used firefighting was theand rescue vehicles of fire in the Rudy Raciborskie Fbrigades, as well as applied tactics and technologies of forest District infirefighting 1992—t[9][10]. These largest fire whichrefer in particular to:
-
Optimization of road network density and geometrical parameters of forest roads, including fire roads [7][8][9]. The high construction costs of many kilometers of forest roads cause the need to optimize their density and geometrical parameters as well, while adapting to requirements on effective and safe rescue operations.
-
Tests of load-bearing capacity of forest fire roads—the existing ones, as well as the newly built ones (Figure 2). The variability of fire roads capacity parameters is still significant and in many cases insufficient; this applies first of all to dirt road surfaces and roads built on loose substrate (G3, G4) [9][11].
-
Changes in the parameters of bearing capacity of forest road surfaces due to heavy rainfall [10][12]. Recognizing the risk of road serviceability loss caused by excessive humidity of road sub-grade and unbound layers of road construction, together with counteracting techniques, is an important direction of research nowadays, when an increase in the frequency of extreme weather events is observed.
-
Development of new technologies increasing the load-bearing capacity of road surfaces (additional discussion of this issue further in the text).
-
Improvement of supervision methods and commissioning of intensively constructed and redeveloped surfaces of fire roads. This applies to, among other things, searching for relationships between the results of load-bearing capacity tests carried out with the use of static plates, and the results of measurements taken with light falling weight deflectometers (Figure 3). Success in this area would give rise to a reduction or even the elimination of widely used, but time-consuming and uncomfortable to operate, load capacity tests with static plates for quick measurements with light dynamic plates.
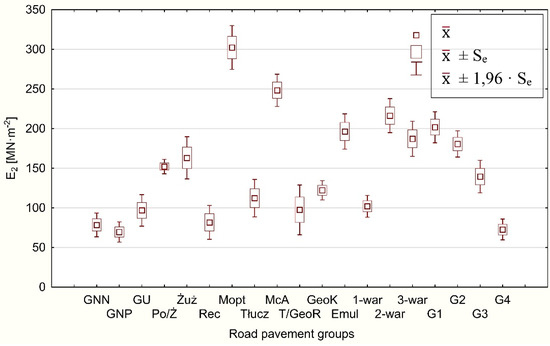
Figure 2. hStas taken place in Poland and then in Central Europe since World War II. The fire lasted from 26 to 30 August and destroyed 9062 ha of forest area [75]. Ctistical characteristics of constrained modulus during secondary compression (E2) according to groups of surfaces in fire roads (GNN: ungraded dirt road; GNP: graded dirt road; GU: improved dirt road surface; Po/Ż: gravelly sand or gravel surrfacently, organizational units of the State Forests—National Forest Holding work on spatial optimization ofs; Żuż: slag surfaces (blast furnace slag); Rec: surfaces of recycled aggregates (concrete debris, construction rubble, brick debris, rail subgrade crusher-run materials); Mopt: optimal dirt mix surfaces; Tłucz: crushed-stone aggregate road systems, also including their number, based on specially prepared forest road plans. As a result, forest districts are providedurfaces; McA: macadam surfaces; T/GeoR: aggregate surfaces on geogrid; GeoK: geogrid surfaces; Emul: asphalt surfaced aggregate pavements; 1-war: single-layer surfaces; 2-war: 2-layer surfaces; 3-war: min. 3-layer surfaces; G1, G2, G3, G4: fire roads with a bodyG1, G2, G3 and G4 subgrades of[9].
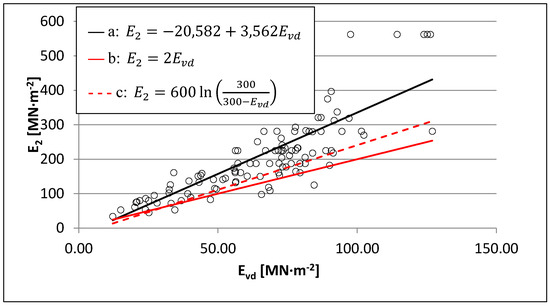
Figure 3. Estinformation to facilitate future operationof the static constrained modulus during secondary compression (E2) bas.ed on The main objevalues of dynamic constrained modulus (Evd) acctordive of these forest roadng to: (a) the original model of linear regression (proposed in [9]); (b) simplans ified conversion of Evd into E2 occasionally to precede investment processesapplied in practice; (c) the formula admissible in case of no data on other dependencies between Evd and E2 [13], in viewith assessment of their economic rationale manifested, am of measurements of load-bearing capacity taken using a static plate on 109 different types of fire road surfaces [9].
The functioning other things, in planned management and protection operationsf the fire protection system in Polish forests may be considered highly effective. The mean area affected by a single fire in Poland is relatively small and shows a downward trend [12]. The mean aroad network is optimizea of a single fire in forests administered by establishthe State Forests, covering the course of required roads, i.e., trunk roads, byways, access roads for machines, as we main organizational and financial burden of fire protection in Polish forests, is almost twice as small as matching maintenancein private forests a[14]. Ind rehabilitlation technologies adequate to the needo climate change affecting Poland, it is necessary to intensify actions minimizing fire hazard in forests.

-
Optimization of road network density and geometrical parameters of forest roads, including fire roads [81,82,83]. The high construction costs of many kilometers of forest roads cause the need to optimize their density and geometrical parameters as well, while adapting to requirements on effective and safe rescue operations.
-
Tests of load-bearing capacity of forest fire roads—the existing ones, as well as the newly built ones (Figure 2
- Instrukcja Ochrony Przeciwpożarowej Obszarów Leśnych 1996; Dyrekcja Generalna Lasów Państwowych: Warsaw, Poland, 1996.
- ). The variability of fire roads capacity parameters is still significant and in many cases insufficient; this applies first of all to dirt road surfaces and roads built on loose substrate (G3, G4) [
-
Changes in the parameters of bearing capacity of forest road surfaces due to heavy rainfall [84,86]. Recognizing the risk of road serviceability loss caused by excessive humidity of road sub-grade and unbound layers of road construction, together with counteracting techniques, is an important direction of research nowadays, when an increase in the frequency of extreme weather events is observed.
-
Development of new technologies increasing the load-bearing capacity of road surfaces (additional discussion of this issue further in the text).
-
Improvement of supervision methods and commissioning of intensively constructed and redeveloped surfaces of fire roads. This applies to, among other things, searching for relationships between the results of load-bearing capacity tests carried out with the use of static plates, and the results of measurements taken with light falling weight deflectometers (Figure 3). Success in this area would give rise to a reduction or even the elimination of widely used, but time-consuming and uncomfortable to operate, load capacity tests with static plates for quick measurements with light dynamic plates.


- Instrukcja Ochrony Przeciwpożarowej Obszarów Leśnych 2020; Dyrekcja Generalna Lasów Państwowych: Warsaw, Poland, 2020.
- Haze, M. (Ed.) Instrukcja Ochrony Przeciwpożarowej Lasu; Załącznik do Zarządzenia nr 54 Dyr. Generalnego Lasów Państwowych z 21 listopada 2011 r. OB. 1.01. 2012; CILP: Warsaw, Poland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rozporządzenie Ministra Środowiska z dnia 22 marca 2006 r. w sprawie szczegółowych zasad zabezpieczenia przeciwpożarowego lasów; Dz. U. z 2006 r. nr 58 poz. 405; Rządowe Centrum Legislacji: Warsaw, Poland, 2006.
- Rozporządzenie Ministra Środowiska z dnia 13 lipca 2015 r. zmieniające rozporządzenie w sprawie szczegółowych zasad zabezpieczenia przeciwpożarowego lasów; Dz. U. z 2015 r. nr 0 poz. 1070; Rządowe Centrum Legislacji: Warsaw, Poland, 2006.
- Czerniak, A.; Gornowicz, R.; Miler, A.T.; Trzciński, G.; Grajewski, S.M.; Kapuścińska, J. Planowanie sieci Dróg Leśnych i Składnic oraz Optymalizacja Wskaźników Gęstości Dróg Leśnych dla Różnych Terenów Polski; Sprawozdanie końcowe z realizacji tematu zleconego przez Dyrekcję Generalną Lasów Państwowych w Warszawie; Maszynopis Katedra Inżynierii Leśnej UPP: Poznań, Poland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Trzciński, G.; Czerniak, A. Stan techniczny dróg leśnych—Potrzeby remontowe. Sylwan 2017, 161, 539–547. [Google Scholar]
- Grajewski, S.M. Funkcjonalność Leśnych Dojazdów Pożarowych Względem Wymogów Współczesnych Pojazdów Ratowniczo-Gaśniczych oraz Aktualnie Stosowanych Taktyk i Technologii Gaszenia Pożarów Lasów; Rozprawy Naukowe 511; Wyd. UP w Poznaniu: Poznań, Poland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Grajewski, S.M.; Czerniak, A.; Szóstakowski, P. Features and performance of forest fire access roads and fire department connections as assessed by employees of the Polish State Fire Service. Saf. Fire Technol. 2019, 53, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grajewski, S.M.; Czerniak, A. Wykorzystanie lekkiej płyty dynamicznej do kontroli robót drogowych prowadzonych w lasach. Przegląd Leśniczy 2015, 10, 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Grajewski, S.M. Wieloletnia zmienność pożarów lasu w wybranych 28 krajach Europy Kanadzie i USA. BiTP 2017, 3, 46–58. [Google Scholar]
- Grajewski, S.M. Effectiveness of forest fire security systems in Poland. Infrastrukt. Ekol. Teren. Wiej. 2017, 4, 1563–1576. [Google Scholar]
- Livneh, M.; Goldberg, Y. Quality assessment during road formation and foundation construction: Use of falling-weight deflectometer and light drop weight. J. Transp. Res. Board 2001, 1755, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
References
- Łańduch, A; Przyroda wzięła odwet. Przegląd Pożarniczy 2012, 9, 8.
- Instrukcja Ochrony Przeciwpożarowej Obszarów Leśnych 1996; Dyrekcja Generalna Lasów Państwowych: Warsaw, Poland, 1996.
- Instrukcja Ochrony Przeciwpożarowej Obszarów Leśnych 2020; Dyrekcja Generalna Lasów Państwowych: Warsaw, Poland, 2020.
- Haze, M. (Ed.) Instrukcja Ochrony Przeciwpożarowej Lasu; Załącznik do Zarządzenia nr 54 Dyr. Generalnego Lasów Państwowych z 21 listopada 2011 r. OB. 1.01. 2012; CILP: Warsaw, Poland, 2011.
- Rozporządzenie Ministra Środowiska z dnia 22 marca 2006 r. w sprawie szczegółowych zasad zabezpieczenia przeciwpożarowego lasów; Dz. U. z 2006 r. nr 58 poz. 405; Rządowe Centrum Legislacji: Warsaw, Poland, 2006.
- Rozporządzenie Ministra Środowiska z dnia 13 lipca 2015 r. zmieniające rozporządzenie w sprawie szczegółowych zasad zabezpieczenia przeciwpożarowego lasów; Dz. U. z 2015 r. nr 0 poz. 1070; Rządowe Centrum Legislacji: Warsaw, Poland, 2006.
- Czerniak, A.; Gornowicz, R.; Miler, A.T.; Trzciński, G.; Grajewski, S.M.; Kapuścińska, J. Planowanie sieci Dróg Leśnych i Składnic oraz Optymalizacja Wskaźników Gęstości Dróg Leśnych dla Różnych Terenów Polski; Sprawozdanie końcowe z realizacji tematu zleconego przez Dyrekcję Generalną Lasów Państwowych w Warszawie; Maszynopis Katedra Inżynierii Leśnej UPP: Poznań, Poland, 2016.
- Trzciński, G.; Czerniak, A; Stan techniczny dróg leśnych—Potrzeby remontowe. Sylwan 2017, 161, 539–547.
- Grajewski, S.M. Funkcjonalność Leśnych Dojazdów Pożarowych Względem Wymogów Współczesnych Pojazdów Ratowniczo-Gaśniczych oraz Aktualnie Stosowanych Taktyk i Technologii Gaszenia Pożarów Lasów; Rozprawy Naukowe 511; Wyd. UP w Poznaniu: Poznań, Poland, 2019.
- Sylwester Grajewski; Andrzej Czerniak; Paweł Szóstakowski; Features and Performance of Forest Fire Access Roads and Fire Department Connections as Assessed by Employees of the Polish State Fire Service. Safety & Fire Technology 2019, 53, 68-87, 10.12845/sft.53.1.2019.4.
- Grajewski, S.M.; Czerniak, A; Wykorzystanie lekkiej płyty dynamicznej do kontroli robót drogowych prowadzonych w lasach. Przegląd Leśniczy 2015, 10, 10–11.
- Grajewski, S.M; Wieloletnia zmienność pożarów lasu w wybranych 28 krajach Europy Kanadzie i USA. BiTP 2017, 3, 46–58.
- Moshe Livneh; Yair Goldberg; Quality Assessment During Road Formation and Foundation Construction: Use of Falling-Weight Deflectometer and Light Drop Weight. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board 2001, 1755, 69-77, 10.3141/1755-08.
- Grajewski, S.M; Effectiveness of forest fire security systems in Poland. Infrastrukt. Ekol. Teren. Wiej. 2017, 4, 1563–1576.
