Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by ALESSANDRA VERARDI and Version 2 by Jessie Wu.
Carotenoids are secondary metabolites present in microorganisms (bacteria, yeast, fungi, and microalgae) and higher plants. They cannot be produced by the human organism. In nature, their principal role is to attract different light wavelengths and transfer their energy to chlorophylls, a function occurring mainly in photosynthetic organisms. Moreover, they can act as photo-protectors, precursors of hormonal substances, antistress secondary metabolites, and attractive agents in plant–insect interaction.
- carotenoids
- delivery systems
- chitosan
1. Chemical Characteristics and Functional Properties of Chitosan
Chitosan is a natural polysaccharide composed of random distributions of N-acetyl-d-glucosamine (GlcNAc) and d-glucosamine (GlcN), with GlcN imparting its cationic properties at neutral/physiological pH [1][208]. It derives from full or partial deacetylation of N-acetyl-d-glucosamine-containing chitin (Figure 1).
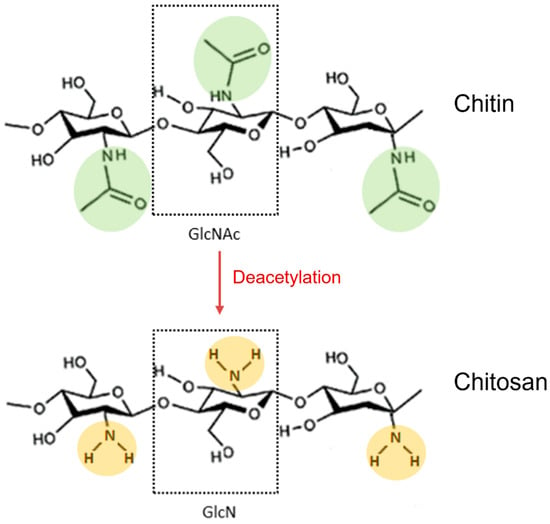
Figure 1. Deacetylation reaction of chitin to obtain its fully deacetylated derivative chitosan. N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) and glucosamine (GlcN) monomers are shown in dotted boxes; the acetamido groups of chitin are highlighted in green, while the amino groups of chitosan are highlighted in orange.
Currently, the most common commercial source of chitin and chitosan is the exoskeletons of crustaceans [2][209]. Chitin and chitosan also occur in nature in fungal cell walls and insects [3][210].
Chitin deacetylation can be achieved chemically or biologically. The conventional chemical methods under high-concentration alkaline conditions are the most widely used, but their environmental impact and high cost prevent their scaling up and industrial application [4][14]. An alternative chemical method for chitin deacetylation relies on the use of the green solvent glycerol, a recyclable and stable by-product of biodiesel. Nevertheless, it has drawbacks since it requires high temperatures for an extended period [5][211]. Applying microwaves or ultrasounds can accelerate chitin deacetylation, thus reducing extraction times and chemical solvent concentration [4][14].
The biological method employs chitin deacetylase enzymes derived from fungi and bacteria. Due to its mild reaction conditions, it is an eco-friendly alternative to chemical methods. Despite this, high enzyme costs and long reaction times limit this process’s scaling up [6][212].
Chitin becomes chitosan when it is deacetylated to a deacetylation degree (DDA) of 50% [7][8][213,214]. DDA indicates the percentage of d-glucosamine units to the total monomer units (i.e., d-glucosamine and N-acetyl-d-glucosamine) in the chitosan polymer chain. DDA plays a major role in influencing chitosan’s physicochemical properties, such as solubility, flexibility, crystallinity, conductivity, viscosity, and surface tension [9][215]. In this way, DDA affects chitosan’s biological properties and performance in many applications [10][11][216,217]. A 70–96% DDA and molecular weight of 1000–2500 kDa are typical of commercial chitosan [12][218].
Chitosan has unique characteristics, such as biodegradability, biocompatibility, low toxicity, and low allergenicity [13][14][219,220]. It exhibits many biological activities, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antitumoral, hypocholesterolemic, blood anticoagulant, etc. [15][221].
Chitosan contains native amine groups that are positively charged; hence, it is a natural cationic biopolymer in water at pH < 6. The positive charge enables the interaction with negatively charged molecules, including phospholipids, fatty acids, proteins, DNA, RNA, and anionic polysaccharides, such as carrageenan and alginate. The cationic form explains its antimicrobial, gelling, and coating properties. Moreover, chitosan occurs negatively charged at alkaline pH due to the hydroxyl groups of its d-glucosamine units. In the anionic form, it can chelate various metal cations, including copper, iron, and cadmium [16][222]. In addition, primary amino and hydroxyl groups of chitosan are fundamental reactive sites for its easy conversion to other derivatives, such as phosphorylated chitosan, quaternary ammonium chitosan salts, carboxymethyl chitosans, and many other substituted chitosans [17][223].
2. Chitosan Nanocarriers for Effective Delivery of Carotenoids (as Advanced Delivery Systems)
Chitosan exhibits numerous functional properties, making it well suited to a wide range of applications from chemical and agrochemical industries to pharmaceutical, medical, and cosmetic industries, food and nutrition industries, textile and paper industries, etc., as summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Applications of chitosan in different fields.
| Field | Chitosan Applications | Form |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Biofertilizer and biocontrol agent (time release of products) Booster of plant growth and plant production Controlled agrochemical release Frost protection Modify plant-microbial interactions Pesticide formulations Soil conditioner Stimulator of crop yield Stimulator of secondary metabolites to induce plant defenses |
Solution Film Powder Spray Coating Gel Powder Nanoparticle |
| Aquaculture | Removal of organic/inorganic compounds Removal of bacteria Removal of ammonia Functional food Micro-carrier for bioactive compounds Probiotics Drugs microencapsulation Drug delivery Oral delivery (vaccination) Antimicrobial and antioxidant |
Microsphere Bead Powder |
| Pharmaceutical and medical/biomed | Excipients Gene, drug, and vaccine delivery system Antimicrobial agent (antibacterial, antifungal) Anti-inflammatory, antiulcer, and antihypertensive agent Dermatological products Hydrating agents Nutraceutical ingredient Hemostatic and anticoagulant compound Antitumor agent and tumor inhibition Anti-HIV agent Innate immune cell recruitment and activation agent Treatment of leukemia, diabetes Sutures, surgical threads, bandages, sponges Biocompatible and biodegradable materials for use as implants, blood substitutes, blood vessels or wound dressing material Dental implants Contact lenses Magnetic resonance imaging |
Solution Powder Tablet Nanoparticle Nanocomposite Sponge Gel and hydrogel Microsphere Capsule and microcapsule Bead Film Fiber and nanofiber |
| Food and nutrition | Additives for human and animal Antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidants Astringency Diet foods and dietary fibers Edible films Hypolipidemic and hypocholesterolemia activities Infant feed ingredient Prebiotics |
Solution Film Blend Coating Bead |
| Cosmetic | Antistatic effect Bacteriostatic Body cleaning products Encapsulating agent Functional additives Hydrating and film-forming agent Products for hair care Products for oral/dental care Products: shampoos, creams, lotions, nail polish, make-up powder, etc. Skin delivery formulations Thickening agent |
Solution Film Powder |
| Environmental | Adsorbent/biosorbent Antibacterial material Antifouling agent Coagulant/flocculant Interactions with proteins and amino acids Material for treatment of contaminant water Polymer for ultrafiltration Reduce odors |
Adsorbent/biosorbent Coagulant/flocculant Antifouling agent Interactions with proteins and amino acids Reduce odors Polymer for ultrafiltration Material for treatment of contaminant water Antibacterial material |
| Textile | Dye-binder for textiles Impregnated textile materials Binding agent for non-woven Surface modification of textiles Textiles with anti-bacterial properties Textile antimicrobial finishing Sanitary fibrous products Surgical threads Textile preservative and deodorant agent Non-allergenic fibers |
Microcapsule Fiber Gel and gelatinous dispersion Coating |
| Paper and pulp | Wet strength agent Reduction in paper water vapor permeability Antibacterial and antimicrobial protective coating for paper packaging Antitermite in papermaking Retention and drainage agents Biodegradable packaging Wrapping and toilet paper Carbonless copy paper Cardboard Chromatography paper Modification of cellulose fibers Photochromic paper Papermaking wastewater treatments |
Nanoparticle Powder Coating |
| Biotechnology and chemistry | Adhesive activity between metallic surfaces Analytical reagent Binders for silicon/graphite Biosensors, electronic and electrochemical devices Cell-recovery composite electrodes in lithium-ion batteries Corrosion protection of aluminum Enzyme and cell immobilization Ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents Matrix for chromatography Membranes for lithium batteries Metabolic Analysis of biological fluids Permeability control Protein separation Reverse osmosis Solvent separation Transport direction of target molecules |
Powder Bead Nanoparticle Microsphere Sponge Coating Fiber Solution Ionic liquids Membrane Sensors Composite Blend |
Chitosan can be easily functionalized to develop a highly effective delivery system for food ingredients, nutraceuticals, drugs, genes, and vaccines due to its several properties, including biocompatibility, bioactivity, mucoadhesive ness, high charge density, and non-toxicity [1][24][25][26][10,208,230,231].
Developing delivery systems for food ingredients and nutraceuticals implies the use of GRAS substances (generally regarded as safe), which must be recognized previously as suitable for human consumption, for example, by the EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) in Europe or by the US FDA (United States Food and Drug Administration) in the USA [27][28][9,13]. Chitosan is recognized as GRAS and approved for dietary use in Italy, Japan, and Finland [29][232]. Chitosan-coating treatments significantly retarded enzymatic browning on the surface of fresh-cut fruits and vegetables during storage, extending their shelf life and preserving their quality attributes [10][216]. Moreover, the polycationic nature of chitosan makes it one of the most potent antimicrobials, capable of inhibiting a wide range of microorganisms, including Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, as well as yeast and mold [30][233]. Four main mechanisms are implicated in chitosan’s ability to kill microorganisms [4][10][30][14,216,233], as shown in Figure 2.
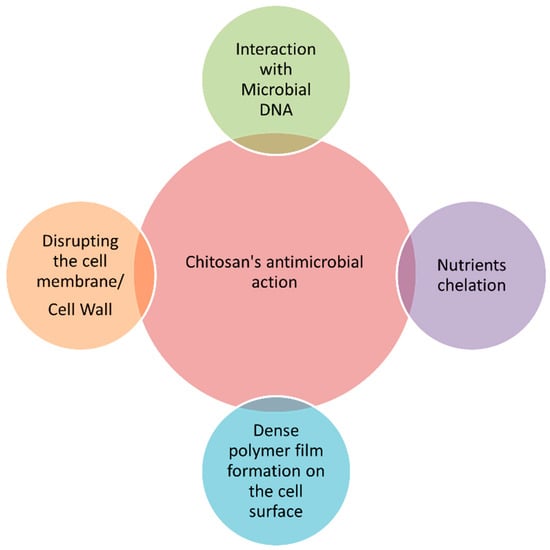
Figure 2.
Main mechanisms of action of chitosan against microorganisms.
Carotenoids’ incorporation into chitosan-based delivery systems has been shown to benefit these nutritional components [28][29][13,232]. Carotenoids’ biological activity is heavily influenced by preserving their bioavailability or the fraction of an ingested compound that is absorbed and available for physiological functions (i.e., enters the systemic circulation in an active form) [28][13]. Several factors can compromise carotenoid bioavailability, including insufficient gastric residence time, low permeability and/or solubility within the gastrointestinal tract, and instability [28][31][13,234]. As a result, chitosan-based delivery systems improve the stability, bioactivity, and bioavailability of carotenoids, and control their release, thus increasing their efficacy. [24][27][28][32][33][9,10,11,12,13].
Two types of chitosan-based delivery systems are widely employed for carotenoid encapsulation: lipid-based and biopolymeric systems [27][9]. In lipid-based delivery systems, chitosan has been extensively studied as a coating material to make nanoemulsions and nanoliposomal vehicles designed for greater solubilization and micellarization of the carried carotenoids than the crystalline form in which they are found in plant tissues [34][235] (Rostamabadi et al., 2019). Adding chitosan to nanoemulsions and nanoliposomes protects encapsulated compounds and controls their release [35][236]. Biopolymeric delivery systems include polysaccharide-based and biopolymeric nanogels [27][36][9,237]. Several techniques can be used to prepare biopolymer nanoparticles developed for carotenoid delivery, including emulsification, desolvation, coacervation, and electrospray drying [37][238].
Figure 3 shows nanomaterials developed using chitosan for application as carotenoid delivery systems.
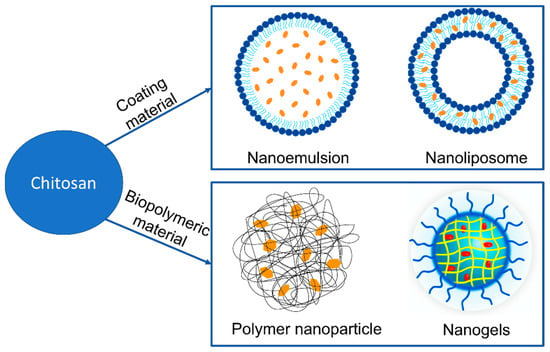
Figure 3.
Nanomaterials developed using chitosan for application as carotenoid delivery systems.
Table 2 summarizes some chitosan-based delivery systems used for the encapsulation of carotenoids.
Table 2.
Chitosan-based delivery systems for encapsulating carotenoids.
| Delivery System | Carotenoids | Particle Size (nm) | Encapsulation Efficiency (%) | Storage Stability (Days) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan-coated Nanoemulsion | β-carotene | 218; 143.7 | NA | 21 at 37 °C | [38][18] |
| Chitosan-coated Nanoliposomes | β-carotene, Lutein, Lycopene, Canthaxanthin | 70 to 100 | 75 | NA | [39][239] |
| Chitosan (Polysaccharide)-Based Nanocarriers | β-carotene | NA | >95 | NA | [40][240] |
| Chitosan-based Nanogels | Fucoxanthin | 200 to 500 | 47 to 90 | 6 at 37 °C | [41][241] |
NA = Not applicable.
2.1. Chitosan-Coated Nanoemulsions
Nanoemulsions (NEs) represent an effective bioactive molecule delivery system for enhancing physicochemical stability, water dispersibility, and bioavailability [27][42][9,242]. Small droplet sizes and improved functional properties characterize these kinetically stable colloidal systems. The most employed NEs are oil-in-water (o/w) and water-in-oil (w/o) types, although multiple emulsion types (o/w/o and w/o/w) are also used occasionally [42][242].
Baek et al. (2020) [38][18] employed chitosan to coat β-carotene-loaded NEs obtained by mixing an appropriate proportion of β-carotene (10 mg), medium chain triglycerides oil (10%), Tween 80 (4.5%), lecithin (4.5%) and deionized water (80%). This mixing was undergone via high-speed homogenization at 5000 rpm for 10 min and probe sonication for 40 min. The prepared β-carotene NEs were then mixed with 2% water-soluble chitosan (WSC) in a 1:1 ratio, obtaining water-soluble chitosan-β-carotene NEs (WSC-BC-NEs) with a mean particle size at 218 nm. Compared to uncoated β-carotene NEs, WSC-BC-NEs showed enhanced stability, exhibiting β-carotene retention of 82% or 77.6% as well as improved thermal stability by 45.1% or 28.6% after 21-day storage at 37 °C or 21-day UV light exposure at room temperature, respectively. Then, using chitosan to coat nanoemulsions successfully increased both the thermal and UV light stability of the encapsulated β-carotene. The zeta potential of the coated nanoemulsions (WSC-BC-NEs) shifted from negative to positive after chitosan coating and was high (+40 mV), suggesting a stable nanoemulsion [38][18]. Therefore, water-soluble chitosan coating could be an effective strategy in the food industry to produce β-carotene emulsions with enhanced stability.
2.2. Chitosan-Coated Nanoliposomes (Chitosomes)
Nanoliposomes are nanoscale colloidal structures formed by concentric phospholipid bilayered vesicles and an aqueous core [32][11]. Due to their amphiphilic nature, they are versatile structures that can incorporate and carry both hydrophilic and hydrophobic molecules, separated or simultaneously [43][243]. Hydrophilic molecules can be located in the aqueous core, whereas hydrophobic molecules can be found between the two phospholipid layers [27][9]. Nanoliposomes have a smaller size and a higher surface-to-volume ratio than macro- and micro-liposomes. These characteristics can improve the bioaccessibility, bioavailability, and stability of the encapsulated compounds [44][244]. Finally, they are biocompatible, biodegradable, and well suited for carotenoids’ encapsulation and delivery [45][46][245,246]. Tan et al. (2014) [47][247] effectively encapsulated carotenoids, including lutein, β-carotene, lycopene, and canthaxanthin, in nano liposomal structures and assessed their bioaccessibility. Lutein exhibited the highest bioaccessibility, followed by β-carotene, lycopene, and canthaxanthin. Due to their encapsulation in liposomes, these carotenoids also showed an increase in their antioxidant activity in the following order: lutein > β-carotene > lycopene > canthaxanthin [47][247]. As recently as 2020, Hamadou et al. successfully developed β-carotene-loaded marine and egg phospholipids nanoliposomes. The nanoliposomes produced using marine phospholipids were smaller, better at inhibiting lipid peroxidation, and stable at 4 °C for 70 days [45][245].
However, nanoliposomal particles suffer from drawbacks related to the stability and leakage of the encapsulated compound during storage or digestion, which limits their applicability [48][248]. Using chitosan as a coating material appears to be a promising approach for nanoliposomal surface modification aimed at improving stability during processing and in gastrointestinal conditions. As an example, conventional nanoliposomes are susceptible to gastric pH and enzymatic degradation. Then, a polymeric coating based on chitosan could enhance the bioavailability of ingredients absorbed in the intestine and protect the bioactive during food processing in which some conditions, such as temperature and pH, are employed [35][236].
Hybrid systems containing chitosan-coated nanoliposomes are known as “chitosomes” [49][249]. Tan et al. (2016) [39][239] successfully developed 70–100 nanometer-sized chitosomes by combining nanoliposomes with chitosan to encapsulate four kinds of carotenoids, specifically lycopene, β-carotene, lutein, and canthaxanthin. Chitosan was flatly adsorbed onto nanoliposome membrane surfaces via electrostatic attraction, inducing charge inversion but maintaining the nanoliposome spherical shape. Chitosan linked to the nanoliposomal surface prevents lipid molecules from moving freely, enhancing their ordering at the polar headgroup region and hydrophobic core of the membrane. These rigidifying effects enhanced nanoliposome stability against heating (at 37 °C for 6 h, 65 °C for 30 min, and 90 °C for 30 s), gastrointestinal stress (0.06–0.31% release over 4 h), and centrifugal sedimentation. The authors have also demonstrated that chitosomes’ encapsulating and retaining ability is highly dependent on the molecular structures of carotenoids. As a result, the liposomal membrane preserved β-carotene and lutein more efficiently than lycopene and canthaxanthin [39][239]. This research tudy suggests that chitosomes could be used to deliver bioactive compounds in nutraceuticals and functional foods.
2.3. Chitosan-Based Nanocarriers
Using chitosan as a polysaccharide biopolymer to bind a poorly soluble bioactive molecule enhances the molecule’s stability and keeps it from degrading [50][250]. Furthermore, polysaccharide-based nanocarriers are more stable at high temperatures than lipid- or protein-based nanocarriers, which melt or denature at high temperatures [51][251].
Table 3 summarizes different studies testing the encapsulation of carotenoids in nanocarriers based on chitosan as a polymer.
Table 3.
Summary of different studies testing the encapsulation of carotenoids in nanocarriers based on chitosan as a polymer.
| Delivery System | Biopolymer | Loaded Compound | Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polysaccharide-based nanocarrier | Chitosan | Lutein | Bioavailability improved by 27.7%. Postprandial levels in blood plasma (54.5%), liver (53.9%), and eyes (62.8%) in mice higher than control. | [52][21] |
| Poly (ethylene oxide)-4-methoxycinnamoylphthaloyl-chitosan (PCPLC)/ poly(vinylalcohol-co-vinyl-4-methoxycinnamate) (PB4)/ ethylcellulose (EC) |
Astaxanthin | In PCLC: high encapsulation efficiency (98%), loading (40%), and high stability to heat. No positive results with PB4 or EC encapsulation | [53][20] | |
| Chitosan + sodium tripolyphosphate/ chitosan + carboxymethylcellulose |
β-carotene | Chitosan + sodium tripolyphosphate carrier: high β-carotene release in aqueous media and gastric fluid, and adequate release in intestinal fluids. Chitosan + carboxymethylcellulose carrier: efficient release in aqueous media and gastric fluid; small release in intestinal fluid. β-carotene release enhanced in food systems with both carriers. |
[40][240] |
Arunkumar et al. (2013) [54][124] developed water-soluble low-molecular-weight chitosan (LMWC) nanoencapsules with lutein to improve the bioavailability of this carotenoid. This researchtudy obtained particles ranging in size from 80 to 600 nm. Both in vitro and in vivo tests revealed that the bioavailability of lutein enclosed in LMWC nanoencapsules was significantly higher than the non-encapsulated control. Postprandial lutein levels in the plasma (54.5%), liver (53.9%), and eyes (62.8%) of mice fed on nanoencapsulated lutein were higher than those found in mice fed on non-encapsulated lutein [54][124]. Based on the results of this researchtudy, LMWC could be used as a carrier to enhance lutein bioavailability and as an efficient dietary compound in food and pharmaceutical applications.
Tachaprutinun et al. (2009) [53][20] evaluated astaxanthin encapsulated into the following three different polymers: poly (ethylene oxide)-4-methoxycinnamoylphthaloyl-chitosan (PCPLC), poly(vinylalcohol-co-vinyl-4-methoxycinnamate) (PB4), and ethylcellulose (EC). PCPLC led to a high encapsulation (98%) and loading (40%) efficiency. Moreover, astaxanthin-loaded PCPLC exhibited high stability when heated for 2 h at 70 °C in an aqueous environment. By contrast, EC failed to encapsulate astaxanthin, while PB4 showed low encapsulation efficiency. Both suffered complete degradation upon heating [53][20].
Rutz et al. (2016) [40][240] encapsulated β-carotene in microparticles formed by chitosan/sodium tripolyphosphate or chitosan/carboxymethylcellulose. The authors evaluated the performance of these microparticles in food systems by analyzing the carotenoid release profile under simulated gastric and intestinal conditions. A higher than 95% encapsulation efficiency was achieved. Chitosan/sodium tripolyphosphate-coated microparticles yielded approximately 55%, while chitosan/carboxymethylcellulose-coated microparticles yielded 87%. In water and gastric fluid, chitosan/carboxymethylcellulose-encapsulated particles showed optimal release behavior, while their release in the intestinal fluid was low. When applied to food systems, these particles produced enhanced carotenoid releases in the intestinal fluid, but they released low amounts of carotenoids during storage. In contrast, chitosan/sodium tripolyphosphate carriers provided adequate β-carotene release in aqueous media and gastric fluid, as well as an acceptable release in intestinal fluids. Like its counterpart, β-carotene released from these carriers was enhanced when incorporated into food systems. Conversely, these carriers released more β-carotene during storage [40][240].
2.4. Chitosan-Based Nanogels
Chitosan can be used as biopolymeric material to prepare nanogels that are dispersions of hydrogel nanoparticles derived from physically or chemically cross-linked polymeric networks [55][56][19,252]. Nanogels represent next-generation drug delivery systems due to their ability to encapsulate drugs efficiently, ease of preparation, and low toxicity [56][252].
Chitosan-based nanogels are synthesized by reacting amino groups on chitosan in aqueous droplets with an ionic crosslinker, such as tripolyphosphate (TPP), or chemical crosslinker, such as glutaraldehyde [57][253].
Ravi et al. (2015) [58][254] developed chitosan–glycolipid nanogels loaded with fucoxanthin (Fx) by using an ionic-gelation method with polymeric chitosan dispersed in glycolipid (GL) as a carrier. Fx is a marine xanthophyll carotenoid present in brown algae that exhibits antioxidative properties. In this researchtudy, nanoencapsulation improved the bioavailability of Fx. Furthermore, the authors investigated the adverse effect of acute and sub-acute toxicity of chitosan nanogels (CS-NGs) loaded with Fx + GL in rats, determining that the CS-NGs are safe for delivering Fx even at higher doses [58][254]. In addition, Ravi and Baskaran (2015) used an ionic gelation method to develop fucoxanthin-loaded chitosan–glycolipid hybrid nanogels (Fx-CH-GL NGs) composed of chitosan and glycoside (1:0.5 w/w), sodium tripolyphosphate in water (0.03%) and fucoxanthin (1 mg). Fx-CH-GL-NGs were demonstrated to have higher stability and bioavailability in vitro (68%) than those of standard Fx (51%) and Fx + GL (35.5%) [41][241].
