Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zuzanna Sobańska | + 2443 word(s) | 2443 | 2021-04-26 04:48:46 | | | |
| 2 | Bruce Ren | Meta information modification | 2443 | 2021-05-18 04:04:35 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Sobańska, Z. Manganese and Manganese Oxide Nanoparticles. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/9710 (accessed on 12 March 2026).
Sobańska Z. Manganese and Manganese Oxide Nanoparticles. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/9710. Accessed March 12, 2026.
Sobańska, Zuzanna. "Manganese and Manganese Oxide Nanoparticles" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/9710 (accessed March 12, 2026).
Sobańska, Z. (2021, May 17). Manganese and Manganese Oxide Nanoparticles. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/9710
Sobańska, Zuzanna. "Manganese and Manganese Oxide Nanoparticles." Encyclopedia. Web. 17 May, 2021.
Copy Citation
Manganese and its oxides in the form of nanoparticles could be a promising alternative for gadolinium-based contrast agents used in diagnostic imaging. Manganese, which is essential for living organisms as an enzyme cofactor, under excessive exposure—for example, due to water contamination or as an occupational hazard for welders—can lead to neurological disorders, including manganism—a condition similar to Parkinson’s disease. This review attempts to summarise the available literature data on the potential applications of manganese and manganese oxide nanoparticles.
manganese oxides
nanoparticles
in vitro
in vivo
biological effects
1. Introduction
The rapidly growing field of nanotechnology opens new scientific pathways from technology to medicine. Nanoparticles (NPs) attract increasing attention since their unique and often innovative features, much different from those of their bulk forms, make them a promising tool for new solutions. NPs might be perceived as a separate substance because even a slight change in their size or shape may evidently influence their physical and biological properties [1][2][3][4]. Such an easy shift in nanomaterial characteristics creates a clear need for thorough toxicological assessment of NPs, but at the same time, it makes data analysis very difficult due to a multitude of nanoforms used in the research.
Manganese oxides, including MnO, MnO2, Mn2O3, and Mn3O4, whose properties predestine them as a novel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agent and potential theranostic tool, are an example of these promising nanomaterials. The manganese itself plays a crucial biological role in mammals as an enzyme cofactor; therefore, its levels are maintained in fragile homeostasis, where both deficiency and excess of this element may be dangerous for mammals by causing neurological disturbances [5]. Therefore, medical applications of manganese oxides at different oxidation states, although attractive from the physicochemical perspective, require a thorough toxicological analysis.
Manganese (Mn) is a transition metal, existing in oxidation states of −3 to +7; however, the most common are +2, +3, +4, +6, and +7. Due to such a variety of valence states, compounds with Mn in an oxidation state of +3 or higher easily enter redox reactions. Compounds with +3, +5, and +6 valence states can undergo a disproportionation process. Compounds with divalent and tetravalent manganese are considered the most stable.
Manganese monoxide (MnO) reacts quite easily with atmospheric oxygen, forming another oxide, i.e., Mn3O4. Effectively assimilated by plants, MnO is used as a fertilizer.
Manganese dioxide (MnO2) is used in a battery production process due to its electrochemical properties. Moreover, depending on the reagents present in the environment, the compound can play a role of an oxidant or (in a reaction with strong alkali) can be oxidized to Mn(V) and Mn(VI) compounds [6].
Manganese, a cofactor necessary for the activity of several enzymes, plays a crucial role in human health. An optimal Mn level is needed to maintain proper cellular redox status, urea metabolism, neurotransmitter synthesis, as well as autophagy processes [5][7]. Due to the ubiquity of this element in food and water, Mn deficiency and the resulting diseases are very rare. On the other hand, the widespread use of manganese and its oxides in the industry poses an occupational risk of excessive exposure for factory workers, miners, and welders. Elevated levels of manganese in the body have been linked with neurological and neurobehavioural disturbances, including manganism, an illness with symptoms similar to Parkinson disease (PD) [8][9].
Catalytic activity of manganese and a relatively large surface area of nanoparticles (compared to bulk form) makes manganese oxide NPs a good candidate as a soil remediation agent. Effective decontamination was reported, e.g., for arsenic, selenium, thallium, cadmium, and lead species in the soil [10][11][12][13]. MnO2 was proven to remediate soil and water contaminated with toxic dyes, released as industrial waste [14][15] and estradiol, an endocrine disruptor chemical harmful to human and aquatic fauna [16][17][18].
Electrochemical and oxidative properties of Mn oxides predestine them to be used as a component of nanocomposites, sensitive to a broad range of compounds. MnO2—based biosensors can detect, i.a., α-glucosidase, glucose, or glutathione (GSH) in human blood [19][20][21] or Salmonella typhimurium, a pathogenic bacterium, in food products [22].
Nanoparticles, which possess unique physicochemical properties, slowly enter the field of medical applications. The emerging tools and solutions develop into new branches, e.g., nanomedicine or nanotheranostics. Nanomaterials have the potential to replace current techniques due to better biocompatibility, cell targeting ability, effective internalisation, etc. This research area is further explored in the review (Figure 1).
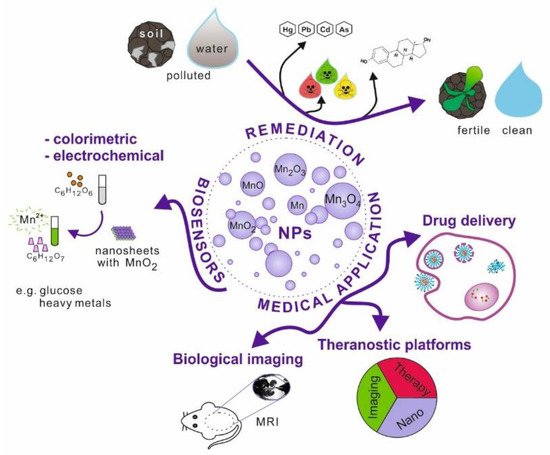
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of manganese and its oxides nanoparticles possible applications.
2. Medical Applications of Manganese and Manganese Oxide Nanoparticles
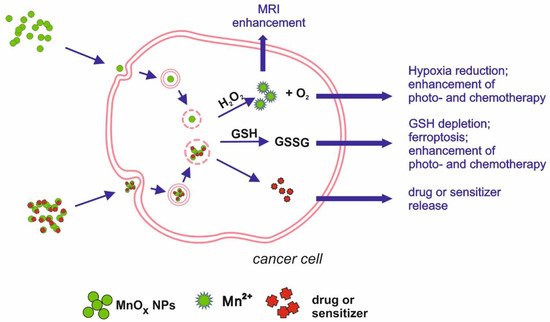
Figure 2. Schematic illustration of main mechanisms underlying manganese oxides medical applications.
2.1. Biological Imaging
One of the exemplary applications of Mn-oxide NPs is their potential as MRI contrasting agents (CAs). The most widely used CAs, which are based on gadolinium (Gd), are known to cause kidney fibrosis in some cases, justifying the search for a new solution. Xiao et al. [23] synthesised Mn3O4 NPs, showing high relaxivity, twice higher than that of commercially used CA, Gd-DTPA (gadolinium-diethylenetriamine penta-acetic acid). The relaxivity value specifies the ability to contrast the image by brightening specific tissues; therefore, agents with higher relaxivity can be administered at a lower dose, which increases their safety. Another nanomaterial, MnO NPs coated with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), turned out to have good contrasting properties in MRI, enhancing the brightness in a dose-dependent manner [24]. Mn3O4 NPs modified with polyethylene glycol (PEG) and fluorescent dye from the cyanine group (Cy7.5), developed by Zhan et al. [25], allowed a dual-modality imaging based on magnetic resonance and fluorescence. The invention was intended to map and monitor sentinel lymph nodes, which is a crucial step in tumour metastasis detection, and showed effectiveness in contrasting both MRI and fluorescence images. Im et al. [26] reported the successful development of Fe3O4/MnO nanocrystals that can be used as CAs in T1- and T2-weighted images. The two modes can be used to highlight different structures, with T1 more suitable for morphological structure and T2 more suitable for pathological states. The contrasting of T1 images relies on signal enhancement (positive effect), whereas T2 contrasting agents tend to reduce the signal (negative effect). Due to their dual mode, T1 and T2 CAs have proved to be effective in differentiating the human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) xenograft from the surrounding liver parenchyma, which can be applied in tumour diagnosis. The mode of action involves the release of Mn2+ ions from the nanocrystals. The T2 signal is emitted by the entire crystal, while the ions released in a low pH environment (intracellular) are responsible for the T1 signal. As shown by the dissolution study, 53% of Mn2+ ions were released from the nanocrystals after 3 days of incubation in phthalate buffer solution at pH 4.6.
2.2. Modulating Tumour Microenvironment, Drug Delivery/Chemotherapy, Photo- and Radiotherapy
Cancer treatment is another field where Mn nanoparticles show their potential. Tang et al. [27] developed Mn-doped mesoporous silica nanoparticles to induce ferroptosis in HCC cells. Intracellular degradation of SiO2/Mn NPs is associated with GSH oxidation and the loss of redox balance. Moreover, the mesoporous SiO2/Mn NPs can be loaded with sorafenib, an anticancer drug inhibiting GSH production in the cell, released during NPs degradation. Such dually induced GSH depletion leads to ferroptosis, resulting in cell death. Other approaches to cancer treatment are photothermal therapy (PTT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT), using a high temperature or light-released ROSs to inhibit tumour growth. To induce the intracellular effect, a photosensitizer has to be administered. Nanoparticles can be loaded with such a photosensitizing agent and anticancer drugs. Moreover, they can enhance the phototherapy effects due to their physical features, e.g., acting as a photothermal agent or by depleting GSH, thus diminishing its antioxidative and protective capability [28]. Zeng et al. [29] proposed an example of such a platform, targeted at prostatic carcinoma tumours. MnO2 NPs were functionalized with chlorin e6 (Ce6), a photosensitizer, and polyethylene glycol-cyclic arginine-glycine-aspartic acid tripeptide (PEG-cRGD) to enhance NP biocompatibility and cell selectiveness. MnO2-PEG-cRGD/Ce6 NPs were effective as a photothermal and photodynamic agent, inducing in vitro hyperthermia and hypoxia after light irradiation, leading to cell death. Another complex nanoplatform was developed to target breast cancer, combining photo- and chemotherapy. Nanosized MnO2 combined with bovine serum albumin (BSA) was coated with IR780, a photosensitizer, and doxorubicin—an anticancer drug. MnO2 degradation, leading to redox imbalance, together with doxorubicin activity and photothermal therapy, were proven effective in vitro and in vivo [30]. MnO2 NPs were also effective in enhancing radiotherapeutic efficiency by delivering a radiosensitizer—acridine orange (AO). Under X-ray irradiation, AO promotes DNA damage, which, together with the Mn-induced release of O2, produced in the presence of H2O2 (characteristic for tumour environment) and radiotherapeutically inhibited cancer cell growth, confirmed in in vitro and in vivo experiments [31]. A combined anticancer effect was achieved by developing a nanotheranostic tool, consisting of BSA base and loaded with MnO2 NPs and indocyanine green (ICG) [32]. ICG, delivered into tumour cells, acts as a photosensitizer, enabling photodynamic and photothermal therapy after the application of laser light. The presence of MnO2 leads to H2O2 disproportionation, which influences the hypoxic environment of the tumour and significantly enhances the effects of laser irradiation.
2.3. Theranostic Nanoplatforms
In agreement with theranostic objectives (combining diagnostics with therapy), nano-sized Mn compounds can be utilised for MRI with simultaneous drug delivery or therapeutic activity. Theranostic applications are usually complex nanoplatforms, where each compound plays a carefully planned role.
MnO nanoparticles functionalised with PEG and cyanide dye Cy5.5 showed not only potential as a T1-weighted MRI contrasting agent, dedicated to the myocardial infarction diagnosis, but also a good retention index in the infarcted myocardium. Therefore, loading NPs with drugs would enable a targeted therapy, making the treatment safer and reducing systemic side effects [33]. Additionally, MnO2 chemical properties predestine this compound to be a base for theranostic solutions. Due to the specific conditions characteristic for tumour microenvironment (TME)—low pH, high GSH level and H2O2 concentration [34][35]—MnO2 NPs can play a role as a carrier of chosen drug that can be released after the dissolution of NPs into Mn2+ [36]. Released Mn2+ ions can react with H2O2 present in the TME, decreasing hypoxia and changing the environment to be less favourable for tumour cells. Released oxygen can also enhance the effects of PDT. An example of such an application of MnO2 NPs was developed by Wang et al. [37]. Nanocomposite, produced from MnO2 nanosheets and verteporfin (BPD), targeted the HCC tumour cells—more specifically, tumour vessel endothelial cells (TVECs)—and released BPD, starting a coagulation cascade in the tumour vessels. The nanocomposite proved to be a good contrasting agent in multimodal imaging (MRI, fluorescence, and photoacoustic), allowing for the evaluation of tumour vessel density. Manganese oxide plays a role as a drug carrier by improving retention and tissue penetration, as well as inducing the red-ox imbalance. Bi et al. [38] designed a theranostic tool, combining chemotherapy, photodynamic therapy, and MRI imaging possibility, based on MnO2 nanosheets as a carrier. NPs were loaded with photosensitizer (Au25 nanoclusters) and chemotherapeutic platinum(IV) (Pt(IV)) prodrug. Apart from delivering the compounds into cancer cells, enabling multimode therapy, the reduction of manganese oxide resulted in a lower GSH concentration, which was beneficial for PDT effects. Released Mn2+ ions acted as T1 CA, enhancing the MRI image. Manganese oxide is an important factor of another theranostic platform, based on lyotropic liquid crystalline nanostructures (LCNs). LCNs, loaded with MnO NPs and betulinic acid (BA), were targeted at breast cancer, acting on few levels. Manganese oxide, reduced in acidic tumour environment into ions, catalyse a Fenton-like reaction, resulting in the release of ROS. In addition to oxidative stress, the breast cancer cells (4T1 and MDA-MB-231 cell lines) were exposed to BA, which enhanced the anti-tumour effect. Moreover, loaded LCNs were proven to be effective CA for MRI, combining the diagnostic and therapeutic potential [39]. Chemical features of MnO2 were used in nanotheranostic application, based on a tumour starvation mechanism [40]. MnO2 nanosheets were conjugated with glucose oxidase (GOx), enabling combined oxygenation/hyperthermia therapy as well as dual-mode MR and photoacoustic imaging. The decomposition of H2O2, present in tumour cells in high concentration, by MnO2 NPs releases O2, necessary for GOx catalytic activity. The oxidase uses up available glucose, which leads to the starvation of the cancer cells. The effect can be further enhanced by hyperthermia obtained by laser irradiation.
Table 1. Summary of potential medical applications of manganese oxides in nanoform.
| Mn/Mn Oxide Nanoform | Modification | Application | Comments | Research Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn3O4 | - | MRI contrasting agent | - | Balb/c nude mice with nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC)2 xenografted tumour | Xiao et al. 2013 [23] |
| MnO | PVP | MRI contrasting agent | - | Human lung carcinoma cell line (SPCA-1 cells) KM mice |
Hu et al. 2013 [24] |
| Mn3O4 | PEG, Cy7.5 | Dual modality contrasting agent (MRI + fluorescence) | - | BALB/c mice | Zhan et al. 2017 [25] |
| Fe3O4/MnO nanocrystals | - | MRI contrasting agent | T1 and T2 mode | BALB/c nude mice | Im et al. 2013 [26] |
| Mn | Doped on silica NPs | Cancer treatment + drug delivery | induce ferroptosis via GSH depletion; might be loaded with drugs, e.g., sorafenib | Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (HepG2) | Tang et al. 2019 [27] |
| MnO2 | Ce6, PEG-cRGD | Photosensitizer delivery for PTT and PDT | - | Human prostate adenocarcinoma cell line (PC3) | Zeng et al. 2019 [29] |
| MnO2 | BSA, IR780, doxorubicin | Combined photo- and chemotherapy for cancer treatment | MnO2 degradation leading to red-ox imbalance as additional anti-cancer mechanism | Human breast adenocarcinoma (MCF-7), Balb/c nude mice inoculated with MCF-7 tumor | Yuan et al. 2019 [30] |
| MnO2 | OA | Radiosensitizer delivery | Mn-induced O2 release as additional anti-cancer mechanism | Human non-small cell lung cancer cell line (H1299), human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell line (SCC7), athymic female nude mice inoculated with H1299 cells |
Liu et al. 2020 [31] |
| MnO2 | BSA, ICG | Combined photothermal and photodynamic for cancer treatment | Mn-induced O2 release as additional anti-cancer mechanism | Nude mice inoculated with murine melanoma (B16F10) cells | Wen et al. 2020 [32] |
| MnO | PEG, Cy5.5 | MRI contrasting agent + drug delivery for targeted therapy | Good retention and selectiveness | Sprague–Dawley rats with surgically developed myocardial ischemia | Zheng et al. 2018 [33] |
| MnO2 | BPD | Drug delivery for targeted therapy + MRI contrasting agent | Mn-induced O2 release as additional anti-cancer mechanism | HepG2 orthotopic mice | Wang et al. 2020 [37] |
| MnO2 | captopril–stabilized Au nanoclusters, DSP | Sensitizer (PDT) and drug delivery for targeted therapy +MRI contrasting agent | Mn ion-related depletion of GSH as mechanism supporting the effects of PDT | Mice inoculated with mouse cervical carcinoma (U14) cells |
Bi et al. 2018 [38] |
| MnO | Loaded into LCN with BA | Chemodynamic therapy + fluorescent imaging | Mn ions catalyse Fenton-like reaction, triggering apoptosis | Balb/c mice with 4T1 (breast cancer) xenografted tumour | Urandur et al. 2020 [39] |
| MnO2 | GOx | Starvation/hyperthermia therapy+ MRI and PA contrasting agent | Mn-dependent reaction releases O2 necessary for GOx activity | Human melanoma (A375 cells), nude mice inoculated with A375 cells | He et al. 2020 [40] |
References
- Warheit, D.B.; Sayes, C.M.; Reed, K.L.; Swain, K.A. Health effects related to nanoparticle exposures: Environmental, health and safety considerations for assessing hazards and risks. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 120, 35–42.
- Chng, E.L.; Sofer, Z.; Pumera, M. MoS2 exhibits stronger toxicity with increased exfoliation. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 14412–14418.
- Hoshyar, N.; Gray, S.; Han, H.; Bao, G. The effect of nanoparticle size on in vivo pharmacokinetics and cellular interaction. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 673–692.
- Jeevanandam, J.; Barhoum, A.; Chan, Y.S.; Dufresne, A.; Danquah, M.K. Review on nanoparticles and nanostructured materials: History, sources, toxicity and regulations. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1050–1074.
- Pfalzer, A.C.; Bowman, A.B. Relationships Between Essential Manganese Biology and Manganese Toxicity in Neurological Disease. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2017, 4, 223–228.
- Reidies, A.H. Manganese Compounds. Ullmann’s Encycl. Chem. Technol. 2007, 22.
- Horning, K.J.; Caito, S.W.; Tipps, K.G.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschner, M. Manganese Is Essential for Neuronal Health. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2015, 35, 71–108.
- Park, R.M.; Bouchard, M.F.; Baldwin, M.; Bowler, R.; Mergler, D. Respiratory manganese particle size, time-course and neurobehavioral outcomes in workers at a manganese alloy production plant. Neurotoxicology 2014, 45, 276–284.
- Erikson, K.M.; Aschner, M. Manganese: Its Role in Disease and Health. Met. Ions. Life Sci. 2019, 19.
- Michálková, Z.; Komárek, M.; Veselská, V.; Číhalová, S. Selected Fe and Mn (nano)oxides as perspective amendments for the stabilization of as in contaminated soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 10841–10854.
- Xie, W.; Liang, Q.; Qian, T.; Zhao, D. Immobilization of selenite in soil and groundwater using stabilized Fe-Mn binary oxide nanoparticles. Water Res. 2015, 70, 485–494.
- Kim, E.J.; Lee, C.S.; Chang, Y.Y.; Chang, Y.S. Hierarchically structured manganese oxide-coated magnetic nanocomposites for the efficient removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous systems. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 9628–9634.
- Huangfu, X.; Ma, C.; Ma, J.; He, Q.; Yang, C.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z. Significantly improving trace thallium removal from surface waters during coagulation enhanced by nanosized manganese dioxide. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 264–271.
- Sabna, V.; Thampi, S.G.; Chandrakaran, S. Degradation of rhodamine B with manganese dioxide nanorods. J. Water Health 2018, 16, 846–856.
- Oliveira, L.V.F.; Bennici, S.; Josien, L.; Limousy, L.; Bizeto, M.A.; Camilo, F.F. Free-standing cellulose film containing manganese dioxide nanoparticles and its use in discoloration of indigo carmine dye. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115621.
- Han, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, D.; Feng, Y. Degradation of aqueous and soil-sorbed estradiol using a new class of stabilized manganese oxide nanoparticles. Water Res. 2015, 70, 288–299.
- Han, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, D. In-situ degradation of soil-sorbed 17β-estradiol using carboxymethyl cellulose stabilized manganese oxide nanoparticles: Column studies. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 238–246.
- Ning, Q.; Yin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tan, X.; Zeng, G.; Jiang, L.; Liu, S.; Tian, S.; Liu, N.; Wang, X. Fabrication of Stabilized Fe–Mn Binary Oxide Nanoparticles: Effective Adsorption of 17β-Estradiol and Influencing Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2218.
- Liu, J.; Duan, X.; Wang, M.; Su, X. A label-free fluorescent sensor based on silicon quantum dots-MnO2 nanosheets for the detection of α-glucosidase and its inhibitor. Analyst 2019, 144, 7398–7405.
- Lee, P.C.; Li, N.S.; Hsu, Y.P.; Peng, C.; Yang, H.W. Direct glucose detection in whole blood by colorimetric assay based on glucose oxidase-conjugated graphene oxide/MnO. Analyst 2019, 144, 3038–3044.
- Liu, J.; Meng, L.; Fei, Z.; Dyson, P.J.; Jing, X.; Liu, X. MnO2 nanosheets as an artificial enzyme to mimic oxidase for rapid and sensitive detection of glutathione. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 69–74.
- Hao, L.; Xue, L.; Huang, F.; Cai, G.; Qi, W.; Zhang, M.; Han, Q.; Wang, Z.; Lin, J. A Microfluidic Biosensor Based on Magnetic Nanoparticle Separation, Quantum Dots Labeling and MnO. Micromachines 2020, 11, 281.
- Xiao, J.; Tian, X.M.; Yang, C.; Liu, P.; Luo, N.Q.; Liang, Y.; Li, H.B.; Chen, D.H.; Wang, C.X.; Li, L.; et al. Ultrahigh relaxivity and safe probes of manganese oxide nanoparticles for in vivo imaging. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3424.
- Hu, X.; Ji, Y.; Wang, M.; Miao, F.; Ma, H.; Shen, H.; Jia, N. Water-soluble and biocompatible nanoparticles for MR imaging in vitro and in vivo. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 976–984.
- Zhan, Y.; Zhan, W.; Li, H.; Xu, X.; Cao, X.; Zhu, S.; Liang, J.; Chen, X. In Vivo Dual-Modality Fluorescence and Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided Lymph Node Mapping with Good Biocompatibility Manganese Oxide Nanoparticles. Molecules 2017, 22, 2208.
- Im, G.H.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, D.G.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, I.S. Fe(3)O(4)/MnO hybrid nanocrystals as a dual contrast agent for both T(1)- and T(2)-weighted liver MRI. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2069–2076.
- Tang, H.; Chen, D.; Li, C.; Zheng, C.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Q.; Fei, W. Dual GSH-exhausting sorafenib loaded manganese-silica nanodrugs for inducing the ferroptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 572, 118782.
- Fan, H.; Yan, G.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Fu, X.; Fu, T.; Zhang, X.B.; Tan, W. A Smart Photosensitizer-Manganese Dioxide Nanosystem for Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy by Reducing Glutathione Levels in Cancer Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 5477–5482.
- Zeng, D.; Wang, L.; Tian, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, H. Synergistic photothermal/photodynamic suppression of prostatic carcinoma by targeted biodegradable MnO. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 661–672.
- Yuan, X.; Yin, Y.; Zan, W.; Sun, X.; Yang, Q. Hybrid manganese dioxide-bovine serum albumin nanostructure incorporated with doxorubicin and IR780 for enhanced breast cancer chemo-photothermal therapy. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 1254–1264.
- Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Kumar, A.; Rong, X.; Yang, W.; Chen, H.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y. Acridine Orange Encapsulated Mesoporous Manganese Dioxide Nanoparticles to Enhance Radiotherapy. Bioconjug. Chem. 2020, 31, 82–92.
- Wen, L.; Hyoju, R.; Wang, P.; Shi, L.; Li, C.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Hydrogen-Peroxide-Responsive Protein Biomimetic Nanoparticles for Photothermal-Photodynamic Combination Therapy of Melanoma. Lasers Surg. Med. 2020.
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Y.; Bai, L.; Xue, J. MnO nanoparticles with potential application in magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery for myocardial infarction. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 6177–6188.
- Bansal, A.; Simon, M.C. Glutathione metabolism in cancer progression and treatment resistance. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 2291–2298.
- Yang, N.; Xiao, W.; Song, X.; Wang, W.; Dong, X. Recent Advances in Tumor Microenvironment Hydrogen Peroxide-Responsive Materials for Cancer Photodynamic Therapy. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12.
- Raja, I.S.; Kang, M.S.; Kim, K.S.; Jung, Y.J.; Han, D.W. Two-Dimensional Theranostic Nanomaterials in Cancer Treatment: State of the Art and Perspectives. Cancers 2020, 12, 1657.
- Wang, Y.; Shang, W.; Zhong, H.; Luo, T.; Niu, M.; Xu, K.; Tian, J. Tumor Vessel Targeted Self-Assemble Nanoparticles for Amplification and Prediction of the Embolization Effect in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 14907–14918.
- Bi, H.; Dai, Y.; Yang, P.; Xu, J.; Yang, D.; Gai, S.; He, F.; An, G.; Zhong, C.; Lin, J. Glutathione and H2O2 consumption promoted photodynamic and chemotherapy based on biodegradable MnO2–25 nanosheets. Chem. Eng. J. 2019.
- Urandur, S.; Banala, V.T.; Shukla, R.P.; Gautam, S.; Marwaha, D.; Rai, N.; Sharma, M.; Sharma, S.; Ramarao, P.; Mishra, P.R. Theranostic lyotropic liquid crystalline nanostructures for selective breast cancer imaging and therapy. Acta Biomater. 2020, 113, 522–540.
- He, T.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, S.; Cui, R.; Xing, S.; Wei, C.; Lin, J.; Huang, P. Glucose Oxidase-Instructed Traceable Self-Oxygenation/Hyperthermia Dually Enhanced Cancer Starvation Therapy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1544–1554.
More
Information
Subjects:
Nanoscience & Nanotechnology
Contributor
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
1.9K
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
18 May 2021
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No





