
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Maria Raimo | + 1697 word(s) | 1697 | 2021-05-09 12:51:19 | | | |
| 2 | Lily Guo | + 2 word(s) | 1699 | 2021-05-12 09:27:39 | | |
Video Upload Options
Polycrystalline materials can be defined as the counterpart of single crystals. These latter arise from solution crystallization by transfer of a solute from the liquid phase to the crystalline phase. Crystallization from melt originates instead crystallites or grains, that is regular crystalline regions randomly oriented and separated one anoher by borders with geometric shapes, Polycrystalline materials are the result of a multiple nucleation process, whereas monocrystals are ideally obtainable by dipping a seed crystal into a supercooled melt. Polycrystalline materials often consist of spherulites, i.e. crystalline aggregates growing with a rounded shape up to impingment with adjacent spherulites. The borders amongst spherulites and the size and the final shape of spherulites affect considerably the properties of polycrystalline materials.
1. Introduction
The solid state has been subjected to morphological investigations of long-held interest, as the shape plays an important role in determining the mechanical resistance of solids and almost all industrial processes involve solidification. Morphology of crystalline substances can be analyzed at different length scales, ranging from macroscopic size to molecular and atomic positions and distances. At microscopic scale, polymers show a spherulitic structure, arising from the start of crystallization (i.e., nucleation) in several points of the liquid phase. A spherulite is a polycrystalline entity growing with a rounded shape up to impingement with surrounding spherulites. For instance, in Figure 1, spherulites of poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) and poly(3-d-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB), respectively, are shown.

2. Polycrystalline Materials
Coalescence leads to a tessellated structure where the original spherulites are separated from one another by interfaces, whose analytical shape depends on the relative overall growth rates of adjacent spherulites. Figure 2 shows hyperbola-shaped and linear interfaces between couples of adjacent PHB spherulites growing at the same linear rate but nucleated, respectively, at different times or simultaneously.

To discuss some aspects of crystallization, the crystalline structure has to be considered, since the prediction of the type of phase and morphology originated by a substance cannot be made without taking into account parameters connected to local crystal order and symmetry. Such parameters affect the properties not only of crystals, but also of crystal aggregates as spherulites. Non-symmetric crystalline lattice, for instance, causes the appearance of four birefringent sectors in spherulites that, because of radial arrangement of elongated crystals, are separated by a distinctive dark cross characteristic of extinction. Although mainly determined by the molecular and crystalline structures, the physical properties of a material depend considerably also on the microstructure and orientation generated by solidification; the microstructure and properties of composite materials are affected, in turn, by the shape, orientation, dispersion, and thermal properties of fillers.
The relative position of atoms within an ideal solid is defined by a crystalline entity (the unit cell) whose translation in the three spatial dimensions reproduces the whole solid structure (the space lattice). Therefore, the description of the crystalline structure of a polymer is based on the inherent admission that a regular order along three spatial directions is present. As underlined by Natta and Corradini, the crystal structure of linear polymers follows the same principles derived for proteins by Pauling. Therefore, each single polymer chain has to have a periodic structure not only constitutionally and configurationally but also from a conformational point of view. In other words, polymers are able to crystallize only if the need of geometric equivalence, relatively to a chain axis, of the structural units may be achieved. This entails that the macromolecular axis (coinciding, for helical conformations, with the helical axis) is parallel to one of the crystallographic axes.
Often a substance can crystallize in more than one solid phase, originating polymorphs with different crystalline structures and, hence, different physical properties. Polymorphs may be related by a monotropic or an enantiotropic relationship. In the former case, one polymorph is metastable, whereas in the latter case, each polymorph has its own stability range and, at least theoretically, a definite transition temperature between the two forms exists. In Figure 3, the two crystalline structures of polyoxymethylene (POM), as schematic projections on a plane perpendicular to the chain axis, are shown.
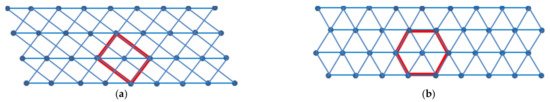
POM helices are orthogonal to the plane of the figure and parallel to the crystallographic c axis. The orthorhombic unit cell contains, as a whole, two polymer chains, since four of the five pieces of helices belong to the unit cell for 1/4. The pieces of helices in the orthorhombic crystal contain 2 monomeric units CH2-O- for each complete turn, which defines the size of the cell along the vertical c axis. The hexagonal form (a = b ≠ c, α = β = 90°, γ = 120°) is the low-density crystalline phase of POM and represents the common form of the solid polymer, but chains can be also arranged in an orthorhombic crystal lattice (a ≠ b ≠ c, α = β = γ = 90°). The elemental cell of hexagonal POM, indeed, may be considered of rhombohedral type. Each chain in a primitive rhombohedral cell belongs to four adjacent cells, so that each cell can be considered occupied by the volume of a single polymer chain. Moreover, each chain is shaped as a 9/5 helix (the repeating unit of the helix is made up of 9 chemical units coiled into 5 turns). The orthorhombic POM cell, which corresponds to a rectangle in the ab plane, contains instead two 2/1 helices (a 2/1 helix can be considered as a 10/5 helix and, therefore, is shorter and wider than a 9/5 helix with the same number of constitutional units CH2O). It is worth noting that the orthorhombic phase is the high-density crystalline form of POM because of the high compactness of 2/1 helices along the c axis. According to the density rule, the less dense hexagonal form is the less stable phase at low temperature and the most stable phase at high temperatures. By heating, indeed, the high-density orthorhombic form is found to undergo an endothermal transformation (at about 70 °C) to the less dense hexagonal form, a further evidence of an enantiotropic relationship between the two POM crystalline forms. This endothermal phase transformation indicates that the orthorhombic POM has higher stability below 70 °C, whereas at higher temperatures, the thermodynamically stable phase is hexagonal. Differently from monotropic polymorphs, the enantiotropic POM modifications have two temperature ranges of stability and, in principle, under atmospheric pressure, a reversible transition from one form to the other at a fixed temperature should be observed, because of the stability inversion. However, thermodynamically permitted processes may be hindered by kinetic reasons, so that chemico-physical procedures do not necessarily lead to the most stable products. For instance, when solid POM is obtained at temperatures above the transition temperature, it is likely found in the hexagonal phase and, because of the very slow tendency to transform in the orthorhombic phase, it remains in the same crystal structure also by subsequent cooling to ambient temperature. Orthorhombic POM, however, can be directly obtained at temperature below 70 °C: under this condition, it is not only the most stable product but it is also formed faster than the less stable hexagonal phase. The inverse hexagonal-orthorhombic phase transformation, although possible in principle even at ordinary pressure by cooling the hexagonal form at a temperature below 70 °C, has not been observed, likely because the needed structural changes are hindered or extremely slow at low temperatures and pressure. However, at least in theory, it might be possible to obtain crystals of orthorhombic POM from the rhombohedral phase, by recrystallization at temperatures lower than 70 °C after dissolution of the latter phase in an appropriate solvent. Crystallization from melt, instead, favors the hexagonal phase, since this latter is formed rapidly during cooling, before temperatures lower than 70 °C have been reached.
Kinetics and thermodynamics of liquid–solid transitions are very sensitive to small variations of experimental conditions, and this is even more evident for polymers that usually show constitutional, configurational, and conformational variability. The presence of metallic and ceramic particles or fibers alters heat exchange within polymer matrices, producing thermal effects during crystallization and the formation of distinctive morphology. Indeed, composites may show not only polymorphic crystalline structures not easily found in neat matrices but also morphology and thermal behavior different from those observed in the neat matrix crystallized under the same conditions. Hereinafter, polymer crystallization and morphology will be examined in order to compare the microstructure of composite materials to that of the neat matrices. This entry reviews the crystallization process of polymer matrices in the framework of crystal growth and heat transport theories and explains microstructural differences between composites and neat matrices on the basis of the differences in thermal capacity and conductivity between polymers and additives. An intuitive approach, although rigorously based on physico-mathematical concepts, has been undertaken for the sake of simplicity. Previous reviews cover several other specific aspects of polymer crystallization. Here, instead an overall view, including not only basic theories and models but also fundamental issues often forgotten or neglected in polymer science, has been offered in order to stimulate deeper investigation of thermal effects of great practical potentiality and make easier recognition and explanation of thermal phenomena and morphology occurring in polymers and their composites. Indeed, a general view of solidification favors the right connections amongst morphology and thermal, structural, and stereochemical properties of macromolecular chains, avoiding the risk of incorrect data interpretation. In order to encompass a wide range of readers from different fields, the theoretical background includes basic concepts of stereochemistry and the general theory of crystallization, which are essential for the comprehension of distinctive properties of polymorphs and of the strictly interconnected kinetic and thermodynamic aspects of solidification. Without a deep knowledge of all the factors affecting the crystallization of neat polymer matrices, it is, indeed, impossible to clearly link the crystallization changes of the matrix to thermal effects due to fillers. According to their expertise, readers may decide to skip some side issues aiming the attention towards the final paragraphs.[2][1][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16][17][18]
References
- Raimo, Maria; Analysis of layer-by-layer phase transformation of a polyoxymethylene copolymer film. Acta Materialia 2008, 56, 4217.
- Maria Raimo; Estimation of polymer nucleation and growth rates by overall DSC crystallization rates. Polymer Journal 2010, 43, 78-83, 10.1038/pj.2010.111.
- M. Raimo; E. Martuscelli; Influence of titanium dioxide on crystallization behavior of an ethylene-propylene copolymer. Journal of Polymer Science 2003, 90, 3409-3416, 10.1002/app.13028.
- Maria Raimo; An optical test to unveil twisting of birefringent crystals in spherulites. Royal Society Open Science 2019, 6, 181215, 10.1098/rsos.181215.
- Maria Raimo; Elvira Lotti; Rebuilding growth mechanisms through visual observations. ChemTexts 2016, 2, 11, 10.1007/s40828-016-0030-8.
- Maria Raimo; An overview on the processing of polymers growth rate data and on the methods to verify the accuracy of the input parameters in crystallization regime analysis. Progress in Crystal Growth and Characterization of Materials 2011, 57, 65-92, 10.1016/j.pcrysgrow.2011.06.001.
- Maria Raimo; On the origin of transcrystalline morphology in polymers and their composites: Re-evaluation of different views. Materials Today Communications 2015, 3, 137-140, 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2015.01.003.
- Maria Raimo; Growth of spherulites: foundation of the DSC analysis of solidification. ChemTexts 2015, 1, 13, 10.1007/s40828-015-0013-1.
- Maria Raimo; “Kinematic” analysis of growth and coalescence of spherulites for predictions on spherulitic morphology and on the crystallization mechanism. Progress in Polymer Science 2007, 32, 597-622, 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2007.02.001.
- Pieter Rein Ten Wolde; Maria J. Ruiz-Montero; Daan Frenkel; Numerical Evidence for bcc Ordering at the Surface of a Critical fcc Nucleus. Physical Review Letters 1995, 75, 2714-2717, 10.1103/physrevlett.75.2714.
- Stefan Auer; Daan Frenkel; Prediction of absolute crystal-nucleation rate in hard-sphere colloids. Nature 2001, 409, 1020-1023, 10.1038/35059035.
- U. Gasser; Eric R. Weeks; Andrew Schofield; P. N. Pusey; D. A. Weitz; Real-Space Imaging of Nucleation and Growth in Colloidal Crystallization. Science 2001, 292, 258-262, 10.1126/science.1058457.
- Natta, G.; Corradini, P.; Aspetti generali della struttura cristallina dei polimeri stereoregolari. La chimica e l'industria 1963, 45, 299.
- Linus Pauling; Robert B. Corey; Compound Helical Configurations of Polypeptide Chains: Structure of Proteins of the α-Keratin Type. Nature 1953, 171, 59-61, 10.1038/171059a0.
- Valentino Zamboni; Giuseppe Zerbi; Vibrational spectrum of a new crystalline modification of polyoxymethylene. Journal of Polymer Science Part C: Polymer Symposia 2007, 7, 153-161, 10.1002/polc.5070070111.
- Gian Alvisé Carazzolo; Structure of the normal crystal form of polyoxymethylene. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: General Papers 1963, 1, 1573-1583, 10.1002/pol.1963.100010510.
- Gianalvise Carazzolo; Mario Mammi; Crystal structure of a new form of polyoxymethylene. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: General Papers 1963, 1, 965-983, 10.1002/pol.1963.100010311.
- Burger, A.; Ramberger, R.; On the Polymorphism of Pharmaceuticals and Other Molecular Crystals. I Theory of Thermodynamic Rules.. Mikrochim. Acta 1979, 2, 259.





