
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mukhamad N. Malawani | + 3346 word(s) | 3346 | 2021-04-07 06:06:35 | | | |
| 2 | Karina Chen | Meta information modification | 3346 | 2021-04-14 04:32:41 | | |
Video Upload Options
Volcanic eruptions are considered major (very large) when the Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) ≥ 5. The nature of the impacts of a VEI ≥ 5 eruption ranges from the destruction of a city, an entire region, climate disturbances as well as to air travel. Even an eruption with VEI < 5 may also have the potential to modify the environment and landscape particularly in proximal and medial facies, as well as surrounding human societies. The variety of environmental destructions due to volcanic eruption differs from primary (e.g., summit collapse, vegetation burning, death), secondary (e.g., atmospheric cooling, global warming), and tertiary (e.g., flood, famine, disease) effects. It is mostly generated by gas emissions, ashes, lava flow, pyroclastic flow, lahar, debris flow, and landslide which results in local and global impacts.
1. Local Impacts of Volcanic Eruptions
1.1. Impacts on the Drainage Systems
Volcanic eruptions can lead to geomorphological transformations in valleys, talweg, and the hydrographic network due to erosion and sedimentation processes. For example, at Merapi volcano, the sediment supply from pyroclastic density currents into the river network leads to riverbed aggradation and subsequently riverbed incision [1]. The river valley morphology has changed from the old Merapi (before 4.8 ka BP) to the new Merapi (after 4.8 ka BP) edifice by detrital fan deposits, andesitic lava flows, tephra, lapilli, and ash layers [2]. These materials buried the eastern drainage system of Merapi during a major flank collapse. During the 2006 CE eruption, Merapi’s block-and-ash flow covered the interfluve region and the main valley on the southern flank as long as ~7 km [3]. It indicates that the materials produced by volcanic eruptions are substantial in shaping morphology and channel stability. In the case of lahar/pyroclastic input, the most hazardous location along a drainage system is river confluence. For instance, the Mapanuepe and Marella rivers’ confluence widened up to 1.3 km after lahar input from the 1991 CE Pinatubo eruption in Philippines [4].
In the tropics, sediment-discharge in volcanic rivers increases during and after eruptions due to lahars, which can be either eruption-induced or rain-triggered during the rainy season [5][6][7]. Channels that are buried by lahars is often creating difficulties for extracting the necessary water for everyday uses. For example, lahars on the southern flank of Merapi obstructed the irrigation channels for three years after the 2010 event, and this led to the worst harvest in the last decade [8]. Furthermore, when volcanic materials settle in the drainage system, they reduce the system capacity and can cause overbank floods during heavy rainfall [9]. The morphology of a river valley can transform dramatically due to lahars, predominantly in two ways: (1) burial of the main channel and (2) scouring of a new valley and, therefore, abandon of the former one [10]. During the 2011 Merapi lahar events, a new 1.5 m-wide river channel formed as the lahar came through and eroded the main road of Sirahan village on the western flank [11]. The example of a river valley on Merapi that has been buried by lahars and now abandoned is presented in Figure 2.
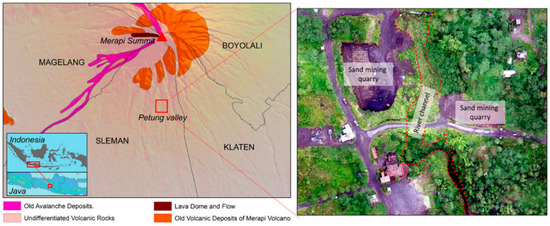
Figure 2. The abandoned channel of Petung River, on the southern flank of Merapi after lahar event in 2011. It is located in undifferentiated volcanic rock formation (left). An aerial image of Petung River segment was taken in 2018 during the rainy season (right) (drone image by Handayani, 2018).
1.2. Impacts on the Volcanic Structure
An eruption may alter the structure of a volcano and its evolution, depending on the type of eruption. On andesitic and rhyolitic volcanoes, structural changes during the growth of lava domes are frequently observed using geophysical monitoring systems, or other methods such as aerial photographs, which allow detecting even minor changes [12]. Hydrothermal alteration during the dome growth is often accompanied by structural weakening that potentially causes sector collapse [13]. Dome growth during a pre-eruptive event may also control a crater displacement, as identified in the 2007–2008 CE Kelud eruption in East Java, Indonesia [14]. However, dome growth can be associated with the VEI, i.e., a faster dome growth most likely creates a high VEI [15].
Volcano edifice can drastically evolve in two ways, i.e., caldera-forming eruption and sector collapse. Several volcanoes in Indonesia formed a caldera after a major eruption. There are three infamous volcanoes that resulted in caldera during the historic time in Indonesia, i.e., Samalas in Lombok (1257 CE), Tambora in Sumbawa (1815 CE), and Krakatoa in the Sunda Strait (1883 CE) [16][17][18][19]. Compared to the two others, caldera in Krakatoa is non-visible due to total collapse of the volcano in 1883 CE [20]. Samalas caldera is the largest (~6 km-wide) (Figure 3A–C). The caldera-forming eruption of Samalas was also responsible for extreme morphological changes in its eastern part of the island. The 1257 CE eruption ejected at least 4.4 × 106 m3 of pumice rich PDCs (pyroclastic density currents) forming deposits with a thickness up to ~30 m, and it has significantly changed the valley pattern of eastern Lombok Island back in the year 1257 to the one existing today [21].
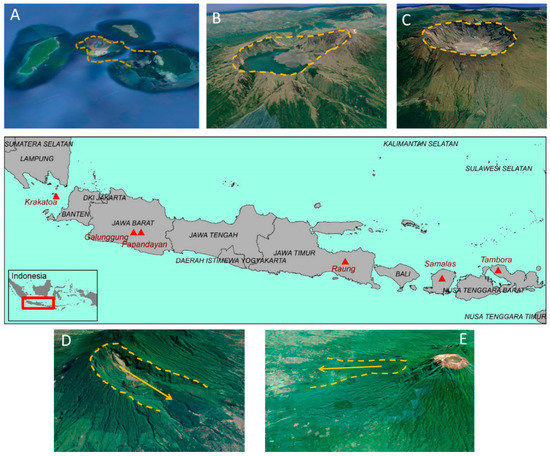
Figure 3. Massive caldera-forming eruptions during modern historic time in Indonesia: (A) Krakatoa, (B) Samalas, and (C) Tambora. The morphological remnant of horse-shoe edifice resulted from sector collapse of (D) Galunggung and (E) Gunung Gadung, Raung volcano, visible from Google Earth imagery.
Many factors can lead to sector collapse during the process of eruption. Most of them are destabilizing factors such as an earthquake (tectonic faulting), magma intrusion, hydrothermal activity, gravitational loading, and progressive shearing [22][23]. Hummocky hills are typically formed by debris-avalanches, which induces morphological transformation through two ways: obstacle-free spreading and valley-filling distribution [24]. The textural materials (wet and dry) of hummocky hills is valuable to characterize their triggering factor, such as in Colima volcano (Mexico): dry materials most probably result from volcano-tectonic deformation, whereas wet materials are likely due to phreatic activity [25].
In Indonesia, three locations with extensive hummocky terrain resulting from debris avalanches can be observed from DEMs and aerial imagery. (1) In Tasikmalaya, West Java, the hummocky hills formed after an eruption of Galunggung volcano in 4200 + 150 BP that ejected 20 km3 of materials, creating a horse-shoe caldera (Figure 3D). Debris avalanche at that time formed hummocky hills 6.5–23 km away from the summit [26]. (2) The hummocky hills located in Jember, East Java, resulted from a flank collapse of Gunung Gadung, a composite volcano of Raung, which also left a horse-shoe shape with 13 km long and 8.5 km wide at the branch [27] (Figure 3E). Abundant hummocks can be found in the proximal-medial facies, and smaller hummocks with size < 20 m-height scattered in distal facies [27]. (3) Another hummocky hills system has been recently identified on Lombok Island. Debris avalanche deposits on Lombok Island covers an area of ~195 km2 with total number of hummocks is >750 [28].
1.3. Impacts on the Water Bodies
The impacts of volcanic eruptions on water bodies include impacts on lakes, sea or ocean, and manmade reservoirs. At some volcanoes, water bodies are distributed at the volcano’s foot. They can also be the results of volcanic eruption and collapse, such as Mt. Bandai in Japan, where a group of lakes was formed by the sector collapse [29]. At the summit of the volcano, another type of water body is the crater lake and the caldera lake. In turn, the water-bodies can affect the eruptions, with notably the frequent breakout floods from crater lakes that can turn into lahars [30][31]. In Indonesia, access to water is important as in Merdada caldera lake, Central Java, a massive water extraction for agricultural purposes [32]. The modification of the chemistry of a crater and a caldera lake can have significant implications, notably in the pre and post-eruption [33]. Volcanic ash deposits in a lake system can increase water toxicity to living biota [34]. Tephra and ashfall can contaminate the lacustrine ecosystem [35], e.g., in Lake Van (Eastern Anatolia, Turkey) [36]. However, hazards and managements related to volcanic lake’s water quality are poorly developed [33]. For instance, water quality monitoring of volcanic lakes is useful for determining water’s common uses [32].
One of the well-known impacts of volcanic eruptions on water bodies is tsunamis. Volcanic eruptions can trigger tsunami through several processes: underwater explosion, volcanic blast, pyroclastic flow, underwater caldera collapse, subaerial failure, and submarine failure [37][38]. At least 24 known volcanic eruption-induced tsunamis in Indonesia are listed [38]. The latest one, which occurred in the Sunda Strait between Java and Sumatra Island in December 2018, was triggered by the eruption of Krakatoa volcano and its partial collapse, as shown from the Sentinel imagery (Figure 4). Prior to this event, Ref. [39] modeled a flank collapse with a volume of 0.28 km3 that would generate a tsunami with an initial wave height of 43 m and reach the Java coastline in 35–45 min. There are plenty of similar examples in other of the world, notably along the subduction-arcs archipelago, e.g., the 3500-year B.P. tsunami triggered by the eruption of Aniakchak volcano in Alaska [40] and the Late-Bronze age tsunami in Crete and Turkey triggered by the eruption of Santorini volcano in Greece [41].
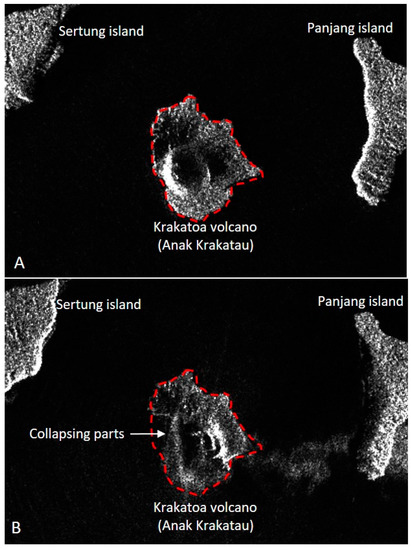
Figure 4. Comparison of the Sentinel images (https://apps.sentinel-hub.com/eo-browser/ (accessed on 27 December 2020)) pre (A) and post-eruption (B) of Krakatoa in December 2018. The red-dashed line marks the initial volcanic island, and the white arrow shows the area of collapse (after Ref. [42]).
1.4. Impacts on Societies and the Environment
Major volcanic eruptions can also cause fatal incidents, as indicated by the number of victims. The seven eruptions with the most significant death tolls globally are over 5000 fatalities [43], among of them, four events are located in Indonesia (Table 1). The largest number of victims ever recorded in modern history is 36,000 casualties during the 1883 Krakatoa eruption. However, the victims were mostly killed by the eruption-induced tsunami. The highest fatalities caused by a direct impact are recorded in the 1902 Pelée eruption that involved a PDC surge which killed 28,000 people. We assume that the 1257 CE Samalas eruption may also have large death tolls in Indonesia’s modern-historical eruptions. Indeed, a written source named Babad Lombok mentions that the city of Pamatan had an estimated population of more than 10,000 inhabitants when the eruption destroyed it.
Table 1. List of most enormous fatalities due to volcanic eruptions since 1500 (source: Ref. [43]).
| Volcano (Year) | Country | Fatalities |
|---|---|---|
| Krakatoa (1883) | Indonesia | 36,000 |
| Mount Pelée (1902) | Martinique | 28,000 |
| Nevado del Ruiz (1985) | Colombia | 24,000 |
| Tambora (1815) | Indonesia | 12,000 |
| Unzen (1792) | Japan | 10,139 |
| Kelud (1586) | Indonesia | 10,000 |
| Kelud (1919) | Indonesia | 5110 |
In the event of an eruption, people living on and near the volcano are likely to be directly impacted, which for the farming population means loss of livelihood and access to its means, e.g., in Merapi (Indonesia) and San Vicente (El Salvador) [44][45]. In Indonesia, numerous ancient routes and cities are located on and near active volcanoes. For instance, the ancient Mataram Kingdom of Central Java had routes that climbed on Merapi and Merbabu volcanoes, with temples along the road and associated settlements, to avoid the swamp areas of the Borobudur basin [46]. Thus, despite being fertile, many cities and villages are located close to active volcanoes for economic and historical reasons. Similar cases are also figured in Lombok. Based on the written sources (Babad Lombok), the colossal eruption of Samalas has buried Pamatan, the capital city of Lombok, which is located in the foot-slope of the volcano. In addition, this ancient city was occupied by thousands of inhabitants, predominantly working on agriculture and aquaculture activities. The written source also described how they responded and conducted an evacuation to avoid the hazards and finally built a new civilization that completely differed from the former. This example emphasizes that ancient civilization also faced livelihood shifting due to volcanic eruptions.
The fragmentation of the volcanic material into fine ash and lapilli creates soils that are rich yet light to work with, and the volcanoes of Indonesia all have vegetated slopes. This land-cover often gets disrupted by eruption processes and there is a balance of vegetation destruction and revegetation occurring on volcanoes (e.g., [47]). This changing balance is often used to determine the extent of the volcanic deposits [48]. This results from the burying process and the burning process. It was shown at Mt. Shiveluch in Kamchatka and Sarychev Peak in the Kuril Islands (Russia), the pyroclastic surge and lava flows traveled through forest areas burned hectares of trees [49][50]. The prediction analysis shows that vegetation recovery requires several decades after the eruption event [50]. On volcanic islands, where most of the land-cover can be lost, the return of natural vegetation succession is controlled by seed dispersals and soil conditions, as it has been shown on the Krakatoa Volcano [51]. Human intervention is also known to influence vegetation successions and alter the vegetation species that used to grow before an eruption. The vegetation on the flanks of Mt. St. Helens volcano started to increase in number in the first 14 years after the eruption, notably accelerated by management practices [52].
Much of the research classifying volcanic impacts has been done for single events. It now appears as a logical continuity, with benefits for both the local inhabitant and the scientific community. The geographical division of local impacts are more feasible to develop concerning to DRR programs. However, at the global scale, the issues concerning DRR are more complex if only consider the geographical division. The interaction into DRR program for global impacts is more feasible to develop by involving two different factors, i.e., volcanic gases/aerosols and volcanic ashes.
2. Global Impacts of Volcanic Eruptions
We define here the global impacts of volcanic eruption is a scale of the globe, with an eruption having the potential of impacting anyone on the planet, regardless of their geographic position. These impacts may be (i) climatic disturbances related to the aerosols dispersion in the stratosphere and/or (ii) economic and social perturbations caused by volcanic ashes, which may disturb the air traffic thousands of miles away from the source volcano.
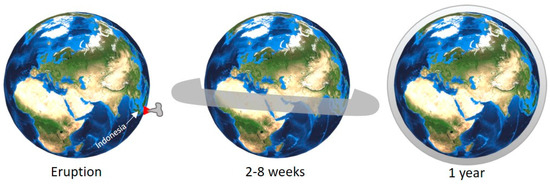
Volcanic gases (e.g., SO2, H2S, and CO2) contribute more significantly to atmospheric-warming than volcanic ashes, and they exist in relatively high concentrations in the atmosphere. At high VEI, the volcanic column can eject material up to the stratosphere, in which case ejecta can travel rapidly worldwide. In the short term, SO2 is one of the most ejected gases into the atmosphere. SO2 become the significant factor in climate change, especially when converted to H2SO4 (Figure 5). It has been demonstrated to affect the global climate, potentially triggering temporary or long-term climate change [53]. In addition, the sulfate particle will stay between one and three weeks within the troposphere, whereas this duration may reach 1 to 3 years for stratospheric eruptions. In the long term, large VEI volcanic eruptions can alter variations in the global carbon cycles on Earth [54]. For example, the Samalas eruption in Lombok in 1257 CE [16], released 1.58 ± 0.12 gt (gt: gigatonnes) of sulfur dioxide, 2.27 ± 0.18 gt of chlorine, and 0.013 gt of bromine in the stratosphere [55]. It would have had far-reaching effects compared to contemporary eruptions for which data is available: the 1982 CE eruptions of El Chichon in Mexico and the 1991 CE eruption of Pinatubo in the Philippines that led to increase greenhouse gases and anthropogenic aerosols [56]. Not only a major volcanic eruption, even VEI 4 eruptions or less are also possible to affect the global climate anomalies [57].
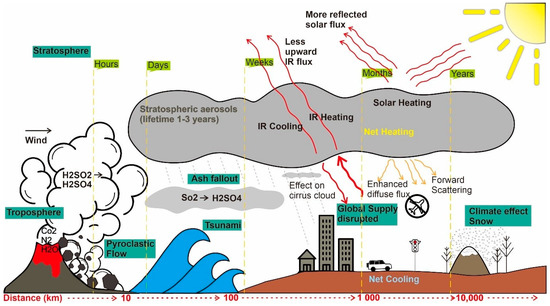
Figure 5. Short term and long term effects of a large volcanic eruption on the atmosphere and the environment (modified from Refs. [54][58]).
The global impacts of the Samalas eruption 1257 CE have disturbed the global climate. As it is reported by Ref. [59] that the years 1258 and 1259, part of the Northern Hemisphere experienced the coldest summers in the past millennium. The effects were also aggravated by societal impacts, e.g., environmental and societal crises in England, France and Japan [59]. The nature of climate effects that were caused by Samalas led to the proposition that this eruption was one of the eruptions responsible for the Little Ice Age, part of a cluster of eruptions in the mid-13th century [60].
In Indonesia, another major eruption from Tambora volcano occurred in West Nusa Tenggara (Sumbawa Island) in 1815 CE. It produced 0.06 gt of sulfur in the stratosphere, causing a global spread of sulfate aerosols and, subsequently climatic perturbations [61]. This eruption modified air temperatures and precipitation in Europe, as recorded by the Czech Meteorological Station; the year 1816 is commonly known as the “year without summer” [62]. These anomalies returned to pre-eruption conditions in 1818, but many glaciers in the Alps continued to grow until 1820 as the glacial-systems reaction is much slower [63]. The schematic impact of the 1815 CE Tambora eruption on the global atmosphere is schematized in Figure 6. As the aerosols and gas spread near the equator, they impacted both the Northern and the Southern hemispheres, while atmospheric circulation usually confines most of the ejecta to the half-hemisphere, where the volcano is located. For this reason, Indonesia has a crucial position in term of global volcanic impacts, as the effects can rapidly reach both the Northern and Southern hemispheres.
For the historical period, global volcanic impacts are often recorded in written sources, such as the eruption of Eldgja in 934 CE [64]. This eruption has been suggested as a reason for the sweltering followed by hundreds of victims in China. It was affected by drought, plague, and famine that continued until 942–943 CE [65]. Despite the essential role these eruptions have played in history, many older eruptions that have impacted the climate remain debatable as to their origin. For example, two mystery volcanoes which erupted closely in 535–536 CE and 539–540 CE, injected SO2 into the atmosphere at a similar volume to Samalas [66][67]. Potential sources for these eruptions have been recently proposed: Illopango in Salvador for the 535–536 CE event [68]; and El Chichon in Mexico for the 539–540 CE event [69]. These cluster eruptions have been suggested to be responsible for societal crises, pandemics, and human migration [70]. The 539–540 CE events were also reported to have disturbed the Maya’s society and environment, and led to massive migration on the core of Maya civilization [69].
The global volcanic impacts on climate are significant and are supposedly an essential concern for DRR and the contemporary human activities. The characteristics of these impacts are relatively similar across the globe: it starts with unusual weather variability and may result in societal crises, famine, and fatalities. Various examples have shown that societal impacts can occur everywhere on Earth, and may be devastating. Unfortunately, the risks associated with global environmental, economic and societal disruptions are not considered in DRR programs. This deficiency could result from the uncertainty in the volume of chemical elements ejected and the method of modeling. The development of research and technology on the volcanic study must be able to accommodate this issue for future mitigation.
If the volcanic gases strongly impact the climate conditions and recent human activities in the case of stratospheric eruptions, the volcanic ash is mainly responsible for modern air traffic disruption. Volcanic ash is ejected into the atmosphere and is sucked into the high-temperature turbine causing it to melt and solidify as glass that can cause the engine to stall, resulting in severe damage or failure [71]. Ref. [72] published a review of known aircraft incidents due to volcanic ash clouds from 1953–2009. The famous one occurred in 1982 when a plane from a British company flying from Australia to UK almost crashed due to the eruption of Galunggung volcano in West Java, Indonesia. Among other recent events, the Eyjafjallajökull eruption in Iceland, and the eruption of Merapi in Yogyakarta, Indonesia, both in 2010 also resulted in essential disruptions in global human activities. In April-May, the volcanic ash released from Eyjafjallajökull interrupted the air traffic throughout Europe, canceling over thousand flights [73]. In November the same year, Merapi eruption disturbed the air traffic for 15 days in the Central Java region, and perturbed 1950 flights departing from and to Yogyakarta [74]. At that time, one of vulnerable airline companies in Indonesia declared bankruptcy on January 2011 [74]. The societal impacts were also severe because of the timing of the eruption of Merapi, which happened at the same period as the period of pilgrimage to Mecca for the largest Muslim country in the world: Indonesia. With the occurrence of those eruptions, the air traffic warning system related to volcanic activity has then been improved to include real-time warnings through the International Airways Volcano Watch (IAVW) and the Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC) [75].
References
- Gob, F.; Gautier, E.; Virmoux, C.; Grancher, D.; Tamisier, V.; Primanda, K.W.; Wibowo, S.B.; Sarrazin, C.; de Belizal, E.; Ville, A.; et al. River responses to the 2010 major eruption of the Merapi volcano, central Java, Indonesia. Geomorphology 2016, 273, 244–257.
- Selles, A.; Deffontaines, B.; Hendrayana, H.; Violette, S. The eastern flank of the Merapi volcano (Central Java, Indonesia): Architecture and implications of volcaniclastic deposits. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 108, 33–47.
- Gertisser, R.; Cassidy, N.J.; Charbonnier, S.J.; Nuzzo, L.; Preece, K. Overbank block-and-ash flow deposits and the impact of valley-derived, unconfined flows on populated areas at Merapi volcano, Java, Indonesia. Nat. Hazards 2012, 60, 623–648.
- Umbal, J.V.; Rodolfo, K.S. The 1991 Lahars of Southwestern Mount Pinatubo and Evolution of the Lahar-Dammed Mapanuepe Lake. In Fire mud eruptions lahars Mt Pinatubo, Philippines; Newhall, C.G., Punongbayan, R.S., Eds.; University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1996.
- Lavigne, F.; Thouret, J.C.; Voight, B.; Suwa, H.; Sumaryono, A. Lahars at Merapi volcano, Central Java: An overview. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2000, 100, 423–456.
- De Bélizal, E.; Lavigne, F.; Hadmoko, D.S.; Degeai, J.-P.; Dipayana, G.A.; Mutaqin, B.W.; Marfai, M.A.; Coquet, M.; Le Mauff, B.; Robin, A.-K.; et al. Rain-triggered lahars following the 2010 eruption of Merapi volcano, Indonesia: A major risk. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2013, 261, 330–347.
- Künzler, M.; Huggel, C.; Ramírez, J.M. A risk analysis for floods and lahars: Case study in the Cordillera Central of Colombia. Nat. Hazards. 2012, 64, 767–796.
- Sarrazin, C.; Gautier, E.; Hollé, A.; Grancher, D.; de Bélizal, E.; Hadmoko, D.S. Resilience of socio-ecological systems in volcano risk-prone areas, but how much longer? Assessment of adaptive water governance in Merapi volcano, Central Java, Indonesia. GeoJournal 2019, 84, 183–213.
- Todesco, M.; Todini, E. Volcanic eruption induced floods. A rainfall-runoff model applied to the Vesuvian Region (Italy). Nat. Hazards 2004, 33, 223–245.
- Ville, A.; Lavigne, F.; Virmoux, C.; Brunstein, D.; de Bélizal, É.; Wibowo, S.B.; Hadmoko, D.S. Geomorphological evolution of the Gendol valley following the October 2010 eruption of Mt Merapi (Java, Indonesia). Géomorphologie Relief Process Environ. 2015, 21, 235–250.
- Hadmoko, D.S.; De Belizal, E.; Mutaqin, B.W.; Dipayana, G.A.; Marfai, M.A.; Lavigne, F.; Sartohadi, J.; Worosuprojo, S.; Starheim, C.C.A.; Gomez, C. Post-eruptive lahars at Kali Putih following the 2010 eruption of Merapi volcano, Indonesia: Occurrences and impacts. Nat. Hazards 2018, 94, 419–444.
- Darmawan, H.; Walter, T.R.; Brotopuspito, K.S.; Subandriyo; Nandaka, I.G. Morphological and structural changes at the Merapi lava dome monitored in 2012–15 using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2018, 349, 256–267.
- Darmawan, H.; Walterm, T.R.; Troll, V.R.; Budi-Santoso, A. Dome instability at Merapi volcano identified by drone photogrammetry and numerical modeling. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2018, 1–27.
- Jeffery, A.J.; Gertisser, R.; Troll, V.R.; Jolis, E.M.; Dahren, B.; Harris, C.; Tindle, A.G.; O’Driscoll, B.; Humaida, H.; Chadwick, J.P. The pre-eruptive magma plumbing system of the 2007-2008 dome-forming eruption of Kelut volcano, East Java, Indonesia. Contrib. Miner. Petrol. 2013, 166, 275–308.
- Ogburn, S.E.; Loughlin, S.C.; Calder, E.S. The association of lava dome growth with major explosive activity (VEI ≥ 4): DomeHaz, a global dataset. Bull. Volcanol. 2015, 77, 1–77.
- Lavigne, F.; Degeai, J.-P.; Komorowski, J.-C.; Guillet, S.; Robert, V.; Lahitte, P.; Oppenheimer, C.; Stoffel, M.; Vidal, C.M.; Surono; et al. Source of the great A.D. 1257 mystery eruption unveiled, Samalas volcano, Rinjani Volcanic Complex, Indonesia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16742–16747.
- Zaennudin, A. The characteristic of eruption of Indonesian active volcanos in the last four decades. J. Ling. Benc. Geol. 2010, 1, 113–129.
- Mutaqin, B.W.; Lavigne, F. Oldest description of a caldera-forming eruption in Southeast Asia unveiled in forgotten written sources. GeoJournal 2019, 5, 1–10.
- Rachmat, H.; Rosana, M.; Wirakusumah, A.D.; Jabbar, G.A. Petrogenesis of Rinjani post-1257 caldera-forming-eruption lava flows. Indones. J. Geosci. 2016, 3, 107–126.
- Madden-Nadeau, A.L.; Cassidy, M.; Pyle, D.M.; Mather, T.A.; Watt, S.F.L.; Enfwell, S.L.; Abdurrachman, M.; Nursha, M.E.M.; Tappin, D.R.; Ismail, T. The magmatic and eruptive evolution of the 1883 caldera-forming eruption of Krakatau: Integrating field- to crystal-scale observations. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2021, 411.
- Mutaqin, B.W.; Lavigne, F.; Sudrajat, Y.; Handayani, L.; Lahitte, P.; Virmoux, C.; Hiden; Hadmoko, D.S.; Komorowski, J.-C.; Hananto, N.D.; et al. Landscape evolution on the eastern part of Lombok (Indonesia) related to the 1257 CE eruption of the Samalas Volcano. Geomorphology 2019, 327, 338–350.
- Reid, M.E.; Keith, T.E.C.; Kayen, R.E.; Iverson, N.R.; Iverson, R.M.; Brien, D.L. Volcano collapse promoted by progressive strength reduction: New data from Mount St. Helens. Bull. Volcanol. 2010, 72, 761–766.
- Norini, G.; Bustos, E.; Arnosio, M.; Baez, W.; Zuluaga, M.C.; Roverato, M. Unusual volcanic instability and sector collapse configuration at Chimpa volcano, central Andes. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2020. 393, 106807.
- Yoshida, H. Hummock alignment in Japanese volcanic debris avalanches controlled by pre-avalanche slope of depositional area. Geomorphology 2014, 223, 67–80.
- Roverato, M.; Capra, L.; Sulpizio, R.; Norini, G. Stratigraphic reconstruction of two debris avalanche deposits at Colima Volcano (Mexico): Insights into pre-failure conditions and climate influence. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2011, 207, 33–46.
- Bronto, S. Volcanic Geology of Galunggung, West Java, Indonesia. Ph.D. Thesis, University Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zeland, 1989; 511p. Available online: (accessed on 11 December 2019).
- Siebert, L. Landslide resulting from structural failure of volcanoes. In Catastrophic Landslide: Effects, Occurrence, and Mechanisms; Evans, S., De Graff, J., Eds.; Geological Society of America Reviews in Engineering Geology: Boulder, CO, USA, 2002; pp. 209–235.
- Malawani, M.N.; Lavigne, F.; Hadmoko, D.S.; Marfai, M.A.; Mutaqin, B.W. Hummocky terrain of the Kalibabak debris avalanche deposit, Lombok Island, Indonesia. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 200, 02015.
- Yamamoto, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Glicken, H. Pyroclastic density current from the 1888 phreatic eruption of Bandai volcano, NE Japan. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1999, 90, 191–207.
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.H. Simulating floods triggered by volcanic activities in the Cheon-ji caldera lake for hazards and risk analysis. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, 479–488.
- Schaefer, L.N.; Kennedy, B.M.; Villeneuve, M.C.; Cook, S.C.; Jolly, A.D.; Keys, H.J.; Leonard, G.S.; Jolly, A. Stability assessment of the Crater Lake Te Wai-a-moe channel at Mt. Ruapehu (New Zealand), and implications for volcanic lake break-out triggers. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2018, 358, 31–44.
- Sudarmadji; Suprayogi, S.; Lestari, S.; Malawani, M.N. Water quality and sustainability of Merdada Lake, Dieng, Indonesia. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 76, 02003.
- Gunkel, G.; Beulker, C.; Grupe, B.; Viteri, F. Hazards of volcanic lakes: Analysis of Lakes Quilotoa and Cuicocha, Ecuador. Adv. Geosci. 2008, 14, 29–33.
- D’Addabbo, M.; Sulpizio, R.; Guidi, M.; Capitani, G.; Mantecca, P.; Zanchetta, G. Ash leachates from some recent eruptions of Mount Etna (Italy) and Popocatepetl (Mexico) volcanoes and their impact on amphibian living freshwater organisms. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 7087–7106.
- Mayr, C.; Smith, R.E.; García, M.L.; Massaferro, J.; Lücke, A.; Dubois, N.; Maidana, N.I.; Meier, W.J.-H.; Wissel, H.; Zolitschka, B. Historical eruptions of Lautaro Volcano and their impacts on lacustrine ecosystems in southern Argentina. J. Paleolimnol. 2019, 62, 205–221.
- Sumita, M.; Schmincke, H.U. Impact of volcanism on the evolution of Lake Van I: Evolution of explosive volcanism of Nemrut Volcano (eastern Anatolia) during the past >400,000 years. Bull. Volcanol. 2013, 75, 1–32.
- Paris, R.; Wassmer, P.; Lavigne, F.; Belousov, A.; Belousova, M.; Iskandarsyah, Y.; Benbakkar, M.; Ontowirjo, B.; Mazzoni, N. Coupling eruption and tsunami records: The Krakatau 1883 case-study, Indonesia. Bull. Volcanol. 2014, 76, 814.
- Mutaqin, B.W.; Lavigne, F.; Hadmoko, D.S.; Ngalawani, M.N. Volcanic Eruption-Induced Tsunami in Indonesia: A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 256, 012023.
- Giachetti, T.; Paris, R.; Kelfoun, K.; Ontowirjo, B. Tsunami hazard related to a flank collapse of Anak Krakatau Volcano, Sunda Strait, Indonesia. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2012, 361, 79–90.
- Waythomas, C.F.; Neal, C.A. Tsunami generation by pyroclastic flow during the 3500-year B.P. caldera-forming eruption of Aniakchak Volcano, Alaska. Bull. Volcanol. 1998, 60, 110–124.
- Novikova, T.; Papadopoulos, G.A.; McCoy, F.W. Modelling of tsunami generated by the giant Late Bronze Age eruption of Thera, South Aegean Sea, Greece. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 186, 665–680.
- European Commission. Indonesia-Volcanic Eruption & Tsunami; JRC Emergency Reporting—Activation #029; European Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Brown, S.K.; Jenkins, S.F.; Sparks, R.S.J.; Odbert, H.; Auker, M.R. Volcanic fatalities database: Analysis of volcanic threat with distance and victim classification. J. Appl. Volcanol 2017, 6, 15.
- Warsini, S.; Buettner, P.; Mills, J.; West, C.; Usher, K. The Psychosocial Impact of the Environmental Damage Caused by the MT Merapi Eruption on Survivors in Indonesia. Ecohealth 2014, 11, 491–501.
- Bowman, L.J.; Henquinet, K.B. Disaster risk reduction and resettlement efforts at San Vicente (Chichontepec) Volcano, El Salvador: Toward understanding social and geophysical vulnerability. J. Appl. Volcanol. 2015, 4, 14.
- Gomez, C.; Janin, M.; Lavigne, F.; Gertisser, R.; Charbonnier, S.; Lahitte, P.; Hadmoko, S.R.; Fort, M.; Wassmer, P.; Degroot, V.; et al. Borobudur, a basin under volcanic influence: 361, 000 years BP to present. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2010, 196, 245–264.
- Tsuruyaki, S. Vegetation changes from 1984 to 2008 on Mont Usu, northern Japan, after the 1977–1978 eruptions. Ecol. Res. 2019, 34, 813–820.
- Syifa, M.; Kadavi, P.R.; Lee, C.W.; Pradhan, B. Landsat images and artificial intelligence techniques used to map volcanic ashfall and pyroclastic material following the eruption of Mount Agung, Indonesia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 13, 13.
- Grishin, S.Y. Forest die-off under the impact of burning pyroclastic surge on the Shiveluch Volcano (Kamchatka, 2005). Russ. J. Ecol. 2009, 40, 146–148.
- Grishin, S.Y. Environmental impact of the powerful eruption of Sarychev Peak volcano (Kuril Islands, 2009) according to satellite imagery. Izv—Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2011, 47, 1028–1031.
- Tagawa, H. Primary succession and the effect of first arrivals on subsequent development of forest types. GeoJournal 1992, 28, 175–183.
- Teltscher, K.; Fassnacht, F.E. Using multispectral Landsat and sentinel-2 satellite data to investigate vegetation change at Mount St. Helens since the great volcanic eruption in 1980. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 1851–1867.
- Rampino, M.R.; Self, R. Sulphur-rich volcanic eruptions and stratospheric aerosols. Nature 1984, 310, 677–679.
- Cooper, C.L.; Swindles, G.T.; Savov, I.P.; Schmidt, A.; Bacon, K.L. Evaluating the relationship between climate change and volcanism. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 177, 238–247.
- Vidal, C.M.; Métrich, N.; Komorowski, J.-C.; Pratomo, I.; Michel, A.; Kartadinata, N.; Robert, V.; Lavigne, F. The 1257 Samalas eruption (Lombok, Indonesia): The single greatest stratospheric gas release of the Common Era. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6.
- Bertrand, C.; Van Ypersele, J.P.; Berger, A. Volcanic and solar impacts on climate since 1700. Clim. Dyn. 1999, 15, 355–367.
- Piscini, A.; Marchetti, D.; De Santis, A. Multi-Parametric Climatological Analysis Associated with Global Significant Volcanic Eruptions During 2002–2017. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2019, 176, 3629–3647.
- Fischer, E.M. Climate response to tropical eruptions. Pages News. 2006, 13, 8–10.
- Guillet, S.; Corona, C.; Stoffel, M.; Khodri, M.; Lavigne, F.; Ortega, P.; Eckert, N.; Sielenou, P.D.; Daux, V.; Sidorova, O.V.C.; et al. Climate response to the Samalas volcanic eruption in 1257 revealed by proxy records. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 123–128.
- Miller, G.H.; Geirsdóttir, Á.; Zhong, Y.; Larsen, D.J.; Otto-Bliesner, B.L.; Holland, M.M.; Bailey, D.A.; Refsnider, K.A.; Lehman, S.J.; Southon, J.R.; et al. Abrupt onset of the Little Ice Age triggered by volcanism and sustained by sea-ice/ocean feedbacks. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 39.
- Oppenheimer, C. Climatic, environmental and human consequences of the largest known historic eruption: Tambora volcano (Indonesia) 1815. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2003, 27, 230–259.
- Brázdil, R.; Řezníčková, L.; Valášek, H.; Dolák, L.; Kotyza, O. Climatic effects and impacts of the 1815 eruption of Mount Tambora in the Czech Lands. Clim. Past. 2016, 12, 1361–1374.
- Brönnimann, S.; Krämer, D. Tambora and the “Year Without a Summer” of 1816. A Perspective on Earth and Human Systems Science; Geographica Bernensia: Gerlafingen, Switzerland, 2016; Volume G90, 48p.
- Stothers, R.B. Far reach of the tenth century eldgjá eruption, Iceland. Clim. Chang. 1998, 39, 715–726.
- Fei, J.; Zhou, J. The possible climatic impact in China of Iceland’s Eldgjá eruption inferred from historical sources. Clim. Chang. 2006, 76, 443–457.
- Sigl, M.; Winstrup, M.; McConnell, J.R.; Welten, K.C.; Plunkett, G.; Ludlow, F.; Buntgen, U.; Caffee, M.W.; Chellman, N.; Dahljensen, D.; et al. Timing and climate forcing of volcanic eruptions for the past 2500 years. Nature 2015, 523, 543–549.
- Toohey, M.; Krüger, K.; Sigl, M.; Stordal, F.; Svensen, H. Climatic and societal impacts of a volcanic double event at the dawn of the Middle Ages. Clim. Chang. 2016, 136, 401–412.
- Dull, R.A.; Southon, J.R.; Kutterolf, S.; Anchukaitis, K.J.; Freundt, A.; Wahl, D.B.; Sheets, P.; Amaroli, P.; Hernandez, W.; Wiemann, M.C.; et al. Radiocarbon and geologic evidence reveal Ilopango volcano as source of the colossal ‘mystery’ eruption of 539/40 CE. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2019, 222.
- Nooren, K.; Hoek, W.; Plicht, H.; Sigl, M.; Bergen, M.; Al, E. Explosive eruption of El Chichón volcano (Mexico) disrupted 6 th century Maya civilization and contributed to global cooling. Geology 2017, 45, 175–178.
- Büntgen, U.; Myglan, V.S.; Ljungqvist, F.C.; McCormick, M.; di Cosmo, N.; Sigl, M.; Jungclaus, J.; Wagner, S.; Krusic, P.J.; Esper, J.; et al. Cooling and societal change during the Late Antique Little Ice Age from 536 to around 660 AD. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 231–236.
- Thurber, C.; Prejean, S. Volcanoes, Observations and Impact. In Earth System Monitoring: Selected Entries from the Encyclopedia of Sustainability Science and Technology; Orcutt, J., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 473–505.
- Guffanti, B.M.; Casadevall, T.J.; Budding, K. Encounters of Aircraft with Volcanic Ash Clouds: A Compilation of Known Incidents, 1953–2009; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2010.
- Langmann, B.; Folch, A.; Hensch, M.; Matthias, V. Volcanic ash over Europe during the eruption of Eyjafjallajökull on Iceland, April-May 2010. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 48, 1–8.
- Picquout, A.; Lavigne, F.; Mei, E.; Grancher, D.; Noer, C.; Vidal, C.; Hadmoko, D. Air traffic disturbance due to the 2010 Merapi volcano eruption. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2013, 261, 366–375.
- Lechner, P.; Tupper, A.; Guffanti, M.; Loughlin, S.; Casadevall, T. Volcanic Ash and Aviation—The Challenges of Real-Time, Global Communication of a Natural Hazard. Adv. Volcanol. 2018, 69, 51–64.




