| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jochen Mattner | + 1987 word(s) | 1987 | 2021-02-04 04:15:02 | | | |
| 2 | Bruce Ren | -21 word(s) | 1966 | 2021-02-20 04:33:23 | | | | |
| 3 | Bruce Ren | -21 word(s) | 1966 | 2021-02-20 04:43:10 | | |
Video Upload Options
After their synthesis from cholesterol in hepatic tissues, bile acids (BAs) are secreted into the intes-tinal lumen. Most BAs are subsequently re-absorbed in the terminal ileum and are transported back for recycling to the liver. Some of them, however, reach the colon and change their physico-chemical properties upon modification by gut bacteria, and vice versa, BAs also shape the compo-sition and function of the intestinal microbiota. This mutual interplay of both BAs and gut micro-biota regulates many physiological processes, including the lipid, carbohydrate and energy metab-olism of the host. Emerging evidence also implies an important role of this enterohepatic BA cir-cuit in shaping mucosal colonization resistance as well as local and distant immune responses, tissue physiology and carcinogenesis.
1. Introduction
The microenvironment, the tissue milieu and metabolic processes of the host’s own cells and colonizing microbial commensals have a tremendous impact on the development and function of various hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cell populations in humans. The gut microbiota and their metabolites, for example, contribute to the regulation of many physiological processes and exhibit a pivotal role in maintaining human health. Thus, microbiota signal not only to neighboring but also to distant organs and tissues in the body and interfere, for example, with the brain (brain–gut axis), the liver (liver–gut axis) and the immune and hormone system of the host [1], and vice versa, the host also shapes the intraluminal microbiota. Although the genetic traits of the host as well as dietary and micro-environmental factors presumably contribute to these complex interactions [2][3][4][5][6], it is largely unknown how commensal microbiota are selectively influenced.
Nonetheless, disrupted intestinal microbiota that accompany inflammatory processes in the gut and the subsequent altered availability of microbial- or host-derived products and metabolites are frequently associated with the pathogenesis of various complex disorders [7][8][9][10]. As the etiology of these diseases is multifactorial, they develop as a consequence of a malfunctioning network rather than of a single cause [11]. Thus, the versatile host–microbiota interactions are pivotal for maintaining physiologic homeostasis.
One interesting aspect of host–microbiota interactions is that host- and microbiota-derived enzymes frequently regulate the same pool of intraluminal metabolites [12]. Some physiologic signaling cascades and metabolic processes even require co-metabolism between the host and the microbiota. A classic example of shared alternating enzymatic reactions between mammalians and their intraluminal microbiota is the biosynthesis of bile acids (BAs). In this case, the host synthesizes primary BAs in the liver, which the intestinal microbiota subsequently transform in the gut. This conjugation and deconjugation of BAs plays a pivotal role in many physiological and pathophysiological processes in the liver–gut axis. Here, we discuss a few of them using selected examples of infectious, immune-mediated and tumor diseases.
2. Bile Acids (BAs) and Enterohepatic Circulation
Bile acids (BAs) are hydroxylated, amphipathic steroid acids that are synthesized in the peroxisomes of the liver from cholesterol [13]. In hepatic tissues, BAs are also conjugated to the hydrophilic amino acids glycine (Gly), taurine (Tau) or sulfate. These BAs are now named primary or conjugated BAs. They consist of cholic acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) or tauro- and glycoconjugated versions thereof (Table 1). While humans preferably use glycine for conjugation, taurine is the most common conjugate of BAs in rodents.
Table 1. Primary bile acids and their functions under physiological and pathophysiological conditions. (UC = ulcerative colitis, CRC = colorectal cancer, HCC = hepatocellular carcinoma).
|
Abbrevation |
Bile Acid Name |
Physiologic Functions |
Pathophysiologic Functions |
|
CA |
Cholic acid |
facilitate digestion [14]; emulsify hydrophobic food components such as fats into micelles for intestinal absorption [14]; protect from CRC induced by Bacteroides fragilis toxin [15] |
favor infections with pathogenic bacteria (Salmonella spp., E. coli, Shigella dysenteriae) [16][17][18][19][20][21][22][23] and the germination of C. difficile spores [24][25][26]; can cause colitis and diarrhea in UC patients [27]; promote the accumu-lation of CXCR6+-NKT-cells in the liver and protects from HCC [28] |
|
CDCA |
Chenodeoxycholic acid |
||
|
GCA |
Glycocholic acid |
||
|
GCDCA |
Glycochenodeoxycholic acid |
||
|
TCA |
Taurocholic acid |
||
|
TCDCA |
Taurochenodeoxycholic acid |
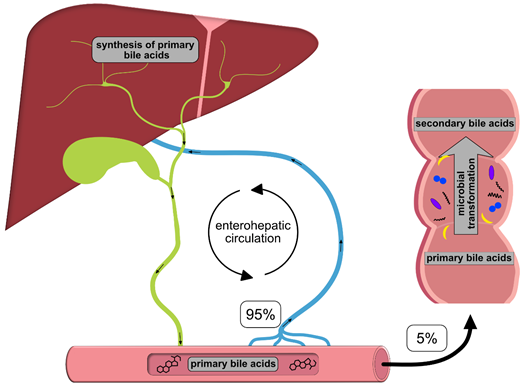
Once synthesized, these primary BAs are secreted into the bile, where they comprise about 80% of the organic compounds [29] and are concentrated for storage in the gallbladder [30]. Ingestion of food triggers the release of cholecystokinin by enteroendocrine cells, which causes gallbladder contraction and the release of primary BAs into the duodenum [31]. There, the primary purpose of BAs is to facilitate the digestion and absorption of dietary lipids, fatty acids, cholesterol, fat-soluble vitamins and other hydrophobic components of the diet via its surfactant properties, which emulsify fats into micelles. Usually, more than 95% of the primary BAs are re-absorbed from the terminal ileum and transported back into the liver via the so-called enterohepatic circulation (EHC) (Figure 1). Upon their return to the liver via the portal vein, primary BAs inhibit cholesterol biosynthesis and further BA biosynthesis [29].
Figure 1. Schematic overview of the enterohepatic circulation (EHC). Primary bile acids (BAs) are synthesized in the liver and secreted into the duodenum with the bile; 95% of the BAs are re-absorbed in the terminal ileum and transported back to the liver for recycling. The remaining 5% enter the colon, where they are transformed into secondary BAs by colonic microbiota.
However, small quantities of primary BAs also reach the colon, where certain gut bacteria transform them into secondary BAs, such as deoxycholic acid (DCA), ursodeoxycholic (UDCA) and lithocholic acid (LCA), by deconjugation, oxidation/epimerization, (7-α-) dehydroxylation and esterification [32][33][34][35] (Table 2). In particular, secondary BAs exhibit strong antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity. Thus, BAs also regulate the composition of gut bacterial communities and host physiology [32], features that are described in more detail below. Immunoglobulin A (IgA), the major immunoglobulin at mucosal surfaces, enhances the antimicrobial properties of BAs; thus, both BAs and IgA inhibit bacterial growth and adhesion and subsequently protect against ascending infections within the biliary tract. In addition, BAs eliminate bilirubin from the body via the feces [36].
Table 2. Secondary bile acids and their (patho-)physiologic functions (CRC = colorectal cancer, PBS = primary biliary cirrhosis, ILC3 = type 3 innate lymphoid cells, PSC = primary sclerosing cholangitis, NASH = non-alcoholic steatohepatitis).
|
Abbrevation |
Bile Acid Name |
Physiologic Functions |
Pathophysiologic Functions |
|
DCA |
Deoxycholic acid |
exhibit antimicrobial activity [32]; maintain colonic microbiota [32]; perpetuate endocrine functions via binding to nuclear factor X receptor (FXR) and G-protein-coupled bile acid receptor (TGR5) |
enhanced levels are associated with CRC development [41] |
|
UDCA |
Ursodeoxycholic acid |
drug for the treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) |
|
|
HDCA |
Hyodeoxycholic acid |
suppresses intestinal cell proliferation and enhances abundance of microbiota [42] |
|
|
GDCA |
Glycodeoxycholic acid |
induces interleukin-22 production by ILC3s and improves ovulatory dysfunction and insulin resistance in patients suffering from polycystic ovary syndrome (POCS) [43] |
|
|
GUDCA |
Glycoursodeoxycholic acid |
neuroprotective agent (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Glycoursodeoxycholic-acid) |
|
|
LCA |
Lithocholic acid |
enhanced levels in patients suffering from Alzheimer´s disease [44] |
|
|
GLCA |
Glycolithocholic acid |
|
|
|
TLCA |
Taurolithocholic acid |
induces biliary dysbiosis in PSC patients |
|
|
TDCA |
Taurodeoxycholic acid |
|
|
|
TUDCA |
Tauroursodeoxycholic acid |
protective effects in NASH [45]; associated with attenuated hepatocarcinogenesis [46] |
|
|
THDCA |
Taurohyodeoxycholic acid |
protective effects in experimentally induced colitis [47] |
|
|
TMCA (a+b) |
Tauromuricholic acid (alpha + beta) |
maintains lipid and glucose metabolism [48]; reduced levels in the plasma of APP/PS1 mice, which are a mouse model for Alzheimer’s disease [49] |
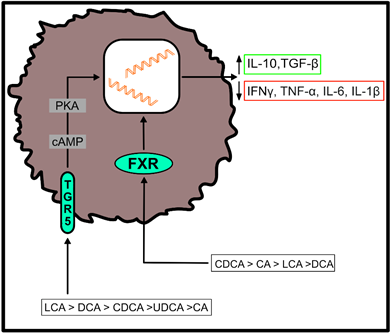
Both, primary and secondary BAs exert biological effects on cells of the host by activating nuclear and plasma membrane receptors, including the nuclear farnesoid X receptor (FXR) or the G protein-coupled receptor (TGR5) [37][38][39][40]. These receptors control the synthesis and metabolism of BAs. However, engagement of these receptors enables BAs to contribute to the regulation of glucose homeostasis, lipid metabolism and energy expenditure [50]. Furthermore, BAs regulate immune responses upon ligation of these two receptors (Figure 2), which are located at the interface of the host immune system with the intestinal microbiota [51]. Both receptors are highly expressed on cells of the innate immune system, including macrophages, dendritic cells and natural killer T (NKT) cells [51]. In particular, TGR5 and FXR regulate the polarization of macrophages and can also rescue mice from severe colitis [52][53].
Figure 2. Effects of bile acid (BA) receptor engagement on immune cell function. After binding to the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) or the G protein-coupled receptor (TGR5), primary and secondary BAs shift the cytokine profile of myeloid cells to an anti-inflammatory phenotype. Their agonistic functions thereby depend on the affinity of individual BAs for the respective receptor, as indicated in the figure. (IL-10 = interleukin-10; TGF-β = transforming growth factor beta; IFNγ = interferon gamma; TNF-α = tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL-6 = interleukin-6; IL-1β = interleukin-1 beta).
In summary, the main functions of BAs include (a) emulsifying and digesting fat, (b) regulating and excreting cholesterol, (c) exerting antimicrobial effects and (d) eliminating bilirubin from the body. However, as there exist multiple microbes that are tolerant against bile [54], the antimicrobial effects of bile (acids) selectively restrain certain microbial species and subsequently affect the composition of the complete intestinal or biliary microflora.
3. Local Site Microbiota in the Gut and Bile
The intestine hosts complex and dynamic populations of highly diverse microorganisms. These include various bacteria, archaea and eukarya, which form a mutually beneficial relationship with the host. Diet, for example, strongly influences the composition of the microbiota [55][56], and vice versa, intestinal microbiota produce metabolites and extract nutrients from a large range of molecules that enzymes of the host are unable to convert. any of these nutrients and metabolites derived from commensal microbiota have been implicated in the development, homeostasis and function of the immune system, suggesting that microbial commensals influence host immunity via nutrient- and metabolite-dependent mechanisms [57]. Accordingly, an altered composition of the gut microbiota, known as dysbiosis, accompanies many intestinal and extra-intestinal disorders [58].
Similar to the gut, the gallbladder also harbors a complex microbiota. In contrast to the intestine, the microbiota of the biliary tract contains relatively low levels of Bacteroidetes, while numbers of Proteobacteria, Tenericutes, Actinobacteria and Cyanobacteria are increased [59][60][61]. Similar to what is observed with intestinal microbiota, although less well studied, the bile microbiota can be disrupted [59].
4. Crosstalk between BAs and Microbiota
The regulation of the BA pool is one example of the interference of the microbial metabolism with the host [62]. The deconjugation, oxidation/epimerization, (7-α-) dehydroxylation and esterification of BAs by the intestinal microbiota can dramatically change their physicochemical properties and subsequently affect their microbial toxicity and intestinal absorption.
For example, the deconjugation of BAs by microbial bile salt hydrolases (BSH)—abundant enzymes found in all major bacterial phyla—enhances their intestinal re-absorption. Furthermore, it promotes the colonization of the gut by microbiota and can serve as a nutritional source of sulfur, nitrogen and carbon [63][64][65]
7-α-Dehydroxylation converts the primary BAs cholic (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acids (CDCA) into the secondary BAs deoxycholic (DCA) and lithocholic acids (LCA). It is quantitatively the most important and the most physiologically significant conversion of BAs in humans. Deoxycholic acid may even account for up to 25% of the total BA pool. The bacterial species that possess 7-α-dehydroxylation activity include members of the Firmicutes phylum, such as Clostridium or Eubacterium.
The effects of the intestinal microbiota presumably extend further beyond BA composition and biotransformation. In fact, germ-free and antibiotic-treated mice exhibit reduced BA excretion in the feces. In contrast, the BA pool is increased along with enhanced BA secretion and re-absorption from the intestine and an overall altered metabolic homeostasis of the host [66][67][68][69].
As mentioned above, their amphipathic character also supplies BAs with antimicrobial activities. Thus, BAs alter the fluidity, permeability and function of cellular membranes and membrane-bound proteins [70][71]. BAs also cause DNA damage and oxidative stress and affect the formation of RNAs and proteins [70][71][72]. The application of BAs expands Firmicutes at the expense of Bacteroidetes in the gut. Accordingly, increased intraluminal BA concentrations favor the growth of bacterial species that 7-α-dehydroxylate primary BAs into secondary BAs [73][74]. In contrast, lower intraluminal BA levels predominantly favor the growth of Gram-negative bacteria. In addition, BAs also influence the integrity of intestinal epithelial cells and mucosal immune responses and thus indirectly regulate the composition of microbial communities [75][76][77]. As discussed below, secondary BAs can also exhibit toxic effects (Table 2) and promote infectious, inflammatory or malignant diseases.
References
- Schroeder, B.O.; Backhed, F. Signals from the gut microbiota to distant organs in physiology and disease. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1079–1089, doi:10.1038/nm.4185.
- Liu, S.; da Cunha, A.P.; Rezende, R.M.; Cialic, R.; Wei, Z.; Bry, L.; Comstock, L.E.; Gandhi, R.; Weiner, H.L. The Host Shapes the Gut Microbiota via Fecal MicroRNA. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 32–43, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2015.12.005.
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484, doi:10.1038/nature07540.
- Backhed, F.; Ley, R.E.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 2005, 307, 1915–1920, doi:10.1126/science.1104816.
- Goodrich, J.K.; Waters, J.L.; Poole, A.C.; Sutter, J.L.; Koren, O.; Blekhman, R.; Beaumont, M.; Van Treuren, W.; Knight, R.; Bell, J.T.; et al. Human genetics shape the gut microbiome. Cell 2014, 159, 789–799, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.053.
- Ley, R.E.; Backhed, F.; Turnbaugh, P.; Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R.D.; Gordon, J.I. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11070–11075, doi:10.1073/pnas.0504978102.
- Belkaid, Y.; Harrison, O.J. Homeostatic Immunity and the Microbiota. Immunity 2017, 46, 562–576, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2017.04.008.
- Pickard, J.M.; Zeng, M.Y.; Caruso, R.; Nunez, G. Gut microbiota: Role in pathogen colonization, immune responses, and inflammatory disease. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 279, 70–89, doi:10.1111/imr.12567.
- Xavier, J.B.; Young, V.B.; Skufca, J.; Ginty, F.; Testerman, T.; Pearson, A.T.; Macklin, P.; Mitchell, A.; Shmulevich, I.; Xie, L.; et al. The Cancer Microbiome: Distinguishing Direct and Indirect Effects Requires a Systemic View. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 192–204, doi:10.1016/j.trecan.2020.01.004.
- Sharon, G.; Sampson, T.R.; Geschwind, D.H.; Mazmanian, S.K. The Central Nervous System and the Gut Microbiome. Cell 2016, 167, 915–932, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.10.027.
- de Souza, H.S.P.; Fiocchi, C.; Iliopoulos, D. The IBD interactome: An integrated view of aetiology, pathogenesis and therapy. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 739–749, doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2017.110.
- Baier, J.; Gansbauer, M.; Giessler, C.; Arnold, H.; Muske, M.; Schleicher, U.; Lukassen, S.; Ekici, A.; Rauh, M.; Daniel, C.; et al. Arginase impedes the resolution of colitis by altering the microbiome and metabolome. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5703–5720, doi:10.1172/JCI126923.
- Ferdinandusse, S.; Houten, S.M. Peroxisomes and bile acid biosynthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1763, 1427–1440, doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.09.001.
- Hofmann, A.F.; Borgstroem, B. The Intraluminal Phase of Fat Digestion in Man: The Lipid Content of the Micellar and Oil Phases of Intestinal Content Obtained during Fat Digestion and Absorption. J. Clin. Investig. 1964, 43, 247–257, doi:10.1172/JCI104909.
- Metz, P.; Tjan, M.J.H.; Wu, S.; Pervaiz, M.; Hermans, S.; Shettigar, A.; Sears, C.L.; Ritschel, T.; Dutilh, B.E.; Boleij, A. Drug Discovery and Repurposing Inhibits a Major Gut Pathogen-Derived Oncogenic Toxin. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 364, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2019.00364.
- Wotzka, S.Y.; Kreuzer, M.; Maier, L.; Arnoldini, M.; Nguyen, B.D.; Brachmann, A.O.; Berthold, D.L.; Zund, M.; Hausmann, A.; Bakkeren, E.; et al. Escherichia coli limits Salmonella Typhimurium infections after diet shifts and fat-mediated microbiota perturbation in mice. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 2164–2174, doi:10.1038/s41564-019-0568-5.
- Hernandez, S.B.; Cota, I.; Ducret, A.; Aussel, L.; Casadesus, J. Adaptation and preadaptation of Salmonella enterica to Bile. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002459, doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002459.
- Johnson, R.; Ravenhall, M.; Pickard, D.; Dougan, G.; Byrne, A.; Frankel, G. Comparison of Salmonella enterica Serovars Typhi and Typhimurium Reveals Typhoidal Serovar-Specific Responses to Bile. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86, e00490-17, doi:10.1128/IAI.00490-17.
- Rosenberg, E.Y.; Bertenthal, D.; Nilles, M.L.; Bertrand, K.P.; Nikaido, H. Bile salts and fatty acids induce the expression of Escherichia coli AcrAB multidrug efflux pump through their interaction with Rob regulatory protein. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 1609–1619, doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03531.x.
- Sistrunk, J.R.; Nickerson, K.P.; Chanin, R.B.; Rasko, D.A.; Faherty, C.S. Survival of the Fittest: How Bacterial Pathogens Utilize Bile To Enhance Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 819–836, doi:10.1128/CMR.00031-16.
- Kramer, V.C.; Nickerson, K.W.; Hamlett, N.V.; O'Hara, C. Prevalence of extreme detergent resistance among the Enterobacteriaceae. Can. J. Microbiol. 1984, 30, 711–713, doi:10.1139/m84-106.
- Kwan, B.W.; Lord, D.M.; Peti, W.; Page, R.; Benedik, M.J.; Wood, T.K. The MqsR/MqsA toxin/antitoxin system protects Escherichia coli during bile acid stress. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3168–3181, doi:10.1111/1462-2920.12749.
- Sengupta, C.; Ray, S.; Chowdhury, R. Fine tuning of virulence regulatory pathways in enteric bacteria in response to varying bile and oxygen concentrations in the gastrointestinal tract. Gut. Pathog. 2014, 6, 38, doi:10.1186/s13099-014-0038-9.
- Giel, J.L.; Sorg, J.A.; Sonenshein, A.L.; Zhu, J. Metabolism of bile salts in mice influences spore germination in Clostridium difficile. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8740, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008740.
- Sorg, J.A.; Sonenshein, A.L. Inhibiting the initiation of Clostridium difficile spore germination using analogs of chenodeoxycholic acid, a bile acid. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 4983–4990, doi:10.1128/JB.00610-10.
- Weingarden, A.R.; Chen, C.; Bobr, A.; Yao, D.; Lu, Y.; Nelson, V.M.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Khoruts, A. Microbiota transplantation restores normal fecal bile acid composition in recurrent Clostridium difficile infection. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 306, G310–G319, doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00282.2013.
- Fitzpatrick, L.R.; Jenabzadeh, P. IBD and Bile Acid Absorption: Focus on Pre-clinical and Clinical Observations. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 564, doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.00564.
- Ma, C.; Han, M.; Heinrich, B.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Sandhu, M.; Agdashian, D.; Terabe, M.; Berzofsky, J.A.; Fako, V.; et al. Gut microbiome-mediated bile acid metabolism regulates liver cancer via NKT cells. Science 2018, 360, doi:10.1126/science.aan5931.
- Hofmann, A.F. The continuing importance of bile acids in liver and intestinal disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 2647–2658, doi:10.1001/archinte.159.22.2647.
- Chen, I.; Cassaro, S. Physiology, Bile Acids; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020.
- Di Ciaula, A.; Garruti, G.; Lunardi Baccetto, R.; Molina-Molina, E.; Bonfrate, L.; Wang, D.Q.; Portincasa, P. Bile Acid Physiology. Ann. Hepatol. 2017, 16, s4–s14, doi:10.5604/01.3001.0010.5493.
- Ridlon, J.M.; Harris, S.C.; Bhowmik, S.; Kang, D.J.; Hylemon, P.B. Consequences of bile salt biotransformations by intestinal bacteria. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 22–39, doi:10.1080/19490976.2015.1127483.
- Jones, B.V.; Begley, M.; Hill, C.; Gahan, C.G.; Marchesi, J.R. Functional and comparative metagenomic analysis of bile salt hydrolase activity in the human gut microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13580–13585, doi:10.1073/pnas.0804437105.
- Gerard, P. Metabolism of cholesterol and bile acids by the gut microbiota. Pathogens 2013, 3, 14–24, doi:10.3390/pathogens3010014.
- Hamilton, J.P.; Xie, G.; Raufman, J.P.; Hogan, S.; Griffin, T.L.; Packard, C.A.; Chatfield, D.A.; Hagey, L.R.; Steinbach, J.H.; Hofmann, A.F. Human cecal bile acids: Concentration and spectrum. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 293, G256–G263, doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00027.2007.
- Hofmann, A.F.; Hagey, L.R.; Krasowski, M.D. Bile salts of vertebrates: Structural variation and possible evolutionary significance. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 226–246, doi:10.1194/jlr.R000042.
- Fiorucci, S.; Mencarelli, A.; Palladino, G.; Cipriani, S. Bile-acid-activated receptors: Targeting TGR5 and farnesoid-X-receptor in lipid and glucose disorders. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2009, 30, 570–580, doi:10.1016/j.tips.2009.08.001.
- Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Hollister, K.; Sowers, L.C.; Forman, B.M. Endogenous bile acids are ligands for the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 543–553, doi:10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80348-2.
- Maruyama, T.; Miyamoto, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Tamai, Y.; Okada, H.; Sugiyama, E.; Nakamura, T.; Itadani, H.; Tanaka, K. Identification of membrane-type receptor for bile acids (M-BAR). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 298, 714–719, doi:10.1016/s0006-291x(02)02550-0.
- Kawamata, Y.; Fujii, R.; Hosoya, M.; Harada, M.; Yoshida, H.; Miwa, M.; Fukusumi, S.; Habata, Y.; Itoh, T.; Shintani, Y.; et al. A G protein-coupled receptor responsive to bile acids. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9435–9440, doi:10.1074/jbc.M209706200.
- Ridlon, J.M.; Wolf, P.G.; Gaskins, H.R. Taurocholic acid metabolism by gut microbes and colon cancer. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 201–215, doi:10.1080/19490976.2016.1150414.
- Song, M.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, F.L.; Chen, L.; Su, H.; Yang, X.H.; He, H.W.; Liu, F.F.; Zheng, J.S.; Ling, M.F.; et al. Hyodeoxycholic acid (HDCA) suppresses intestinal epithelial cell proliferation through FXR-PI3K/AKT pathway, accompanied by alteration of bile acids metabolism profiles induced by gut bacteria. Faseb. J. 2020, 34, 7103–7117, doi:10.1096/fj.201903244R.
- Qi, X.Y.; Yun, C.Y.; Sun, L.L.; Xia, J.L.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.N.; Zhang, Y.M.; Liang, X.Y.; Wang, L.Y.; et al. Gut microbiota-bile acid-interleukin-22 axis orchestrates polycystic ovary syndrome. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1225–1233, doi:10.1038/s41591-019-0509-0.
- Marksteiner, J.; Blasko, I.; Kemmler, G.; Koal, T.; Humpel, C. Bile acid quantification of 20 plasma metabolites identifies lithocholic acid as a putative biomarker in Alzheimer's disease. Metabolomics 2018, 14, doi:10.1007/s11306-017-1297-5.
- Wang, W.J.; Zhao, J.F.; Gui, W.F.; Sun, D.; Dai, H.J.; Xiao, L.; Chu, H.K.; Du, F.; Zhu, Q.J.; Schnabl, B.; et al. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid inhibits intestinal inflammation and barrier disruption in mice with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Br. J. Pharm. 2018, 175, 469–484, doi:10.1111/bph.14095.
- Vandewynckel, Y.P.; Laukens, D.; Devisscher, L.; Paridaens, A.; Bogaerts, E.; Verhelst, X.; Van den Bussche, A.; Raevens, S.; Van Steenkiste, C.; Van Troys, M.; et al. Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid Dampens Oncogenic Apoptosis Induced by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress during Hepatocarcinogen Exposure. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S402–S403, doi:10.1016/S0168-8278(15)30474-8.
- He, J.; Liang, J.R.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, W.N.; Zhang, Y.M.; Sun, W.J. Protective effect of taurohyodeoxycholic acid from Pulvis Fellis Suis on trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. 2011, 670, 229–235, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.08.036.
- Li, F.; Jiang, C.T.; Krausz, K.W.; Li, Y.F.; Albert, I.; Hao, H.P.; Fabre, K.M.; Mitchell, J.B.; Patterson, A.D.; Gonzalez, F.J. Microbiome remodelling leads to inhibition of intestinal farnesoid X receptor signalling and decreased obesity. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2384, doi:10.1038/ncomms3384.
- Pan, X.B.; Elliott, C.T.; McGuinness, B.; Passmore, P.; Kehoe, P.G.; Holscher, C.; McClean, P.L.; Graham, S.F.; Green, B.D. Metabolomic Profiling of Bile Acids in Clinical and Experimental Samples of Alzheimer's Disease. Metabolites 2017, 7, 28, doi:ARTN 2810.3390/metabo7020028.
- McGlone, E.R.; Bloom, S.R. Bile acids and the metabolic syndrome. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 56, 326–337, doi:10.1177/0004563218817798.
- Fiorucci, S.; Biagioli, M.; Zampella, A.; Distrutti, E. Bile Acids Activated Receptors Regulate innate immunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1853, doi:ARTN 185310.3389/fimmu.2018.01853.
- Wammers, M.; Schupp, A.K.; Bode, J.G.; Ehlting, C.; Wolf, S.; Deenen, R.; Kohrer, K.; Haussinger, D.; Graf, D. Reprogramming of pro-inflammatory human macrophages to an anti-inflammatory phenotype by bile acids. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 255, doi:ARTN 25510.1038/s41598-017-18305-x.
- Biagioli, M.; Carino, A.; Cipriani, S.; Francisci, D.; Marchiano, S.; Scarpelli, P.; Sorcini, D.; Zampella, A.; Fiorucci, S. The Bile Acid Receptor GPBAR1 Regulates the M1/M2 Phenotype of Intestinal Macrophages and Activation of GPBAR1 Rescues Mice from Murine Colitis. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 718–733, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1700183.
- Begley, M.; Gahan, C.G.; Hill, C. The interaction between bacteria and bile. Fems. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 625–651, doi:10.1016/j.femsre.2004.09.003.
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.M.; et al. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180, doi:10.1038/nature09944.
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108, doi:10.1126/science.1208344.
- Brestoff, J.R.; Artis, D. Commensal bacteria at the interface of host metabolism and the immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 676–684, doi:10.1038/ni.2640.
- Zeng, M.Y.; Inohara, N.; Nunez, G. Mechanisms of inflammation-driven bacterial dysbiosis in the gut. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 18–26, doi:10.1038/mi.2016.75.
- Molinero, N.; Ruiz, L.; Milani, C.; Gutierrez-Diaz, I.; Sanchez, B.; Mangifesta, M.; Segura, J.; Cambero, I.; Campelo, A.B.; Garcia-Bernardo, C.M.; et al. The human gallbladder microbiome is related to the physiological state and the biliary metabolic profile. Microbiome 2019, 7, 100, doi:10.1186/s40168-019-0712-8.
- Folseraas, T.; Melum, E.; Rausch, P.; Juran, B.D.; Ellinghaus, E.; Shiryaev, A.; Laerdahl, J.K.; Ellinghaus, D.; Schramm, C.; Weismuller, T.J.; et al. Extended analysis of a genome-wide association study in primary sclerosing cholangitis detects multiple novel risk loci. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 366–375, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2012.03.031.
- Verdier, J.; Luedde, T.; Sellge, G. Biliary Mucosal Barrier and Microbiome. Viszeralmedizin 2015, 31, 156–161, doi:10.1159/000431071.
- Ridlon, J.M.; Kang, D.J.; Hylemon, P.B.; Bajaj, J.S. Bile acids and the gut microbiome. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 30, 332–338, doi:10.1097/MOG.0000000000000057.
- Grill, J.P.; Perrin, S.; Schneider, F. Bile salt toxicity to some bifidobacteria strains: Role of conjugated bile salt hydrolase and pH. Can. J. Microbiol. 2000, 46, 878–884, doi:10.1139/w00-066.
- Dussurget, O.; Cabanes, D.; Dehoux, P.; Lecuit, M.; Buchrieser, C.; Glaser, P.; Cossart, P.; European Listeria Genome Consortium. Listeria monocytogenes bile salt hydrolase is a PrfA-regulated virulence factor involved in the intestinal and hepatic phases of listeriosis. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 45, 1095–1106, doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03080.x.
- Carbonero, F.; Benefiel, A.C.; Alizadeh-Ghamsari, A.H.; Gaskins, H.R. Microbial pathways in colonic sulfur metabolism and links with health and disease. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 448, doi:10.3389/fphys.2012.00448.
- Out, C.; Patankar, J.V.; Doktorova, M.; Boesjes, M.; Bos, T.; de Boer, S.; Havinga, R.; Wolters, H.; Boverhof, R.; van Dijk, T.H.; et al. Gut microbiota inhibit Asbt-dependent intestinal bile acid reabsorption via Gata4. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 697–704, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2015.04.030.
- Sayin, S.I.; Wahlstrom, A.; Felin, J.; Jantti, S.; Marschall, H.U.; Bamberg, K.; Angelin, B.; Hyotylainen, T.; Oresic, M.; Backhed, F. Gut microbiota regulates bile acid metabolism by reducing the levels of tauro-beta-muricholic acid, a naturally occurring FXR antagonist. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 225–235, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2013.01.003.
- Wahlstrom, A.; Sayin, S.I.; Marschall, H.U.; Backhed, F. Intestinal Crosstalk between Bile Acids and Microbiota and Its Impact on Host Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 41–50, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2016.05.005.
- Zarrinpar, A.; Chaix, A.; Xu, Z.Z.; Chang, M.W.; Marotz, C.A.; Saghatelian, A.; Knight, R.; Panda, S. Antibiotic-induced microbiome depletion alters metabolic homeostasis by affecting gut signaling and colonic metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2872, doi:10.1038/s41467-018-05336-9.
- Long, S.L.; Gahan, C.G.M.; Joyce, S.A. Interactions between gut bacteria and bile in health and disease. Mol. Asp. Med. 2017, 56, 54–65, doi:10.1016/j.mam.2017.06.002.
- Urdaneta, V.; Casadesus, J. Interactions between Bacteria and Bile Salts in the Gastrointestinal and Hepatobiliary Tracts. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2017, 4, 163, doi:10.3389/fmed.2017.00163.
- Bernstein, C.; Bernstein, H.; Payne, C.M.; Beard, S.E.; Schneider, J. Bile salt activation of stress response promoters in Escherichia coli. Curr. Microbiol. 1999, 39, 68–72, doi:10.1007/s002849900420.
- Islam, K.B.; Fukiya, S.; Hagio, M.; Fujii, N.; Ishizuka, S.; Ooka, T.; Ogura, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Yokota, A. Bile acid is a host factor that regulates the composition of the cecal microbiota in rats. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1773–1781, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.046.
- Kakiyama, G.; Pandak, W.M.; Gillevet, P.M.; Hylemon, P.B.; Heuman, D.M.; Daita, K.; Takei, H.; Muto, A.; Nittono, H.; Ridlon, J.M.; et al. Modulation of the fecal bile acid profile by gut microbiota in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 949–955, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2013.01.003.
- Inagaki, T.; Moschetta, A.; Lee, Y.K.; Peng, L.; Zhao, G.; Downes, M.; Yu, R.T.; Shelton, J.M.; Richardson, J.A.; Repa, J.J.; et al. Regulation of antibacterial defense in the small intestine by the nuclear bile acid receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3920–3925, doi:10.1073/pnas.0509592103.
- Vavassori, P.; Mencarelli, A.; Renga, B.; Distrutti, E.; Fiorucci, S. The bile acid receptor FXR is a modulator of intestinal innate immunity. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6251–6261, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0803978.
- Cipriani, S.; Mencarelli, A.; Chini, M.G.; Distrutti, E.; Renga, B.; Bifulco, G.; Baldelli, F.; Donini, A.; Fiorucci, S. The bile acid receptor GPBAR-1 (TGR5) modulates integrity of intestinal barrier and immune response to experimental colitis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25637, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025637.