
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Helmut Cölfen | + 4830 word(s) | 4830 | 2021-02-04 05:19:32 | | | |
| 2 | Vivi Li | Meta information modification | 4830 | 2021-02-05 05:08:12 | | |
Video Upload Options
A centrifugal field can provide an external force for the ordering of nanoparticles. Especially with the knowledge from in-situ characterization by analytical (ultra)centrifugation, nanoparticle ordering can be rationally realized in preparative (ultra)centrifugation. This study summarizes the work back to the 1990s, where intuitive use of centrifugation was achieved for the fabrication of colloidal crystals to the very recent work where analytical (ultra)centrifugation is employed to tailor-make concentration gradients for advanced materials. This review is divided into three main parts. In the introduction part, the history of ordering microbeads in gravity is discussed and with the size of particles reduced to nanometers, a centrifugal field is necessary. In the next part, the research on the ordering of nanoparticles in analytical and preparative centrifugation in recent decades is described. In the last part, the applications of the functional materials, fabricated from centrifugation-induced nanoparticle superstructures are briefly discussed.
1. Introduction
1.1. The Era of Microbeads in Gravity
The sedimentation of particles is a long-standing phenomenon in nature. One of the most impressive examples may be the formation of opals [1][2][3][4] where the sedimentation of silica particles gradually forms iridescent mineraloids over a long period of time. Besides these great phenomena in nature, the first experimental work to study particle sedimentation was conducted by Jean Perrin [5] in 1912. He used an optical microscope to observe the 3-dimensional motions of microscopic gamboge particles during their sedimentation, under gravity. The observation directly proved the constant random motion of any small object, was raised by Albert Einstein [6] in 1905 and also led to an experimental estimation of the Boltzmann constant. This work paved the way to the understanding of the reality of atoms and molecules, and thus earned Jean Perrin the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1926. After this breakthrough work, extensive research on the movement of particles in sedimentation has been conducted from the early-20th century on, especially the establishment of fundamental theories of sedimentation [7][8][9][10][11]. Besides these theoretical advances, experimental research also saw major progress [12][13][14][15][16], especially the classical experiments conducted by P.N. Pusey and W. van Megen. They synthesized hard-sphere latex particles, which represent the simplest possible interparticle interaction [17] case. They observed the ordering process of these microbeads with a good size monodispersity (diameter: 0.61 µm ± 0.02 µm) under gravity and the final formation of Bragg-reflecting crystalline samples [18], which demonstrated an iridescent structural color [19][20] in front of a beam of white light, as shown in Figure 1. The phase diagram was also obtained, which described the ordering transition from fluid to crystal [21][22] and then to glass with an increasing volume fraction. Research on the ordering of binary hard sphere mixtures in dispersion followed [23][24], which displays a richer phase diagram [2] with a large variety of ordered structures, as shown in Figure 2. With these exciting experimental observations, the theoretical studies also stepped forward [25][26], particularly in the area of fundamental studies on crystal nucleation and growth [27][28] of particles. At the beginning of the 21st century, the idea of a combination of fluorescence labelling [29] and refractive index matching was realized by van Blaaderen et al. and thus allowed in-situ observation [30][31][32] of the whole sedimentation and ordering process of colloidal particles in a gravitational field. The representative examples [33][34] are displayed in Figure 3. These studies led to the visualization of the whole ordering process of the particles during sedimentation and provide insights into the tuning [35][36] of the ordering of superlattice structures, typically for near-micrometer-sized colloids.
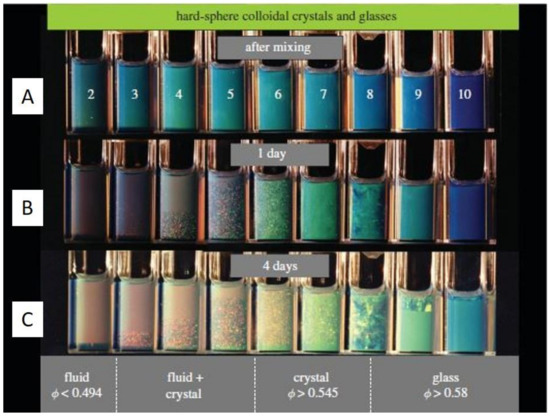

Figure 1. Hard-sphere latex suspensions in cuvettes, illuminated obliquely from behind by white light, (A) immediately after mixing, (B) after 1 day, and (C) after 4 days. In the lowest column (after 4 days), the lower part of the right cuvettes shows the glassy phase with the volume fraction larger than 0.58, the middle cuvettes show the nucleated crystal phase with the volume fraction between 0.545 and 0.58 while the left cuvettes show mostly the fluid phase when the volume fraction is lower than 0.494. Reproduced with permission from [18], Copyright the Royal Society, 2009.
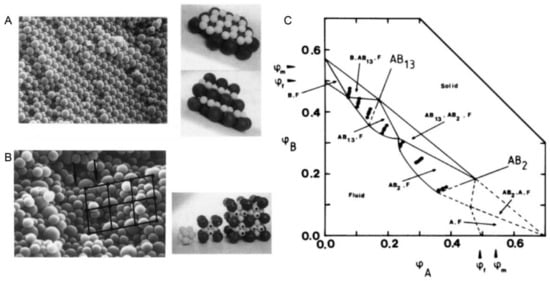
Figure 2. (A). Scanning electron micrograph and model of an AB2 superlattice of the sample composition: nB/nA = 6, φA + φB = 0.536 for a binary hard sphere mixture at size ratio RB/RA = 0.58; (B). Scanning electron micrograph and model of an AB13 superlattice of the sample composition: nB/nA = 9, φA + φB = 0.552 for a binary hard sphere mixture at the same size ratio; (C). Phase-diagram of a binary hard sphere mixture at size ratio RB/RA = 0.58. The axes are the volume fractions φA of particle A and φB of particle B. φf and φm indicate the freezing and melting concentrations of each species. The points show the samples studied. At the low concentration, the phase is fluid (F), while at higher concentrations four regions of coexistence of crystal (B, AB13, AB2, or A) and fluid (F) are found, where B or A denotes the crystal phase of only one species of B or A, AB2 the atomic analogue of borides such as AlB2 and AB13 the atomic analogue of NaZn13, UBe13, etc. Reproduced with permission from [24], Copyright the American Physical Society, 1992.
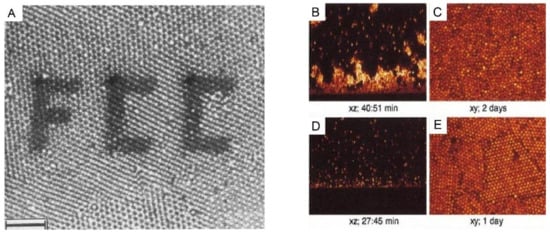
Figure 3. (A): A polycrystalline section of 1-octadecanol-coated silica spheres (particle radius 505 nm, initial volume fraction 20%) in chloroform inside the capillary, observed by confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM). The photobleached pattern (FCC) was created by the high-intensity illumination with the imaging beam. Scale bar: 10 µm. (B–E): CSLM images of xz scans after an hour and of xy scans after several days for the sedimentation of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) particles in a reactive index matching solvent of (B,C): initial volume fraction: 2.05%, polymer concentration: 51.72 mg/mL; and (D,E): initial volume fraction: 2.18%, polymer concentration: 51.18 mg/mL. The polymers were used here to tune the interaction strength between these colloidal particles. Reproduced with the permission from [34], Copyright the American Chemistry Society, 1992; and [33], Copyright the American Physical Society, 2001.
1.2. The Era of Nanoparticles: Gravity Is Not Sufficient Anymore
Nanotechnology [37][38][39] has been developing rapidly since its emergence in the 1980s, especially in the field of nanoparticles. A large variety of nanoparticles (with the diameter typically between 1 and 100 nm in at least one dimension [40]) can be synthesized by well-established protocols, such as quantum dots [41], silica [42], and noble metal nanoparticles [43]. These nanoparticles can be furthermore ordered into superstructures via so-called bottom-up organization [44]. The important examples are colloidal crystals made of spherical nanoparticles [45] as well as mesocrystals [46][47][48] made from anisotropic nanocrystals, as shown in Figure 4. These superstructures are proven to be promising as functional materials in many different applications [49][50][51][52][53][54]. The preparation approaches for these superstructures are reviewed in several key papers [55][56][57]. Especially in the review paper by Boles et al. [55], all widely used methods are summarized, as shown in Figure 5. Among these methods, solvent evaporation and destabilization are the two most popular methods, with a wide selection of examples [58][59][60]. However, the traditional gravitational sedimentation approach, which worked quite well for near-micrometer-sized colloids, becomes a much less commonly used method for nanoparticles due to the lack of effective sedimentation for particles <1 μm under gravity, consequently resulting in very limited research [61]. The plausible hurdles may be two-fold. Firstly, it is the intrinsically small size of nanoparticles that makes the sedimentation extremely slow under gravity. To elaborate this in a quantitative manner [62], the gravitational energy to move a particle with the mass m by its own diameter, d can be calculated: mgd (g is the Earth’s gravity resp. gravitational acceleration). The significance of the gravity to the sedimentation of particles can be calculated: mgd/kBT with kBT being the thermal energy scale. For microbeads with a typical diameter of 1 µm, the value is in the order of 106, which means that the gravity is so significant compared to thermal motion that sedimentation progresses in a relatively reasonable time scale. In comparison, for nanoparticles with a diameter of 100 nm, the value is significantly decreased to 10−6. This means that the gravity becomes so insignificant that nanoparticles can hardly sediment in a gravitational field but move by diffusion caused by particle collisions. Thus, an external centrifugal field [63] is compulsory for the sedimentation of nanoparticles instead of natural sedimentation. The second hurdle is the lack of in-situ analytics to monitor the sedimentation of nanoparticles during centrifugation. For example, confocal laser scanning microscopy [34][64][65] (CLSM), which worked perfectly with microbeads, does not have enough resolution to observe nanoparticles in-situ. Therefore, the understanding of the ordering process for nanoparticles is still missing, not to mention the significant turbidity of the dispersion at very high nanoparticle concentration, especially close to the fluid to crystal transition point (at around 50 vol%), which severely hinders the in-situ observation. These main problems may have caused the sedimentation method to be unpopular so far for the ordering of nanoparticles, even though it is quite intuitive, convenient, and can be easily scaled-up.
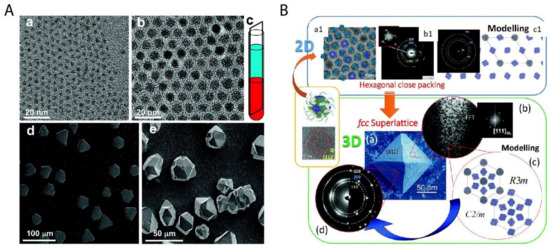
Figure 4. Two important examples of superstructures from the bottom-up organization of nanoparticles. (A) The colloidal superlattices made of spherical PbS nanoparticles of 3.1 nm (a) and 8.0 nm (b) are shown in (d) and (e) respectively; (c) shows the schematic fabrication approach of the oversaturation technique for growing superlattices. (B) The piece of mesocrystal, as shown in the green box: (a) is the SEM image of the mesocrystal with (b) the corresponding Fast Fourier transform (FFT) of one Focused ion beam (FIB) slice, (c) the simulated structural models of the mesocrystal, and (d) the experimental and simulated electron diffraction (ED) pattern. The mesocrystal was synthesized by the bottom-up fabrication from truncated octahedrally shaped PbS nanoparticles of 5.5 nm, as shown in upper left (a1) with (b1) the corresponding ED pattern of the 2D assembly and (c1) the structural modeling of the assembly in the blue box. Reproduced with permission from [45], Copyright the American Chemical Society, 2010; and [47] Copyright the Royal Society of Chemistry, 2016.
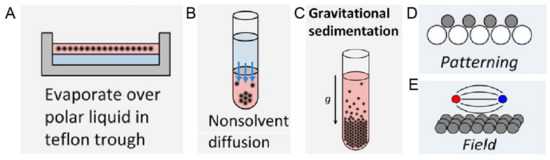
Figure 5. Schematic experimental approaches to prepare superstructures from nanoparticles, including (A) Solvent evaporation based methods, such as evaporation over a polar liquid in a Teflon trough; (B) Solvent destabilization-based methods, such as nonsolvent diffusion; (C) Gravitational sedimentation, which is a less common method due to insignificant gravitational forces for intrinsically small sizes of nanoparticles; (D) Pattering, where the template is normally used to guide the ordering and (E) Ordering in an external field, especially magnetic and electric fields. Reproduced with permission from [55], Copyright the American Chemical Society, 2016.
1.3. Ordering of Nanoparticles: Centrifugation Needs to Be Involved
Recent decades have seen the development in both analytical (ultra)centrifugation (AUC) [66] and preparative [67] (ultra)centrifugation (PUC) techniques, with important software and hardware advances [68][69][70][71][72]. The application of this knowledge may make the ordering of nanoparticles more accessible in the centrifugal field, finally reaching the goal of tailor-made superstructures by centrifugation. It is worthwhile mentioning that one key advantage of using centrifugation is the possibility of a continuous variation of the force exerted on the nanoparticles with the distance to the rotational center and thus the formation of concentration gradients. This will be extremely useful for the ordering of nanoparticles as richer superstructures will be possible in this out-of-equilibrium gradient [57][73] rather than a homogenously distributed suspension. In this review, we will focus on the ordering of nanoparticles in a centrifugal field, both in analytical and preparative instruments. Both the intuitive use of centrifugation for nanoparticle ordering and more rational research work with the assistance from powerful analytical (ultra)centrifugation in recent years will be summarized. At the end of the review, the current problems and the future possibilities in this field will be discussed.
2. Ordering of Nanoparticles in Preparative (Ultra)Centrifugation (PUC)
2.1. General Introduction to PUC
Preparative (ultra)centrifugation (PUC) is a widely used method in a variety of disciplines, especially in chemistry and biology. It is employed to apply an enhanced gravity effect up to 100,000 rpm (correspondingly roughly 800,000× g), which is suitable for the sedimentation of samples of a wide size range from micron-sized species down to the smallest nanoparticles [74][75]. Its conventional application relies on the isolation/purification of a mixture of species. The mechanism is that different species have varied sedimentation velocities due to their intrinsic properties such as size, density and shape. The main centrifugation-assisted separation methods [76][77][78] include differential centrifugation, isopycnic separation and density gradient centrifugation [79]. The rotors for PUC can be divided into four main categories: swinging-bucket, fixed-angle, vertical and near-vertical, as shown in Figure 10. In recent decades, PUC has demonstrated its advantage in nanoparticle purification. Gold nanoparticle mixtures of different shapes [80][81] and sizes [82], graphene oxide [83] and carbon nanotube mixtures [84] of different lengths were all demonstrated to be purified quite well by PUC, especially with the pre-knowledge from AUC experiments. In this chapter, we focus, however, on the ordering of nanoparticles in PUC, which has also shown many promising results in recent decades. Especially with the assistance of AUC, the PUC experiments become more rational, inducing fully controllable ordered superstructures.
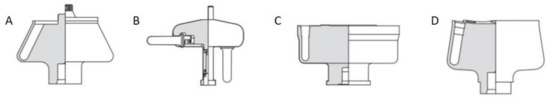
Figure 10. Four main types of rotors used in the preparative ultracentrifugation experiments, including (A) fixed-angle rotor, (B) swinging-bucket rotor, (C) vertical rotor and (D) near-vertical rotor. For the ordering of nanoparticles, a swinging-bucket rotor is recommended since all the nanoparticles can sediment horizontally towards the bottom of the tube, which is most comparable to an AUC cell. Reproduced with permission from [85], Copyright Beckman-Coulter, 1993.
2.2. Ordering of Monodisperse Nanoparticles in PUC
The ordering of monodisperse nanoparticles in PUC was demonstrated in the 1990s by several groups [86][87][88][89][90][91][92][93][94] to be a quick, robust and versatile approach for the formation of three-dimensional crystalline superstructures, which can be further fabricated into microporous materials. A representative example was shown by Holland et al. [95][96]. In their study, monodisperse latex nanoparticles with a very narrow size distribution were firstly synthesized. Then a dispersion of these latex nanoparticles was centrifuged into a sediment (which showed an iridescent color) at the bottom of a centrifuge tube. Finally, the sediment was observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), to be a close-packed array of latex nanoparticles, as shown in Figure 11A. This piece of three-dimensional close-packed crystal can be further used as a template for a variety of inorganic or hybrid porous structures, particularly of titania [97] (TiO2) and silicon [98] (Si) which both have a very high refractive index and are thus very promising for photonic applications [99]. Besides three-dimensional structures, monodisperse silica nanoparticles were demonstrated by Fan et al. [100] to order into two-dimensional crystalline films by centrifugation, as shown in Figure 11B. During centrifugation, the aqueous phase was forced to float with the sinking of the hydrocarbon mixture phase (as less dense hexane in the mixture evaporated). In this case, the silica nanoparticles were separated from the aqueous phase and ended up in the interface between the hydrocarbon mixture and oil phases. At the interface, these nanoparticles were finally ordered into a crystalline film due to interparticle capillary water bridges. In addition to crystalline superstructures, nanoparticles were also demonstrated to be ordered into glassy superstructures [101][102][103] in the PUC. Garcia et al. [101] found the two methods, namely the destabilization of charge-stabilized nanoparticles and the introduction of nanoparticles of a different size, to make colloidal glasses, as shown in Figure 11C–E. Recently, it was shown by Chen et al. [104] that by the use of AUC as an in-situ characterization technique, the amount of oligomers formed during the centrifugation could even be quantified in nanoparticle dispersions with different salt concentrations. Therefore, the nanoparticle ordering can be controlled rationally in the PUC by varying salt concentrations, as shown in Figure 12. The final example is the research work presented by Roca et al. [105] They found that by using the PUC, gold nanoparticles can be ordered into clusters of different sizes. Moreover, the composition of the gold nanoparticle clusters can be controlled by tuning the angular velocity in the PUC. To conclude, we showed that the ordering of monodisperse nanoparticles in the PUC began with intuitive centrifugation experiments, which proved robust in the ordering of nanoparticles into both crystalline and glassy superstructures. Nevertheless, with the assistance of AUC techniques as an in-situ characterization method, the PUC experiments can become more rational and controllable, with the ordering of monodisperse nanoparticles fully tunable between crystals and glasses.
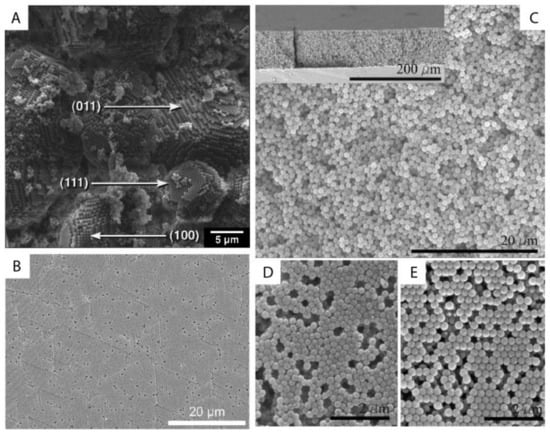
Figure 11. (A) SEM image of a small colloidal crystal of monodisperse latex nanoparticles after the centrifugation with (100), (111) and (011) faces being labelled; (B) SEM image of a crystalline film of monodisperse silica nanoparticles after the centrifugation experiment; (C–E) SEM image of a colloidal glass of latex nanoparticles after the centrifugation experiments. In (C), salt was added to break the stability of these particles and to introduce the coagulation for the disordered structure. In (D,E), a second type of nanoparticle was introduced first and then selectively etched for the disordered structure. Reproduced with permission from [96], Copyright the American Chemical Society, 1999, and [101], Copyright Wiley-VCH, 2007.
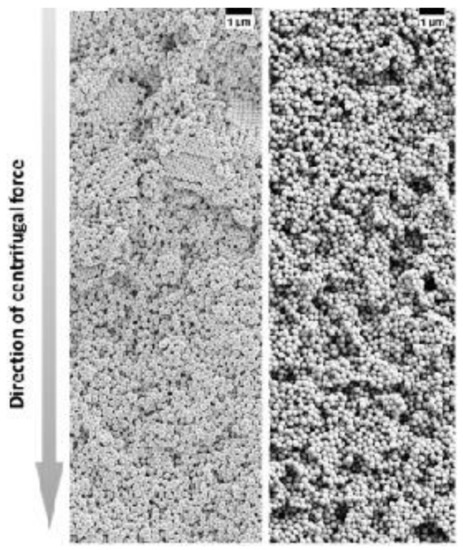
Figure 12. SEM images of colloidal glasses prepared in centrifugation in the presence of different salt concentrations. With a lower salt concentration, small crystalline domains can be still present in the upper part of the sediment (left panel) while at a higher salt concentration, the superstructure becomes totally disordered (right panel). Reproduced with permission from [104], Copyright Wiley-VCH, 2017.
2.3. Ordering of Binary Nanoparticles in PUC
The ordering of binary nanoparticles in PUC is much more complicated compared to the ordering of one species of nanoparticles, because much more parameters play vital roles in the ordering process, including the particle size/number/charge ratio, the total particle concentration, the centrifugation time, the centrifugal force and so on [106]. Therefore, an intuitive PUC experiment is even impossible for binary nanoparticles, which otherwise worked very well for the ordering of the single species cases. Only recently, Chen et al. [107] showed that with the important sedimentation coefficient information obtained from AUC experiments, the rational design of binary nanoparticle ordering in PUC became possible. In their study, they first evaluated the sedimentation coefficient distributions, which are dependent on the total volume fraction, for the binary latex nanoparticles by using the AUC. With this information, they designed the PUC experiments with different conditions by varying total particle volume fractions, number ratios, total volumes, centrifugation time and centrifugal force. They finally found that binary nanoparticles ordered into different superstructures in the PUC experiments, which showed dependence on different radial positions in a centrifugation tube, as shown in Figure 13A. The main reason for this is the formation of different concentration gradients of the binary nanoparticles by centrifugation. Xu et al. found that the concentration gradients could be tailor-made [108] (as shown in Figure 8B) for a rational fabrication of a superstructure gradient along the radius in the sediment after the PUC, as shown in Figure 13B. Therefore, AUC is proven to be an important tool for the tailor-made concentration gradients, which helps with the formation of different binary nanoparticle-ordered structures in PUC. Moreover, this protocol may even be useful for the discovery of a library of crystalline phases for other species, such as a metal organic framework (MOF) [109]. For example, Park et al. [110] used reaction diffusion (RD) systems [111] to obtain the concentration gradients of both coordinating metal ions and organic ligands in a gel, which finally led to several bands of different microcrystals at different positions (which also evolved with time), as shown in Figure 13C. A final piece of work, which used PUC to order binary nanoparticles, was shown by Song et al. [112] They ordered binary gold nanoparticles of two different sizes into hetero clusters of different sizes by “crashing” one type of gold nanoparticles into a layer of the other type under the centrifugal force in PUC. To sum up, binary nanoparticles can be rationally ordered into a variety of superstructures in PUC with the sufficient knowledge from AUC experiments beforehand.
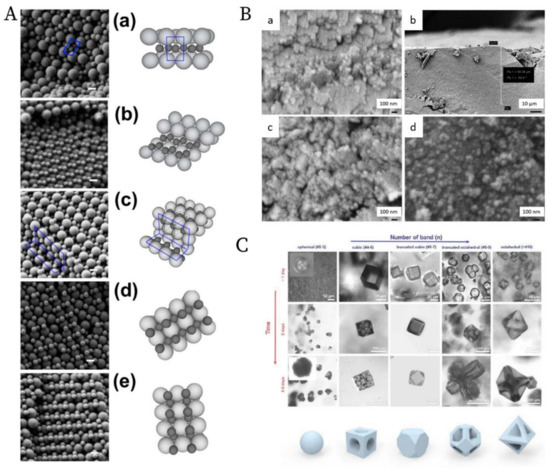

Figure 13. (A). SEM images and schematics of the corresponding binary crystal lattices at different radial positions for a binary mixture of 150 nm and 300 nm latex nanoparticles after the PUC: (a) layered structure akin to AlB2; (b) distorted AlB2 structure; (c) the tetragonal A3B variant; the tetragonal A2B variant before (d) and after distortion (e). Scale bars = 200 nm; (B). SEM images at different radial positions for a binary mixture of 30 nm and 40 nm silica nanoparticles after the PUC: (a) Representative image of a crystalline structure in the upper part of the sediment; (b) Overview of the transition position where the last piece of crystalline structure was observed (≈50 µm from the meniscus); (c) Representative zoom-in image of the transition position where only discrete small pieces of crystalline structures were observed. (d) Representative image of a glassy structure below the transition position; The crystal to glass transition agreed with the previous study [113]; (C). Confocal microscopy images of the morphology evolution of the MOF-crystal in the precipitation bands at different positions (horizontal axis) due to the concentration gradients of both metal ions and ligands, and at different time (vertical axis). Reproduced with permission from [107], Copyright the American Chemical Society, 2015, [108], Copyright the American Chemical Society, 2019 and [110], Copyright Wiley-VCH, 2020.
2.4. Highlight of Gradient Materials
A unique application of the PUC is the fabrication of gradient materials [114], which have a gradient transition in microstructure features instead of a sharp boundary. The application of centrifugation in making gradient materials is summarized in several books [115][116] and reviews [117][118]. We already showed in Figure 9 that nanoparticle gradient materials can be achieved in the PUC for monodisperse nanoparticles. This can be extended to more complicated binary nanoparticle mixtures. Chen et al. [119] showed that the latex nanoparticles of two different sizes can be ordered into gradient materials in the PUC, with the concentration of smaller nanoparticles gradually decreasing and that of larger nanoparticles gradually increasing along the radius, as shown in Figure 14. It was further shown that this method is even applicable to ternary nanoparticle mixtures [119] or a mixture of nanoparticles of completely different chemical natures, such as the mixture of latex and metal organic framework (MOF) nanoparticles [120]. Moreover, a functional gradient can be added into this structural gradient to make a double graded material, as shown by Bahner et al. [121] They modified latex nanoparticles of one size with silver patches and then mixed these functionalized nanoparticles with bare latex nanoparticles of a different size. Then the sediment after the PUC featured both structure and chemical gradients. These nanoparticle gradient materials indeed represent a new class of material, which may be easily fabricated in the PUC in a controllable fashion.
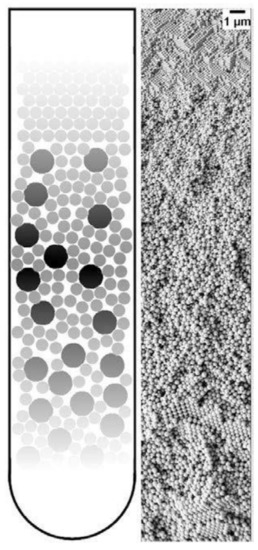
Figure 14. Schematic image of a nanoparticle gradient material, made of a binary mixture of latex nanoparticles (left) and a representative SEM image of this gradient structure (right). Reproduced with permission from [107], Copyright the American Chemical Society, 2015.
2.5. Current Status and Future Possibilities
We demonstrated in this chapter that ordering of nanoparticles in the PUC has shown a series of promising results in recent decades. Dating back to the 1990s, the ordering of monodisperse nanoparticles was conducted in the PUC only empirically, because nanoparticles with a narrow size and shape distribution crystallize very fast [122], which is not sensitive at all to nanoparticle concentration and centrifugal force. The same story holds for glassy superstructures, since the presence of oligomers suppresses the crystal nucleation and growth significantly [27][89]. Nevertheless, we showed that with the assistance of the AUC, the tuning of nanoparticle ordering can be rational, which means that AUC can provide important information about the amount of oligomers in the dispersion during centrifugation [104], which finally determines whether a crystal or glass may form. Therefore, we have a handle to tailor-make superstructures with different degrees of order by systematically changing the ionic strength of the dispersion and the centrifugation force. The importance of AUC becomes more evident when multi-modal nanoparticles are ordered in the PUC because the final superstructures after centrifugation are heavily dependent on so many different factors that the in-situ characterization of nanoparticles in the AUC becomes vital. We thus showed that with the sedimentation information from AUC, different binary superstructures can be realized and tuned in the PUC due to tailor-made concentration gradients. The field of rational nanoparticle ordering in the PUC just emerged and we shall see more developments in the future with the following aspects: (1) software development may be needed by which we can design tailor-made concentration gradients in a convenient way for the fabrication of desired superstructures in PUC experiments; (2) the ordering of nanoparticles may be realized on an industrial scale, which will increase the impact beyond academics; (3) the ordering of a mixture of nanoparticles with complicated shapes and chemical compositions can be targeted if multi-functionality is desired; (4) templating or confinement can be combined with the centrifugation for a more controllable ordering process; (5) the measurement of concentration gradients without the need of fluorescence labelling and refractive index matching, especially at high concentrations, will improve the versatility of this approach.
3. Applications
3.1. Crystals and Glasses
The most direct application of these materials relies on the structural order of nanoparticles after the centrifugation. Generally speaking, the nanoparticle ordering can be classified into two categories: a crystal, which is periodically ordered across a long range [123], and a glass, which lacks a long-range order [124]. The most promising application of these ordered/disordered structures is the utilization of their photonic properties [125]. Photonic crystals [99][126][127] have been studied for more than a decade so far to control and manipulate light [128][129]. Of particular interest is the photonic bandgap of a photonic crystal. In this bandgap, within a specific range of frequencies, light is forbidden to exist inside the crystal. However, any defect existence in the otherwise perfect crystal will lead to localized photonic states, which can be used to “mold” or control the properties of light, as shown in Figure 15A. A very promising example, which attracted much attention recently, was presented by Hynninen et al. [130] They found that by constructing crystal superstructures of a MgCu2 Laves phase [131] from binary nanoparticles, a bandgap in the visible region can be achieved, which may bring about many exciting possibilities in the future. In the meantime, disordered photonics [132] also attract much research interest. Due to the random packing of nanoparticles in the materials, light is multiply scattered [133][134] and leads to many disorder-based optical applications. For example, Garcia et al. [135] demonstrated the resonant behavior (such as in diffusion constant and energy velocity of light) for photonic glasses, as shown in Figure 15B. This study opens a new route to tune the light diffusion by employing photonic glasses.
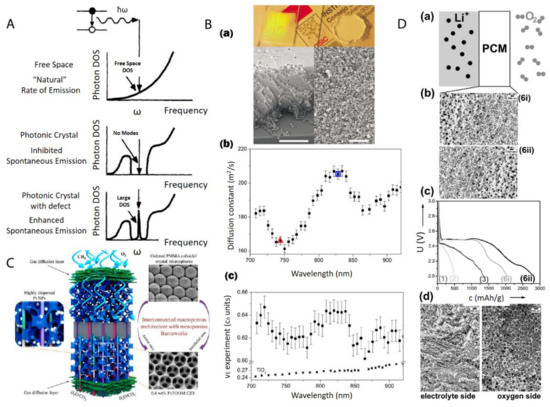
Figure 15. (A) Photon density of states (DOS) in free space, a photonic crystal, and a photonic crystal with a local defect. A perfect photonic crystal inhibits spontaneous photon emission within a band gap centered at a frequency ω while the spontaneous photon emission can be enhanced dramatically at frequency ω by a localized point defect in the colloidal crystal; (B) (a) Top: picture shows a photonic crystal (left), which shows visible iridescences and a photonic glass (right) white and without any iridescences. Bottom: Left is the SEM image from a photonic crystal (scale bar is 10 µm) while Right is the SEM image from a photonic glass (scale bar is 10 µm); (b) Experimental diffusion constant in a photonic glass made of PS spheres. Two particular wavelengths are marked with a triangle (λ1 = 744 nm) and a square (λ2 = 828 nm). These two wavelengths correspond to the maximum and minimum value of a Mie resonance; (c) Experimental values of the energy velocity (νE) as a function of the wavelength (λ) for a photonic glass made of PS spheres and for TiO2 powder. For the photonic glass, a full oscillation of around 5% amplitude is illustrated, while for the TiO2 powder, a flat velocity dispersion is illustrated; (C) Schematic picture of a highly efficient catalysis system for methane combustion, which is composed of Pt nanoparticles embedded in latex nanoparticle-templated macroporous structures; (D) (a,b) porous gradient material-based Li-O2 battery testing setup; (c) different Li-O2 electrochemical discharge curves by using different gradient pore sizes; (d) SEM image of a typical porous gradient structure after charging/cycling. Reproduced with permission from [128], Copyright Elsevier, 1997; [135], Copyright the American Physical Society, 2008; [136], Copyright the American Chemical Society, 2015; and [119], Copyright Wiley-VCH, 2017.
3.2. Porous Materials
After the infiltration and removal of templating nanoparticles, porous materials [137] can be fabricated. There is a large number of reviews [138][139][140] on the applications of macro- (pore diameters larger than 50 nm) and meso- (pore diameters between 2 and 50 nm) porous materials [141]. Most applications arise from the presence of the pore structure, which provides an extremely large surface area over a relatively small volume. This makes porous materials suitable for many applications, such as catalysis, chemical sensing, selective adsorption, and molecular separation. For example, Arandiyan et al. [136] demonstrated that Pt nanoparticles embedded in macroporous materials made of Ce0.6Zr0.3Y0.1O2 (3DOM CZY) possessed an excellent efficiency for the catalysts of methane combustion, as shown in Figure 15C.
3.3. Functional Gradient Materials
Functional gradient materials [142] exhibit spatial gradients of microstructures and properties [114][118][143]. Humans have extensively used these materials since the old ages of craftsmanship and engineering constructions, especially those like case-hardened steel, which is still commonly used today [114]. The microstructure gradient can be quantitatively controlled for the optimization of material properties for specific requirements, such as mechanical [144], thermal [116] and chemical properties [143]. The related applications [145] range into different industrial fields, such as aerospace, defense, mining, power and tool manufacturing sectors. Especially, nanoparticle gradient materials have recently proven to be rather feasible to tailor-make by employing the centrifugation technique [146]. Chen et al. [119] demonstrated that binary nanoparticle gradients such as a mixture of latex nanoparticles of different sizes were fabricated by centrifugation. The resulting gradient material was then infiltrated with resorcinol-formaldehyde. The thermal treatment finally induced the transformation to gradient porous materials. The final material can be applied as an electrode in a Li-O2 cell [147], as shown in Figure 15D. The cell performance can be easily tuned by both the gradient structure and the gradient direction.
References
- Darragh, P.; Gaskin, A.; Sanders, J. Opals. Sci. Am. 1976, 234, 84–95.
- Murray, M.; Sanders, J. Close-packed structures of spheres of two different sizes II. The packing densities of likely arrangements. Philos. Mag. A 1980, 42, 721–740.
- Sanders, J. Colour of precious opal. Nature 1964, 204, 1151–1153.
- Sanders, J. Close-packed structures of spheres of two different sizes I. Observations on natural opal. Philos. Mag. A 1980, 42, 705–720.
- Perrin, J. Atoms; Hammick, D.L.D., Translator; Van Nostrand Company: New York, NY, USA, 1916.
- Einstein, A. Über die von der molekularkinetischen Theorie der Wärme geforderte Bewegung von in ruhenden Flüssigkeiten suspendierten Teilchen. Ann. Phys. 1905, 322, 549–560.
- Kynch, G.J. A theory of sedimentation. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1952, 48, 166–176.
- Batchelor, G.K. Sedimentation in a dilute dispersion of spheres. J. Fluid Mech. 1972, 52, 245–268.
- Vrij, A. Sedimentation equilibrium in concentrated, multicomponent particle dispersions. Hard spheres in the Percus-Yevick approximation. J. Chem. Phys. 1980, 72, 3735–3739.
- Lamm, O. Die Differentialgleichung der Ultrazentrifugierung; Almqvist & Wiksell: Stockholm, Sweden, 1929.
- Svedberg, T.; Pedersen, K.O. The ultracentrifuge. In Ultracentrifuge; The Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1940.
- Pusey, P.N.; Van Megen, W. Phase behaviour of concentrated suspensions of nearly hard colloidal spheres. Nature 1986, 320, 340–342.
- Pusey, P.N.; van Megen, W. Observation of a glass transition in suspensions of spherical colloidal particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 59, 2083.
- Pusey, P.N.; van Megen, W.; Bartlett, P.; Ackerson, B.J.; Rarity, J.G.; Underwood, S.M. Structure of crystals of hard colloidal spheres. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1989, 63, 2753–2756.
- Hachisu, S.; Takano, K. Pressure of disorder to order transition in monodisperse latex. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1982, 16, 233–252.
- Kose, A.; Ozaki, M.; Takano, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hachisu, S. Direct observation of ordered latex suspension by metallurgical microscope. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1973, 44, 330–338.
- Israelachvili, J.N. Intermolecular and Surface Forces; Academic Press: London, UK, 2015.
- Pusey, P.; Zaccarelli, E.; Valeriani, C.; Sanz, E.; Poon, W.C.; Cates, M.E. Hard spheres: Crystallization and glass formation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367, 4993–5011.
- Parker, A.R. 515 million years of structural colour. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2000, 2, R15.
- Kinoshita, S.; Yoshioka, S.; Kawagoe, K. Mechanisms of structural colour in the Morpho butterfly: Cooperation of regularity and irregularity in an iridescent scale. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2002, 269, 1417–1421.
- Mau, S.-C.; Huse, D.A. Stacking entropy of hard-sphere crystals. Phys. Rev. E 1999, 59, 4396–4401.
- Woodcock, L.V. Entropy difference between the face-centred cubic and hexagonal close-packed crystal structures. Nature 1997, 385, 141–143.
- Bartlett, P.; Ottewill, R.H.; Pusey, P.N. Freezing of binary mixtures of colloidal hard spheres. J. Chem. Phys. 1990, 93, 1299–1312.
- Bartlett, P.; Ottewill, R.H.; Pusey, P.N. Superlattice formation in binary mixtures of hard-sphere colloids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 3801–3804.
- Buscall, R. The sedimentation of concentrated colloidal suspensions. Colloids Surf. 1990, 43, 33–53.
- Biben, T.; Hansen, J.P.; Barrat, J.L. Density profiles of concentrated colloidal suspensions in sedimentation equilibrium. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 7330–7344.
- Auer, S.; Frenkel, D. Suppression of crystal nucleation in polydisperse colloids due to increase of the surface free energy. Nature 2001, 413, 711–713.
- Auer, S.; Frenkel, D. Prediction of absolute crystal-nucleation rate in hard-sphere colloids. Nature 2001, 409, 1020–1023.
- Van Blaaderen, A.; Vrij, A. Synthesis and characterization of colloidal dispersions of fluorescent, monodisperse silica spheres. Langmuir 1992, 8, 2921–2931.
- Kegel, W.K.; van Blaaderen, A. Direct Observation of Dynamical Heterogeneities in Colloidal Hard-Sphere Suspensions. Science 2000, 287, 290–293.
- Van Blaaderen, A.; Ruel, R.; Wiltzius, P. Template-directed colloidal crystallization. Nature 1997, 385, 321–324.
- Hoogenboom, J.P.; Derks, D.; Vergeer, P.; Blaaderen, A.v. Stacking faults in colloidal crystals grown by sedimentation. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 11320–11328.
- De Hoog, E.H.; Kegel, W.K.; van Blaaderen, A.; Lekkerkerker, H.N. Direct observation of crystallization and aggregation in a phase-separating colloid-polymer suspension. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 021407.
- Van Blaaderen, A.; Imhof, A.; Hage, W.; Vrij, A. Three-dimensional imaging of submicrometer colloidal particles in concentrated suspensions using confocal scanning laser microscopy. Langmuir 1992, 8, 1514–1517.
- Yethiraj, A.; van Blaaderen, A. A colloidal model system with an interaction tunable from hard sphere to soft and dipolar. Nature 2003, 421, 513–517.
- Leunissen, M.E.; Christova, C.G.; Hynninen, A.-P.; Royall, C.P.; Campbell, A.I.; Imhof, A.; Dijkstra, M.; van Roij, R.; van Blaaderen, A. Ionic colloidal crystals of oppositely charged particles. Nature 2005, 437, 235–240.
- Eric, D.K. Engines of Creation. The Coming Era of Nanotechnology; Anchor Book: Palatine, IL, USA, 1986.
- Whitesides, G.M. Nanoscience, nanotechnology, and chemistry. Small 2005, 1, 172–179.
- Ozin, G.A.; Arsenault, A. Nanochemistry: A Chemical Approach to Nanomaterials; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2015.
- Michel, V.; Yoshiharu, D.; Karl-Heinz, H.; Michael, H.; Philip, H.; Przemyslaw, K.; Marguerite, R.; François, S. Terminology for biorelated polymers and applications (IUPAC Recommendations 2012). Pure Appl. Chem. 2012, 84, 377–410.
- Murray, C.B.; Norris, D.J.; Bawendi, M.G. Synthesis and characterization of nearly monodisperse CdE (E = sulfur, selenium, tellurium) semiconductor nanocrystallites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 8706–8715.
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69.
- Schmid, G. Large clusters and colloids. Metals in the embryonic state. Chem. Rev. 1992, 92, 1709–1727.
- Whitesides, G.M.; Grzybowski, B. Self-assembly at all scales. Science 2002, 295, 2418–2421.
- Rupich, S.M.; Shevchenko, E.V.; Bodnarchuk, M.I.; Lee, B.; Talapin, D.V. Size-Dependent Multiple Twinning in Nanocrystal Superlattices. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 289–296.
- Cölfen, H.; Antonietti, M. Mesocrystals and Nonclassical Crystallization; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008.
- Sturm, E.V.; Cölfen, H. Mesocrystals: Structural and morphogenetic aspects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5821–5833.
- Song, R.-Q.; Cölfen, H. Mesocrystals—Ordered Nanoparticle Superstructures. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1301–1330.
- Lu, Z.; Yin, Y. Colloidal nanoparticle clusters: Functional materials by design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 6874–6887.
- Ciesla, U.; Schüth, F. Ordered mesoporous materials. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 27, 131–149.
- Yang, H.; Xu, Z.; Fan, M.; Gupta, R.; Slimane, R.B.; Bland, A.E.; Wright, I. Progress in carbon dioxide separation and capture: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 14–27.
- Huh, S.; Chen, H.T.; Wiench, J.W.; Pruski, M.; Lin, V.S.Y. Cooperative catalysis by general acid and base bifunctionalized mesoporous silica nanospheres. Angew. Chem. 2005, 44, 1826–1830.
- Lu, S.; Wang, D.; Jiang, S.P.; Xiang, Y.; Lu, J.; Zeng, J. HPW/MCM-41 phosphotungstic acid/mesoporous silica composites as novel proton-exchange membranes for elevated-temperature fuel cells. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 971–976.
- Ma, M.-G.; Cölfen, H. Mesocrystals—Applications and potential. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 19, 56–65.
- Boles, M.A.; Engel, M.; Talapin, D.V. Self-assembly of colloidal nanocrystals: From intricate structures to functional materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 11220–11289.
- Li, F.; Josephson, D.P.; Stein, A. Colloidal assembly: The road from particles to colloidal molecules and crystals. Angew. Chem. 2011, 50, 360–388.
- Mann, S. Self-assembly and transformation of hybrid nano-objects and nanostructures under equilibrium and non-equilibrium conditions. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 781–792.
- Grosso, D.; Cagnol, F.; Soler-Illia, G.d.A.; Crepaldi, E.L.; Amenitsch, H.; Brunet-Bruneau, A.; Bourgeois, A.; Sanchez, C. Fundamentals of mesostructuring through evaporation-induced self-assembly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2004, 14, 309–322.
- Brinker, C.J.; Lu, Y.; Sellinger, A.; Fan, H. Evaporation-induced self-assembly: Nanostructures made easy. Adv. Mater. 1999, 11, 579–585.
- Talapin, D.V.; Shevchenko, E.V.; Kornowski, A.; Gaponik, N.; Haase, M.; Rogach, A.L.; Weller, H. A new approach to crystallization of CdSe nanoparticles into ordered three-dimensional superlattices. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 1868–1871.
- Henzie, J.; Grünwald, M.; Widmer-Cooper, A.; Geissler, P.L.; Yang, P. Self-assembly of uniform polyhedral silver nanocrystals into densest packings and exotic superlattices. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 131.
- Jaeger, H.M.; Nagel, S.R.; Behringer, R.P. Granular solids, liquids, and gases. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1996, 68, 1259–1273.
- Ford, T.; Graham, J.M. An Introduction to Centrifugation; Bios Scientific Publishers: Oxford, UK, 1991.
- Paddock, S.W. Confocal laser scanning microscopy. Biotechniques 1999, 27, 992–1004.
- Van Blaaderen, A. Quantitative real-space analysis of colloidal structures and dynamics with confocal scanning light microscopy. In Optical Methods and Physics of Colloidal Dispersions; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 1997; pp. 59–65.
- Uchiyama, S.; Arisaka, F.; Stafford, W.F.; Laue, T. Analytical Ultracentrifugation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016.
- Rickwood, D. Preparative Centrifugation: A Practical Approach; IRL Press: Oxford, UK, 1992.
- Mächtle, W.; Börger, L. Analytical Ultracentrifugation of Polymers and Nanoparticles; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2006.
- Stephen, E.; Harding, A.J.R.; Scott, D. (Eds.) Analytical Ultracentrifugation: Techniques and Methods; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2007.
- Cölfen, H. Analytical ultracentrifugation of nanoparticles. Polym. News 2004, 29, 101–116.
- Planken, K.L.; Cölfen, H. Analytical ultracentrifugation of colloids. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1849–1869.
- Pearson, J.Z.; Krause, F.; Haffke, D.; Demeler, B.; Schilling, K.; Cölfen, H. Next-generation AUC adds a spectral dimension: Development of multiwavelength detectors for the analytical ultracentrifuge. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 562, pp. 1–26.
- Grzybowski, B.A.; Huck, W.T.S. The nanotechnology of life-inspired systems. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 585–592.
- Graham, J.M. Biological Centrifugation; Bios Scientific Publishers: Oxford, UK, 2001.
- Rickwood, D.; Ford, T.; Steensgaard, J. Centrifugation: Essential Data; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1994.
- Griffith, O.M. Practical Techniques for Centrifugal Separations; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.: Waltham, MA, USA, 2010.
- Hsu, H.-W. Separations by Centrifugal Phenomena; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1981.
- Leung, W.W.-F. Centrifugal Separations in Biotechnology; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2020.
- Price, C.A. Centrifugation in Density Gradients; Academic Press: London, UK, 2014.
- Bai, L.; Ma, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, X.; Zhao, D.; Evans, D.G. Rapid separation and purification of nanoparticles in organic density gradients. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2333–2337.
- Chen, G.; Wang, Y.; Tan, L.H.; Yang, M.; Tan, L.S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H. High-purity separation of gold nanoparticle dimers and trimers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4218–4219.
- Qiu, P.; Mao, C. Viscosity Gradient as a Novel Mechanism for the Centrifugation-Based Separation of Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4880–4885.
- Sun, X.; Liu, Z.; Welsher, K.; Robinson, J.T.; Goodwin, A.; Zaric, S.; Dai, H. Nano-graphene oxide for cellular imaging and drug delivery. Nano Res. 2008, 1, 203–212.
- Sun, X.; Zaric, S.; Daranciang, D.; Welsher, K.; Lu, Y.; Li, X.; Dai, H. Optical properties of ultrashort semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotube capsules down to sub-10 nm. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 6551–6555.
- Ralston, G. Introduction to Analytical Ultracentrifugation; Beckman California: Brea, CA, USA, 1993; Volume 1.
- Imhof, A.; Pine, D.J. Ordered macroporous materials by emulsion templating. Nature 1997, 389, 948–951.
- Wijnhoven, J.E.G.J.; Vos, W.L. Preparation of Photonic Crystals Made of Air Spheres in Titania. Science 1998, 281, 802–804.
- Holland, B.T.; Blanford, C.F.; Stein, A. Synthesis of Macroporous Minerals with Highly Ordered Three-Dimensional Arrays of Spheroidal Voids. Science 1998, 281, 538–540.
- Holland, B.T.; Blanford, C.F.; Do, T.; Stein, A. Synthesis of Highly Ordered, Three-Dimensional, Macroporous Structures of Amorphous or Crystalline Inorganic Oxides, Phosphates, and Hybrid Composites. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 795–805.
- Yan, H.; Blanford, C.F.; Holland, B.T.; Parent, M.; Smyrl, W.H.; Stein, A. A Chemical Synthesis of Periodic Macroporous NiO and Metallic Ni. Adv. Mater. 1999, 11, 1003–1006.
- Velev, O.D.; Kaler, E.W. Structured Porous Materials via Colloidal Crystal Templating: From Inorganic Oxides to Metals. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 531–534.
- Blanco, A.; Chomski, E.; Grabtchak, S.; Ibisate, M.; John, S.; Leonard, S.W.; Lopez, C.; Meseguer, F.; Miguez, H.; Mondia, J.P.; et al. Large-scale synthesis of a silicon photonic crystal with a complete three-dimensional bandgap near 1.5 micrometres. Nature 2000, 405, 437–440.
- Vos, W.L.; Megens, M.; Van Kats, C.M.; Bösecke, P. X-ray diffraction of photonic colloidal single crystals. Langmuir 1997, 13, 6004–6008.
- Rhodes, K.H.; Davis, S.A.; Caruso, F.; Zhang, B.; Mann, S. Hierarchical Assembly of Zeolite Nanoparticles into Ordered Macroporous Monoliths Using Core−Shell Building Blocks. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 2832–2834.
- Holland, B.T.; Blanford, C.F.; Stein, A. Synthesis of Macroporous Minerals with Highly Ordered Three-Dimensional Arrays of Spheroidal Voids. Science 1998, 281, 538–540.
- Holland, B.T.; Blanford, C.F.; Do, T.; Stein, A. Synthesis of Highly Ordered, Three-Dimensional, Macroporous Structures of Amorphous or Crystalline Inorganic Oxides, Phosphates, and Hybrid Composites. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 795–805.
- Wijnhoven, J.E.G.J.; Vos, W.L. Preparation of Photonic Crystals Made of Air Spheres in Titania. Science 1998, 281, 802–804.
- Blanco, A.; Chomski, E.; Grabtchak, S.; Ibisate, M.; John, S.; Leonard, S.W.; Lopez, C.; Meseguer, F.; Miguez, H.; Mondia, J.P.; et al. Large-scale synthesis of a silicon photonic crystal with a complete three-dimensional bandgap near 1.5 micrometres. Nature 2000, 405, 437–440.
- Meade, R.; Winn, J.N.; Joannopoulos, J. Photonic Crystals: Molding the Flow of Light; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1995.
- Fan, W.; Chen, M.; Yang, S.; Wu, L. Centrifugation-assisted assembly of colloidal silica into crack-free and transferrable films with tunable crystalline structures. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12100.
- García, P.D.; Sapienza, R.; Blanco, Á.; López, C. Photonic glass: A novel random material for light. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2597–2602.
- García, P.D.; Sapienza, R.; López, C. Photonic glasses: A step beyond white paint. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 12–19.
- Aubry, G.J.; Schertel, L.; Chen, M.; Weyer, H.; Aegerter, C.M.; Polarz, S.; Cölfen, H.; Maret, G. Resonant transport and near-field effects in photonic glasses. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 043871.
- Chen, M.; Fischli, D.; Schertel, L.; Aubry, G.J.; Häusele, B.; Polarz, S.; Maret, G.; Cölfen, H. Free-Standing Photonic Glasses Fabricated in a Centrifugal Field. Small 2017, 13, 1701392.
- Roca, M.; Pandya, N.H.; Nath, S.; Haes, A.J. Linear assembly of gold nanoparticle clusters via centrifugation. Langmuir 2010, 26, 2035–2041.
- Chen, M.; Cölfen, H.; Polarz, S. The Effect of centrifugal force on the assembly and crystallization of binary colloidal systems: Towards structural gradients. Z. Naturforschung B 2013, 68, 103–110.
- Chen, M.; Cölfen, H.; Polarz, S. Centrifugal Field-Induced Colloidal Assembly: From Chaos to Order. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 6944–6950.
- Xu, X.; Franke, T.; Schilling, K.; Sommerdijk, N.A.J.M.; Cölfen, H. Binary Colloidal Nanoparticle Concentration Gradients in a Centrifugal Field at High Concentration. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 1136–1142.
- Zakhia Douaihy, R.; Al-Ghoul, M.; Hmadeh, M. Liesegang Banding for Controlled Size and Growth of Zeolitic-Imidazolate Frameworks. Small 2019, 15, 1901605.
- Park, J.H.; Paczesny, J.; Kim, N.; Grzybowski, B. Shaping microcrystals of metal-organic frameworks by reaction-diffusion. Angew. Chem. 2020, 59, 10301–10305.
- Grzybowski, B.A. Chemistry in Motion: Reaction-Diffusion Systems for Micro-and Nanotechnology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009.
- Song, S.; Kuang, Y.; Luo, L.; Sun, X. Asymmetric hetero-assembly of colloidal nanoparticles through “crash reaction” in a centrifugal field. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 5994–5997.
- Hunt, N.; Jardine, R.; Bartlett, P. Superlattice formation in mixtures of hard-sphere colloids. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62, 900–913.
- Rabin, B.; Shiota, I. Functionally gradient materials. MRS Bull. 1995, 20, 14–18.
- Reynolds, N.J.; Nathan, J. Functionally Graded Materials; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2012.
- Miyamoto, Y.; Kaysser, W.; Rabin, B.; Kawasaki, A.; Ford, R.G. Functionally Graded Materials: Design, Processing and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 5.
- Saleh, B.; Jiang, J.; Fathi, R.; Al-hababi, T.; Xu, Q.; Wang, L.; Song, D.; Ma, A. 30 Years of functionally graded materials: An overview of manufacturing methods, Applications and Future Challenges. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2020, 201, 108376.
- Bhavar, V.; Kattire, P.; Thakare, S.; Patil, S.; Singh, R.K.P. A Review on Functionally Gradient Materials (FGMs) and Their Applications. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 229, 012021.
- Chen, M.; Hagedorn, K.; Cölfen, H.; Polarz, S. Functional Gradient Inverse Opal Carbon Monoliths with Directional and Multinary Porosity. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603356.
- Ge, Q.; Chen, M.; Lou, X.; Zhang, W.; Shen, M.; Yang, Q.; Hu, B. Centrifugal Field Guided Dual Templating Synthesis of Functional Macro-Microporous Carbon. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2018, 35, 1800262.
- Bahner, J.; Klinkenberg, N.; Frisch, M.; Brauchle, L.; Polarz, S. Creating Directionality in Nanoporous Carbon Materials: Adjustable Combinations of Structural and Chemical Gradients. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1904058.
- Markov, I.V. Crystal Growth for Beginners: Fundamentals of Nucleation, Crystal Growth and Epitaxy; World Scientific: Singapore, 2003.
- Okubo, T. 3—Colloidal Crystallization. In Colloidal Organization; Okubo, T., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 82–191. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-802163-7.00003-9 (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Poon, W.C. Colloidal glasses. MRS Bull. 2004, 29, 96–99.
- Saleh, B.E.; Teich, M.C. Fundamentals of Photonics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019.
- Subramania, G.; Constant, K.; Biswas, R.; Sigalas, M.; Ho, K.-M. Optical photonic crystals fabricated from colloidal systems. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 74, 3933–3935.
- Soukoulis, C.M. Photonic Crystals and Light Localization in the 21st Century; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 563.
- Joannopoulos, J.D.; Villeneuve, P.R.; Fan, S. Photonic crystals. Solid State Commun. 1997, 102, 165–173.
- Colvin, V.L. From opals to optics: Colloidal photonic crystals. MRS Bull. 2001, 26, 637–641.
- Hynninen, A.-P.; Thijssen, J.H.J.; Vermolen, E.C.M.; Dijkstra, M.; van Blaaderen, A. Self-assembly route for photonic crystals with a bandgap in the visible region. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 202–205.
- Pearson, W.B. The Crystal Chemistry and Physics of Metals and Alloys; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1972; 824p.
- Wiersma, D.S. Disordered photonics. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 188–196.
- Wiersma, D.S. The physics and applications of random lasers. Nat. Phys. 2008, 4, 359–367.
- Gottardo, S.; Sapienza, R.; García, P.D.; Blanco, A.; Wiersma, D.S.; López, C. Resonance-driven random lasing. Nat. Photonics 2008, 2, 429–432.
- Garcia, P.; Sapienza, R.; Bertolotti, J.; Martín, M.; Blanco, A.; Altube, A.; Vina, L.; Wiersma, D.; López, C. Resonant light transport through Mie modes in photonic glasses. Phys. Rev. A 2008, 78, 023823.
- Arandiyan, H.; Dai, H.; Ji, K.; Sun, H.; Li, J. Pt nanoparticles embedded in colloidal crystal template derived 3D ordered macroporous Ce0. 6Zr0. 3Y0. 1O2: Highly efficient catalysts for methane combustion. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 1781–1793.
- Velev, O.D.; Lenhoff, A.M. Colloidal crystals as templates for porous materials. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 5, 56–63.
- Cecilia, J.A.; Moreno Tost, R.; Retuerto Millán, M. Mesoporous Materials: From Synthesis to Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3213.
- Stein, A.; Schroden, R.C. Colloidal crystal templating of three-dimensionally ordered macroporous solids: Materials for photonics and beyond. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2001, 5, 553–564.
- Li, W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, D. Mesoporous materials for energy conversion and storage devices. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16023.
- Rougquerolt, J.; Avnir, D.; Fairbridge, C.; Evertt, D.; Haynes, J.; Pernicone, N.; Ramsay, J.; Sing, K.; Unger, K. Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids (Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 1739–1758.
- Kieback, B.; Neubrand, A.; Riedel, H. Processing techniques for functionally graded materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 362, 81–106.
- Cherradi, N.; Kawasaki, A.; Gasik, M. Worldwide trends in functional gradient materials research and development. Compos. Eng. 1994, 4, 883–894.
- Luo, R.; Wu, J.; Dinh, N.-D.; Chen, C.-H. Gradient Porous Elastic Hydrogels with Shape-Memory Property and Anisotropic Responses for Programmable Locomotion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 7272–7279.
- Li, W.; Han, B. Research and Application of Functionally Gradient Materials. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 394, 022065.
- Spinnrock, A.; Cölfen, H. Putting a New Spin on It: Gradient Centrifugation for Analytical and Preparative Applications. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 10026–10032.
- Holtappels, P.; Sorof, C.; Verbraeken, M.C.; Rambert, S.; Vogt, U. Preparation of Porosity-Graded SOFC Anode Substrates. Fuel Cells 2006, 6, 113–116.




