
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Guochao Wei | + 5781 word(s) | 5781 | 2021-01-25 07:59:30 | | | |
| 2 | Dean Liu | -2241 word(s) | 3540 | 2021-01-27 10:39:33 | | |
Video Upload Options
Within the family of Retroviridae, foamy viruses (FVs) are unique and unconventional with respect to many aspects in their molecular biology, including assembly and release of enveloped viral particles. Both components of the minimal assembly and release machinery, Gag and Env, display significant differences in their molecular structures and functions compared to the other retroviruses.
1. Introduction
Several unique or at least uncommon features of the molecular biology of currently circulating FVs, which also partly exist in ancient, endogenized FVs, have led to their classification into the distinct subfamily of Spumaretrovirinae with only few genera within the family of Retroviridae[1]. The rest of the RVs, all members of the Orthoretrovirinae subfamily, follow the canonical, orthodox pathway of what is generally assumed or known to characterize RVs in many aspects[2]. The true FV-specific features relate to several aspects of their molecular biology, including defined mechanisms and unique features of particle formation and assembly and are discussed in this review. Really FV-specific features not known for any other RV relate to the:
- (i)
-
Genome coding strategy;
- (ii)
-
Processing and numbers of particle-associated polymerase Pol and envelope Env proteins;
- (iii)
-
Sequence features and the mode and timing of Gag polyprotein processing;
- (iv)
All of this leads to the release of virus particles with a unique and characteristic morphology that even allows proper classification via thin-section electron microscopy[5]. Re-evaluation of FV morphology via novel imaging technologies has led to the identification of a novel structural feature amongst RV particles, the matrix (MA) layer or intermediate shell (Figure 1) that follows the virus membrane at budding and subsequently relocates to the capsid’s edges[6][7]. The MA layer is visible evidence that FV assembly, release and maturation is different from that of the other RVs. Besides these features, FV assembly is characterized by the utilization of pathways and mechanisms rarely found in other RVs, for instance, the cytoplasmic pre-assembly of capsids and their subsequent envelopment, budding, and release at the plasma membrane or internal membranes[5].
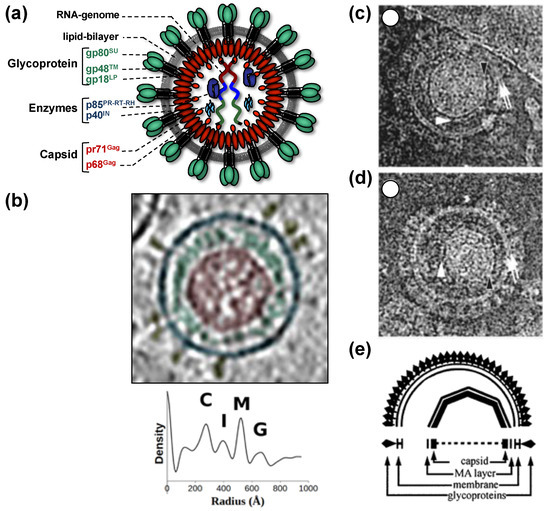
Figure 1. Structure of foamy virus (FV) virions. (a) Schematic representation of the prototype FV isolate (PFV) particle structure. pr: precursor protein; p: protein; gp: glycoprotein; (b) cryo-electron tomography of PFV virion and the corresponding radial density profile with the various peaks corresponding to the capsid (C), intermediate shell (I), viral membrane (M), glycoprotein (G), labeled and colored in red, green, blue, and yellow respectively. (c–e) Ultrastructure of feline FV (FFV) virions by cryo-electron microscopy analysis. The MA layer (white arrowheads) follows the shape of the capsid in particles with central (c) and off-center (d) capsids as schematically shown in panel (e). Many particles in the population show internal angular capsid (the edge of the capsid is marked by black arrowheads) displaced from the center of the particle. Panel (a) adapted from[3][8]; panel (b) adapted from[7]; panel (c–e) adapted from[6].
The utilization of several unique and non-canonical pathways connects to the fact that FVs are the most ancient RVs according to genetic analyses of fossilized endogenous FV (EndFV) genomes preserved in members of all vertebrate branches (classes) from fish to mammals[9][10][11]. FVs combine a deep-rooted, ancient evolutionary history with an almost complete co-speciation with their authentic host and host clades (simians, cattle, cat, equines, and bats) and a high genome conservation possibly due to a tightly cell-associated transmission and a persistent/latent life cycle[4][12][13]. These features may allow us to track the development and evolution of their unique molecular biology and to identify or at least postulate mechanisms that (may) have led to this mosaic of unique and unconventional features. Unravelling the basic mechanisms of FV biology has already opened new avenues of FV vector development, but may also shed new light into the evolution of their apparent apathogenicity and peaceful co-evolution/co-habitation with their hosts[14][15][16].
2. The Viral Machinery and Cellular Partners of FV Particle Formation, Envelopment, and Release
2.1. FV Gag Proteins
The FV Gag proteins are unique among RVs due to a strongly restricted proteolytic processing as the mature retroviral matrix (MA), capsid (CA), and nucleocapsid (NC) proteins may be only generated during particle disassembly in the newly-infected cell [20][21][22]. A consistent and functionally relevant proteolytic processing site is located about 30 amino acids (aa) upstream of the C terminus of the 52 to 71 kDa Gag precursor (Figure 2a)[20][23]. It is not required for the release of morphologically deviant particles but it is essential for particles gaining full infectivity. The potential function of the terminal 3–4 kDa C-terminal Gag peptide in the Gag precursor and its fate, localization, and function after proteolytic release by the FV protease (PR) are unknown, but of high scientific interest.
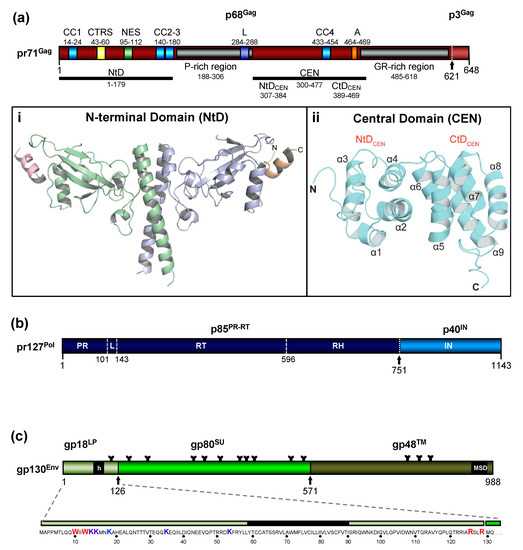
Figure 2. Schematic representation of the FV Gag, Pol, and Env protein organization. (a) Schematic illustration of the PFV Gag protein organization and selected functional motifs. Several functional motifs of PFV Gag are highlighted in differently colored boxes. Numbers indicate amino acid (aa) positions of the PFV Gag protein. The black arrow marks the cleavage site of pr71Gag for processing into p68Gag and p3Gag. Gray boxes represent the proline-rich (PR-rich) and glycine-arginine-rich (GR-rich) regions respectively. CC1 to CC4: coiled-coil domain 1 to 4; CTRS: cytoplasmic targeting and retention signal; NES: nuclear export sequence; L: late budding domain motif; A: assembly motif. (i) Cartoon representation of the three-dimensional (3D) structure of the PFV Gag N-terminal domain (NtD, aa 1–179) homodimer in complex with Env leader protein (Elp/LP) peptides. The Gag-NtD monomer-A is shown in pale blue and monomer-B in green. The helical Elp/LP peptides bound at the periphery of each head domain are colored magenta and gold with N and C termini indicated (ii) Cartoon representation of the 3D structure of the PFV-Gag central domain (CEN, aa 300–477) with its two subdomains NtDCEN and CtDCEN. The peptide backbone is shown in cyan. The secondary structure elements are numbered sequentially from the amino-terminus and the N and C termini are indicated. Helices α1 to α4 and α5 to α9 that comprise NtDCEN and CtDCEN, respectively, are indicated. (b) Schematic illustration of the PFV Pol protein organization. Numbers indicate aa positions of the PFV Pol protein. The black arrow marks the cleavage site of pr127Pol for processing into p85PR-RT-RH and p40IN. PR: protease domain; L: linker sequence; RT: reverse transcriptase domain; RH: RNase H domain; IN: integrase domain. (c) Schematic organization of PFV Env protein. The furin cleavage sites within the gp130Env precursor that are used for generation of the mature gp18LP, gp80SU, and gp48TM subunits are indicated by arrows. The individual subunits are shown as boxes in different shades of green. Hydrophobic sequences spanning the membrane in Elp/LP (h) and transmembrane (TM) (membrane-spanning domain, MSD) subunit are indicated. The aa sequence of the PFV Env Elp/LP subunit is shown in the enlargement below. The conserved WxxW and RxxR motif are highlighted in red, the lysine residues potentially ubiquitinated are highlighted in blue. The approximate positions of PFV Env N-glycosylation sites are marked by Y-shaped symbols. Panel (a,b,c) adapted from[3][8][22]; panel (ai) adapted from[25]; panel (aii) adapted from[24].
Due to the very limited processing of FV Gag and the lack of sequence and structural homology to the orthoretroviral MA and NC proteins ([20][24] and see below), nomenclature of the functional domains of FV Gag is challenging and may need revision. Until more structural data on FV Gag proteins and FV capsids become available, we propose to use the current nomenclature of retroviral Gag domains (MA, CA, NC) as an interim solution: the overall spatial domain organization is retained in FV Gag and several functions are conserved but probably have different evolutionary roots (see below). However, to reflect the lack of conventional Gag processing, we propose adding the term domain as follows: MA-domain, CA-domain, and NC-domain.
The FV Gag proteins lack the canonical major homology region (MHR) in the CA-domain and the Cys-His fingers in the NC-domain[23]. The approximately 20 aa-long Gag MHR of orthoretroviruses is required for proper particle/capsid assembly, while one or two Cys-His fingers are essential for RNA binding and viral genome encapsidation[5]. A MHR-corresponding element has not been found in FV Gag, however, the glycine- and arginine-rich (GR) sequences in the NC-domain may be the functional counterpart for nucleic acid binding conferred by the Cys-His fingers in the orthoretroviruses (Figure 2a). In primate FVs, the GR-rich NC-domain is organized in three 11 to 13 aa-long motifs (GR boxes I to III,[26]) which is not the case in the other known FVs including the ancient EndFVs[4][23]. In addition, an N-terminal Gag myristoylation signal and/or hints for Gag acetylation are not present in the N terminus of Gag, an additional distinguishing feature of FVs.
When comparing different members of orthoretrovirus genera, the Gag protein sequence has a higher conservation than Env, an observation that reflects the naming of Gag as the group-specific antigen[5]. However, this is not the case for FVs where Env proteins of different FV genera show higher degrees of homology/similarity than Gag[27]. Gag proteins of different FVs genera also vary considerably in size (between about 510 to 650 aa residues,[28]). This size variation is mainly due to a proline-rich and thus highly flexible region, which is flanked at its N terminus by a domain corresponding to the MA protein of other RVs, and at its C terminus by the capsid-forming and well-conserved CA-domain (Figure 2a)[23][28]. Since the FV MA- and this proline-rich domain are not separated by proteolytic processing in released particles, differences in the width of the MA layer formed by these N-terminal elements of FFV Gag are visible in cryo electron micrographs (Figure 1)[6][7].
2.2. FV Pol Proteins
The most obvious unique feature of FV Pol is the fact that it is not expressed as a Gag-Pol fusion protein[29][30]. Instead, it is translated from a spliced, sub-genomic pol transcript as a separate Pol protein independent of Gag [27][31][32][33] (Figure 3). The level of the Pol mRNA appears to be regulated by use of a suboptimal splice site[34]. However, in BFV, the spliced FV pol mRNA has been found to have similar levels compared to full-length RNA[27], which may result in substantial Pol protein levels. This unique situation is very likely to affect several “downstream” features of the different pol-encoded proteins, but also of the Pol polyprotein precursor, for instance, processing and activation/regulation of the individual enzymatic functions with only vaguely known secondary effects concerning RT and PR activation. Most importantly, Pol is only processed into a PR-RT-RH “polyprotein” and the mature integrase (IN)[35](Figure 2b). The absence of a free PR protein within released virus particles and newly infected cells may be one of the consequences of this unique translation/expression strategy (via a spliced transcript) as a means to control unscheduled and premature PR activation. Some unique or deviant sequence features of Pol proteins, for instance the unusual catalytic center of PR or the comparative ease of obtaining integrase (IN) crystals and thus the first authentic structural insights into RV/retroid element IN structure and function[20][36] may be consequences of the unique Pol expression strategy and its molecular features. Additionally, a “passive” co-packaging of Pol as a Gag-Pol protein during capsid assembly is not possible during FV assembly as discussed below (see Section 3.2).
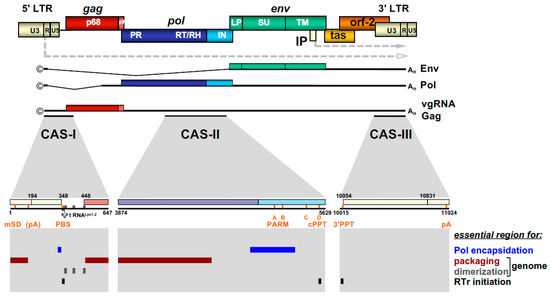
Figure 3. FV provirus organization, genomic and structural gene transcripts, and essential cis-acting viral RNA sequence elements. Schematic illustration of the PFV proviral DNA genome structure with long terminal repeats (LTRs) and open reading frames (ORFs) indicated as boxes. For ORFs encoding Gag, Pol, and Env precursor proteins, the regions encompassing the mature subunits generated by proteolytic processing are indicated by different colors and are labeled accordingly. Transcription initiation sites in the LTR and internal promoter (IP) and direction of transcription are indicated by dashed line arrows. Spliced and unspliced viral transcripts originating from the LTR and encompassing the viral RNA genome (vgRNA) or encoding the structural proteins Gag, Pol, and Env are schematically illustrated below and their respective coding capacity indicated to the right. Transcripts originating at the IP are omitted. Cis-acting sequence (CAS) elements localized within the full-length viral RNA genome, which are essential for viral replication, are indicated by black bars underneath the vgRNA. Individual functionally important or essential RNA sequence motifs are marked in the enlarged individual CAS elements below. Numbers represent nucleotide positions of the viral PFV RNA genome (HSRV2 isolate). At the bottom, individual regions within the vgRNA, which are essential for specific functions in viral replication as indicated to the right, are marked as differentially colored bars. U3: unique 3′ LTR region; R: repeat LTR region; U5: unique 5′ LTR region; ©: cap structure; An: poly A tail; mSD: major splice donor; PBS: primer binding site; PARM: protease activating RNA motif; cPPT: central poly-purine tract; 3′ PPT: 3′ poly-purine tract; pA: polyadenylation signal; A-D: purine-rich sequence motifs PPT A through D; RTr: reverse transcription; tas: transactivator of spumaviruses; bel-2: between envelope and LTR ORF-2. Adapted from[8].
2.3. FV Env Proteins
In contrast to Pol, the transcription and endoplasmatic reticulum (ER) membrane-targeted translation of FV Env follow the general strategy of RV gene expression via a family of singly or doubly spliced transcripts with small non-coding upstream exons and/or differences in the untranslated region upstream of a unique start codon[37] (Figure 3). However, co- and posttranslational processing of FV Env contains several unique aspects amongst RVs.
The organization of the FV Env precursor follows the domain structure of retroviral Env proteins and the peptide backbone of its surface (SU) and transmembrane (TM) regions comprise similar numbers of aa[5] (Figure 2c). The N-terminal signal- (SPs) or leader peptides (LPs) of orthoretroviral Env proteins, which are needed for ER-targeted biosynthesis and concomitant translocation of most of Env into the ER lumen, are usually small (<35 aa residues) and co-translationally processed by signal peptidase(s) (SPase). They are not a component of the mature, oligomeric retroviral glycoprotein complex (GPC) of virus particles, and are rapidly degraded. None of this is the case for FVs [3][5][38].
In FV glycoproteins, the functional homologue of the LP (for ER targeting) is embedded in a domain/subunit of about 120 to 130 aa length (Figure 2c). This glycoprotein subunit, designated either Elp for Env leader peptide or just LP for leader peptide, is derived from the N terminus of the Env precursor mainly via posttranslational processing by furin or furin-like cellular proteases during intracellular Env precursor trafficking[39][40]. FV Elp/LP has a type II membrane topology and is a stable and abundant component of released and infectious FV particles[41][42] (Figure 1a and Figure 2c). Its N-terminal, cytoplasmic domain (CyD) of about 60 aa in size, is followed by a standard hydrophobic membrane-spanning domain (MSD), and a short, about 40 aa-long C-terminal extracellular domain. In addition to processing at the two furin-cleavage sites, one between Elp/LP and SU and the other separating SU from TM, the PFV (gp130Env) and FFV Env precursors and possibly Elp/LP as well, are substrates for SPase and signal peptide peptidase-like (SPPL) proteases[39][42][43]. SPPL2a/b appears to process only PFV gp18LP whereas SPPL3 processes both PFV gp18LP and gp130Env within the MSD of the Elp/LP domain, although the exact cleavage site(s) could not be identified. Whether SPase- and SPPL-mediated cleavage of FV Env is of functional relevance for viral replication or just involved in cellular degradation of Elp/LP, and whether SPPL-mediated cleavage products are an integral component of released FV virions, has not been investigated[43]. If they are not just intermediate products prone for final degradation, these SPPL-derived Elp/LP processing products may possess essential functions in the FV replication cycle.
Strikingly, env open reading frame (ORF) encoded LPs of other exogenous (mouse mammary tumor virus, MMTV, and Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus, JSRV) or endogenous RVs (human endogenous retrovirus K, HERV-K) have reported functions as nuclear export factors of not fully spliced viral mRNAs[44][45][46][47][48]. In case of MMTV and HERV-K, these env ORF-encoded LP can be derived from both the Env precursor and separate nuclear export factors (Rem, Rec), translated from alternatively spliced Env mRNAs[44][48][49], whereas in case of JSRV, a prematurely polyadenylated Env mRNA variant has been reported as additional source for Env LP[46]. Interestingly, for their nuclear export function, these retroviral env ORF encoded-LPs require extraction from the ER membrane prior to nuclear localization. In case of MMTV Env LP, this involves a new retro-translocation mechanism[50]. Perhaps FV Elp/LP, and in particular its SPPL-derived processing products may extract from cellular membranes and have similar yet undiscovered function in FV RNA export.
Like other retroviruses, FV Env is not only known to be modified by proteolytic processing, but also undergoes additional posttranslational modifications. Similarly to orthoretroviral Env proteins, FV Env is heavily glycosylated at 14 of 15 N-glycosylation sites[51] (Figure 2c). However, only three sites (N8 in SU and N13, N15 in TM) appear to be individually essential for virus morphogenesis. Absence of N-glycosylation at either of these sites results in intracellular transport defects of the respective mutant, putatively due to glycoprotein misfolding and abolished Env-dependent particle release. Whether FV Env proteins also contain O-linked sugars, such as some other retroviral Env proteins, has not yet been investigated.
Among retroviral glycoproteins, another posttranslational modification is unique[52]. The Elp/LP subunit of primate FV Env proteins is ubiquitinated at several lysine residues located in its N-terminal CyD (Figure 2c). Primate Elp/LP ubiquitination appears to reduce cell surface glycoprotein abundance and suppresses the intrinsic capacity of primate FV glycoproteins to promote release of capsid-less, subviral particles (SVPs)[52][53]. Analyses in FFV do not reveal indications of Elp/LP myristoylation and the two lysine residues implicated in the regulation of PFV particle release via ubiquitination are conserved only among SFVs[39][42]. In addition, a di-lysine ER retrieval signal is present in most known FVs except EFV and BFV[37]. It would be interesting to determine whether different pathways co-exist to regulate Elp/LP functions and particle release in individual FV groups.
As discussed in more detail below, the intact FV Env protein is required for FV particle budding. In particular, a pair of tryptophan residues close to the N terminus of Elp/LP have been shown to be absolutely required for FV budding and infectivity due to specific interactions with N-terminal Gag (MA-domain) residues (Figure 2c). This finding further supports the special role of FV Env as “more than just needed for targeting and entering the host cell”, which may be the case for most orthoretroviruses.
2.4. FV RNA Genome
The retroviral RNA genome is characterized by specific folding resulting in secondary and tertiary structures, which allow its interaction with specific protein effectors, for instance for nucleo-cytoplasmic transport, but most importantly, for specific particle packaging or encapsidation[5]. The Psi genome packaging element on the full-length RNA is usually located in the 5′ part of the genome. In most cases, it is located in the untranslated region upstream of the gag ORF and possibly extends further into coding sequences[5]. This feature is also shared by FVs and the respective genomic element is designated the cis-acting sequence I (CAS-I) (Figure 3). However, FVs require another cis-acting genomic RNA element, CAS-II, for viral infectivity and FV vector function[54][55][56][57]. CAS-II is reported to harbor in its 5′ part additional RNA packaging elements, while its 3′ part contains the major Pol encapsidation signal (PES) and four purine-rich sequence elements (PPT A-D)[58][59][60]. PPT-D has been demonstrated to function as a second internal or central PPT (cPPT) serving, similarly to what has been reported for HIV, as an additional initiation site for plus-strand DNA synthesis during FV reverse transcription[58][59][61]. PPT-A and -B appear to be essential elements of the PES element of CAS-II and have been attributed functions in promoting FV PR-RT-RH dimerization (protease-activating RNA motif, PARM) and through it also possibly Pol precursor encapsidation[62].
2.5. Potential Contribution of Other Foamy Viral and Cellular (co)Factors
Recently, a cluster of high-abundance miRNAs with a unique precursor pri-miRNA has been detected in different SFVs and BFV[63][64][65]. Elimination of the whole miRNA cassette from non-coding sequences in the U3 region of the long terminal repeats (LTRs) does not grossly affect structural protein expression, processing and particle release but it does impair overall BFV fitness and replication competence. These data indicate that the miRNAs do not play an obvious or prominent role in FV assembly and release[66].
FV gene expression and the basic aspects of particle assembly and release including the ESCRT-machinery-directed pinching off of infectious virus seem to be possible in cell lines from different organs and non-authentic, heterologous host species[67][68][69]. This indicates a low level of cell- and species-specific requirements of FVs in this regard. However, as described below, FV particle assembly is restricted to the microtubule organizing center (MTOC) and particle budding is targeted to different degrees to intracellular membranes (e.g., PFV)[70] or to the plasma membrane (e.g., FFV)[71][72]. Additionally, incoming particles are routed to the MTOC highlighting the importance of this sub-cellular site as well as the dependence on the intracellular trafficking machinery of the cell for this bi-directional transport of the FV capsids[73].
Finally, FV replication, including the processes of particle assembly and release, is also targeted by host-encoded restriction factors and intrinsic immunity, for instance in the form of APOBEC3 cytidine deaminase packaging, membrane tethering, and interference with full particle release by BST-2/Tetherin and restriction by TRIM5 proteins [74][75][76]. These aspects are not covered here, but the interested reader is referred to a recent review, which does discuss this aspect[4].
References
- Khan, A.S.; Bodem, J.; Buseyne, F.; Gessain, A.; Johnson, W.; Kuhn, J.H.; Kuzmak, J.; Lindemann, D.; Linial, M.L.; Löchelt, M.; et al. Spumaretroviruses: Updated taxonomy and nomenclature. Virology 2018, 516, 158–164.
- Krupovic, M.; Blomberg, J.; Coffin, J.M.; Dasgupta, I.; Fan, H.; Geering, A.D.; Gifford, R.; Harrach, B.; Hull, R.; Johnson, W.; et al. Ortervirales: New Virus Order Unifying Five Families of Reverse-Transcribing Viruses. J. Virol. 2018, 92.
- Lindemann, D.; Rethwilm, A. Foamy virus biology and its application for vector development. Viruses 2011, 3, 561–585.
- Materniak-Kornas, M.; Tan, J.; Heit-Mondrzyk, A.; Hotz-Wagenblatt, A.; Löchelt, M. Bovine Foamy Virus: Shared and Unique Molecular Features in Vitro and In Vivo. Viruses 2019, 11, 1084.
- Goff, S.P. Retroviridae. In Fields Virology, 6th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a Wolters Kluwer Business: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 1424–1473.
- Wilk, T.; Geiselhart, V.; Frech, M.; Fuller, S.D.; Flügel, R.M.; Löchelt, M. Specific interaction of a novel foamy virus env leader protein with the n-terminal gag domain. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 7995–8007.
- Effantin, G.; Estrozi, L.F.; Aschman, N.; Renesto, P.; Stanke, N.; Lindemann, D.; Schoehn, G.; Weissenhorn, W. Cryo-electron Microscopy Structure of the Native Prototype Foamy Virus Glycoprotein and Virus Architecture. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005721.
- Hamann, M.V.; Lindemann, D. Foamy Virus Protein-Nucleic Acid Interactions during Particle Morphogenesis. Viruses 2016, 8, 243.
- Chen, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhang, G.; Holmes, E.C.; Cui, J. Identification and evolution of avian endogenous foamy viruses. Virus Evol. 2019, 5, vez049.
- Aiewsakun, P.; Simmonds, P.; Katzourakis, A. The First Co-Opted Endogenous Foamy Viruses and the Evolutionary History of Reptilian Foamy Viruses. Viruses 2019, 11, 641.
- Xu, X.; Zhao, H.; Gong, Z.; Han, G.Z. Endogenous retroviruses of non-avian/mammalian vertebrates illuminate diversity and deep history of retroviruses. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007072.
- Katzourakis, A.; Gifford, R.J.; Tristem, M.; Gilbert, M.T.; Pybus, O.G. Macroevolution of complex retroviruses. Science 2009, 325, 1512.
- Switzer, W.M.; Salemi, M.; Shanmugam, V.; Gao, F.; Cong, M.E.; Kuiken, C.; Bhullar, V.; Beer, B.E.; Vallet, D.; Gautier-Hion, A.; et al. Ancient co-speciation of simian foamy viruses and primates. Nature 2005, 434, 376–380.
- Herchenröder, O.; Löchelt, M.; Buseyne, F.; Gessain, A.; Soares, M.A.; Khan, A.S.; Lindemann, D. Twelfth International Foamy Virus Conference-Meeting Report. Viruses 2019, 11, 134.
- Buseyne, F.; Gessain, A.; Soares, M.A.; Santos, A.F.; Materniak-Kornas, M.; Lesage, P.; Zamborlini, A.; Löchelt, M.; Qiao, W.; Lindemann, D.; et al. Eleventh International Foamy Virus Conference-Meeting Report. Viruses 2016, 8, 318.
- Materniak, M.; Kubis, P.; Rola-Luszczak, M.; Khan, A.S.; Buseyne, F.; Lindemann, D.; Löchelt, M.; Kuzmak, J. Tenth International Foamy Virus Conference 2014—achievements and perspectives. Viruses 2015, 7, 1651–1666.
- Heneine, W.; Switzer, W.M.; Sandstrom, P.; Brown, J.; Vedapuri, S.; Schable, C.A.; Khan, A.S.; Lerche, N.W.; Schweizer, M.; Neumann-Haefelin, D.; et al. Identification of a human population infected with simian foamy viruses. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 403–407.
- Achong, B.G.; Mansell, P.W.; Epstein, M.A.; Clifford, P. An unusual virus in cultures from a human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1971, 46, 299–307.
- Herchenröder, O.; Renne, R.; Loncar, D.; Cobb, E.K.; Murthy, K.K.; Schneider, J.; Mergia, A.; Luciw, P.A. Isolation, cloning, and sequencing of simian foamy viruses from chimpanzees (SFVcpz): High homology to human foamy virus (HFV). Virology 1994, 201, 187–199.
- Flügel, R.M.; Pfrepper, K.I. Proteolytic processing of foamy virus Gag and Pol proteins. Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol. 2003, 277, 63–88.
- Lehmann-Che, J.; Giron, M.L.; Delelis, O.; Löchelt, M.; Bittoun, P.; Tobaly-Tapiero, J.; de The, H.; Saib, A. Protease-dependent uncoating of a complex retrovirus. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 9244–9253.
- Hütter, S.; Müllers, E.; Stanke, N.; Reh, J.; Lindemann, D. Prototype Foamy Virus Protease Activity Is Essential for Intraparticle Reverse Transcription Initiation but Not Absolutely Required for Uncoating upon Host Cell Entry. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 3163–3176.
- Müllers, E. The foamy virus Gag proteins: What makes them different? Viruses 2013, 5, 1023–1041.
- Ball, N.J.; Nicastro, G.; Dutta, M.; Pollard, D.J.; Goldstone, D.C.; Sanz-Ramos, M.; Ramos, A.; Müllers, E.; Stirnnagel, K.; Stanke, N.; et al. Structure of a Spumaretrovirus Gag Central Domain Reveals an Ancient Retroviral Capsid. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005981.
- Goldstone, D.C.; Flower, T.G.; Ball, N.J.; Sanz-Ramos, M.; Yap, M.W.; Ogrodowicz, R.W.; Stanke, N.; Reh, J.; Lindemann, D.; Stoye, J.P.; et al. A Unique Spumavirus Gag N-terminal Domain with Functional Properties of Orthoretroviral Matrix and Capsid. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003376.
- Yu, S.F.; Edelmann, K.; Strong, R.K.; Moebes, A.; Rethwilm, A.; Linial, M.L. The carboxyl terminus of the human foamy virus Gag protein contains separable nucleic acid binding and nuclear transport domains. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 8255–8262.
- Holzschu, D.L.; Delaney, M.A.; Renshaw, R.W.; Casey, J.W. The nucleotide sequence and spliced pol mRNA levels of the nonprimate spumavirus bovine foamy virus. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 2177–2182.
- Winkler, I.; Bodem, J.; Haas, L.; Zemba, M.; Delius, H.; Flower, R.; Flügel, R.M.; Löchelt, M. Characterization of the genome of feline foamy virus and its proteins shows distinct features different from those of primate spumaviruses. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 6727–6741.
- Enssle, J.; Jordan, I.; Mauer, B.; Rethwilm, A. Foamy virus reverse transcriptase is expressed independently from the Gag protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 4137–4141.
- Löchelt, M.; Flügel, R.M. The human foamy virus pol gene is expressed as a Pro-Pol polyprotein and not as a Gag-Pol fusion protein. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 1033–1040.
- Jordan, I.; Enssle, J.; Güttler, E.; Mauer, B.; Rethwilm, A. Expression of human foamy virus reverse transcriptase involves a spliced pol mRNA. Virology 1996, 224, 314–319.
- Yu, S.F.; Baldwin, D.N.; Gwynn, S.R.; Yendapalli, S.; Linial, M.L. Human foamy virus replication: A pathway distinct from that of retroviruses and hepadnaviruses. Science 1996, 271, 1579–1582.
- Bodem, J.; Löchelt, M.; Winkler, I.; Flower, R.P.; Delius, H.; Flügel, R.M. Characterization of the spliced pol transcript of feline foamy virus: The splice acceptor site of the pol transcript is located in gag of foamy viruses. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 9024–9027.
- Lee, E.G.; Kuppers, D.; Horn, M.; Roy, J.; May, C.; Linial, M.L. A premature termination codon mutation at the C terminus of foamy virus Gag downregulates the levels of spliced pol mRNA. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1656–1664.
- Roy, J.; Linial, M.L. Role of the foamy virus Pol cleavage site in viral replication. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 4956–4962.
- Hare, S.; Gupta, S.S.; Valkov, E.; Engelman, A.; Cherepanov, P. Retroviral intasome assembly and inhibition of DNA strand transfer. Nature 2010, 464, 232–236.
- Lindemann, D.; Goepfert, P.A. The foamy virus envelope glycoproteins. Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol. 2003, 277, 111–129.
- Kehl, T.; Tan, J.; Materniak, M. Non-simian foamy viruses: Molecular virology, tropism and prevalence and zoonotic/interspecies transmission. Viruses 2013, 5, 2169–2209.
- Geiselhart, V.; Bastone, P.; Kempf, T.; Schnolzer, M.; Löchelt, M. Furin-mediated cleavage of the feline foamy virus Env leader protein. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 13573–13581.
- Duda, A.; Stange, A.; Lüftenegger, D.; Stanke, N.; Westphal, D.; Pietschmann, T.; Eastman, S.W.; Linial, M.L.; Rethwilm, A.; Lindemann, D. Prototype foamy virus envelope glycoprotein leader peptide processing is mediated by a furin-like cellular protease, but cleavage is not essential for viral infectivity. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 13865–13870.
- Lindemann, D.; Pietschmann, T.; Picard-Maureau, M.; Berg, A.; Heinkelein, M.; Thurow, J.; Knaus, P.; Zentgraf, H.; Rethwilm, A. A particle-associated glycoprotein signal peptide essential for virus maturation and infectivity. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 5762–5771.
- Geiselhart, V.; Schwantes, A.; Bastone, P.; Frech, M.; Löchelt, M. Features of the Env leader protein and the N-terminal Gag domain of feline foamy virus important for virus morphogenesis. Virology 2003, 310, 235–244.
- Voss, M.; Fukumori, A.; Kuhn, P.H.; Kunzel, U.; Klier, B.; Grammer, G.; Haug-Kroper, M.; Kremmer, E.; Lichtenthaler, S.F.; Steiner, H.; et al. Foamy Virus Envelope Protein Is a Substrate for Signal Peptide Peptidase-like 3 (SPPL3). J. Biol. Chem 2012, 287, 43401–43409.
- Mertz, J.A.; Simper, M.S.; Lozano, M.M.; Payne, S.M.; Dudley, J.P. Mouse mammary tumor virus encodes a self-regulatory RNA export protein and is a complex retrovirus. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14737–14747.
- Indik, S.; Gunzburg, W.H.; Salmons, B.; Rouault, F. A novel, mouse mammary tumor virus encoded protein with Rev-like properties. Virology 2005, 337, 1–6.
- Caporale, M.; Arnaud, F.; Mura, M.; Golder, M.; Murgia, C.; Palmarini, M. The signal peptide of a simple retrovirus envelope functions as a posttranscriptional regulator of viral gene expression. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4591–4604.
- Hofacre, A.; Nitta, T.; Fan, H. Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus encodes a regulatory factor, Rej, required for synthesis of Gag protein. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12483–12498.
- Magin, C.; Hesse, J.; Lower, J.; Lower, R. Corf, the Rev/Rex homologue of HTDV/HERV-K, encodes an arginine-rich nuclear localization signal that exerts a trans-dominant phenotype when mutated. Virology 2000, 274, 11–16.
- Byun, H.; Halani, N.; Mertz, J.A.; Ali, A.F.; Lozano, M.M.; Dudley, J.P. Retroviral Rem protein requires processing by signal peptidase and retrotranslocation for nuclear function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12287–12292.
- Byun, H.; Das, P.; Yu, H.; Aleman, A.; Lozano, M.M.; Matouschek, A.; Dudley, J.P. Mouse Mammary Tumor Virus Signal Peptide Uses a Novel p97-Dependent and Derlin-Independent Retrotranslocation Mechanism To Escape Proteasomal Degradation. mBio 2017, 8.
- Lüftenegger, D.; Picard-Maureau, M.; Stanke, N.; Rethwilm, A.; Lindemann, D. Analysis and function of prototype foamy virus envelope N glycosylation. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7664–7672.
- Stanke, N.; Stange, A.; Lüftenegger, D.; Zentgraf, H.; Lindemann, D. Ubiquitination of the Prototype Foamy Virus Envelope Glycoprotein Leader Peptide Regulates Subviral Particle Release. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 15074–15083.
- Stange, A.; Lüftenegger, D.; Reh, J.; Weissenhorn, W.; Lindemann, D. Subviral particle release determinants of prototype foamy virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 9858–9869.
- Heinkelein, M.; Schmidt, M.; Fischer, N.; Moebes, A.; Lindemann, D.; Enssle, J.; Rethwilm, A. Characterization of a cis-acting sequence in the pol region required to transfer human foamy virus vectors. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 6307–6314.
- Heinkelein, M.; Dressler, M.; Jarmy, G.; Rammling, M.; Imrich, H.; Thurow, J.; Lindemann, D.; Rethwilm, A. Improved primate foamy virus vectors and packaging constructs. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 3774–3783.
- Erlwein, O.; Bieniasz, P.D.; McClure, M.O. Sequences in pol are required for transfer of human foamy virus-based vectors. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 5510–5516.
- Liu, W.; Backes, P.; Löchelt, M. Importance of the major splice donor and redefinition of cis-acting sequences of gutless feline foamy virus vectors. Virology 2009, 394, 208–217.
- Peters, K.; Barg, N.; Gärtner, K.; Rethwilm, A. Complex effects of foamy virus central purine-rich regions on viral replication. Virology 2008, 373, 51–60.
- Wiktorowicz, T.; Peters, K.; Armbruster, N.; Steinert, A.F.; Rethwilm, A. Generation of an improved foamy virus vector by dissection of cis-acting sequences. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90 Pt 2, 481–487.
- Peters, K.; Wiktorowicz, T.; Heinkelein, M.; Rethwilm, A. RNA and protein requirements for incorporation of the Pol protein into foamy virus particles. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7005–7013.
- Arhel, N.; Munier, S.; Souque, P.; Mollier, K.; Charneau, P. Nuclear import defect of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 DNA flap mutants is not dependent on the viral strain or target cell type. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 10262–10269.
- Hartl, M.J.; Bodem, J.; Jochheim, F.; Rethwilm, A.; Rosch, P.; Wöhrl, B.M. Regulation of foamy virus protease activity by viral RNA: A novel and unique mechanism among retroviruses. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4462–4469.
- Whisnant, A.W.; Kehl, T.; Bao, Q.; Materniak, M.; Kuzmak, J.; Löchelt, M.; Cullen, B.R. Identification of novel, highly expressed retroviral microRNAs in cells infected by bovine foamy virus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 4679–4686.
- Kincaid, R.P.; Chen, Y.; Cox, J.E.; Rethwilm, A.; Sullivan, C.S. Noncanonical microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis gives rise to retroviral mimics of lymphoproliferative and immunosuppressive host miRNAs. mBio 2014, 5, e00074.
- Cao, W.; Heit, A.; Hotz-Wagenblatt, A.; Löchelt, M. Functional characterization of the bovine foamy virus miRNA expression cassette and its dumbbell-shaped pri-miRNA. Virus Genes 2018, 54, 550–560.
- Cao, W.; Stricker, E.; Hotz-Wagenblatt, A.; Heit-Mondrzyk, A.; Pougialis, G.; Hugo, A.; Kuzmak, J.; Materniak-Kornas, M.; Löchelt, M. Functional Analyses of Bovine Foamy Virus-Encoded miRNAs Reveal the Importance of a Defined miRNA for Virus Replication and Host-Virus Interaction. Viruses 2020, 12, 1250.
- Patton, G.S.; Morris, S.A.; Chung, W.; Bieniasz, P.D.; McClure, M.O. Identification of domains in gag important for prototypic foamy virus egress. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 6392–6399.
- Stange, A.; Mannigel, I.; Peters, K.; Heinkelein, M.; Stanke, N.; Cartellieri, M.; Göttlinger, H.; Rethwilm, A.; Zentgraf, H.; Lindemann, D. Characterization of prototype foamy virus gag late assembly domain motifs and their role in particle egress and infectivity. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 5466–5476.
- Hill, C.L.; Bieniasz, P.D.; McClure, M.O. Properties of human foamy virus relevant to its development as a vector for gene therapy. J. Gen Virol. 1999, 80 Pt 8, 2003–2009.
- Yu, S.F.; Eastman, S.W.; Linial, M.L. Foamy virus capsid assembly occurs at a pericentriolar region through a cytoplasmic targeting/retention signal in Gag. Traffic 2006, 7, 966–977.
- Liu, Y.; Betts, M.J.; Lei, J.; Wei, G.; Bao, Q.; Kehl, T.; Russell, R.B.; Löchelt, M. Mutagenesis of N-terminal residues of feline foamy virus Gag reveals entirely distinct functions during capsid formation, particle assembly, Gag processing and budding. Retrovirology 2016, 13, 57.
- Zemba, M.; Wilk, T.; Rutten, T.; Wagner, A.; Flügel, R.M.; Löchelt, M. The carboxy-terminal p3Gag domain of the human foamy virus Gag precursor is required for efficient virus infectivity. Virology 1998, 247, 7–13.
- Petit, C.; Giron, M.L.; Tobaly-Tapiero, J.; Bittoun, P.; Real, E.; Jacob, Y.; Tordo, N.; De The, H.; Saib, A. Targeting of incoming retroviral Gag to the centrosome involves a direct interaction with the dynein light chain 8. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 3433–3442.
- Löchelt, M.; Romen, F.; Bastone, P.; Muckenfuss, H.; Kirchner, N.; Kim, Y.B.; Truyen, U.; Rösler, U.; Battenberg, M.; Saib, A.; et al. The antiretroviral activity of APOBEC3 is inhibited by the foamy virus accessory Bet protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7982–7987.
- Xu, F.; Tan, J.; Liu, R.; Xu, D.; Li, Y.; Geng, Y.; Liang, C.; Qiao, W. Tetherin inhibits prototypic foamy virus release. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 198.
- Yap, M.W.; Lindemann, D.; Stanke, N.; Reh, J.; Westphal, D.; Hanenberg, H.; Ohkura, S.; Stoye, J.P. Restriction of foamy viruses by primate Trim5alpha. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 5429–5439.




