| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Linyi Chen | + 1073 word(s) | 1073 | 2020-04-10 06:15:49 | | | |
| 2 | Linyi Chen | -13 word(s) | 1060 | 2020-11-01 10:45:37 | | | | |
| 3 | Camila Xu | -361 word(s) | 699 | 2020-11-02 10:27:54 | | |
Video Upload Options
Upon traumatic brain injury, epigenome reprograms allowing gene expressions for injury response and regeneration. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation-sequencing of histone marks, we identify a novel enhancer region for induced WNT3A transcription during regeneration of injured cortical neurons. An increased mono-methylation of histone H3 at lysine 4 (H3K4me1) modification and a topological transformation of this enhancer and with promoter of WNT3A gene orchestrate the transcription of WNT3A gene during neuronal regeneration.
1. Introduction
There are approximately 70 million individuals suffering from traumatic brain injury (TBI) each year, which has been a major cause of morbidity and lifelong disability worldwide [1]. TBI is caused by external mechanical force, such as a blow to the brain, or by other mechanisms of displacement of the brain tissue that leads to focal (e.g., penetrating injuries) or diffuse brain damage (e.g., blast exposure) [2]. Following primary injury, secondary injury can evolve and sustain complexed pathophysiological cascades. Secondary injury-initiated cascades include hypoxia, ischemia, increased neurotransmitter excitotoxicity (e.g., increased release of glutamate), diffuse neuronal depolarization and an excessive cellular influx of calcium, leading to cellular/molecular/metabolic derangements and ultimate cellular dysfunction or cell death [3].
2. Discussion
In this regard, long-lasting and progressive nature of pathophysiology after TBI warrants secondary injury cascades a potential target for therapeutic intervention. Unfortunately, due to the heterogeneity of pathophysiology, severity, outcomes upon brain injury and the lack of knowledge about the underlying molecular mechanism, there is currently no therapy for TBI. Promising outcomes in preclinical studies did not lead to clinical efficacy. There are neither efficacy-proven neuroprotective nor neuroregenerative agents available to treat TBI in clinical trials [4]. Poor regeneration of the injured central nervous system in part due to inhibitory gliosis and an aging-related decline of intrinsic regenerative capacity [5][6][7]. However, inhibiting the non-permissive environment alone has not been a successful strategy to promote regeneration of injured brain neurons [8][9][10]. TBI was reported to reprogram epigenome [11][12]. Epigenomic profiling of mice hippocampus after TBI exposure revealed injury-induced inter-correlated transcriptomic and methylomic perturbations [12]. Significant epigenetic changes identified in the brain after TBI in animals and humans include DNA methylation, histone methylation/acetylation and microRNAs expression. Cognitive or functional recovery was assayed following administration of epigenetic modifying drugs in post-TBI animal models, demonstrating variable behavioral outcomes [11]. As more attention has been drawn on the epigenetic mechanism upon TBI, TBI-relevant epigenetic changes are found implicated in shaping neuronal functions and plasticity [13]. It is believed that better understating of the pathophysiology following brain injury in an epigenetic scale would gain insight into therapeutic development for TBI. To this point, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation-sequencing (ChIP-seq) of histone marks, tri-methylation of histone H3 at lysine 4 (H3K4me3) and histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac), to investigate transcriptional regulation of candidate regeneration-associated genes (RAGs). Our laboratory identified WNT3A gene as a promising RAG of which expression was up-regulated during regeneration of injured cortical neurons [14]. Nonetheless, the transcriptional regulation of WNT3A expression remains to be determined. This study predicted the novel enhancer for WNT3A expression and characterized the long range enhancer-promoter interaction that dynamically orchestrated the induced transcription of WNT3A.
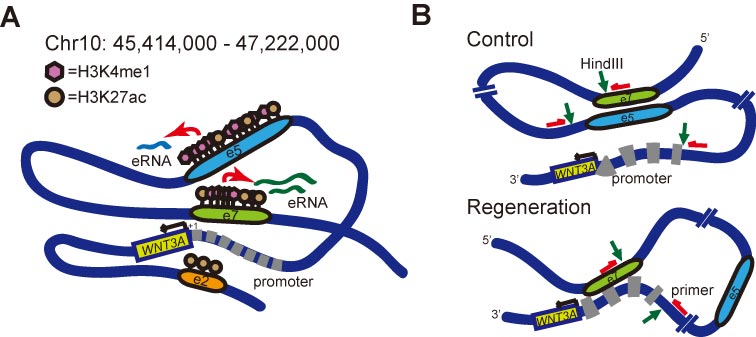
Figure 1. H3K4me1 modifications, enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) and topological transformation at WNT3A enhancer/promoter regions during neuronal regeneration. (A) Schematic summary of histone H3K4me1- and eRNA-mediated enhancer regulation for WNT3A transcription during regeneration. Dark blue line depicts genomic DNA ranging from predicted enhancer, sub-regions e1 to e10. Relative position of the e2, e5, e7 enhancer regions are denoted. Pink hexagon represents H3K4me1. Brown circle represents H3K27ac. eRNAs derived from e5 and e7 are indicated as light blue and green lines, respectively. Red arrows point to the activation of eRNA transcription mediated by increased histone modification during regeneration. Black arrow marks the transcription of WNT3A. Promoter region for WNT3A is depicted by thick gray dashed line. The transcription start site (TSS) is denoted as “+1”. (B) Schematic model of topological transformation of enhancer-promoter looping mechanism for WNT3A regulation during neuronal regeneration. Green arrows point to HindIII cutting sites. Red arrows indicate the site and direction of primers designed for chromosome conformation capture analysis.
References
- Dewan, M.C.; Rattani, A.; Gupta, S.; Baticulon, R.E.; Hung, Y.C.; Punchak, M.; Agrawal, A.; Adeleye, A.O.; Shrime, M.G.; Rubiano, A.M.; et al. Estimating the global incidence of Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurosurg 2018, 130, 1080–1097, doi:10.3171/2017.10.JNS17352.
- Hegde, M.N. A Coursebook on Aphasia and Other Neurogenic Language Disorders, 3 ed.; Delmar Cengage Learning: Clifton Park, NY, USA, 2006.
- Xiong, Y.; Mahmood, A.; Chopp, M. Animal models of Traumatic Brain Injury. Nature reviews. Neuroscience 2013, 14, 128–142, doi:10.1038/nrn3407.
- McGuire, J.L.; Ngwenya, L.B.; McCullumsmith, R.E. Neurotransmitter changes after Traumatic Brain Injury: An update for new treatment strategies. Psychiatry 2018, 24, 995–1012, doi:10.1038/s41380-018-0239-6.
- Yiu, G.; He, Z. Glial inhibition of CNS axon regeneration. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 617–627, doi:10.1038/nrn1956.
- Giger, R.J.; Hollis, E.R., 2nd; Tuszynski, M.H. Guidance molecules in axon regeneration. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a001867, doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a001867.
- Shen, Y.; Tenney, A.P.; Busch, S.A.; Horn, K.P.; Cuascut, F.X.; Liu, K.; He, Z.; Silver, J.; Flanagan, J.G. PTPsigma is a receptor for chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan, an inhibitor of neural regeneration. Science 2009, 326, 592–596, doi:10.1126/science.1178310.
- Fawcett, J.W.; Asher, R.A. The glial scar and central nervous system repair. Brain Res. Bull. 1999, 49, 377–391.
- Lee, J.K.; Chan, A.F.; Luu, S.M.; Zhu, Y.; Ho, C.; Tessier-Lavigne, M.; Zheng, B. Reassessment of corticospinal tract regeneration in Nogo-deficient mice. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 8649–8654, doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1864-09.2009.
- Sun, F.; He, Z. Neuronal intrinsic barriers for axon regeneration in the adult CNS. Opin. Neurobiol. 2010, 20, 510–518, doi:10.1016/j.conb.2010.03.013.
- Wong, V.S.; Langley, B. Epigenetic changes following Traumatic Brain Injury and their implications for outcome, recovery and therapy. Lett. 2016, 625, 26–33, doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2016.04.009.
- Meng, Q.; Zhuang, Y.; Ying, Z.; Agrawal, R.; Yang, X.; Gomez-Pinilla, F. Traumatic Brain Injury Induces Genome-Wide Transcriptomic, Methylomic, and Network Perturbations in Brain and Blood Predicting Neurological Disorders. EBioMedicine 2017, 16, 184–194, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.01.046.
- Nagalakshmi, B.; Sagarkar, S.; Sakharkar, A.J. Epigenetic Mechanisms of Traumatic Brain Injuries. Prog Mol Biol. Transl. Sci. 2018, 157, 263–298, doi:10.1016/bs.pmbts.2017.12.013.
- Chang, C.Y.; Liang, M.Z.; Wu, C.C.; Huang, P.Y.; Chen, H.I.; Yet, S.F.; Tsai, J.W.; Kao, C.F.; Chen, L. WNT3A Promotes Neuronal Regeneration upon Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1463, doi:10.3390/ijms21041463.