Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Héctor García-Ortega | -- | 2443 | 2023-10-24 16:56:21 | | | |
| 2 | Rita Xu | -3 word(s) | 2440 | 2023-10-25 03:43:16 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Cruz-Morales, J.A.; Gutiérrez-Flores, C.; Zárate-Saldaña, D.; Burelo, M.; García-Ortega, H.; Gutiérrez, S. Polyisoprene Rubber. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/50750 (accessed on 07 March 2026).
Cruz-Morales JA, Gutiérrez-Flores C, Zárate-Saldaña D, Burelo M, García-Ortega H, Gutiérrez S. Polyisoprene Rubber. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/50750. Accessed March 07, 2026.
Cruz-Morales, Jorge A., Carina Gutiérrez-Flores, Daniel Zárate-Saldaña, Manuel Burelo, Héctor García-Ortega, Selena Gutiérrez. "Polyisoprene Rubber" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/50750 (accessed March 07, 2026).
Cruz-Morales, J.A., Gutiérrez-Flores, C., Zárate-Saldaña, D., Burelo, M., García-Ortega, H., & Gutiérrez, S. (2023, October 24). Polyisoprene Rubber. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/50750
Cruz-Morales, Jorge A., et al. "Polyisoprene Rubber." Encyclopedia. Web. 24 October, 2023.
Copy Citation
Rubber materials have been used in a wide range of applications, from automotive parts to special-design engineering pieces, as well as in the pharmaceutical, food, electronics, and military industries, among others. Since the discovery of the vulcanization of natural rubber (NR) in 1838, the continuous demand for this material has intensified the quest for a synthetic substitute with similar properties.
natural rubber
synthetic polyisoprene rubber
nanocomposites
1. Introduction
Natural rubber (NR) is a well-known biopolymer used for almost eight centuries. During the Second World War, a substantial increase in its demand was registered, causing several synthesis pathways to be investigated to develop a synthetic substitute. In the 1950’s, polyisoprene synthetic rubber (IR) was successfully obtained using petroleum derivatives as starting materials in the presence of Ziegler–Natta stereospecific catalysts.
Currently, polyisoprene rubber (IR) can be obtained synthetically with different conformations (cis-1,4-; trans-1,4-; 1,2-, and 3,4-) and stereoregular controlled (isotactic, syndiotactic, and atactic), with cis-1,4-polyisoprene (˃98%) being the most produced and commercialized due to its elastomeric properties like high resilience and abrasion resistance, which could lead to a wide range of applications.
It is well known that some of the properties of IR are more or less similar to those of NR, with a small difference in stereoregularity. Typically, IR is composed of between 95 and 98% of cis-1,4-PI, compared with almost 100% of NR. Previously, it was believed that this apparently “small” difference in the stereoregularity results in the difference between NR and IR, specifically the mechanical properties [1]. Breakthroughs made in the last two decades allowed prepared IR with a cis-1,4-PI unit content of 99% or greater, employing a Gd-based catalyst, i.e., synthetic rubber with the same cis-1,4-PI unit content as the NR [2]. Unexpectedly, this synthetic rubber (cis-1,4-PI > 99%) exhibited inferior mechanical properties compared with those of NR, even though both polymers had the same stereoregularity [3]. As seen, the difference in the physical properties between IR and NR is attributable to a lack of understanding of the structure of NR. It was discovered that NR is a naturally occurring nanocomposite with proteins and lipids. In order to prove this postulate, a nanostructured material consisting of NR and non-rubber components was prepared, and it was demonstrated that the mechanical properties increased dramatically when the number of non-rubber components also increased. For this consideration, a nanocompound IR with identical tensile strength to that of NR was successfully prepared [4][5].
It is important to note that, impacted by SARS-CoV-2, global economies suffered setbacks, and NR production contracted more than IR production due to a labor shortage, among other factors. This fact highlights the importance of synthetic rubber, and now, thanks to the study and preparation of nanocomposites, it is known that synthetic polyisoprene rubber (IR) can mimic natural rubber (IR).
Although there is a long road of study on synthetic polyisoprene-based nanocomposites, there is a significant advance in the field of reinforcement additives and methodologies of synthesis, culminating in their application in the fields of tire engineering, automotive components, sporting goods, medical devices, human-tissue-mimicking materials, electrical insulating materials, shape-memory materials, and more recently in healthcare and the environment.
2. Polyisoprene Rubber
2.1. Polyisoprene Synthetic (IR) and Natural Rubber (NR)
Polyisoprene exists in nature (natural rubber) but can also be produced synthetically (isoprene rubber). Natural rubber (NR) is an old biopolymer used by ancient Mesoamerican people (1600–1200 B.C.), who discovered the advantages of crosslinking it with the juice of Ipomoea alba L. [6]. NR is produced by more than 2000 plant species [7], most of them belonging to the Euphorbiaceae or Compositaceae families like the Hevea brasiliensis (willd. Ex A. Juss.) Müll. Arg. and the Castilla elastica Sessé ex Cerv. trees, which synthesize polyisoprenes with a cis-1,4 configuration; in the same way, the Parthenium argentatum A. Gray shrub or guayule, which occurs in the south of the United States and north of Mexico.
In contrast, only a few species, like Palaquium gutta (Hook.) Burck and Manilkara bidentata (A. DC.) A. Chev. trees, also called gutta-percha and balata [8], respectively, synthesize the isomer with conformation trans-1,4. According to reports, the Manilkara zapota or chicle tree produces a 1/4 mixture of cis/trans polyisoprene [9] (Ch. 29–59, [10]). In spite of the wide diversity of rubber species, Hevea brasiliensis is the main industrial source of NR (99%), while guayule is marketed as “non-allergenic NR” (1%) [8][11]. Thus, NR is obtained from the tree Hevea brasiliensis as latex, which contains about (wt/wt) 30.0–35.0% rubber, 1.0–1.8% protein, 1.0–2.0% carbohydrates, 0.4–1.1% neutral lipids, 0.5–0.6% polar lipids, 0.4–0.6% inorganic components, 0.4% amino acids, amides, and 50.0–70.0% water [8]. It is important to note that NR is obtained by coagulation of latex and has been industrially used for about 200 years now, after the discovery of vulcanization in 1838 by Charles Goodyear.
On the other hand, synthetic rubber was created in response to the strategic importance of rubber during World War II. Synthetic rubber is made of raw materials derived from petroleum. Synthetic rubbers were produced at the beginning of the last century (polybutadiene, styrene–butadiene rubber), but polyisoprene rubber (IR) was synthesized after 1950 with the development of Ziegler–Natta stereospecific catalysts [11]. Currently, IR can be obtained with different conformations (cis-1,4-; trans-1,4-; 1,2-; and 3,4-) and microstructures depending on the polymerization conditions and the catalysts used. Even the isoprene can be converted to a high cis-1,4-polyisoprene with physical properties similar to those of NR, and thanks to nanocompounds (IR nanocompounds), the IR can be a true mimic of NR. Thus, it is only required that isoprene be available at a low cost for polyisoprene synthetic rubber (IR) to become commercially competitive with the NR.
2.2. Structure and Isomers
2-Methyl-1,3-butadiene better known as isoprene (I), is a monomer with conjugated double bonds in its structure, and its homopolymerization can lead to several polymers (Figure 1). The 1,4 addition can produce cis-1,4- or trans-1,4-polyisoprene (II, III), while the 1,2- (IV) and 3,4-additions (V) yield structures with an asymmetric carbon (marked by an asterisk), which will result in an R or S configuration (Figure 1).
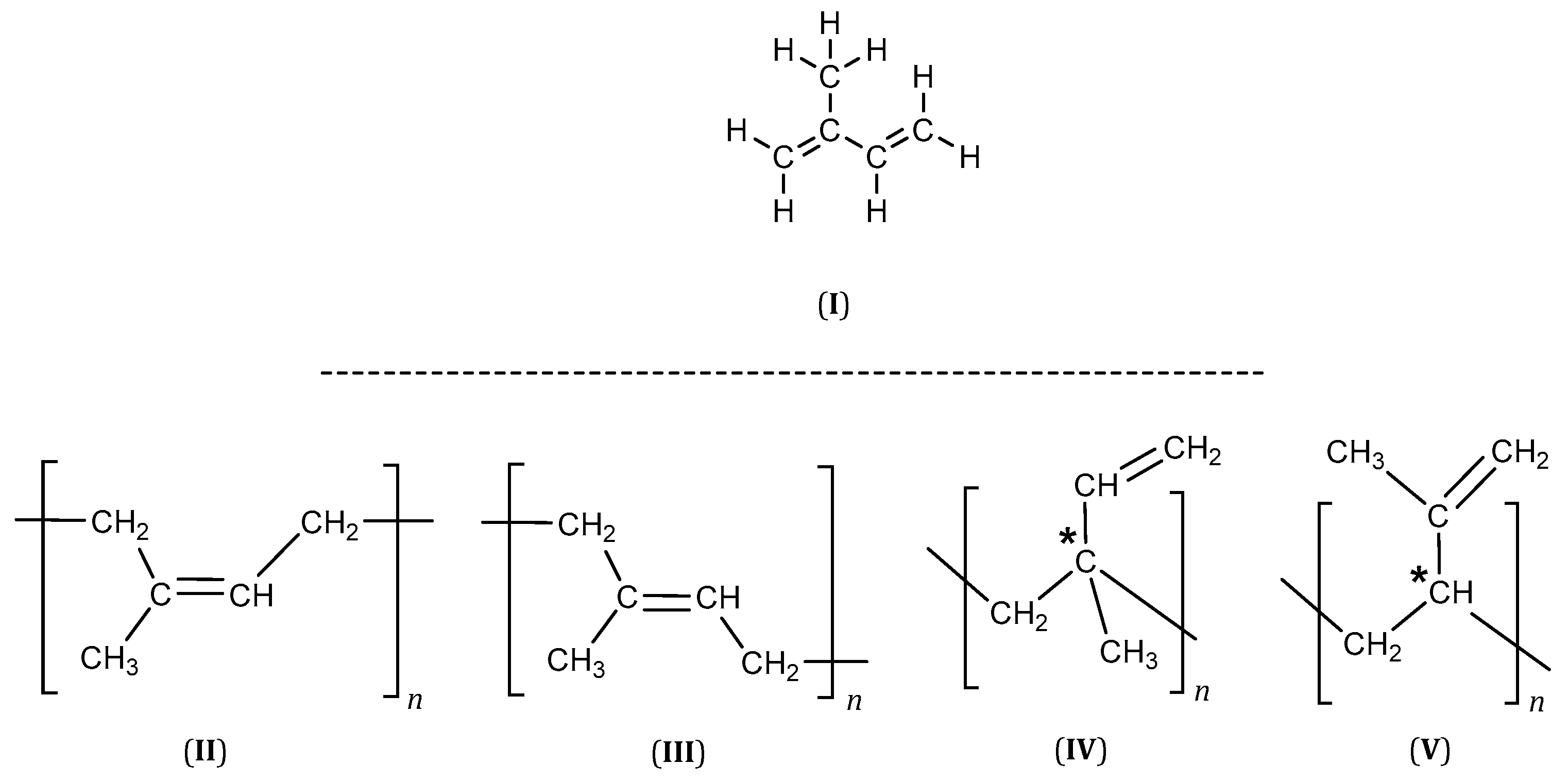
Figure 1. Polyisoprene structures (* an asymmetric carbon).
Thus, the arrangement of the R and S configurations along the polymer chain gives rise to diastereoisomers. Although many sequences are possible, only three simple arrangements are commonly differentiated in polymers: isotactic, atactic, and syndiotactic [12]. In isotactic polymers, all the monomer units have the same configuration (either R or S) (VI). The atactic polymer shows a random configuration (VII), while the syndiotactic polymer has a chain composed of alternating configurations (VIII). Figure 2 depicts the tacticity of the polyisoprene rubber.

Figure 2. Tacticity of the polyisoprene rubber.
The eight basic structures of the polyisoprene shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2 are further complicated since the microstructures have important variations. In this regard, monomer units can be linked in head-to-tail, head-to-head, or tail-to-tail arrangements, as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3. Microstructures of the polyisoprene synthetic rubber (IR).
As can be seen, the different arrangements and configurations discussed previously give rise to eight possible polyisoprene isomers. However, from these, the stereospecific polymerization of isoprene has permitted the synthesizing of the following highly stereoregular polymers: cis-1,4-; trans-1,4-; 3,4-isotactic; and 3,4-syndiotactic (Figure 2) [13].
High cis-1,4-polyisoprene (98%) [14][15] with predominantly head-tail arrangements can be obtained with titanium [16][17] or neodymium-based catalysts [18][19], when a catalyst based on gadolinium (Gd) is employed the IR obtained (99.99%) is able to mimic the cis- content NR (>99%) [16]. High trans-1,4-polyisoprene (TPI) (98%), with a structure very close to that found in natural gutta-percha (99%) and balata (99%) [12], is synthesized using titanium [20][21] or vanadium catalysts [20][22]. 3,4-syndiotactic polyisoprene was obtained with iron catalysts (80–93%) [23][24][25] and with rare earth catalysts by living polymerization [26]. The isotactic isomer (99%) is synthesized in the presence of cationic rare earth metal alkyl species resulting from a binuclear precursor [27], while an atactic 3,4-polyisoprene (90%) is obtained with the chromium system [28]. None of the three possible 1,2-polyisoprene isomers (syndiotactic, isotactic, and atactic) has been synthesized with a high yield.
2.3. Properties
As described above, natural and synthetic rubbers differ in their microstructure. NR exhibits almost entirely the cis-1,4-polymer, whereas IR is a blend of cis-1,4-; trans-1,4-; 1,2-; and 3,4- conformations; and several microstructures: head-head, head-tail, and tail-tail (see Table 1). It is well known that an increase in cis-1,4 usually lowers the glass transition temperature, increases the crystallinity, and improves the mechanical strength. Previously, it was believed that the IR with a cis-1,4-isoprene unit content of 99.9% or greater would have the same properties as the NR. However, it has been shown that not only the cis content defines the properties of such material. It was recently established that NR is a naturally occurring nanocomposite formed by proteins and lipids, and precisely the nanomatrix structure gives it its extraordinary properties [4][5]. Therefore, the tensile strength and tear resistance of IR are usually somewhat lower than those of NR. However, IR nanocomposites can fully mimic the mechanical properties of NR [4], which is fundamental for specific applications. In spite of differences in mechanical properties, IR can replace its naturally occurring counterpart [29] in most industrial applications. IR high cis-1,4 (98%, predominantly head-tail linkages) exhibits many good properties, such as NR (high resilience, strength, and abrasion resistance), and both can be used with water, polar organic solvents (organic acids, alcohols, ketones), and some dilute acids and alkalis. However, other elastomers, such as EPDM, are preferable for these applications. By contrast, both NR and IR are attacked by non-polar solvents, fuels, and petroleum-based oils, as are the other diene-based elastomers. Furthermore, these rubbers are susceptible to attack by ozone due to the presence of double bonds in the main polymer chain, which are prone to thermal and oxidative degradation. The degradation generally occurs through chain scission and causes a drop in the mechanical properties [30].
2.4. Productions
The Asia–Pacific region is the unrivaled leader in terms of both natural (NR) and synthetic rubber (SR) production. In 2022, worldwide rubber production was estimated at 29.6 million tons (MMT), establishing a ratio of natural rubber to synthetic rubber of NR/SR = 49/51 [31]. Impacted by SAR-CoV-2, global economies suffered setbacks, causing world total rubber production to drop by 5.7% in 2020, with NR production (5.1%) contracting more than SR production (4.5%) due to labor shortages, among other factors [32][33]. Fortunately, during the last two years, such a trend has changed, experiencing an increase of 7.3% (in 2021) and 0.5% (in 2022) [31]. Regarding NR, around 88% is produced in the Asia–Pacific region, even though rubber trees are native to America. Regions of Europe, Africa, and the Middle East represent 9%, while North, Central, and South America only account for just less than 3% of the global NR production [33]. On the other hand, SR comprises the polymers known as large-volume production elastomers: styrene-butadiene (SBR), polybutadiene (BR), and ethylene-propylene (EPDM) rubbers, as well as cis-1,4-polyisoprene (IR), isobutylene-isoprene (IIR), neoprene (CR), and acrylonitrile butadiene (NBR), quite important in terms of quantity used worldwide. The rest of the SR is called specialty rubber. These are produced in small quantities but are very important for their applications. Currently, the SR industry is based primarily on the polymers and copolymers of butadiene and styrene; however, polyisoprene and copolymers containing isoprene should not be overlooked. In 2022, world SR output reached 14.9 MMT [31], where IR represented almost 5% of the market [34]. As mentioned above, SR production dropped during COVID-19; nonetheless, as the pandemic eases, global SR production rebounds steadily and will hopefully reach 17.69 MMT by 2027 [35].
About 95% of isoprene production is used to produce cis-1,4-polyisoprene (IR), usually known as the synthetic version of NR [36]. Table 1 shows the many types of IR manufactured industrially.
Table 1. Commercial synthetic polyisoprenes (IR).
| Manufacturer | Trade Names |
Cat a | Cis/Trans Content |
Mooney Viscosity b |
Special Features | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hevea brasiliensis | NR | N/A | 99 cis | 112 | General purpose rubber | [37] |
| 2 | Goodyear Tire and Rubber, Akron, Ohio USA | Natsyn 2200 | Ti | 98 cis | 80 | Production of tires and other rubber products | [15] |
| 3 | Goodyear Tire and Rubber, Akron, Ohio, USA | Natsyn 2100 | Ti | 98 cis | 60 | General purpose rubber | [15] |
| 4 | Kraton Polymers, Houston, Texas, USA | Cariflex IR 307 | Li | 91 cis | N/A | Sensitive applications such as food contact, and pharmaceuticals, and adhesives | [38] |
| 5 | Kraton Polymers, Houston, Texas, USA |
Cariflex IR 310 | Li | 91 cis | 40–53 | Sensitive applications such as food contact, pharmaceuticals, and adhesives | [38] |
| 6 | JCS Synthez-Kauchuk, Bashkortostan, Sterlitamak, Russia | SKI-3S | Ti | 98 cis | 72–84 | Medical articles, Pharmaceutical stoppers, gaskets, hoses, and transportation belts |
[39] |
| 7 | JCS Synthez-Kauchuk, Bashkortostan, Sterlitamak, Russia | SKI-5PM group II |
N/A | N/A | 66 | Pharmaceutical application | [39] |
| 8 | JCS Synthez- Kauchuk, Bashkortostan, Sterlitamak, Russia | SKI-5PM group I |
N/A | N/A | 78 | Pharmaceutical application | [39] |
| 9 | Zeon, Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan | Nippol 2200 | Ti | 98 cis | 82 | General purpose rubber | [40] |
| 10 | Zeon, Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan | Nippol 2200 L | Ti | 98 cis | 70 | Medical articles | [40] |
| 11 | Versalis Eni, Milan, Lombardy, Italy |
Europrene IP 80 |
Li | N/A | 72 | Medical articles | [41] |
| 12 | Versalis Eni, Milan, Lombardy, Italy |
Europrene SOL T 9133 c |
Li | N/A | N/A | Hot-melt pressure-sensitive adhesives for labels or high-tack tapes | [41] |
| 13 | Sinopec, Pekin, China | SIS d | Li | N/A | N/A | Adhesives, plastic, and asphalt modifications | [42] |
| 15 | Rimpex, Xiamen, Fujian, China | TPI-I | V/Ti | 97 trans | 20 | Used as dispersion additives in granulation | [43] |
| 16 | Rimpex, Xiamen, Fujian, China | TPI-II | V/Ti | 97 trans | 20~40 | Good machining performance, generally used in medical materials | [43] |
| 17 | Rimpex, Xiamen, Fujian, China | TPI-III | V/Ti | 97 trans | 40~60 | Used in rubber products and shape-memory materials | [43] |
| 18 | Rimpex, Xiamen, Fujian, China | TPI-IV | V/Ti | 97 trans | 60~80 | Used in tires and shock absorption products | [43] |
2.5. General Applications
cis-1,4-IR is used in a wide variety of industries and products requiring low water swell, high tensile strength, and good resilience; for instance, in rubber bands, belting, pacifiers/baby bottle nipples, conveyor belts, rubber thread, hose, tires (bicycles, aircraft, auto tires), packings, seals, motor mounts, shock absorber bushings, and other extruded and molded mechanical goods, pipe gaskets, footwear, sponges, and sporting goods [12]. Isoprene from NR or IR is also used like liquid rubber with high value-added, such as plasticizers, adhesives, functionalized liquid rubber for the synthesis of diols, macrodiols, polyols, esters, the synthesis of polymers by polycondensation reaction, and new materials with bio-based resources [44][45][46][47].
On the other hand, recent reports have shown that [48] certain substances found in natural rubber, such as protein and protein derivatives, cause irritation and allergies in the human body, so the demand for products made from alternative materials is on the rise. Thus, synthetic polyisoprene rubber has emerged as an ideal substitute for the manufacture of membranes, diaphragms, blood pressure cuff coils, seals, covers, tubes, medical gloves, condoms, different parts of medical and dental equipment, and innovative medical applications [49].
trans-isomer of polyisoprene has only limited commercial applications in non-elastomeric applications, such as covers for golf balls, material for orthopedic splits, electrical insulating materials, and shape-memory materials. Blends of TPI with NR, SBR, and BR have excellent processability and mechanical properties; thus, such blends can be used for high-performance tires [20].
Nowadays, a significant growth in the applications of synthetic rubber (IR) has been reported. Such applications are related to obtaining nanocomposites by adding a reinforcing material, on a nanometric scale, to the synthetic rubber matrix. IR nanocomposites have shown an increase in their properties and become more versatile, to the point of mimicking the mechanical properties of NR.
References
- Ikeda, Y.; Kato, A.; Kohjiya, S.; Nakajima, Y. Rubber Science; Springer: Singapore, 2018.
- Kaita, S.; Doi, Y.; Kaneko, K.; Horiuchi, A.C.; Wakatsuki, Y. An Efficient Gadolinium Metallocene-Based Catalyst for the Synthesis of Isoprene Rubber with Perfect 1,4-Cis Microstructure and Marked Reactivity Difference between Lanthanide Metallocenes toward Dienes As Probed by Butadiene−Isoprene Copolymerization Catalysis. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 5860–5862.
- Gent, A.N.; Kawahara, S.; Zhao, J. Crystallization and Strength of Natural Rubber and Synthetic cis-1,4-Polyisoprene. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1998, 71, 668–678.
- Kawahara, S.; Nishioka, H.; Yamano, M.; Yamamoto, Y. Synthetic Rubber with the Tensile Strength of Natural Rubber. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 2323–2328.
- Kawahara, S.; Chaikumpollert, O.; Akabori, K.; Yamamoto, Y. Morphology and properties of natural rubber with nanomatrix of non-rubber components. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2010, 22, 2665–2667.
- Hosler, D.; Burkett, S.L.; Tarkanian, M.J. Prehistoric Polymers: Rubber Processing in Ancient Mesoamerica. Science 1999, 284, 1988–1991.
- Bode, H.B.; Kerkhoff, K.; Jendrossek, D. Bacterial Degradation of Natural and Synthetic Rubber. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 295–303.
- Rose, K.; Steinbuchel, A. Biodegradation of Natural Rubber and Related Compounds: Recent Insights into a Hardly Understood Catabolic Capability of Microorganisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2803–2812.
- Reyes-Gómez, S.; Montiel, R.; Tlenkopatchev, M.A. Chicle Gum from sapodilla (Manilkara zapota) as a Renewable Resource for Metathesis Transformations. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2018, 62, 1–15.
- Bhowmick, A.K.; Stephens, H. Handbook of Elastomers, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000.
- Cornish, K. Hypoallergenic Natural Rubber Products from Parthenum Argentatum (Gray) and Other Non-Hevea Brasiliensis Species. United States Patent US5580942, 3 December 1996.
- Schoenberg, E.; Marsh, H.A.; Walters, S.J.; Saltman, W.M. Polyisoprene. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1979, 52, 526–604.
- Ricci, G.; Leone, G.; Boglia, A.; Boccia, A.C.; Zetta, L. cis-1,4-alt-3,4 Polyisoprene: Synthesis and Characterization. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 9263–9267.
- Van Amerongen, G.J. Transition Metal Catalyst Systems for Polymerizing Butadiene and Isoprene. In Elastomer Stereospecific Polymerization; Johnson, B.L., Goodman, M., Eds.; American Chemical Society (ACS): Washington, DC, USA, 1966; Volume 52, pp. 136–152.
- Polybutadiene Rubber (BR) Product Details | Goodyear Chemical. Available online: https://www.goodyearchemical.com/products/polybutadiene-rubber (accessed on 7 June 2023).
- Stavely, F.W.; Biddison, P.H.; Forster, M.J.; Dawson, H.G.; Binder, J.L. The Structure of Various Natural Rubbers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1961, 34, 423–432.
- Thiele, S.K.-H.; Wilson, D.R. Alternate Transition Metal Complex Based Diene Polymerization. J. Macromol. Sci. Part C Polym. Rev. 2003, 43, 581–628.
- Osakada, K.; Takeuchi, D. Coordination Polymerization of Dienes, Allenes, and Methylenecycloalkanes. In Polymer Synthesis. Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 171, pp. 137–194.
- Fischbach, A.; Meermann, C.; Eickerling, G.; Scherer, W.; Anwander, R. Discrete Lanthanide Aryl(alk)oxide Trimethylaluminum Adducts as Isoprene Polymerization Catalysts. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6811–6816.
- Song, J.-S.; Huang, B.-C.; Yu, D.-S. Progress of synthesis and application oftrans-1,4-polyisoprene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 82, 81–89.
- Natta, G.; Porri, L.; Giorgio, M. Crystalline Linear High Polymers of Diolefins. Italy Patent IT536631, 7 December 1955.
- Ricci, G.; Italia, S.; Porri, L. Polymerization of 1,3-dienes with methylaluminoxanetriacetylacetonatovanadium. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1994, 195, 1389–1397.
- Bazzini, C.; Giarrusso, A.; Porri, L.; Pirozzi, B.; Napolitano, R. Synthesis and characterization of syndiotactic 3,4-polyisoprene prepared with diethylbis(2,2′-bipyridine)iron–MAO. Polymer 2004, 45, 2871–2875.
- Bazzini, C.; Giarrusso, A.; Porri, L. Diethylbis(2,2′-bipyridine)iron/MAO. A Very Active and Stereospecific Catalyst for 1,3-Diene Polymerization. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2002, 23, 922–927.
- Ricci, G.; Morganti, D.; Sommazzi, A.; Santi, R.; Masi, F. Polymerization of 1,3-dienes with iron complexes based catalysts Influence of the ligand on catalyst activity and stereospecificity. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2003, 204–205, 287–293.
- Wang, B.; Cui, D.; Lv, K. Highly 3,4-Selective Living Polymerization of Isoprene with Rare Earth Metal Fluorenyl N-Heterocyclic Carbene Precursors. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 1983–1988.
- Zhang, L.; Luo, Y.; Hou, Z. Unprecedented Isospecific 3,4-Polymerization of Isoprene by Cationic Rare Earth Metal Alkyl Species Resulting from a Binuclear Precursor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 14562–14563.
- Ricci, G.; Battistella, M.; Porri, L. Chemoselectivity and Stereospecificity of Chromium(II) Catalysts for 1,3-Diene Polymerization. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 5766–5769.
- Kuzma, L.J. Polybutadiene and Polyisoprene Rubbers. In Rubber Technology, 3rd ed.; Morton, M., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 235–259.
- Fried, J.R. Biopolymers, Natural Polymers, and Fibers. In Polymer Science & Technology, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall, Ed.; Pearson Education: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 331–359.
- Malaysian Rubber Council. Available online: https://www.myrubbercouncil.com/industry/world_production.php (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Statista. Rubber–Statistics & Facts. 2023. Available online: https://www.statista.com/topics/3268/rubber/#topicOverview (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- International Rubber Study Group. 2020. Available online: https://www.rubberstudy.org/welcome (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Makhiyanov, N.; Akhmetov, I.G.; Vagizov, A.M. Microstructure of polyisoprenes synthesized with titanium- and neodymium-containing catalytic systems. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2012, 54, 942–949.
- Rubber World. Global Synthetic Rubber Market Production Forecast at 17,690 kt by 2027. Available online: https://rubberworld.com/global-synthetic-rubber-market-production-forecast-at-17690-kt-by-2027/?doing_wp_cron=1682020685.2811911106109619140625 (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Asghar, U.; Masoom, A.; Javed, A.; Abbas, A. Economic Analysis of Isoprene Production from Good Year Scientific Process. Am. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 63.
- Ramos-DeValle, L.F.; Aramburo, F. Effect of Flow-Induced Crystallization on the End Correction Factor. I. Raw Gum Elastomers. J. Rheol. 1983, 27, 295–309.
- Kraton Corporation, Special Polymers. Available online: https://kraton.com/ (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Americas International, Rubber Chemical Products. Available online: https://americasinternational.com/products-suppliers/ (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Zeon Corporation IR (Polyisoprene Rubber). Available online: https://www.zeon.co.jp/en/business/enterprise/rubber/ir/ (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Versalis Eni, Elastomers. Available online: https://www.versalis.eni.com/en-IT/portfolio/polymers-and-intermediates/elastomers.html (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Sinopec Corporation, Special Rubbers. Available online: http://www.sinopecgroup.com/group/en/products/Finechem/Product/SpecialRubber.shtml (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Rimpex Rubber-TPI, Trans Isoprene Rubber. Available online: http://www.rubberimpex.com/TPI/ (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Gutiérrez, S.; Tlenkopatchev, M.A. Metathesis of renewable products: Degradation of natural rubber via cross-metathesis with β-pinene using Ru-alkylidene catalysts. Polym. Bull. 2010, 66, 1029–1038.
- Burelo, M.; Martínez, A.; Cruz-Morales, J.A.; Tlenkopatchev, M.A.; Gutiérrez, S. Metathesis reaction from bio-based resources: Synthesis of diols and macrodiols using fatty alcohols, β-citronellol and natural rubber. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 166, 202–212.
- Martínez, A.; Tlenkopatchev, M.A.; Gutiérrez, S.; Burelo, M.; Vargas, J.; Jiménez-Regalado, E. Synthesis of Unsaturated Esters by Cross-Metathesis of Terpenes and Natural Rubber Using Ru-Alkylidene Catalysts. Curr. Org. Chem. 2019, 23, 1356–1364.
- Pineda-Contreras, A.; Vargas, J.; Santiago, A.A.; Martínez, A.; Cruz-Morales, J.A.; Reyes-Gómez, S.E.; Burelo, M.; Gutiérrez, S. Metátesis de olefinas en México: Desarrollo y aplicaciones en nuevos materiales poliméricos y en química sustentable. Mater. Av. 2018, 29, 65–81. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/39630128/Metátesis_de_olefinas_en_México_desarrollo_y_aplicaciones_en_nuevos_materiales_poliméricos_y_en_química_sustentable (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Jain, A.K.; Deval, R.; Ramesh, V.; Prasad, G. Natural rubber latex allergy. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2008, 74, 304–310.
- Rahimi, A.; Mashak, A. Review on rubbers in medicine: Natural, silicone and polyurethane rubbers. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2013, 42, 223–230.
More
Information
Subjects:
Polymer Science
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
3.6K
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
25 Oct 2023
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No





