Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vladimir S. Tyurin | -- | 3335 | 2023-08-19 11:17:17 | | | |
| 2 | Lindsay Dong | Meta information modification | 3335 | 2023-08-21 04:58:57 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Tyurin, V.S.; Shkirdova, A.O.; Koifman, O.I.; Zamilatskov, I.A. Meso-Formylporphyrins. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/48239 (accessed on 07 February 2026).
Tyurin VS, Shkirdova AO, Koifman OI, Zamilatskov IA. Meso-Formylporphyrins. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/48239. Accessed February 07, 2026.
Tyurin, Vladimir S., Alena O. Shkirdova, Oscar I. Koifman, Ilya A. Zamilatskov. "Meso-Formylporphyrins" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/48239 (accessed February 07, 2026).
Tyurin, V.S., Shkirdova, A.O., Koifman, O.I., & Zamilatskov, I.A. (2023, August 19). Meso-Formylporphyrins. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/48239
Tyurin, Vladimir S., et al. "Meso-Formylporphyrins." Encyclopedia. Web. 19 August, 2023.
Copy Citation
Insertion of the formyl group into porphyrins is a primary functionalization of the tetrapyrrole ring, opening opportunities for further transformations including, but not limited to, Wittig, Grignard, McMurry, cycloaddition, Knoevenagel reactions, and Schiff bases preparation.
porphyrins
tetrapyrrole ring
Meso-Formylporphyrins
1. Preparation of Meso-Formylporphyrins
One of the strategies for the preparation of functionalized porphyrins is the utilization of the correspondingly functionalized precursors in the synthesis of the porphyrin core. The formyl group is actively involved in the condensation reaction during tetrapyrrole ring construction, and it needs to be protected. Formylporphyrins were obtained by the usual macrocyclization route to the porphyrins from the masked formyl-containing precursors: 2-formyl-1,3-dithiolane was converted to 5-(1,3-dithian-2-yl)dipyrromethane and mixed MacDonald [2 + 2] condensation with 5-mesytyldipyrromethane and p-tolualdehyde led to 5-(1,3-dithian-2-yl)-15-mesytyl-10,20-di(4-tolyl)porphyrin 1 which gave the corresponding 5-formyl-15-mesytyl-10,20-di(4-tolyl)porphyrin 2 after deprotection with DDQ/BF3(OEt2) (Scheme 1) [1].
Scheme 1. Synthesis of meso-formylporphyrin from the semi-protected oxalic aldehyde.
Similar methods of preparation of formylporphyrins from 1,3-dithiane were proposed by Lindsey [2] and Senge [3]. These methods open opportunities for obtaining 5-, 5,10-, 5,15-, 5,10,15,20-thianyl substituted porphyrins (Scheme 2), which can easily be deprotected to the corresponding formylporphyrins with quantitative yield.
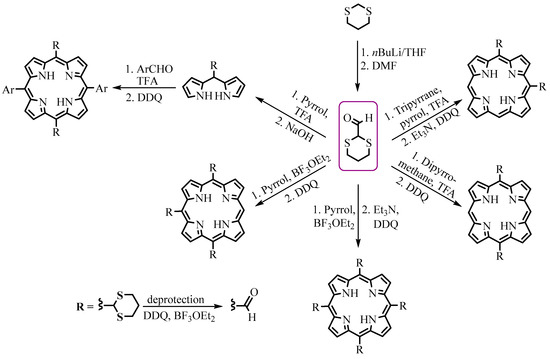
Scheme 2. Synthesis of variously substituted meso-formylporphyrins.
The insertion of the formyl group into the already assembled tetrapyrrole macrocycle can be realized both by electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution reactions. 1,3-dithiolane as an umpolung formyl synthon, developed by Seebach and Corey [4], was used to insert formyl via nucleophilic addition of the corresponding lithium salt to the porphyrin. Senge investigated the reaction of the addition of 1,3-dithiane, deprotonated with n-butyllithium, in the presence of N,N,N,N-tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA), to porphyrins [3]. The products of the nucleophilic addition of the 1,3-dithianyl anion to the 5,15-diphenylporphyrin (DPP) 3, 5,15,20-triphenylporphyrin (TrPP) 4, and their nickel complexes (3Ni and 4Ni) were protonated, and the corresponding porphyrinogens were oxidized with DDQ. Subsequent deprotection of the formyl group was carried out with DDQ but in the presence of BF3 etherate to give the corresponding meso-formyl DPP and TrPP derivatives 5 and 6 (Scheme 3). However, low yields and functional group intolerance of the method limit its use.
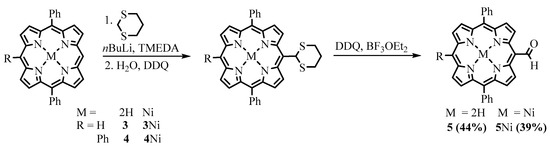
Scheme 3. Synthesis of meso-formylporphyrins via nucleophilic addition.
Takanami developed a more efficient and functional group-tolerant method of nucleophilic formyl group insertion using 2-(trimethylsilyl)pyridine. The reaction proceeded via nucleophilic addition of (2-pyridylmethylsilyl)lithium to DPP 3, followed by protonation of the intermediate anion and oxidation of the porphyrinogen back to the aromatic porphyrin ring to give DPP-CHO 5 (Scheme 4) [5][6]. It should be noted that mild oxidation of the meso-silyl porphyrinogen by air led to the meso-(hydroxymethyl)porphyrins 7 [7].
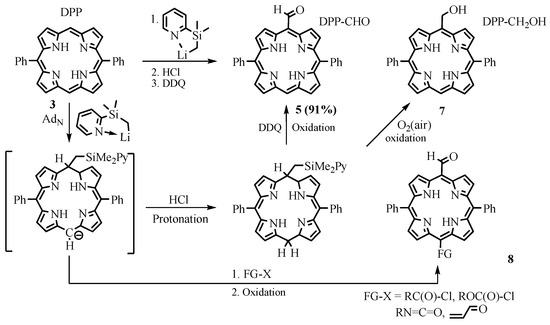
Scheme 4. Formylation with (2-pyridylmethylsilyl)lithium.
The reaction proceeds under mild conditions, and it is applicable to aryl- and alkyl-substituted porphyrins as well as their metal complexes. In addition to monoformyl derivatives, this method makes it possible to obtain diformyl derivatives, as well as more complex aldehydes with high yields. To confirm the mechanism, reactions were carried out with the addition of various electrophiles, such as acyl chloride, methyl chloroformate, isocyanates, and enones, resulting in the corresponding formyl derivatives 8, variously substituted at the opposite formyl meso position [8].
Osuka obtained porphyrin Grignard reagents for the first time using metal-iodine exchange between meso-iodoporphyrins and iPrMgCl. The utilization of the meso-magnesiumporphyrins in reaction with DMF led to the formation of the meso-formyl derivatives (Scheme 5) [9].
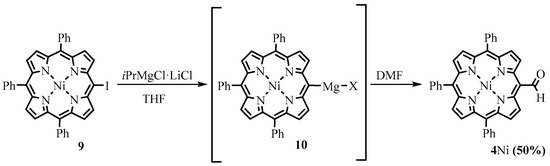
Scheme 5. Formylation through the porphyrin Grignard reagent.
Reactions of electrophilic substitution have found the greatest application in the chemistry of porphyrins as electron-rich aromatics. More reactive meso positions are usually attacked by electrophiles. The electrophilic formylation can easily be performed using the Vilsmeier–Haack reaction. The synthesis of meso-formyl-β-octaalkylporphyrins using Vilsmeier–Haack formylation was first reported more than half a century ago [10][11]. To date, this reaction has become one of the most popular and efficient for obtaining meso-formylporphyrins.
Porphyrin metal complexes resistant to HCl, released during the reaction, are substrates for formylate. It is known that the rate of formylation decreases with increasing electron acceptor ability of the metal cation in the series M(II) > M(III) > M(IV) and among M(II) in the series Ni(II) > Cu(II) > Pd(II) > Pt(II). Of the numerous variants of the reaction, the Vilsmeier reagent made from DMF/POCl3 is usually used in porphyrin chemistry. The mechanism of the reaction is as follows: at the first stage, the electrophilic Vilsmeier reagent attacks the nucleophilic meso position of porphyrin, resulting in the formation of the iminium salt, which is the so-called “phosphorus complex”. Subsequent treatment of the phosphorus complex with water leads to the hydrolysis of the iminium salt, resulting in the formation of formylporphyrin (Scheme 6).
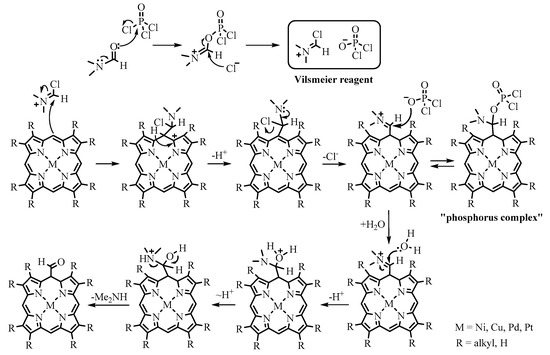
Scheme 6. Mechanism of the Vilsmeier–Haack formylation reaction.
2. Reactions of Meso-Formylporphyrins with Nitrogen Nucleophiles
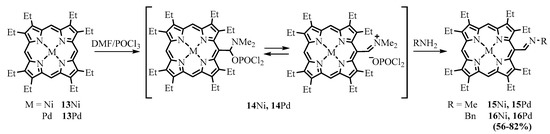
Ponomarev investigated the Vilsmeier–Haack formylation of a number of Cu(II), Ni(II), and Pd(II) complexes of β-octaalkylporphyrins and chlorins and the subsequent transformations of the meso-formyl derivatives [12][13]. As an electrophile, the formyl group can react with a variety of nucleophiles, including organometallic reagents, CH-acids, heteroatom nucleophiles (amines, thiols), electron-rich aromatic cycles, and heterocycles. The reaction of formylporphyrins with amines leads to azomethines or Schiff bases, and the corresponding studies up to the mid-1990s were summarized in the review of Ponomarev [14]. Meso-formyl porphyrins react with amines to give the corresponding imines; hydroxylamines give oximes; and hydrazines produce hydrazones. The Vilsmeier–Haack formylation of β-octaalkylporphyrin 13 produces the stable phosphorus complex 14 due to the sterical hindrances retarding hydrolysis of the complex. Ponomarev isolated phosphorus complexes of various porphyrins and used them instead of formylporphyrins for the preparation of Schiff bases [14]. The iminium group of the phosphorus complex is more active to nucleophilic attack compared to the formyl group. Azomethine derivatives of nickel and palladium complexes of various porphyrinoids, including OEP, tetraalkyl esters of coproporphyrins I and II, mesoporphyrin IX, and mesochlorin e6, were obtained by direct interaction of “phosphorus complexes” with amines (Scheme 7) [15][16][17].

Scheme 7. Preparation of azomethine derivatives of metal complexes of OEP (MOEP) from the intermediate phosphorus complex obtained from formylation of MOEP.
Azomethine substitution at the meso position noticeably shifts the UV-Vis absorption spectra of porphyrins to long wavelengths, thus making their metal complexes potential photosensitizers [16]. Schiff bases also impart basic properties to the porphyrins, and the corresponding Pt(II) and Pd(II) complexes of azomethine derivatives of OEP and tetramethyl coproporphyrin I were investigated as sensor dyes for measuring proton and oxygen concentrations using an optical noninvasive method [18][19]. The corresponding phosphorescent probe, based on the Pt(II) complex of meso-(N-methylimino)-OEP for cellular diagnostics using dual oxygen and pH measurements in living cells, has been reported [20].
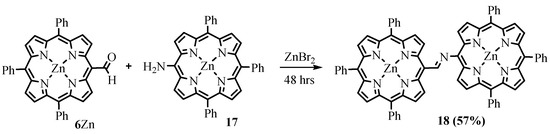
The imino group, which can be obtained by interacting the formyl group with an amine, was used as a linker to bond two tetrapyrrole chromophores into a dyad. The interaction of Zn(II) complexes of meso-formyltriphenylporphyrin 6Zn and meso-aminotriphenylporphyrin 17, catalyzed by Lewis acid ZnBr2, led to the corresponding dimer of TrPP 18 (Scheme 8) [21]. The TrPP macrocycles are not coplanar in dimer 18 and consequently not conjugated. Nevertheless, there is some interchromophore communication, and dimer 18 features increased two-photon absorption, which can be used in PDT, providing deeper and more targeted treatment [22].

Scheme 8. Synthesis of the TrPP dimer bridged with the imino group.
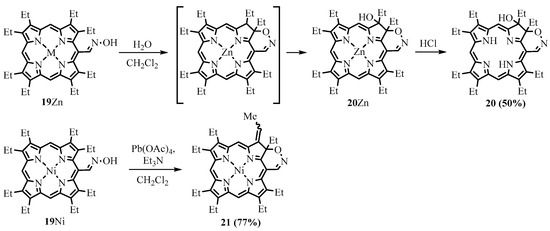
Schiff bases are useful synthons, as they can be subjected to further transformations. Elimination of meso-oximes led to meso-cyanoporphyrins [23]. Intramolecular cyclization was observed when meso-oxime 19Zn was vigorously stirred for a few hours in methylene chloride with a small amount of water. The probable intermediate chlorin with the fused 1,2-oxazin ring underwent hydroxylation via a peroxide mechanism to form stable hydroxychlorin 20Zn. The use of an oxidant, lead tetraacetate, gave the product the same fused 1,2-oxazin but with a vinyl group instead of ethyl and hydroxyl (Scheme 9) [24][25]. Apparently, the difference between products 20 and 21 is in the water molecule, which was probably eliminated in the case of 21. The UV-Vis spectra of the 1,2-oxazin annulated porphyrinoids 20 and 21 possess strong absorption bands in the red region.

Scheme 9. Synthesis of porphyrinoids with fused 1,2-oxazin rings via oxime cyclization.
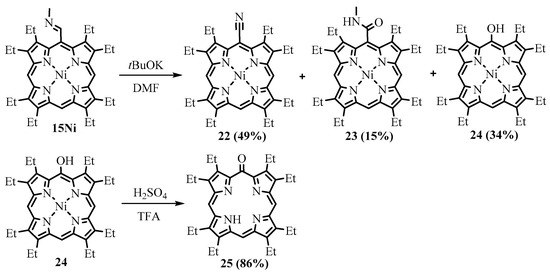
Treatment of the Ni(II) complex of meso-(N-methylimino)-OEP 15Ni with t-BuOK led to the formation of the corresponding meso-nitrile 22, meso-amide 23, and meso-hydroxy 24 derivatives (Scheme 10). The latter was demetalated with sulfuric acid, resulting in phlorin 25 with strong light absorption in the region of 700 nm [17].

Scheme 10. Treatment of the N-methylimine derivative of NiOEP with tBuOK.
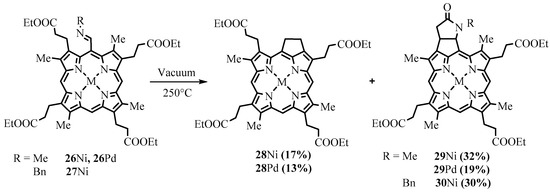
Thermolysis of meso-alkylimines of β-substituted metal porphyrins led to the formation of cyclopentane-fused derivatives (Scheme 11) [26][27][28]. The meso-imines of the tetraalkyl ester of coproporphyrin I (26 and 27) were transformed into a mixture of cyclopentane and cyclopentane-lactam bicycle fused derivatives (28–30) [17].

Scheme 11. Preparation of cyclopentane-annelated derivatives of coproporphyrins.
Meso-hydrazones of nickel and palladium complexes of OEP and coproporphyrin I ethyl esters were obtained as a mixture of E- and Z-isomers by the reaction of the corresponding meso-formyl derivatives with hydrazines catalyzed by trifluoroacetic acid (Scheme 12) [29].

Scheme 12. Synthesis of hydrazones of metal complexes of OEP and coproporphyrin I.
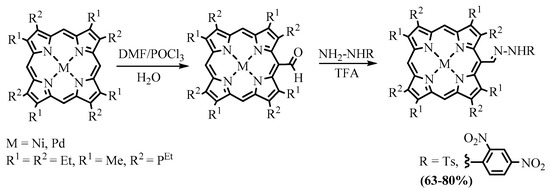
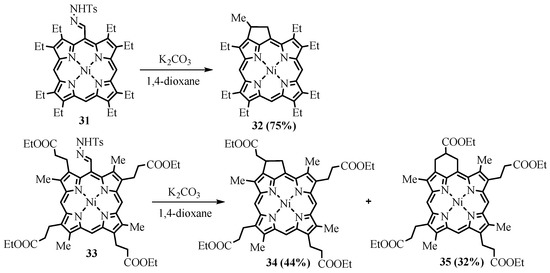
N-tosylhydrazones 31 and 33 reacted with bases, generating an in situ porphyrin derivative of diazomethane, which released nitrogen molecules to give meso-carbene derivatives of porphyrins. Subsequent intramolecular insertion of the carbene into the CH bond of the neighboring β-substituent led to the corresponding fused cyclopentane (32 and 34) [30]. The cyclopentane fused products obtained were the same as in the thermolysis of azomethine 26; however, the second product in the carbene-based reaction of 33 was cyclohexane fused product 35 instead of bicyclic lactam 29 obtained in the thermolysis of azomethine 26 [17], and yields of the products in the carbene-based cyclization were appreciably higher compared to the thermolysis (Scheme 13).

Scheme 13. Preparation of annelated porphyrins via intramolecular carbene CH insertion.
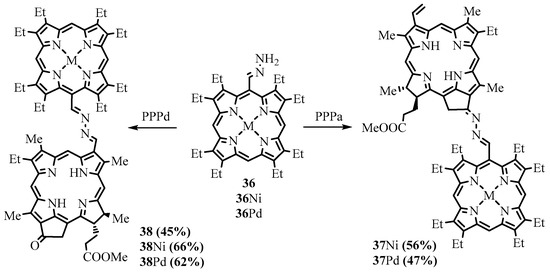
Unsubstituted meso-hydrazones of OEP 36 and also β-octaethylchlorin (OEC) were used in the preparation of dyads 37 and 38 bridged with the azine group [31]. Derivatives of the natural chlorins, methyl pyropheophorbide-a (PPPa) and methyl pyropheophorbide-d (PPPd), reacted with the meso-hydrazones of OEP and OEC, leading to the formation of the corresponding porphyrin-chlorin and chlorin-chlorin dyads (Scheme 14) [31]. Upon irradiation of the dyads, the energy of the excited state was efficiently transferred from the OEP (OEC) components to the pyropheophorbide chromophore. However, the chromophores weakly interacted in the ground state; therefore, the azine group was regarded as a conjugation switch, usually in the off state but capable of being turned on with a sufficiently strong driving force.

Scheme 14. Synthesis of dyads linked by the azine bridge.
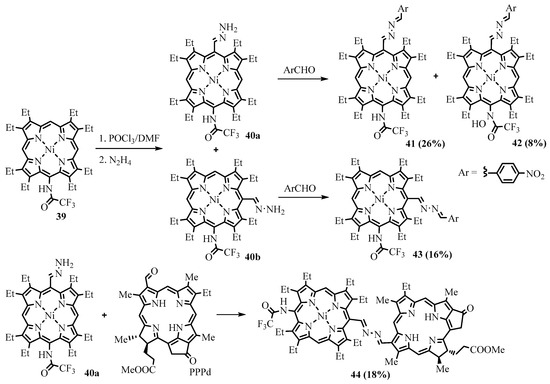
One-pot meso-formylation, hydrazone, and azine formation were performed for meso-(trifluoroacetamido)-OEP 39 [32]. Under the conditions of formylation, the amide group was unexpectedly partially oxidized to form hydroxamic acid 42 (Scheme 15). The combined influence of trifluoroacetamide and arylazine groups in the products 41–43 led to strongly increased absorption near 500 nm and considerably red-shifted Q-bands up to 650 nm. Azine-bridged porphyrin-chlorin dyad 44 was obtained from meso-(trifluoroacetamido)-OEP 40a and PPPd (Scheme 15). The dyad features substantial growth in the Q-band intensity as well as a red-shifting Soret band compared to the similar dyad without the trifluoroacetamido substituent.

Scheme 15. Synthesis of β-octaethylporphyrin, oppositely substituted with trifluoroacetamide and azine groups.
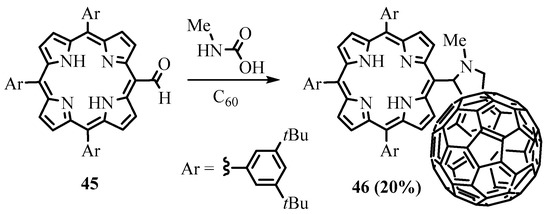
The meso-formyl group of porphyrins can be transformed to azomethine ylide by interaction with N-methylglycine. 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of the intermediate azomethine ylide to the double bond leads to porphyrins with meso-fused heterocycles. The porphyrin—fullerene conjugate 46 was obtained this way from meso-formyltriarylporphyrin 45, N-methylglycine, and C60 fullerene (Scheme 16) [33]. The irradiation of the dyad led to the formation of the exciplex due to the strong interaction between the porphyrin and C60 chromophores at short distances.

Scheme 16. Synthesis of meso-linked porphyrin—fullerene conjugate.
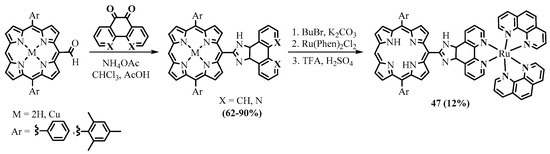
Porphyrins functionalized with meso-fused 2-imidazolyl heterocycles were synthesized from the 5-formyl-10,20-diarylporphyrins and phenanthrene- or phenanthroline-5,6-dione in the presence of ammonium acetate (Scheme 17) [34]. The ruthenium phenanthroline complex of the free base porphyrin-imidazo[4,5-f]phenanthroline conjugate showed good binding ability to DNA and was capable of DNA photocleavage, which allows us to regard the complex as a potential photosensitizer for PDT [35].

Scheme 17. Synthesis of porphyrins with meso-fused 2-imidazolyl heterocycles.
3. Reactions of Meso-Formylporphyrins with Miscellaneous Nucleophiles
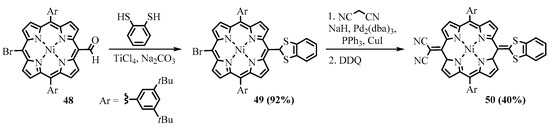
A family of push-pull quinoidal porphyrins was obtained from a meso-formyl porphyrin 48 through the attachment of 1,3-dithiolane (benzo-1,3-dithiolane) and malononitrile fragments at the opposite meso positions of the 5,15-diarylporphyrin (Scheme 18) [36].

Scheme 18. Synthesis of porphyrins with meso-fused 2-imidazolyl heterocycles.
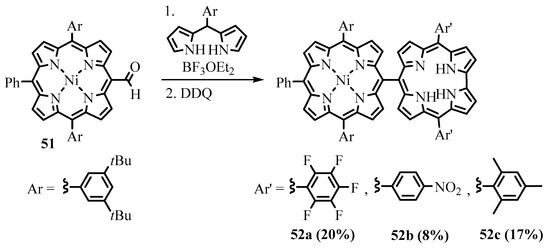
Directly linked porphyrin-corrole dyads 52a–c were formed during condensation of the meso-formyltriarylporphyrin 51 with dipyrromethane (Scheme 19) [37]. A similar corrole-porphyrin-corrole triad was obtained when the 5,15-bisformylporphyrin was placed into the reaction. The strong exciton coupling between closely placed chromophores and reversible energy transfer were shown to exist in the dyad [38]. Directly meso-meso-linked porphyrin dimers and oligomers were obtained using condensation of meso-formylated porphyrins with pyrrole [1]. Such porphyrin dimers and oligomers were shown to act as prospective photosensitizers [39].

Scheme 19. Synthesis of porphyrin-corrole dyads.
4. Reactions of Meso-Formylporphyrins with Organometallic Reagents
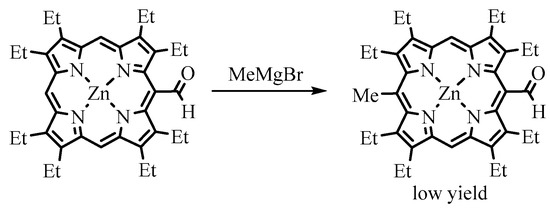
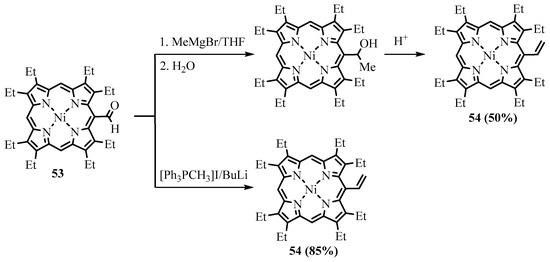
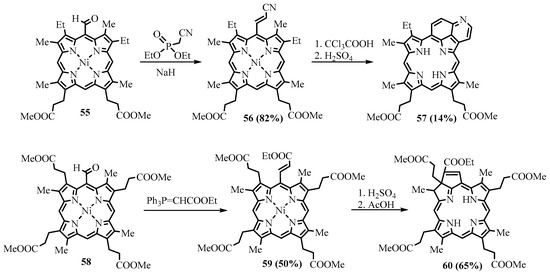
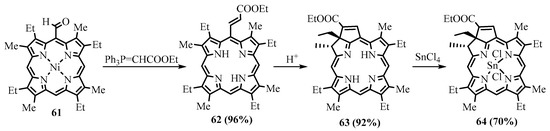
Among organometallic reagents, Grignard reagents were usually employed in the reactions for meso-formylporphyrins. Alkyllithium reagents gave the expected products of addition to the carbonyl group only with less hindered β-formyl derivatives [40]. Grignard reagents interact with meso-formylporphyrins, leading to the formation of the corresponding secondary alcohols, but due to steric factors and perhaps other causes, this reaction proceeds somewhat slowly. Especially retarding is the presence of β-alkyl substituents. For example, Ponomarev reported the formation of the Mg complex of the formylporphyrin without significant formation of the target meso-(1-hydroxyethyl)-OEP upon treatment of meso-formyl-OEP (OEP-CHO) with MeMgI under heating [41]. Smith carried out a similar reaction with a free base of OEP-CHO and a Zn(II) complex of OEP-CHO (ZnOEP-CHO), which resulted in 15-alkylated products, and the formyl group remained intact (Scheme 20) [42]. However, when Johnson and Arnold used the Ni(II) complex of OEP-CHO in the same reaction, Ni(II) 5-(1-hydroxyethyl)-OEP was obtained, as expected [43]. Water was easily eliminated, yielding Ni(II) 5-vinyl-OEP 54 (Scheme 21). The Wittig reaction is cleaner and more efficient, as well as tolerating various functional groups such as esters. Various Wittig regents interacted with the meso-formyl group of β-substituted porphyrins to form meso-vinyl 54 (Scheme 21), 2-(ethoxycarbonyl)ethenyl 59, 2-cyanoethenyl 56 (Scheme 22), and other alkenyl groups [12][44]. meso-formylporphyrins with meso-aryl groups without β-substituents were transformed to the corresponding meso-vinylporphyrins [45]. The products of the Wittig alkenylation can further be cyclized; for example, the methyl ester of coproporphyrin I was converted to the corresponding derivative of copropurpurin I 60 (Scheme 22). Purpurins and benzochlorins have an additional annealed cycle through meso positions and β-positions, which affect the π-electron system, leading to a bathochromic shift of the absorption bands. These annelated porphyrins and chlorins are more stable compared to other chlorins and have comparable electron-optical properties suitable for PDT. They have a higher efficiency than meso tetraphenylporphyrin and higher absorption in the longer wavelength region. The benzochlorins were shown to be of low dark toxicity towards Chinese Hamster ovary cells, whereas in the presence of light, total cell killing was observed at concentrations of the photosensitizer below 1 μg/mL [46]. These promising properties of the annelated porphyrin derivatives attract the attention of medical researchers [47]. One of the representatives of this type of compound, tin etiopurpurin complex 64, was used as a photosensitizer for PDT in human clinical trials. The drug was obtained from nickel etioporphyrin, which was formylated and reacted with a Wittig reagent, yielding meso-acrylate derivative 62, which was cyclized in acid to give etiopurpurin 63. The latter was metalated with tin(IV) chloride to give the drug for PDT (Scheme 23) [48]. The selectivity for the cyclization proceeding exclusively towards the carbon carrying the ethyl group vs. the carbon carrying the methyl group.

Scheme 20. The Grignard reaction of Zn(II) meso-formyl-OEP.

Scheme 21. The Grignard and Wittig reaction of NiOEP-CHO.

Scheme 22. Wittig alkenylation of Ni(II) complexes of methyl esters of mesoporphyrin IX and coproporphyrin I with subsequent cyclization.

Scheme 23. Synthesis of the photosensitizer for the PDT tin(IV) etiopurpurin complex.
There are several published papers devoted to the synthesis of benzochlorin derivatives based on octaethylporphyrin and hematoporphyrin IX, as well as the study of their properties as photosensitizers [49][50][51][52]. In particular, the preparation of variously substituted benzochlorins containing fluorinated or alkyl groups has been reported [50].
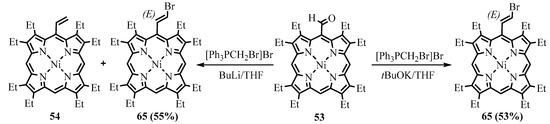
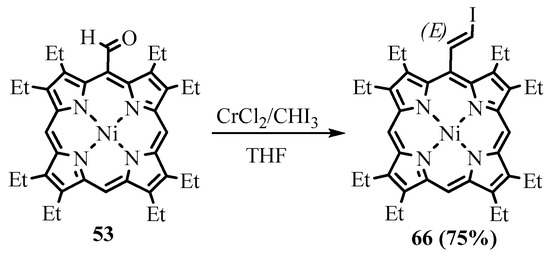
The formyl group can be transformed to the 2-haloethenyl group in one step using two different reactions. The Wittig reaction of NiOEP-CHO 53 with bromomethyltriphenylphorphonium bromide led to meso-(2-bromoethynyl)NiOEP 65 as a major (E)-isomer with a 55% yield [53]. However, the side metal-halogen exchange reaction led to the formation of lithiated methylene ylide and subsequently the formation of meso-vinyl byproduct 54, which was hard to separate. The use of potassium t-butoxide in THF avoided contamination and produced a 53% yield (Scheme 24) [54]. Alternatively, the Takai reaction with iodoform catalyzed by CrCl2 led to the formation of meso-(2-iodoethynyl)porphyrin 66 (Scheme 25). The obtained 2-haloethenyl derivatives were used as substrates of the cross-coupling reactions and precursors for the preparation of meso-ethynylporphyrins.

Scheme 24. Wittig bromoethenylation of NiOEP-CHO.

Scheme 25. Takai iodoethenylation of NiOEP-CHO.
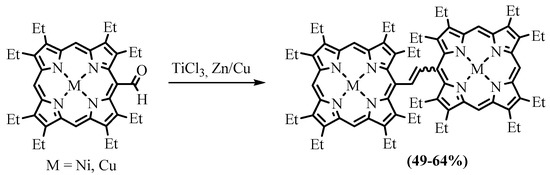
Transformation of the formylporphyrins into dimers bonded with an ethene bridge can be performed using low-valent titanium, which is called the McMurry reaction [55]. Cu(II) and Ni(II) complexes of OEP-CHO were dimerized under the action of TiCl3 and Zn/Cu to form the corresponding complexes of dimers linked with the ethylene bridge in the form of a mixture of cis and trans isomers (Scheme 26) [56].

Scheme 26. McMurry dimerization of NiOEP-CHO and CuOEP-CHO [56].
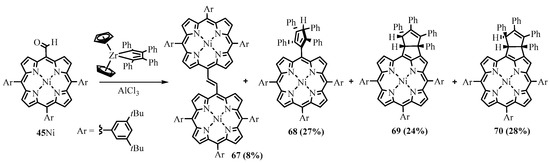
The similar dimerization of the Ni(II) meso-formyltriarylporphyrin 45 Ni was observed as a side reaction of coupling with tetraphenylzirconacyclopentadiene in the presence of AlCl3, along with products of cross-coupling: porphyrin—cyclopentene 69, 70, and cyclopentadiene 68 hybrids (Scheme 27) [57].

Scheme 27. Reaction of meso-formyltriarylporphyrin with tetraphenylzirconacyclopentadiene.
5. The Reaction of Meso-Formylporphyrins with CH Acids
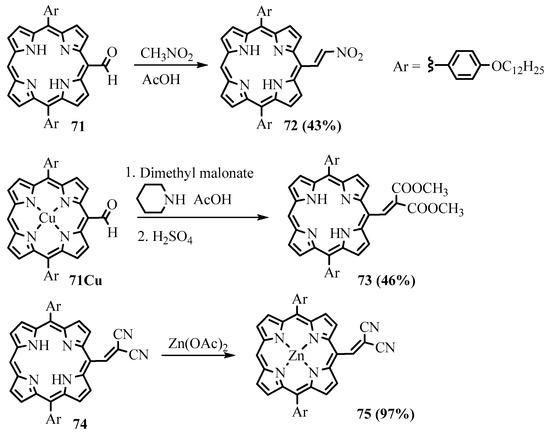
The Knoevenagel reaction allows for the transformation of formylporphyrins into the corresponding acrylic acid derivatives. The CH acid nucleophiles were introduced into the reaction with meso-formylporphyrins, leading to the formation of substituted meso-ethenyl porphyrin derivatives. Meso-formyl-diarylporphyrin 71 reacted with nitromethane, dimethylmalonate, and malononitrile in a mixture of piperidine, acetic acid, and toluene, leading to the corresponding substituted meso-(2-nitroethylene) 72 and meso-methylenemalonate 73 derivatives (Scheme 28) [58]. The meso-cyanoacrylate derivative 74 of Zn(II) meso-formyl-triarylporphyrin was obtained by heating in a mixture of piperidine and methanol for 16 h [59]. The product 75 of the reaction of meso-formyldiarylporphyrin with malononitrile containing a meso-dicyanovinyl group was shown to act as a fluorescence ‘‘turn-on’’ cyanide probe [60]. The meso-nitroethylene derivative 72 was utilized as fluorescence turn-on probes for biothiols as it exhibited fast fluorescence enhancement and high selectivity towards thiols based on the Michael addition mechanism [58]. It was also successfully applied to fluorescent cell imaging in the NIR wavelength range.

Scheme 28. The reaction of meso-formyldiarylporphyrin with CH acids.
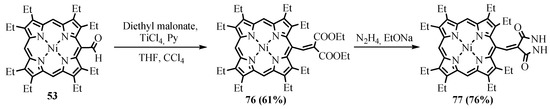
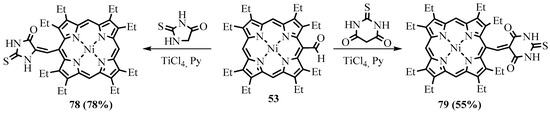
NiOEP-CHO 53 was much less reactive in the Knoevenagel reaction compared to β-unsubstituted porphyrins due to the sterical hindrances and was gradually degraded under basic reaction conditions. In order to activate the formyl group against the attack of CH acid nucleophiles, Lewis acid TiCl4 was used in pyridine. The Lewis acid promoted the Knoevenagel reaction of the NiOEP-CHO 53 with malonic ester and heterocyclic CH acids [61]. The heterocyclic derivatives of porphyrins 77–79 linked with an exocyclic C=C double bond were obtained both by cyclization of the Knoevenagel product 76 from the reaction with malonic ester (Scheme 29) and by the Knoevenagel condensation of formylporphyrin with thiohydantoin and thiobarbituric acid (Scheme 30) [62].

Scheme 29. Synthesis of the conjugate of NiOEP with pyrazolidine-3,5-dione.

Scheme 30. Synthesis of the conjugate of Ni(II) OEP with thiohydantoin and thiobarbituric acid.
The UV-Vis spectra of the heterocyclic conjugates contain new bands that arose from the interaction of the conjugated chromophores as well as bathochromically shifted original absorption bands. Particularly dramatic changes were observed in the UV-Vis spectrum of the porphyrin conjugate with thiobarbituric acid, which exhibited substantial absorption enhancement in the visible spectral range due to the considerable π-electron conjugation between tetrapyrrole and heterocyclic chromophores.
To sum up, meso-functionalization of porphyrins with the formyl group provides a powerful tool for the development of diverse porphyrin derivatives possessing valuable properties. In particular, promising photosensitizers with strong, red-shifted absorption bands, including NIR bands, were obtained from the meso-formyl porphyrins via the formation of annulated cycles such as benzochlorins and dibenzobacteriochlorins. Meso-imino derivatives were applied as sensor dyes in the multi-modal, multi-analyte optochemical sensing platform for cell diagnostics. Easily formed with the help of the formyl group, porphyrin conjugates with heterocycles can be used as biologically active compounds and in sensing applications. Imino- and azino-bridges represent two alternatives for bonding porphyrins into dyads, utilizing various pathways for energy transfer between the chromophores. Currently, the post-derivatization of the meso-formylporphyrins is under intense development.
References
- Hong, S.-K.; Jeoung, E.; Lee, C.-H. Meso-meso linked hybrid porphyrin arrays from meso-formylated porphyrins. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 2005, 9, 285–289.
- Balakumar, A.; Muthukumaran, K.; Lindsey, J.S. A New Route to meso-Formyl Porphyrins. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 5112–5115.
- Senge, M.O.; Hatscher, S.S.; Wiehe, A.; Dahms, K.; Kelling, A. The Dithianyl Group as a Synthon in Porphyrin Chemistry: Condensation Reactions and Preparation of Formylporphyrins under Basic Conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 13634–13635.
- Seebach, D.; Corey, E.J. Generation and synthetic applications of 2-lithio-1,3-dithianes. J. Org. Chem. 1975, 40, 231–237.
- Takanami, T.; Wakita, A.; Sawaizumi, A.; Iso, K.; Onodera, H.; Suda, K. One-Pot Synthesis of meso-Formylporphyrins by SNAr Reaction of 5,15-Disubstituted Porphyrins with (2-Pyridyldimethylsilyl)methyllithium. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 685–687.
- Takanami, T.; Wakita, A.; Matsumoto, J.; Sekine, S.; Suda, K. An efficient one-pot procedure for asymmetric bifunctionalization of 5,15-disubstituted porphyrins: A simple preparation of mesoacyl-, alkoxycarbonyl-, and carbamoyl-substituted meso-formylporphyrins. Chem. Commun. 2009, 101–103.
- Takanami, T.; Matsumoto, J.; Kumagai, Y.; Sawaizumi, A.; Suda, K. A facile one-pot preparation of meso-hydroxymethylporphyrins via a sequential SNAr reaction with (2-pyridyldimethylsilyl)methyllithium followed by hydrolysis and aerobic oxidation. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 68–70.
- Takanami, T.; Hayashi, S.; Iso, K.; Matsumoto, J.; Hino, F. An efficient one-pot protocol for asymmetric bifunctionalization of 5,15-disubstituted porphyrins: Direct access to meso activated alkenyl-substituted meso-formylporphyrins. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 5345–5348.
- Fujimoto, K.; Yorimitsu, H.; Osuka, A. Efficient Synthesis and Versatile Reactivity of Porphyrinyl Grignard Reagents. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 2014, 4327–4334.
- Inhoffen, H.H.; Fuhrhop, J.-H.; Voigt, H.; Brockmann, H., Jr. Zur weiteren Kenntnis des Chlorophylls und des Hämins, VI. Formylierung der meso-Kohlenstoffatome von Alkyl-substituierten Porphyrinen. Justus Liebigs Ann. Der Chem. 1966, 695, 133–143.
- Johnson, A.W.; Oldfield, D. meso-Substitution products of ætioporphyrin I. J. Chem. Soc. C Org. 1966, 794–798.
- Ponomarev, G.V. Formylporphyrins and their derivatives in the chemistry of porphyrins (review). Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 1994, 30, 1444–1465.
- Ponomarev, G.V.; Rozynov, B.V. Synthesis of copper and iron complexes of meso-substituted etioporphyrin derivatives. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 1973, 9, 1065–1068.
- Ponomarev, G.V. Synthesis and properties of Schiff bases of mesoformylporphyrins (Review). Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 1996, 32, 1263–1280.
- Volov, A.N.; Zamilatskov, I.A.; Mikhel, I.S.; Erzina, D.R.; Ponomarev, G.V.; Koifman, O.I.; Tsivadze, A.Y. Synthesis of the First Azomethine Derivatives of Pd-II Coproporphyrins I and II. Macroheterocycles 2014, 7, 256–261.
- Tyurin, V.S.; Erzina, D.R.; Zamilatskov, I.A.; Chernyadyev, A.Y.; Ponomarev, G.V.; Yashunskiy, D.V.; Maksimova, A.V.; Krasnovskiy, A.A.; Tsivadze, A.Y. Palladium Complexes of Azomethine Derivatives of Porphyrins as Potential Photosensitizers. Macroheterocycles 2015, 8, 376–383.
- Erzina, D.R.; Zamilatskov, I.A.; Stanetskaya, N.M.; Tyurin, V.S.; Kozhemyakin, G.L.; Ponomarev, G.V.; Chernyshev, V.V.; Fitch, A.N. Transformations of meso-Iminofunctionalized Pd(II) and Ni(II)-Complexes of β-Alkylsubstituted Porphyrins. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 2019, 1508–1522.
- Papkovsky, D.B.; Ponomarev, G.V.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Protonation of porphyrins in liquid PVC membranes: Effects of anionic additives and application to pH-sensing. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 1997, 104, 151–158.
- Borchert, N.B.; Ponomarev, G.V.; Kerry, J.P.; Papkovsky, D.B. O2/pH Multisensor Based on One Phosphorescent Dye. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 18–22.
- Zhdanov, A.V.; Li, L.; Yang, P.; Shkirdova, A.O.; Tang, S.; Yashunsky, D.V.; Ponomarev, G.V.; Zamilatskov, I.A.; Papkovsky, D.B. Advanced multi-modal, multi-analyte optochemical sensing platform for cell analysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 355, 131116.
- Harper, S.R.; Pfrunder, M.C.; Esdaile, L.J.; Jensen, P.; McMurtrie, J.C.; Arnold, D.P. Synthetic, Structural, and Spectroscopic Studies of Bis(porphyrinzinc) Complexes Linked by Two-Atom Conjugating Bridges. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 2015, 2807–2825.
- Dahlstedt, E.; Collins, H.A.; Balaz, M.; Kuimova, M.K.; Khurana, M.; Wilson, B.C.; Phillips, D.; Anderson, H.L. One- and two-photon activated phototoxicity of conjugated porphyrin dimers with high two-photon absorption cross sections. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 897–904.
- Yashunsky, D.V.; Morozova, Y.V.; Ponomarev, G.V. Chemistry ofmeso-formly-porphyrin oximes. An elegant synthesis ofmeso-cyanoporphyrins. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2000, 36, 485–486.
- Yashunsky, D.V.; Morozova, Y.V.; Ponomarev, G.V. Chemistry ofmeso-formylporphyrin oximes. The synthesis of the hetero analog of australochlorin. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2000, 36, 487–488.
- Yashunsky, D.V.; Morozova, Y.V.; Ponomarev, G.V. Chemistry of Metal Complexes of Oximes of meso-Formylporphyrins. Oxidative Cyclization to Metal Complexes of Hydroxy-1,2-oxazinochlorins. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2001, 37, 380–381.
- Ponomarev, G.V.; Shul’ga, A.M. Porphyrins. 16. Thermolysis of schiff bases of meso-formylporphyrins—A convenient method for the synthesis of porphyrins with a cyclopentane ring. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 1984, 20, 383–388.
- Ponomarev, G.V.; Shul’ga, A.M. Porphyrins. 22. Synthesis of porphyrins with two cyclopentane rings. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 1987, 23, 757–762.
- Ponomarev, G.V.; Shul’ga, A.M.; Rozynov, B.V. Porphyrin. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 1993, 29, 155–162.
- Shkirdova, A.O.; Zamilatskov, I.A.; Stanetskaya, N.M.; Tafeenko, V.A.; Tyurin, V.S.; Chernyshev, V.V.; Ponomarev, G.V.; Tsivadze, A.Y. Synthesis and Study of New N-Substituted Hydrazones of Ni(II) Complexes of beta-Octaethylporphyrin and Coproporphyrin I Tetraethyl Ester. Macroheterocycles 2017, 10, 480–486.
- Kozhemyakin, G.L.; Tyurin, V.S.; Shkirdova, A.O.; Belyaev, E.S.; Kirinova, E.S.; Ponomarev, G.V.; Chistov, A.A.; Aralov, A.V.; Tafeenko, V.A.; Zamilatskov, I.A. Carbene functionalization of porphyrinoids through tosylhydrazones. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 9199–9210.
- Belyaev, E.S.; Shkirdova, A.O.; Kozhemyakin, G.L.; Tyurin, V.S.; Emets, V.V.; Grinberg, V.A.; Cheshkov, D.A.; Ponomarev, G.V.; Tafeenko, V.A.; Radchenko, A.S.; et al. Azines of porphyrinoids. Does azine provide conjugation between chromophores? Dye Pigment. 2021, 191, 109354.
- Andreeva, V.D.; Ponomarev, G.V.; Shkirdova, A.O.; Tyurin, V.S.; Zamilatskova, I.A. Modification of β-Octaethylporphyrin via Insertion of Amino and Azino Groups into meso-Positions. Macroheterocycles 2021, 14, 201–207.
- Tkachenko, N.V.; Lemmetyinen, H.; Sonoda, J.; Ohkubo, K.; Sato, T.; Imahori, H.; Fukuzumi, S. Ultrafast Photodynamics of Exciplex Formation and Photoinduced Electron Transfer in Porphyrin−Fullerene Dyads Linked at Close Proximity. J. Phys. Chem. A 2003, 107, 8834–8844.
- Birin, K.P.; Gorbunova, Y.G.; Tsivadze, A.Y. New approach for post-functionalization of meso-formylporphyrins. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 67242–67246.
- Jiang, J.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, F.; Yang, K.; Wang, K. Synthesis, DNA binding mode, singlet oxygen photogeneration and DNA photocleavage activity of ruthenium compounds with porphyrin-imidazophenanthroline conjugated ligand. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4468.
- Smith, M.J.; Blake, I.M.; Clegg, W.; Anderson, H.L. Push–pull quinoidal porphyrins. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 3648–3654.
- Chen, C.; Zhu, Y.-Z.; Fan, Q.-J.; Song, H.-B.; Zheng, J.-Y. Syntheses, Crystal Structure, and Spectroscopic Properties of Meso–Meso-Linked Porphyrin–Corrole Hybrids. Chem. Lett. 2013, 42, 936–938.
- Murugavel, M.; Reddy, R.V.R.; Sankar, J. A new meso–meso directly-linked corrole–porphyrin–corrole hybrid: Synthesis and photophysical properties. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 13669–13672.
- Higashino, T.; Imahori, H. Development of Efficient Sensitizers Based on Porphyrin Dimers and Fused Porphyrins for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. ECS Meet. Abstr. 2021, MA2021-01, 769.
- Runge, S.; Senge, M.O. Reaction of β-formylporphyrins with organometallic reagents—A facile method for the preparation of porphyrins with exocyclic double bonds. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 10375–10390.
- Ponomarev, G.V.; Sidorov, A.N. Porphyrins. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 1977, 13, 742–747.
- Jiang, X.; Nurco, D.J.; Smith, K.M. Direct meso-alkylation of meso-formylporphyrins using Grignard reagents. Chem. Commun. 1996, 1759–1760.
- Arnold, D.P.; Johnson, A.W.; Mahendran, M. Some reactions of meso-formyloctaethylporhyrin. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1978, 366–370.
- Dahms, K.; Senge, M.O.; Bakri Bakar, M. Exploration of meso-substituted formyl porphyrins and their Grignard and Wittig reactions. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 2007, 3833–3848.
- Locos, O.B.; Arnold, D.P. The Heck reaction for porphyrin functionalisation: Synthesis of meso-alkenyl monoporphyrins and palladium-catalysed formation of unprecedented meso–β ethene-linked diporphyrins. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 004, 902–916.
- van der Haas, R.N.S.; de Jong, R.L.P.; Noushazar, M.; Erkelens, K.; Smijs, T.G.M.; Liu, Y.; Gast, P.; Schuitmaker, H.J.; Lugtenburg, J. The Synthesis of the Dimethyl Ester of Quino-Annulated 7-Demethyl-8-deethylmesoporphyrin and Three of Its Isomers with Unprecedented peri-Condensed Quinoline Porphyrin Structures. Molecules with Outstanding Properties as Sensitizers for Photodynamic Therapy in the Far-Red Region of the Visible Spectrum. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 2004, 4024–4038.
- Kessel, D.; Morgan, A. Photosensitization with Etiobenzochlorins and Octaethylbenzochlorins. Photochem. Photobiol. 1993, 58, 521–526.
- Morgan, A.R.; Rampersaud, A.; Garbo, G.M.; Keck, R.W.; Selman, S.H. New sensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Controlled synthesis of purpurins and their effect on normal tissue. J. Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 904–908.
- Li, G.; Graham, A.; Potter, W.; Grossman, Z.D.; Oseroff, A.; Dougherty, T.J.; Pandey, R.K. A Simple and Efficient Approach for the Synthesis of Fluorinated and Nonfluorinated Octaethylporphyrin-Based Benzochlorins with Variable Lipophilicity, Their in Vivo Tumor Uptake, and the Preliminary in Vitro Photosensitizing Efficacy. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 1316–1325.
- Meunier, I.; Pandey, R.K.; Senge, M.O.; Dougherty, T.J.; Smith, K.M. Benzoporphyrin derivatives: Synthesis, structure and preliminary biological activity. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1994, 961–969.
- Li, G.; Pandey, S.K.; Graham, A.; Dobhal, M.P.; Mehta, R.; Chen, Y.; Gryshuk, A.; Rittenhouse-Olson, K.; Oseroff, A.; Pandey, R.K. Functionalization of OEP-Based Benzochlorins To Develop Carbohydrate-Conjugated Photosensitizers. Attempt To Target β-Galactoside-Recognized Proteins. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 158–172.
- Kohli, D.H.; Morgan, A.R. Preparation of substituted chlorins and benzochlorins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1995, 5, 2175–2178.
- Arnold, D.P.; Nitschinsk, L.J. Porphyrin Dimers Linked by Conjugated Butadiynes. Tetrahedron 1992, 48, 8781–8792.
- Arnold, D.P.; Hartnell, R.D. Butadiyne-linked bis(chlorin) and chlorin–porphyrin dyads and an improved synthesis of bisbutadiyne using the Takai iodoalkenation. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 1335–1345.
- Smith, K.M. The McMurry Reaction in Porphyrinoid Chemistry. In Synthesis and Modifications of Porphyrinoids; Paolesse, R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 1–34.
- Vicente, M.G.H.; Smith, K.M. Vilsmeier reactions of porphyrins and chlorins with 3-(dimethylamino)acrolein to give meso-(2-formylvinyl)porphyrins: New syntheses of benzochlorins, benzoisobacteriochlorins, and benzobacteriochlorins and reductive coupling of porphyrins and chlorins using low-valent titanium complexes. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 4407–4418.
- Rong, J.; Wu, Y.; Ji, X.; Zhao, T.; Yin, B.; Rao, Y.; Zhou, M.; Osuka, A.; Xu, L.; Song, J. Porphyrinatonickel(II)–Cyclopentene and Porphyrinatonickel(II)–Cyclopentadiene Hybrids: Zirconacyclopentadiene-Mediated Syntheses, Structures, and Mechanistic Study. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 6128–6132.
- Wang, Q.; Ma, F.; Tang, W.; Zhao, S.; Li, C.; Xie, Y. A novel nitroethylene-based porphyrin as a NIR fluorescence turn-on probe for biothiols based on the Michael addition reaction. Dye Pigm. 2018, 148, 437–443.
- Muthiah, C.; Taniguchi, M.; Kim, H.-J.; Schmidt, I.; Kee, H.L.; Holten, D.; Bocian, D.F.; Lindsey, J.S. Synthesis and Photophysical Characterization of Porphyrin, Chlorin and Bacteriochlorin Molecules Bearing Tethers for Surface Attachment. Photochem. Photobiol. 2007, 83, 1513–1528.
- Chen, B.; Ding, Y.; Li, X.; Zhu, W.; Hill, J.P.; Ariga, K.; Xie, Y. Steric hindrance-enforced distortion as a general strategy for the design of fluorescence “turn-on” cyanide probes. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 10136–10138.
- Fuhrhop, J.-H.; Witte, L.; Sheldrick, W.S. Darstellung, Struktur und Reaktivität hochsubtituierter Porphyrine. Justus Liebigs Ann. Der Chem. 1976, 1976, 1537–1559.
- Shkirdova, A.O.; Orlova, E.A.; Ponomarev, G.V.; Tyurin, V.S.; Zamilatskov, I.A.; Buryak, A.K. Synthesis of β-Octaethylporphyrin Conjugates with Nitrogen and Sulfur Containing Heterocycles. Macroheterocycles 2021, 14, 208–212.
More
Information
Subjects:
Chemistry, Organic
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
1.1K
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
23 Aug 2023
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




