Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Juan Rong | -- | 4090 | 2023-08-16 10:19:11 | | | |
| 2 | Alfred Zheng | Meta information modification | 4090 | 2023-08-16 10:29:36 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Rong, J.; Fu, F.; Han, C.; Wu, Y.; Xia, Q.; Du, D. The Pharmacological of Tectorigenin. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/48117 (accessed on 08 February 2026).
Rong J, Fu F, Han C, Wu Y, Xia Q, Du D. The Pharmacological of Tectorigenin. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/48117. Accessed February 08, 2026.
Rong, Juan, Fei Fu, Chenxia Han, Yaling Wu, Qing Xia, Dan Du. "The Pharmacological of Tectorigenin" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/48117 (accessed February 08, 2026).
Rong, J., Fu, F., Han, C., Wu, Y., Xia, Q., & Du, D. (2023, August 16). The Pharmacological of Tectorigenin. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/48117
Rong, Juan, et al. "The Pharmacological of Tectorigenin." Encyclopedia. Web. 16 August, 2023.
Copy Citation
Tectorigenin is a well-known natural flavonoid aglycone and an active component that exists in numerous plants. Growing evidence suggests that tectorigenin has multiple pharmacological effects, such as anticancer, antidiabetic, hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, antimicrobial, cardioprotective, and neuroprotective. These pharmacological properties provide the basis for the treatment of many kinds of illnesses, including several types of cancer, diabetes, hepatic fibrosis, osteoarthritis, Alzheimer’s disease, etc.
tectorigenin
pharmacology
1. Introduction
It is well known that natural products or botanicals are valuable resources in the treatment of dozens of diseases. Up until now, natural products remain an important basis for the development of emerging therapeutic agents [1]. Newman and Cragg (2020) showed that between 1981 and 2019, natural products, natural product derivatives, and botanical drugs accounted for 33.5% of all newly approved drugs [2]. Flavonoids are secondary metabolites of plants that function as signaling molecules, antioxidants, and detoxifying agents, and protect plants against various biotic and abiotic threats [3]. Flavonoids belong to polyphenol groups, and have been found to exert anti-inflammatory [4], antioxidative [5], antibacterial [6], antidiabetic [7], neuroprotective [8], anticancer, and other activities [9][10][11][12]. Therefore, they have the potential to be used in several fields, including medicine [13], nutraceuticals as dietary supplements [14], as well as the food and cosmetic industries as biopreservatives for their antibacterial activity together with antioxidant potential [15][16].
Tectorigenin is an isoflavone that exists in numerous plant resources, and it is especially abundant in Belamcandae Rhizoma and Puerariae flos [17][18], which both have the effects of clearing away heat, removing toxic substances, relieving sore throat, and reducing swelling [19][20]. As one of the most important active ingredients, the pharmacological effects of tectorigenin have been demonstrated by an increasing number of investigators [21][22][23][24]. Due to its extensive pharmacological activities, including anticancer, antioxidation, hepatoprotection, anti-inflammation, etc., tectorigenin has received a large amount of attention [21][22][23][24].
2. Pharmacological Insights of Tectorigenin
As a ubiquitous plant isoflavone, tectorigenin has been widely reported to be effective in many areas, such as anticancer, anti-diabetes, hepatoprotection, anti-inflammation, antioxidation, antimicrobial, etc. (Figure 1) It seems to exert its pharmacological effects via modulating the signaling pathways, including PPARγ/NF-κB, PI3K/AKT, TLR4/NF-κB, IKKβ/NF-κB/JNK, ERK/JNK, MAPK/JNK/AP-1, AKT/MAPK, and TGF-β1/Smad.
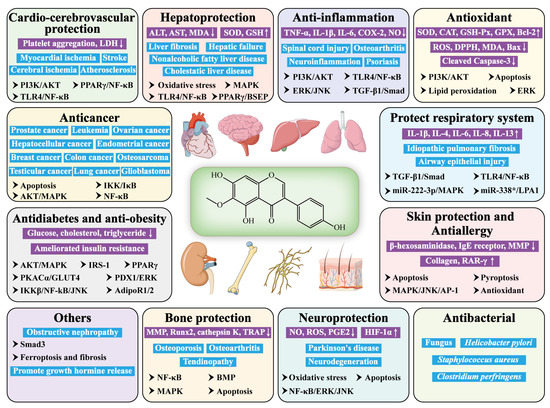
Figure 1. Pharmacological activity and relative mechanism of tectorigenin. (“↑” means up-regulation; “↓” means down-regulation).
2.1. Anticancer Effects
2.1.1. Prostatic Cancer
Several epidemiological studies support the role of phytoestrogens, nonsteroidal plant-derived compounds with estrogenic activity, in reducing cancer risk [25]. In the prostate, phytoestrogens could bind to estrogen receptor β (ERβ), which might be closely related to the prevention of prostate cancer progression [25][26]. Isoflavones were reported to exhibit estrogenic effects [27][28][29]. A study revealed that tectorigenin, as a phytoestrogen, could reverse the abnormal expression of some key factors that lead to prostate cancer malignancy [30]. Actually, tectorigenin has been proven to be a selective estrogen-receptor modulator that could bind to estrogen receptors ERα and Erβ, with a higher affinity for Erβ, and prevent the proliferation of some hormone-dependent prostate cancer cells [30][31]. Morrissey et al. (2004) [32] reported the positive effects of tectorigenin alone or combined with bicalutamide on a range of prostate epithelial cells in vitro, showing that tectorigenin caused cell cycle G1 arrest. In another study, tectorigenin extracted from the flowers of Puerariae thomsonii was found to possess the highest anti-proliferation activity against prostate cancer cells (IC50 = 0.08 μM) [33]. Stettner et al. [26] also reported that tectorigenin treatment with LNCaP prostate cancer cells up-regulated ERβ, resulting in antiproliferative effects.
2.1.2. Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is a major life-threatening malignancy that affects women all around the world [34]. MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, and T-47D are three commonly used breast cancer cells as models for breast tumors [35]. Zeng et al. (2018) [36] found that tectorigenin suppressed MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cell proliferation both in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The mechanisms of tectorigenin on human breast cancer cell apoptosis and metastasis might owe to the downregulation of protein kinase B (AKT)/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling and upregulation of the expression of the caspase family. However, two earlier reports showed an opposite phenomenon: tectorigenin could stimulate the growth of MCF-7 and T-47D [37][38]. One explanation for this discrepancy is the difference in the number of cells and the concentration of tectorigenin [36]. Therefore, future studies in more diverse cell lines and animals are needed to confirm the protective effect against breast cancer of this molecule as well as its underlying mechanisms.
2.1.3. Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is another common gynecologic malignancy with a high mortality rate [39][40]. New therapeutic agents for ovarian cancer are urgently needed. It was reported that many plant-derived drugs and their derivatives induce apoptosis in ovarian cancer cell lines [41]. In paclitaxel-resistant ovarian cancer cells, tectorigenin heightened the growth-inhibitory activity of paclitaxel through downregulating the AKT/IκB kinase (IKK)/inhibitor of NF-κB (IκB)/noncanonical nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway [42]. To be specific, tectorigenin combined with paclitaxel inhibited the NF-κB nuclear translocation and phosphorylation of IκB and IKK by activating caspases-3/8/9 and AKT, and downregulated the expression of NF-κB-dependent genes, thereby promoting synergistic apoptosis [42]. Another study investigated the anti-ovarian cancer effect of the methanol extract of Puerariae Flos and found that the extract presented a good anti-proliferation effect against the human ovarian cancer cell line A2780. Among the active compounds, the IC50 of tectorigenin against A2780 cells was 48.67 ± 0.31 μM [43].
2.1.4. Lung Cancer
There are also several studies on the effect of tectorigenin on lung cancer. The ethyl acetate extract of Chinese water chestnut peel, which contains tectorigenin at levels of 12.41 mg/g, showed good inhibitory activities on human alveolar adenocarcinoma cell line A549 (IC50 = 776.12 μg/mL) [44]. Tectorigenin (30 mg/kg) isolated from Belamcandae Rhizoma was administered subcutaneously to mice transplanted with Lewis lung carcinoma, and the inhibition ratio on tumor volume reached 30.8% [45]. In general, tumors try to escape from the host immune system and contrive to benefit from infiltrating immune cells by altering immune cell function, thereby creating a pro-inflammatory microenvironment that is conducive to tumor progression and metastasis [46]. It was reported by Amin et al. [46] that tectorigenin could restrain the pro-inflammatory response of monocytes induced by lung cancer cells, repressing the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, TNF-α and IL-6. Nevertheless, the mechanism needs to be further elucidated.
2.1.5. Other Cancer
It has been shown by Jiang et al. [47] that tectorigenin could reduce the vitality of HepG2 (a human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line) in a time- and concentration-dependent manner via a mitochondrial-mediated pathway to induce apoptosis. Moreover, tectorigenin restrained the proliferation of Saos2 and U2OS, which are two osteosarcoma cell lines, and it dramatically inhibited the migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells [21]. A similar study showed that tectorigenin inhibited tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) via NF-κB inhibition, thereby decreasing CXCL10 overproduction to hinder the invasion of Caco-2, which is a human colon cancer cell line [48]. In another experiment, tectorigenin could not only induce human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells differentiation into granulocytes and monocytes/macrophages but also cause intracellular apoptotic variations of DNA [49]. A point of view was put forward that the 5-hydroxyl group of tectorigenin was valuable for its cytotoxic activities, which may be instructive to us [49]. Moreover, tectorigenin lowered the expression of the stem cell factors POU5F1 and NANOG, and inhibited the proliferation of malignant testicular germ cell tumor (TGCT) cells [50]. A genomic hybridization microarrays analysis displayed that over 20% of the microarray genes, including telomeres, microdeletions, oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, were aberrated in endometrial cancer cells treated with tectorigenin [51].
2.2. Antidiabetic and Anti-Obesity Effects
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia that has become a global epidemic [52]. Tectorigenin was reported to effectively decrease the serum glucose level of rats in streptozotocin-induced or high-fat and high-sucrose diet models [53][54][55][56], and it was reported as a potential antidiabetic agent exhibiting potent inhibitory activity on aldose reductase in rat lenses [57][58]. In vitro, tectorigenin inhibited glucotoxicity- and lipotoxicity-induced oxidative stress, apoptosis, and endoplasmic reticulum stress in islet cells. The mechanism was that tectorigenin regulated the expression of pancreas/duodenum homeobox protein 1 (PDX1) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) [56]. Endothelial dysfunction is frequently seen in diabetic patients [59][60]. Tectorigenin was demonstrated to alleviate diabetic nephropathy, which was attributed to its protective effect on injured endothelial cells by inhibiting inflammation and lipotoxicity, and by restoring insulin sensitivity [61]. Mechanistically, the pharmacological properties of tectorigenin were related to the adiponectin receptor 1/2 (AdipoR1/2)-mediated activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) pathways [61]. Similarly, tectorigenin exerted positive regulation of insulin action in palmitate-injured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) via modulating reactive oxygen species (ROS)-related inflammation and insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) signaling [62]. Glucose transporter protein 4 (GLUT4) is the major glucose transporter, whose decrease is one of the important molecular bases of insulin resistance [63]. Recently, it was proven that tectorigenin targeted protein kinase A catalytic subunit α (PKACα) to promote the PKA/AMPK/myocyte enhancer factor 2 (MEF2) pathway, subsequently enhancing GLUT4 expression, and thus slowing and stopping insulin resistance progression for the intervention and treatment of glucose metabolism syndrome [64].
Diabetes is closely linked to the epidemic of obesity [65]. The anti-obesity effects of tectorigenin were also investigated, as evidenced by the decreased body weight, triglycerides, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in several animal models [53][54][56]. According to the findings of Li et al. [66], tectorigenin restrained 3T3-L1 adipogenesis and reversed TNF-α-induced changes of IL-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), and adiponectin. Further investigation identified tectorigenin as a functional peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors γ (PPARγ) partial agonist (IC50 = 13.3 mM) and suggested that tectorigenin may ameliorate hyperglycemia through the inhibition of preadipocyte differentiation and adipocytokine secretion [66]. The studies presented above highlight the potential therapeutic value of tectorigenin in diabetes and obesity.
2.3. Hepatoprotective Effects
The liver plays a pivotal role in bile synthesis, metabolic function, and the degradation of toxins in the body [67]. Several factors, including oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, and proinflammatory mediators (chemokines and cytokines), are involved in hepatic diseases [68]. Tectorigenin is a potential hepatoprotective agent that has been evaluated by many researchers. It has been demonstrated that tectorigenin exerted protective functions against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and tert-butyl hyperoxide-induced liver damage [69][70][71][72]. Tectorigenin significantly inhibited the activities of aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and the protective activity of tectorigenin was higher than that of dimethyl diphenyl bicarboxylate and silybin [70][72]. Several studies showed a regulation in the activities of antioxidative enzymes, lipid peroxides, and cytokines in the tectorigenin-treated group, as evidenced by the superoxide dismutase (SOD), ROS, malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH), TNF-α, interleukin (IL)-1β levels, etc., which demonstrated that the hepatoprotective mechanisms of tectorigenin might be related to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions [69][71][73]. Liver damage can lead to hepatic fibrosis, cirrhosis, liver failure, and even liver cancer [74]. It has been revealed that tectorigenin exhibited anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic activities on hepatic stellate cells and human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells, and might possess anti-fibrotic and anti-hepatoma potential [47][75]. An in vivo study suggested that tectorigenin significantly prevented fat accumulation, promoted bile acid circulation, and exerted beneficial effects on mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through anti-inflammation and improvement of gut microbial dysbiosis [76]. Another study specifically reported the effects of tectorigenin on cholestatic liver disease, and the results proved that tectorigenin alleviated intrahepatic cholestasis via the activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) and subsequent NF-κB inhibition and bile salt export pump (BSEP) activation [23]. Additionally, tectorigenin mitigated experimental fulminant hepatic failure via modulating the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/MAPK and TLR4/NF-κB pathways and autophagy [73].
2.4. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Several flavonoids, including tectorigenin, have been reported to inhibit nitric oxide (NO) production, one of the inflammatory mediators [77]. Tectorigenin was also found in multiple studies to inhibit the induction of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in a dose-dependent manner to restrain the production of prostaglandin E2 in inflammatory cells. This may be one of the mechanisms of action by which Belamcandae Rhizoma exert an anti-inflammatory effect [78][79][80][81]. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), an endotoxin, could upregulate inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1/6/12, TNF-α, p-MAPK, and p-NF-κB. Those changes above were attenuated by tectorigenin in PC12 cells with spinal cord injury [82], LPS-stimulated BV-2 Microglia [81], and mice with acute lung injury [83]. In the A549: THP-1 co-culture model, A549 cells activated and induced THP-1 cells to secrete IL-6, TNF-α, and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Co-incubation of tectorigenin with A549 cells prevented this induction behavior [46]. An in vivo model of acute inflammation study showed that tectorigenin (60 mg/kg) significantly alleviated carrageenan-induced edema in an inflammatory rat model [84]. Wang et al. [24] (2020) also investigated the anti-inflammatory ability of tectorigenin and explored the underlying mechanism in treating the allergic asthma model of guinea pigs. In that study, tectorigenin (25 mg/kg) efficiently reduced the frequency of cough, inflammatory cell numbers, and the content of pro-inflammatory factors. Further research found that tectorigenin might mitigate pulmonary fibrosis and airway inflammation through the TLR4/NF-κB and transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1)/Smad signaling pathways, which was consistent with the conclusion of another study that tectorigenin was suggested to play an anti-inflammatory role by antagonizing the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway [66]. Tectorigenin protected HaCaT keratinocytes against M5 cytokine-induced abnormal proliferation and inflammatory response via suppression of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway [85]. In addition, tectorigenin also protected against multiple organ damage by alleviating inflammation-related pathways or oxidative stress [73][83][86].
2.5. Antioxidant Effects
A loss of balance in biological systems between the production of ROS and antioxidant defense levels can induce oxidative stress, which may result in extensive intracellular damage [87][88]. The harmful effects brought by oxidative stress are mainly on account of the overproduction of oxidants or depleting antioxidant potential [89], which causes cellular damage through the oxidation of protein, lipids, and DNA [90][91]. Oxidative stress participates in the nosogenesis of many illnesses, including several cancers, Alzheimer’s disease, and atherosclerosis [91]. Flavonoids are reported as natural scavengers of free radicals, and this may be due to the relatively strong reduction capacity of their phenol groups, which could form resonance-stabilized anion radicals [92]. Both tectorigenin and tectoridin have been reported to show antioxidant ability in vivo and in vitro [53][69]. In an early study, the evaluation of the antioxidant ability of Belamcandae Rhizoma extract containing tectorigenin showed the results of reducing free-radical 1,1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and transition-metal ions and decreasing linoleic acid peroxidation [93]. Another antioxidant capacity assay of tectorigenin displayed that tectorigenin at 10 μg/mL exerted significant intracellular ROS scavenging activity (63.2 ± 2.3%) and DPPH radical scavenging activity (54.3 ± 2.3%), which was superior to tectoridin [94]. In addition, tectorigenin increased the activities and protein expression of the antioxidants, including catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and SOD, which might be related to the restraint of the overproduction of ROS and lipid peroxidation. Therefore, the antioxidant capacity of tectorigenin might originate from two aspects: direct scavenging of oxygen free radicals and an indirect effect on the induction of antioxidative enzymes. In vivo experiments also revealed the antioxidative potentiality of tectorigenin, which showed that tectorigenin restrained CCl4 and bromobenzene-induced malondialdehyde formation in the rats [69][95]. Tectorigenin sodium sulfonate, reported by Han et al. [96], maintained and elevated the antioxidant activity of tectorigenin through Fe3+/ferricyanide reduction, hydroxyl radical and superoxide anion radical scavenging, DPPH, and lipid peroxidation assays in vitro. Another study evaluated the effects of Belamcandae Rhizoma extract containing tectorigenin on collagen degradation and apoptosis in UV-B-induced HaCaT cells. The extract exhibited good free radical scavenging capability and cytoprotective effects, and mitigated cell apoptosis through diminishing caspase-3 levels and increasing the B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2)/Bcl-2 associated X (Bax) ratio [97]. Taken together, these findings suggest that tectorigenin has a certain antioxidant capacity.
2.6. Antimicrobial Effects
The increasing incidence of microorganisms’ drug resistance makes the search for new antimicrobial agents urgent. In this connection, medicinal plants are promising resources [98]. In 2001, two reports revealed the antimicrobial potential of tectorigenin. Its minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) against four species of dermatophytes of the genera Trichophyton ranged from 3.12–6.25 μg/mL [99], and also inhibited the growth of six Helicobacter pylori strains (MIC: 50–100 μg/mL) [100]. In another similar study, tectorigenin from the Belamcandae Rhizoma exerted antibacterial activity against S. aureus ATCC 33591, S. aureus ATCC 25923, which were strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and three clinical isolates of MRSA with MIC values of 125 μg/mL [17]. Further examination confirmed that the anti-MRSA effect of tectorigenin was achieved by suppressing the adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) and enhancing the permeability of the cytoplasmic membrane. In a cell experiment for in vitro treatment of Clostridium perfringens infection, the biofilm formation rates in the presence of 4, 8, 16, and 32 μg/mL tectorigenin were well below the control in a dose-dependent manner [101]. In addition, tectorigenin noteworthily suppressed the gliding movement, biofilm formation, and adhesion of Caco-2 cells by targeting type IV pilus (TFP) and suppressing TFP-associated genes, although it exhibited little antibacterial activity directly against Clostridium perfringens. However, more research is still needed to further verify the antibacterial activity of tectorigenin in cells and animals [101].
2.7. Bone-Protective Effects
Common skeletal diseases, such as osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, fractures, etc., greatly affect the quality of life of older adults [102]. The homeostasis of bone metabolism is critical for bone health [103]. Bone homeostasis is sustained by the balance between osteoblast-mediated bone formation and osteoclast-mediated bone resorption [104]. Many factors, including aging, postmenopausal estrogen deficiency, and prolonged immobilization, can lead to the disturbance of bone metabolism and result in bone-related diseases [105]. Some phytoestrogens, isoflavonoids, and plant-derived nonsteroidal compounds possessing estrogen-like activity could function as inhibitors of osteoporosis [106]. The healthy functional food containing tectorigenin effectively reduced bone resorption and promoted bone formation in ovariectomized-induced osteoporosis mice [107]. Ma et al. [108] investigated the therapeutic effects of tectorigenin on osteoporosis, and the results showed that tectorigenin reduced mRNA levels of osteoclast-specific genes, including nuclear factor of activated T cell cytoplasmic 1 (NFATc1), tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP), matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 and cathepsin K in RAW264.7 cells, and bone marrow mononuclear cells, and mitigated the bone loss in osteoporosis mice [108]. Another study also showed that tectorigenin regulated bone homeostasis by stimulating osteogenic differentiation and inhibiting osteoclast differentiation through bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) and MAPK pathways [86]. Tectorigenin is also attractive as an anti-osteoarthritis drug due to its anti-inflammatory activities. Tectorigenin observably suppressed the NF-κB P65 pathway and inhibited articular cartilage degeneration and chondrocyte apoptosis [109]. Tendinopathy, as a painful overuse musculoskeletal injury, is extremely common in athletes and middle-aged overweight patients [110]. As an inhibitor of MAPK and NF-κB pathways, tectorigenin has the capability to attenuate the inflammation, apoptosis, and ossification of tendon-derived stem cells in vitro and in vivo, thus effectively improving tendinopathy [111].
2.8. Anti-Skin-Damage and Antiallergic Effects
Ultraviolet radiation (UV) can induce skin photoaging and inflammation, and also lead to free radical and ROS accumulation, collagen loss and degradation, epidermal pigmentation, and abnormal cell death [112]. Several reports have uncovered the skin-protective effect potential of tectorigenin. Belamcandae Rhizoma extract containing tectorigenin exhibited good free radical scavenging and cytoprotective activities by increasing antioxidant enzyme expression and improving UV-B-induced collagen degradation and apoptosis [97]. Noh et al. [22] also reported that in human keratinocytes, tectorigenin (1 and 10 µM) exerted anti-skin-damage effects through mitigating UV-B-induced hyperoxidation, collagen degradation, and apoptosis. Recently, Dai et al. [113] designed a study to pick out a new retinoic acid γ receptor (RAR-γ)-selective agonist. Computational screening suggested that tectorigenin was a matching selective RAR-γ agonist. In this study, tectorigenin was validated to be able to inhibit UV-induced release of inflammatory factors, oxidative damage, and MMP production, and also to reverse collagen loss. Further research suggested that tectorigenin exerted its effects mainly via regulating the MAPK/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)/activating protein-1 (AP-1) pathway. Tretinoin can attenuate skin photoaging and inflammation, but its use is restricted because of the strong skin irritation and teratogenic effect [114]. Therefore, it is necessary to find a new agent with protective effects on the skin. These evidences above suggest that tectorigenin has the potential to be an effective strategy for the treatment of UV-induced skin damage. Moreover, Tamura et al. [115] disclosed tectorigenin and another compound from the extract of Puerariae Flos as inhibitors against the expression of immunoglobulin E (IgE) receptor, the key molecule triggering the allergic reactions, via diminishing the generation of γ-chain subunit. Another study demonstrated that tectorigenin effectively attenuated passive skin allergic reaction and restrained IgE-induced release of β-hexosaminidase from RBL-2H3 cells [116].
2.9. Cardioprotective and Cerebroprotective Effects
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, including angor pectoris, myocardial infarction, stroke, etc., are the leading causes of death globally [117]. Atherosclerosis is the main cause of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease development [118]. Blood vessels severely affected by atherosclerosis are prone to enhance platelet aggregation, resulting in vessel occlusion and ischemia [119]. Tectorigenin was an effective antiplatelet compound with a much better effect than acetylsalicylic acid [120]. Tectorigenin was also reported as a lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) inhibitor from several Chinese medicinal herbs by UF-HPLC-DAD-MS [121]. The protective mechanism of tectorigenin was related to oxidative stress and inflammation in which phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT, TLR4/NF-κB, PPARγ/NF-κB pathways were involved [122][123][124]. Chen et al. [122] revealed that tectorigenin effectively prevented HUVECs from H2O2-induced oxidative stress injury by upregulating the PI3K/AKT pathway. In addition, tectorigenin could alleviate cognitive impairment, hippocampal tissue and myelin damage, and inflammation of chronic cerebral ischemia mice [124]. In vitro, tectorigenin benefited HT-22 cell survival and protected against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) damage. However, overexpressing TLR4, or using PI3K/AKT inhibitor LY294002, PPARγ inhibitor GW9662, or NF-κB activator LPS reversed the protection of tectorigenin, suggesting that PI3K/AKT, TLR4, PPARγ, and NF-κB pathways were crucial in the cardioprotective and cerebroprotective effects of tectorigenin [123][124].
2.10. Protective Effects on the Respiratory System
Tectorigenin was regarded as an interventional strategy by inhibiting respiratory dysfunction and death in respiratory diseases. Several studies have illustrated the protective effect of tectorigenin in respiratory disorders, including asthma, airway epithelial injury, and pulmonary fibrosis [24][125][126]. Asthma is a common chronic disease characterized by variable respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation [127]. Tectorigenin significantly diminished the frequency of coughs, the number of inflammatory cells, and the levels of inflammation-related factors in the allergic asthma guinea pigs model [24]. For the clinical treatment of asthma, glucocorticoids are currently the first-line drugs, but can also cause airway epithelial injury [24]. It was demonstrated that tectorigenin regulated migration, invasion, and apoptosis of human airway epithelial cells in the treatment of glucocorticoids. Mechanistically, tectorigenin enhanced miR-222-3p expression and inhibited the MAPK pathway, thus protecting the airway epithelium [125]. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is also a chronic, progressive pulmonary disease characterized by the anomalous accumulation of fibrotic tissue in the lung’s parenchyma [128]. In vitro, tectorigenin prevented the proliferation of pulmonary fibroblasts in rats treated with bleomycin, indicating that tectorigenin has the potential to ameliorate pulmonary fibrosis. Further results revealed that its mechanism was related to the regulation of miR-338* (miR-338-5p) expression [126].
2.11. Neuroprotective Effects
In neurodegenerative diseases caused by multiple pathological procedures, neuroprotection is an interventional strategy to delay and even stop neuronal dysfunction and abnormal death [129]. Microglia are the primary immune cells in the central nervous system, and their activation is associated with neurodegeneration and alcoholic toxication [130]. Yuan et al. [131] found that isoflavonoids from Puerariae Flos, which included tectorigenin, had obvious inhibitory effects on the release of NO from microglia activated by LPS (IC50 values were 1.3–2.3 μM). From the structure-activity relationships of a number of isoflavonoids with inhibitory activity against microglial activation, the methoxyl group at the 6-position of tectorigenin enhanced the activity. Glioblastoma cell viability was dose-dependently decreased after 24 h exposure to tectorigenin, and 200 μM and 300 μM could block the cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase [132]. Another study also confirmed the anti-neuroinflammatory effects of tectorigenin in both LPS-treated BV-2 microglial and mouse models [81]. As a glycoprotein hormone, Erythropoietin (EPO) has neuroprotective function [133][134], but EPO circulating in the blood cannot cross the blood-brain barrier [135]. Tectorigenin was proved to promote the stacking of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α to induce EPO gene expression in rat cortical neurons and neuron-like NT2/D1 cells, raising endogenous cerebral EPO levels [136]. Monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) can produce ROS to directly damage neuronal cells, which is a possible target for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease [137]. Li et al. [137] isolated tectorigenin from Pueraria thomsonii, and the IC50 value of tectorigenin against MAO-B was 54.36 μg/mL. In addition, pretreatment with tectorigenin exhibited a protective effect against neuronal damage in PC12 cells. Gong et al. (2017) [138] investigated whether tectorigenin could prevent the neurotoxicity of SH-SY5Y cells and illuminated the potential protection mechanism. In that study, tectorigenin (0.1, 1 and 10 μM) exhibited neuroprotective effect against cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by MPP+ (1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium), which may be related to the reduction of oxidative stress and the enhancement of the antioxidant defense activity of tectorigenin [138].
2.12. Other Effects
Except for the pharmacological activities mentioned above, tectorigenin also has other biological activities. For instance, tectorigenin was verified as a therapeutic strategy for the treatment of obstructive nephropathy. In mice suffering unilateral ureteral obstruction, tectorigenin significantly decreased the levels of the kidney injury index, including creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, and kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), and alleviated pathological damage and renal interstitial fibrosis [139]. In vitro, tectorigenin treatment inhibited Smad3-mediated ferroptosis and fibrosis [139]. It was also revealed that tectorigenin could induce the release of growth hormone in rat pituitary cells [140].
References
- Sin, V.J.; Anand, G.S.; Koh, H.L. Botanical medicine and natural products used for erectile dysfunction. Sex. Med. Rev. 2021, 9, 568–592.
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803.
- Mutha, R.E.; Tatiya, A.U.; Surana, S.J. Flavonoids as natural phenolic compounds and their role in therapeutics: An overview. Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 7, 25.
- Maleki, S.J.; Crespo, J.F.; Cabanillas, B. Anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125124.
- Hernandez, I.; Alegre, L.; Van Breusegem, F.; Munne-Bosch, S. How relevant are flavonoids as antioxidants in plants? Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 125–132.
- Cushnie, T.P.; Lamb, A.J. Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2005, 26, 343–356.
- Proenca, C.; Ribeiro, D.; Freitas, M.; Carvalho, F.; Fernandes, E. A comprehensive review on the antidiabetic activity of flavonoids targeting PTP1B and DPP-4: A structure-activity relationship analysis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 4095–4151.
- Calderaro, A.; Patane, G.T.; Tellone, E.; Barreca, D.; Ficarra, S.; Misiti, F.; Lagana, G. The neuroprotective potentiality of flavonoids on Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14835.
- Sun, Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, H.; Sun, C. Flavonoids regulate tumor-associated macrophages—From structure-activity relationship to clinical potential (Review). Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 184, 106419.
- Williamson, G.; Kay, C.D.; Crozier, A. The bioavailability, transport, and bioactivity of dietary flavonoids: A review from a historical perspective. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1054–1112.
- Terahara, N. Flavonoids in foods: A review. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 521–528.
- Hodgson, J.M.; Croft, K.D. Tea flavonoids and cardiovascular health. Mol. Aspects Med. 2010, 31, 495–502.
- Kafi, M.K.; Bolvari, N.E.; Pour, S.M.; Moghadam, S.K.; Shafaei, N.; Karimi, E.; Oskoueian, E. Encapsulated phenolic compounds from Ferula gummosa leaf: A potential phytobiotic against Campylobacter jejuni infection. J. Food Process. Pres. 2022, 46, e16802.
- Poorbagher, M.R.M.; Karimi, E.; Oskoueian, E. Hepatoprotective effect of nanoniosome loaded Myristica fragrans phenolic compounds in mice-induced hepatotoxicity. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 5517–5527.
- Karimi, E.; Oskoueian, E.; Karimi, A.; Noura, R.; Ebrahimi, M. Borago officinalis L. flower: A comprehensive study on bioactive compounds and its health-promoting properties. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 826–838.
- Oskoueian, E.; Karimi, E.; Noura, R.; Ebrahimi, M.; Shafaei, N.; Karimi, E. Nanoliposomes encapsulation of enriched phenolic fraction from pistachio hulls and its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-melanogenic activities. J. Microencapsul. 2020, 37, 1–13.
- Joung, D.K.; Mun, S.H.; Lee, K.S.; Kang, O.H.; Choi, J.G.; Kim, S.B.; Gong, R.; Chong, M.S.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, D.S.; et al. The antibacterial assay of tectorigenin with detergents or ATPase inhibitors against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014, 2014, 716509.
- Han, J.; Xu, K.; Yan, Q.; Sui, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Han, F. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of Flos Puerariae by using chemical fingerprint in combination with chemometrics method. J. Pharm. Anal. 2022, 12, 489–499.
- Wozniak, D.; Matkowski, A. Belamcandae chinensis rhizome—A review of phytochemistry and bioactivity. Fitoterapia 2015, 107, 1–14.
- Chen, C.; Li, X.; Kano, Y.; Yuan, D.; Qu, J. Oriental traditional herbal Medicine--Puerariae Flos: A systematic review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 306, 116089.
- Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Cheng, Z.H.; Ou-Yang, H.N.; Luo, C.; Guo, Z.L. Tectorigenin inhibits osteosarcoma cell migration through downregulation of matrix metalloproteinases in vitro. Anticancer Drugs 2016, 27, 540–546.
- Noh, D.; Choi, J.G.; Huh, E.; Oh, M.S. Tectorigenin, a flavonoid-based compound of leopard lily rhizome, attenuates UV-B-induced apoptosis and collagen degradation by inhibiting oxidative stress in human keratinocytes. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1998.
- Xiang, J.; Yang, G.; Ma, C.; Wei, L.; Wu, H.; Zhang, W.; Tao, X.; Jiang, L.; Liang, Z.; Kang, L.; et al. Tectorigenin alleviates intrahepatic cholestasis by inhibiting hepatic inflammation and bile accumulation via activation of PPARγ. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 2443–2460.
- Wang, Y.; Jing, W.; Qu, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Qi, X.; Liu, L. Tectorigenin inhibits inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis in allergic asthma model of ovalbumin-sensitized guinea pigs. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 956–968.
- Strom, S.S.; Yamamura, Y.; Duphorne, C.M.; Spitz, M.R.; Babaian, R.J.; Pillow, P.C.; Hursting, S.D. Phytoestrogen intake and prostate cancer: A case-control study using a new database. Nutr. Cancer 1999, 33, 20–25.
- Stettner, M.; Kaulfuss, S.; Burfeind, P.; Schweyer, S.; Strauss, A.; Ringert, R.H.; Thelen, P. The relevance of estrogen receptor-beta expression to the antiproliferative effects observed with histone deacetylase inhibitors and phytoestrogens in prostate cancer treatment. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 2626–2633.
- Branca, F. Dietary phyto-oestrogens and bone health. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2003, 62, 877–887.
- Lehmann, L.; Esch, H.L.; Wagner, J.; Rohnstock, L.; Metzler, M. Estrogenic and genotoxic potential of equol and two hydroxylated metabolites of daidzein in cultured human ishikawa cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2005, 158, 72–86.
- Beck, V.; Rohr, U.; Jungbauer, A. Phytoestrogens derived from red clover: An alternative to estrogen replacement therapy? J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 94, 499–518.
- Thelen, P.; Scharf, J.G.; Burfeind, P.; Hemmerlein, B.; Wuttke, W.; Spengler, B.; Christoffel, V.; Ringert, R.H.; Seidlova-Wuttke, D. Tectorigenin and other phytochemicals extracted from leopard lily Belamcanda chinensis affect new and established targets for therapies in prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 1360–1367.
- Seidlova-Wuttke, D.; Hesse, O.; Jarry, H.; Rimoldi, G.; Thelen, P.; Christoffel, V.; Wuttke, W. Belamcanda chinensis and the thereof purified tectorigenin have selective estrogen receptor modulator activities. Phytomedicine 2004, 11, 392–403.
- Morrissey, C.; Bektic, J.; Spengler, B.; Galvin, D.; Christoffel, V.; Klocker, H.; Fitzpatrick, J.M.; Watson, R.W. Phytoestrogens derived from Belamcanda chinensis have an antiproliferative effect on prostate cancer cells in vitro. J. Urol. 2004, 172, 2426–2433.
- Wang, Q.; Cheng, X.L.; Li, H.; Qin, X.Y.; Ge, C.Y.; Liu, R.; Qi, L.W.; Qin, M.J. Application of an efficient strategy for discovery and purification of bioactive compounds from chinese herbal medicines, a case study on the Puerariae thomsonii flos. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 75, 25–32.
- Barzaman, K.; Karami, J.; Zarei, Z.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Kazemi, M.H.; Moradi-Kalbolandi, S.; Safari, E.; Farahmand, L. Breast cancer: Biology, biomarkers, and treatments. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 84, 106535.
- Lacroix, M.; Leclercq, G. Relevance of breast cancer cell lines as models for breast tumours: An update. Breast Cancer Res. Treat 2004, 83, 249–289.
- Zeng, L.; Yuan, S.; Shen, J.; Wu, M.; Pan, L.; Kong, X. Suppression of human breast cancer cells by tectorigenin through downregulation of matrix metalloproteinases and MAPK signaling in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 3935–3943.
- Umehara, K.; Nemoto, K.; Matsushita, A.; Terada, E.; Monthakantirat, O.; De-Eknamkul, W.; Miyase, T.; Warashina, T.; Degawa, M.; Noguchi, H. Flavonoids from the heartwood of the thai medicinal plant Dalbergia parviflora and their effects on estrogenic-responsive human breast cancer cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 2163–2168.
- Monthakantirat, O.; De-Eknamkul, W.; Umehara, K.; Yoshinaga, Y.; Miyase, T.; Warashina, T.; Noguchi, H. Phenolic constituents of the rhizomes of the thai medicinal plant Belamcanda chinensis with proliferative activity for two breast cancer cell lines. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 361–364.
- Reid, B.M.; Permuth, J.B.; Sellers, T.A. Epidemiology of ovarian cancer: A review. Cancer Biol. Med. 2017, 14, 9–32.
- Jayson, G.C.; Kohn, E.C.; Kitchener, H.C.; Ledermann, J.A. Ovarian cancer. Lancet 2014, 384, 1376–1388.
- Pistollato, F.; Calderon Iglesias, R.; Ruiz, R.; Aparicio, S.; Crespo, J.; Dzul Lopez, L.; Giampieri, F.; Battino, M. The use of natural compounds for the targeting and chemoprevention of ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 411, 191–200.
- Yang, Y.I.; Lee, K.T.; Park, H.J.; Kim, T.J.; Choi, Y.S.; Shih Ie, M.; Choi, J.H. Tectorigenin sensitizes paclitaxel-resistant human ovarian cancer cells through downregulation of the Akt and NFκB pathway. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 2488–2498.
- Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Son, S.R.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, J.H.; Jang, D.S. Chemical constituents of the flowers of Pueraria lobata and their cytotoxic properties. Plants 2022, 11, 1651.
- Zhan, G.; Pan, L.; Tu, K.; Jiao, S. Antitumor, antioxidant, and nitrite scavenging effects of Chinese water chestnut (Eleocharis dulcis) peel flavonoids. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, 2578–2586.
- Jung, S.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, S.; Lim, S.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Ohuchi, K.; Shin, K.H. Anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor activities of isoflavonoids from the rhizomes of Belamcanda chinensis. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 617–622.
- Amin, A.; Mokhdomi, T.A.; Bukhari, S.; Wani, S.H.; Wafai, A.H.; Lone, G.N.; Qadri, A.; Qadri, R.A. Tectorigenin ablates the inflammation-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in a co-culture model of human lung carcinoma. Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 67, 382–387.
- Jiang, C.P.; Ding, H.; Shi, D.H.; Wang, Y.R.; Li, E.G.; Wu, J.H. Pro-apoptotic effects of tectorigenin on human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 1753–1764.
- Dai, X.Y.; Yu, Y.M.; Kong, Z.F.; Cao, Y.S.; Zhang, S. Tectorigenin inhibits Caco-2 human colon cells via NF-κB pathway suppression. Bangl. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 10, 948.
- Lee, K.T.; Sohn, I.C.; Kim, Y.K.; Choi, J.H.; Choi, J.W.; Park, H.J.; Itoh, Y.; Miyamoto, K. Tectorigenin, an isoflavone of Pueraria thunbergiana Benth., induces differentiation and apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 24, 1117–1121.
- Hasibeder, A.; Venkataramani, V.; Thelen, P.; Radzun, H.J.; Schweyer, S. Phytoestrogens regulate the proliferation and expression of stem cell factors in cell lines of malignant testicular germ cell tumors. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 1385–1394.
- O’Toole, S.A.; Sheppard, B.L.; Sheils, O.; O’Leary, J.J.; Spengler, B.; Christoffel, V. Analysis of DNA in endometrial cancer cells treated with phyto-estrogenic compounds using comparative genomic hybridisation microarrays. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 435–439.
- Eid, S.; Sas, K.M.; Abcouwer, S.F.; Feldman, E.L.; Gardner, T.W.; Pennathur, S.; Fort, P.E. New insights into the mechanisms of diabetic complications: Role of lipids and lipid metabolism. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1539–1549.
- Lee, K.T.; Sohn, I.C.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, J.W.; Kwon, S.H.; Park, H.J. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of tectorigenin and kaikasaponin III in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat and their antioxidant activity in vitro. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2000, 23, 461–466.
- Bae, E.A.; Han, M.J.; Lee, K.T.; Choi, J.W.; Park, H.J.; Kim, D.H. Metabolism of 6″-O-xylosyltectoridin and tectoridin by human intestinal bacteria and their hypoglycemic and in vitro cytotoxic activities. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 22, 1314–1318.
- Jung, S.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, S.; Lim, S.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Shin, K.H. Isoflavonoids from the rhizomes of Belamcanda chinensis and their effects on aldose reductase and sorbitol accumulation in streptozotocin induced diabetic rat tissues. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2002, 25, 306–312.
- Yao, X.; Li, K.; Liang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Yu, C.L.; Song, Z.B.; Bao, Y.L.; et al. Tectorigenin enhances PDX1 expression and protects pancreatic β-cells by activating ERK and reducing ER stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 12975–12992.
- Moon, H.I.; Jung, J.C.; Lee, J. Aldose reductase inhibitory effect by tectorigenin derivatives from Viola hondoensis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 7592–7594.
- Qu, J.; Wu, Z.; Gao, J.; Wen, H.; Wang, T.; Yuan, D. Excretion of tectoridin metabolites in rat urine and bile orally administrated at different dosages and their inhibitory activity against aldose reductase. Fitoterapia 2014, 99, 99–108.
- Munoz, M.; Lopez-Oliva, M.E.; Rodriguez, C.; Martínez, M.P.; Saenz-Medina, J.; Sanchez, A.; Climent, B.; Benedito, S.; Garcia-Sacristan, A.; Rivera, L.; et al. Differential contribution of Nox1, Nox2 and Nox4 to kidney vascular oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in obesity. Redox Biol. 2020, 28, 101330.
- Ghosh, A.; Gao, L.; Thakur, A.; Siu, P.M.; Lai, C.W.K. Role of free fatty acids in endothelial dysfunction. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 50.
- Yang, S.; Ma, C.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, F.; Yang, G.; Yang, Q.; Jia, L.; Liang, Z.; Kang, L. Tectorigenin attenuates diabetic nephropathy by improving vascular endothelium dysfunction through activating AdipoR1/2 pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 153, 104678.
- Wang, Q.; Cheng, X.L.; Zhang, D.Y.; Gao, X.J.; Zhou, L.; Qin, X.Y.; Xie, G.Y.; Liu, K.; Qin, Y.; Liu, B.L.; et al. Tectorigenin attenuates palmitate-induced endothelial insulin resistance via targeting ROS-associated inflammation and IRS-1 pathway. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66417.
- Zanquetta, M.M.; Alves-Wagner, A.B.; Mori, R.C.; Campello, R.S.; Machado, U.F. Recovery of insulin sensitivity and Slc2a4 mRNA expression depend on T3 hormone during refeeding. Metabolism 2014, 63, 328–334.
- Yao, X.; Liu, L.; Shao, W.; Bai, M.; Ding, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, S.; Zheng, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, G.; et al. Tectorigenin targets PKACα to promote GLUT4 expression in skeletal muscle and improve insulin resistance in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 1579–1596.
- Pappachan, J.M.; Fernandez, C.J.; Chacko, E.C. Diabesity and antidiabetic drugs. Mol. Aspects Med. 2019, 66, 3–12.
- Li, Q.Y.; Chen, L.; Yan, M.M.; Shi, X.J.; Zhong, M.K. Tectorigenin regulates adipogenic differentiation and adipocytokines secretion via PPARγ and IKK/NF-κB signaling. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 1567–1575.
- Zhou, M.; Deng, Y.; Liu, M.; Liao, L.; Dai, X.; Guo, C.; Zhao, X.; He, L.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. The pharmacological activity of berberine, a review for liver protection. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 890, 173655.
- Elufioye, T.O.; Habtemariam, S. Hepatoprotective effects of rosmarinic acid: Insight into its mechanisms of action. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108600.
- Jung, S.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Lim, S.S.; Lee, S.; Shin, K.H.; Kim, Y.S. Antioxidant activities of isoflavones from the rhizomes of Belamcanda chinensis on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic injury in rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2004, 27, 184–188.
- Lee, H.W.; Choo, M.K.; Bae, E.A.; Kim, D.H. Beta-glucuronidase inhibitor tectorigenin isolated from the flower of Pueraria thunbergiana protects carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury. Liver Int. 2003, 23, 221–226.
- Gao, X.X.; Shi, D.H.; Chen, Y.X.; Cui, J.T.; Wang, Y.R.; Jiang, C.P.; Wu, J.H. The therapeutic effects of tectorigenin on chemically induced liver fibrosis in rats and an associated metabonomic investigation. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 1479–1493.
- Lee, H.U.; Bae, E.A.; Kim, D.H. Hepatoprotective effect of tectoridin and tectorigenin on tert-butyl hyperoxide-induced liver injury. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 97, 541–544.
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, L.; Xu, K.; Ji, F.; Xie, Z.; Ouyang, X.; Wu, D.; Li, L. Tectorigenin protects against experimental fulminant hepatic failure by regulating the TLR4/mitogen-activated protein kinase and TLR4/nuclear factor-κB pathways and autophagy. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1055–1064.
- Asrani, S.K.; Devarbhavi, H.; Eaton, J.; Kamath, P.S. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 151–171.
- Wu, J.H.; Wang, Y.R.; Huang, W.Y.; Tan, R.X. Anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects of tectorigenin on hepatic stellate cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 3911–3918.
- Duan, R.; Huang, K.; Guan, X.; Li, S.; Xia, J.; Shen, M.; Sun, Z.; Yu, Z. Tectorigenin ameliorated high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through anti-inflammation and modulating gut microbiota in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 164, 112948.
- Kim, H.K.; Cheon, B.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.P. Effects of naturally occurring flavonoids on nitric oxide production in the macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 and their structure-activity relationships. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 759–765.
- Kim, Y.P.; Yamada, M.; Lim, S.S.; Lee, S.H.; Ryu, N.; Shin, K.H.; Ohuchi, K. Inhibition by tectorigenin and tectoridin of prostaglandin E2 production and cyclooxygenase-2 induction in rat peritoneal macrophages. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1438, 399–407.
- Hong, J.; Shin, K.H.; Lim, S.S.; Kwak, J.H.; Zee, O.; Ishihara, K.; Hirasawa, N.; Seyama, T.; Ohuchi, K. Lead compounds for anti-inflammatory drugs isolated from the plants of the traditional oriental medicine in Korea. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2008, 7, 195–202.
- Pan, C.H.; Kim, E.S.; Jung, S.H.; Nho, C.W.; Lee, J.K. Tectorigenin inhibits IFN-gamma/LPS-induced inflammatory responses in murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2008, 31, 1447–1456.
- Lim, H.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, B.Y.; Park, G.; Jeong, S.J. The anti-neuroinflammatory activity of tectorigenin pretreatment via downregulated NF-κB and ERK/JNK pathways in BV-2 microglial and microglia inactivation in mice with lipopolysaccharide. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 462.
- Zhou, L.; Yan, K.; Xing, S.; Cheng, J. Tectorigenin alleviates the apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury cell model through inhibiting insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 6. Open Med. 2023, 18, 20230680.
- Ma, C.H.; Liu, J.P.; Qu, R.; Ma, S.P. Tectorigenin inhibits the inflammation of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 12, 841–846.
- Ha, L.M.; Que, D.T.N.; Huyen, D.T.T.; Long, P.Q.; Dat, N.T. Toxicity, analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of tectorigenin. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2013, 35, 336–340.
- Li, J.; Yan, W.; Ren, F.; Sang, H. Tectorigenin inhibits inflammation in keratinocytes by inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome regulated by the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2023, 51, 82–89.
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, G.T.; Yun, H.M.; Kim, Y.C.; Kwon, I.K.; Kim, E.C. Tectorigenin promotes osteoblast differentiation and in vivo bone healing, but suppresses osteoclast differentiation and in vivo bone resorption. Mol. Cells 2018, 41, 476–485.
- Forman, H.J.; Zhang, H. Targeting oxidative stress in disease: Promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 689–709.
- Tayab, M.A.; Chowdhury, K.A.A.; Jabed, M.; Mohammed Tareq, S.; Kamal, A.; Islam, M.N.; Uddin, A.M.K.; Hossain, M.A.; Emran, T.B.; Simal-Gandara, J. Antioxidant-rich woodfordia fruticosa leaf extract alleviates depressive-like behaviors and impede hyperglycemia. Plants 2021, 10, 287.
- Akhter, S.; Arman, M.S.I.; Tayab, M.A.; Islam, M.N.; Xiao, J. Recent advances in the biosynthesis, bioavailability, toxicology, pharmacology, and controlled release of citrus neohesperidin. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022; Online ahead of print.
- Chen, W.; Zhuang, J.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, X. Myricitrin protects against peroxynitrite-mediated DNA damage and cytotoxicity in astrocytes. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 927–933.
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84.
- Arct, J.; Pytkowska, K. Flavonoids as components of biologically active cosmeceuticals. Clin. Dermatol. 2008, 26, 347–357.
- Wozniak, D.; Janda, B.; Kapusta, I.; Oleszek, W.; Matkowski, A. Antimutagenic and anti-oxidant activities of isoflavonoids from Belamcanda chinensis (L.) DC. Mutat. Res. 2010, 696, 148–153.
- Kang, K.A.; Lee, K.H.; Chae, S.; Zhang, R.; Jung, M.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, D.H.; Hyun, J.W. Cytoprotective effect of tectorigenin, a metabolite formed by transformation of tectoridin by intestinal microflora, on oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 519, 16–23.
- Park, K.Y.; Jung, G.O.; Choi, J.; Lee, K.T.; Park, H.J. Potent antimutagenic and their anti-lipid peroxidative effect of kaikasaponin III and tectorigenin from the flower of Pueraria thunbergiana. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2002, 25, 320–324.
- Han, T.; Cheng, G.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Hu, Y.T.; Huang, W. In vitro evaluation of tectoridin, tectorigenin and tectorigenin sodium sulfonate on antioxidant properties. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 409–414.
- Noh, D.; Choi, J.G.; Lee, Y.B.; Jang, Y.P.; Oh, M.S. Protective effects of Belamcandae Rhizoma against skin damage by ameliorating ultraviolet-B-induced apoptosis and collagen degradation in keratinocytes. Environ. Toxicol. 2019, 34, 1354–1362.
- Vaou, N.; Stavropoulou, E.; Voidarou, C.; Tsigalou, C.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Towards advances in medicinal plant antimicrobial activity: A review study on challenges and future perspectives. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2041.
- Oh, K.B.; Kang, H.; Matsuoka, H. Detection of antifungal activity in Belamcanda chinensis by a single-cell bioassay method and isolation of its active compound, tectorigenin. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2001, 65, 939–942.
- Bae, E.A.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. In vitro anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of irisolidone isolated from the flowers and rhizomes of Pueraria thunbergiana. Planta Med. 2001, 67, 161–163.
- Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, Q.; Hu, N.; Shen, X.; Deng, X. Tectorigenin reduces type IV pilus-dependent cell adherence in Clostridium perfringens. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, 112.
- Guan, Z.; Luo, L.; Liu, S.; Guan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Tao, K. The role of depletion of gut microbiota in osteoporosis and osteoarthritis: A narrative review. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 847401.
- Shan, S.K.; Lin, X.; Li, F.; Xu, F.; Zhong, J.Y.; Guo, B.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.H.; Wu, F.; Yuan, L.Q. Exosomes and bone disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 4536–4549.
- Wang, S.; Deng, Z.; Ma, Y.; Jin, J.; Qi, F.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; Lyu, F.J.; Zheng, Q. The role of autophagy and mitophagy in bone metabolic disorders. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2675–2691.
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.L.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, H. Exercise for osteoporosis: A literature review of pathology and mechanism. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1005665.
- Riggs, B.L.; Hartmann, L.C. Selective estrogen-receptor modulators—Mechanisms of action and application to clinical practice. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 618–629.
- Jeong, H.J.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.Y.; Nam, S.Y.; Han, N.R.; Lee, B.; Cho, H.; Moon, P.D.; Kim, H.M. PCE17 and its active compounds exert an anti-osteoporotic effect through the regulation of receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand in ovariectomized mice. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, e12561.
- Ma, C.; Xu, K.; Meng, J.; Ran, J.; Adel Abdo Moqbel, S.; Liu, A.; Yan, S.; Wu, L. Tectorigenin inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via suppression of NF-κB signalling and decreases bone loss in ovariectomized C57BL/6. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5121–5131.
- Wang, C.L.; Li, D.; Wang, C.D.; Xiao, F.; Zhu, J.F.; Shen, C.; Zuo, B.; Cui, Y.M.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; et al. Anti-inflammatory and anti-osteoarthritis effects of tectorigenin. Biol. Open 2017, 6, 1130–1136.
- Aicale, R.; Oliviero, A.; Maffulli, N. Management of achilles and patellar tendinopathy: What we know, what we can do. J. Foot Ankle. Res. 2020, 13, 59.
- Moqbel, S.A.A.; Xu, K.; Chen, Z.; Xu, L.; He, Y.; Wu, Z.; Ma, C.; Ran, J.; Wu, L.; Xiong, Y. Tectorigenin alleviates inflammation, apoptosis, and ossification in rat tendon-derived stem cells via modulating NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 568894.
- Kammeyer, A.; Luiten, R.M. Oxidation events and skin aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 21, 16–29.
- Dai, X.; Jin, J.; Jia, Y.; Yang, K.; Han, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, X.; Yao, C.; Sun, T.; Zhu, C.; et al. A non-retinol retinoic acid receptor-γ (RAR-γ/NR1B3) selective agonist, tectorigenin, can effectively inhibit the ultraviolet a-induced skin damage. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 4722–4737.
- Khalil, S.; Bardawil, T.; Stephan, C.; Darwiche, N.; Abbas, O.; Kibbi, A.G.; Nemer, G.; Kurban, M. Retinoids: A journey from the molecular structures and mechanisms of action to clinical uses in dermatology and adverse effects. J. Dermatolog. Treat 2017, 28, 684–696.
- Tamura, S.; Yoshihira, K.; Tokumaru, M.; Zisheng, X.; Murakami, N. Inhibitors for expression of IgE receptor on human mast cell from Puerariae Flos. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3872–3875.
- Park, E.K.; Shin, Y.W.; Lee, H.U.; Lee, C.S.; Kim, D.H. Passive cutaneous anaphylaxis-inhibitory action of tectorigenin, a metabolite of tectoridin by intestinal microflora. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 1099–1102.
- Pan, Y.; Wu, W.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Y. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases: From mechanisms to therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 163, 114817.
- Liberale, L.; Ministrini, S.; Carbone, F.; Camici, G.G.; Montecucco, F. Cytokines as therapeutic targets for cardio- and cerebrovascular diseases. Basic. Res. Cardiol. 2021, 116, 23.
- Chaturvedi, S.; Yadav, J.S. The role of antiplatelet therapy in carotid stenting for ischemic stroke prevention. Stroke 2006, 37, 1572–1577.
- Applova, L.; Karlíckova, J.; Ríha, M.; Filipsky, T.; Macakova, K.; Spilkova, J.; Mladenka, P. The isoflavonoid tectorigenin has better antiplatelet potential than acetylsalicylic acid. Phytomedicine 2017, 35, 11–17.
- Tang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Yang, X.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C. Screening and isolation of potential lactate dehydrogenase inhibitors from five chinese medicinal herbs: Soybean, Radix pueraria, Flos pueraria, Rhizoma belamcandae, and Radix astragali. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 2043–2049.
- Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Sun, L.; Lian, Y. Tectorigenin protect HUVECs from H2O2 -induced oxidative stress injury by regulating PI3K/Akt pathway. Tissue. Cell. 2021, 68, 101475.
- Yao, L.; Yang, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, Q.; Xie, X.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Q.; Su, H.; Zhai, J.; et al. Tectorigenin attenuates the OGD/R-induced HT-22 cell damage through regulation of the PI3K/AKT and the PPARγ/NF-κB pathways. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 1320–1331.
- Feng, W. Tectorigenin attenuates cognitive impairments in mice with chronic cerebral ischemia by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2021, 85, 1665–1674.
- Qian, X.; Xiao, Q.; Li, Z. Tectorigenin regulates migration, invasion, and apoptosis in dexamethasone-induced human airway epithelial cells through up-regulating miR-222-3p. Drug Dev. Res. 2021, 82, 959–968.
- Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Wu, J.; Ye, X.; Xu, L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, D.; Tan, R.; Wang, Y. Tectorigenin inhibits the in vitro proliferation and enhances miR-338* expression of pulmonary fibroblasts in rats with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 131, 165–173.
- Papi, A.; Brightling, C.; Pedersen, S.E.; Reddel, H.K. Asthma. Lancet 2018, 391, 783–800.
- Richeldi, L.; Collard, H.R.; Jones, M.G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1941–1952.
- Cummings, J. Disease modification and Neuroprotection in neurodegenerative disorders. Transl. Neurodegener. 2017, 6, 25.
- Crews, F.T.; Bechara, R.; Brown, L.A.; Guidot, D.M.; Mandrekar, P.; Oak, S.; Qin, L.; Szabo, G.; Wheeler, M.; Zou, J. Cytokines and alcohol. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 720–730.
- Yuan, D.; Xie, Y.Y.; Bai, X.; Wu, X.; Yang, J.Y.; Wu, C.F. Inhibitory activity of isoflavones of Pueraria flowers on nitric oxide production from lipopolysaccharide-activated primary rat microglia. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 11, 471–481.
- Yeh, L.T.; Hsu, L.S.; Chung, Y.H.; Chen, C.J. Tectorigenin inhibits glioblastoma proliferation by G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. Medicina 2020, 56, 681.
- Marti, H.H.; Wenger, R.H.; Rivas, L.A.; Straumann, U.; Digicaylioglu, M.; Henn, V.; Yonekawa, Y.; Bauer, C.; Gassmann, M. Erythropoietin gene expression in human, monkey and murine brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 666–676.
- Sun, Y.Y.; Lin, S.H.; Lin, H.C.; Hung, C.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Hung, K.S.; Lien, C.C.; Kuan, C.Y.; Lee, Y.H. Cell type-specific dependency on the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway for the endogenous Epo and VEGF induction by baicalein in neurons versus astrocytes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69019.
- John, M.J.; Jaison, V.; Jain, K.; Kakkar, N.; Jacob, J.J. Erythropoietin use and abuse. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, 220–227.
- Liu, E.Y.; Zheng, Z.X.; Zheng, B.Z.; Xia, Y.; Guo, M.S.; Dong, T.T.; Tsim, K.W.K. Tectorigenin, an isoflavone aglycone from the rhizome of Belamcanda chinensis, induces neuronal expression of erythropoietin via accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 1329–1337.
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Niu, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y. Ionic-liquid-based ultrasound-assisted extraction combined with countercurrent chromatography and semipreparative LC for the preparation of monoamine oxidase B inhibitors from Pueraria thomsonii. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 1116–1127.
- Gong, P.; Deng, F.; Zhang, W.; Ji, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Hu, J. Tectorigenin attenuates the MPP(+)-induced SH-SY5Y cell damage, indicating a potential beneficial role in Parkinson’s disease by oxidative stress inhibition. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 4431–4437.
- Li, J.; Yang, J.; Zhu, B.; Fan, J.; Hu, Q.; Wang, L. Tectorigenin protects against unilateral ureteral obstruction by inhibiting Smad3-mediated ferroptosis and fibrosis. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 475–487.
- Jung, D.Y.; Ha, H.; Kim, C. Induction of growth hormone release by Pueraria thunbergiana BENTH. Horm. Metab. Res. 2004, 36, 86–91.
More
Information
Subjects:
Medical Informatics
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
849
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
16 Aug 2023
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




