Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Edoardo Monfrini | -- | 2669 | 2023-08-10 09:09:25 | | | |
| 2 | Catherine Yang | Meta information modification | 2669 | 2023-08-10 09:35:46 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Monfrini, E.; Arienti, F.; Rinchetti, P.; Lotti, F.; Riboldi, G.M. Brain Calcifications. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/47881 (accessed on 07 February 2026).
Monfrini E, Arienti F, Rinchetti P, Lotti F, Riboldi GM. Brain Calcifications. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/47881. Accessed February 07, 2026.
Monfrini, Edoardo, Federica Arienti, Paola Rinchetti, Francesco Lotti, Giulietta M. Riboldi. "Brain Calcifications" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/47881 (accessed February 07, 2026).
Monfrini, E., Arienti, F., Rinchetti, P., Lotti, F., & Riboldi, G.M. (2023, August 10). Brain Calcifications. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/47881
Monfrini, Edoardo, et al. "Brain Calcifications." Encyclopedia. Web. 10 August, 2023.
Copy Citation
Brain calcifications (BC) are intracranial calcium deposits localized in the brain parenchyma and its microvasculature. Their prevalence ranges from 1% in young individuals up to 38% in elderly subjects. Calcified areas are easily identified by clinicians as hyperdense alterations on brain CT. A certain degree of intracranial calcifications, particularly of the basal ganglia, pineal gland, choroid plexus, and habenula, can be considered a normal phenomenon associated with aging. Indeed, BC are often incidental findings on neuroimaging of asymptomatic individuals; however, they can also be associated with many genetic and acquired disorders. BC can be primary, as observed in several early- and late-onset genetic syndromes, or can be secondary to systemic alterations of phosphate–calcium metabolism (genetic and also acquired forms), intrauterine (e.g., TORCH) and post-natal infections (e.g., neurocysticercosis), hypoxic-ischemic injuries, toxic exposures (e.g., lead), brain tumors (e.g., oligodendrogliomas), and autoimmune disorders (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus).
primary familial brain calcification (PFBC)
SLC20A2
PDGFB
PDGFRB
XPR1
CMPK2
Brain Calcifications
1. Genetics of Brain Calcification
In the past decades, genetic etiology of IBGC was suspected based on the identification of several familial clusters [1][2][3][4]. However, no genetic cause of IBGC was recognized before the identification in 2012 of SLC20A2 as the first associated gene [5]. Since then, six genes have been definitively linked with PFBC: four inherited in an autosomal dominant manner (SLC20A2, PDGFB, PDGFRB, and XPR1) and two displaying an autosomal recessive inheritance (MYORG and JAM2) [6][7][8][9][10]. Very recently, a novel gene (i.e., CMPK2) has been proposed to be associated with autosomal recessive brain calcifications and this awaits confirmation in independent studies [11]. A review of data from 555 genetically diagnosed patients with PFBC revealed the following frequency of mutations: SLC20A2~60%, MYORG~13%, PDGFB~13%, PDGFRB~6%, XPR1~6%, JAM2~2% [12][13]. A brief genetic characterization of each these genes is provided below in association with the genetic evidence deriving from knock-out or hypomorphic animal models.
SLC20A2 (chr. 8p11.21, 11 exons) encodes the sodium-dependent phosphate transporter 2 (652 amino acids), which plays a fundamental role in cellular phosphate transport. Several pathogenic variants have been reported, including missense, nonsense, splice-disruptive, small indels, and gross deletions. Pathogenic variants have been shown to impair uptake of phosphate (loss-of-function mechanism of disease) [5]. Interestingly, a complete Slc20a2 knockout mouse showed extensive, bilateral calcifications in the thalamus, basal ganglia, and cortex, recapitulating the human disease [14].
MYORG (chr. 9p13.3, one coding exon) encodes the myogenesis regulating glycosidase (putative) (714 amino acids), a protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum and nuclear membranes whose functions remain poorly defined, but are probably linked to protein glycosylation [15]. Many pathogenic variants have been described, including missense, nonsense, and small indels. The presence of biallelic nonsense mutations of MYORG in PFBC patients strongly suggests that a functional loss of MYORG is associated with brain calcifications. Indeed, Myorg-KO mice and zebrafish develop progressive brain calcifications [7][16].
PDGFRB (chr. 5q32, 23 exons) encodes the platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFR-β) (1106 amino acids), a cell surface tyrosine kinase receptor for mesenchymal cell mitogens. Several pathogenic variants are known, including missense and start-loss mutations. Pdgfrb-deficient mice lack pericytes, essential for blood–brain barrier (BBB) formation, and display increased vascular permeability [17].
PDGFB (chr. 22q13.1, six exons) encodes the platelet-derived growth factor subunit B (241 amino acids), which is a potent mitogen for cells of mesenchymal origin, by binding and activating PDGF receptor tyrosine kinases such as PDGFR-β. A number of pathogenic variants have been reported in association with PFBC, including missense, nonsense, splice-disruptive, start loss, stop loss, and gross deletions. Hypomorphic Pdgfb mice develop brain calcifications that correlate with the degree of pericyte and BBB deficiency [10].
XPR1 (chr. 1q25.3, 15 exons) encodes the xenotropic and polytropic retrovirus receptor 1 (696 amino acids), which plays a role in phosphate homeostasis and mediates phosphate export from the cells. Few pathogenic variants have been reported, which include missense and splice disruptive. Remarkably, the majority of these are located in the SPX putative regulatory domain of the protein [8][18].
JAM2 (chr. 21q21.3, 10 exons) encodes the junctional adhesion molecule 2 (298 amino acids), which is localized at the tight junctions of both epithelial and endothelial cells and mediates heterotypic cell–cell interactions [19]. Being the most recently described gene, few pathogenic variants have been reported, including missense, start-loss, nonsense, and splice-disruptive. Pathogenic variants lead to reduction/absence of JAM2 protein, consistent with a loss-of-function mechanism. The brain calcification phenotype is replicated in the Jam2 complete knockout mouse [6].
Genetics of Early-Onset Syndromes Associated with Brain Calcifications
Calcifications in the basal ganglia and other brain structures are also observed in several genetic diseases with normal calcium–phosphate metabolism. This clinically and genetically highly heterogeneous group of syndromes includes mitochondrial diseases (predominantly mtDNA mutations), Aicardi–Goutières syndrome (ADAR, RNASEH2A, RNASEH2B, RNASEH2C, SAMHD1, TREX1, IFIH1), Coats plus syndrome (CTC1), leukoencephalopathy with calcifications and cysts (SNORD118), Cockayne syndrome (DDB2, ERCC1, ERCC2, ERCC3, ERCC4, ERCC5, ERCC6, ERCC8, GTF2H5, MPLKIP, POLH, XPA, XPC) and many others. Deep clinical phenotyping is crucial before genetic testing in this context [20]. In the absence of specific diagnostic clues for a particular form (see below) the best genetic approach is next-generation sequencing (e.g., gene panels or exome sequencing) [20]. A detailed genetic description of every one of the many genes involved in these syndromes is beyond the scope of this research. A complete list is provided in Table 1.
Table 1. Genetic syndromes associated with brain calcifications—The table summarizes the genetic forms presenting brain calcifications. Demographic, clinical, and imaging traits for each syndrome are summarized in the table. MOI = mode of inheritance, AD = autosomal dominant, AR = autosomal recessive, mt = mitochondrial, XLR = X-linked recessive, IC = isolated cases. For the specific references of each condition, please refer to the main text.
| Gene (Age of Onset (Range, Years)/Penetrance (%)/MOI) |
Main Neurological Symptoms | Other Symptoms | Brain Calcification |
|---|---|---|---|
| SLC20A2 (1–84/60%/AD) |
>20%: Parkinsonism, cognitive deficit, headache 10–20%: Tremor, dysarthria, dystonia <10%: Depression, psychosis, ataxia, anxiety, seizure, chorea |
Basal ganglia, subcortical white matter, and dentate nuclei | |
| PDGFB (1–70/86%/AD) |
>20%: Headache, cognitive deficit, depression 10–20%: Parkinsonism, psychosis, ataxia, tremor, chorea, anxiety <10%: Dystonia, dysarthria, seizure |
Basal ganglia, subcortical white matter, and dentate nuclei | |
| PDGFBR (6–82/48%/AD) |
>20%: Headache, cognitive deficit 10–20%: Depression, Parkinsonism <10%: Tremor, anxiety, dysarthria, seizure, psychosis, ataxia, tremor, chorea, dystonia |
Basal ganglia, subcortical white matter, and dentate nuclei | |
| XPR1 (16–79/70%/AD) |
>20%: Cognitive deficit, Parkinsonism, dysarthria 10–20%: Tremor, ataxia <10%: Headache, anxiety, seizure, psychosis, depression, dystonia, chorea |
Basal ganglia, subcortical white matter, and dentate nuclei | |
| MYORG (8–87/91%/AR) |
>20%: Dysarthria, cognitive deficit, ataxia, parkinsonism, psychosis, tremor 10–20%: Depression <10%: Headache, dystonia, chorea, seizure, anxiety |
Basal ganglia, subcortical white matter, and dentate nuclei | |
| JAM2 (7–50/85%/AR) |
>20%: Parkinsonism, ataxia, cognitive deficit, dysarthria, seizure <10%: Dystonia |
Basal ganglia, subcortical white matter, and dentate nuclei, midbrain | |
| Mitochondrial conditions (MERRF, Leigh syndrome, KSS—mtDNA) (Childhood, adulthood/full/matrilinear) |
Epilepsy, myoclonus, ataxia, spasticity Dysphagia (LS) |
Short stature, optic atrophy, hearing loss, ptosis, diabetes mellitus, cardiomyopathy, neuropathy, myopathy, diarrhea, vomiting (LS), lactic acidosis |
Basal ganglia calcifications |
| Coats plus syndrome (CTC1) (Childhood/full/AR) |
Developmental delay, epilepsy, spasticity, dystonia, ataxia | Retinal telangiectasia and exudates, osteopenia and fractures, gastrointestinal and hepatic bleeding, portal hypertension, bone marrow suppression Growth retardation |
Calcification with leukoencephalopathy and brain cysts |
| Aicardi-Goutières syndrome (ADAR, RNASEH2A, RNASEH2B, RNASEH2C, SAMHD1, TREX1, IFIH1) (Childhood (usually after a short period of normal development)/full/AR/AD) |
Dystonia, hypotonia, developmental delay Increased startle reaction |
Acquired microcephaly, Hepatosplenomegaly Sterile pyrexias Chilblain lesions (ears, hands, fee) Skin mottling Increased liver enzyme, thrombocytopenia (transitory), interferon signature |
Calcifications of basal ganglia and white matter Leukoencephalopathy Progressive cerebral atrophy |
| Leukoencephalopathy, cystic, without megalencephaly (RNASET2) (1 year/full/AR) |
Seizure Neurological deterioration |
Microcephaly | Brain calcification Cystic lesions (anterior, subcortical) Leukoencephalopathy |
| Claudin-5 (CLDN5) (1 year/full/AR) |
Seizure Developmental delay |
Atrophy of the pons Calcification of the vertical pontine white matter bundles Cortical and basal ganglia calcification |
|
| Hoyeraal Hreidarsson syndrome (DKC1, TINF2) and Congenital Dyskeratosis (Zinsser-Engman-Cole syndrome) (TERC, TERT, NHP2, NOP10, WRAP53, RTEL1) (Childhood (first months)/full/AR X-linked/AD/AR) |
Neurodevelopmental delay | Microcephaly Persistent pancytopenia Hepatic and pulmonary fibrosis Dyskeratosis (skin pigmentation, leukoplakia, toenail dystrophy) Scoliosis |
Cerebellar hypoplasia Basal ganglia and subcortical calcifications |
| 3-hydroxyisobutyric aciduria (1st decade/NA/NA) |
Hypotonia and impaired neurological development | Microcephaly Facial dysmorphism Episodes of ketoacidosis |
Migration brain disorder Calcification in the frontal and subependymal region and periventricular |
| Inborn error of folates Metabolism (FOLR1, SLC46A1, MTHFR, DHFR, MTFD1) (1st decade/full/AR) |
Seizure Severe neurological deterioration |
Leukopenia, megaloblastic bone marrow, hypoimmunoglobulinemia. | Demyelination Calcification of basal ganglia and white matter |
| Carbonic anhydrase II deficiency syndrome (CA2) (Congenital/full/AR) |
Possible mental retardation | Osteopetrosis Renal tubular acidosis |
Calcification of the basal ganglia, thalamus, subcortical white matter |
| Collagen IV disorders (COL4A1, COL4A2) (Childhood–adult/full/AD) |
Seizure Ischemic or hemorrhagic events Migraine with aura (also isolated) Severe cases with intellectual disability and infantile motor symptoms Neuropathy, muscle cramps |
Systemic vascular involvement (aneurysms) and symptoms (renal, ocular, muscular) | Microhemorrhage or and deep intracerebral hemorrhages Lacunar infarcts Dilated perivascular spaces Leukoencephalopathy Porencephaly Intracranial calcifications |
| Cockayne syndrome (DDB2, ERCC1, ERCC2, ERCC3, ERCC4, ERCC5, ERCC6, ERCC8, GTF2H5, MPLKIP, POLH, XPA, XPC) (1st decade/Full/AR) |
Spectrum of conditions Neurodevelopmental and growth delay Impaired vision, hearing and severe neurological deficits |
Cataract Scoliosis, contractures Arthrogryposis, microphthalmia |
Calcification in the basal ganglia (possible) |
| Nasu Hakola Disease—Polycystic lipomembranous osteodysplasia with sclerosing leukoencephalopathy 1 and 2 (TYROBP, TREM2) (3rd decade (bone changes) 4th decade (neurological symptoms)/full/AR) |
Presenile dementia Parkinsonism Seizure |
Cyst-like bone lesions | Brain atrophy Leukodystrophy Basal ganglia calcification |
| Nakajo Nishimura syndrome (PSMB8) (Childhood (Japanese)/full/AR) |
Nodular-erythema like changes Lipodystrophy Finger Joint deformities Specific inflammatory signature and hyperpyrexia Possible cardiac alteration |
Basal ganglia calcification Vessel calcifications (brain and systemic) |
|
| Adams Oliver syndrome 2 (DOCK6) (Congenital/full/AR) |
Epilepsy | Facial dysmorphism Ophthalmological abnormalities (congenital cataract, rod dystrophy, vitreoretinal abnormalities, optic atrophy) Aplasia cutis congenita of the scalp Terminal transverse limb defects Systemic abnormalities (cardiac, renal, hepatic) |
Periventricular calcifications and ventricular enlargement |
| Raine Syndrome (FAM20C) (77) (Congenital/full/AR) |
Neurodevelopmental delay Hydrocephalus Self-mutilating behavior |
Microcephaly Facial dysmorphism Exophthalmos, gum hyperplasia, osteosclerosis |
Punctiform periventricular and white matter calcifications |
| Keutel Syndrome (MGP) (Childhood/full/AR) |
Developmental delay (mild) (epilepsy) |
Dysmorphisms due to calcification of cartilages (facial, brachytelephalangism) Hearing loss Cardiovascular defects and pulmonary stenosis, respiratory symptoms |
|
| Fried Syndrome (AP1S2) (Childhood/full/X-linked recessive) |
Neurodevelopmental delay hydrocephalus Hypotonia, mental retardation, stereotypies |
Microcephaly Short stature Facial dysmorphism Optic nerve atrophy |
Basal ganglia calcification |
| RAB39B (<40 years/full/X-linked) |
Parkinsonism | Juvenile Parkinsonism Intellectual disability |
Basal ganglia calcifications reported in some cases |
| Hemorrhagic destruction of the brain, subependymal calcification, and cataracts (JAM3) | Seizure Severe neurological deterioration Early death |
Congenital cataract | Brain hemorrhagic destruction Subependymal calcification |
| Pseudo-TORCH syndrome 1 (OCLN) (Congenital/full/AR) |
Seizure Pyramidal signs Hypotonia |
Microcephaly Possible dysmorphic features |
Calcification of the white matter, basal ganglia, cerebellum, brain stem Cortical dysgenesis |
| Pseudo-TORCH syndrome 2 (USP18) (Congenital/full/AR) |
Seizure Neurological deterioration |
Microcephaly Possible dysmorphic features Immune abnormalities Intravascular coagulopathy |
Calcifications Cerebral hemorrhage Cortical dysgenesis |
| Immunodeficiency 38 with basal ganglia calcification (ISG15) (1st–2nd decade/full/AR) |
Seizure | Recurrent infections | Basal ganglia and cortical calcification |
| Spondyloenchondrodysplasia with immune dysregulation (ACP5) (1st decade/full/AR) |
Developmental delay Spasticity |
Spondyloenchondrodysplasia Short statue Skeletal dysplasia Immune dysregulation (multiple infections and autoimmune diseases) |
Late-onset cerebral calcification |
| Rajab interstitial lung disease with brain calcifications (FARSA, FARSB) (Infancy–early childhood/full/AR) |
Delayed motor development Cognitive development can be preserved |
Delayed growth Interstitial lung disease Systemic abnormalities (hepatic, renal, skeletal) Dysmorphic features (possible immune abnormalities) |
Calcifications of the basal ganglia and cortex Possible leukoencephalopathy |
| Seizures, early onset, with neurodegeneration and brain calcification (NRROS) (1st decade/full/AR) |
Seizure Developmental regression Pyramidal signs |
Brain atrophy White matter abnormalities Calcifications Possible corpus callosum hypoplasia Possible cystic degeneration of the white matter |
|
| Spastic paraplegia 56, autosomal recessive (CYP2U1) (1st decade/full/AR) |
Spastic paraplegia (and also upper limbs involvement) Dystonia Cognitive impairment |
Macular dystrophy Pseudoxanthoma elasticum |
White matter lesion Atrophy of the corpus callosum Calcifications of the globus pallidus |
| Down syndrome (Trisomy 21) (Congenital/full/IC) |
Mental retardation Decreased muscle tone |
Dysmorphic features, palm crease, large tongue, umbilical hernia, intestinal blockage, congenital heart disease | Basal ganglia (mostly globus pallidus) |
| Pseudohypoparathyroidism (GNAS, PRKAR1A, PDE4D, PDE3A) (1st–5th decade/full/AD) |
Hypocalcemia tetani Seizure Mental retardation |
Short stature Subcutaneous calcifications Brachydactyly Hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, and increased serum concentration of PTH (PTH resistance) Normal renal function |
Calcification of the basal ganglia, thalamus, subcortical white matter |
2. Molecular Mechanisms of Brain Calcifications
The pathophysiology of PFBC is profoundly linked to the loss of integrity of the BBB and should be distinguished from the calcification processes that take place in secondary brain calcifications, in which calcium deposition develops via two main pathways: dystrophic calcification resulting from membrane disruption and uncontrolled calcium entry (hypoxic ischemic injury, intrauterine infections), and calcium–phosphate metabolism alterations (pseudohypoparathyroidism and pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism, mainly linked to loss of function mutations of GNAS, involved in the intracellular transmittal pathway of PTH) [21].
Considering the functions of the known causative genes, the pathology of PFBC can be ascribed to altered phosphate transportation or impaired permeability through the BBB, which both result in increased inorganic phosphate (Pi) levels in CSF and brain interstitial fluid. The excess of Pi induces its deposition in the form of calcium hydroxyapatite (Ca10[PO4]6[OH]2) in the vascular extracellular matrix (Figure 1).
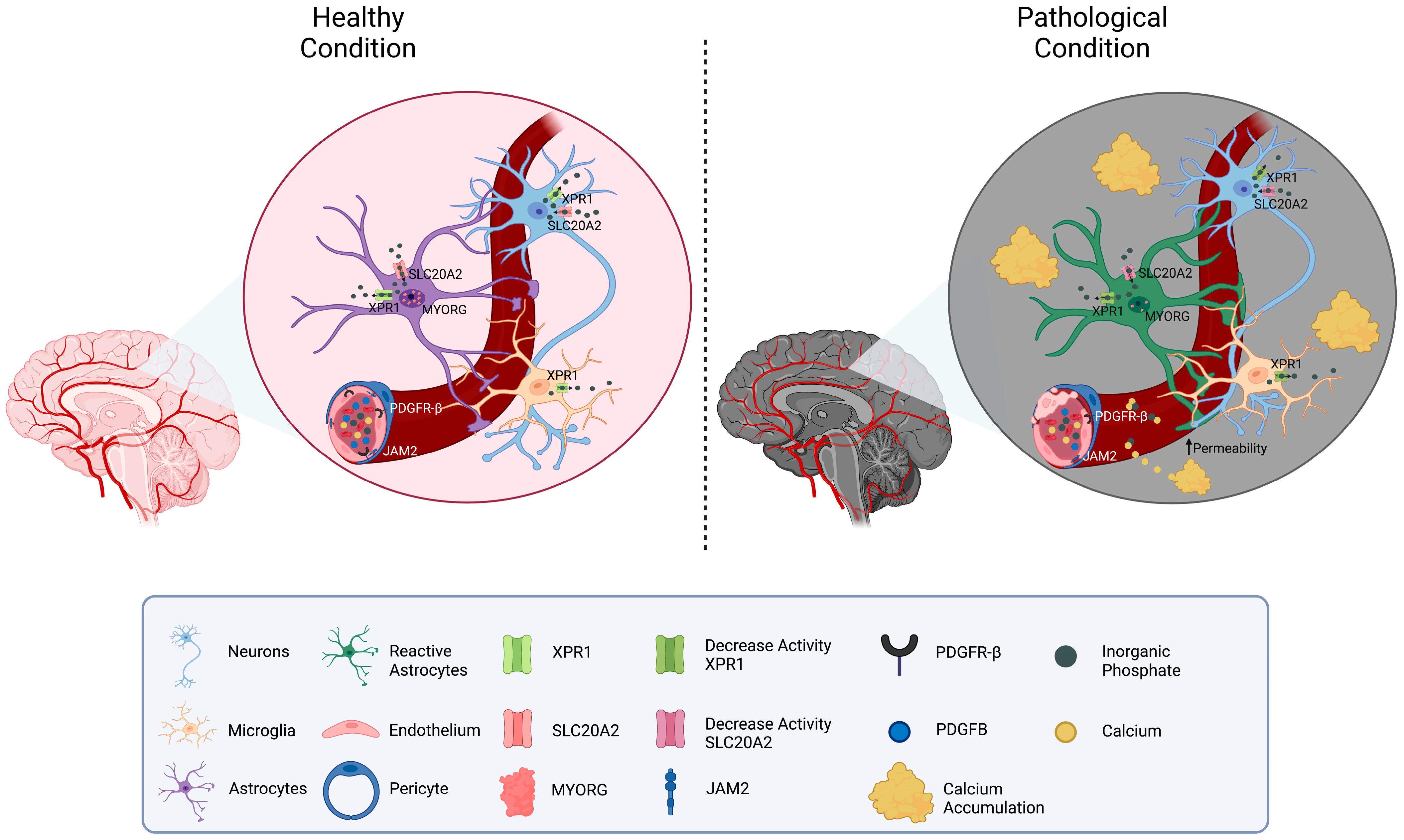
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the molecular mechanisms related to PFBC-genes. A neurovascular unit is depicted. The localization of the genes related to PFBC (SLC20A2, PDGFB, PDGFRB, XPR1, MYORG, and JAM2) is shown in the figure. On the left side, physiological Pi homeostatic processes are illustrated (mostly modulated by SLC20A2 (import) and XPR1 (export)). On the right side, pathological conditions due to gene mutations’ protein down-regulation are depicted. Reduced levels of MYORG result in impaired function and confirmation of astrocytes. Disfunction of PDGFB, PDGFRB, and JAM2 causes increased permeability of the vessels and calcium leakage. Interstitial accumulation of Pi and calcium is responsible for the formation of brain calcifications.
The reasons for the greater basal ganglia vulnerability to calcium deposition are not completely understood but may depend on the higher expression of the causative genes in the basal ganglia neurovascular system, as well as on the peculiar vascularization of these areas [22].
SLC20A2 and XPR1 operate directly in inorganic phosphate transportation: the former, mainly expressed by neurons, astrocytes, and vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC), imports extracellular Pi into the cell mediating its transportation from CSF to blood; the latter exports intracellular Pi out of cells such as neurons, astrocytes, and microglia [8]. Mutations of these transporters lead to the accumulation of extracellular Pi, due to reduced Pi internalization in SLC20A2 mutants, and to intracellular accumulation with subsequent down-regulation of uptake in XPR1 mutants. It has been hypothesized that persistent elevation in extracellular Pi may induce intracranial calcification, possibly via trans-differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) into osteoblast-like cells [23].
Conversely, PDGFRB, PDGFB, MYORG, and JAM2 operate in the brain neurovascular unit (made of neurons, astrocytes, endothelial cells, pericytes, and VSMCs) and indirectly impair the BBB permeability [24]. PDGFR-β is expressed mainly by pericytes and VSMCs, while PDGFB is predominantly released by the endothelium, enabling the recruitment of PDGFR-β-expressing cells and thus promoting the wrapping of the cerebral vessel [25]. Deficiency of PDGF-B/PDGFR-β signaling causes alteration in pericyte recruitment and endothelial cell morphology, leading to increased vascular permeability. MYORG is predominantly expressed in astrocytes and localized in the endoplasmic reticulum; though presumed to act as an α-glucosidase, its molecular function remains largely unknown [15]. Astrocytic endfeet connect the endothelial cells to the extracellular matrix and neurons, thus exerting an important function in the maintenance of the BBB. Speculatively, intracellular ER alterations may impair astrocytes’ properties and conformation, causing BBB disruption. JAM2 is a key component of the tight junctions between endothelial cells in the neuro-vascular unit. JAM2 loss-of-function causes disarrangement of tight junctions, leading to high Pi leakage from the blood to the brain tissue [6].
Concerning genetic brain calcifications other than PFBC, at least three additional pathogenetic mechanisms haver been identified:
-
Cerebral microangiopathies and gliosis, resulting from the malfunctioning of cellular systems fundamental in vessels’ stability and/or angiogenesis, such as small nucleolar RNA involved in ribosome biogenesis in leukoencephalopathy with calcification and cysts (LCC) [26], telomeres in Coats plus syndrome, nucleases in Aicardi–Goutières syndrome and type IV collagen in COL4A1-related disease [26][27][28][29].
-
Reaction to microgliopathy and neuronal loss, often seen in more complex encephalopathies such as Cockayne syndrome where microscopic examination has highlighted the presence of both iron and calcium deposits, or the NRROS-related disorders, Adams–Oliver syndrome and Nasu–Hakola disease [30].
-
Mitochondriopathies, where brain calcification may be attributed to co-present endocrine alterations (hypoparathyroidism) and/or to progressive cell degeneration caused by mitochondrial dysfunction in the brain [31].
The underlying pathogenetic mechanisms of ectopic/dystrophic calcifications of non-cerebral soft tissues are extremely different and are mainly associated with systemic mineral imbalance (i.e., hyperparathyroidism) or tissue alteration and necrosis (i.e., myositis ossificans) [32].
References
- Foley, J. Calcification of the Corpus Stiatum and Dentate Nuclei Occurring in a Family. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1951, 14, 253–261.
- Ellie, E.; Julien, J.; Ferrer, X. Familial Idiopathic Striopallidodentate Calcifications. Neurology 1989, 39, 381–385.
- Boller, F.; Boller, M.; Gilbert, J. Familial Idiopathic Cerebral Calcifications. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1977, 40, 280–285.
- Moskowitz, M.A.; Winickoff, R.N.; Heinz, E.R. Familial Calcification of the Basal Ganglions: A Metabolic and Genetic Study. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 285, 72–77.
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Shi, L.; Ren, J.; Patti, M.; Wang, T.; de Oliveira, J.R.M.; Sobrido, M.-J.; Quintáns, B.; Baquero, M.; et al. Mutations in SLC20A2 Link Familial Idiopathic Basal Ganglia Calcification with Phosphate Homeostasis. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 254–256.
- Schottlaender, L.V.; Abeti, R.; Jaunmuktane, Z.; Macmillan, C.; Chelban, V.; O’Callaghan, B.; McKinley, J.; Maroofian, R.; Efthymiou, S.; Athanasiou-Fragkouli, A.; et al. Bi-Allelic JAM2 Variants Lead to Early-Onset Recessive Primary Familial Brain Calcification. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 106, 412–421.
- Yao, X.-P.; Cheng, X.; Wang, C.; Zhao, M.; Guo, X.-X.; Su, H.-Z.; Lai, L.-L.; Zou, X.-H.; Chen, X.-J.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Biallelic Mutations in MYORG Cause Autosomal Recessive Primary Familial Brain Calcification. Neuron 2018, 98, 1116–1123.e5.
- Legati, A.; Giovannini, D.; Nicolas, G.; López-Sánchez, U.; Quintáns, B.; Oliveira, J.R.M.; Sears, R.L.; Ramos, E.M.; Spiteri, E.; Sobrido, M.-J.; et al. Mutations in XPR1 Cause Primary Familial Brain Calcification Associated with Altered Phosphate Export. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 579–581.
- Nicolas, G.; Pottier, C.; Maltête, D.; Coutant, S.; Rovelet-Lecrux, A.; Legallic, S.; Rousseau, S.; Vaschalde, Y.; Guyant-Maréchal, L.; Augustin, J.; et al. Mutation of the PDGFRB Gene as a Cause of Idiopathic Basal Ganglia Calcification. Neurology 2013, 80, 181–187.
- Keller, A.; Westenberger, A.; Sobrido, M.J.; García-Murias, M.; Domingo, A.; Sears, R.L.; Lemos, R.R.; Ordoñez-Ugalde, A.; Nicolas, G.; da Cunha, J.E.G.; et al. Mutations in the Gene Encoding PDGF-B Cause Brain Calcifications in Humans and Mice. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1077–1082.
- Zhao, M.; Su, H.-Z.; Zeng, Y.-H.; Sun, Y.; Guo, X.-X.; Li, Y.-L.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Huang, X.-J.; Lin, K.-J.; et al. Loss of Function of CMPK2 Causes Mitochondria Deficiency and Brain Calcification. Cell. Discov. 2022, 8, 128.
- Balck, A.; Schaake, S.; Kuhnke, N.S.; Domingo, A.; Madoev, H.; Margolesky, J.; Dobricic, V.; Alvarez-Fischer, D.; Laabs, B.-H.; Kasten, M.; et al. Genotype-Phenotype Relations in Primary Familial Brain Calcification: Systematic MDSGene Review. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 2468–2480.
- Xu, X.; Sun, H.; Luo, J.; Cheng, X.; Lv, W.; Luo, W.; Chen, W.-J.; Xiong, Z.-Q.; Liu, J.-Y. The Pathology of Primary Familial Brain Calcification: Implications for Treatment. Neurosci. Bull. 2022, 39, 659–674.
- Jensen, N.; Schrøder, H.D.; Hejbøl, E.K.; Füchtbauer, E.-M.; de Oliveira, J.R.M.; Pedersen, L. Loss of Function of Slc20a2 Associated with Familial Idiopathic Basal Ganglia Calcification in Humans Causes Brain Calcifications in Mice. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 51, 994–999.
- Meek, R.W.; Brockerman, J.; Fordwour, O.B.; Zandberg, W.F.; Davies, G.J.; Vocadlo, D.J. The Primary Familial Brain Calcification-Associated Protein MYORG Is an α-Galactosidase with Restricted Substrate Specificity. PLoS Biol. 2022, 20, e3001764.
- Zhao, M.; Lin, X.-H.; Zeng, Y.-H.; Su, H.-Z.; Wang, C.; Yang, K.; Chen, Y.-K.; Lin, B.-W.; Yao, X.-P.; Chen, W.-J. Knockdown of Myorg Leads to Brain Calcification in Zebrafish. Mol. Brain 2022, 15, 65.
- Daneman, R.; Zhou, L.; Kebede, A.A.; Barres, B.A. Pericytes Are Required for Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity during Embryogenesis. Nature 2010, 468, 562–566.
- Anheim, M.; López-Sánchez, U.; Giovannini, D.; Richard, A.-C.; Touhami, J.; N’Guyen, L.; Rudolf, G.; Thibault-Stoll, A.; Frebourg, T.; Hannequin, D.; et al. XPR1 Mutations Are a Rare Cause of Primary Familial Brain Calcification. J. Neurol. 2016, 263, 1559–1564.
- Cen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Wang, L.; Tang, S.; Ye, J.; et al. Biallelic Loss-of-Function Mutations in JAM2 Cause Primary Familial Brain Calcification. Brain 2020, 143, 491–502.
- Tonduti, D.; Panteghini, C.; Pichiecchio, A.; Decio, A.; Carecchio, M.; Reale, C.; Moroni, I.; Nardocci, N.; Campistol, J.; Garcia-Cazorla, A.; et al. Encephalopathies with Intracranial Calcification in Children: Clinical and Genetic Characterization. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 135.
- Deng, H.; Zheng, W.; Jankovic, J. Genetics and Molecular Biology of Brain Calcification. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 22, 20–38.
- Lagrue, E.; Abe, H.; Lavanya, M.; Touhami, J.; Bodard, S.; Chalon, S.; Battini, J.-L.; Sitbon, M.; Castelnau, P. Regional Characterization of Energy Metabolism in the Brain of Normal and MPTP-Intoxicated Mice Using New Markers of Glucose and Phosphate Transport. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, 91.
- Steitz, S.A.; Speer, M.Y.; Curinga, G.; Yang, H.Y.; Haynes, P.; Aebersold, R.; Schinke, T.; Karsenty, G.; Giachelli, C.M. Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Transition Associated with Calcification: Upregulation of Cbfa1 and Downregulation of Smooth Muscle Lineage Markers. Circ. Res. 2001, 89, 1147–1154.
- Schaeffer, S.; Iadecola, C. Revisiting the Neurovascular Unit. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 1198–1209.
- Betsholtz, C.; Keller, A. PDGF, Pericytes and the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Basal Ganglia Calcification (IBGC). Brain Pathol. 2014, 24, 387–395.
- Jenkinson, E.M.; Rodero, M.P.; Kasher, P.R.; Uggenti, C.; Oojageer, A.; Goosey, L.C.; Rose, Y.; Kershaw, C.J.; Urquhart, J.E.; Williams, S.G.; et al. Mutations in SNORD118 Cause the Cerebral Microangiopathy Leukoencephalopathy with Calcifications and Cysts. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1185–1192.
- Meuwissen, M.E.C.; Schot, R.; Buta, S.; Oudesluijs, G.; Tinschert, S.; Speer, S.D.; Li, Z.; van Unen, L.; Heijsman, D.; Goldmann, T.; et al. Human USP18 Deficiency Underlies Type 1 Interferonopathy Leading to Severe Pseudo-TORCH Syndrome. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 1163–1174.
- Barth, P.G. The Neuropathology of Aicardi-Goutières Syndrome. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2002, 6 (Suppl. SA), A27–A31; discussion A37–A39, A77–A86.
- Livingston, J.; Doherty, D.; Orcesi, S.; Tonduti, D.; Piechiecchio, A.; La Piana, R.; Tournier-Lasserve, E.; Majumdar, A.; Tomkins, S.; Rice, G.; et al. COL4A1 Mutations Associated with a Characteristic Pattern of Intracranial Calcification. Neuropediatrics 2011, 42, 227–233.
- Wilson, B.T.; Stark, Z.; Sutton, R.E.; Danda, S.; Ekbote, A.V.; Elsayed, S.M.; Gibson, L.; Goodship, J.A.; Jackson, A.P.; Keng, W.T.; et al. The Cockayne Syndrome Natural History (CoSyNH) Study: Clinical Findings in 102 Individuals and Recommendations for Care. Genet. Med. 2016, 18, 483–493.
- Finsterer, J.; Kopsa, W. Basal Ganglia Calcification in Mitochondrial Disorders. Metab. Brain Dis. 2005, 20, 219–226.
- Giachelli, C.M. Ectopic calcification: Gathering hard facts about soft tissue mineralization. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 154, 671–675.
More
Information
Subjects:
Neurosciences; Pathology
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
1.5K
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
10 Aug 2023
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




