Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Julieta Mendoza-Torreblanca | -- | 2835 | 2023-06-20 20:19:06 | | | |
| 2 | Sirius Huang | Meta information modification | 2835 | 2023-06-21 11:15:44 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Bandala, C.; Cárdenas-Rodríguez, N.; Mendoza-Torreblanca, J.G.; Contreras-García, I.J.; Martínez-López, V.; Cruz-Hernández, T.R.; Carro-Rodríguez, J.; Vargas-Hernández, M.A.; Ignacio-Mejía, I.; Alfaro-Rodriguez, A.; et al. Dopamine and Related Drugs as Anti-Inflammatories and Antioxidants. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/45885 (accessed on 07 February 2026).
Bandala C, Cárdenas-Rodríguez N, Mendoza-Torreblanca JG, Contreras-García IJ, Martínez-López V, Cruz-Hernández TR, et al. Dopamine and Related Drugs as Anti-Inflammatories and Antioxidants. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/45885. Accessed February 07, 2026.
Bandala, Cindy, Noemi Cárdenas-Rodríguez, Julieta Griselda Mendoza-Torreblanca, Itzel Jatziri Contreras-García, Valentín Martínez-López, Teresita Rocio Cruz-Hernández, Jazmín Carro-Rodríguez, Marco Antonio Vargas-Hernández, Iván Ignacio-Mejía, Alfonso Alfaro-Rodriguez, et al. "Dopamine and Related Drugs as Anti-Inflammatories and Antioxidants" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/45885 (accessed February 07, 2026).
Bandala, C., Cárdenas-Rodríguez, N., Mendoza-Torreblanca, J.G., Contreras-García, I.J., Martínez-López, V., Cruz-Hernández, T.R., Carro-Rodríguez, J., Vargas-Hernández, M.A., Ignacio-Mejía, I., Alfaro-Rodriguez, A., & Lara-Padilla, E. (2023, June 20). Dopamine and Related Drugs as Anti-Inflammatories and Antioxidants. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/45885
Bandala, Cindy, et al. "Dopamine and Related Drugs as Anti-Inflammatories and Antioxidants." Encyclopedia. Web. 20 June, 2023.
Copy Citation
Dopamine (DA), its derivatives, and dopaminergic drugs are compounds widely used in the management of diseases related to the nervous system. However, DA receptors have been identified in nonneuronal tissues, which has been related to their therapeutic potential in pathologies such as sepsis or septic shock, blood pressure, renal failure, diabetes, and obesity, among others. In addition, DA and dopaminergic drugs have shown anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties in different kinds of cells.
dopamine
anti-inflammatory
antioxidant
antiangiogenic
antinociceptive
nonneurological disease
1. Introduction
Dopamine (DA) is a monoamine synthesized mainly in neurons of the midbrain cores, ventral tegmental area, and substantia nigra pars compacta. The synthesis of the neurotransmitter takes place in the dopaminergic nerves [1]. Hydroxylation of the amino acid L-tyrosine is the point of regulation of the synthesis of catecholamines, including DA, in the central nervous system (CNS), and consequently, the tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) enzyme is the limiting enzyme of the synthesis of DA, norepinephrine, and adrenaline. Through their receptors, DA has been shown to have physiological functions in the CNS, such as wakefulness, attention, memory formation and consolidation, novelty-induced memory encoding, and reward/addiction [2][3][4][5]. DA is a neuromodulator that has the ability to diffuse away from the site of its release, activating receptors that are far from the terminal; this ability is called transmission volume [2]. In this sense, DA receptors have been identified in nonneuronal tissues, which has been related to their therapeutic potential in pathologies such as sepsis or septic shock, blood pressure, renal failure, diabetes, and obesity, among others [6][7][8]. In addition, it has been reported that DA and dopaminergic drugs such as bromocriptine, cabergoline, pramipexole, and ropinirole have shown anti-inflammatory and antioxidant functions in different kinds of cells, reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation, preserving glutathione (GSH) and other antioxidant enzymes, and decreasing lipid peroxidation [9][10][11][12][13][14]. Additionally, some herbal compounds have shown dopaminergic properties; for example, Hepad S1, a Korean medicinal herbal combination, is an important source of dopamine with neuroprotective properties that improve Parkinson’s symptoms; it could modulate adverse cellular events such as inflammation and oxidation in neuronal cells [15]. Curcumine has shown neuroprotective properties and is an important component of dopamine [16], and Hordenine, a natural compound of germinated barley, is an agonist of the dopamine D2 receptor [17]. These and other herbs have been mainly studied in neuronal diseases, with less research in nonneuronal diseases.
2. Dopamine Synthesis, Release, Catabolism, and Postsynaptic Action
This section describes DA and its pharmacological properties at the molecular level. The synthesis of DA (Figure 1) begins with the hydroxylation of L-tyrosine by the TH enzyme to generate L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA); then, aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC or DOPA decarboxylase) allows the production of cytosolic dopamine [18][19][20]. The DA synthesized in the presynaptic terminal is loaded in synaptic vesicles by vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT-2); subsequently, DA is released to the synaptic cleft. Next, the Na+-dependent dopamine transporter (DAT), localized in neurons and glial cells, reuptakes the neurotransmitter [18]. DA is recycled into synaptic vesicles or degraded by specialized enzymes [21], where its catabolism takes place. In presynaptic terminal and glial cells, the monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzyme, localized in mitochondria, breaks down DA through oxidative deamination, producing 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (DOPAL); in turn, aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) converts DOPAL to carboxylic acid 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) by oxidation, or alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) reduces DOPAL to 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethanol (DOPET) [20][22]. The catechol O-methyl-transferase (COMT) enzyme, localized in the synaptic cleft, catalyzes the methylation of dopamine to 3-methoxytyramine (3-MT), which is a MAO substrate that forms 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (HMPAL). Finally, the ALDH enzyme catalyzes HMPAL to generate homovanillic acid (HVA), which is the main end-product of DA degradation [20][22][23]. At the post-synapse, DA binds to D1-like and D2-like receptors, which are G-protein-coupled channels [24]. The D1-like receptor activates the Gαs/olf subunit protein that stimulates the adenylyl cyclase (AC) protein; then, it generates the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) second messenger, which activates protein kinase A (PKA), resulting in target action and increasing protein phosphorylation. On the other hand, the D2-like receptor, by activating the Gαi/o subunit, inhibits the effector protein AC, inhibiting the cAMP second messenger and, thereby, PKA, generating a decrease in protein phosphorylation [18][24][25][26].
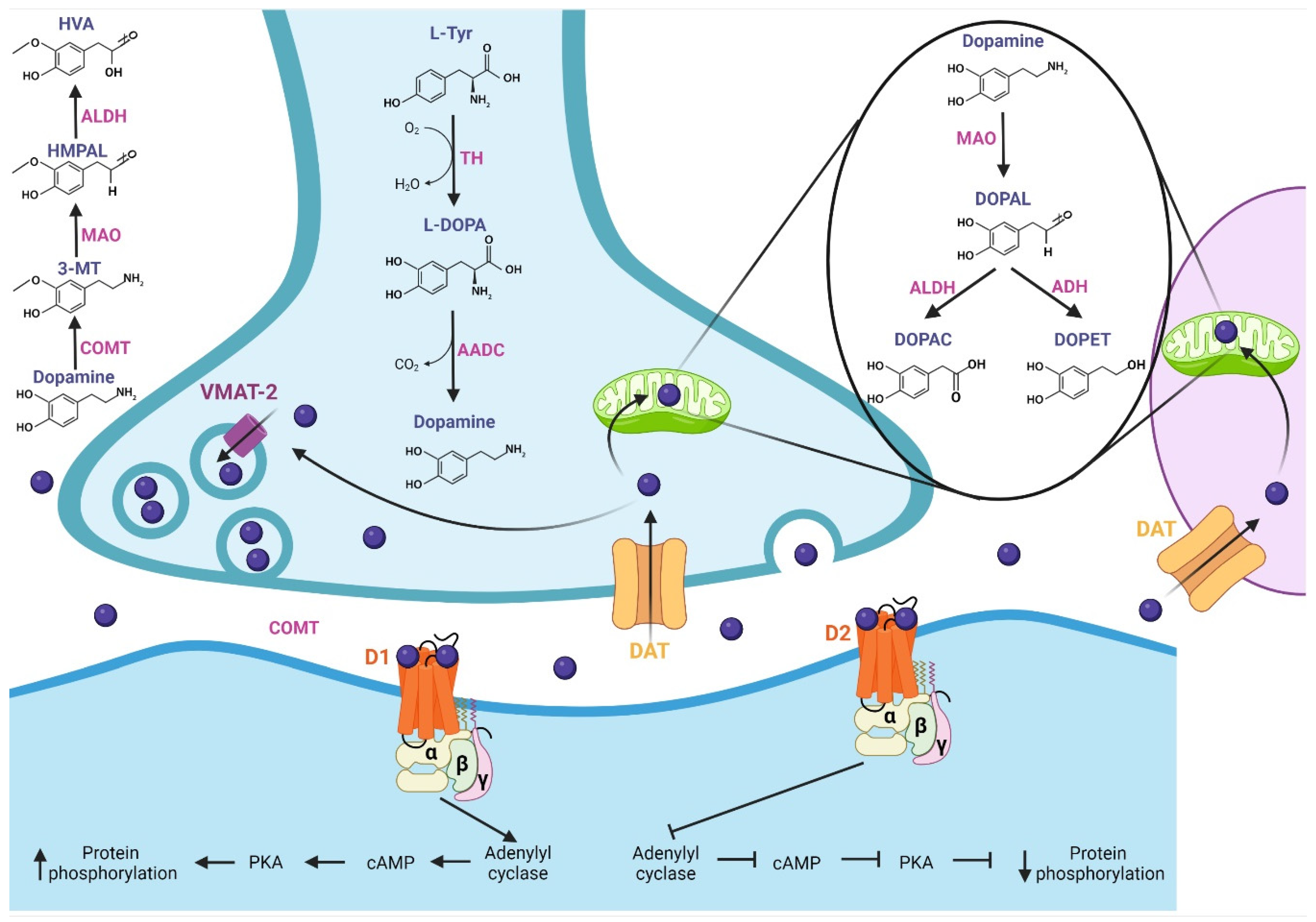
Figure 1. Synthesis, release, catabolism, and postsynaptic action of dopamine. Synthesis: The TH enzyme converts L-tyrosine to L-DOPA; then, the AADC enzyme allows the production of dopamine, which is loaded into synaptic vesicles by VMAT-2. Release and recycling: once released in the synaptic cleft, the DAT transporter reuptakes dopamine, which is recycled into synaptic vesicles. Catabolism: Dopamine is degraded by specialized enzymes; the MAO enzyme breaks down dopamine to DOPAC and DOPET. In the synaptic cleft, the COMT enzyme catalyzes dopamine to HVA, which is the main end-product of dopamine degradation. At the post-synapse, dopamine binds with D1-like and D2-like receptors. The D1-like receptor activates the Gαs/olf subunit, which stimulates adenylyl cyclase protein, increasing protein phosphorylation. D2-like receptor, by activating the Gαi/o subunit, inhibits the protein adenylyl cyclase, generating a decrease in protein phosphorylation. TH: tyrosine hydroxylase, L-DOPA: L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, AADC: L-amino acid decarboxylase, VMAT-2: vesicular monoamine transporter 2, DAT: dopamine transporter, MAO: monoamine oxidase, DOPAL: 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde, ALDH: aldehyde dehydrogenase, DOPAC: 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, ADH: alcohol dehydrogenase, DOPET: 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethanol, COMT: catechol O-methyl-transferase, HMPAL: 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde, HVA: homovanillic acid.
3. Chemical Compounds and Drugs Related to the Dopaminergic System
There are more than 200 chemical compounds and drugs related to the dopaminergic system [27][28][29], and mentioning each of them is beyond the scope of this discussion; however, they can be grouped, according to their activity, as precursors [30][31][32][33], agonists and antagonists of receptors [34], DA reuptake inhibitors [35][36] DA releasing agents [36][37], activity enhancers [38][39][40], and enzyme inhibitors [41], among others. Three DA precursors are used in the clinic, L-phenylalanine, L-tyrosine, and L-DOPA; tyrosine is a nonessential amino acid that is synthesized from the essential aromatic amino acid phenylalanine, and both amino acids constitute the two initial steps in the biosynthesis of DA [31]. Levodopa (L-DOPA) is a dopamine precursor and is the most effective and commonly used drug for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Levodopa is prescribed in most cases with Carbidopa, which is an inhibitor of L-amino acid decarboxylase, the enzyme that metabolizes levodopa peripherally [42].
DA agonists exert their effects by acting directly on dopamine receptors and mimicking endogenous neurotransmitters. There are two subclasses, ergoline, and nonergoline agonists, with a variable affinity for different DA receptors [43][44]. DA antagonists block the effects of dopamine or its agonists by binding to DA receptors. A variety of DA antagonists are used for the treatment of psychotic disorders; however, their therapeutic effects are mostly due to long-term adjustments rather than acute blockade of DA receptors [29]. Some DA antagonists have been used to treat Tourette’s syndrome or hiccups [45][46], and they have also been used as antiemetics to treat various causes of nausea and vomiting [47]. Table 1 details the mechanisms of action and indications of DA precursors and the most representative dopaminergic agonist and antagonist drugs.
Table 1. Mechanism of action and indications of dopamine precursors and dopaminergic agonist and antagonist drugs.
| Drug | Mechanism of Action | Indications |
|---|---|---|
| Precursors | ||
| Levodopa (L-DOPA) | Levodopa mimics the role of endogenous dopamine; crosses the blood–brain barrier through various pathways, and is decarboxylated to form dopamine stimulating the dopamine receptors | Parkinson’s disease [29][30] |
| L-phenylalanine | Precursor of tyrosine, dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) | Antidepressant effects Vitiligo [31][32] |
| L-tyrosine | Precursor of dopamine, norepinephrine and epinephrine |
Antidepressant [31][33] |
| Receptor agonists | ||
| Apomorphine | A nonergoline dopamine agonist with binding affinity to dopamine D2, D3, and D5 receptors | Parkinson’s disease [29][42][48] |
| Bromocriptine | Ergoline derivative with strong agonist activity on the D2 dopamine receptors | Parkinsonian Syndrome Amenorrhea Galactorrhea Acromegaly Premenstrual syndrome Female infertility [29][42] |
| Cabergoline | Ergoline derivative; dopamine agonist (with a high affinity for D2 receptors) and prolactin inhibitor. | Hyperprolactinemic disorders. Parkinsonian Syndrome [29][49][50] |
| DA | Agonist to the D1, D2, D3, D4, D5 dopamine receptors. Interacts on the synaptic terminals, causing neuronal excitation or inhibition at the target neuron | Hemodynamic imbalances Blood pressure Hypotension Poor perfusion of vital organs Low cardiac output [29][51] |
| Fenoldopam | Benzazepine derivative; selective dopamine D1 receptor agonist. Decreases peripheral vascular resistance in renal capillary beds | Hypertension [29][52] |
| Lisuride | Ergoline derivative, agonist to dopamine D2 receptors. It can be an antagonist to dopamine D1 receptors. Additionally, activates some serotonin receptors | Parkinson’s disease [27][29] |
| Piribedil | Nonergoline, piperazine derivative, dopamine agonist that acts on D2 and D3 receptors | Parkinson’s disease [53] |
| Pramipexole | Nonergoline, a dopamine agonist showing specificity and strong activity at dopamine D2 receptors | Parkinson’s disease Restless legs syndrome [54][55] |
| Quinagolide | Nonergoline derivative; it selectively binds to D2 receptors on the surface of lactotroph cells, resulting in reduced adenylyl cyclase activity and inhibition of prolactin secretion from the anterior pituitary | Hyperprolactinemia [27][29] |
| Ropinirole | Nonergoline derivative, selectively binds to dopamine D2 receptors, with highest affinity at D3 receptors | Parkinson’s disease Restless legs syndrome [56][57] |
| Rotigotine | Nonergoline derivative; a nonselective agonist of dopamine receptors with higher affinity at D3 receptors | Parkinson’s disease Restless legs syndrome [29][42] |
| Experimental agonists | ||
| Dihydrexidine (LS-186,899) | Selective full agonist at the dopamine D1 receptors. It has some affinity for the D2 receptor | Scientific research [58][59] |
| Pukateine | Aporphine derivative; agonist at the D2 dopamine receptor and antagonist at the α1 adrenergic receptor | Scientific research [60][61] |
| Quinpirole | Selective D2 and D3 receptor agonist | Scientific research [62][63] |
| SKF 38393 | A selective D1-like receptor agonist | Scientific research [64] |
| Antagonists and receptor blockers | ||
| Typical antipsychotics | ||
| Chlorpromazine | Phenothiazine derivative. It binds strongly to the D2 receptor, blocking its action; this blockade, in the nigrostriatal pathway, is responsible for its extrapyramidal side effects | Schizophrenia, Bipolar disorder Acute psychosis, Nausea and vomiting Relief of apprehension before surgery Persistent singultus (chronic hiccups) [29][46][65] |
| Fluphenazine | Phenothiazine derivative. Blocks postsynaptic mesolimbic dopaminergic D2 receptors in the brain | Management of psychosis in schizophrenia [29][66] |
| Haloperidol | It is a first-generation antipsychotic and one of the most frequently used worldwide. It is not selective for the D2 receptor, but, has a strong antagonism to this dopamine receptor in mesolimbic and mesocortical pathways in the brain | Schizophrenia Tourette syndrome Behavioral disorders in children Hyperactivity [29][45] |
| Loxapine | Dibenzoazepine tricyclic derivative. Antagonist with high affinity for the D2 receptor, also a serotonin 5-HT2 blocker | Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders [27][67] |
| Molindone | Indole derivative. Antagonizes dopamine D2 receptor sites in the reticular limbic systems in the brain, decreasing dopamine activity | Schizophrenia [27][29] |
| Perphenazine | Phenothiazine derivative. It binds to the dopamine D1 and dopamine D2 receptors inhibiting their activity. Its antiemetic effect is mainly due to blockade of D2 receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone and the vomiting center | Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders Nausea and vomiting [27][29] |
| Pimozide | Diphenylbutylpiperidine derivative. It binds and inhibits the dopamine D2 receptor | Tourette syndrome Schizophrenia [27][42] |
| Thioridazine | Phenothiazine derivative. It blocks postsynaptic mesolimbic dopaminergic D1 and D2 receptors | Schizophrenia Other psychotic disorders Generalized anxiety disorder Depressive disorders [27][68] |
| Thiothixene | Thioxanthene derivative. Is a highly potent antagonist of the D1, D2, D3 and D4 dopamine receptors. | Schizophrenia [27][29] |
| Atypical antipsychotics | ||
| Amisulpride | Benzamide derivative. It is a selective dopamine D2 and D3 receptor antagonist | Schizophrenia Nausea and vomiting [27][29] |
| Clozapine | Dibenzodiazepine derivative. It binds to the D4 dopamine receptors with a higher affinity than D2 receptor. Additionally, it has antagonistic effects at 5-HT2A receptors and is a partial agonist at 5-HT1A receptors | Resistant schizophrenia [27][69] |
| Olanzapine | Thienobenzodiazepine derivative. It exerts its action primarily on dopamine D1, D2, D3 and D4 and serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C, 5-HT3 and 5-HT6 receptors, blocking their action | Schizophrenia, Bipolar disorder [27][70] |
| Quetiapine | Thiazepine derivative. Antagonizes to D2 dopamine receptors and to 5-HT2A receptors (it has strong affinity for the latter) | Schizophrenia Bipolar disorder Major depressive disorder [27][71] |
| Risperidone | Benzisoxazole derivative. It blocks D2, but more 5-HT2A receptors in the brain. | Schizophrenia, Bipolar mania Autism-associated irritability [29][72] |
| Sulpiride | Benzamide derivative. Selective antagonist at dopamine D2, D3 receptors | Schizophrenia [27][29] |
| Ziprasidone | Benzothiazolylpiperazine derivative. Binds to 5-HT2A and dopamine D2 receptors with high affinity | Schizophrenia Bipolar mania Acute agitation in schizophrenic patients [29][73] |
| Antiemetics | ||
| Domperidone | Benzimidazole derivative. It has strong affinity for the D2 and D3 dopamine receptors, blocking their activity | Peristaltic stimulant, Dyspepsia, Indigestion, Epigastric pain Nausea and vomiting [27][29][74] |
| Metoclopramide | Benzamide derivative. Inhibit dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT3 receptors | Nausea and vomiting Gastroesophageal reflux disease [29][75] |
| Prochlorperazine | Phenothiazine derivative. It mainly blocks the D2 dopamine receptors in the mesolimbic system | Schizophrenia, Schizoaffective Other conditions with psychosis symptoms Nausea and vomiting [29][76] |
| Experimental antagonists | ||
| Eticlopride | Antagonizes D2 dopamine receptor | Scientific research [77] |
| Raclopride | Potent and selective antagonist on D2/D3 dopamine receptors | Trials studying Parkinson’s disease [29][78] |
| SCH23390 | Highly potent and selective of D1 dopamine receptor | Scientific research of drug addiction [79] |
On the other hand, DA reuptake inhibitors may be classified as DAT inhibitors and VMAT inhibitors. The former block the action of DAT, and DA reuptake inhibition occurs when extracellular DA, which does not bind to the postsynaptic neuron, is blocked from re-entering the presynaptic neuron, resulting in increased extracellular concentrations of DA and an increase in dopaminergic neurotransmission [80]. DAT inhibitors are indicated for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, major depressive disorder, and seasonal affective disorder and as an aid to smoking cessation; examples are methylphenidate [27][29]. On the other hand, VMAT inhibitors prevent the reuptake and storage of monoamine neurotransmitters in synaptic vesicles, making them vulnerable to metabolism by cytosolic enzymes. Inhibition of VMAT-2 results in decreased reuptake of monoamines and depletion of their reserves in nerve terminals. They are used to treat chorea due to neurodegenerative diseases or dyskinesias due to neuroleptic medications; examples are tetrabenazine, deutetrabenazine, and valbenazine [27][42][81][82][83].
DA-releasing agents are a type of drug that induces, through various mechanisms, the release of DA from the presynaptic neuron into the synaptic cleft, leading to an increase in extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitter. Examples are amphetamine, lisdexamfetamine (L-lysine-d-amphetamine; vyvanse), methamphetamine, methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), and 4-methylaminorex [27][84][85][86][87]. Moreover, (-)1-(benzofuran-2-yl)-2-propylaminopentane, (-)BPAP, (-)-1-phenyl-2-propylaminopentane, and (-)PPAP are enhancers of dopamine activity. BPAP and PPAP act as potent stimulants of neurotransmitter release in dopaminergic neurons, leaving MAO activity largely unchanged. BPAP and PPAP controllably increase the quantity of neurotransmitters that are released when a neuron is stimulated by a neighboring neuron, and they are currently in the research phase [39][88][89].
DA enzyme inhibitors can be classified into DA synthesis inhibitors and DA degradation inhibitors. There are three kinds of dopamine synthesis inhibitors: (1) TH inhibitors (for example, 3-iodo-tyrosine and metyrosine), which are able to inhibit TH activity, the rate-limiting enzyme in DA biosynthesis [90]; (2) phenylalanine hydroxylase inhibitors (for example, 3,4-dihydroxystyrene), which inhibit the enzyme that converts phenylalanine to tyrosine [91]; and (3) DOPA decarboxylase inhibitors, which block the biosynthesis of L-DOPA to DA. Examples of these inhibitors are benserazide and carbidopa, commonly used in combination with levodopa. Since they can hardly cross the blood–brain barrier, they prevent the formation of dopamine in extracerebral tissues, minimizing the occurrence of extracerebral side effects [92][93].
Finally, the main DA degradation inhibitors can be classified into MAO and COMT inhibitors. The most prescribed MAO inhibitors are selegiline, isocarboxazid, phenelzine, and tranylcypromine. They have in common the ability to block oxidative deamination of DA and subsequently provoke its elevation in brain levels, enhancing dopaminergic activity [29][94]. Selegiline is close structurally to (-) methamphetamine and is a selective and irreversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase type B (MAO-B). Selegiline is the first catecholaminergic activity-enhancing substance in clinical use that does not continually release catecholamines and is, therefore, free of amphetamine dependence [38][40]. Likewise, the most common COMT inhibitors are entacapone, opicapone, and tolcapone. They inhibit the COMT enzyme and are frequently used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease as an adjunct to levodopa/carbidopa medication [95][96][97]. Many Parkinson’s disease patients treated with levodopa plus carbidopa experience motor complications over time; when COMT inhibitors are administered, plasma levodopa levels are increased and maintained, resulting in more consistent dopaminergic stimulation, leading to further reduction of the manifestations of parkinsonian syndrome [98].
In summary, dopaminergic compounds and drugs act through a variety of mechanisms of action within the process of synthesis, release, catabolism, and postsynaptic action of dopamine, as shown in Figure 2. It should be noted that these main mechanisms are often accompanied by secondary mechanisms (such as antioxidant or anti-inflammatory mechanisms, see below, which are not yet fully understood) that give a wide variety of effects and indications as potential adjuvants in most chronic and degenerative diseases.
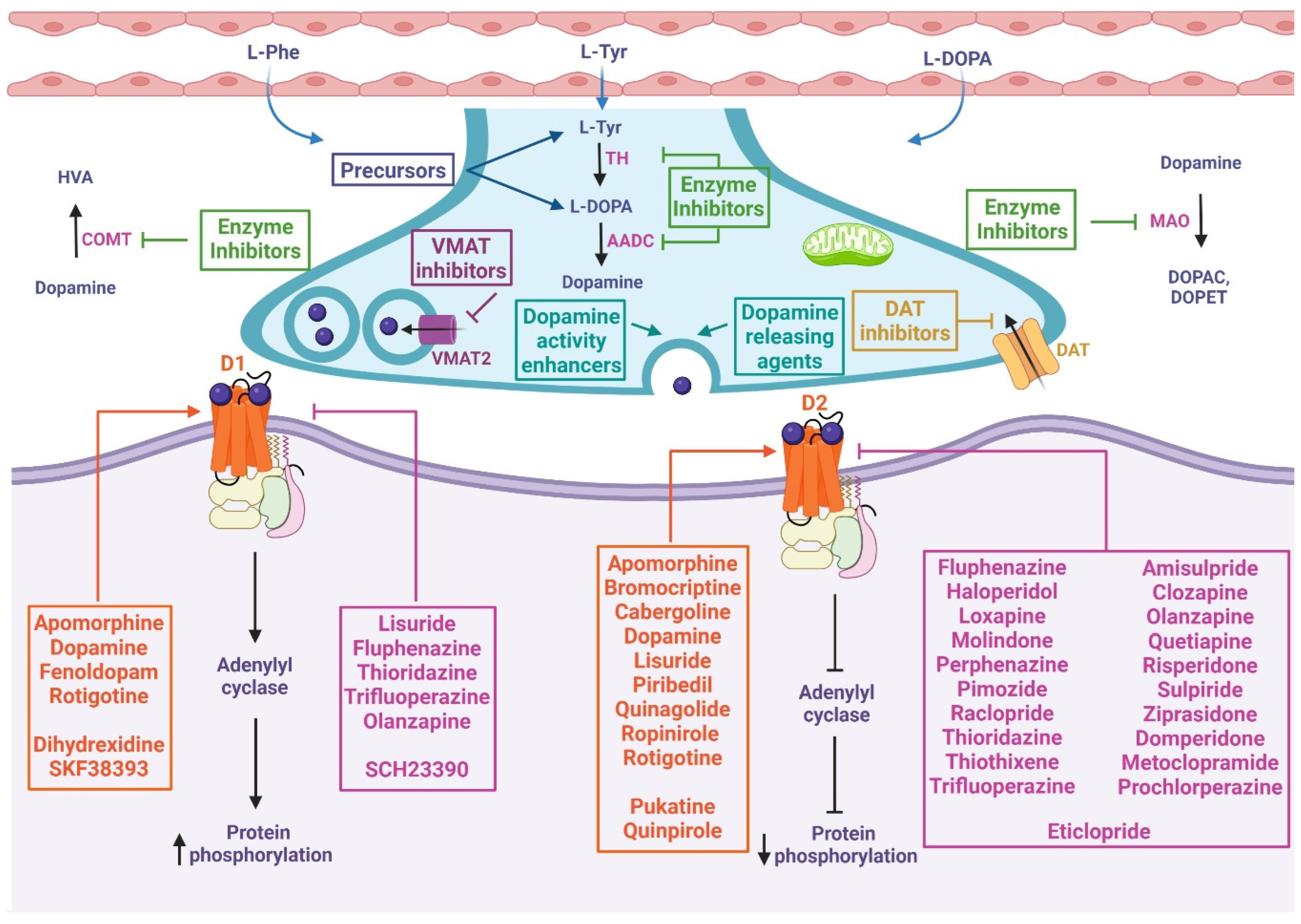
Figure 2. Mechanism of action of chemical compounds and drugs related to the dopaminergic system. These drugs can inhibit or activate diverse proteins involved in dopamine metabolism, including precursors, enzyme inhibitors, dopamine-releasing agents, dopamine reuptake inhibitors, dopamine activity enhancers, and agonists or antagonists of D1-like and D2-like receptors. At presynapses: The precursors enable the biosynthesis of dopamine. VMAT inhibitors prevent the storage of monoamines in synaptic vesicles, resulting in the depletion of these neurotransmitters. DAT inhibitors keep dopamine in the synaptic cleft longer by inhibiting its reuptake. Dopamine-releasing agents and dopamine activity enhancers increase the release of the activity of dopamine into the synaptic cleft. Dopamine synthesis inhibitors prevent the formation of dopamine as an endpoint. Dopamine degradation inhibitors enhance dopaminergic activity by blocking dopamine catabolism. At postsynapses: The dopamine agonist (orange box) mimics endogenous dopamine function, thus activating or inhibiting adenylyl cyclase depending on whether it binds to D1-like or D2-like receptors, respectively. Dopamine antagonists (pink box) bind to but do not activate dopamine receptors, thereby blocking the actions of dopamine. L-Phe: L-phenylalanine, L-Tyr: L-tyrosine, TH: tyrosine hydroxylase, L-DOPA: L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, AADC: L-amino acid decarboxylase, VMAT2: vesicular monoamine transporter 2, DAT: dopamine transporter, MAO: monoamine oxidase, DOPAC: 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, DOPET: 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethanol, COMT: catechol O-methyl-transferase, HVA: homovanillic acid, D1: dopamine 1 receptor, D2: dopamine 2 receptor.
References
- Poulin, J.F.; Caronia, G.; Hofer, C.; Cui, Q.; Helm, B.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Chan, C.S.; Dombeck, D.A.; Deisseroth, K.; Awatramani, R. Mapping Projections of Molecularly Defined Dopamine Neuron Subtypes Using Intersectional Genetic Approaches. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1260–1271.
- Ranjbar-Slamloo, Y.; Fazlali, Z. Dopamine and Noradrenaline in the Brain; Overlapping or Dissociate Functions? Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 12, 334.
- Eban-Rothschild, A.; Rothschild, G.; Giardino, W.J.; Jones, J.R.; Lecea, L. de VTA Dopaminergic Neurons Regulate Ethologically Relevant Sleep-Wake Behaviors. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1356–1366.
- Yamasaki, M.; Takeuchi, T. Locus Coeruleus and Dopamine-Dependent Memory Consolidation. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 8602690.
- Cox, J.; Witten, I.B. Striatal Circuits for Reward Learning and Decision-Making. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 482–494.
- Luo, S.; Ezrokhi, M.; Cominos, N.; Tsai, T.H.; Stoelzel, C.R.; Trubitsyna, Y.; Cincotta, A.H. Experimental Dopaminergic Neuron Lesion at the Area of the Biological Clock Pacemaker, Suprachiasmatic Nuclei (SCN) Induces Metabolic Syndrome in Rats. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 13, 11.
- De Donato, A.; Buonincontri, V.; Borriello, G.; Martinelli, G.; Mone, P. The Dopamine System: Insights between Kidney and Brain. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2022, 47, 493–505.
- Nissimov, S.; Joye, S.; Kharrat, A.; Zhu, F.; Ripstein, G.; Baczynski, M.; Choudhury, J.; Jasani, B.; Deshpande, P.; Ye, X.Y.; et al. Dopamine or Norepinephrine for Sepsis-Related Hypotension in Preterm Infants: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022.
- Yoshikawa, T.; Minamiyama, Y.; Naito, Y.; Kondo, M. Antioxidant Properties of Bromocriptine, a Dopamine Agonist. J. Neurochem. 1994, 62, 1034–1038.
- Yoshioka, M.; Tanaka, K.; Miyazaki, I.; Fujita, N.; Higashi, Y.; Asanuma, M.; Ogawa, N. The Dopamine Agonist Cabergoline Provides Neuroprotection by Activation of the Glutathione System and Scavenging Free Radicals. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 43, 259–267.
- Le, W.D.; Jankovic, J.; Xie, W.; Appel, S.H. Antioxidant Property of Pramipexole Independent of Dopamine Receptor Activation in Neuroprotection. J. Neural Transm. 2000, 107, 1165–1173.
- Jr, J.P.B.; Piercey, M.F. Pramipexole—A New Dopamine Agonist for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 1999, 163, 25–31.
- Ferger, B.; Teismann, P.; Mierau, J. The Dopamine Agonist Pramipexole Scavenges Hydroxyl Free Radicals Induced by Striatal Application of 6-Hydroxydopamine in Rats: An in Vivo Microdialysis Study. Brain Res. 2000, 883, 216–223.
- Iida, M.; Miyazaki, I.; Tanaka, K.; Kabuto, H.; Iwata-Ichikawa, E.; Ogawa, N. Dopamine D2 Receptor-Mediated Antioxidant and Neuroprotective Effects of Ropinirole, a Dopamine Agonist. Brain Res. 1999, 838, 51–59.
- Kim, D.H.; Choi, J.J.; Park, B.-J. Herbal Medicine (Hepad) Prevents Dopaminergic Neuronal Death in the Rat MPTP Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Integr. Med. Res. 2019, 8, 202–208.
- Zakaria, H.; El Kurdi, R.; Patra, D. Curcumin-PLGA Based Nanocapsule for the Fluorescence Spectroscopic Detection of Dopamine. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 28245–28253.
- Sommer, T.; Göen, T.; Budnik, N.; Pischetsrieder, M. Absorption, Biokinetics, and Metabolism of the Dopamine D2 Receptor Agonist Hordenine (N,N-Dimethyltyramine) after Beer Consumption in Humans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1998–2006.
- Purves, D.; Augustine, G.J.; Fitzpatrick, D.; Hall, W.; Lamantia, A.S.; McNamara, J.O.; Williams, S.M. Neurotransmitters and Their Receptors. In Neuroscience; Sinauer Associates, Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 129–163.
- Best, J.A.; Nijhout, H.F.; Reed, M.C. Homeostatic Mechanisms in Dopamine Synthesis and Release: A Mathematical Model. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2009, 6, 21.
- Meiser, J.; Weindl, D.; Hiller, K. Complexity of Dopamine Metabolism. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 11, 34.
- Graves, S.M.; Xie, Z.; Stout, K.A.; Zampese, E.; Burbulla, L.F.; Shih, J.C.; Kondapalli, J.; Patriarchi, T.; Tian, L.; Brichta, L.; et al. Dopamine Metabolism by a Monoamine Oxidase Mitochondrial Shuttle Activates the Electron Transport Chain. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 15–20.
- Kamal, S.; Lappin, S.L. Biochemistry, Catecholamine Degradation; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545235/ (accessed on 7 November 2022).
- Muñoz, P.; Huenchuguala, S.; Paris, I.; Segura-Aguilar, J. Dopamine Oxidation and Autophagy. Park. Dis. 2012, 2012, 920953.
- Hasbi, A.; O’Dowd, B.F.; George, S.R. Dopamine D1-D2 Receptor Heteromer Signaling Pathway in the Brain: Emerging Physiological Relevance. Mol. Brain 2011, 4, 26.
- Ledonne, A.; Mercuri, N.B. Current Concepts on the Physiopathological Relevance of Dopaminergic Receptors. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 27.
- Boyd, K.N.; Mailman, R.B. Dopamine Receptor Signaling and Current and Future Antipsychotic Drugs. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2012, 212, 53–86.
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/#query= (accessed on 7 November 2022).
- National Library of Medicine. National Center for Biotechnology Information. STATPEARLS. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430685/ (accessed on 7 November 2022).
- DRUGBANK Online. Available online: https://go.drugbank.com/ (accessed on 7 November 2022).
- Gandhi, K.R.; Saadabadi, A. Levodopa (L-Dopa). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482140/ (accessed on 7 November 2022).
- Daubner, S.C.; Le, T.; Wang, S. Tyrosine Hydroxylase and Regulation of Dopamine Synthesis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 508, 1–12.
- Gianfaldoni, S.; Tchernev, G.; Lotti, J.; Wollina, U.; Satolli, F.; Rovesti, M.; França, K.; Lotti, T. Unconventional Treatments for Vitiligo: Are They (Un) Satisfactory? Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 170–175.
- Alabsi, A.; Khoudary, A.C.; Abdelwahed, W. The Antidepressant Effect of L-Tyrosine-Loaded Nanoparticles: Behavioral Aspects. Ann. Neurosci. 2016, 23, 89–99.
- Beaulieu, J.M.; Gainetdinov, R.R. The Physiology, Signaling, and Pharmacology of Dopamine Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 182–217.
- German, C.L.; Baladi, M.G.; McFadden, L.M.; Hanson, G.R.; Fleckenstein, A.E. Regulation of the Dopamine and Vesicular Monoamine Transporters: Pharmacological Targets and Implications for Disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 1005–1024.
- Walker, Q.D.; Morris, S.E.; Arrant, A.E.; Nagel, J.M.; Parylak, S.; Zhou, G.; Caster, J.M.; Kuhn, C.M. Dopamine Uptake Inhibitors but Not Dopamine Releasers Induce Greater Increases in Motor Behavior and Extracellular Dopamine in Adolescent Rats than in Adult Male Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 335, 124–132.
- Gruner, J.A.; Marcy, V.R.; Lin, Y.G.; Bozyczko-Coyne, D.; Marino, M.J.; Gasior, M. The Roles of Dopamine Transport Inhibition and Dopamine Release Facilitation in Wake Enhancement and Rebound Hypersomnolence Induced by Dopaminergic Agents. Sleep 2009, 32, 1425–1438.
- Knoll, J. (-)Deprenyl (Selegiline), a Catecholaminergic Activity Enhancer (CAE) Substance Acting in the Brain. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1998, 82, 57–66.
- Harsing, L.G.; Knoll, J.; Miklya, I. Enhancer Regulation of Dopaminergic Neurochemical Transmission in the Striatum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8543.
- Knoll, J. (-) Deprenyl (Selegiline): Past, Present and Future. Neurobiology (Bp. Hung.) 2000, 8, 179–199.
- Finberg, J.P.M. Inhibitors of MAO-B and COMT: Their Effects on Brain Dopamine Levels and Uses in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neural. Transm. 2019, 126, 433–448.
- Parkinson Disease Agents. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury . Parkinson Disease Agents. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548855/ (accessed on 7 November 2022).
- Reichmann, H.; Bilsing, A.; Ehret, R.; Greulich, W.; Schulz, J.B.; Schwartz, A.; Rascol, O. Ergoline and Non-Ergoline Derivatives in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurol. 2006, 253 (Suppl. 4), iv36–iv38.
- Choi, J.; Horner, K.A. Dopamine Agonists. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551686/ (accessed on 8 November 2022).
- Rahman, S.; Marwaha, R. Haloperidol. StatPearls . Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560892/ (accessed on 8 November 2022).
- Mann, S.K.; Marwaha, R. Chlorpromazine. StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553079/ (accessed on 8 November 2022).
- Athavale, A.; Athavale, T.; Roberts, D.M. Antiemetic Drugs: What to Prescribe and When. Aust. Prescr. 2020, 43, 49–56.
- Carbone, F.; Djamshidian, A.; Seppi, K.; Poewe, W. Apomorphine for Parkinson’s Disease: Efficacy and Safety of Current and New Formulations. CNS Drugs 2019, 33, 905–918.
- Colao, A.; Lombardi, G.; Annunziato, L. Cabergoline. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2000, 1, 555–574.
- Curran, M.P.; Perry, C.M. Cabergoline: A Review of Its Use in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Drugs 2004, 64, 2125–2141.
- Sonne, J.; Goyal, A.; Lopez-Ojeda, W. Dopamine. . In StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535451/ (accessed on 8 November 2022).
- Szymanski, M.W.; Richards, J.R. Fenoldopam. . In StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526058/ (accessed on 8 November 2022).
- Peihua, L.; Jianqin, W. Clinical Effects of Piribedil in Adjuvant Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Open Med. 2018, 13, 270–277.
- Li, T.; Zou, S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, M.; Liang, Z. Efficacy of Pramipexole on Quality of Life in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Neurol. 2022, 22, 320.
- Singh, R.; Parmar, M. Pramipexole. . In StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557539/ (accessed on 8 November 2022).
- Rewane, A.; Nagalli, S. Ropinirole. . In StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554532/ (accessed on 8 November 2022).
- Shill, H.A.; Stacy, M. Update on Ropinirole in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2008, 5, 33–36.
- Salmi, P.; Isacson, R.; Kull, B. Dihydrexidine—The First Full Dopamine D1 Receptor Agonist. CNS Drug Rev. 2004, 10, 230–242.
- Mailman, R.B.; Yang, Y.; Huang, X. D1, Not D2, Dopamine Receptor Activation Dramatically Improves MPTP-Induced Parkinsonism Unresponsive to Levodopa. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 892, 173760.
- Dajas-Bailador, F.A.; Asencio, M.; Bonilla, C.; Scorza, M.C.; Echeverry, C.; Reyes-Parada, M.; Silveira, R.; Protais, P.; Russell, G.; Cassels, B.K.; et al. Dopaminergic Pharmacology and Antioxidant Properties of Pukateine, a Natural Product Lead for the Design of Agents Increasing Dopamine Neurotransmission. Gen. Pharmacol. 1999, 32, 373–379.
- Dalefield, R. Veterinary Toxicology for Australia and New Zealand; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017.
- Boulougouris, V.; Castañé, A.; Robbins, T.W. Dopamine D2/D3 Receptor Agonist Quinpirole Impairs Spatial Reversal Learning in Rats: Investigation of D3 Receptor Involvement in Persistent Behavior. Psychopharmacology 2009, 202, 611–620.
- Van Reij, R.R.I.; Salmans, M.M.A.; Eijkenboom, I.; van den Hoogen, N.J.; Joosten, E.A.J.; Vanoevelen, J.M. Dopamine-Neurotransmission and Nociception in Zebrafish: An Anti-Nociceptive Role of Dopamine Receptor Drd2a. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 912, 174517.
- Tobaldini, G.; Reis, R.A.; Sardi, N.F.; Lazzarim, M.K.; Tomim, D.H.; Lima, M.M.S.; Fischer, L. Dopaminergic Mechanisms in Periaqueductal Gray-Mediated Antinociception. Behavioral. Pharmacol. 2018, 29, 225–233.
- Seeman, M.V. History of the Dopamine Hypothesis of Antipsychotic Action. World J. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 355–364.
- Siragusa, S.; Bistas, K.G.; Saadabadi, A. Fluphenazine. . In StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL). 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459194/ (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Popovic, D.; Nuss, P.; Vieta, E. Revisiting Loxapine: A Systematic Review. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2015, 14, 15.
- Feinberg, S.M.; Fariba, K.A.; Saadabadi, A. Thioridazine. . In StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459140/ (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Haidary, H.A.; Padhy, R.K. Clozapine. . In StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535399/ (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Thomas, K.; Saadabadi, A. Olanzapine. . In StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532903/ (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Maan, J.S.; Ershadi, M.; Khan, I.; Saadabadi, A. Quetiapine. . In StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459145/ (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- McNeil, S.E.; Gibbons, J.R.; Cogburn, M. Risperidone. . In StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459313/ (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Bouchette, D.; Fariba, K.A.; Marwaha, R. Ziprasidone. . In StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448157/ (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Reddymasu, S.C.; Soykan, I.; McCallum, R.W. Domperidone: Review of Pharmacology and Clinical Applications in Gastroenterology. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 2036–2045.
- Isola, S.; Hussain, A.; Dua, A.; Singh, K.; Adams, N. Metoclopramide. . In StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519517/ (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Din, L.; Preuss, C.V. Prochlorperazine. . In StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537083/ (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Chakroborty, D.; Goswami, S.; Basu, S.; Sarkar, C. Catecholamines in the Regulation of Angiogenesis in Cutaneous Wound Healing. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 14093–14102.
- Papenberg, G.; Jonasson, L.; Karalija, N.; Johansson, J.; Köhncke, Y.; Salami, A.; Andersson, M.; Axelsson, J.; Wåhlin, A.; Riklund, K.; et al. Mapping the Landscape of Human Dopamine D2/3 Receptors with Raclopride. Brain Struct. Funct. 2019, 224, 2871–2882.
- Bourne, J.A. SCH 23390: The First Selective Dopamine D1-like Receptor Antagonist. CNS Drug Rev. 2001, 7, 399–414.
- Song, R.; Zhang, H.Y.; Li, X.; Bi, G.H.; Gardner, E.L.; Xi, Z.X. Increased Vulnerability to Cocaine in Mice Lacking Dopamine D3 Receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17675–17680.
- Kaur, N.; Kumar, P.; Jamwal, S.; Deshmukh, R.; Gauttam, V. Tetrabenazine: Spotlight on Drug Review. Ann. Neurosci. 2016, 23, 176–185.
- Dean, M.; Sung, V.W. Review of Deutetrabenazine: A Novel Treatment for Chorea Associated with Huntington’s Disease. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 313–319.
- Gupta, H.; Moity, A.R.; Jumonville, A.; Kaufman, S.; Edinoff, A.N.; Kaye, A.D. Valbenazine for the Treatment of Adults with Tardive Dyskinesia. Health Psychol. Res. 2021, 9, 38–70.
- Martin, D.; Le, J.K. Amphetamine. . In StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556103/ (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- Sessa, B.; Higbed, L.; Nutt, D. A Review of 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA)-Assisted Psychotherapy. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 138.
- Seibert, E.; Kunert, O.; Pferschy-Wenzig, E.M.; Schmid, M.G. Characterization of Three Novel 4-Methylaminorex Derivatives Applied as Designer Drugs. Molecules 2022, 27, 5770.
- Yasaei, R.; Saadabadi, A. Methamphetamine. . In StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535356/ (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- Knoll, J.; Yoneda, F.; Knoll, B.; Ohde, H.; Miklya, I. (-)1-(Benzofuran-2-Yl)-2-Propylaminopentane, , a Selective Enhancer of the Impulse Propagation Mediated Release of Catecholamines and Serotonin in the Brain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 128, 1723–1732.
- Knoll, J. Antiaging Compounds: (-)Deprenyl (Selegeline) and (-)1-(Benzofuran-2-Yl)-2-Propylaminopentane, , a Selective Highly Potent Enhancer of the Impulse Propagation Mediated Release of Catecholamine and Serotonin in the Brain. CNS Drug Rev. 2001, 7, 317–345.
- Gruber, L.M.; Jasim, S.; Ducharme-Smith, A.; Weingarten, T.; Young, W.F.; Bancos, I. The Role for Metyrosine in the Treatment of Patients With Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, E2393–E2401.
- Koizumi, S.; Matsushima, Y.; Nagatsu, T.; Iinuma, H.; Takeuchi, T.; Umezawa, H. 3,4-Dihydroxystyrene, a Novel Microbial Inhibitor for Phenylalanine Hydroxylase and Other Pteridine-Dependent Monooxygenases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1984, 789, 111–118.
- Jonkers, N.; Sarre, S.; Ebinger, G.; Michotte, Y. Benserazide Decreases Central AADC Activity, Extracellular Dopamine Levels and Levodopa Decarboxylation in Striatum of the Rat. J. Neural. Transm. 2001, 108, 559–570.
- Montioli, R.; Voltattorni, C.B.; Bertoldi, M. Parkinson’s Disease: Recent Updates in the Identification of Human Dopa Decarboxylase Inhibitors. Curr. Drug Metab. 2016, 17, 513–518.
- Sub Laban, T.; Saadabadi, A. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI) . In StatPearls . Treasure Island (FL). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539848/ (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- Chong, B.S.; Mersfelder, T.L. Entacapone. Ann. Pharmacother. 2000, 34, 1056–1065.
- Berger, A.A.; Winnick, A.; Izygon, J.; Jacob, B.M.; Kaye, J.S.; Kaye, R.J.; Neuchat, E.E.; Kaye, A.M.; Alpaugh, E.S.; Cornett, E.M.; et al. Opicapone, a Novel Catechol-O-Methyl Transferase Inhibitor, for Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease “Off” Episodes. Health Psychol. Res. 2022, 10, 36074.
- Truong, D.D. Tolcapone: Review of Its Pharmacology and Use as Adjunctive Therapy in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Clin. Interv. Aging 2009, 4, 109–113.
- Rivest, J.; Barclay, C.L.; Suchowersky, O. COMT Inhibitors in Parkinson’s Disease. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 1999, 26 (Suppl. 2), S34–S38.
More
Information
Subjects:
Neurosciences
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
1.9K
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
21 Jun 2023
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




