1. PT-Symmetric LC Sensors in Exact Phase
Superior detection and great robustness to noise have been a long-sought goal for
LC microsensors, which require sensors to exhibit high Q-factor and sharp, narrowband resonant reflection dips. However, due to the inevitable power dissipation caused by skin effects and eddy currents
[1], traditional
LC microsensors usually have a low modal Q-factor
[2]. A PT-symmetric telemetric sensor system designed to work in the exact PT-symmetric phase can exhibit sharp and deep resonant reflection dips, boosting the effective Q-factor and sensitivity. Moreover, the single-port scattering multi-frequency resonance characteristics in the exact PT-symmetric phase can realize the simultaneous measurement of multiple parameters of the
LC single-resonance circuit sensor.
1.1. High Q-Factor and Deep Reflection Dips
Sakhdari et al. presented an
LC wireless readout sensor based on the theory of PT symmetry
[3]. It is pointed out that the exact PT-symmetric phase results in real eigenfrequencies, which introduces the narrow band and sharp-peaked resonances. Compared with the conventional coil-antenna readout technique, it is evidently seen that the PT-symmetric wireless readout sensors enable the exhibition of much sharper reflection dips and greater Q-factor when operated in the exact phase. They explained the cause of improvement to be that the reflectionless property in one-port measurement owes to the impedance matching. In the exact PT-symmetric phase, the input impedance looking into the active reader can be matched to the impedance of the generator (
Z0) at the eigenfrequencies, leading to the dips observed in the reflection spectrum.
Based on the second-order PT-symmetric circuit, Yin et al.
[4] proposed a sandwich-type wireless capacitance readout mechanism based on a perturbed PT-symmetric electronic trimer consisting of a gain–neutral–loss
LC resonator chain to realize a higher Q-factor. Different from the standard second-order and third-order PT-symmetric systems, the proposed sandwich-type sensing system can maintain a high Q-factor in the whole range of
k, rather than only in the exact phase, and extend the interrogation distance while maintaining ultrahigh resolution even in the weak coupling regime.
1.2. The Multi-Parameter Sensitive Measurement
In the practical application of wireless sensor networks, it is necessary to measure multiple target parameters in the environment simultaneously. Therefore, inspired by the method of Ren et al.
[5], Zhou et al. utilized the multi-frequency resonance characteristics of the PT-symmetric
LC passive wireless sensor system in the exact PT-symmetric phase to realize the simultaneous measurement of multiple parameters in the single-port
LC sensor
[6].
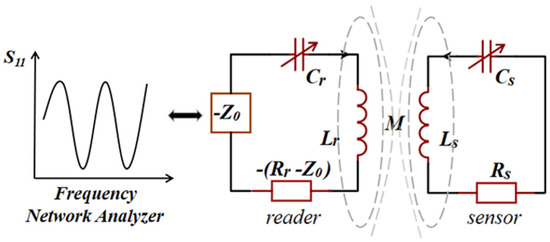
Figure 1 shows the equivalent circuit model for single-port measurement of a PT-symmetric system, where
Z0 is the impedance of the frequency network analyzer.
can be derived as
Figure 1. The schematic of PT-symmetric LC passive wireless sensor for multi-parameter measurement in the single-port.
They analyzed the two frequencies by extracting the amplitude extremum of the amplitude-frequency characteristics curve of S11 in the PT-symmetric exact phase, and obtained two sensitive parameters by decoupling the equations. This method improves the limitation of the double-parameter scheme that requires known coupling coefficients. In addition, a three-parameter sensing method for a single-loop LC sensor is proposed by using the three resonant frequencies at the zero phase of amplitude-frequency characteristics, which provides a feasible way to realize LC passive wireless multi-parameter sensing.
1.3. Generalized Parity–Time Symmetry
Despite the advantages of traditional PT-symmetric systems, practical implementations of an exact PT-symmetric phase for the LC wireless sensors still encounters many difficulties. For instance, given the limited physical space of medical bioimplants and MEMS sensors, the inductance of the sensor’s microcoil is usually designed to be smaller than that of the reader’s coil. Although downscaling the reader’s coil does not affect the match between them, it will reduce the mutually inductive coupling and degrade the operation of the wireless sensor.
To overcome the limitations in the spatial dimensions and significantly improve the performance of PT-symmetric
LC sensors, Chen et al. introduced the concept of parity–time-reciprocal scaling symmetry (PTX), consisting of an active reader (−
RLC tank), wirelessly interrogating a passive microsensor (
RLC tank)
[2]. In the system,
x is the reciprocal-scaling coefficient, an arbitrary positive real number, which means that PTX-symmetric systems do not have to maintain a strict symmetry mechanism as PT-symmetric systems do. Despite the introduction of the
X operator, the whole system has an unequal gain and loss coefficient; the PTX-symmetric system and its associated PT-symmetric system exhibit exactly the same eigenspectrum and bifurcation points, thus leading to sharp and deep resonant reflection dips. The scaling operation
X offers an additional degree of flexibility in system designs, allowing arbitrary scaling of the coil inductance and other parameters. More importantly, the scaling provided by the
X(
x > 1) operator leads to linewidth sharpening, boosting the Q-factor, sensing resolution, and overall sensitivity.
2. PT-Symmetric LC Sensors Based on Exceptional Points (EPs)
As already described, the PT-symmetric EP is the merging point in the physical system, at which the eigenvalues and eigenvectors merge and the eigenfrequencies undergo a bifurcation process branching out in the complex plane. It is precisely due to this large bifurcation effect that the PT-symmetric system can significantly exhibit greater sensitivity and resonance frequency shift when operated around EP.
2.1. PT-Symmetric LC Sensors with Enhanced Sensitivity
In 2019, an ultrasensitive wireless displacement sensing technique operated around EP was proposed
[7]. Specifically, such a non-Hermitian electronic system obeying the PT symmetry achieves drastic frequency responses and high sensitivity, well beyond the limit of conventional fully passive wireless displacement sensors. They theoretically point out that, for the EP case, the normalized resonance frequency shift can be derived as
, where
c is a constant associated with the
γ. However, the resonance frequency is approximately given by
in the conventional passive-coil reader. Obviously, the smaller the
is, the more excellent the sensitivity of EP sensors is. The PT-symmetric system can achieve more excellent sensitivity.
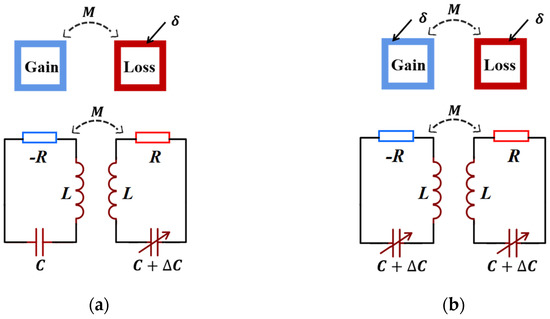
Based on the presence of the gain and the loss, Zhou et al. established a second-order PT-symmetric
LC passive wireless sensor to analyze the frequency responses of asymmetric and symmetric perturbations shown in
Figure 2 [8]. Although the results show that the frequency splitting caused by the two kinds of perturbations is proportional to the square root of the perturbation, the sensitivity of the asymmetric perturbation is the highest. Theoretical derivation shows that the asymmetric perturbation is more sensitive than
times the symmetric.
Figure 2. The PT-symmetric-coupled resonator system: (a) asymmetric perturbation and (b) symmetric perturbation.
2.2. LC Sensors Based on High-Order PT-Symmetric EP and DEP
Although sensors working in the second-order EP have demonstrated sensitivity responses beyond conventional sensors, the emergence of the higher-order PT symmetry theory still opened the door to a new
LC sensing world. The eigenfrequency splitting of a higher-order PT symmetry telemetry wireless
LC sensor will be more dramatic. An
N-level PT-symmetric system can obtain
N + 1 eigenfrequency branches, leading to the ever-boosted level of eigenfrequency bifurcation and greater sensitivity to perturbation
[9]. In addition, increasing the order
N can also downshift the exceptional point so that the exact symmetry phase can be obtained with real eigenfrequencies and high Q-factor resonances.
Figure 3 illustrates
Nth-order PT-symmetric
RLC telemetric electric circuit with
N = 2 and
N = 3.
Figure 3. Nth-order PT-symmetric RLC telemetric electric circuit with N = 2 and N = 3.
Inspired by the higher-order PT symmetry, a battery-free, wearable wireless sensor based on the third-order was presented, which is capable of simultaneously detecting temperature and relative humidity during the wound healing process with extraordinary sensitivity and accuracy
[10]. Similarly to the schematic of third-order PT in
Figure 3, the sensing system also consists of a passive RLC tank, a neutral LC tank, and an active −RLC tank inductively coupled with the adjacent one. In particular, the passive RLC tank is composed of a thermistor and a capacitive humidity sensor for responding to changes in temperature and humidity simultaneously. During the experimental demonstration, the resonant frequencies appear as dips in the reflection spectra, which respond sensitively and differently to changes in temperature and relative humidity.
2.3. Noise and Precision of LC Sensors Based on the EPs
Although numerous theories and experiments have confirmed that the PT-symmetric EP sensor does achieve enhanced sensitivity, Langbein et al. pointed out back in 2018 that the sensitivity was a very ambiguous quantity
[11]. It can either refer to the sensors’ transduction coefficient from the quantity to be measured to some intermediate output quantity, or to the smallest measurable change in the input quantity given by the noise of the output. The second expression is also defined as the precision of the measurement, different from the sensitivity in the traditional sense. Due to the existence of additional noise during the gain process in signal, EP has higher noise in measuring the perturbation than DP. Therefore, it is obvious that the complex frequency splitting of the EP sensor is not suitable for estimating the precision.
2.4. Solutions to Overcome Noise Effect
Considering the above issues, a PT-symmetric sensing circuit bearing a sixth-order EP is fabricated to address the potential drawbacks of EP sensing, including both fundamental resolution limit and noise effects
[12]. The sixth-order EP achieved an enhanced resonance shift proportional to the fourth-order root of the perturbation strength and enhanced sensitivity compared to corresponding DP sensors. At the same time, due to the low-pass feature of the sixth-order circuit by choosing a proper working capacitance in the resonator, thermal noise is mitigated down to the identical level of the DP sensing scheme, solving the problem of noise limitation.
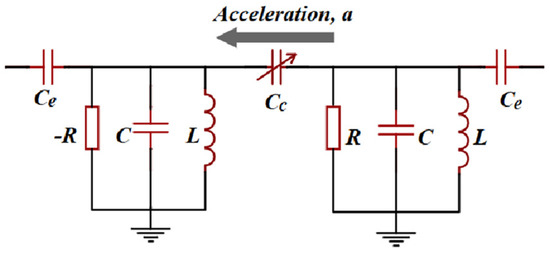
Kononchuk et al. proposed a PT-symmetric electromechanical accelerometer-based EP in the proximity of the detuning from a transmission peak degeneracy (TPD) as a measurement of the sensitivity to the influence of excess noise effects
[13]. TPD would form when the system is weakly coupled to transmission lines. Thanks to the existence of coupling
Ce shown in
Figure 4, the TPDs occur at distinct parameter values from the EP, ensuring completeness of the eigenbasis. The experiments demonstrated a three times signal-to-noise ratio enhancement and a ten times increase in responsivity to small perturbations compared to configurations operating away from the TPD.
Figure 4. Schematic of the PT-symmetric electromechanical accelerometer.
3. PT-Symmetric LC Sensors in Broken Phase
Zhou et al. proposed and demonstrated that the PT symmetry-breaking regime could be utilized to extend the remote distance of the
LC passive wireless sensors
[14]. The impedance matching enables non-reflection energy transfer, and the negative resistance (−
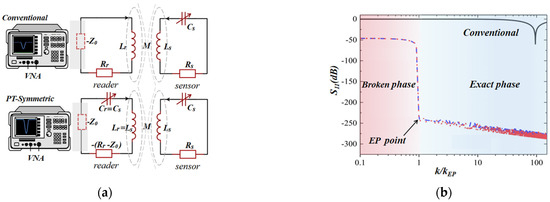
R0) at the reader has an amplifying effect on the signal. The combination of impedance matching and negative resistance realizes longer read-out distances compared to conventional sensors. Experimental results show that the read-out distance of PT-symmetric sensors is approximately four times as long as that of conventional sensors, while keeping the same sensitivity. The schematics of conventional and PT-symmetric sensing systems are shown in
Figure 5a, in which
Z0 is the characteristic impedance of the transmission line of the Vector Network Analyzer (VNA). As previously mentioned, the eigenfrequencies are coming in complex conjugate pairs with nonvanishing real parts in the PT-symmetric broken phase. Different from the double-frequency resonance of the exact phase
[6], when the system enters the PT-symmetric broken phase,
will be a complex conjugate pair. The real-domain sweep cannot read the imaginary information, so the single frequency at the minimum value of the reflection coefficient
S11 is the real part of its eigenfrequency
Figure 5. (a) The circuit schematic of conventional and PT-symmetric LC passive wireless sensing systems; (b) reflection coefficient S11, at the resonant frequency of the remote system, as a function of coupling strength k for conventional and PT-symmetric LC passive wireless sensors.
Figure 5b shows the change in S11 at the resonant frequency with the coupling coefficient k, intuitively illustrating the enhancement effect of the readout distance. Even in the weak coupling regime of the PT-symmetric broken phase corresponding to a longer distance, the reflection coefficient almost remains constant as the coupling strength weakens. In contrast, the conventional method can only obtain the dip of the S11 signal over a shorter distance. Therefore, longer detection distances can be obtained by working in the broken phase of PT-symmetric LC passive wireless sensing systems, which overcomes the long-standing challenge of extending the interrogation distance of the scaled-down LC passive wireless sensor.
Moreover, the third-order PT-symmetry-breaking regime also shows the same superiority in long interrogation distances
[4]. A sandwich-type wireless capacitance readout system consisting of a gain–neutral–loss
LC resonator chain is fabricated, extending the interrogation distance in the PT-symmetric broken phase compared to the standard second-order PT-symmetric system. PT symmetry-breaking regimes for the
LC passive wireless sensors can be used in the interrogation of implanted or sealed fields, where a longer interrogation distance is necessary.
Although there are still many controversies regarding the performance of the PT-symmetric sensors, the PT symmetry LC passive wireless sensors have been widely applied and developed in many fields, including biomedical and biotelemetry applications, industrial measurement and telemetry, and various wearable and implantable devices, as listed in Table 1.
Table 1. Application fields of PT symmetry LC passive wireless sensors and numbered references.
| Application Fields |
References |
| biomedical and biotelemetry |
[4][10][15][16] |
| industrial measurement and telemetry |
[2][8][9][12][14][17][18] |
| wearable and implantable devices |
[3][4][10][19] |