Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | In-Sung Yeo | -- | 3665 | 2023-06-12 12:20:55 | | | |
| 2 | Camila Xu | Meta information modification | 3665 | 2023-06-13 03:58:39 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Choi, S.; Kang, Y.S.; Yeo, I.L. Biomechanical Aspects at Dental Implant-Abutment Interfaces. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/45445 (accessed on 28 February 2026).
Choi S, Kang YS, Yeo IL. Biomechanical Aspects at Dental Implant-Abutment Interfaces. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/45445. Accessed February 28, 2026.
Choi, Sunyoung, Young Suk Kang, In-Sung Luke Yeo. "Biomechanical Aspects at Dental Implant-Abutment Interfaces" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/45445 (accessed February 28, 2026).
Choi, S., Kang, Y.S., & Yeo, I.L. (2023, June 12). Biomechanical Aspects at Dental Implant-Abutment Interfaces. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/45445
Choi, Sunyoung, et al. "Biomechanical Aspects at Dental Implant-Abutment Interfaces." Encyclopedia. Web. 12 June, 2023.
Copy Citation
The interface between a dental implant and an abutment is stabilized by two mechanical characteristics: a preload of an abutment screw and the friction between the contact surfaces of the implant and the abutment. These mechanical properties are quantitatively analyzed by using physical and mechanical formulas. The important thing is that such mechanical properties cause various biological phenomena when medical devices are inserted into human bodies. Some mechanical complications in dental implant prostheses are closely associated with biological complications.
dental abutments
dental implant–abutment connection
dental implants
1. Introduction
The introduction of osseointegration by Per-Ingvar Brånemark in the mid-1960s led to the advent of dental endosteal implants. These implants have both partially and completely benefited edentulous patients around the world in regaining functions, such as speech, mastication, and deglutition, and have provided aesthetic quality and comfort [1]. The early Brånemark implants were designed to support and retain mandibular complete dentures. Over the following decades, applications of dental implants have been expanded to include single crowns, fixed partial dentures, full-arch fixed complete dentures, removable complete implant-retained overdentures, implant-assisted removable partial dentures, and complex maxillofacial prostheses. It is now impossible to discuss prosthodontics without mentioning dental implants, which have demonstrated predictable success and survival in supporting various types of dental prostheses [2].
Early dental implants were machined, smooth-surfaced fixtures made of titanium (Ti), which offered excellent biocompatibility and affordability [1]. Most titanium dental implants are made from commercially pure Grade 4 titanium (cpTi). Titanium can be alloyed with vanadium (V) and aluminum (Al) to increase the implant’s elastic modulus and tensile strength while reducing the risk of corrosion [3].
2. Complications in Implant-Supported Prostheses
2.1. Mechanical Complications
In the literature, there are three types of mechanical (technical) complications: (1) implant-related, such as implant fractures; (2) connection-related, such as a screw loosening in the prosthesis, a screw loosening in the abutment, screw fractures, and abutment fractures; and (3) suprastructure-related, such as metal framework fractures, worn materials, acrylic resin base fractures for implant overdentures, facial and occlusal veneer porcelain fractures, cement failure, prosthetic material failure, prosthesis replacement due to complications, opposing prosthesis fractures, and problems with mechanical retention (bar or clip attachments) in overdentures [4][5][6][7].
Mechanical complications are caused by either occlusal overload or excessive force caused by the muscles of mastication, or they are caused by improperly designed or manufactured prostheses. Factors that can contribute to occlusal overload include immediate loading, under-engineered design (not enough supporting implants or inadequate anterior–posterior spread), large cantilevers, steep cuspal inclinations, a poor distribution of force, occlusal interferences, and parafunctional habits such as nocturnal bruxism [8][9].
The most commonly reported mechanical complication is the loosening of screws and abutments [2][7][9][10][11]. To address this issue, implant manufacturers modified the fixture design by introducing internal friction connections (which will be later discussed in detail) using gold alloy screws, as well as by introducing a tightening technique with a counter-torque device [9][11]. In addition, the advent of monolithic zirconia restorative material in recent years has reduced the use of acrylic and porcelain veneers in implant-supported prostheses [12][13][14][15].
2.2. Biologic Complications
Biological complications can be classified into two categories: (1) early implant failure, which is characterized by the loss of osseointegration in the first year or before loading, and (2) late implant failure, which occurs after osseointegration and loading, such as in mucositis, peri-implantitis, fistula, and dehiscence [8][16].
Early implant failure can be caused by surgical complications such as neurosensory disturbance; hematoma; mandibular fracture; hemorrhage; the impingement of the implant to vital structures, such as the sinus membrane, the inferior alveolar nerve, a natural tooth, or an adjacent implant; and an overheating of the bone at the time of implant placement. Other causes include a contamination of the implant surface; underlying systemic medical conditions, such as uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, heavy smoking, intravenous bisphosphonate therapy, and current chemotherapy or radiation therapy; inadequate initial stability due to poor quality bone or overcountersinking; unsterile surgical techniques; and the premature loading of the implant [4][17]. Studies have shown that reducing surgical complications can lead to the greatest improvement in decreasing early implant failures [8].
Late implant failures can be caused by several factors such as implant inflammatory responses to bacterial infection, occlusal overload, parafunction (bruxism), incomplete removals of dental cement, a history of chronic periodontitis, poor plaque control, inadequate maintenance, a lack of peri-implant keratinized mucosa, mal-positioned implants with exposed threads, residual titanium particles, and adjacent pathology [16][18][19]. Moreover, the intaglio surface of an implant-supported fixed partial denture, if uncleanable due to concavity or heavy contact with soft tissue, can also lead to biological complications.
The two most common late implant failures are mucositis and peri-implantitis. Mucositis is a localized lesion without bone loss around an osseointegrated implant, while peri-implantitis is a localized lesion that includes bone loss around an osseointegrated implant [20][21]. Late implant failures can be diagnosed by bleeding on probing, suppuration, increased probing depth, implant mobility, and radiographic interpretation [5]. The prevalence of peri-implantitis has been estimated as quite high in previous studies [22][23][24]. Most of these failures require local and systemic antimicrobial treatment regimens, mechanical debridement, the polishing of implants, and resective or regenerative surgical procedures [5][23].
2.3. Association between Mechanical and Biological Complications
Researchers often discuss mechanical and biological complications separately in order to simplify their studies. However, in both classic and recent publications, a causal relationship between mechanical and biological complications has been suggested to explain the pathogenesis of peri-implantitis [7][10][25]. In the 1990s, most dental implants on the market were external hex implant systems. Schwarz, in 2000, explained the widespread loosening of implant parts by stating that the “rotational motion of the abutment on the implant, which results from machining tolerances of the external hexagons and their abutment counterparts, ultimately leads to failure of the screw” [7]. After the screw loosens, metal fatigue may result in screw fracture [10][11]. The resulting micromotion, caused by a poor fit between the structures, may lead to implant fractures or peri-implant inflammation and bone loss [26][27]. In a recent 2022 study, Kim and his colleagues discussed that the loosening of an abutment screw and the instability of an implant–abutment connection structure may ultimately result in peri-implantitis and implant failure [10].
3. Connection Biomechanics and Its Biological Meaning
There are two widely applied implant–abutment connection structures in clinical implant dentistry: the external hex connection and the internal friction connection (Figure 1). The external hex connection is stabilized by preloading an abutment screw, which is performed when the area between an implant and an abutment is tightened [10]. Abutment screw biomechanics in the field of implant dentistry have been well described in a previous study [11]. Basically, the theoretical amount of preload required to prevent screw loosening (75% of the yield strength of the abutment screw material) is too large (corresponding to a torque of over 200 Ncm for grade 5 titanium) to be applied to implant–abutment connection as it would lead to abutment screw fracture [10][11][28]. Therefore, the preload naturally decreases due to the bending moment exerted on the abutment screw by a masticatory force, and micromovements of the abutment are allowed in the external hex connection implant [10][25]. Such micromovements weaken the attachment of the gingival epithelium and connective tissue to the abutment, disrupting the soft tissue seal, which is defined as the attachment of epithelial and connective tissues to the surfaces of the implant system [25]. The internal friction connection is stabilized, literally by friction between the inner inclined plane of the implant and the outer inclined plane of the abutment [29]. The friction biomechanics at the implant–abutment interface show that the friction contributes to the stability of the implant–abutment connection to a great extent, depending on the contacting area between the two frictional surfaces and the tapered angles of the inclined planes to the long axis of the implant [10][29]. Certain implant systems with internal friction connections maintain implant–abutment connection stability; this is despite the fact that abutment screw loosening occurs because the friction between the two surfaces is a major contributor to its stability over the preload of screw tightening [10][30]. Therefore, the abutment is stable without micromovements, and the soft tissue seal is maintained [10][31]. The soft tissue seal is an important factor for the long-term clinical success of an implant, preventing bacterial invasion from the oral environment [25][27][32].
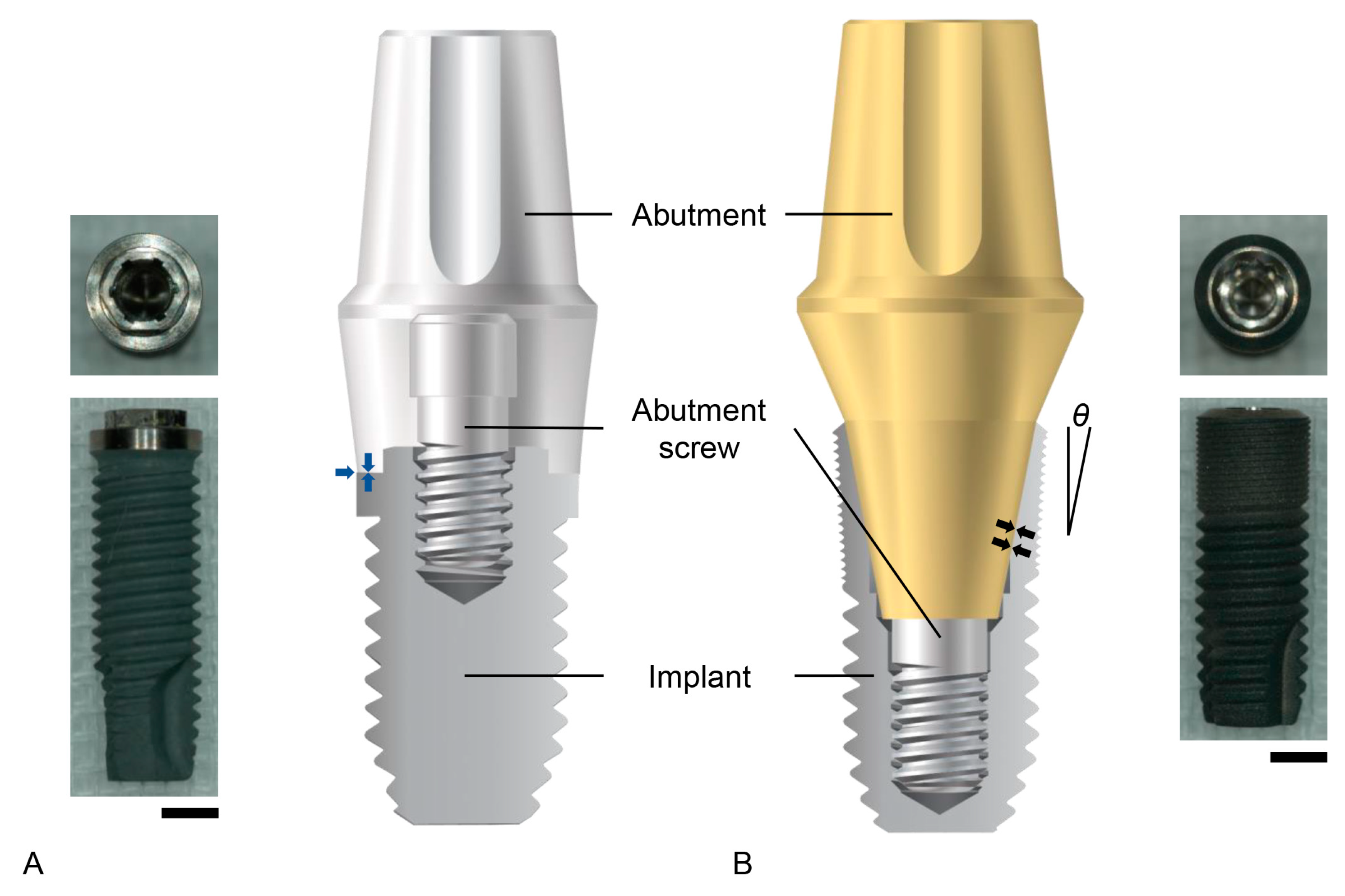
Figure 1. Implant–abutment connection structures. (A) The external hex connection. On the left, the real image of an implant is shown. From the top view, the meaning of ‘hex’ is clarified. On the right, the schematic diagram shows that the abutment is placed with flat-on-flat surface contact on the top of the implant (blue arrows). (B) The internal friction connection. On the left, the schematic diagram shows that the inclined plane of the outer abutment surface has frictional contact with that of the interimplant surface (black arrows). Note that the thickness of the implant wall decreases from the lower to the upper surfaces at the implant coronal area. Additionally, notice that the larger the taper angle (θ), the thicker the wall becomes. On the right, a real image of an internal friction connection implant is shown. Scale bars: 2 mm.
The internal friction connection is advantageous for the preservation of the bone surrounding the implant. The abutment tends to sink into the implant during mastication, and the resultant coronal expansion of the implant occurs [33]. This biomechanical feature effectively delivers strain to the bone, which is stimulated by the strain to preserve the bone quantity [34][35]. The occlusal force, or occlusal stress, is delivered to the implants with both the external hex connection and the internal friction connection. The important aspect to consider is that the bone is stimulated only by an appropriate level of strain, which is where this stress is conveyed [35][36]. The structure of internal friction connections allows for more effective transmission into the bone compared to external hex connection implants [37][38][39]. The bone stimulation capacity of internal friction connections depends on the implant diameter and the tapered angles of the inclined planes to the long axis of the implant [10]. Generally, larger implant diameters produce thicker implant walls at the coronal area unless the connection depth between the implant and the abutment increases (Figure 1). The implant wall at the coronal area becomes thicker as the degree of the taper becomes larger, which causes less strain to the bone, although implant fracture is less possible [29] (Figure 1). In summary, the stability and the stress–strain conversion of implant–abutment connections are important biomechanical factors that determine the biological phenomena surrounding the prostheses supported by dental implants in the oral environment.
Process in which Screw Loosening Leads to Peri-Implantitis
Peri-implant soft tissues, which include the mucosal epithelium and the connective tissue, play a crucial role in protecting both natural teeth and dental implants from external stresses and microorganisms by attaching to the tooth surfaces and the abutment surfaces [10][25]. These interfaces between the gingiva and the tooth, or abutment, are referred to as the soft tissue seals [10][25]. Once this seal is disrupted, bacteria can penetrate the internal environment via the transmucosal rupture site, which can lead to peri-implant diseases and inflammation.
Unfortunately, the soft tissue seals of teeth and abutments are different. Although epithelial attachments, an internal basal lamina, and hemi-desmosomes are similar in both interfaces, it is the connective tissue that differs. The dento-gingival fibers, such as Sharpey’s fibers, of connective tissue vertically attach to the cementum of natural teeth; however, they are absent around the abutments. According to a scanning electron study, the connective tissue attachment to the dental implant abutment is maintained by fibroblasts, and it is circularly arranged around the abutment [25]. Additionally, the attached gingiva around the abutment and the implant is either bone-attached or abutment/implant-attached. While bone-attached gingiva provides solid immobility, the abutment-attached gingiva is weaker and is almost equal in strength to free gingiva [10].
Therefore, the gingiva–abutment interface is vulnerable when there is instability in the peri-implant mucosa or the implant–abutment assembly. If mechanical complications such as the loosening or fracturing of the screws occur, they may destabilize the soft tissue seal. As mentioned earlier, screw loosening is more common in external hex connections due to bending moments and elongation by lateral occlusal force. In the 1990s, researchers believed that a microgap, a small gap formed between the abutment and the implant, caused marginal bone resorption by acting as a haven for microorganisms [32]. However, recent studies suggest that abutment movement or micromotion can break the soft tissue seal, leading to potential marginal bone resorption around the implant [10][31][40].
Dentists, including both clinicians and researchers, recognize peri-implantitis as a major cause of peri-implant bone loss and implant failure [10][21][41]. While some researchers argue that peri-implantitis is not a disease but, rather, a provoked foreign body reaction, it is generally considered a disease due to its signs and symptoms, which include increased probing depth, bleeding on probing and/or suppuration, and radiographic evidence of progressive bone loss [42].
The cause of peri-implantitis has been demonstrated to involve inflammation, which is produced by an overwhelming bacterial insult and subsequent host immune response, as is seen in periodontitis. Peri-implant diseases have been associated with Gram-negative anaerobic bacteria, similar to those found in severe chronic periodontitis. The critical factor is that a peri-implant pocket is formed by the breakdown of the soft tissue seal before bacterial invasion occurs [10][25]. Mechanical complications such as abutment screw loosening and fracture make the implant–abutment connection unstable and disrupt the soft tissue seal, thus allowing bacterial invasion, which leads to biological complications, such as peri-implantitis and implant failure [10]. Compared to periodontitis, the rate of disease progression and the severity of inflammatory signs for peri-implantitis are more severe [10][25]. As previously mentioned, the absence of connective tissue (collagen) fibers being inserted into dental implants increases susceptibility to marginal bone loss around implants [10][25].
A number of risk factors for peri-implantitis have been identified, including previous periodontal disease, poor plaque control, residual cement, poorly designed prostheses, smoking, genetic factors (such as IL-1 gene polymorphism), diabetes, occlusal overload, as well as other potential factors such as rheumatoid arthritis [43][44][45][46][47]. Once peri-implantitis progresses, the primary objective of treatment for both peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis is the effective elimination of biofilm from the implant surface. Non-surgical therapy has been shown to be effective for the treatment of peri-implant mucositis, while only surgical therapy has been shown to be effective for the treatment of peri-implantitis [43]. However, the maintenance of the soft tissue seal with a stable implant–abutment connection and an early intervention to control peri-implant diseases at the initial stage is more important than treatment [10][47].
4. Zirconia Dental Implants: Merits and Limits
4.1. Overview of Zirconia Dental Implants
Although titanium is an excellent implant material, its grayish color is a significant drawback. This dark shade is not only detectable by a spectrophotometer but also visible, especially in thin gingival biotypes [48][49]. Moreover, exposing the titanium implant above the gingival tissue seriously compromises the aesthetic outcome [50]. Another concern with titanium implants is titanium sensitivity. Hypersensitivity, an allergic reaction, and titanium corrosion have been reported to be related to titanium in the oral cavity [51][52][53]. As a result, the demand for titanium substitutes that can overcome these disadvantages has been gradually increasing. In addition, ceramic implants, which are metal-free and highly aesthetic, have also been attracting more attention. Alumina was originally used as a ceramic implant, but it could not withstand occlusal pressure in the oral cavity [54][55]. Since zirconia was introduced as an alternative to alumina, it has become the primary material used for ceramic implants [56].
The use of zirconia implants has been successful when compared to the previously used alumina implants; this is because fracture resistance and flexural strength were greatly improved due to the transformation toughening in 3% yttria-stabilized zirconia [57][58]. Zirconia exists in three phases: monoclinic, cubic, and tetragonal (depending on the temperature). When the crystal structure changes from tetragonal to monoclinic, there is a volume expansion of approximately 3–5%. Zirconia exists in the monoclinic phase at room temperature, but with 3% yttria, it can exist in the tetragonal phase [59]. This 3% yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (3Y-TZP) transforms into its monoclinic phase when a crack occurs and expands in volume, which prevents further crack propagation. Due to this phenomenon, 3Y-TZP has been successfully used as an implant material.
Clinical outcomes of zirconia implants when compared to titanium implants have been reported [60][61][62]. The survival rates of zirconia implants varied from 71.2% at 1 year to 100% at 7.8 years, and the success rate ranged from 67.6% at 1 year to 100% at 5.1 years [63][64][65][66]. Recently, Brunello et al. reported that only one implant was lost out of thirty zirconia implants during a 9-year follow-up period [60]. A previous study also reported that zirconia implants show a lower survival rate but a similar success rate when compared to titanium implants [3]. In terms of osseointegration, the bone-to-implant contact and removal torque values of zirconia implants were comparable to those of titanium implants [67][68]. Zirconia is also known to be more resistant to bacterial growth and to form a stronger mucosal barrier than titanium [69][70]. Since bacterial invasion around implants, or implant abutments, and the soft tissue seal is a factor that can influence the development of peri-implantitis, zirconia implants would be more resistant to peri-implantitis than titanium [21].
Both zirconia and titanium are stiff materials [71]. Stiffness refers to the ability to return to the original form after being subjected to a force, and it is related to the modulus of elasticity. Zirconia is brittle, whereas titanium is ductile [72]. Titanium shows plastic deformation under pressure, while zirconia has no plastic deformation when under pressure and when subjected to excessive stress and fractures.
4.2. Two Types of Zirconia Implants
Zirconia implants were initially designed in a one-piece form in which the implant and abutment were connected as a solid piece. This design was suitable for the anterior region, especially in cases of thin biotypes and for single-tooth restoration [60]. However, during the osseointegration phase, the one-piece implant must withstand immediate loading since the abutment part is necessarily subjected to loads [73][74]. Additionally, grinding the abutment part is prohibited as it reduces the fracture toughness of the implant and increases the risk of fracture [75]. A two-piece design consists of a separate abutment part and an implant, which are connected with a screw or cement [76]. In cases of posterior rehabilitation with limited mouth openings or poor bone quality, a two-piece implant system may be a more appropriate option than a one-piece implant as it can be submerged and different shapes of abutments can be used [75][77].
In two-piece zirconia implants, there are currently five types of implant connections used in dental clinics: external hex, internal hex, internal multi-lobe, internal cone, and internal square. The implant–abutment connection plays a critical role in distributing the load from the prosthesis to the bone–implant interface. Although the connection shapes of zirconia implants are similar to those of titanium implants, the results of load distribution in the connections are quite different between the two materials. While titanium implants show plastic deformation by a sinking down of the abutments in internal friction connection types [25][33], zirconia implants fracture without any deformation [59]. Thus, the occlusal force applied to the implants by abutments is barely converted into a strain on the surrounding bone [25].
4.3. Stress Shielding Effect
The transfer of a mechanical load through the interface between dental implants and the surrounding bone is closely related to the maintenance of the surrounding bone tissue [78]. The load from a dental implant prosthesis induces strain onto the surrounding bone, which subsequently affects the bone modeling and remodeling processes [79]. To optimize the transfer of the load, the modulus of elasticity of an implant should be similar to that of bone. Therefore, the way in which mechanical stresses are transferred to the surrounding bone affects the likelihood of successful osseointegration and its clinical longevity [80].
The modulus of elasticity of 3Y-TZP is more than 200 GPa, while that of cortical bone is around 16 GPa, and that of cancellous or trabecular bone is around 8 GPa [79][81]. The elastic modulus of titanium or titanium alloy is in the range of 100 to 110 GPa [71]. The significant difference in stiffness between the implant and surrounding bone can cause an imbalance in stress distribution, resulting in bone resorption and implant failure [78]. This phenomenon is related to the stress shielding effect commonly observed in the orthopedic field [82][83]. The stress shielding effect occurs when the bone remodels after implant placement, leading to a reduction in bone width or density, which increases the risk of implant failure or periprosthetic fracture. Wolff’s law explains this effect and states that healthy animal bones will adapt to the loads under which they are placed [35]. As the load on a particular bone increases, the bone rebuilds over time and becomes stronger in order to withstand that type of load. That is, when we subject our bones to increased mechanical loading or stress, the bones undergo remodeling and become stronger over time, better withstanding those specific forces. Stress shielding is an alteration in the mechanical stimulus in the bone that is adjacent to the implant after implant placement [84]. The changed mechanical environment drives an adaptive response in the bone, resulting in the bone structure and density becoming more appropriate to mechanical needs [35][84]. The loss of strain transfer from zirconia implants to surrounding bone induces the stress shielding effect, leading to the disuse atrophy of the bone surrounding the zirconia implants.
While zirconia implants offer excellent aesthetics, high fracture resistance, and comparable osseointegration to titanium implants, their significantly higher stiffness compared to bone means that they do not transfer strain to the surrounding bone. This lack of strain can result in the disuse atrophy of the bone despite the implant’s other strengths. A zirconia dental implant is clearly an alternative to titanium, particularly with regard to aesthetics, such as achieving a natural gingival shade. However, zirconia dental implants have limitations in mechanical properties at the implant–abutment connection area, irrespective of the connection designs (one-piece or two-piece structures). These mechanical weak points can lead to clinical complications, including marginal bone loss, due to the stress shielding effect and the peri-implant inflammatory response resulting from the implant fracture. Currently, the scientific literature evaluating the clinical performance of zirconia dental implants is too limited to be used for a systematic review or a meta-analysis [65][85][86][87][88][89][90][91][92][93][94]. Numerous clinical trials with long-term follow-up periods are undoubtedly necessary to assess the efficacy of zirconia dental implants.
References
- Sales, P.; Barros, A.W.P.; Oliveira-Neto, O.B.; de Lima, F.J.C.; Carvalho, A.A.T.; Leao, J.C. Do zirconia dental implants present better clinical results than titanium dental implants? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 124, 101324.
- Albrektsson, T.; Donos, N.; Working, G. Implant survival and complications. The Third EAO consensus conference 2012. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23 (Suppl. 6), 63–65.
- Vaghela, H.; Eaton, K. Is Zirconia a Viable Alternative to Titanium for Dental Implantology? Eur. J. Prosthodont. Restor. Dent. 2022, 30, 1–13.
- Goodacre, C.J.; Kan, J.Y.; Rungcharassaeng, K. Clinical complications of osseointegrated implants. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1999, 81, 537–552.
- Lang, N.P.; Berglundh, T.; Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.; Pjetursson, B.E.; Salvi, G.E.; Sanz, M. Consensus statements and recommended clinical procedures regarding implant survival and complications. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2004, 19, 150–154.
- Sailer, I.; Karasan, D.; Todorovic, A.; Ligoutsikou, M.; Pjetursson, B.E. Prosthetic failures in dental implant therapy. Periodontol. 2000 2022, 88, 130–144.
- Schwarz, M.S. Mechanical complications of dental implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2000, 11 (Suppl. 1), 156–158.
- Carr, A.B.; Sinha, N.; Lohse, C.M.; Muller, O.M.; Salinas, T.J. Association Between Early Implant Failure and Prosthodontic Characteristics. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 28, 30–35.
- Sadid-Zadeh, R.; Kutkut, A.; Kim, H. Prosthetic failure in implant dentistry. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 59, 195–214.
- Kim, J.C.; Lee, M.; Yeo, I.L. Three interfaces of the dental implant system and their clinical effects on hard and soft tissues. Mater. Horiz. 2022, 9, 1387–1411.
- Jeong, C.G.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Yeo, I.S.L. Clinically available preload prediction based on a mechanical analysis. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2017, 87, 2003–2009.
- Pjetursson, B.E.; Asgeirsson, A.G.; Zwahlen, M.; Sailer, I. Improvements in implant dentistry over the last decade: Comparison of survival and complication rates in older and newer publications. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2014, 29, 308–324.
- Kim, W.; Li, X.C.; Bidra, A.S. Clinical outcomes of implant-supported monolithic zirconia crowns and fixed partial dentures: A systematic review. J. Prosthodont. 2023, 32, 102–107.
- Lemos, C.A.A.; Verri, F.R.; de Luna Gomes, J.M.; Santiago Junior, J.F.; Miyashita, E.; Mendonca, G.; Pellizzer, E.P. Survival and prosthetic complications of monolithic ceramic implant-supported single crowns and fixed partial dentures: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022.
- Pjetursson, B.E.; Sailer, I.; Latyshev, A.; Rabel, K.; Kohal, R.J.; Karasan, D. A systematic review and meta-analysis evaluating the survival, the failure, and the complication rates of veneered and monolithic all-ceramic implant-supported single crowns. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2021, 32 (Suppl. 21), 254–288.
- Schwarz, F.; Ramanauskaite, A. It is all about peri-implant tissue health. Periodontol. 2000 2022, 88, 9–12.
- Strasding, M.; Hicklin, S.P.; Todorovic, A.; Fehmer, V.; Mojon, P.; Sailer, I. A multicenter randomized controlled clinical pilot study of buccally micro-veneered lithium-disilicate and zirconia crowns supported by titanium base abutments: 1-year outcomes. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2023, 34, 56–65.
- Koka, S.; Bensoussan, J.; Curtis, D. Influence of clinician gender, age, and geographic work location on the relative rankings of risk factors for biological complications with dental implant therapy. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2023, 129, 582–588.
- Papaspyridakos, P.; Barizan Bordin, T.; Kim, Y.J.; DeFuria, C.; Pagni, S.E.; Chochlidakis, K.; Rolim Teixeira, E.; Weber, H.P. Implant survival rates and biologic complications with implant-supported fixed complete dental prostheses: A retrospective study with up to 12-year follow-up. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 881–893.
- Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.A.; Salvi, G.E. Peri-implant mucositis. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S257–S266.
- Schwarz, F.; Derks, J.; Monje, A.; Wang, H.L. Peri-implantitis. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S267–S290.
- Mombelli, A.; Muller, N.; Cionca, N. The epidemiology of peri-implantitis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23 (Suppl. 6), 67–76.
- Sadowsky, S.J. Peri-implantitis after 40 years: Evidence, mechanisms, and implications: A mapping review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2023.
- Derks, J.; Tomasi, C. Peri-implant health and disease. A systematic review of current epidemiology. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42 (Suppl. 16), S158–S171.
- Kim, J.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.C.; Lee, J.B.; Yeo, I.L. Biological Responses to the Transitional Area of Dental Implants: Material- and Structure-Dependent Responses of Peri-Implant Tissue to Abutments. Materials 2019, 13, 72.
- Donati, M.; Ekestubbe, A.; Lindhe, J.; Wennstrom, J.L. Marginal bone loss at implants with different surface characteristics—A 20-year follow-up of a randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 480–487.
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.C.; Kim, H.Y.; Yeo, I.L. Influence of Connections and Surfaces of Dental Implants on Marginal Bone Loss: A Retrospective Study Over 7 to 19 Years. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2020, 35, 1195–1202.
- Lang, L.A.; Kang, B.; Wang, R.F.; Lang, B.R. Finite element analysis to determine implant preload. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2003, 90, 539–546.
- Bozkaya, D.; Muftu, S. Mechanics of the tapered interference fit in dental implants. J. Biomech. 2003, 36, 1649–1658.
- Bozkaya, D.; Muftu, S. Mechanics of the taper integrated screwed-in (TIS) abutments used in dental implants. J. Biomech. 2005, 38, 87–97.
- Hermann, J.S.; Schoolfield, J.D.; Schenk, R.K.; Buser, D.; Cochran, D.L. Influence of the size of the microgap on crestal bone changes around titanium implants. A histometric evaluation of unloaded non-submerged implants in the canine mandible. J. Periodontol. 2001, 72, 1372–1383.
- Hermann, J.S.; Buser, D.; Schenk, R.K.; Cochran, D.L. Crestal bone changes around titanium implants. A histometric evaluation of unloaded non-submerged and submerged implants in the canine mandible. J. Periodontol. 2000, 71, 1412–1424.
- Lee, J.H.; Huh, Y.H.; Park, C.J.; Cho, L.R. Effect of the Coronal Wall Thickness of Dental Implants on the Screw Joint Stability in the Internal Implant-Abutment Connection. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, 1058–1065.
- De Vasconcellos, L.G.; Kojima, A.N.; Nishioka, R.S.; de Vasconcellos, L.M.; Balducci, I. Axial loads on implant-supported partial fixed prostheses for external and internal hex connections and machined and plastic copings: Strain gauge analysis. J. Oral Implantol. 2015, 41, 149–154.
- Frost, H.M. A 2003 update of bone physiology and Wolff’s Law for clinicians. Angle Orthod. 2004, 74, 3–15.
- Kim, H.Y.; Yang, J.Y.; Chung, B.Y.; Kim, J.C.; Yeo, I.S. Peri-implant bone length changes and survival rates of implants penetrating the sinus membrane at the posterior maxilla in patients with limited vertical bone height. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2013, 43, 58–63.
- Bozkaya, D.; Muftu, S.; Muftu, A. Evaluation of load transfer characteristics of five different implants in compact bone at different load levels by finite elements analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 92, 523–530.
- Hansson, S. Implant-abutment interface: Biomechanical study of flat top versus conical. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2000, 2, 33–41.
- Jeong, K.-W.; Kim, J.C.; Yeo, I.-S. Clinical Significance of Internal Friction Connection and Micro-Threads in Implant-Supported Prostheses: A Literature Review. Recent. Prog. Mater. 2020, 2, 024.
- Koutouzis, T.; Gholami, F.; Reynolds, J.; Lundgren, T.; Kotsakis, G.A. Abutment Disconnection/Reconnection Affects Peri-implant Marginal Bone Levels: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2017, 32, 575–581.
- Bornes, R.; Montero, J.; Correia, A.; Marques, T.; Rosa, N. Peri-implant diseases diagnosis, prognosis and dental implant monitoring: A narrative review of novel strategies and clinical impact. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 183.
- Albrektsson, T.; Dahlin, C.; Jemt, T.; Sennerby, L.; Turri, A.; Wennerberg, A. Is marginal bone loss around oral implants the result of a provoked foreign body reaction? Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 155–165.
- Peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: A current understanding of their diagnoses and clinical implications. J. Periodontol. 2013, 84, 436–443.
- Dioguardi, M.; Cantore, S.; Quarta, C.; Sovereto, D.; Zerman, N.; Pettini, F.; Muzio, L.L.; Cosola, M.D.; Santacroce, L.; Ballini, A. Correlation Between Diabetes Mellitus and Peri-implantitis: A Systematic Review. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug. Targets 2023, 23, 596–608.
- Martin, A.; Zhou, P.; Singh, B.B.; Kotsakis, G.A. Transcriptome-wide Gene Expression Analysis in Peri-implantitis Reveals Candidate Cellular Pathways. JDR Clin. Trans. Res. 2022, 7, 415–424.
- Di Fiore, A.; Montagner, M.; Sivolella, S.; Stellini, E.; Yilmaz, B.; Brunello, G. Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Overload: A Systematic Review Focusing on Occlusal Analysis through Digital and Analogic Methods. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4812.
- Sun, T.C.; Chen, C.J.; Gallucci, G.O. Prevention and management of peri-implant disease. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2023.
- Park, S.E.; Da Silva, J.D.; Weber, H.P.; Ishikawa-Nagai, S. Optical phenomenon of peri-implant soft tissue. Part I. Spectrophotometric assessment of natural tooth gingiva and peri-implant mucosa. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2007, 18, 569–574.
- Van Brakel, R.; Noordmans, H.J.; Frenken, J.; de Roode, R.; de Wit, G.C.; Cune, M.S. The effect of zirconia and titanium implant abutments on light reflection of the supporting soft tissues. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 1172–1178.
- Figuero, E.; Graziani, F.; Sanz, I.; Herrera, D.; Sanz, M. Management of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis. Periodontol. 2000 2014, 66, 255–273.
- Bianco, P.D.; Ducheyne, P.; Cuckler, J.M. Titanium serum and urine levels in rabbits with a titanium implant in the absence of wear. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 1937–1942.
- Muller, K.; Valentine-Thon, E. Hypersensitivity to titanium: Clinical and laboratory evidence. Neuroendocrinol. Lett. 2006, 27, 31–35.
- Sicilia, A.; Cuesta, S.; Coma, G.; Arregui, I.; Guisasola, C.; Ruiz, E.; Maestro, A. Titanium allergy in dental implant patients: A clinical study on 1500 consecutive patients. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2008, 19, 823–835.
- De Wijs, F.L.; Van Dongen, R.C.; De Lange, G.L.; De Putter, C. Front tooth replacement with Tubingen (Frialit) implants. J. Oral Rehabil. 1994, 21, 11–26.
- Koth, D.; McKinney, R.; Steflik, D.; Davis, Q. Clinical and statistical analyses of human clinical trials with the single crystal aluminum oxide endosteal dental implant: Five-year results. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1988, 60, 226–234.
- Cionca, N.; Hashim, D.; Mombelli, A. Zirconia dental implants: Where are we now, and where are we heading? Periodontol. 2000 2017, 73, 241–258.
- Hannink, R.H.J.; Kelly, P.M.; Muddle, B.C. Transformation Toughening in Zirconia-Containing Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 83, 461–487.
- Kelly, J.R.; Denry, I. Stabilized zirconia as a structural ceramic: An overview. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 289–298.
- Piconi, C.; Maccauro, G. Zirconia as a ceramic biomaterial. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 1–25.
- Brunello, G.; Rauch, N.; Becker, K.; Hakimi, A.R.; Schwarz, F.; Becker, J. Two-piece zirconia implants in the posterior mandible and maxilla: A cohort study with a follow-up period of 9 years. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2022, 33, 1233–1244.
- Pieralli, S.; Kohal, R.J.; Jung, R.E.; Vach, K.; Spies, B.C. Clinical Outcomes of Zirconia Dental Implants: A Systematic Review. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 96, 38–46.
- Roehling, S.; Schlegel, K.A.; Woelfler, H.; Gahlert, M. Performance and outcome of zirconia dental implants in clinical studies: A meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29 (Suppl. 16), 135–153.
- Grassi, F.R.; Capogreco, M.; Consonni, D.; Bilardi, G.; Buti, J.; Kalemaj, Z. Immediate occlusal loading of one-piece zirconia implants: Five-year radiographic and clinical evaluation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2015, 30, 671–680.
- Lorenz, J.; Giulini, N.; Holscher, W.; Schwiertz, A.; Schwarz, F.; Sader, R. Prospective controlled clinical study investigating long-term clinical parameters, patient satisfaction, and microbial contamination of zirconia implants. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 263–271.
- Osman, R.B.; Swain, M.V.; Atieh, M.; Ma, S.; Duncan, W. Ceramic implants (Y-TZP): Are they a viable alternative to titanium implants for the support of overdentures? A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 1366–1377.
- Siddiqi, A.; Kieser, J.A.; De Silva, R.K.; Thomson, W.M.; Duncan, W.J. Soft and Hard Tissue Response to Zirconia versus Titanium One-Piece Implants Placed in Alveolar and Palatal Sites: A Randomized Control Trial. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, 483–496.
- Kohal, R.J.; Weng, D.; Bächle, M.; Strub, J.R. Loaded custom-made zirconia and titanium implants show similar osseointegration: An animal experiment. J. Periodontol. 2004, 75, 1262–1268.
- Sennerby, L.; Dasmah, A.; Larsson, B.; Iverhed, M. Bone tissue responses to surface-modified zirconia implants: A histomorphometric and removal torque study in the rabbit. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2005, 7 (Suppl. 1), S13–S20.
- Al-Radha, A.S.D.; Dymock, D.; Younes, C.; O’Sullivan, D. Surface properties of titanium and zirconia dental implant materials and their effect on bacterial adhesion. J. Dent. 2012, 40, 146–153.
- Lee, D.-J.; Ryu, J.-S.; Shimono, M.; Lee, K.-W.; Lee, J.-M.; Jung, H.-S. Differential healing patterns of mucosal seal on zirconia and titanium implant. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 796.
- Hanawa, T. Zirconia versus titanium in dentistry: A review. Dent. Mater. J. 2020, 39, 24–36.
- Daou, E.E. The zirconia ceramic: Strengths and weaknesses. Open Dent. J. 2014, 8, 33.
- Payer, M.; Arnetzl, V.; Kirmeier, R.; Koller, M.; Arnetzl, G.; Jakse, N. Immediate provisional restoration of single-piece zirconia implants: A prospective case series–results after 24 months of clinical function. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 569–575.
- Zembić, A.; Johannesen, L.; Schou, S.; Malo, P.; Reichert, T.; Farella, M.; Hämmerle, C. Immediately restored one-piece single-tooth implants with reduced diameter: One-year results of a multi-center study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23, 49–54.
- Cionca, N.; Muller, N.; Mombelli, A. Two-piece zirconia implants supporting all-ceramic crowns: A prospective clinical study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 413–418.
- Joos, M.; Sailer, I.; Filippi, A.; Mukaddam, K.; Rosentritt, M.; Kuhl, S. Stability of screw-retention in two-piece zirconia implants: An in vitro study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2020, 31, 607–614.
- Jank, S.; Hochgatterer, G. Success Rate of Two-Piece Zirconia Implants: A Retrospective Statistical Analysis. Implant. Dent. 2016, 25, 193–198.
- Li, J.; Jansen, J.A.; Walboomers, X.F.; van den Beucken, J.J. Mechanical aspects of dental implants and osseointegration: A narrative review. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 103, 103574.
- Halldin, A.; Jimbo, R.; Johansson, C.B.; Wennerberg, A.; Jacobsson, M.; Albrektsson, T.; Hansson, S. Implant stability and bone remodeling after 3 and 13 days of implantation with an initial static strain. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 383–393.
- Leucht, P.; Kim, J.-B.; Wazen, R.; Currey, J.A.; Nanci, A.; Brunski, J.B.; Helms, J.A. Effect of mechanical stimuli on skeletal regeneration around implants. Bone 2007, 40, 919–930.
- Lucas, T.J.; Lawson, N.C.; Janowski, G.M.; Burgess, J.O. Effect of grain size on the monoclinic transformation, hardness, roughness, and modulus of aged partially stabilized zirconia. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 1487–1492.
- Pilliar, R.M.; Cameron, H.U.; Binnington, A.G.; Szivek, J.; Macnab, I. Bone ingrowth and stress shielding with a porous surface coated fracture fixation plate. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1979, 13, 799–810.
- Weinans, H.; Huiskes, R.; Grootenboer, H. Effects of fit and bonding characteristics of femoral stems on adaptive bone remodeling. J. Biomech. Eng. 1994, 116, 393–400.
- Sumner, D.R. Long-term implant fixation and stress-shielding in total hip replacement. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 797–800.
- Borgonovo, A.E.; Fabbri, A.; Vavassori, V.; Censi, R.; Maiorana, C. Multiple teeth replacement with endosseous one-piece yttrium-stabilized zirconia dental implants. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2012, 17, e981–e987.
- Borgonovo, A.E.; Vavassori, V.; Censi, R.; Calvo, J.L.; Re, D. Behavior of endosseous one-piece yttrium stabilized zirconia dental implants placed in posterior areas. Minerva Stomatol. 2013, 62, 247–257.
- Cionca, N.; Hashim, D.; Mombelli, A. Two-piece zirconia implants supporting all-ceramic crowns: Six-year results of a prospective cohort study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2021, 32, 695–701.
- Payer, M.; Heschl, A.; Koller, M.; Arnetzl, G.; Lorenzoni, M.; Jakse, N. All-ceramic restoration of zirconia two-piece implants—A randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 371–376.
- Kohal, R.J.; Knauf, M.; Larsson, B.; Sahlin, H.; Butz, F. One-piece zirconia oral implants: One-year results from a prospective cohort study. 1. Single tooth replacement. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2012, 39, 590–597.
- Koller, M.; Steyer, E.; Theisen, K.; Stagnell, S.; Jakse, N.; Payer, M. Two-piece zirconia versus titanium implants after 80 months: Clinical outcomes from a prospective randomized pilot trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2020, 31, 388–396.
- Jung, R.E.; Grohmann, P.; Sailer, I.; Steinhart, Y.N.; Feher, A.; Hammerle, C.; Strub, J.R.; Kohal, R. Evaluation of a one-piece ceramic implant used for single-tooth replacement and three-unit fixed partial dentures: A prospective cohort clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, 751–761.
- Cannizzaro, G.; Torchio, C.; Felice, P.; Leone, M.; Esposito, M. Immediate occlusal versus non-occlusal loading of single zirconia implants. A multicentre pragmatic randomised clinical trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2010, 3, 111–120.
- Akca, K.; Cavusoglu, Y.; Uysal, S.; Cehreli, M.C. A prospective, open-ended, single-cohort clinical trial on early loaded titanium-zirconia alloy implants in partially edentulous patients: Up-to-24-month results. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2013, 28, 573–578.
- Blaschke, C.; Volz, U. Soft and hard tissue response to zirconium dioxide dental implants—A clinical study in man. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2006, 27 (Suppl. 1), 69–72.
More
Information
Subjects:
Dentistry, Oral Surgery & Medicine
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
3.6K
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
13 Jun 2023
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No





