Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Samir Kamel | -- | 1786 | 2023-02-08 07:11:26 | | | |
| 2 | Dean Liu | Meta information modification | 1786 | 2023-02-10 03:26:30 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
D’amora, U.; Dacrory, S.; Hasanin, M.S.; Longo, A.; Soriente, A.; Kamel, S.; Raucci, M.G.; Ambrosio, L.; Scialla, S. Cellulose and Cellulose Derivatives. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/40955 (accessed on 28 February 2026).
D’amora U, Dacrory S, Hasanin MS, Longo A, Soriente A, Kamel S, et al. Cellulose and Cellulose Derivatives. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/40955. Accessed February 28, 2026.
D’amora, Ugo, Sawsan Dacrory, Mohamed Sayed Hasanin, Angela Longo, Alessandra Soriente, Samir Kamel, Maria Grazia Raucci, Luigi Ambrosio, Stefania Scialla. "Cellulose and Cellulose Derivatives" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/40955 (accessed February 28, 2026).
D’amora, U., Dacrory, S., Hasanin, M.S., Longo, A., Soriente, A., Kamel, S., Raucci, M.G., Ambrosio, L., & Scialla, S. (2023, February 08). Cellulose and Cellulose Derivatives. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/40955
D’amora, Ugo, et al. "Cellulose and Cellulose Derivatives." Encyclopedia. Web. 08 February, 2023.
Copy Citation
Among the biomaterials, cellulose is the most abundant, cheap, sustainable, chemical reactive and modifiable natural macromolecular compound on the Earth. It is a carbohydrate homopolymer, which is composed of repeating long linear chains of β-anhydro-D-glucopyranose units, linked together by an ether bond between -OH group of C4, and the C1 carbon atom, via a β-1,4-glycosidic bond.
cellulose
graphene oxide
antimicrobial
angiogenesis
1. Introduction
Among the biomaterials, cellulose is the most abundant, cheap, sustainable, chemical reactive and modifiable natural macromolecular compound on the Earth. It is a carbohydrate homopolymer, which is composed of repeating long linear chains of β-anhydro-D-glucopyranose units, linked together by an ether bond between -OH group of C4, and the C1 carbon atom, via a β-1,4-glycosidic bond, as represented in Figure 1 [1].
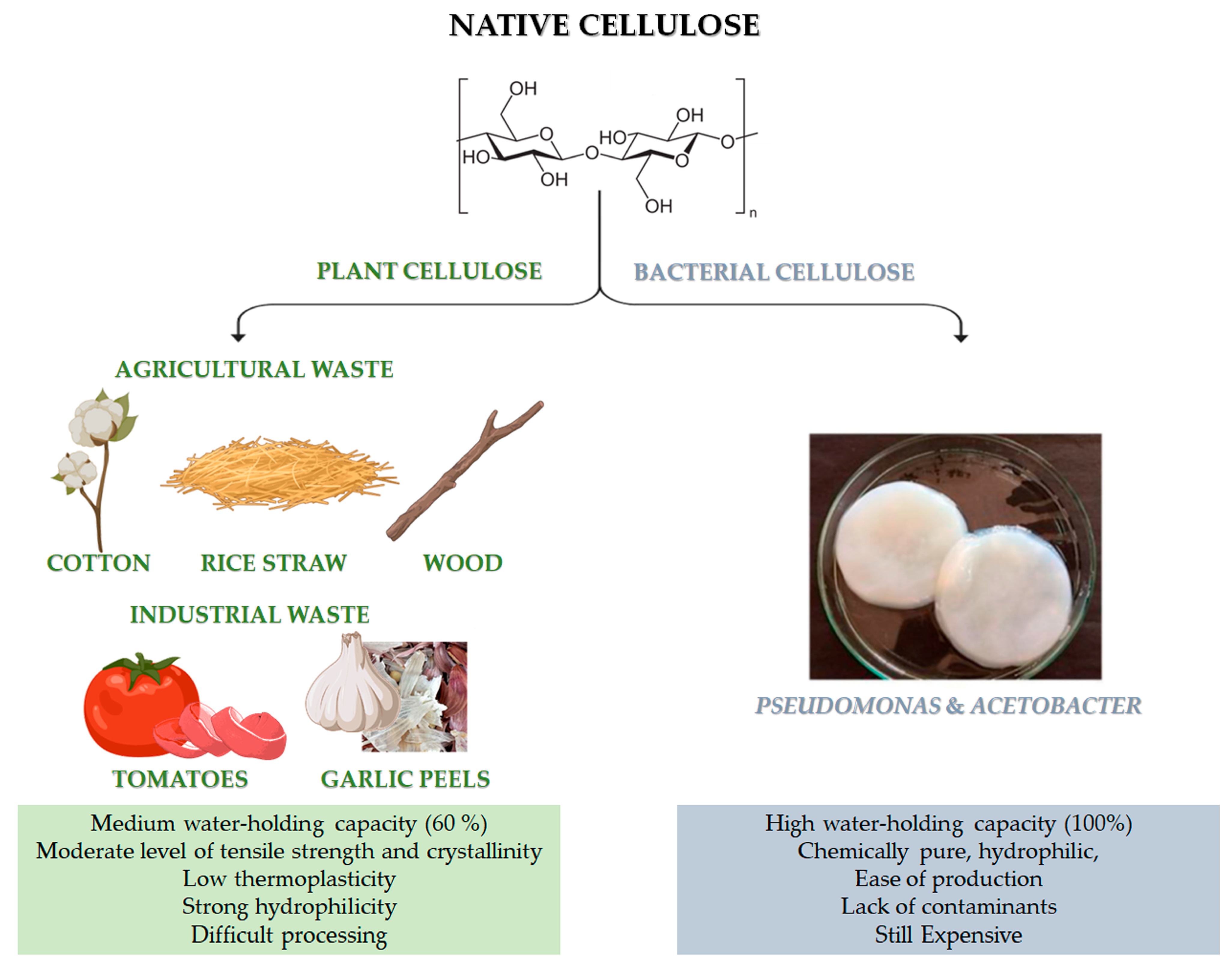
Figure 1. Chemical structure of cellulose and different sources of: native cellulose (from agricultural and industrial wastes) and bacterial cellulose (BC). Advantages and disadvantages of both kinds of cellulose. The image of BC is adapted from [2]. Copyright 2022 by the authors. License MDPI, Basel, Switzerland.
Native cellulose can be mainly classified into plant-derived and bacterial-derived cellulose (BC) [3]. It is worth noting that cellulose can be also obtained by animal sources [4]. In particular, some marine animals, called tunicate, represent the only animal source of cellulose [4]. However, it is still limited and not available for large-scale applications. Naturally-derived cellulose is a versatile, structural polysaccharide polymer, which mainly provides robust mechanical properties to plant cells, thanks to the hierarchical organisation of its natural fibres [5]. However, the structural backbone skeleton of plants represents a non-pure formulation that is usually based on lignocellulose, consisting of lignin, cellulose, hemicellulose, silica and some other impurities with different ratios, according to the plant type, as reported in Table 1. Indeed, plant cellulose widely exists in cotton, wood, and other flora species, such as phloem fibre, seed fibre, and wood fibre, which is the most abundant organic substance in nature [6]. Native cellulose also has the benefit of being able to be derived from agricultural wastes, such as cotton, bamboo, bagasse, and rice straw, which are affordable, readily available, and sustainable material sources [7]. Moreover, food processing is another possible source for cellulose recovery, even though it has highlighted many restrictions related to the solid waste collectability and the status of these wastes after gathering, which are usually contaminated with microorganisms and other impurities. Lately, industrial wastes (i.e., tomato, garlic peels) are also emerging as a promising source of cellulose.
Table 1. Cellulose content within different biomasses from agricultural waste.
| Agriculture | Cellulose (%) |
|---|---|
| Wood | 35–50 |
| Wheat straw | 33–40 |
| Switchgrass | 30–50 |
| Bagasse | 44 |
| Olive husk | 24 |
| Sunflowers | 26 |
| Rice straw | 33 |
| Rice husk | 49 |
| Cotton | 80–95 |
| Nutshells | 25–30 |
| Banana fibers | 60–65 |
| Corn cob | 42–45 |
| Oat straw | 33–35 |
| Hazelnut shell | 29 |
Recently, bacterial cellulose has gained particular interest [8]. BC can be produced by strictly aerobic, non-photosynthetic Gram− bacteria [8][9]. For their growth, these bacteria need carbon sources, which can be found in different raw materials (such as fruit, vegetable or lignocellulosic wastes) and other nutrients (such as nitrogen, iron, zinc and vitamins) [8][10]. Pseudomonas, Gluconacetobacter and Acetobacter are among the most important bacteria for the BC synthesis (Figure 1). Numerous studies have been carried out on the potential benefits of BC and plant-derived cellulose as biomaterials. In particular, the macromolecular characteristics of bacterial- and plant-derived cellulose differ. In addition, 60% of plant-derived cellulose can hold a medium amount of water, and it has a medium level of tensile strength and crystallinity. Conversely, BC is chemically pure, due to its hydrophilic nature, 100% water-holding capacity and lack of lignin, hemicellulose, and other impurities [6]. Furthermore, compared to plant-derived cellulose, BC has high crystallinity [6]. However, BC is still a high cost cellulose if compared to other conventional cellulose [11]. The versatility of BC’s biomedical uses is supported by its simple, contaminant-free manufacture and flexibility to modify the material’s properties during synthesis, such as crystallinity index, aspect ratio, and morphology, to precisely meet the needs of the intended application [6].
Native cellulose has multiple shortcomings, such as poor solubility in water and most organic solvents, due to intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonds, low thermoplasticity, strong hydrophilicity, and difficulty in processing, which limit its development and application in the biomedical and pharmaceutical fields [6]. The intra- and inter-molecular hydrogen bonds, between the -OH groups of the chain, provide cellulose with a crystalline and stiff structure. For this reason, it is insoluble in water but can be dissolved in strong acidic or alkaline conditions [12] (Figure 2). In particular, cellulose cannot dissolve in common solutions, except for two kinds of solvents: non-derivatizing solvents (i.e., sodium hydroxide, melts of inorganic salts, hydrates of inorganic salts, N, N-dimethylacetamide/lithium chlorideandmineral acids) and derivatizing solvents (i.e., trifluoroacetic acid, formic acid, dimethyl sulfoxide/para-formaldehyde, N, N-dimethyl formamide/dinitrogen tetroxide) [13]. Fortunately, insolubility can be overcome by obtaining cellulose derivatives, also known as cellulosics, through various physical and chemical modification procedures, such as esterification, etherification, or oxidation [14]. By this point of view, cellulose is the most known polysaccharide that can be easily converted to many cellulose derivatives. Among them, there are cellulose derivatives, which can be non-soluble, soluble in organic solvents and water-soluble, with a high safety profile towards biological systems [15].
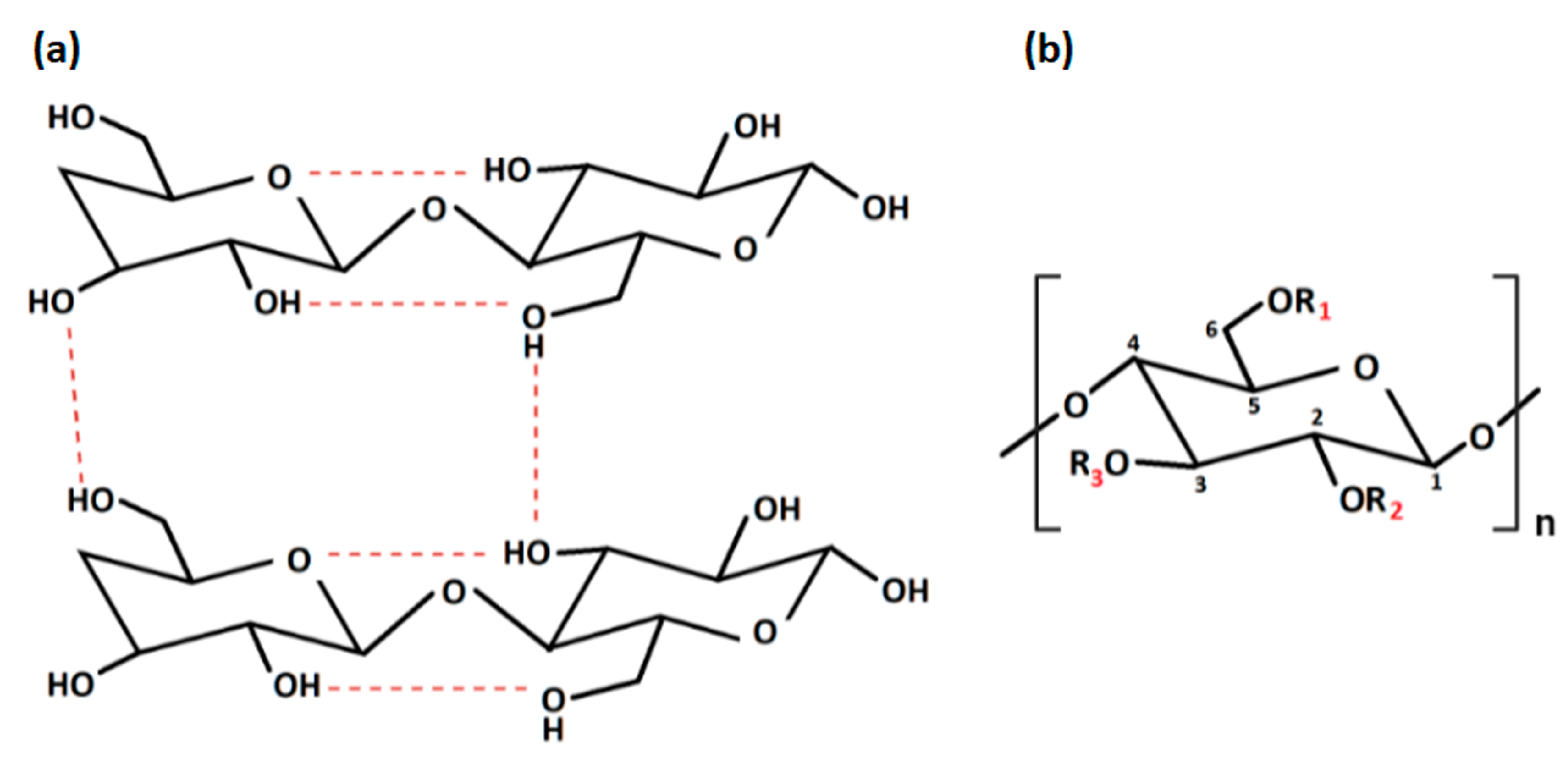
Figure 2. (a) Intra- and inter-molecular hydrogen bonds in cellulose; (b) repeating unit of cellulose derivatives. “Created with BioRender.com“.
2. Cellulose Physical Modifications
By altering the structure and surface properties of cellulose, physical modification is mostly used to create new qualities and functions. Briefly, the physical alteration largely entails mechanical swelling, recombining, surface adsorption, and grinding without changing the chemical composition of cellulose. Physically-modified cellulose forms are regenerated cellulose, membrane cellulose, microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), spherical cellulose, and nanocellulose (NC) in its two categories: cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) and cellulose nanofibers (CNF) [5]. NC is attracting a wide research attention for its physico-chemical properties: high specific surface area, easy modification, biodegradability, non-toxicity, biocompatibility, and antimicrobial properties, which are making it a suitable biomaterial for biomedical applications (i.e., wound healing).
3. Cellulose Chemical Modifications
With regard to the chemical modification, two different types of reactions are involved: -OH groups derivatisation and cellulose degradation. Acid/base, oxidative, biological, and mechanical processing are all examples of degradation reactions [6]. On the other hand, derivatisation may provide the synthesis of useful chemical products. At a macromolecular level, cellulose is characterised by both crystalline and amorphous regions. The crystalline region is distinguished by densely and firmly packed -OH groups that become unavailable. For this reason, this region is less reactive in comparison with the other one. The amorphous region is more available with high reactivity toward chemical species. Indeed, the majority of the chemical modifications involve the amorphous region [16]. Moreover, cellulose chains are linear, and their aggregation occurs via both intra- and inter-molecular hydrogen bonds as presented in Figure 2a, affecting its degree of crystallinity. This aspect is of paramount importance as the physico-chemical properties of cellulose are fine-tuned by the degree of crystallinity, as well as the hydrogen bonding [17]. Additionally, the reaction behaviour of cellulose and accessibility depend on cellulose morphology, degree of polymerization, crystallinity degree, purity and particle size. It is worth noting that cellulose units have three active -OH groups C6 > C2 > C3, with the C6–OH group, which can react ten times faster than the other two groups C2 and C3 (Figure 2b).
Modification via carboxymethylation, oxidation and Micheal addition reaction can introduce new functional groups in the cellulose backbone including -OH, carboxyl (-COOH), cyano (-C=N), aldehyde (-CH=O) and tetrazole groups, leading to derivatives, such as carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), methylcellulose (MC), dialdehyde cellulose (DAC) and hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC), as summarised in Table 2. Over the past years, because of the increasing demand for environmentally eco-friendly and biocompatible products, the possibility to chemically modify the cellulose has boosted great advances in material science and engineering, leading to the use of cellulose derivatives in promising fields of applications, such as pharmaceutical and biomedical [18], but also electronic [19][20], as well as a water treatment one [21][22].
Table 2. Common cellulose derivatives.
| Derivative | R1 | R2 | R3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) | COONa | COONa | COONa |
| Methylcellulose (MC) | CH3 | CH3 | CH3 |
| Dialdehyde cellulose (DAC) | H | C=O | C=O |
| Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) | CH2CH2OH | CH2CH2OH | CH2CH2OH |
Cellulose derivatives are semi-synthetic highly water-soluble biopolymers, having high biocompatibility, biodegradability, non-toxicity, non-immunogenicity properties [23], and also a thermo-gelling behaviour [24]. In addition, cellulose derivatives can absorb and retain a large amount of wound exudates within the interstitial sites of the matrixes, maintaining an optimal local moisture at the lesion site, to avoid skin tissue water loss and tissue necrosis [23][24]. Therefore, they represent a good alternative to water-insoluble cellulose. However, mechanical strength and toughness continue to be the most difficult problems, which scientists have attempted to solve in a variety of ways: (i) by the use of non-covalent (i.e., citric acid, polyphenols) or covalent (i.e., epichlorohydrin, aldehyde-based reagents, urea derivatives, carbodiimides and multifunctional carboxylic acids) crosslinking agents [25], (ii) by designing blends with other synthetic (i.e., polyurethane, poly (vinyl alcohol), polyvinylpyrrolidone) [26] or natural (i.e., collagen, gelatin, chitosan, k-carrageenan, alginate) biopolymers [27]; (iii) by employing gelling agents [28]; (iv) by using nanomaterials as fillers (i.e., graphene oxide derivatives, titanium oxide, silver nanoparticles, zinc oxide, ceramics) [29][30][31].
4. Cellulose from Agricultural Waste: Extraction Methods and Properties
Nowadays, taking into consideration the environmental problems arising from a rapidly growing industry, the demand of products obtained starting from renewable and sustainable non-petroleum-based resources is increasing. For this reason, exploring naturally-derived biomaterials, such native cellulose extracted from agricultural wastes, is attracting outstanding attention in the scientific community. Extraction of cellulose can be carried out using different approaches that are mainly based on chemical, biological and physical methodologies [32]. In this context, the chemical method is considered as the best approach, in terms of productivity and low-time consumption. However, low sustainability is among the main drawbacks [33][34]. Additionally, the biological method deals with microbial enzymes, such as ligninolytic enzymes, lignin peroxidases and laccases enzymes, which are able to extract cellulose [35][36]. This approach is highly eco-friendly but has many limitations, such as having low productivity, specificity, high-cost facilities and being time-consuming. The physical method specifically employs a mechanical treatment for lignocellulosic materials to produce high lignin content pulp that is used in specific applications not as pure cellulose [37]. However, each extraction method can build up a unique cellulose in terms of properties and reactivity. The chemical method of cellulose extraction usually produces cellulose contaminated with trace elements that can be found in a cellulose molecular structure during the pulping and the bleaching process, such as sulphur, chlorine, sodium and iodine. On the other hand, this method produces cellulose with good chemical properties with different shapes, including MCC, cellulose fibres and cellulose nanoforms [38]. The biological method overcomes the drawback of the chemical method, obtaining highly pure products. Finally, the physically extracted cellulose enables the production of a material with a high lignin content pulp, which is mainly used in packaging and high mechanical stress applications [39].
References
- Hasanin, M.S. Cellulose-Based Biomaterials: Chemistry and Biomedical Applications. Starch Stärke 2022, 74, 2200060.
- Choi, S.M.; Rao, K.M.; Zo, S.M.; Shin, E.J.; Han, S.S. Bacterial Cellulose and Its Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 1080.
- Naomi, R.; Bt Hj Idrus, R.; Fauzi, M.B. Plant-vs. Bacterial-Derived Cellulose for Wound Healing: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6803.
- Dunlop, M.J.; Clemons, C.; Reiner, R.; Sabo, R.; Agarwal, U.P.; Bissessur, R.; Sojoudiasli, H.; Carreau, P.J.; Acharya, B. Towards the Scalable Isolation of Cellulose Nanocrystals from Tunicates. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19090.
- Szychlinska, M.A.; Bucchieri, F.; Fucarino, A.; Ronca, A.; D’Amora, U. Three-Dimensional Bioprinting for Cartilage Tissue Engineering: Insights into Naturally-Derived Bioinks from Land and Marine Sources. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 118.
- Zou, P.; Yao, J.; Cui, Y.-N.; Zhao, T.; Che, J.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Gao, C. Advances in Cellulose-Based Hydrogels for Biomedical Engineering: A Review Summary. Gels 2022, 8, 364.
- Malladi, R.; Nagalakshmaiah, M.; Robert, M.; Elkoun, S. Importance of Agriculture and Industrial Waste in the Field of Nano Cellulose and Its Recent Industrial Developments: A Review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2807–2828.
- Wang, J.; Tavakoli, J.; Tang, Y. Bacterial Cellulose Production, Properties and Applications with Different Culture Methods—A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 219, 63–76.
- Castro, C.; Zuluaga, R.; Álvarez, C.; Putaux, J.-L.; Caro, G.; Rojas, O.J.; Mondragon, I.; Gañán, P. Bacterial Cellulose Produced by a New Acid-Resistant Strain of Gluconacetobacter Genus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 1033–1037.
- Hussain, Z.; Sajjad, W.; Khan, T.; Wahid, F. Production of Bacterial Cellulose from Industrial Wastes: A Review. Cellulose 2019, 26, 2895–2911.
- Abdelraof, M.; Hasanin, M.S.; El-Saied, H. Ecofriendly Green Conversion of Potato Peel Wastes to High Productivity Bacterial Cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 211, 75–83.
- Alves, L.; Medronho, B.; Antunes, F.E.; Topgaard, D.; Lindman, B. Dissolution State of Cellulose in Aqueous Systems. 1. Alkaline Solvents. Cellulose 2016, 23, 247–258.
- Abou-Yousef, H.; Dacrory, S.; Hasanin, M.; Saber, E.; Kamel, S. Biocompatible Hydrogel Based on Aldehyde-Functionalized Cellulose and Chitosan for Potential Control Drug Release. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 21, 100419.
- Aziz, T.; Farid, A.; Haq, F.; Kiran, M.; Ullah, A.; Zhang, K.; Li, C.; Ghazanfar, S.; Sun, H.; Ullah, R.; et al. A Review on the Modification of Cellulose and Its Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 3206.
- Xing, L.; Hu, C.; Zhang, W.; Guan, L.; Gu, J. Biodegradable Cellulose I (II) Nanofibrils/Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) Composite Films with High Mechanical Properties, Improved Thermal Stability and Excellent Transparency. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1766–1775.
- Zaman, A.; Huang, F.; Jiang, M.; Wei, W.; Zhou, Z. Preparation, Properties, and Applications of Natural Cellulosic Aerogels: A Review. Energy Built Environ. 2020, 1, 60–76.
- Wei, Z.; Cai, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, P.; Song, J.; Deng, L.; Fu, Y. Strong Biodegradable Cellulose Materials with Improved Crystallinity via Hydrogen Bonding Tailoring Strategy for UV Blocking and Antioxidant Activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 27–36.
- Dacrory, S.; Hashem, A.H.; Kamel, S. Antimicrobial and Antiviral Activities with Molecular Docking Study of Chitosan/ Clove Oil Beads. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 17, 2100298.
- Dacrory, S.; Kamel, S.; Turky, G. Development of Dielectric Film Based on Cellulose Loaded Nano-Silver and Carbon for Potential Energy Storage. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 123004.
- Dacrory, S.; Abou Hammad, A.B.; El Nahrawy, A.M.; Abou-Yousef, H.; Kamel, S. Cyanoethyl Cellulose/BaTiO3/GO Flexible Films with Electroconductive Properties. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 83004.
- Al-Shemy, M.T.; Al-Sayed, A.; Dacrory, S. Fabrication of Sodium Alginate/Graphene Oxide/Nanocrystalline Cellulose Scaffold for Methylene Blue Adsorption: Kinetics and Thermodynamics Study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 290, 120825.
- Dacrory, S. Development of Mesoporous Foam Based on Dicarboxylic Cellulose and Graphene Oxide for Potential Oil/Water Separation. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 9563–9574.
- Seddiqi, H.; Oliaei, E.; Honarkar, H.; Jin, J.; Geonzon, L.C.; Bacabac, R.G.; Klein-Nulend, J. Cellulose and Its Derivatives: Towards Biomedical Applications. Cellulose 2021, 28, 1893–1931.
- Tudoroiu, E.-E.; Ghica, M.-V.; Albu-Kaya, G.M.; Dinu-Pirvu, C.-E.; Popa, L.; Anuta, V.; Velescu, B.S.; Kaya, D.A.; Marin, M.M.; Prisada, R.M. Rheological Characterization of Some Cellulose Derivatives-Based Hydrogels. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Advanced Materials and Systems, Online, 26–28 October 2022.
- Nasution, H.; Harahap, H.; Dalimunthe, N.F.; Ginting, M.H.S.; Jaafar, M.; Tan, O.O.H.; Aruan, H.K.; Herfananda, A.L. Hydrogel and Effects of Crosslinking Agent on Cellulose-Based Hydrogels: A Review. Gels 2022, 8, 568.
- Manna, S.; Dhanalakshmi, D.; Bhowmik, M.; Jana, S.; Jana, S. Cellulose Derivative-Based Bioadhesive Blend Patch for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 835507.
- Douglass, E.F.; Avci, H.; Boy, R.; Rojas, O.J.; Kotek, R. A Review of Cellulose and Cellulose Blends for Preparation of Bio-Derived and Conventional Membranes, Nanostructured Thin Films, and Composites. Polym. Rev. 2018, 58, 102–163.
- Imeson, A. Food Stabilisers, Thickeners and Gelling Agents; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011.
- Oprea, M.; Panaitescu, D.M. Nanocellulose Hybrids with Metal Oxides Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 4045.
- Yan, N.; Capezzuto, F.; Lavorgna, M.; Buonocore, G.G.; Tescione, F.; Xia, H.; Ambrosio, L. Borate Cross-Linked Graphene Oxide--Chitosan as Robust and High Gas Barrier Films. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 10783–10791.
- Raucci, M.G.; Giugliano, D.; Longo, A.; Zeppetelli, S.; Carotenuto, G.; Ambrosio, L. Comparative Facile Methods for Preparing Graphene Oxide--Hydroxyapatite for Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 11, 2204–2216.
- Seo, Y.-R.; Kim, J.-W.; Hoon, S.; Kim, J.; Chung, J.H.; Lim, K.-T. Cellulose-Based Nanocrystals: Sources and Applications via Agricultural Byproducts. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 43, 59–71.
- Devi, A.; Singh, A.; Bajar, S.; Pant, D.; Din, Z.U. Ethanol from Lignocellulosic Biomass: An in-Depth Analysis of Pre-Treatment Methods, Fermentation Approaches and Detoxification Processes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105798.
- Hasanin, M.S.; Kassem, N.; Hassan, M.L. Preparation and Characterization of Microcrystalline Cellulose from Olive Stones. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021, 1–8.
- Suryadi, H.; Judono, J.J.; Putri, M.R.; Eclessia, A.D.; Ulhaq, J.M.; Agustina, D.N.; Sumiati, T. Biodelignification of Lignocellulose Using Ligninolytic Enzymes from White-Rot Fungi. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08865.
- Hasanin, M.S.; Darwesh, O.M.; Matter, I.A.; El-Saied, H. Isolation and Characterization of Non-Cellulolytic Aspergillus Flavus EGYPTA5 Exhibiting Selective Ligninolytic Potential. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 17, 160–167.
- Liu, K.; Du, H.; Zheng, T.; Liu, W.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Si, C. Lignin-Containing Cellulose Nanomaterials: Preparation and Applications. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 9723–9746.
- Nagarajan, K.J.; Ramanujam, N.R.; Sanjay, M.R.; Siengchin, S.; Surya Rajan, B.; Sathick Basha, K.; Madhu, P.; Raghav, G.R. A Comprehensive Review on Cellulose Nanocrystals and Cellulose Nanofibers: Pretreatment, Preparation, and Characterization. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 1588–1630.
- Kumar, A.; Gupta, V.; Singh, S.; Saini, S.; Gaikwad, K.K. Pine Needles Lignocellulosic Ethylene Scavenging Paper Impregnated with Nanozeolite for Active Packaging Applications. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 170, 113752.
More
Information
Subjects:
Materials Science, Biomaterials
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
3.8K
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
10 Feb 2023
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No





