
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Abir Mahmud | -- | 4482 | 2022-12-22 03:45:52 | | | |
| 2 | Beatrix Zheng | -51 word(s) | 4431 | 2022-12-23 02:25:50 | | |
Video Upload Options
Plastics are a kind of synthetic or semisynthetic polymer that are made up of long chains of carbon atoms, and they may also have oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur atoms attached to them. The majority of plastics are produced by factories that use fossil fuels. Microplastics are small particles of fragments and microfibers of plastic that have a diameter of less than 5 mm. Because of the widespread usage of microbeads in a variety of goods as well as the fragmentation of plastics with increasing age, the quantity of microplastic released in the aquatic environment is alarming, and so effluent water needs to be treated in wastewater plants to remove the microplastics. Different biotic and abiotic approaches have been studied in different research over the years.
1. Biotic Degradation of Microplastics
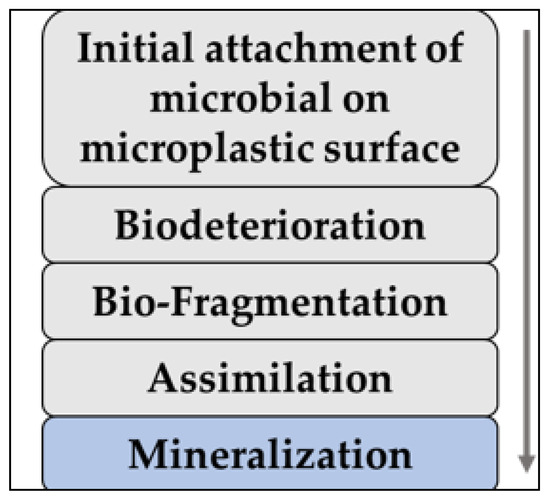
2. Bacterial Degradation
3. Degradation of Microplastics via Fungi
| Strain | Biodegradation Condition | Biodegradation Rate (%) | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Media | Duration | Temperature (°C) | |||
| Zalerion maritimum | Minimum growth media with 0.130 g of polymer |
0.94 months | 25 | 43 | [9] |
| Trichoderma harzianum | Mineral salt medium | 3 months | - | 40 | [10] |
| Aspergillus tubingensis | Mineral salt medium | 0.75 months | 37 | 90 | [11] |
| Phanerochaete chyrosporium | Soil buried (soil mixed with municipal sewage sludge) |
6 months | - | - | [12] |
4. Removal of Microplastics by Algae and Macrophytes
5. Degradation of Microplastics by Periphytic Biofilms
6. Removal of Microplastics through Adsorption
| Characteristics of Adsorbent | Process Parameters | Removed Microplastics | Efficiency of the Process | Involved Mechanisms | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biochar consisting of corn straw and hardwood | pH = 7.56 Filtration column for biochar Hybrid sand |
Polystyrene microplastic spheres (diameter = 10 μm) | Greater than 95% | Sticking, entangling, trapping |
[34] |
| Magnetic biochar modified by Mg/Zn | Temperature = 25 °C | Microplastic spheres of polystyrene (diameter = 1 μm) | Mg-MBC-98% Zn-MBC-99.46% MBC-94.80% |
Chemical bonding, electrostatic interaction | [35] |
| Biochar modified by iron and pyrolyzed at 550 °C and 850 °C | pH = 5.5 Temperature = 25 °C |
Nano-plastics (diameter = 30 nm and 1000 nm) | Around 100% | Surface complexation, electrostatic attraction |
[36] |
| Pine and spruce bark biochar pyrolyzed at 475 °C and steam-activated at 800 °C | Temperature = 25 °C | Spherical, cylindrical and fleece shirt fibers polyethylene microbeads (diameter = 10 μm) | Around 100% in the case of cylindrical polyethylene pieces and fleece fibers. | Adherence between biochar particles. | [37] |
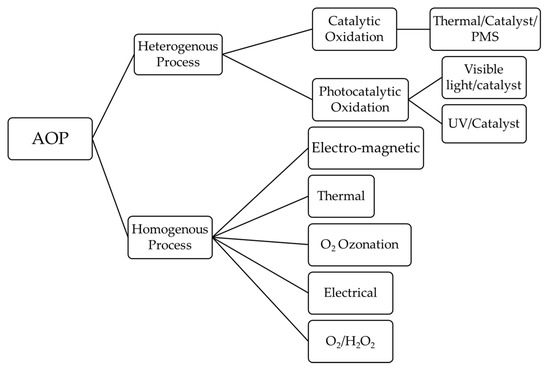
7. Degradation of Microplastics by Advanced Oxidation Process
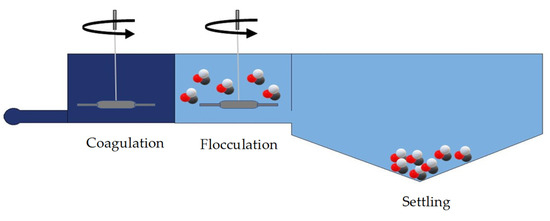
8. Microplastic Treatment by Coagulation and Flocculation
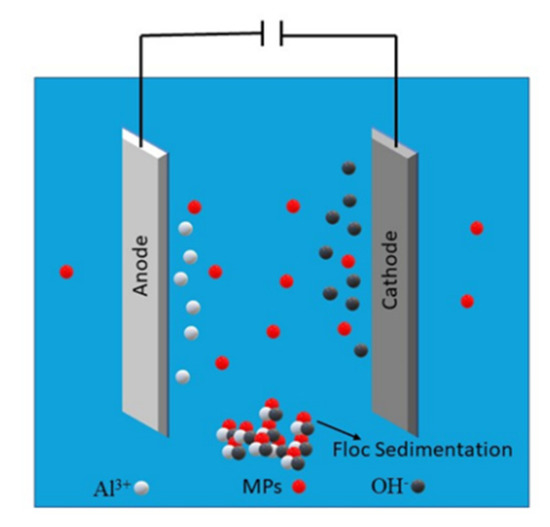
9. Electrocoagulation
10. Thermal Degradation/Plastic to Fuel
References
- Hossain, S.; Rahman, M.A.; Ahmed Chowdhury, M.; Kumar Mohonta, S. Plastic pollution in Bangladesh: A review on current status emphasizing the impacts on environment and public health. Environ. Eng. Res. 2021, 26, 200535.
- Rummel, C.D.; Jahnke, A.; Gorokhova, E.; Kühnel, D.; Schmitt-Jansen, M. Impacts of Biofilm Formation on the Fate and Potential Effects of Microplastic in the Aquatic Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 258–267.
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, X.; Jia, W.; Chai, L.; Huang, M.; Huang, Y. Microplastics from mulching film is a distinct habitat for bacteria in farmland soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 470–478.
- Sharma, S.; Basu, S.; Shetti, N.P.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Microplastics in the environment: Occurrence, perils, and eradication. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127317.
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Jayanthi, B.; Fauziah, S.H. Growth kinetics and biodeterioration of polypropylene microplastics by Bacillus sp. and Rhodococcus sp. isolated from mangrove sediment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 15–21.
- Tareen, A.; Saeed, S.; Iqbal, A.; Batool, R.; Jamil, N. Biodeterioration of Microplastics: A Promising Step towards Plastics Waste Management. Polymers 2022, 14, 2275.
- Yang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xiang, H.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y. Study on methanolytic depolymerization of PET with supercritical methanol for chemical recycling. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2002, 75, 185–191.
- Shimpi, N.; Borane, M.; Mishra, S.; Kadam, M. Biodegradation of polystyrene (PS)-poly(lactic acid) (PLA) nanocomposites using Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Macromol. Res. 2012, 20, 181–187.
- Paço, A.; Duarte, K.; da Costa, J.P.; Santos, P.S.M.; Pereira, R.; Pereira, M.E.; Freitas, A.C.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P. Biodegradation of polyethylene microplastics by the marine fungus Zalerion maritimum. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 10–15.
- Sowmya, H.V.; Ramalingappa; Krishnappa, M.; Thippeswamy, B. Degradation of polyethylene by Trichoderma harzianum—SEM, FTIR, and NMR analyses. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 6577–6586.
- Cosgrove, L.; McGeechan Paula, L.; Robson Geoff, D.; Handley Pauline, S. Fungal Communities Associated with Degradation of Polyester Polyurethane in Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5817–5824.
- Ali, G.; Nisar, J.; Iqbal, M.; Shah, A.; Abbas, M.; Shah, M.R.; Rashid, U.; Bhatti, I.A.; Khan, R.A.; Shah, F. Thermo-catalytic decomposition of polystyrene waste: Comparative analysis using different kinetic models. Waste Manag. Res. 2019, 38, 202–212.
- Chia, W.Y.; Ying Tang, D.Y.; Khoo, K.S.; Kay Lup, A.N.; Chew, K.W. Nature’s fight against plastic pollution: Algae for plastic biodegradation and bioplastics production. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2020, 4, 100065.
- Sharma, M.; Dubey, A.; Pareek, A. Algal flora on degrading polythene waste. CIBTech J. Microbiol. 2014, 3, 43–47.
- Sarmah, P.; Rout, J. Algal colonization on polythene carry bags in a domestic solid waste dumping site of Silchar town in Assam. Phykos 2018, 48, 67–77.
- Chinaglia, S.; Tosin, M.; Degli-Innocenti, F. Biodegradation rate of biodegradable plastics at molecular level. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 147, 237–244.
- Kumar, R.V.; Kanna, G.; Elumalai, S. Biodegradation of polyethylene by green photosynthetic microalgae. J. Bioremediat. Biodegrad. 2017, 8, 2.
- Kim, J.W.; Park, S.-B.; Tran, Q.-G.; Cho, D.-H.; Choi, D.-Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, H.-S. Functional expression of polyethylene terephthalate-degrading enzyme (PETase) in green microalgae. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 1–9.
- Faheem, M.; Shabbir, S.; Zhao, J.; G. Kerr, P.; Ali, S.; Sultana, N.; Jia, Z. Multifunctional periphytic biofilms: Polyethylene degradation and Cd2+ and Pb2+ bioremediation under high methane scenario. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5331.
- Battin, T.J.; Besemer, K.; Bengtsson, M.M.; Romani, A.M.; Packmann, A.I. The ecology and biogeochemistry of stream biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 251–263.
- Eckert, R.A.; Halvorson, H.M.; Kuehn, K.A.; Lamp, W.O. Macroinvertebrate community patterns in relation to leaf-associated periphyton under contrasting light and nutrient conditions in headwater streams. Freshw. Biol. 2020, 65, 1270–1287.
- Ewe, S.M.; Gaiser, E.E.; Childers, D.L.; Iwaniec, D.; Rivera-Monroy, V.H.; Twilley, R.R. Spatial and temporal patterns of aboveground net primary productivity (ANPP) along two freshwater-estuarine transects in the Florida Coastal Everglades. Hydrobiologia 2006, 569, 459–474.
- Martyniuk, N.; Modenutti, B.; Balseiro, E. Forest structure affects the stoichiometry of periphyton primary producers in mountain streams of northern Patagonia. Ecosystems 2016, 19, 1225–1239.
- Miao, L.; Wang, P.; Hou, J.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, T. Distinct community structure and microbial functions of biofilms colonizing microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2395–2402.
- Álvarez-Barragán, J.; Domínguez-Malfavón, L.; Vargas-Suárez, M.; González-Hernández, R.; Aguilar-Osorio, G.; Loza-Tavera, H. Biodegradative activities of selected environmental fungi on a polyester polyurethane varnish and polyether polyurethane foams. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5225–5235.
- Gómez-Méndez, L.D.; Moreno-Bayona, D.A.; Poutou-Piñales, R.A.; Salcedo-Reyes, J.C.; Pedroza-Rodríguez, A.M.; Vargas, A.; Bogoya, J.M. Biodeterioration of plasma pretreated LDPE sheets by Pleurotus ostreatus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203786.
- Debroy, A.; George, N.; Mukherjee, G. Role of biofilms in the degradation of microplastics in aquatic environments. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021.
- Islam, M.S.; Roy, H.; Afrose, S. Phosphoric acid surface modified Moringa oleifera leaves biochar for the sequestration of methyl orange from aqueous solution: Characterizations, isotherm, and kinetics analysis. Remediat. J. 2022, 32, 281–298.
- Jahan, N.; Roy, H.; Reaz, A.H.; Arshi, S.; Rahman, E.; Firoz, S.H.; Islam, M.S. A comparative study on sorption behavior of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide towards methylene blue. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 6, 100239.
- Roy, H.; Islam, M.S.; Arifin, M.T.; Firoz, S.H. Chitosan-ZnO decorated Moringa oleifera seed biochar for sequestration of methylene blue: Isotherms, kinetics, and response surface analysis. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 18, 100752.
- Roy, H.; Prantika, T.R.; Riyad, M.; Paul, S.; Islam, M.S. Synthesis, characterizations, and RSM analysis of Citrus macroptera peel derived biochar for textile dye treatment. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 41, 129–139.
- Roy, H.; Rahman, M.M.; Tarek, Y.A.; Firoz, S.H. Encapsulation of Industrial Cationic Pollutants from Aqueous Solution by Nanocrystalline Cellulose and It’s Modified Forms. In Proceedings of the International Exchange and Innovation Conference on Engineering & Sciences (IEICES) 2021 at: Interdisciplinary Graduate School of Engineering Sciences (IGSES), Kyushu University, Fukoka, Japan, 2 December 2021.
- Roy, H.; Shakil, R.; Tarek, Y.A.; Firoz, S.H. Study of the Removal of Basic Blue-41 from Simulated Wastewater By Activated Carbon Prepared from Discarded Jute Fibre. ECS Trans. 2022, 107, 8407.
- Wang, Z.; Sedighi, M.; Lea-Langton, A. Filtration of microplastic spheres by biochar: Removal efficiency and immobilisation mechanisms. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116165.
- Wang, J.; Sun, C.; Huang, Q.-X.; Chi, Y.; Yan, J.-H. Adsorption and thermal degradation of microplastics from aqueous solutions by Mg/Zn modified magnetic biochars. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126486.
- Singh, N.; Khandelwal, N.; Ganie, Z.A.; Tiwari, E.; Darbha, G.K. Eco-friendly magnetic biochar: An effective trap for nanoplastics of varying surface functionality and size in the aqueous environment. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129405.
- Siipola, V.; Pflugmacher, S.; Romar, H.; Wendling, L.; Koukkari, P. Low-cost biochar adsorbents for water purification including microplastics removal. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 788.
- Akter, S.; Islam, M.S.; Kabir, M.H.; Shaikh, M.A.A.; Gafur, M.A. UV/TiO2 photodegradation of metronidazole, ciprofloxacin and sulfamethoxazole in aqueous solution: An optimization and kinetic study. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103900.
- Al-Mamun, M.R.; Kader, S.; Islam, M.S. Solar-TiO2 immobilized photocatalytic reactors performance assessment in the degradation of methyl orange dye in aqueous solution. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100514.
- Al-Mamun, M.R.; Kader, S.; Islam, M.S.; Khan, M.Z.H. Photocatalytic activity improvement and application of UV-TiO2 photocatalysis in textile wastewater treatment: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103248.
- Al-Mamun, M.R.; Karim, M.N.; Nitun, N.A.; Kader, S.; Islam, M.S.; Khan, M.Z.H. Photocatalytic performance assessment of GO and Ag co-synthesized TiO2 nanocomposite for the removal of methyl orange dye under solar irradiation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101537.
- Hasan Khan Neon, M.; Islam, M.S. MoO3 and Ag co-synthesized TiO2 as a novel heterogeneous photocatalyst with enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity for methyl orange dye degradation. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2019, 12, 100244.
- Rashid Al-Mamun, M.; Hossain, K.T.; Mondal, S.; Afroza Khatun, M.; Shahinoor Islam, M.; Zaved Hossain Khan, D.M. Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic performance of methyl orange in aqueous TiO2 suspension under UV and solar light irradiation. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 40, 113–125.
- Rashid Al-Mamun, M.; Shofikul Islam, M.; Rasel Hossain, M.; Kader, S.; Shahinoor Islam, M.; Zaved Hossain Khan, M. A novel and highly efficient Ag and GO co-synthesized ZnO nano photocatalyst for methylene blue dye degradation under UV irradiation. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100495.
- Perren, W.; Wojtasik, A.; Cai, Q. Removal of Microbeads from Wastewater Using Electrocoagulation. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 3357–3364.
- Moussa, D.T.; El-Naas, M.H.; Nasser, M.; Al-Marri, M.J. A comprehensive review of electrocoagulation for water treatment: Potentials and challenges. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 186, 24–41.
- Elkhatib, D.; Oyanedel-Craver, V.; Carissimi, E. Electrocoagulation applied for the removal of microplastics from wastewater treatment facilities. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 118877.
- Shen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Almatrafi, E.; Hu, T.; Zhou, C.; Song, B.; Zeng, Z.; Zeng, G. Efficient removal of microplastics from wastewater by an electrocoagulation process. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131161.
- Xu, R.; Yang, Z.; Niu, Y.; Xu, D.; Wang, J.; Han, J.; Wang, H. Removal of microplastics and attached heavy metals from secondary effluent of wastewater treatment plant using interpenetrating bipolar plate electrocoagulation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 290, 120905.
- Akarsu, C.; Deniz, F. Electrocoagulation/Electroflotation Process for Removal of Organics and Microplastics in Laundry Wastewater. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 2021, 49, 2000146.
- Akarsu, C.; Kumbur, H.; Kideys, A.E. Removal of microplastics from wastewater through electrocoagulation-electroflotation and membrane filtration processes. Water Sci. Technol. A J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2021, 84, 1648–1662.
- Hu, K.; Tian, W.; Yang, Y.; Nie, G.; Zhou, P.; Wang, Y.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. Microplastics remediation in aqueous systems: Strategies and technologies. Water Res. 2021, 198, 117144.
- Hou, L.; Kumar, D.; Yoo, C.G.; Gitsov, I.; Majumder, E.L.W. Conversion and removal strategies for microplastics in wastewater treatment plants and landfills. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126715.
- Ciuffi, B.; Chiaramonti, D.; Rizzo, A.M.; Frediani, M.; Rosi, L. A Critical Review of SCWG in the Context of Available Gasification Technologies for Plastic Waste. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6307.
- Tavares, R.; Ramos, A.; Rouboa, A. Microplastics thermal treatment by polyethylene terephthalate-biomass gasification. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 162, 118–131.
- Bai, B.; Jin, H.; Zhu, S.; Wu, P.; Fan, C.; Sun, J. Experimental investigation on in-situ hydrogenation induced gasification characteristics of acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) microplastics in supercritical water. Fuel Process. Technol. 2019, 192, 170–178.
- Bai, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, F.; Han, X.; Wang, Q.; Jin, H. Experimental investigation on gasification characteristics of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) microplastics in supercritical water. Fuel 2020, 262, 116630.
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Su, J.; Fang, C.; Xu, D.; Song, W.; Wang, S. Influences of operating parameters on liquefaction performances of Tetra Pak in sub-/supercritical water. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 237, 545–551.




