| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rosa M. Espinosa-Marzal | + 2518 word(s) | 2518 | 2020-11-19 10:10:02 | | | |
| 2 | Lily Guo | -1126 word(s) | 1392 | 2020-12-21 07:47:03 | | | | |
| 3 | Lily Guo | -1126 word(s) | 1392 | 2020-12-21 07:50:13 | | |
Video Upload Options
This entry briefly covers the existing knowledge on the lubrication mechanisms of hydrogels by discussing the main ideas, knowledge gaps and opportunities in the research area.
1. Introduction
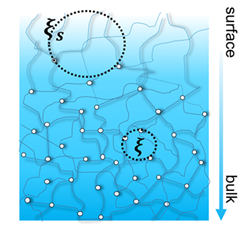
Since their inception, research on hydrogels have gained popularity, most significantly in biomedical research. Figure 1 shows a schematic representation of a hydrogel. Hydrogels are composed of chemically or physically crosslinked polymeric networks imbibed by a good solvent[1] in most cases an aqueous fluid. The blob-like structure of hydrogels is often described via the scaling laws proposed by de Gennes for polymer solutions in the semi-dilute regime. The distance between two crosslinks (labelled as mesh size, ) depends on the polymer concentration and the solvent quality, among others. This characteristic length determines key properties of hydrogels like permeability, elastic modulus and viscoelastic relaxation. Due to their semblance to biological tribosystems, a significant amount of research has been conducted on hydrogels to elucidate biolubrication mechanisms and their possible applications as replacement materials in biological tribosystems. From models developed on the basis of polymer physics to the concept of hydration lubrication, the proposed mechanisms are plenty. One subset of models takes a polymer physics approach based on the scaling laws proposed by de Gennes[2], and emphasizes the role of the mesh size both in boundary and in hydrodynamic lubrication. In contrast to this, the second approach emphasizes the role of a thin fluid film effectively separating the countersurfaces at low velocities and/or full fluid film lubrication at fast sliding velocities.
Figure 1. Hydrogel consisting of polymer chains permanently crosslinked or physically entangled. The mesh size (see dashed circles) may vary as a function of the hydrogel’s depth due to gradients in crosslinking as well as polymer concentration.
2. Overview of Mechanistic Models
Brainchild of Klein[3], the concept of a thin film of water of a few nanometers in thickness separating two surfaces decorated with polymer brushes has found its way to explain lubrication mediated by synthetic and biological hydrogels and the low coefficients of friction[4][5][6][7]. Imagine the hydrated polymer chains at the hydrogel´s surface sliding past each other. The so-termed hydration lubrication presumes the absence of contact between the polymer-bearing surfaces as a result of repulsive interactions, mainly elastic and osmotic in origin, although electrostatic interactions also contribute in the case of charged hydrogels[8]. Hence, it attributes the low friction coefficients to the small viscous force upon shear of a thin (hydration) film separating the surfaces[9][10][11]. However, MD simulations of neutral polymer brushes[12] and experimentally observed contact between polymer and a solid surface via imaging[13][14] or through the measured stick-slip[15][16] point to the absence of such a hydration film separating the two sliding surfaces. This reminds us that the existence of a thin film is not universal, but it strongly depends on the chemical interactions between the polymer and the solid countersurface. Also, to date, it is still unclear under which tribological conditions a fluid film effectively separates permeable surfaces, like hydrogels, yielding hydrodynamic and hydration lubrication. This is mainly due to the inherent difficulty to experimentally prove the presence of this film and to determine its thickness.
Pioneering measurements by Gong reported a non-monotonic velocity dependence of the kinetic friction force and distinguished between the type of interaction, i.e. repulsive vs. adhesive, at the interface[17]. This non-monotonic dependence was confirmed in numerous subsequent studies[18][17][19][20][21][22][23]. For instance, an adsorption-desorption model based on the mechanism of rubber friction was proposed for adhesive contacts, wherein both the fluctuation length () and the characteristic relaxation times of the polymer network dictate attachment and detachment rates of the polymer to the counter surface[17]. According to this model, friction in the adhesive (also called elastic) regime can either increase (velocity-strengthening), decrease (velocity-weakening) or remain constant depending on the time scale of the experimental observation. The transition from the adhesive to viscous regime occurs within an increase in sliding speed when a Newtonian fluid film separates the two surfaces and its shear determines the dissipated energy. More recent studies have revealed deviations from this behavior. For examples, they have shown a non-Newtonian scaling[20][21][22]and stick-slip[24][25] at high sliding velocities, both evidencing the influence of the polymer on friction at high velocities in the so called viscous regime. Frictional models based on a hydrodynamic flow through the porous network[26] and thixotropic flow response of the hydrogel’s interface[27] have also come to light.
The viscous-adhesive model, recently developed by the authors[16] provides a phenomenological model to quantify frictional response of hydrogels by considering an interplay of adhesive and viscous dissipation directly arising from the hydrogel’s microstructure. The model accounts for confinement effects, poroelastic deformation, and the influence of the polymer on the viscous dissipation in an attempt to reconcile the existing discrepancies in previously proposed models for adhesive hydrogel contacts.
3. Knowledge Gaps and Opportunities
As described earlier, the proposed mechanisms for viscous dissipation range from hydrodynamic lubrication mediated by the Newtonian behavior of the solvent to non-Newtonian shear of the hydrogel interfacial region and a polymer-relaxation lubrication mechanism. While all of these assumptions are consistent with experimental observations, measurements dedicated to examining the interfacial rheology of adhesive and repulsive contacts with hydrogels are still needed to provide fundamental insight into the interfacial behavior. Rheological models that specifically account for the time-dependent variation of friction in static contacts have been already considered[27][28][29].
The complexity of the lubrication mechanisms mediated by hydrogels also relies on other factors, including contact roughness and wear. Surface roughness can significantly affect the frictional characteristics. For example, while the friction at relatively smooth hydrogel surfaces follows well the elastic-hydrodynamic friction model by Gong[30], hydrogels with a surface roughness in the microscale (1-10 µm) exhibit only a velocity-weakening regime. Similarly, the roughness of the hard surface is also shown to play a role in the frictional response below the critical velocity[31][32]. On the one hand, hydrogels have an inherent surface roughness owing to polymer dynamics at the interface. On the other one, hydrogels can be prepared with modulated surface topology. Hence, it seems imperative to elucidate the influence of surface roughness on the lubrication mechanisms and friction models. Similarly, the relation between frictional dissipation and wear is still not well understood. While several works have examined the tribologically-induced wear of hydrogels that can serve as biological replacement materials [33][34][35][36], the understanding of the mechanisms underlying tribologically promoted wear is not only lacking, but even more, the correlation is debated.
Another relevant phenomenon for the frictional dissipation of soft materials is static friction. Although only a handful of studies have focused on static friction of hydrogels [37][38][39][40], there is sufficient experimental evidence demonstrating the dependence of adhesion and static friction on contact time. It is worth mentioning that wear of soft biological materials has been often related to adhesion and static friction[41][42][43], and hence, future research should be dedicated to improving our understanding of static friction of hydrogels, as well.
The frictional response of hydrogels is also expected to depend on the chemical make-up and charge of hydrogel surfaces. Precedent works by Gong[18] and Sokoloff[44] have developed models for charged hydrogel friction. Between similarly charged surfaces, a fluid film can be expected[44] Interestingly, it has been shown that friction can be controlled by adjusting the local molecular conformation of a polyelectrolyte brush via an alternating electric field[45]. The intensity of the applied field can regulate the stretching of the polymer chain while sliding, and thereby, the degree of interpenetration between opposite polymer brushes at the interface. The dynamics of the response is controlled by the relaxation times of the polyelectrolyte. While the molecular-level response to an electric field is relatively quick, less is known about the response dynamics of charged hydrogels. Electrotunable behavior offers opportunities for applications in soft robotics, among others, and hence, it is not only fundamentally interesting but also important for these applications. Furthermore, varying the fluid film properties through the modulation of an applied electric field or of the charge density of the hydrogel offers a new avenue to elucidate the mechanism of viscous and electroviscous dissipation.
Note:
Hydrogels are undoubtedly of great interest to the tribology community, but there still remains much work to be done before we can design hydrogels for targeted tribological applications. Elucidating hydrogel lubrication mechanisms is not only paramount to understand better biolubrication but also to advance the knowledge required to achieve this design goal.
References
- Lustig, S.R.; Peppas, N.A. Solute diffusion in swollen membranes. IX. Scaling laws for solute diffusion in gels. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 1988, 36, 735-747, doi:10.1002/app.1988.070360401.
- De Gennes, P.-G.; Gennes, P.-G. Scaling concepts in polymer physics; Cornell university press: 1979; 10.1063/1.2914118.
- Swann, D.A.; Radin, E.L.; Nazimiec, M.; Weisser, P.A.; Curran, N.; Lewinnek, G. Role of hyaluronic acid in joint lubrication. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1974, 33, 318–326, doi:10.1136/ard.33.4.318.
- Naka, M.H.; Morita, Y.; Ikeuchi, K. Influence of proteoglycan contents and of tissue hydration on the frictional characteristics of articular cartilage. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 2005, 219, 175-182, doi:10.1243/095441105X34220.
- Sokoloff, J.B. Theory of hydrostatic lubrication for two like-charge polymer hydrogel coated surfaces. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 3856-3862, doi:10.1039/c000252f.
- Gong, J.P.; Kagata, G.; Osada, Y. Friction of Gels. 4. Friction on Charged Gels. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 1999, 103, 6007-6014, doi:10.1021/jp990256v.
- Ishikawa, Y.; Hiratsuka, K.-i.; Sasada, T. Role of water in the lubrication of hydrogel. Wear 2006, 261, 500-504, doi:10.1016/j.wear.2005.12.001.
- Peppas, N.A.; Bures, P.; Leobandung, W.; Ichikawa, H. Hydrogels in pharmaceutical formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 27–46, doi:10.1016/s0939-6411(00)00090-4.
- Wichterle, O.; Lim, D. Hydrophilic gels for biological use. Nature 1960, 185, 117, doi:10.1038/185117a0.
- Lustig, S.R.; Peppas, N.A. Solute diffusion in swollen membranes. IX. Scaling laws for solute diffusion in gels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1988, 36, 735–747, doi:10.1002/app.1988.070360401.
- De Gennes, P.G. Dynamics of Entangled Polymer Solutions. I. The Rouse Model. Macromolecules 1976, 9, 587–593, doi:10.1021/ma60052a011.
- De Gennes, P.-G.; Gennes, P.-G. Scaling Concepts in Polymer Physics; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA and London, UK, 1979; doi:10.1063/1.2914118.
- Geissler, E.; Hecht, A.M.; Horkay, F.; Zrinyi, M. Compressional Modulus of Swollen Polyacrylamide Networks. Macromolecules 1988, 21, 2594–2599, doi:10.1021/ma00186a048.
- Sokoloff, J.B. Theory of hydrostatic lubrication for two like-charge polymer hydrogel coated surfaces. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 3856–3862, doi:10.1039/c000252f.
- Gong, J.P.; Iwasaki, Y.; Osada, Y.; Kurihara, K.; Hamai, Y. Friction of gels. 3. Friction on solid surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 6001–6006, doi:10.1021/jp9902553.
- Pan, Y.S.; Xiong, D.S. Friction properties of nano-hydroxyapatite reinforced poly(vinyl alcohol) gel composites as an articular cartilage. Wear 2009, 266, 699–703, doi:10.1016/j.wear.2008.08.012.
- Chang, D.P.; Dolbow, J.E.; Zauscher, S. Switchable friction of stimulus-responsive hydrogels. Langmuir 2007, 23, 250–257, doi:10.1021/la0617006.
- Hoffman, A.S. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliver Rev. 2012, 64, 18–23, doi:10.1016/j.addr.2012.09.010.
- Pan, Y.S.; Xiong, D.S.; Ma, R.Y. A study on the friction properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel as articular cartilage against titanium alloy. Wear 2007, 262, 1021–1025, doi:10.1016/j.wear.2006.10.005.
- Gong, J.P.; Kagata, G.; Osada, Y. Friction of gels. 4. Friction on charged gels. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 6007–6014, doi:10.1021/jp990256v.
- Oogaki, S.; Kagata, G.; Kurokawa, T.; Kuroda, S.; Osada, Y.; Gong, J.P. Friction between like-charged hydrogels-combined mechanisms of boundary, hydrated and elastohydrodynamic lubrication. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 1879–1887, doi:10.1039/b815102d.
- Gong, J.P. Friction and lubrication of hydrogels-its richness and complexity. Soft Matter 2006, 2, 544–552, doi:10.1039/b603209p.
- Shoaib, T.; Espinosa-Marzal, R.M. Insight into the Viscous and Adhesive Contributions to Hydrogel Friction. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 96, doi:10.1007/s11249-018-1045-7.
- Yashima, S.; Takase, N.; Kurokawa, T.; Gong, J.P. Friction of hydrogels with controlled surface roughness on solid flat substrates. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 3192–3199, doi:10.1039/c3sm52883a.
- Tominaga, T.; Kurokawa, T.; Furukawa, H.; Osada, Y.; Gong, J.P. Friction of a soft hydrogel on rough solid substrates. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 1645–1652, doi:10.1039/b802568a.
- Gong, J.; Osada, Y. Gel friction: A model based on surface repulsion and adsorption. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 109, 8062–8068, doi:10.1063/1.477453.
- Simič, R.; Yetkin, M.; Zhang, K.; Spencer, N.D. Importance of Hydration and Surface Structure for Friction of Acrylamide Hydrogels. Tribol. Lett. 2020, 68, 1–12, doi:10.1007/s11249-020-01304-x.
- Cuccia, N.L.; Pothineni, S.; Wu, B.; Mendez Harper, J.; Burton, J.C. Pore-size dependence and slow relaxation of hydrogel friction on smooth surfaces. PNAS 2020, 117, 11247–11256, doi:10.1073/pnas.1922364117.
- Kim, J.; Dunn, A.C. Soft hydrated sliding interfaces as complex fluids. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 6536–6546, doi:10.1039/c6sm00623j.
- Pitenis, A.A.; Uruena, J.M.; Schulze, K.D.; Nixon, R.M.; Dunn, A.C.; Krick, B.A.; Sawyer, W.G.; Angelini, T.E. Polymer fluctuation lubrication in hydrogel gemini interfaces. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 8955–8962, doi:10.1039/c4sm01728e.
- Shoaib, T.; Espinosa-Marzal, R.M. Influence of Loading Conditions and Temperature on Static Friction and Contact Aging of Hydrogels with Modulated Microstructures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 42722–42733, doi:10.1021/acsami.9b14283.
- Klein, J. Hydration lubrication. Friction 2013, 1, 1–23, doi:10.1007/s40544-013-0001-7.
- Naka, M.H.; Morita, Y.; Ikeuchi, K. Influence of proteoglycan contents and of tissue hydration on the frictional characteristics of articular cartilage. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2005, 219, 175–182, doi:10.1243/095441105X34220.
- Ishikawa, Y.; Hiratsuka, K.; Sasada, T. Role of water in the lubrication of hydrogel. Wear 2006, 261, 500–504, doi:10.1016/j.wear.2005.12.001.
- Rosenberg, K.J.; Goren, T.; Crockett, R.; Spencer, N.D. Load-induced transitions in the lubricity of adsorbed poly(L-lysine)-g-dextran as a function of polysaccharide chain density. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 3020–3025, doi:10.1021/am200521m.
- Klein, J.; Luckham, P. Forces between 2 Adsorbed Polyethylene Oxide Layers Immersed in a Good Aqueous Solvent. Nature 1982, 300, 429–431, doi:10.1038/300429a0.
- Klein, J.; Kamiyama, Y.; Yoshizawa, H.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Fredrickson, G.H.; Pincus, P.; Fetters, L.J. Lubrication Forces between Surfaces Bearing Polymer Brushes. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 5552–5560, doi:10.1021/ma00073a004.
- Espinosa-Marzal, R.M.; Nalam, P.C.; Bolisetty, S.; Spencer, N.D. Impact of solvation on equilibrium conformation of polymer brushes in solvent mixtures. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 4045–4057, doi:10.1039/c3sm27726g.
- Grest, G.S.; Murat, M. Structure of Grafted Polymeric Brushes in Solvents of Varying Quality—A Molecular-Dynamics Study. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 3108–3117, doi:10.1021/ma00064a019.
- Irfachsyad, D.; Tildesley, D.; Malfreyt, P. Dissipative particle dynamics simulation of grafted polymer brushes under shear. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2002, 4, 3008–3015, doi:10.1039/b110738k.
- Heuberger, M.; Drobek, T.; Spencer, N.D. Interaction forces and morphology of a protein-resistant poly(ethylene glycol) layer. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 495–504, doi:10.1529/biophysj.104.045443.
- Drobek, T.; Spencer, N.D. Nanotribology of surface-grafted PEG layers in an aqueous environment. Langmuir 2008, 24, 1484–1488, doi:10.1021/La702289n.
- Gombert, Y.; Simic, R.; Roncoroni, F.; Dbner, M.; Geue, T.; Spencer, N.D. Structuring Hydrogel Surfaces for Tribology. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1901320, doi:10.1002/admi.201901320.
- Bongaerts, J.H.H.; Rossetti, D.; Stokes, J.R. The Lubricating Properties of Human Whole Saliva. Tribol. Lett. 2007, 27, 277–287, doi:10.1007/s11249-007-9232-y.
- Singh, M.K.; Ilg, P.; Espinosa-Marzal, R.M.; Kroger, M.; Spencer, N.D. Polymer Brushes under Shear: Molecular Dynamics Simulations Compared to Experiments. Langmuir 2015, 31, 4798–4805, doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b00641.
- Singh, M.K.; Ilg, P.; Espinosa-Marzal, R.M.; Kroger, M.; Spencer, N.D. Polymer Brushes under Shear: Molecular Dynamics Simulations Compared to Experiments. Langmuir 2015, 31, 4798–4805, doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b00641.
- Shoaib, T.; Espinosa-Marzal, R.M. Influence of Loading Conditions and Temperature on Static Friction and Contact Aging of Hydrogels with Modulated Microstructures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 42722–42733, doi:10.1021/acsami.9b14283.
- Klein, J. Hydration lubrication. Friction 2013, 1, 1–23, doi:10.1007/s40544-013-0001-7.
- Swann, D.A.; Radin, E.L.; Nazimiec, M.; Weisser, P.A.; Curran, N.; Lewinnek, G. Role of hyaluronic acid in joint lubrication. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1974, 33, 318–326, doi:10.1136/ard.33.4.318.