
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | D. PRAVEEN KUMAR | -- | 2168 | 2022-11-24 06:32:55 | | | |
| 2 | Lindsay Dong | + 1 word(s) | 2169 | 2022-11-24 14:47:20 | | | | |
| 3 | D. PRAVEEN KUMAR | + 22 word(s) | 2191 | 2022-11-28 07:54:59 | | |
Video Upload Options
Solar photovoltaic (PV) devices present a positive approach to sustainable crop production by reducing crop loss in various ways. This might result in the extensive use of PV devices in the near future. PV-based plant protection equipment/devices are primarily utilized in protecting crops from birds, weeds, or insects. The utilization of PV systems for different applications constitutes a new era in agriculture, horticulture, and forest sectors. A PV system is a potential alternative, offering more opportunities in operating different types of electricity-based agricultural equipment. The development of devices with simple construction/operation for plant protection may work well on small-scale farms.
1. Applications of Solar Energy in Agriculture
2. Solar Photovoltaic Technologies
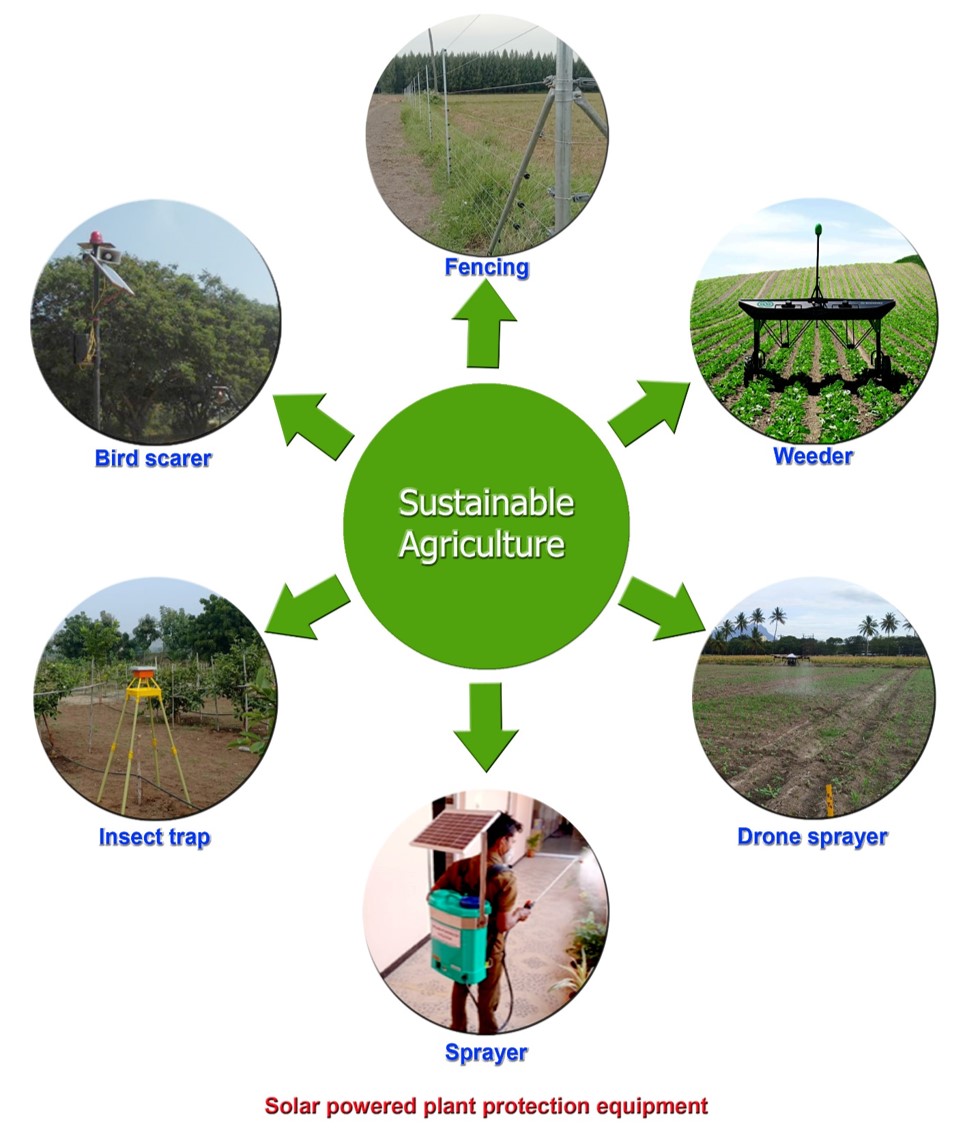
3. Solar-Powered Equipment for Weed Management
4. Solar-Powered Equipment for Pest Management
4.1. Solar Insect Traps

4.2. Solar-Powered Sprayers

4.3. Solar PV Duster
5. Solar-Powered Equipment for Non-Insect Pest Management
5.1. Solar Bird Scarer
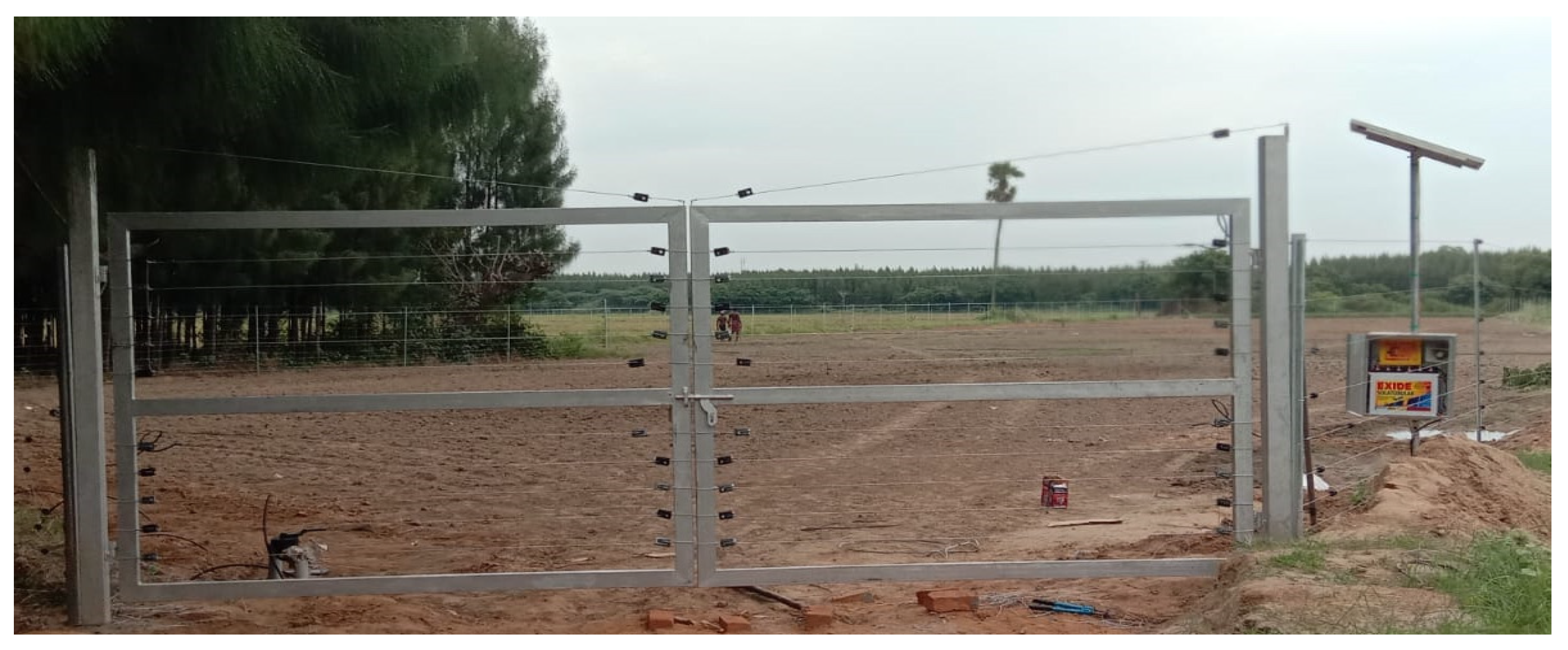
5.2. Solar Fencing
In remote areas, electric fencing is a proven technology to protect and safeguard fields from animals. Farmers may fail to protect their farms from animal attacks mainly due to the non-availability of electricity/absence of power grids. A PV electric fence is an alternative to the existing electric fence system and is well suited for off-grid areas. It is the most effective and economical approach for long-term operations in unelectrified areas. Solar PV fencing systems can fulfill farmers’ requirements to protect their crops (Figure 4). The components of the solar fencing system are solar panels, an energizer or a controller, a rechargeable battery, a main post, a fence wire supporting post, a t-post, a lightning diverter and choke kit, a super-earth kit, a super strain insulator, a permanent wire tightener, a chain wire strainer, tension springs, a double insulated lead-out cable, joint clamps, gateway and gates, cut out switches, electrified flood gates, live light, and a fence voltage alarm [43]. The current from the battery is supplied to the energizer to produce a high voltage with a low current in the fencing wires. Animals touching the fence wires experience a minimal electric shock which makes them leave the field. The fencing system would not cause any fatalities or injuries to animals/humans due to the low current supplied from the solar PV system. Kadam et al. [43] found that a combination of a solar panel (35 kW) and battery (12 V) was sufficient to effectively cover a 3.5 km fence line, which costs about USD 3300/km.

References
- Chock, R.Y.; Clucas, B.; Peterson, E.K.; Blackwell, B.F.; Blumstein, D.T.; Church, K.; Fernández-Juricic, E.; Francescoli, G.; Greggor, A.L.; Kemp, P. Evaluating Potential Effects of Solar Power Facilities on Wildlife from an Animal Behavior Perspective. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2021, 3, e319.
- Kannan, N.; Vakeesan, D. Solar Energy for Future World—A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 62, 1092–1105.
- Kalogirou, S.A. Solar Energy Engineering: Processes and Systems; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2013; ISBN 0123972566.
- Aliyu, M.; Hassan, G.; Said, S.A.; Siddiqui, M.U.; Alawami, A.T.; Elamin, I.M. A Review of Solar-Powered Water Pumping Systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 87, 61–76.
- Chandel, S.S.; Naik, M.N.; Chandel, R. Review of Performance Studies of Direct Coupled Photovoltaic Water Pumping Systems and Case Study. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 163–175.
- Chandel, S.S.; Naik, M.N.; Chandel, R. Review of Solar Photovoltaic Water Pumping System Technology for Irrigation and Community Drinking Water Supplies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 49, 1084–1099.
- Gopal, C.; Mohanraj, M.; Chandramohan, P.; Chandrasekar, P. Renewable Energy Source Water Pumping Systems—A Literature Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 25, 351–370.
- Koner, P.K. A Review on the Diversity of Photovoltaic Water Pumping Systems. Int. Energy J. 2017, 15, 89–110.
- Li, G.; Jin, Y.; Akram, M.W.; Chen, X. Research and Current Status of the Solar Photovoltaic Water Pumping System–A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 440–458.
- Periasamy, P.; Jain, N.K.; Singh, I.P. A Review on Development of Photovoltaic Water Pumping System. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 918–925.
- Poompavai, T.; Kowsalya, M. Control and Energy Management Strategies Applied for Solar Photovoltaic and Wind Energy Fed Water Pumping System: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 107, 108–122.
- Shinde, V.B.; Wandre, S.S. Solar Photovoltaic Water Pumping System for Irrigation: A Review. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2015, 10, 2267–2273.
- Sontake, V.C.; Kalamkar, V.R. Solar Photovoltaic Water Pumping System—A Comprehensive Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 59, 1038–1067.
- Wazed, S.M.; Hughes, B.R.; O’Connor, D.; Calautit, J.K. A Review of Sustainable Solar Irrigation Systems for Sub-Saharan Africa. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1206–1225.
- Muhsen, D.H.; Khatib, T.; Nagi, F. A Review of Photovoltaic Water Pumping System Designing Methods, Control Strategies and Field Performance. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 70–86.
- Rawat, R.; Kaushik, S.C.; Lamba, R. A Review on Modeling, Design Methodology and Size Optimization of Photovoltaic Based Water Pumping, Standalone and Grid Connected System. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 1506–1519.
- Duke, S.O. Why Have No New Herbicide Modes of Action Appeared in Recent Years? Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 505–512.
- Machleb, J.; Peteinatos, G.G.; Kollenda, B.L.; Andújar, D.; Gerhards, R. Sensor-Based Mechanical Weed Control: Present State and Prospects. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 176, 105638.
- Khan, S.U.-D.; Almutairi, Z.A.; Al-Zaid, O.S.; Khan, S.U.-D. Development of Low Concentrated Solar Photovoltaic System with Lead Acid Battery as Storage Device. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2020, 20, 582–588.
- Ecorobotix. Available online: https://www.Ecorobotix.Com/En/Avo-Autonomous-Robot-Weeder/ (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Sheikh, A.H.; Bhandari, R.; Thomas, M.; Bunkar, K. Light Trap and Insect Sampling: An Overview. Int. J. Curr. Res. 2016, 8, 40868–40873.
- Bae, S.-D.; Park, J.-O.; Mainali, B.; Kim, H.; Yoon, Y.; Lee, Y.; Cho, Y. Evaluation of Different Light Colors in Solar Trap as Attractants to Cereal and Legume Insect Pests. Korean J. Int. Agric. 2015, 27, 516–521.
- De Medeiros, B.A.S.; Barghini, A.; Vanin, S.A. Streetlights Attract a Broad Array of Beetle Species. Rev. Bras. Entomol. 2017, 61, 74–79.
- Mwanga, E.P.; Ngowo, H.S.; Mapua, S.A.; Mmbando, A.S.; Kaindoa, E.W.; Kifungo, K.; Okumu, F.O. Evaluation of an Ultraviolet LED Trap for Catching Anopheles and Culex Mosquitoes in South-Eastern Tanzania. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 1–12.
- Sermsri, N.; Torasa, C. Solar Energy-Based Insect Pest Trap. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 197, 2548–2553.
- Reddy, M.R.N.; Ammika, S.G. Modelling and Optimazation of Solar Light Trap for Reducing and Controling the Pest Population. Int. J. Engeenering 2015, 3, 224–234.
- Baehaki, S.E.; Iswanto, E.H.; Munawar, D. Relationship of Predators Flight and Rice Pests That Caught on the Light Trap of Mercury (ML-160 Watt) BSE-G3 Model and Light Trap of Solar Cell-CFL-20 Watt. Int. J. Entomol. Res. 2017, 2, 79–85.
- Kumar, N. Development and Evaluation of Eco-Friendly Solar Energy Based Light Trap. Int. J. Pure Appl. Biosci. 2019, 7, 356–360.
- Thangalakshmi, S.; Ramanujan, R. Electronic Trapping and Monitoring of Insect Pests Troubling Agricultural Fields. Int. J. Emerg. Eng. Res. Technol. 2015, 3, 206–213.
- Calderon, R.A. Solar Powered Rice Black Bug Light Trap. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Advances in Science, Engineering and Technology, Manila, Philippines, 17–18 December 2017; pp. 17–18.
- Brimapureeswaran, R.; Nivas, G.; Meenatchi, R.; Sujeetha, A.R.P.; Loganathan, M. Development of a New Solar Light Cum Glue Trap Model and Its Utilization in Agriculture. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Innov. Eng. 2016, 2, 37–41.
- McQuate, G.T. Green Light Synergistally Enhances Male Sweetpotato Weevil Response to Sex Pheromone. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4499.
- Longing, S.D.; Discua, S.A.; Cokendolpher, J.C. A Solar-Powered UV Light Trap for Long-Term Monitoring of Insects in Remote Habitats. Coleopt. Bull. 2018, 72, 140–144.
- Eccard, J.A.; Scheffler, I.; Franke, S.; Hoffmann, J. Off-grid: Solar Powered LED Illumination Impacts Epigeal Arthropods. Insect Conserv. Divers. 2018, 11, 600–607.
- Hanson, S.M.; Johnson, A.L.; Hou, Y.; Hellwig, M.D. Recharging Centers for Disease Control Light Trap Batteries with Solar Panels. Int. J. Appl. 2012, 2, 76–80.
- Pande, P.C. Development of Photovoltaic Systems for Arid Zone of India. Energy Environ. 1990, 314–319.
- Poonia, S.; Jain, D.; Santra, P.; Singh, A.K. Use of Solar Energy in agricultural production and processing. Indian Farming 2018, 68, 104–107.
- Pande, P.C. A Novel Solar Device for Dusting Insecticide Powder. In Proceedings of the National Solar Energy Convention, Vienna, Austria, 6–10 July 1998; University of Roorkee: Roorkee, India, 1998; pp. 117–122.
- Muminov, A.; Jeon, Y.C.; Na, D.; Lee, C.; Jeon, H.S. Development of a Solar Powered Bird Repeller System with Effective Bird Scarer Sounds. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Information Science and Communications Technologies (ICISCT), Tashkent, Uzbekistan, 2–4 November 2017; pp. 1–4.
- Koyuncu, T.; Lule, F. Design, Manufacture and Test of a Solar Powered Audible Bird Scarer. Int. J. Agric. Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 3, 345–347.
- Suryawanshi, V.R. Design, Manufacture and Test of a Solar Powered Audible Bird Scarer and Study of Sound Ranges Used in It. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2013, 4, SUB159173.
- Siahaan, Y.; Wardijono, B.A.; Mukhlis, Y. Design of Birds Detector and Repellent Using Frequency Based Arduino Uno with Android System. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International conferences on Information Technology, Information Systems and Electrical Engineering (ICITISEE), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 1–2 November 2017; 2017; pp. 239–243.
- Kadam, D.M.; Dange, A.R.; Khambalkar, V.P. Performance of Solar Power Fencing System for Agriculture. J. Agric. Technol. 2011, 7, 1199–1209.





