
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vivi Li | -- | 2455 | 2022-11-17 01:34:45 |
Video Upload Options
Irreligion or nonreligion is the absence or rejection of religion, or indifference to it. Irreligion takes many forms, ranging from the casual and unaware to full-fledged philosophies such as atheism and agnosticism, secular humanism and antitheism. Social scientists tend to define irreligion as a purely naturalist worldview that excludes a belief in anything supernatural. The broadest and loosest definition, serving as an upper limit, is the lack of religious identification, though many non-identifiers express metaphysical and even religious beliefs. The narrowest and strictest is subscribing to positive atheism. According to the Pew Research Center's 2012 global study of 230 countries and territories, 16% of the world's population does not identify with any religion. The population of the religiously unaffiliated, sometimes referred to as "nones", grew significantly in recent years. Measurement of irreligiosity requires great cultural sensitivity, especially outside the West, where the concepts of "religion" or "the secular" are not always rooted in local culture.
1. Etymology
The term irreligion is a combination of the noun religion and the ir- form of the prefix in-, signifying "not" (similar to irrelevant). It was first attested in French as irréligion in 1527, then in English as irreligion in 1598. It was borrowed into Dutch as irreligie in the 17th century, though it is not certain from which language.[1]
2. Types
- Agnostic atheism is a philosophical position that encompasses both atheism and agnosticism. Agnostic atheists are atheistic because they do not hold a belief in the existence of any deity and agnostic because they claim that the existence of a deity is either unknowable in principle or currently unknown in fact.
- Agnosticism is the view that the existence of God, of the divine or the supernatural is unknown or unknowable.
- Alatrism or alatry (Greek: from the privative ἀ- + λατρεία (latreia) = worship) is the recognition of the existence of one or more gods, but with a deliberate lack of worship of any deity. Typically, it includes the belief that religious rituals have no supernatural significance, and that gods ignore all prayers and worship.
- Antireligion is opposition or rejection of religion of any kind.
- Apatheism is the attitude of apathy or indifference towards the existence or non-existence of god(s).
- Atheism is the lack of belief that any deities exist or, in a narrower sense, positive atheism is specifically the position that there are no deities. There are ranges from Negative and positive atheism.
- Antitheism is the opposition to theism. The term has had a range of applications. It typically refers to direct opposition to the belief in any deity.
- Deism is the philosophical position and rationalistic theology that rejects revelation as a source of divine knowledge, and asserts that empirical reason and observation of the natural world are exclusively logical, reliable, and sufficient to determine the existence of a Supreme Being as the creator of the universe.
- Freethought holds that positions regarding truth should be formed on the basis of logic, reason, and empiricism, rather than authority, tradition, revelation, or other dogma.
- Ignosticism, also known as igtheism is the idea that the question of the existence of God is meaningless because the word "God" has no coherent and unambiguous definition.
- Naturalism is the idea or belief that only natural (as opposed to supernatural or spiritual) laws and forces operate in the universe.
- Secular humanism is a system of thought that prioritizes human rather than divine matters.
- Post-theism is a variant of nontheism that proposes that the division of theism vs. atheism is obsolete, that God belongs to a stage of human development now past. Within nontheism, post-theism can be contrasted with antitheism.
- Secularism is overwhelmingly used to describe a political conviction in favour of minimizing religion in the public sphere, that may be advocated regardless of personal religiosity. Yet it is sometimes, especially in the United States, also a synonym for naturalism or atheism.[2]
- "Spiritual but not religious" is a designation coined by Robert C. Fuller for people who reject traditional or organized religion but have strong metaphysical beliefs. The SBNR may be included under the definition of nonreligion,[3] but are sometimes classified as a wholly distinct group.[4]
- Theological noncognitivism is the argument that religious language – specifically, words such as God – are not cognitively meaningful. It is sometimes considered as synonymous with ignosticism.
- Transtheism, refers to a system of thought or religious philosophy that is neither theistic nor atheistic, but is beyond them.
3. Human Rights
In 1993, the UN's human rights committee declared that article 18 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights "protects theistic, non-theistic and atheistic beliefs, as well as the right not to profess any religion or belief."[5] The committee further stated that "the freedom to have or to adopt a religion or belief necessarily entails the freedom to choose a religion or belief, including the right to replace one's current religion or belief with another or to adopt atheistic views." Signatories to the convention are barred from "the use of threat of physical force or penal sanctions to compel believers or non-believers" to recant their beliefs or convert.[6][7]
Most democracies protect the freedom of religion, and it is largely implied in respective legal systems that those who do not believe or observe any religion are allowed freedom of thought.
A noted exception to ambiguity, explicitly allowing non-religion, is Article 36 of the Constitution of the People's Republic of China (as adopted in 1982), which states that "No state organ, public organization or individual may compel citizens to believe in, or not to believe in, any religion; nor may they discriminate against citizens who believe in, or do not believe in, any religion."[8] Article 46 of China's 1978 Constitution was even more explicit, stating that "Citizens enjoy freedom to believe in religion and freedom not to believe in religion and to propagate atheism."[9]
4. Demographics
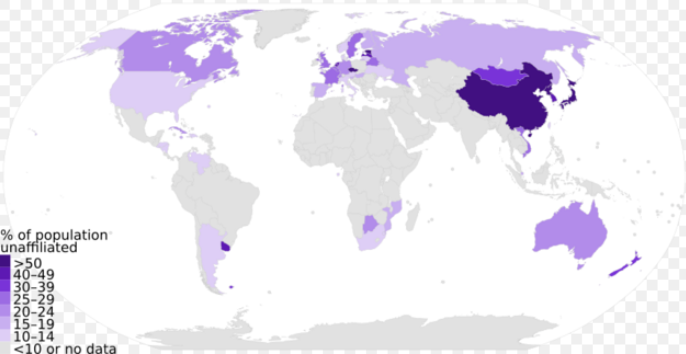
Although 11 countries listed below have nonreligious majorities, it does not necessary correlate with non-identification. For example, 58% of the Swedish population identify with the Lutheran Church.[11] Also, though Scandinavian countries have among the highest measures of nonreligiosity and even atheism in Europe, 47% of atheists who live in those countries are still formally members of the national churches.[12]
Determining objective irreligion, as part of societal or individual levels of secularity and religiosity, requires cultural sensitivity from researchers. This is especially so outside the West, where the Western Christian concepts of "religious" and "secular" are not rooted in local civilization. Many East Asians identify as "without religion" (wú zōngjiào in Chinese, mu shūkyō in Japanese, mu jong-gyo in Korean), but "religion" in that context refers only to Buddhism or Christianity. Most of the people "without religion" practice Shinto and other folk religions. In the Muslim world, those who claim to be "not religious" mostly imply not strictly observing Islam, and in Israel, being "secular" means not strictly observing Orthodox Judaism. Vice versa, many American Jews share the worldviews of nonreligious people though affiliated with a Jewish denomination, and in Russia , growing identification with Eastern Orthodoxy is mainly motivated by cultural and nationalist considerations, without much concrete belief.[13]
A Pew 2015 global projection study for religion and nonreligion, projects that between 2010 and 2050, there will be some initial increases of the unaffiliated followed by a decline by 2050 due to lower global fertility rates among this demographic.[14] Sociologist Phil Zuckerman's global studies on atheism have indicated that global atheism may be in decline due to irreligious countries having the lowest birth rates in the world and religious countries having higher birth rates in general.[15] Since religion and fertility are positively related and vice versa, non-religious identity is expected to decline as a proportion of the global population throughout the 21st century.[16] By 2060, according to projections, the number of unaffiliated will increase by over 35 million, but the percentage will decrease to 13% because the total population will grow faster.[17][18]
According to Pew Research Center's 2012 global study of 230 countries and territories, 16% of the world's population is not affiliated with a religion, while 84% are affiliated.[19] A 2012 Worldwide Independent Network/Gallup International Association report on a poll from 57 countries reported that 59% of the world's population identified as religious person, 23% as not religious person, 13% as "convinced atheists", and also a 9% decrease in identification as "religious" when compared to the 2005 average from 39 countries.[20] Their follow-up report, based on a poll in 2015, found that 63% of the globe identified as religious person, 22% as not religious person, and 11% as "convinced atheists".[21] Their 2017 report found that 62% of the globe identified as religious person, 25% as not religious person, and 9% as "convinced atheists".[22] However, researchers have advised caution with the WIN/Gallup International figures since other surveys which use the same wording, have conducted many waves for decades, and have a bigger sample size, such as World Values Survey; have consistently reached lower figures for the number of atheists worldwide.[23]
Being nonreligious is not necessarily equivalent to being an atheist or agnostic. Pew Research Center's global study from 2012 noted that many of the nonreligious actually have some religious beliefs. For example, they observed that "belief in God or a higher power is shared by 7% of Chinese unaffiliated adults, 30% of French unaffiliated adults and 68% of unaffiliated U.S. adults."[24] Out of the global nonreligious population, 76% reside in Asia and the Pacific, while the remainder reside in Europe (12%), North America (5%), Latin America and the Caribbean (4%), sub-Saharan Africa (2%) and the Middle East and North Africa (less than 1%).[24]
The term "nones" is sometimes used in the U.S. to refer to those who are unaffiliated with any organized religion. This use derives from surveys of religious affiliation, in which "None" (or "None of the above") is typically the last choice. Since this status refers to lack of organizational affiliation rather than lack of personal belief, it is a more specific concept than irreligion. A 2015 Gallup poll concluded that in the U.S. "nones" were the only "religious" group that was growing as a percentage of the population.[25]
4.1. By Population
The Pew Research Centre in the table below reflects "religiously unaffiliated" which "include atheists, agnostics and people who do not identify with any particular religion in surveys".
The Zuckerman data on the table below only reflect the number of people who have an absence of belief in a deity only (atheists, agnostics). Does not include the broader number of people who do not identify with a religion such as deists, spiritual but not religious, pantheists, New Age spiritualism, etc.
| Country | Pew (2012)[26] | Zuckerman (2004)[27][28] |
|---|---|---|
| 010 China
|
700,680,000 | 001 103,907,840 – 181,838,720
|
| 023 India
|
051 102,870,000
|
|
| 026 Japan
|
72,120,000 | 002 81,493,120 – 82,766,450
|
| 050 Vietnam
|
26,040,000 | 003 66,978,900
|
| 037 Russia
|
23,180,000 | 004 34,507,680 – 69,015,360
|
| 020 Germany
|
20,350,000 | 005 33,794,250 – 40,388,250
|
| 019 France
|
17,580,000 | 006 25,982,320 – 32,628,960
|
| 047 United Kingdom
|
007 18,684,010 – 26,519,240
|
|
| 041 South Korea
|
22,350,000 | 008 14,579,400 – 25,270,960
|
| 046 Ukraine
|
009 9,546,400
|
|
| 048 United States
|
50,980,000 | 010 8,790,840 – 26,822,520
|
| 032 Netherlands
|
011 6,364,020 – 7,179,920
|
|
| 009 Canada
|
012 6,176,520 – 9,752,400
|
|
| 042
|
013 6,042,150 – 9,667,440
|
|
| 045 Taiwan
|
014 5,460,000
|
|
| 045 Hong Kong
|
014 5,240,000
|
|
| 013 Czech Republic
|
015 5,328,940 – 6,250,121
|
|
| 004 Australia
|
016 4,779,120 – 4,978,250
|
|
| 007 Belgium
|
017 4,346,160 – 4,449,640
|
|
| 043 Sweden
|
018 4,133,560 – 7,638,100
|
|
| 025 Italy
|
019 3,483,420 – 8,708,550
|
|
| 034 North Korea
|
17,350,000 | 020 3,404,700
|
| 022 Hungary
|
021 3,210,240 – 4,614,720
|
|
| 008 Bulgaria
|
022 2,556,120 – 3,007,200
|
|
| 014 Denmark
|
023 2,327,590 – 4,330,400
|
|
| 021 Turkey
|
025 1,956,990 - 6,320,550
|
|
| 006 Belarus
|
024 1,752,870
|
|
| 021 Greece
|
025 1,703,680
|
|
| 027 Kazakhstan
|
026 1,665,840 – 1,817,280
|
|
| 002 Argentina
|
027 1,565,800 – 3,131,600
|
|
| 005 Austria
|
028 1,471,500 – 2,125,500
|
|
| 018 Finland
|
029 1,460,200 – 3,129,000
|
|
| 035 Norway
|
030 1,418,250 – 3,294,000
|
|
| 044 Switzerland
|
031 1,266,670 – 2,011,770
|
|
| 024 Israel
|
032 929,850 – 2,293,630
|
|
| 033 New Zealand
|
033 798,800 – 878,680
|
|
| 012 Cuba
|
034 791,630
|
|
| 040 Slovenia
|
035 703,850 – 764,180
|
|
| 016 Estonia
|
036 657,580
|
|
| 015 Dominican Republic
|
037 618,380
|
|
| 038 Singapore
|
038 566,020
|
|
| 039 Slovakia
|
039 542,400 – 1,518,720
|
|
| 030 Lithuania
|
040 469,040
|
|
| 029 Latvia
|
041 461,200 – 668,740
|
|
| 036 Portugal
|
042 420,960 – 947,160
|
|
| 003 Armenia
|
043 118,740
|
|
| 049 Uruguay
|
044 407,880
|
|
| 028 Kyrgyzstan
|
045 355,670
|
|
| 011 Croatia
|
046 314,790
|
|
| 001 Albania
|
047 283,600
|
|
| 031 Mongolia
|
048 247,590
|
|
| 023 Iceland
|
050 47,040 – 67,620
|
|
| 051 Brazil
|
15,410,000 |
5. Historical Trends
According to political/social scientist Ronald F. Inglehart, "influential thinkers from Karl Marx to Max Weber to Émile Durkheim predicted that the spread of scientific knowledge would dispel religion throughout the world", but religion continued to prosper in most places during the 19th and 20th centuries.[29] Inglehart and Pippa Norris argue faith is "more emotional than cognitive", and advance an alternative thesis termed "existential security." They postulate that rather than knowledge or ignorance of scientific learning, it is the weakness or vulnerability of a society that determines religiosity. They claim that increased poverty and chaos make religious values more important to a society, while wealth and security diminish its role. As need for religious support diminishes, there is less willingness to "accept its constraints, including keeping women in the kitchen and gay people in the closet".[30]
5.1. Prior to the 1980s
Rates of people identifying as non-religious began rising in most societies as least as early as the turn of the 20th century.[31] In 1968, sociologist Glenn M. Vernon wrote that US census respondents who identified as "no religion" were insufficiently defined because they were defined in terms of a negative. He contrasted the label with the term "independent" for political affiliation, which still includes people who participate in civic activities. He suggested this difficulty in definition was partially due to the dilemma of defining religious activity beyond membership, attendance, or other identification with a formal religious group.[31] During the 1970s, social scientists still tended to describe irreligion from a perspective that considered religion as normative for humans. Irreligion was described in terms of hostility, reactivity, or indifference toward religion, and or as developing from radical theologies.[32]
5.2. 1981–2019
 |
This section relies largely or entirely upon a single source. (July 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this template message)
|
In a study of religious trends in 49 countries from 1981 to 2019, Inglehart and Norris found an overall increase in religiosity from 1981 to 2007. Respondents in 33 of 49 countries rated themselves higher on a scale from one to ten when asked how important God was in their lives. This increase occurred in most former communist and developing countries, but also in some high-income countries. A sharp reversal of the global trend occurred from 2007 to 2019, when 43 out of 49 countries studied became less religious. This reversal appeared across most of the world.[29] The United States was a dramatic example of declining religiosity – with the mean rating of importance of religion dropping from 8.2 to 4.6 – while India was a major exception. Research in 1989 recorded disparities in religious adherence for different faith groups, with people from Christian and tribal traditions leaving religion at a greater rate than those from Muslim, Hindu, or Buddhist faiths.[33]
Inglehart and Norris speculate that the decline in religiosity comes from a decline in the social need for traditional gender and sexual norms, ("virtually all world religions instilled" pro-fertility norms such as "producing as many children as possible and discouraged divorce, abortion, homosexuality, contraception, and any sexual behavior not linked to reproduction" in their adherents for centuries) as life expectancy rose and infant mortality dropped. They also argue that the idea that religion was necessary to prevent a collapse of social cohesion and public morality was belied by lower levels of corruption and murder in less religious countries. They argue that both of these trends are based on the theory that as societies develop, survival becomes more secure: starvation, once pervasive, becomes uncommon; life expectancy increases; murder and other forms of violence diminish. As this level of security rises, there is less social/economic need for the high birthrates that religion encourages and less emotional need for the comfort of religious belief.[29] Change in acceptance of "divorce, abortion, and homosexuality" has been measured by the World Values Survey and shown to have grown throughout the world outside of Muslim-majority countries.[29]
References
- "Irreligie". Instituut voor Nederlandse Lexicologie. Instituut voor de Nederlandse Taal. 2007. http://gtb.inl.nl/iWDB/search?actie=article_content&wdb=WNT&id=A009369.
- Jacques Berlinerblau, How to be Secular: A Field Guide for Religious Moderates, Atheists and Agnostics (2012, Houghton-Mifflin Harcourt). p. 53.
- Zuckerman, Galen et al., p. 119.
- Zuckerman, Shook, (in bibliography), p. 575.
- "CCPR General Comment 22: 30/07/93 on ICCPR Article 18". Minorityrights.org. http://www.minorityrights.org/3273/normative-instruments/ccpr-general-comment-22-300793-on-iccpr-article-18.html.
- International Federation for Human Rights (1 August 2003). "Discrimination against religious minorities in Iran". fdih.org. http://www.fidh.org/IMG/pdf/ir0108a.pdf.
- Davis, Derek H.. "The Evolution of Religious Liberty as a Universal Human Right". http://www.law2.byu.edu/lawreview/archives/2002/2/dav2.pdf.
- "Archived copy". http://www.hkhrm.org.hk/english/law/const03.html.
- (in zh). 1978. https://zh.wikisource.org/wiki/%E4%B8%AD%E5%8D%8E%E4%BA%BA%E6%B0%91%E5%85%B1%E5%92%8C%E5%9B%BD%E5%AE%AA%E6%B3%95_(1978%E5%B9%B4)#%E7%AC%AC%E4%B8%89%E7%AB%A0_%E5%85%AC%E6%B0%91%E7%9A%84%E5%9F%BA%E6%9C%AC%E6%9D%83%E5%88%A9%E5%92%8C%E4%B9%89%E5%8A%A1. Retrieved 24 May 2021.
- "Religious Composition by Country, 2010-2050" (in en-US). 2015-04-02. https://www.pewforum.org/2015/04/02/religious-projection-table/.
- "Statistik". https://www.svenskakyrkan.se/statistik.
- Zuckerman, Phil, ed (2010). "Ch. 9 Atheism And Secularity: The Scandinavian Paradox". Atheism and Secularity Vol.2. Praeger. ISBN 978-0313351815.
- Zuckerman, Galen et al., "Secularity Around the World". pp. 30-32, 37-40, 44, 50-51.
- "The Future of World Religions: Population Growth Projections, 2010–2050". Pew Research Center. April 5, 2012. http://www.pewforum.org/2015/04/02/religious-projections-2010-2050/.
- Zuckerman, Phil (2007). Martin, Michael. ed. The Cambridge Companion to Atheism. Cambridge Univ. Press. p. 59. ISBN 978-0521603676. https://archive.org/details/cambridgecompani00mart_852.
- Ellis, Lee; Hoskin, Anthony W.; Dutton, Edward; Nyborg, Helmuth (8 March 2017). "The Future of Secularism: a Biologically Informed Theory Supplemented with Cross-Cultural Evidence". Evolutionary Psychological Science 3 (3): 224–43. doi:10.1007/s40806-017-0090-z. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007%2Fs40806-017-0090-z
- "Why People With No Religion Are Projected To Decline As A Share Of The World's Population". Pew Research Center. April 7, 2017. http://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2015/04/03/why-people-with-no-religion-are-projected-to-decline-as-a-share-of-the-worlds-population/.
- "The Changing Global Religious Landscape: Babies Born to Muslims will Begin to Outnumber Christian Births by 2035; People with No Religion Face a Birth Dearth". April 5, 2017. http://www.pewforum.org/2017/04/05/the-changing-global-religious-landscape/.
- Pew Forum on Religion & Public Life (18 December 2012). "The Global Religious Landscape". http://www.pewforum.org/2012/12/18/global-religious-landscape-exec/.
- "Global Index of Religion and Atheism". WIN/Gallup International. http://redcresearch.ie/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/RED-C-press-release-Religion-and-Atheism-25-7-12.pdf.
- "Losing our Religion? Two Thirds of People Still Claim to be Religious". WIN/Gallup International. April 13, 2015. http://www.wingia.com/web/files/news/290/file/290.pdf.
- "Religion prevails in the world". WIN/Gallup International. 2017-11-14. http://www.wingia.com/web/files/news/370/file/370.pdf.
- Keysar, Ariela; Navarro-Rivera, Juhem (2017). "36. A World of Atheism: Global Demographics". in Bullivant, Stephen; Ruse, Michael. The Oxford Handbook of Atheism. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0199644650.
- "Religiously Unaffiliated". The Global Religious Landscape. Pew Research Center: Religion & Public Life. December 18, 2012. http://www.pewforum.org/global-religious-landscape-unaffiliated.aspx.
- Inc, Gallup (December 24, 2015). "Percentage of Christians in U.S. Drifting Down, but Still High". https://news.gallup.com/poll/187955/percentage-christians-drifting-down-high.aspx.
- "Religiously Unaffiliated". 18 December 2012. https://www.pewforum.org/2012/12/18/global-religious-landscape-unaffiliated/.
- "The Cambridge Companion to Atheism - PDF Drive". https://www.pdfdrive.com/the-cambridge-companion-to-atheism-d187156887.html.
- "81-F77-Aeb-A404-447-C-8-B95-Dd57-Adc11-E98". https://ibb.co/nBN7JT6.
- Inglehart, Ronald F. (September–October 2020). "Giving Up on God The Global Decline of Religion". Foreign Affairs. https://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/world/2020-08-11/religion-giving-god. Retrieved 20 September 2020.
- Ikenberry, G. John (November–December 2004). "Book review. Sacred and Secular: Religion and Politics Worldwide". Foreign Affairs. doi:10.2307/20034150. https://www.foreignaffairs.com/reviews/capsule-review/2004-11-01/sacred-and-secular-religion-and-politics-worldwide. Retrieved 20 September 2020.
- Vernon, Glenn M. (1968). "The Religious "Nones": A Neglected Category". Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion 7 (2): 219–229. doi:10.2307/1384629. https://dx.doi.org/10.2307%2F1384629
- Schumaker, John F. (1992). Religion and Mental Health. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 54. ISBN 0-19-506985-4.
- Duke, James T.; Johnson, Barry L. (1989). "The Stages of Religious Transformation: A Study of 200 Nations". Review of Religious Research 30 (3): 209–224. doi:10.2307/3511506. https://dx.doi.org/10.2307%2F3511506




