
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Beatrix Zheng | -- | 2649 | 2022-10-28 01:34:58 |
Video Upload Options
Uncompetitive inhibition, also known as anti-competitive inhibition, takes place when an enzyme inhibitor binds only to the complex formed between the enzyme and the substrate (the E-S complex). Uncompetitive inhibition typically occurs in reactions with two or more substrates or products. While uncompetitive inhibition requires that an enzyme-substrate complex must be formed, non-competitive inhibition can occur with or without the substrate present. Uncompetitive inhibition is distinguished from competitive inhibition by two observations: first uncompetitive inhibition cannot be reversed by increasing [S] and second, as shown, the Lineweaver–Burk plot yields parallel rather than intersecting lines. This behavior is found in the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by tertiary amines (R3N). Such compounds bind to the enzyme in its various forms, but the acyl-intermediate-amine complex cannot break down into enzyme plus product.
1. Mechanism
As inhibitor binds, the amount of ES complex is reduced. This reduction in the effective concentration of the ES complex can be explained by the fact that having the inhibitor bound to the ES complex essentially converts it to ESI complex, which is considered a separate complex altogether. This reduction in ES complex decreases the maximum enzyme activity (Vmax), as it takes longer for the substrate or product to leave the active site. The reduction in Km - the substrate concentration at which the enzyme can operate at half of its maximal velocity, often used to approximate an enzyme's affinity for a substrate - can also be linked back to the decrease in ES complex. Le Chatelier's principle opposes this decrease and attempts to make up for the loss of ES, so more free enzyme is converted to the ES form, and the amount of ES increases overall. An increase in ES generally indicates that the enzyme has a high degree of affinity for its substrate. Km decreases as affinity for a substrate increases, though it is not a perfect predictor of affinity since it accounts for other factors as well; regardless, this increase in affinity will be accompanied by a decrease in Km.[1]
In general, uncompetitive inhibition works best when substrate concentration is high. An uncompetitive inhibitor need not resemble the substrate of the reaction it is inhibiting. At no concentration of substrate the activity of the enzyme be higher when an uncompetitive inhibitor is present, but at low concentrations of substrate the enzyme activity difference will be negligible.[2]
2. Mathematical Definition
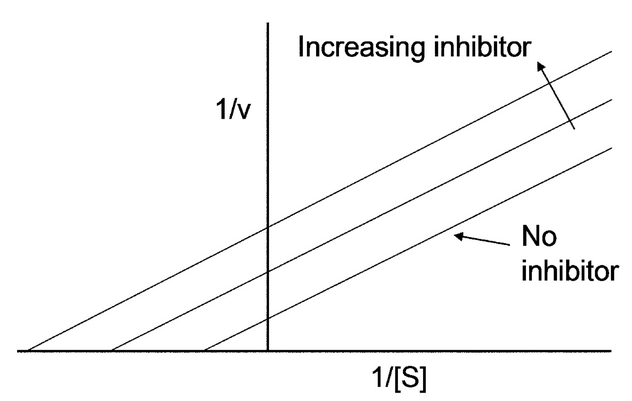
The Lineweaver–Burk equation states that:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \ \frac{1}{v}=\frac{K_m}{V_{max}[S]} + {1 \over V_\max} }[/math]
Where v is the initial reaction velocity, Km is the Michaelis–Menten constant, Vmax is the maximum reaction velocity, and [S] is the concentration of the substrate.[3]
The Lineweaver–Burk plot for an uncompetitive inhibitor produces a line parallel to the original enzyme-substrate plot, but with a higher y-intercept, due to the presence of an inhibition term [math]\displaystyle{ \ \frac{[I]}{K_i} }[/math]:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \ \frac{1}{v}=\frac{K_m}{V_{max}[S]}+\frac{1+\frac{[I]}{K_i}}{V_{max}} }[/math]
Where [I] is the concentration of the inhibitor and Ki is an inhibition constant characteristic of the inhibitor.[4][5]
The Michaelis-Menten equation is altered to:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \ {V_0}=\frac{V_{max}[S]}{K_m+\alpha'[S]} }[/math]
where
- [math]\displaystyle{ \ \alpha'=1+\frac{[I]}{K'_I} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \ K'_I=\frac{[ES][I]}{[ESI]} }[/math]
As described by the equation above, at high concentrations of substrate, V0 approaches Vmax/α'. Thus, an uncompetitive inhibitor lowers the measured Vmax. Apparent Km also decreases, because [S] required to reach one-half Vmax decreases by the factor α'.[6] It is important to note that Vmax and Km decrease at the same rate as a result of the inhibitor.[2] This is apparent when viewing a Lineweaver-Burk plot of uncompetitive enzyme inhibition: the ratio between V and Km remains the same with or without an inhibitor present.
3. Implications and Uses in Biological Systems
The unique traits of uncompetitive inhibition lead to a variety of implications for the inhibition's effects within biological and biochemical systems. Uncompetitive inhibition is present within biological systems in a number of ways. In fact, it often becomes clear that the traits of inhibition specific to uncompetitive inhibitors, such as their tendency to act at their best at high concentrations of substrate, are essential to some important bodily functions operating properly.[7]
3.1. Involvement in Cancer Mechanisms
Uncompetitive mechanisms are involved with certain types of cancer. Human alkaline phosphatases such as CGAP have been found to be over-expressed in certain types of cancers, and those phosphotases often operate via uncompetitive inhibition. It has also been found that a number of the genes that code for human alkaline phosphatases (TSAPs) are inhibited uncompetitively by amino acids such as leucine and phenylalanine.[8] Studies of the involved amino acid residues have been undertaken in attempts to regulate alkaline phosphatase activity and learn more about said activity's relevance to cancer.[9]
Additionally, uncompetitive inhibition works alongside TP53 to help repress the activity of cancer cells and prevent tumorigenesis in certain forms of the illness, as it inhibits G6PD (glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, an enzyme primarily involved in certain metabolic pathways). One of the side roles G6PD is responsible for is helping to regulate is the control of reactive oxygen levels, as reactive oxygen species must be kept at appropriate levels to allow cells to survive. When G6PD's substrate concentration is high, uncompetitive inhibition of the enzyme becomes far more effective.[10] As substrate concentration increases, the amount of ES complex increases as well, and with more ES complex to bind, uncompetitive inhibitors become far more active. This inhibition works such that the higher the concentration of substrate is in the system initially, the harder it is to reach the maximum velocity of the reaction. At low initial substrate concentrations, increasing the concentration of substrate is sometimes enough to entirely or even fully restore the enzyme's function, but as soon as initial concentration increases past a certain point, reaching the maximal enzyme velocity is all but impossible.[7] This extreme sensitivity to substrate concentration within the cancer mechanism implicates uncompetitive inhibition rather than mixed inhibition, which displays similar traits but is often less sensitive to substrate concentration due to some inhibitor binding to free enzymes regardless of the substrate's presence.[7] As such, the extreme strength of uncompetitive inhibitors at high substrate concentrations and the overall sensitivity to substrate amount indicates that only uncompetitive inhibition can make this type of process possible.
3.2. Importance in Cell and Organelle Membranes
Although this form of inhibition is present in various diseases within biological systems, it does not necessarily only relate to pathologies. It can be involved in typical bodily functions. For example, active sites capable of uncompetitive inhibition appear to be present in membranes, as removing lipids from cell membranes and making active sites more accessible through conformational changes has been shown to invoke elements resembling the effects of uncompetitive inhibition (i.e. both KM and VMax decrease). In mitochondrial membrane lipids specifically, removing lipids decreases the alpha-helix content in mitochondria and leads to changes in ATPase resembling uncompetitive inhibition.[11]
This presence of uncompetitive enzymes in membranes has also been supported in a number of other studies. A type of protein called an Arf protein involved in regulating membrane activity was being studied, and it was found that an inhibitor called BFA trapped one of Arf's intermediates via uncompetitive inhibition. This made it clear that this type of inhibition exists within various types of cells and organelles as opposed to just in pathological cells. In fact, BFA was found to relate to the activity of the Golgi apparatus and its role in regulating movement across the cell membrane.[12]
3.3. Presence in the Cerebellar Granule Layer
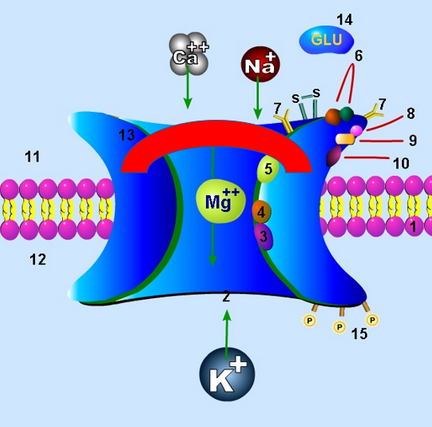
Uncompetitive inhibition can play roles in various other parts of the body as well. It is part of the mechanism by which NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) glutamate receptors are inhibited in the brain, for example. Specifically, this type of inhibition impacts the granule cells that make up a layer of the cerebellum. These cells have the aforementioned NMDA receptors, and the activity of said receptors typically increases as ethanol is consumed. This often leads to withdrawal symptoms if said ethanol is removed. Various uncompetitive blockers act as antagonists at the receptors and modify the process, with one example being an inhibitor called memantine.[13] In fact, in similar cases (involving over-expression of NMDA, though not necessarily via ethanol), it has been shown that uncompetitive inhibition helps in nullifying the over-expression due to its particular properties. Since uncompetitive inhibitors block high concentrations of substrates very efficiently, their traits alongside the innate characteristics of the receptors themselves lead to very effective blocking of NMDA channels when they are excessively open due to massive amounts of NMDA agonists.[14]
4. Derivation of Uncompetitive Michaelis–Menten Equation
Uncompetitive inhibition can be described using the following set of reaction equations:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} E + S &\rightleftharpoons ES \\ ES &\rightarrow E + P \\ ES + I &\rightleftharpoons ESI \end{align} }[/math]
The reaction rate of the first rule defined above where [E] and [S] bind to form the complex [ES] and [ES] can separate to reform the products can be written as:
[math]\displaystyle{ Rate_1 = k_1*[E][S] - k_{-1}[ES] }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ k_1 }[/math] is a second order rate constant representing the rate in which [E] and [S] bind to form the [ES] complex under mass action kinetics
- [math]\displaystyle{ k_{-1} }[/math] is a first order rate constant representing the rate of [ES] unbinding to reform [E] and [S]
The second reaction rate describing the rate of [ES] complex creating the product from substrate [S] and regenerating a free enzyme [E] can be described with the following mass action rate:
[math]\displaystyle{ Rate_2 = k_2*[ES] }[/math]
Where:
- [math]\displaystyle{ k_2 }[/math] is a first order reaction rate of the [ES] complex forming the product [P] and free enzyme [E]
With uncompetitive inhibition, the enzyme substrate complex can be tied up into an enzyme-substrate-inhibitor complex under the following rate:
[math]\displaystyle{ Rate_3 = k_{3} * [ES]*[I] - k_{-3}[ESI] }[/math]
Where:
- [math]\displaystyle{ k_3 }[/math] is a second order rate constant representing the rate in which [ES] and [I] bind to form the [ESI] complex under mass action kinetics
- [math]\displaystyle{ k_{-3} }[/math] is a first order rate constant representing the rate of [ESI] unbinding to reform [ES] and [I]
Putting the above information into a set of ordinary differential equations yields:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \frac{d[E]}{dt} &= -k_1*[E][S] + k_{-1}[ES] +k_2*[ES] \\ \frac{d[S]}{dt} &= -k_1*[E][S] + k_{-1}[ES] +k_2*[ES] \\ \frac{d[P]}{dt} &= k_2*[ES]\\ \frac{d[ES]}{dt} &= k_1*[E][S] - k_{-1}[ES] -k_2*[ES] - k_{3} * [ES]*[I] + k_{-3}[ESI]\\ \frac{d[ESI]}{dt} &= k_{3} * [ES]*[I] - k_{-3}[ESI]\\ \frac{d[I]}{dt} &= -k_{3} * [ES]*[I] + k_{-3}[ESI] \end{align} }[/math]
In order to derive the modified Michaelis-Menten equation, the following assumptions have to be made:
- The substrate is not limiting
- Model species [ES] and [ESI] complexes are in instantaneous equilibrium.
Based on the second assumption stated above, the ODE equations above can be set to zero since the values are not changing: [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \frac{d[ES]}{dt} &= k_1*[E][S] - k_{-1}[ES] -k_2*[ES] - k_{3} * [ES]*[I] + k_{-3}[ESI] = 0 \\ \frac{d[ESI]}{dt} &= k_{3} * [ES]*[I] - k_{-3}[ESI] = 0\\ \end{align} }[/math]
Since we know the following expression is equal to zero:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} k_{3} * [ES]*[I] - k_{-3}[ESI] &= 0\\ \end{align} }[/math]
We can cross out the following part in the [ES] rate equation:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} k_1*[E][S] - k_{-1}[ES] -k_2*[ES] \cancelto{0}{- k_{3} * [ES]*[I] + k_{-3}[ESI]} = 0 \\ \\ k_1*[E][S] - k_{-1}[ES] -k_2*[ES] = 0 \\ \end{align} }[/math]
In order to derive the Michaelis-Menten equation, we must re-write [ES] in terms of only [S]. To start we will modify the above equation to isolate [ES]:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} k_1*[E][S] - k_{-1}[ES] - k_2*[ES] &= 0 \\ k_1*[E][S] - (k_2 + k_{-1}) [ES] &= 0 \\ k_1*[E][S] &= (k_2 + k_{-1}) [ES] \\ \frac{k_1*[E][S]}{(k_2 + k_{-1})} &= [ES] \\ \end{align} }[/math]
Solving for [ESI] in an equation above yields where we can plug in the expression found for [ES]:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} k_{3} * [ES]*[I] - k_{-3}[ESI] &= 0\\ k_{3} * [ES]*[I] &= k_{-3}[ESI] \\ \frac{k_{3} * [ES]*[I]}{k_{-3}} &= [ESI] \\ \frac{k_{3} * \frac{k_1*[E][S]}{(k_2 + k_{-1})}*[I]}{k_{-3}} &= [ESI] \\ \frac{k_{3} *k_1*[E][S][I]}{k_{-3}*(k_2 + k_{-1})} &= [ESI] \\ \end{align} }[/math]
The total enzyme concentration depends on the amount of free enzyme [E], enzyme bound to complex [ES], and enzyme-substrate-inhibitor complex [ESI]. Plugging in the expressions for [ESI] and [ES] will yield:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} [][E]_{Total} &= [E] + [ES] + [ESI] \\ [][E]_{Total} - [ES] - [ESI] &= [E] \\ [][E]_{Total} - \frac{k_1*[E][S]}{(k_2 + k_{-1})} - \frac{k_{3} *k_1*[E][S][I]}{k_{-3}*(k_2 + k_{-1})} &= [E] \\ [][E]_{Total} - \bigg(\frac{k_1*[E][S]}{(k_2 + k_{-1})} + \frac{k_{3} *k_1*[E][S][I]}{k_{-3}*(k_2 + k_{-1})} \bigg) &= [E] \\ [][E]_{Total} - \frac{k_1*[E][S]}{(k_2 + k_{-1})}\bigg(1 + \frac{k_{3}[I]}{k_{-3}} \bigg) &= [E] \\ \end{align} }[/math]
Isolated [E] to only show up on a single side of the above equation:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} [][E]_{Total} - \frac{k_1*[E][S]}{(k_2 + k_{-1})}\bigg(1 + \frac{k_{3}[I]}{k_{-3}} \bigg) &= [E] \\ [][E]_{Total} &= [E]+ \frac{k_1*[E][S]}{(k_2 + k_{-1})}\bigg(1 + \frac{k_{3}[I]}{k_{-3}} \bigg) \\ [][E]_{Total} &= [E] \bigg( 1 + \frac{k_1*[S]}{(k_2 + k_{-1})}\bigg(1 + \frac{k_{3}[I]}{k_{-3}} \bigg) \bigg) \\ \frac{[E]_{Total}}{\bigg( 1 + \frac{k_1*[S]}{(k_2 + k_{-1})}\bigg(1 + \frac{k_{3}[I]}{k_{-3}} \bigg) \bigg)} &= [E] \\ \end{align} }[/math]
From the above derivation of [ES], we can further modify the equation by replacing [E] with the equation directly above:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} [][ES] &= \frac{k_1*[E][S]}{(k_2 + k_{-1})} \\ &= \frac{k_1*\frac{[E]_{Total}}{\bigg( 1 + \frac{k_1*[S]}{(k_2 + k_{-1})}\bigg(1 + \frac{k_{3}[I]}{k_{-3}} \bigg) \bigg)}[S]}{(k_2 + k_{-1})} \\ &= \frac{k_1*[E]_{Total}[S]}{(k_2 + k_{-1})*\bigg( 1 + \frac{k_1*[S]}{(k_2 + k_{-1})}\bigg(1 + \frac{k_{3}[I]}{k_{-3}} \bigg) \bigg)} \\ &= \frac{[E]_{Total}[S]}{\frac{(k_2 + k_{-1})}{k_1}*\bigg( 1 + \frac{k_1*[S]}{(k_2 + k_{-1})}\bigg(1 + \frac{k_{3}[I]}{k_{-3}} \bigg) \bigg)} \\ &= \frac{[E]_{Total}[S]}{\frac{(k_2 + k_{-1})}{k_1} + [S]\bigg(1 + \frac{k_{3}[I]}{k_{-3}} \bigg) \bigg)} \\ \end{align} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ \frac{(k_2 + k_{-1})}{k_1} }[/math] is known as the Michaelis constant and is commonly written as:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} K_M = \frac{k_{cat} + k_r }{k_f} = \frac{(k_2 + k_{-1})}{k_1} \end{align} }[/math]
\textbf{Note:} [math]\displaystyle{ k_{cat} = k_2 }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ k_r = k_{-1} }[/math], and [math]\displaystyle{ k_f = k_1 }[/math]
Finally, to get the Michaelis-Menton equation for uncompetitive inhibition:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} v &= k_2*[ES] \\ &= k_2* \frac{[E]_{Total}[S]}{K_m + [S]\bigg(1 + \frac{k_{3}[I]}{k_{-3}} \bigg) \bigg)} \\ &= \frac{V_{max}}{K_m + [S]\bigg(1 + \frac{k_{3}[I]}{k_{-3}} \bigg) \bigg)} \\ \end{align} }[/math]
Where:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} V_{max} = k_2*[E]_{Total}[S] \end{align} }[/math]
References
- Ahern, Kevin; Rajagopal, Indira; Tan, Taralyn (2017). Biochemistry Free For All Version 1.2. North Carolina: Creative Commons. pp. 367–368.
- Athel, Cornish-Bowden (2014). Principles of Enzyme Kinetics.. Elsevier Science. ISBN 978-1483164670. OCLC 897021733. http://www.worldcat.org/oclc/897021733
- "The kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions with two or more substrates or products. II. Inhibition: nomenclature and theory". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Specialized Section on Enzymological Subjects 67: 173–87. February 1963. doi:10.1016/0926-6569(63)90226-8. PMID 14021668. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2F0926-6569%2863%2990226-8
- Rhodes, David. "Enzyme Kinetics - Single Substrate, Uncompetitive Inhibition, Lineweaver-Burk Plot". Purdue University. http://www.hort.purdue.edu/rhodcv/hort640c/enzkin1/enzkin1.htm.
- "A simple graphical method for determining the inhibition constants of mixed, uncompetitive and non-competitive inhibitors". The Biochemical Journal 137 (1): 143–4. January 1974. doi:10.1042/bj1370143. PMID 4206907. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1166095
- Nelson, David L.; Cox, Michael M. (November 21, 2012). Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry (6 ed.). W.H. Freeman. ISBN 978-1429234146.
- "Lithium and the phosphoinositide cycle: an example of uncompetitive inhibition and its pharmacological consequences". Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 12 (8): 297–303. August 1991. doi:10.1016/0165-6147(91)90581-C. PMID 1658998. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2F0165-6147%2891%2990581-C
- "Alkaline phosphatase as a reporter of cancerous transformation". Clinica Chimica Acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry 209 (1–2): 123–9. July 1992. doi:10.1016/0009-8981(92)90343-O. PMID 1395034. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2F0009-8981%2892%2990343-O
- "Biology of human alkaline phosphatases with special reference to cancer". Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences 32 (1): 1–39. 1995. doi:10.3109/10408369509084680. PMID 7748466. https://dx.doi.org/10.3109%2F10408369509084680
- "Detection of a novel, primate-specific 'kill switch' tumor suppression mechanism that may fundamentally control cancer risk in humans: an unexpected twist in the basic biology of TP53". Endocrine-Related Cancer 25 (11): R497–R517. November 2018. doi:10.1530/ERC-18-0241. PMID 29941676. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=6106910
- "Biophysical studies on agents affecting the state of membrane lipids: biochemical and pharmacological implications". Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 22 (1): 3–32. November 1978. doi:10.1007/bf00241467. PMID 154058. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007%2Fbf00241467
- "Arf, Sec7 and Brefeldin A: a model towards the therapeutic inhibition of guanine nucleotide-exchange factors". Biochemical Society Transactions 33 (Pt 6): 1265–8. December 2005. doi:10.1042/BST20051265. PMID 16246094. https://dx.doi.org/10.1042%2FBST20051265
- "Ethanol, sedative hypnotics, and glutamate receptor function in brain and cultured cells". Behavior Genetics 23 (2): 231–6. March 1993. doi:10.1007/BF01067428. PMID 8390239. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007%2FBF01067428
- "Emerging roles of S-nitrosylation in protein misfolding and neurodegenerative diseases". Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 10 (1): 87–101. January 2008. doi:10.1089/ars.2007.1858. PMID 17961071. https://dx.doi.org/10.1089%2Fars.2007.1858





