
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Camila Xu | -- | 3429 | 2022-11-04 01:52:08 |
Video Upload Options
The access economy is a business model where goods and services are traded on the basis of access rather than ownership: it refers to renting things temporarily rather than selling them permanently. The term arose as a correction to the term sharing economy because major players in the sharing economy, such as Airbnb, Zipcar, and Uber, are commercial enterprises whose businesses do not involve any sharing. This model uses a technology platform, often accessed via mobile phone, to connect suppliers willing to rent assets (e.g., apartments for rent or cars for transportation services) with consumers. This movement was worth around $26 billion a year in 2015. The number of persons involved in the access economy is not easily measured. The "access economy" or "on-demand economy" poses regulatory and political challenges, such as: defining the nature of the employment relationship; designing regulations to safeguard parties to these transactions; the loss of taxes and corporate access that results from moving away from small locally owned companies to large remote technology companies; and the bypassing of local regulations (such as the requirement for taxi drivers to provide wheelchair vans, or provide drivers 24-7).
1. Economic Model
Companies such as Uber and Airbnb provide technology that connects suppliers willing to rent their assets to consumers interested in temporarily using those assets. For example, owners of real estate may offer an apartment or bedroom for rent on a weekly basis, or the owner of a car may offer taxi-like services. Mobile phone applications are the typical platform that connects the consumers and suppliers.
As an economic model, the access economy suggests that "access" to goods and services may become more desirable than "ownership" of them.[1] Steve Denning notes:[2]
The third thing that the Internet did was social. It created a generation of people who began doing something that cut to the heart of the way society has been organized for several hundred years. These people—mainly young—began preferring access to ownership. Instead of planning their lives on the premise of acquiring and owning more private property, this new generation began finding meaning and satisfaction in having access to things and interacting with other people in the process.
2. Business Strategy
The Harvard Business Review has argued that it's important for businesses in this space to think of themselves as being in an access economy. In a 2015 article called "The Sharing Economy Isn't About Sharing at All", authors Giana M. Eckhardt and Fleura Bardhi write,[3]
This insight − that it is an access economy rather than a sharing economy – has important implications for how companies in this space compete. It implies that consumers are more interested in lower costs and convenience than they are in fostering social relationships with the company or other consumers.
The article goes on to argue that a major difference between Uber and its competitor Lyft is that Uber understands the difference: "Uber positions itself squarely around its pricing, reliability, and convenience" with their tagline as being "Better, faster and cheaper than a taxi",[3] while the tagline of the much-less-successful Lyft is, "We're your friend with a car."[3]
In essence, Eckhardt and Bardhi concludes that:
The access economy is changing the structure of a variety of industries, and a new understanding of the consumer is needed to drive successful business models. A successful business model in the access economy will not be based on community, however, as a sharing orientation does not accurately depict the benefits consumers hope to receive. It is important to highlight the benefits that access provides in contrast to the disadvantages of ownership and sharing.[3]
3. Employment Model
The business model of companies situated in the gig economy introduces a different employment concept compared to traditional employment structures. While in traditional industries workers enjoy the benefits of unionisation, healthcare provision, and employee rights with regard to minimum wage, contract termination and working hours, employees within the access economy are perceived as freelancers. These people do not receive pension benefits or other employee rights and benefits and are often not paid on an hourly basis.
A 2016 study by the McKinsey Global Institute concluded that across America and England there were a total of 162 million people that were involved in some type of independent work.[4] Moreover, their payment scheme is linked to the gigs they perform which could be deliveries, rentals or other services.[5] However, recent legal rulings indicated that there is an emerging trend to classify full-time freelancers working for a single main employer of the gig economy as workers and to award them regular worker rights and protection. A popular example is the ruling against Uber in October 2016, which supported the claim of two Uber drivers to be classified as workers and to receive the related worker rights and benefits. However, Uber was granted the right to appeal this claim and a final ruling is expected to be drawn in September 2017.[6]
It is important to distinguish employment in the access economy from employment through zero-hour contracts. Employment in the gig economy entails receiving compensation for one key performance indicator, which, for example, is defined as parcels delivered or taxi lifts conducted. Another feature is that employees can opt to refuse taking an order. Although employers do not have to guarantee employment or employees can also refuse to take an order under a zero-hour contract, workers under such a contract are paid by the hour and not directly through business-related indicators as in the case of the gig economy.[7]
4. Gender
The access economy has affected both genders of the population in numerous ways (some negative, some positive). For women, the access economy provides flexibility. This has led women to have quickly outnumbered the number of men in this economy. This career path has allowed mothers to continue with their families while having the ability to work. For men, one effect that was found was that the gig economy gave them more advantages. Men have gained power in the sense that even in the access economy they are still hired more, paid higher wages, and treated better than women in the workplace. Sexism gives men the advantage, allowing them to acquire customers who are more understanding and respect.[8][9]
5. Elderly
The elderly have also found pros and cons to the access economy. The future of retirement savings are being endangered by the gig-economy. An article by CNBC states that only 16% of independent workers have a retirement savings plan. On the flip side, there are seniors who are earning, according to JPMorgan Chase Institute, an average of $40,000. The percentage of seniors has increased throughout the years from 20.7 percent in 2009 to 23.1 percent in 2015.[10]
6. Alternate Names
There are many related concepts and alternate names currently being used for the access economy. They include:[11][12][13]
- Sharing economy
- On-demand economy
- Circular economy
- Collaborative economy
- Uberisation
- Gig economy
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) economy
- Reputation economy
- Trust economy
The validity of the term "sharing economy" is disputed. For example, both Uber and taxi companies provide access to cars that are not owned by the passenger; the real difference is that taxis are a mature industry that pay living wages and abide by local regulations (such as to ensure that there is always a wheelchair van available), while Uber and its ilk are a new industry that is exploiting the lack of regulations that affect it. Michael Bauwens notes that companies such as Uber aren't operating by a peer-to-peer structure, saying:[14]
A "sharing economy," by definition, is lateral in structure. It is a peer-to-peer economy. But Uber, as its name suggests, is hierarchical in structure. It monitors and controls its drivers, demanding that they purchase services from it while guiding their movements and determining their level of earnings. And its pricing mechanisms impose unpredictable costs on its customers, extracting greater amounts whenever the data suggests customers can be compelled to pay them. This is a top-down economy, not a "shared" one.
7. Economic Effects
7.1. Overview
The impacts of the access economy in terms of costs, wages and employment are not easily measured and appear to be growing.[15] Various estimates indicate that 30-40% of the U.S. workforce is self-employed, part-time, temporary or freelancers. However, the exact percentage of those performing short-term tasks or projects found via technology platforms was not effectively measured as of 2015 by government sources.[16] In the U.S., one private industry survey placed the number of "full-time independent workers" at 17.8 million in 2015, roughly the same as 2014. Another survey estimated the number of workers who do at least some freelance work at 53.7 million in 2015, roughly 34% of the workforce and up slightly from 2014.[17]
Economists Lawrence F. Katz and Alan B. Krueger wrote in March 2016 that there is a trend towards more workers in alternative (part-time or contract) work arrangements rather than full-time; the percentage of workers in such arrangements rose from 10.1% in 2005 to 15.8% in late 2015.[18] Katz and Krueger defined alternative work arrangements as "temporary help agency workers, on-call workers, contract company workers, and independent contractors or free-lancers".[19] They also estimated that approximately 0.5% of all workers identify customers through an online intermediary; this was consistent with two others studies that estimated the amount at 0.4% and 0.6%.[19]
At the individual transaction level, the removal of a higher overhead business intermediary (say a taxi company) with a lower cost technology platform helps reduce the cost of the transaction for the customer while also providing an opportunity for additional suppliers to compete for the business, further reducing costs.[16] Consumers can then spend more on other goods and services, stimulating demand and production in other parts of the economy. Classical economics argues that innovation that lowers the cost of goods and services represents a net economic benefit overall. However, like many new technologies and business innovations, this trend is disruptive to existing business models and presents challenges for governments and regulators.[20]
For example, should the companies providing the technology platform be liable for the actions of the suppliers in their network? Should persons in their network be treated as employees, receiving benefits such as healthcare and retirement plans? If consumers tend to be higher income persons while the suppliers are lower-income persons, will the lower cost of the services (and therefore lower compensation of the suppliers) worsen income inequality? These are among the many questions the on-demand economy presents.[16][21]
7.2. Effects on Particular Industries

One study indicated that ride-sharing company Uber is significantly replacing taxi services in parts of New York City ; comparing the April to June periods in 2014 versus 2015, Uber pickups rose by 6 million (from 2 million to 8 million), while Green cab pickups rose by 1 million and Yellow cab pickups fell by 4 million. Uber's impact was the most significant in Manhattan.[22]
7.3. Pros
- Flexible and Convenient: Access economy allows workers to set their own hours of work. An Uber driver explains, "the flexibility extends far beyond the hours you choose to work on any given week. Since you don’t have to make any sort of commitment, you can easily take time off for the big moments in your life as well, such as vacations, a wedding, the birth of a child, and more."[23] Workers are able to accept or reject additional work based on their needs while using the commodities they already possess to make money.
- Low Barriers to Entry: Depending on their schedules and resources, workers can provide services in more than one area with different companies. This allows workers to relocate and continue earning income. Also, by working for access economy companies, the transaction costs associated with occupational licences are significantly lowered. For example, in New York City, taxi drivers must have a special driver's license and undergo training and background checks,[24] while Uber contractors can offer "their services for little more than a background check."[25]
- Maximum Benefit for Sellers and Buyers: Enables users to improve living standards by eliminating the emotional, physical, and social burdens of ownership. Without the need to maintain a large inventory, deadweight loss is reduced, prices are kept low, all while remaining competitive in the markets.[3]
- Environmental Benefit: Access economies allow the reuse and repurpose of already existing commodities. Under this business model, private owners share the assets they already possess when not in use.[26]
- Breaking of Monopolies: In Zimbabwe, Airbnb, along with other businesses of this type, has led to a rise in consumer benefits stemming from good prices and quality. This model also allows for more opportunities for those that are self employed.
7.4. Cons
- Lack of employee benefits: Since access economy companies rely on independent contractors, they are not offered the same protections as that of full-time salary employees in terms of workers comp, retirement plans, sick leave, and unemployment.[27]
- Quality discrepancies: Since access economy companies rely on independent workers, the quality of service can differ between workers in the same company. Despite Airbnb CEO Brian Chesky efforts to have a gold standard for safety and fire hazards, Steven Hill from the New America Foundation cited his experience signing up to become a host on Airbnb as simple as uploading a few photos to the website "and within 15 minutes my place was “live” as an Airbnb rental. No background check, no verifying my ID, no confirming my personal details, no questions asked. Not even any contact with a real human from their trust and safety team. Nothing."[28]. However, due to the reputation service model, customers are provided with a peer-reviewed rating of the contractor and are given a choice of whether to proceed with the transaction. There is no information, choice or feedback service in the traditional model - and thus also may suffer from quality discrepancies.
- Liability: Though some companies offer liability guarantees such as Airbnb's "Host Guarantee" that promises to pay up to 1 million in damages, it is extremely difficult to prove fault.[29]
- Ownership and usage:This economic model blurs the difference between ownership and usage without establishing a regulation of supervision over either. This allows for the abuse or neglect of absent policies that are not in place given the distinct nature of the system.[30]
- Replacement of small local companies with large international tech companies. For example, taxi companies tend to be locally-owned and operated, while Uber is California-based.[31] Therefore, taxi company profits tend to stay local, while access economy profits, the majority of the money goes to the local driver, a portion of the profits flow out of the local community.
8. Regulations and Legislation
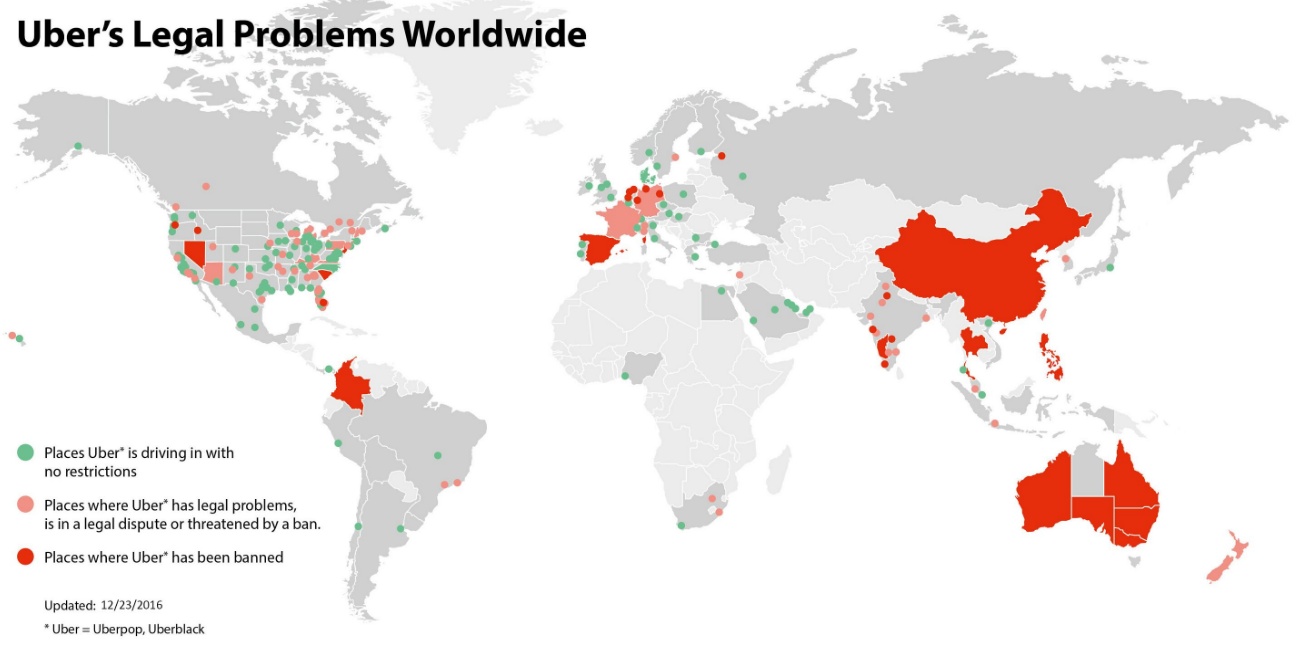
8.1. Uber
The taxi unions in the United States are in full support of strict ride sharing regulations. However, the taxi industry argues that all transportation companies are needed to create a fair competitive environment.
- In Michigan, new legislation requires Uber and Lyft drivers to apply for licenses and carry the same liability insurance as those of taxi drivers. In addition, Bill HB 4637 requires access economy companies to run background checks on all drivers. Uber, Lyft, taxis and other transportation services will be equally regulated under the state.[32]
- In New Jersey, the "Transportation Network Company Safety and Regulatory Act," instructs companies and drivers to meet insurance coverage standards and criminal background checks, according to the Bill A3695. Nonetheless, sharing ride companies such as Uber and Lyft must pay $25,000 to register with the state. Drivers will be banned from work if they had been convicted of homicide, driving under the influence of drugs, or sexual assault. Accidents that occur during a service and which results in injuries to a passenger, will be the financial responsibility of the drivers or the company. Drivers and company may be liable for up to $1.5 million of medical bills of the injured passengers. Uber’s spokesman, Craig Ewer said concerning the bill “We look forward to working constructively with the administration as we implement the new law.” Under New Jersey’s law, vehicles must pass the state inspection and companies have to maintain six years worth of records. The New Jersey Uber general manager, Ana Mahony told the committee “if the rules of the bill don’t get changed Uber will have to leave the state”. "This bill would make it impossible for Uber to continue operating, not because we don't want to, but because it includes poison pills that have driven us out of other markets and would drive us out of New Jersey."Meanwhile, the taxi and limousine industry urged lawmakers to require ride sharing companies to meet the same regulations imposed on them, such as the requirement that taxi and limo drivers must be fingerprinted and pass a drug test.[33]
- In the state of Florida, lawmakers passed a law demanding drivers to carry insurance of $25,000 for the property, $100,000 for death and bodily injury per incident, and $50,000 for death and bodily injury per person. In addition, background checks on all the drivers are required. Uber South Florida General Manager Kasra Moshkani said in a statement, “Ride sharing has changed the way residents and more than 110 million visitors travel around Florida communities.” [34]
- Uber now has 2,000 Saudi drivers, with a target of reaching 100,000 over the next five years. The reason argument made in allowing Uber in Saudi Arabia is that it would provide more jobs for its citizens. Al Madina's newspaper reported, quoting Mr. Gore-Coty spokesman from the kingdom's General Directorate of Traffic, “we are bringing accessibility to employment and entrepreneurialism to cities.”
- In the United Kingdom , Uber requested an appeal to the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom in contest of the tribunal which ruled that its drivers merited workers rights such as minimum wage, but was rejected.[35]
- In Quebec, Uber was requested to follow new regulations from the Ministry of Transportation for Uber drivers to be required to have 35 hours of training and criminal background checks by the local police. In response to these new regulations, Uber management concluded operations in Quebec on October 14, 2017 and resulted in 10,000 drivers and 50 office employees losing their jobs through Uber.[36]
8.2. Airbnb

City, municipal and state laws such as acquiring business licenses, complying with building, city and zoning standards have been implemented in an effort to regulate Airbnb. Airbnb encourages hosts to research their local government’s laws and regulations before becoming a host. In some cities, Airbnb will provide occupancy tax calculations to make it easier for hosts to fulfill their tax obligations.[37]
- The governor of New York, Andrew Cuomo, recently signed a legislation penalizing Airbnb hosts who do not follow property rental limits. Hosts cannot rent their property for less than 30 consecutive days unless they are currently living in the property.[38]
- In California , lawmakers are actively attempting to pass legislation regulating Airbnb. Mike McGuire’s bill (SB 593) would mandate short-term vacation rentals to charge occupancy taxes in addition to requiring data reporting by the renter, and obedience of local laws that restrict short-term rentals. The bill mainly focuses on the collection of taxes on rented properties. This comes after many complaints from the hotel industry, who has seen major declines in bookings in recent years. The bill was not approved after almost 20,000 emails were sent to the Senator against it.[39]
- In Berlin, lawmakers have banned hosts from renting their property short-term without first requesting permission from authorities. Under this new legislation, hosts can be required to pay a fine of up to 100,000 euros if they rent more than 50% of their property space. Landlords can still rent individual rooms with the condition that they live in most of the property. Prior to this legislation, 20,000 apartments were posted on Airbnb in Berlin.[40]
- Lawmakers in Barcelona are also creating legislations to limit listings in the area. Rapid growth in the number of tourists forced authorities to implement laws to regulate home rentals in Barcelona. This occurred after Airbnb experienced double the rental listings from 2014 to 2015. It is estimated that in 2015, 900,000 tourists used Airbnb to book their lodging. Barcelona’s officials penalized Airbnb with a $644,160 fine in November 2016 for advertising unlicensed room rentals.[41]
8.3. The Taylor Review
As a response to the fast-changing nature of working practices in the modern economy, especially the Gig economy, The UK Government has carried out a review and issued guidelines in an attempt to address these issues.[42] The report was published on the 11th July 2017 and the overriding conclusion was that the UK’s economy should be “fair and decent”.[43] A 7-point plan[44] was suggested to improve working conditions and security. In addition, The Taylor Review outlines demands asking the distribution of power be distributed at a more equal level. It asks for workers of these, gig economy businesses be labeled as "dependent contractors with extra benefits". Other demands include, better corporate management, skill development efforts, fostering of a positive workplace,and financial representation provided by the state.[45]
References
- "The Access Economy". http://www.triplepundit.com/topic/access-economy/. Retrieved 13 July 2015.
- Denning, Steve (2014). "Three Strategies For Managing The Economy Of Access". Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/stevedenning/2014/05/02/economic-game-change-from-ownership-to-access/. Retrieved 13 July 2015.
- "The Sharing Economy Isn't About Sharing at All". Harvard Business Review. 2015-01-28. https://hbr.org/2015/01/the-sharing-economy-isnt-about-sharing-at-all. Retrieved 2015-07-11.
- "Independent work: Choice, necessity, and the gig economy" (in en). https://www.mckinsey.com/global-themes/employment-and-growth/independent-work-choice-necessity-and-the-gig-economy.
- B. Wilson. "Employment dynamics". https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/business-38930048. Retrieved 21 Jun 2017.
- M. Gingell. "Uber lawsuit". https://www.independent.co.uk/news/business/news/gig-economy-workers-rights-change-zero-hour-contracts-permanent-staff-a7719831.html. Retrieved 21 Jun 2017.
- "Distinguishing employment under zero-hour contracts and the gig economy". https://fullfact.org/economy/what-gig-economy/. Retrieved 21 Jun 2017.
- Galperin, Hernán. "The gig economy may strengthen the 'invisible advantage' men have at work" (in en). The Conversation. https://theconversation.com/the-gig-economy-may-strengthen-the-invisible-advantage-men-have-at-work-86444.
- Galluzzo, Jenny (2016-10-12). "How the Gig Economy Is Changing Work for Women" (in en). Entrepreneur. https://www.entrepreneur.com/article/282693.
- "How seniors are tapping the gig economy" (in en). https://www.cbsnews.com/news/how-seniors-are-tapping-the-gig-economy/.
- "What is the right name for the "sharing-economy"?". https://medium.com/ouishare-connecting-the-collaborative-economy/is-there-a-better-name-for-the-sharing-economy-2d7489e1f56d.
- "The Rise of the Gig Economy". http://dollarsandsense.org/archives/2014/0314friedman.html.
- "Collaborative Economy: A Transformative Lens, not a Start-up Trend". http://www.collaborativeconsumption.com/2014/11/27/collaborative-economy-a-transformative-lens-not-a-start-up-trend/.
- Bauwens, Michael (1 February 2015). "The sharing economy is a lie: Uber, Ayn Rand and the truth about tech and libertarians". http://www.salon.com/2015/02/01/the_sharing_economy_is_a_lie_uber_ayn_rand_and_the_truth_about_tech_and_libertarians/. Retrieved 14 July 2015.
- "The Gig Economy: Implications of the Growth of Contingent Work". https://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/brainard20161117a.htm. Retrieved November 27, 2016.
- "Gig Economy Hasn't Taken Over". Bloomberg.com. http://www.bloombergview.com/articles/2015-08-26/gig-economy-hasn-t-taken-over-job-market-yet. Retrieved August 28, 2015.
- Bloomberg-Justin Fox-Gig Economy is Growing, But Not Growing Up-October 2, 2015 http://www.bloombergview.com/articles/2015-10-01/gig-economy-is-growing-but-not-growing-up
- Bloomberg-Stilwell and McGregor- Gigonomics The Dismal Science Behind Today's On-Demand Jobs-June 2, 2016 https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2016-06-02/gigonomics-the-dismal-science-behind-today-s-on-demand-jobs
- Katz & Kruger-Princeton-The Rise and Nature of Alternative Work Arrangements in the United States 1995-2015-Retrieved June 2, 2016 https://krueger.princeton.edu/sites/default/files/akrueger/files/katz_krueger_cws_-_march_29_20165.pdf
- Hazlitt, Henry (1979). Economics in One Lesson. Three Rivers Press. ISBN 0-517-54823-2.
- GAO-Contingent Workforce: Size, Characteristics, Earnings, Benefits-April 2015 http://www.gao.gov/assets/670/669766.pdf
- Fivethirtyeight.com Fischer-Baum and Bialik-Uber is Taking Millions of Manhattan Rides Away from Taxis October 13, 2015 https://fivethirtyeight.com/features/uber-is-taking-millions-of-manhattan-rides-away-from-taxis/
- Johnson, Holly. "How to Make Money Driving for Uber". http://www.thesimpledollar.com/how-to-make-money-driving-for-uber/. Retrieved June 22, 2017.
- How to become a New York Taxi Driver https://www.drivers.com/article/1162/
- Given, Casey. "Uber Economics: How Markets are Changing in the Sharing Economy". https://www.atlasnetwork.org/news/article/uber-economics-how-markets-are-changing-in-the-sharing-economy. Retrieved 11 January 2015.
- Lombardo, Crystal. "Pros and Cons of Sharing Economy". http://visionlaunch.com/pros-and-cons-of-sharing-economy/#. Retrieved 29 October 2015.
- Huet, Ellen. "What Happens to Uber Drivers And Other Sharing Economy Workers Injured On The Job?". https://www.forbes.com/sites/ellenhuet/2015/01/06/workers-compensation-uber-drivers-sharing-economy/#64f84eef42c7. Retrieved 6 January 2015.
- Hill, Steven. "The two faces of Airbnb". http://www.businessinsider.com/the-two-faces-of-airbnb-2015-10. Retrieved 30 October 2015.
- Bort, Julie. "Airbnb Banned From Condo Complex After Guest Caused $10,000 Of Damage". http://www.businessinsider.com/airbnb-guest-caused-10000-of-damage-2014-10. Retrieved 9 October 2014.
- "Log in to NewsBank" (in en). http://infoweb.newsbank.com/resources/doc/nb/news/165dfa2b8ee04210.
- Uber newsroom https://www.uber.com/en-CA/newsroom/company-info//
- Lawler, Emily. "Michigan House passes bills changing Uber, Lyft, taxi regulations". http://www.mlive.com/news/index.ssf/2016/12/michigan_house_passes_bills_ch.html. Retrieved June 5, 2017.
- Lagana, Joseph (September 29, 2016). "State of New Jersey 217th Legislature". Assembly Substitute for Assembly, No.3695: 1–20. http://www.njleg.state.nj.us/2016/Bills/A4000/3695_R1a.PDF. Retrieved June 10, 2017.
- Sweeney, Dan. "House passes regulations for Uber, Lyft". http://www.sunsentinel.com/news/politics/florida-politics-blog/fl-reg-uber-lyft-florida-legislature-20170405-story.html. Retrieved June 7, 2017.
- "Uber loses bid to appeal driver case to UK Supreme Court". Reuters. December 4, 2017. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-uber-britain/uber-loses-bid-to-appeal-driver-case-to-uk-supreme-court-idUSKBN1DZ04F.
- "Uber says it will pull out of Canada's Quebec province". Reuters. September 26, 2017. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-uber-quebec/uber-to-withdraw-from-quebec-cbc-news-idUSKCN1C11PR.
- "What legal and regulatory issues should I consider before hosting on Airbnb?". https://www.airbnb.com/help/article/376/what-legal-and-regulatory-issues-should-i-consider-before-hosting-on-airbnb. Retrieved June 8, 2017.
- Dobbins, James. "How to Host on Airbnb Legally". https://www.nytimes.com/2017/04/07/realestate/how-to-host-on-airbnb-legally.html?_r=0. Retrieved June 5, 2017.
- Dillon, Liam. "California lawmakers can't figure out what to do with Airbnb. Here's why". http://www.latimes.com/politics/la-pol-sac-airbnb-laws-california-legislature-20170203-story.html. Retrieved June 4, 2017.
- Oltermann, Philip. "Berlin ban on Airbnb short-term rentals upheld by city court". https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2016/jun/08/berlin-ban-airbnb-short-term-rentals-upheld-city-court. Retrieved June 3, 2017.
- Sweeney, Dan. "House passes regulations for Uber, Lyft". http://www.sun-sentinel.com/news/politics/florida-politics-blog/fl-reg-uber-lyft-florida-legislature-20170405-story.html. Retrieved June 3, 2017.
- https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/good-work-the-taylor-review-of-modern-working-practices
- Chronologic - Good work: the Taylor review of modern working practices https://www.chronologic.co.uk/good-work-taylor-review-modern-working-practices/
- https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/627671/good-work-taylor-review-modern-working-practices-rg.pdf
- "The Taylor review: At-a-glance guide" (in en-GB). BBC News. 2017-07-11. https://www.bbc.com/news/business-40566079.





