
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Camila Xu | -- | 990 | 2022-10-21 01:41:56 |
Video Upload Options
Lories and lorikeets (tribe Loriini) are small to medium-sized arboreal parrots characterized by their specialized brush-tipped tongues for feeding on nectar of various blossoms and soft fruits, preferably berries. The species form a monophyletic group within the parrot family Psittacidae. Traditionally, they were considered a separate subfamily (Loriinae) from the other subfamily (Psittacinae) based on the specialized characteristics, but recent molecular and morphological studies show that the group is positioned in the middle of various other groups. They are widely distributed throughout the Australasian region, including south-eastern Asia, Polynesia, Papua New Guinea, Timor Leste and Australia , and the majority have very brightly coloured plumage.
1. Etymology
The usage of the terms "lory" and "lorikeet" is subjective, like the usage of "parrot" and "parakeet". Species with longer tapering tails are generally referred to as "lorikeets", while species with short blunt tails are generally referred to as "lories".[1]
2. Taxonomy
Traditionally, lories and lorikeets have either been classified as the subfamily, Loriinae, or as a family on their own, Loriidae,[2] but they are currently classified as a tribe. Neither traditional view is confirmed by molecular studies. Those studies show that the lories and lorikeets form a single group, closely related to the budgerigar and the fig parrots (Cyclopsitta and Psittaculirostris).[3][4][5][6][7]
Two main groups are recognized within the lories and lorikeets. The first consist of the genus Charmosyna[3][4] and the closely related Pacific Ocean genera Phigys and Vini.[3] All remaining genera, except Oreopsittacus are in the second group.[3][4] The position of Oreopsittacus is unknown, although one study suggests it could be a third group next to the other two.[7]
2.1. Species
Classification of parrots in the subfamily, Loriinae:
- Genus Chalcopsitta
- Black lory, Chalcopsitta atra
- Brown lory, Chalcopsitta duivenbodei (also called Duyvenbode's lory)
- Yellowish-streaked lory, Chalcopsitta sintillata
- Genus Eos
- Black-winged lory, Eos cyanogenia
- Violet-necked lory, Eos squamata
- Blue-streaked lory, Eos reticulata
- Red-and-blue lory, Eos histrio
- Red lory, Eos bornea
- Blue-eared lory, Eos semilarvata
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phylogeny of the genera of lories and lorikeets with their closest relatives, the fig parrots (Cyclopsitta and Psittaculirostris) and budgerigar, based on the available literature[3][4][5][6][7] |
- Genus Pseudeos
- Dusky lory, Pseudeos fuscata
- Cardinal lory, Pseudeos cardinalis
- Genus Trichoglossus
- Ornate lorikeet, Trichoglossus ornatus (also called ornate lory)
- Sunset lorikeet, Trichoglossus forsteni (also called scarlet-breasted or Forsten's[8] lorikeet)
- Leaf lorikeet, Trichoglossus weberi (also called Flores lorikeet)
- Marigold lorikeet, Trichoglossus capestratus
- Coconut lorikeet, Trichoglossus haematodus
- Biak lorikeet, Trichoglossus rosenbergi
- Rainbow lorikeet, Trichoglossus moluccanus
- Red-collared lorikeet, Trichoglossus rubritorquis
- Olive-headed lorikeet, Trichoglossus euteles (also called Perfect lorikeet)
- Citrine lorikeet, Trichoglossus flavoviridis
- Mindanao lorikeet, Trichoglossus johnstoniae (also called Johnstone's lorikeet)
- Pohnpei lorikeet, Trichoglossus rubiginosus (also called Ponape lory)
- Scaly-breasted lorikeet, Trichoglossus chlorolepidotus
- Genus Psitteuteles (sometimes classified in the Genus Trichoglossus)
- Varied lorikeet, Psitteuteles versicolor
- Iris lorikeet, Psitteuteles iris
- Goldie's lorikeet, Psitteuteles goldiei
- Genus Lorius
- Purple-bellied lory, Lorius hypoinochrous (synonym Stresemann's lory, Lorius amabilis)[9]
- Black-capped lory, Lorius lory
- White-naped lory, Lorius albidinuchus
- Yellow-bibbed lory, Lorius chlorocercus
- Purple-naped lory, Lorius domicellus (synonym blue-thighed lory, Lorius tibialis)[10]
- Chattering lory, Lorius garrulus
- Genus Phigys
- Collared lory, Phigys solitarius
- Genus Vini
- Blue-crowned lorikeet, Vini australis
- Kuhl's lorikeet, Vini kuhlii
- Stephen's lorikeet, Vini stepheni
- Blue lorikeet, Vini peruviana
- Ultramarine lorikeet, Vini ultramarina
- †Sinoto's lorikeet, Vini sinotoi (extinct)
- †Conquered lorikeet, Vini vidivici (extinct)
- Genus Glossopsitta
- Musk lorikeet, Glossopsitta concinna
- Genus Parvipsitta
- Little lorikeet, Parvipsitta pusilla
- Purple-crowned lorikeet, Parvipsitta porphyrocephala
- Genus Charmosyna
- Palm lorikeet, Charmosyna palmarum
- Red-chinned lorikeet, Charmosyna rubrigularis
- Meek's lorikeet, Charmosyna meeki
- Blue-fronted lorikeet, Charmosyna toxopei
- Striated lorikeet, Charmosyna multistriata
- Pygmy lorikeet, Charmosyna wilhelminae (also called Wilhelmina's lorikeet)
- Red-fronted lorikeet, Charmosyna rubronotata (also called red-spotted lorikeet)
- Red-flanked lorikeet, Charmosyna placentis
- †? New Caledonian lorikeet, Charmosyna diadema (possibly extinct, 20th Century?)
- Red-throated lorikeet, Charmosyna amabilis
- Duchess lorikeet, Charmosyna margarethae
- Fairy lorikeet, Charmosyna pulchella
- Josephine's lorikeet, Charmosyna josefinae (also called Josephine's lory)
- Papuan lorikeet, Charmosyna papou (also called Papuan lory)
- Genus Oreopsittacus
- Plum-faced lorikeet, Oreopsittacus arfaki (also called Whiskered lorikeet)
- Genus Neopsittacus
- Yellow-billed lorikeet, Neopsittacus musschenbroekii (also called Musschenbroek's lorikeet)
- Orange-billed lorikeet, Neopsittacus pullicauda (also called Emerald lorikeet)
3. Morphology
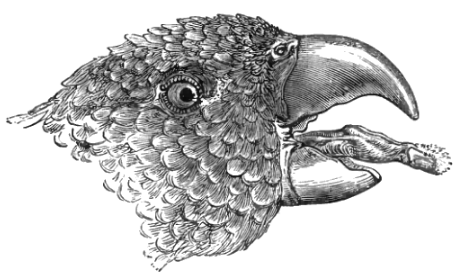
Lories and lorikeets have specialized brush-tipped tongues for feeding on nectar and soft fruits. They can feed from the flowers of about 5,000 species of plants and use their specialized tongues to take the nectar. The tip of their tongues have tufts of papillae (extremely fine hairs), which collect nectar and pollen.
The multi-coloured rainbow lorikeet was one of the species of parrots appearing in the first edition of The Parrots of the World and also in John Gould's lithographs of the Birds of Australia. Then and now, lories and lorikeets are described as some of the most beautiful species of parrot.
4. Diet
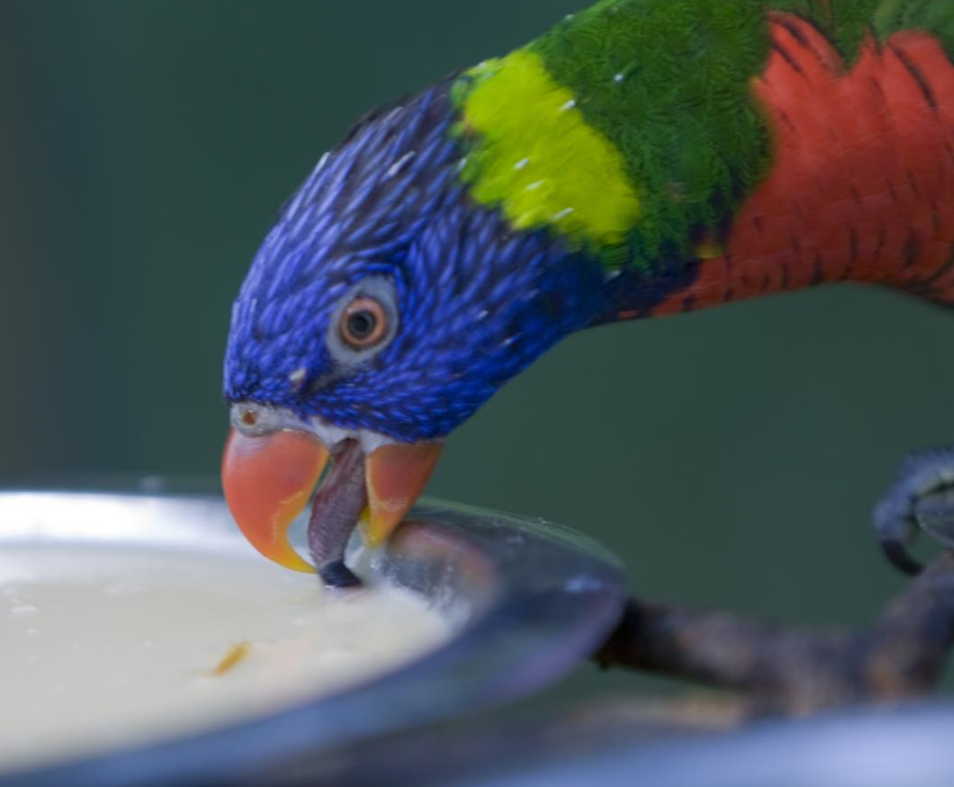
In the wild, rainbow lorikeets feed mainly on pollen and nectar, and possess a tongue adapted especially for their particular diet. Many fruit orchard owners consider them a pest, as they often fly in groups and strip trees containing fresh fruit. They are also frequent visitors at bird feeders that supply lorikeet-friendly treats, such as store-bought nectar, sunflower seeds, and fruits such as apples, grapes and pears.[11] Occasionally they have been observed feeding on meat.[12]
5. Conservation

The ultramarine lorikeet is endangered. It is now one of the 50 rarest birds in the world. The blue lorikeet is classified as vulnerable. The introduction of European rats to the small island habitats of these birds is a major cause of their endangerment.[13] Various conservation efforts have been made to relocate some of these birds to locations free of predation and habitat destruction.
6. In Literature
A "Lory" famously appears in Chapter III of Lewis Carroll's Alice's Adventures in Wonderland. Alice argues with the Lory about its age.
7. Gallery

Black-winged lory
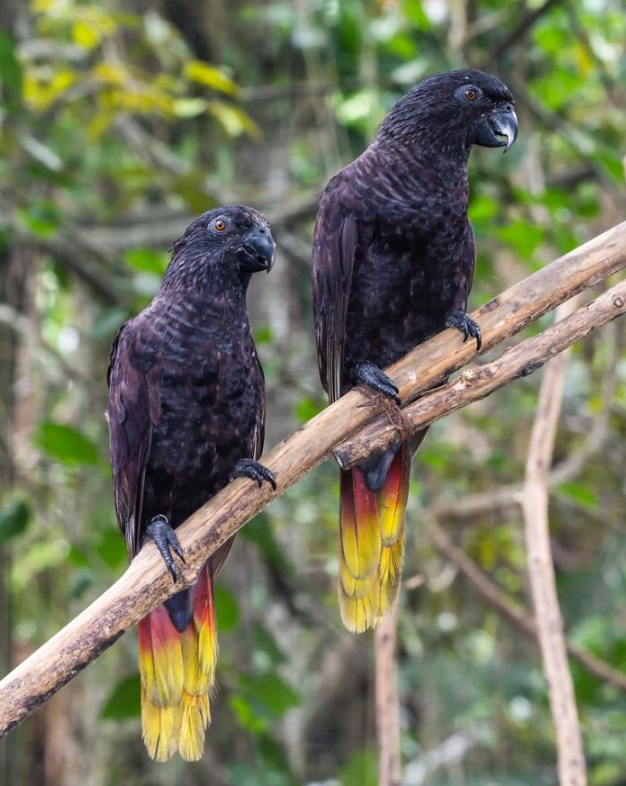

Black lories
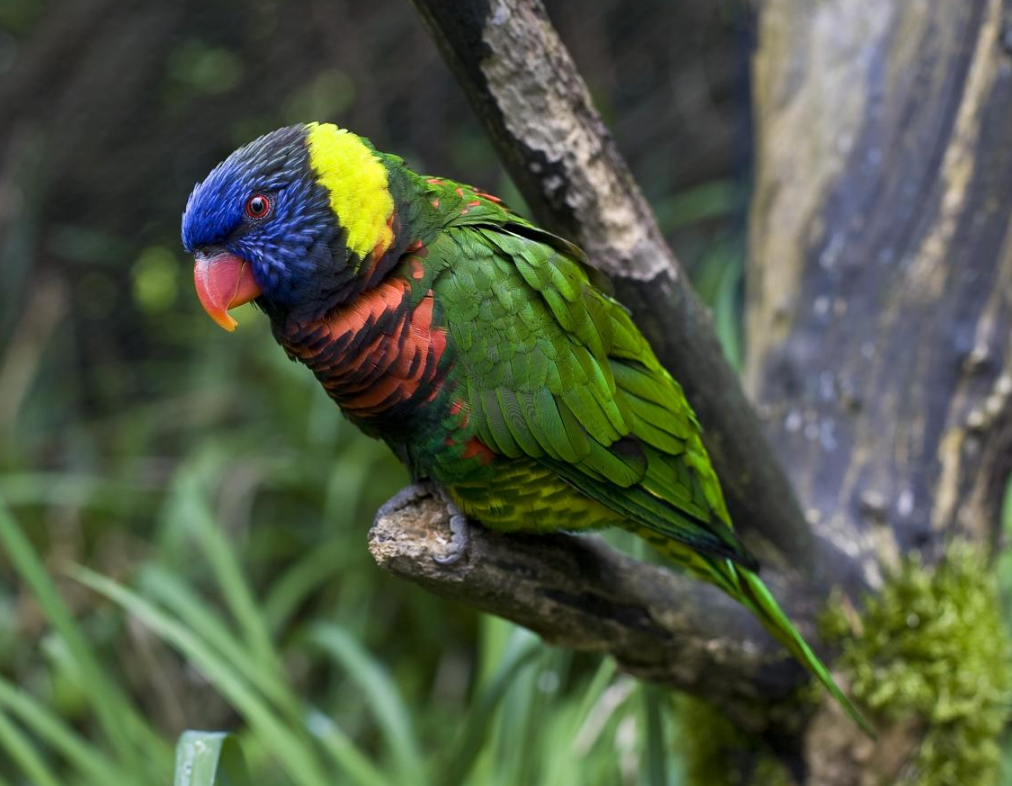

Green-naped lorikeet (subspecies of rainbow lorikeet)
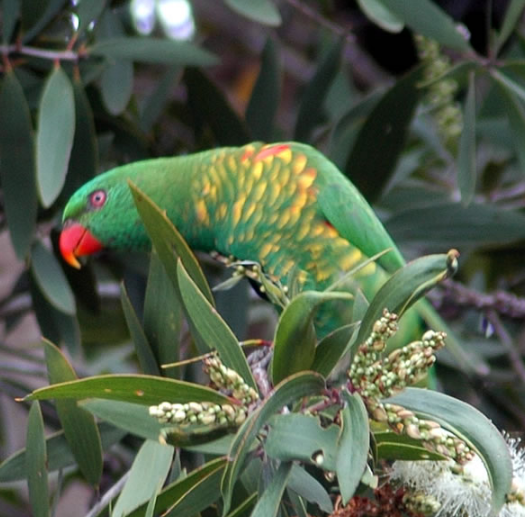

Scaly-breasted lorikeet
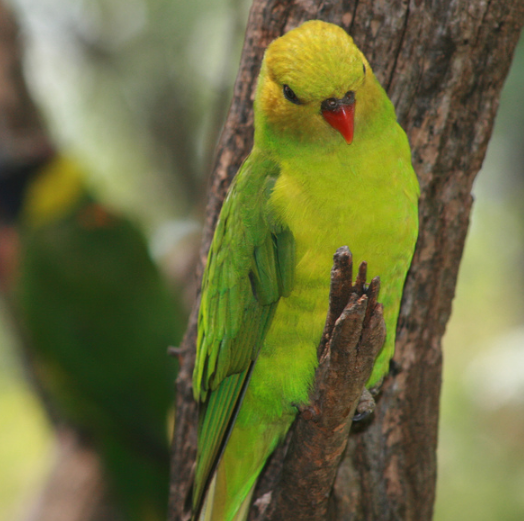

Olive-headed lorikeet
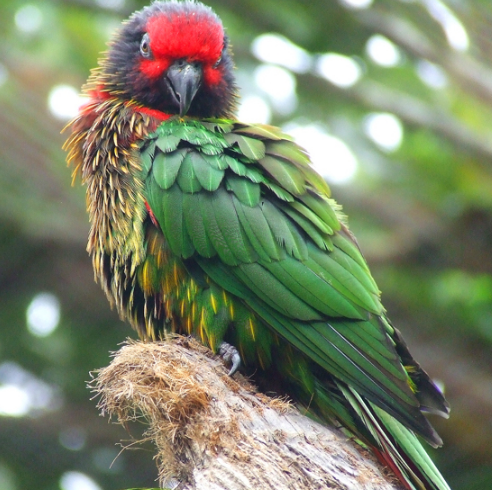

Yellowish-streaked lory
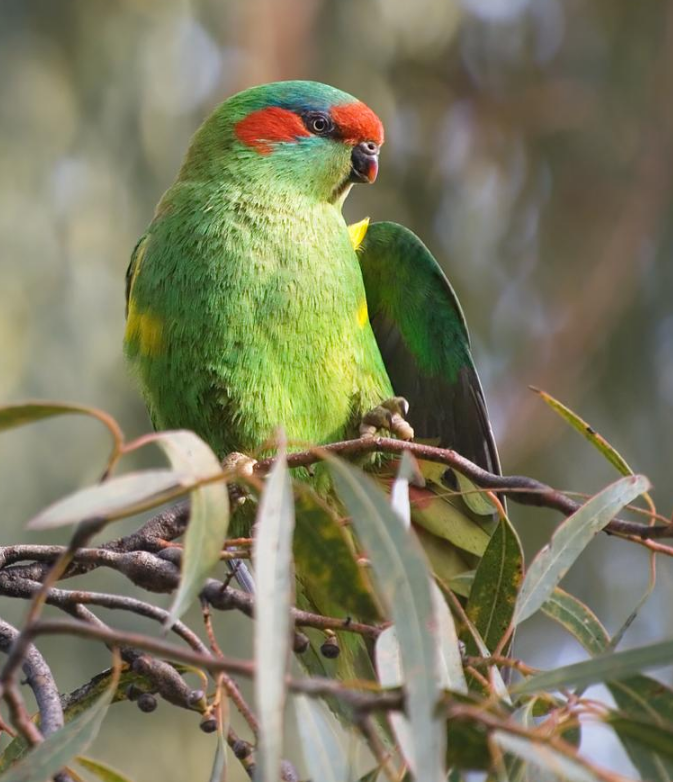

Musk lorikeet
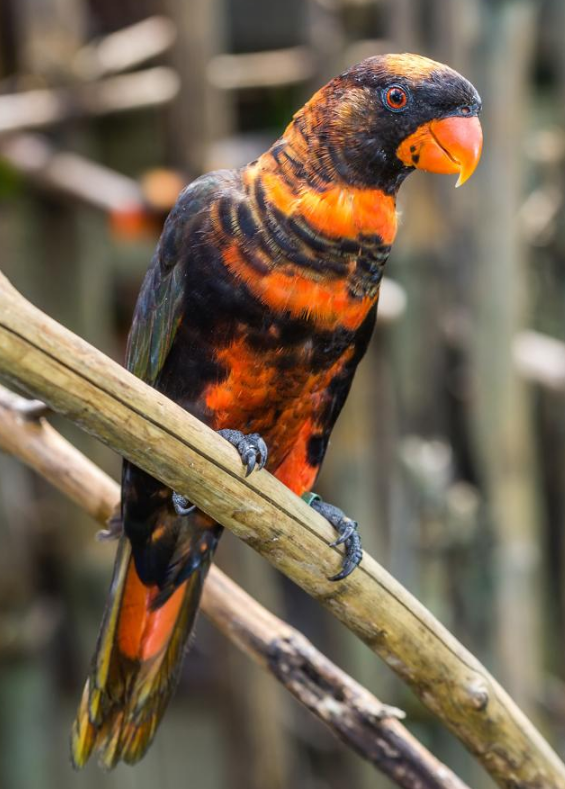

Dusky lory
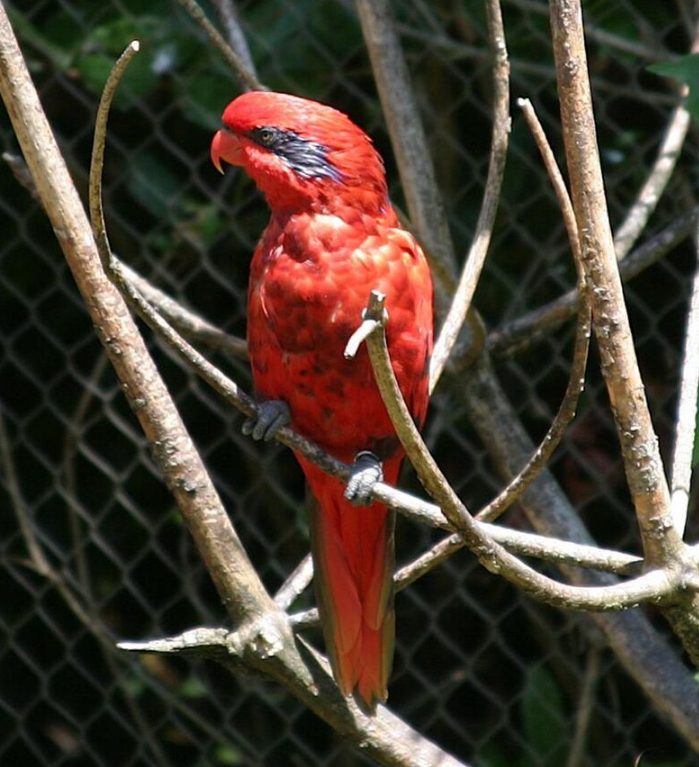

Blue-streaked lory
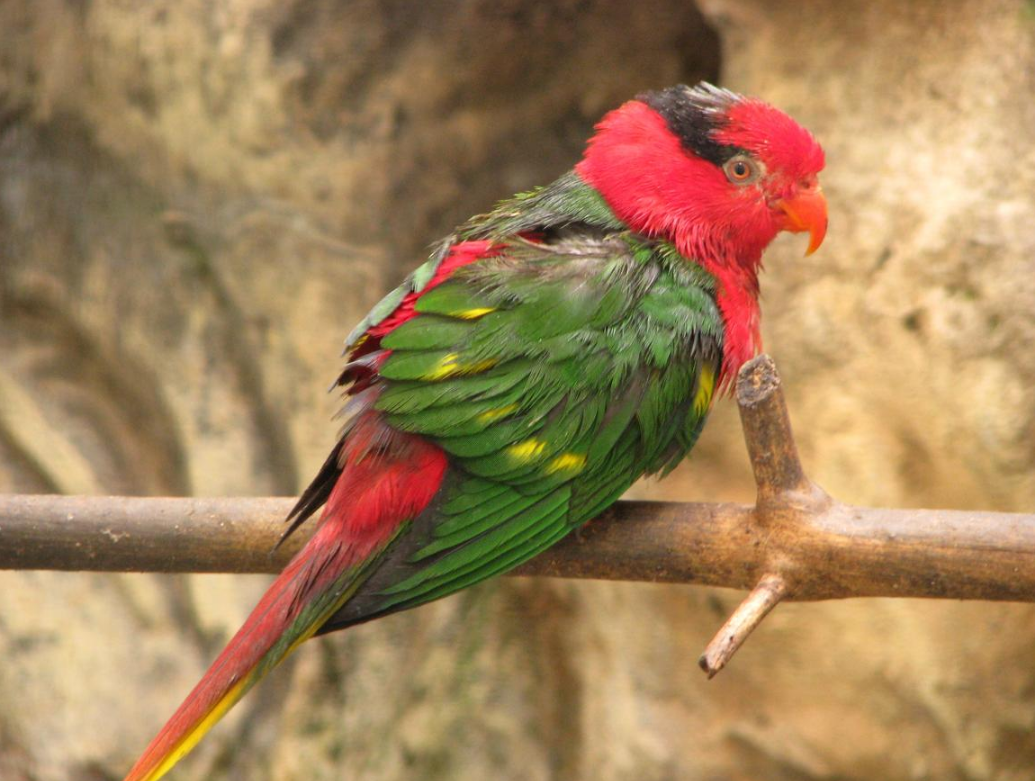

Josephine's lorikeet
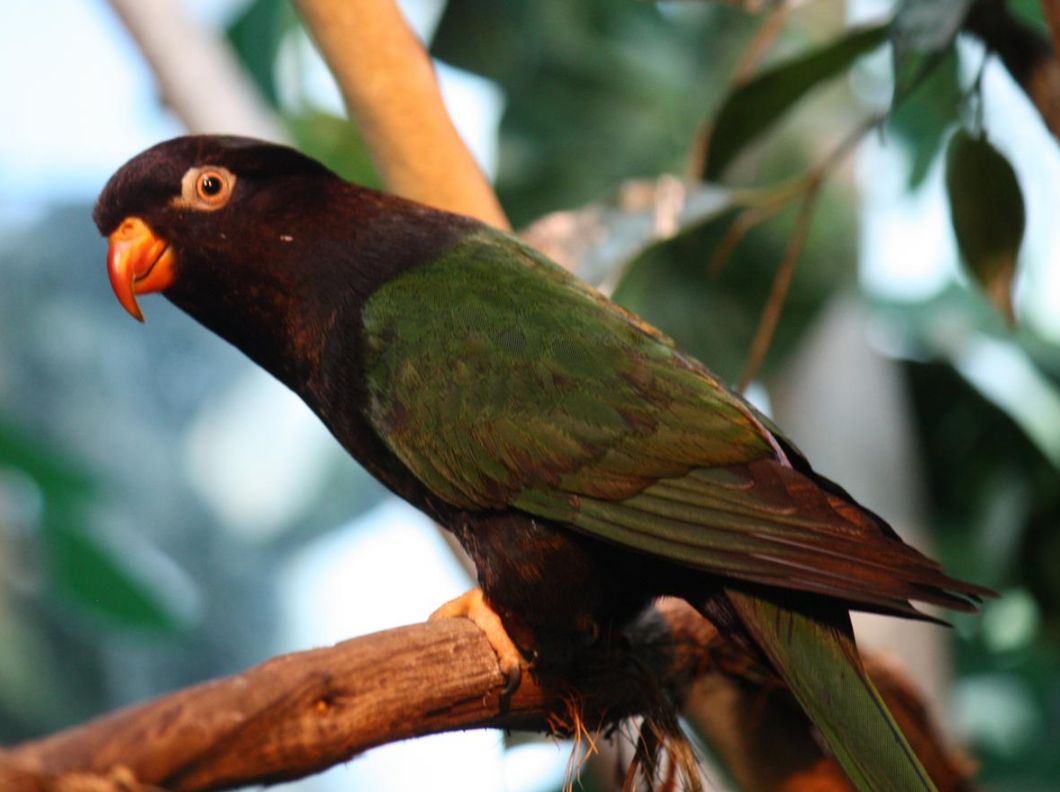

Papuan lorikeet
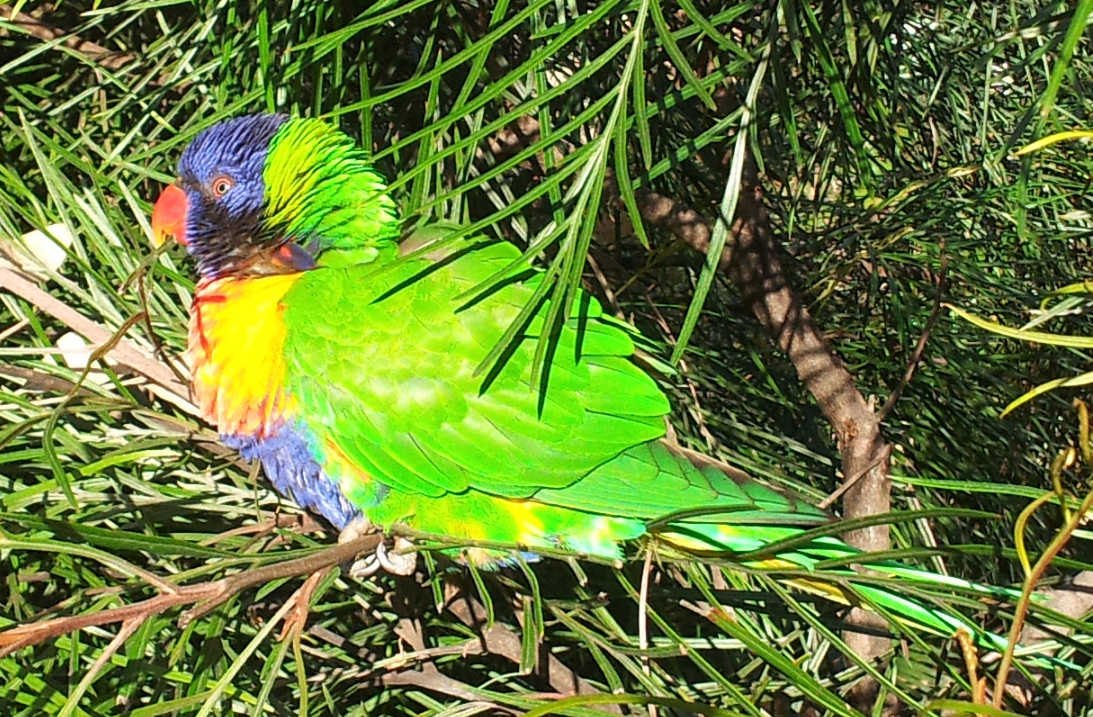

Australian rainbow lorikeet (subspecies of rainbow lorikeet)
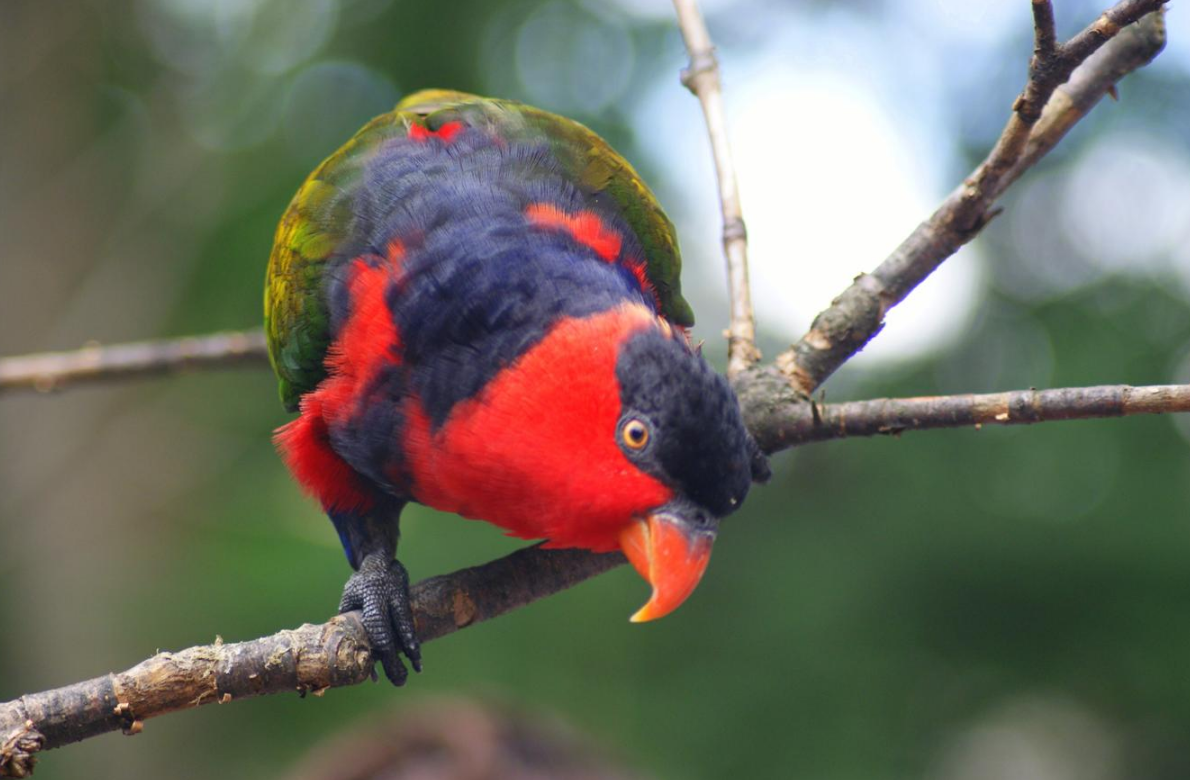

Black-capped lory at the Cincinnati Zoo
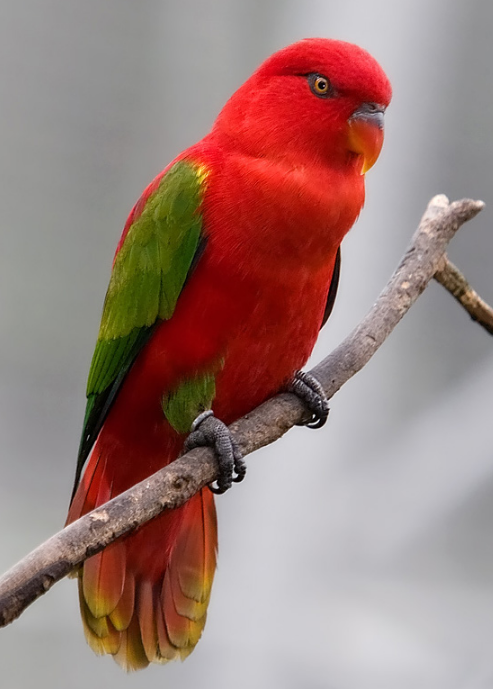

Chattering lory at Jurong Bird Park
References
- Low, Rosemary (1998). Hancock House Encyclopedia of the Lories. Hancock House. pp. 85–87. ISBN 0-88839-413-6.
- Forshaw, Joseph M.; Cooper, William T. (1981) [1973, 1978]. Parrots of the World (corrected second ed.). David & Charles, Newton Abbot, London. ISBN 0-7153-7698-5.
- Wright, T.F.; Schirtzinger E. E.; Matsumoto T.; Eberhard J. R.; Graves G. R.; Sanchez J. J.; Capelli S.; Muller H. et al. (2008). "A Multilocus Molecular Phylogeny of the Parrots (Psittaciformes): Support for a Gondwanan Origin during the Cretaceous". Mol Biol Evol 25 (10): 2141–56. doi:10.1093/molbev/msn160. PMID 18653733. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2727385
- Astuti, Dwi; Azuma,Noriko; Suzuki, Hitoshi; Higashi, Seigo (2006). "Phylogenetic relationships within parrots (Psittacidae) inferred from mitochondrial cytochrome-b gene sequences.". Zoological Science 23 (2): 191–98. doi:10.2108/zsj.23.191. PMID 16603811. https://dx.doi.org/10.2108%2Fzsj.23.191
- de Kloet, RS; de Kloet SR (2005). "The evolution of the spindlin gene in birds: Sequence analysis of an intron of the spindlin W and Z gene reveals four major divisions of the Psittaciformes". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 36 (3): 706–721. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2005.03.013. PMID 16099384. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.ympev.2005.03.013
- Tokita, M; Kiyoshi T; Armstrong KN (2007). "Evolution of craniofacial novelty in parrots through developmental modularity and heterochrony". Evolution & Development 9 (6): 590–601. doi:10.1111/j.1525-142X.2007.00199.x. PMID 17976055. http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/118546207/abstract.
- Christidis, L., L.; Schodde, R.; Shaw, D. D.; Maynes, S. F. (1991). "Relationships among the Australo-Papuan parrots, lorikeets, and cockatoos (Aves, Psittaciformes) - protein evidence". Condor 93: 302–17. doi:10.2307/1368946. https://dx.doi.org/10.2307%2F1368946
- "Sunset lorikeet" (in en). Wikipedia. 2017-11-16. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Sunset_lorikeet&oldid=810674622.
- "UNEP-WCMC Species Database Lorius amabilis". Unep-wcmc.org. http://www.unep-wcmc.org/isdb/Taxonomy/tax-species-result.cfm?Genus=Lorius&species=amabilis&source=animals. Retrieved 2013-02-09.
- "UNEP-WCMC Species Database Lorius tibialis". Unep-wcmc.org. http://www.unep-wcmc.org/isdb/Taxonomy/tax-species-result.cfm?Genus=Lorius&species=tibialis&source=animals. Retrieved 2013-02-09.
- "Rainbow Lorikeet / Rainbow Lory aka Green Naped Lory / Lorikeet" (in en). https://www.beautyofbirds.com/rainbowlorikeet.html.
- "Meat-eating rainbow lorikeets puzzle bird experts" (in en-AU). ABC News. 2015-03-23. http://www.abc.net.au/news/2015-03-23/rainbow-lorikeets-eating-meat-baffles-bird-experts/6337984.
- Steadman D, (2006). Extinction and Biogeography in Tropical Pacific Birds, University of Chicago Press. ISBN:978-0-226-77142-7




