
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SILVANA MIHAELA DĂNĂILĂ-GUIDEA | -- | 2440 | 2022-10-20 15:23:09 | | | |
| 2 | Lindsay Dong | Meta information modification | 2440 | 2022-10-21 04:43:46 | | |
Video Upload Options
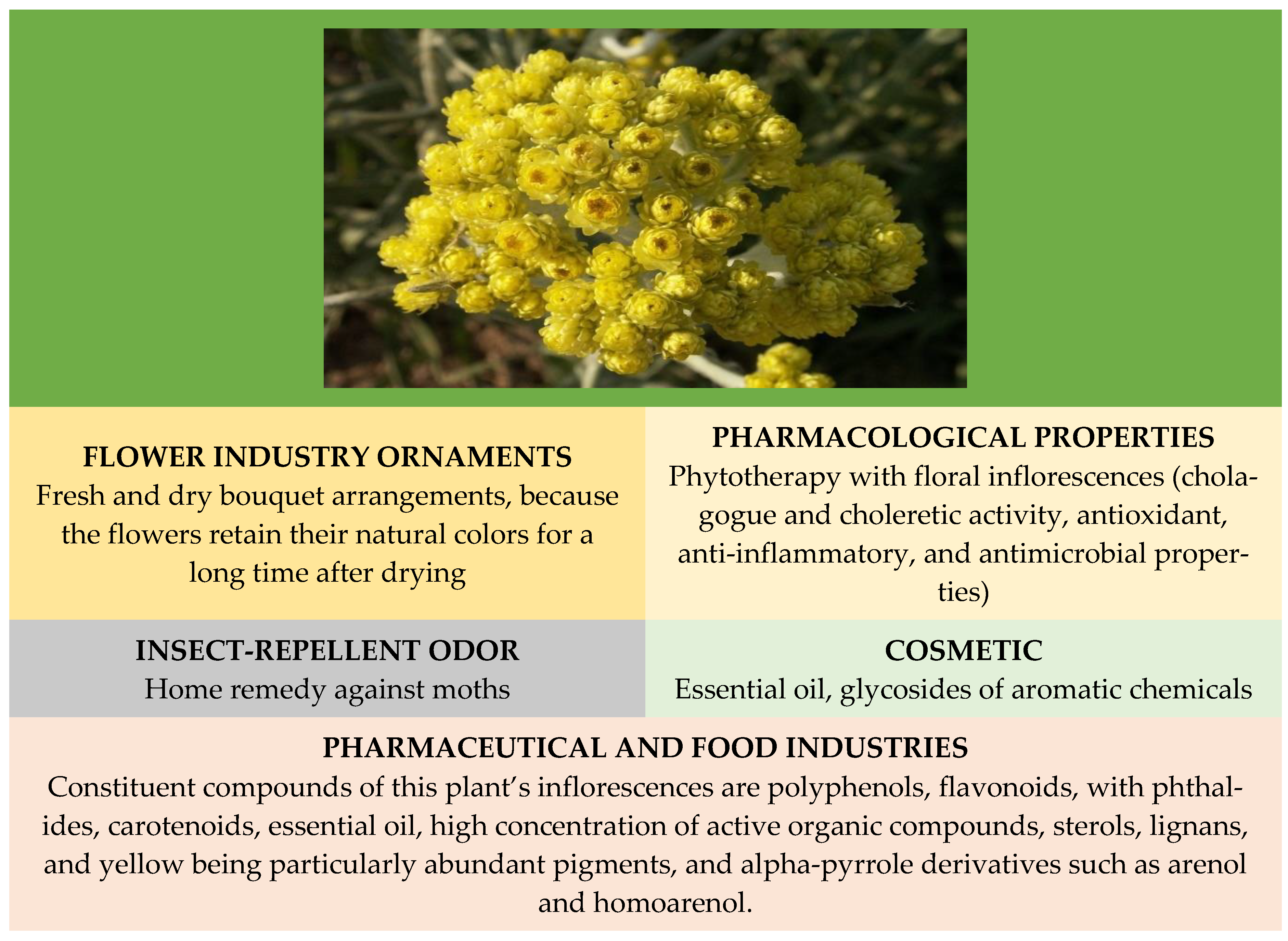
Helichrysum arenarium (L.) Moench, belonging to the Asteraceae family, is known in traditional medicine for its diuretic, choleretic, and anti-inflammatory properties. Helichrysum arenarium (sandy everlasting) is a source of active pharmacological compounds used in complementary medicine to prevent digestive and hepatobiliary illnesses.
1. Introduction
2. Area of Spread, Cultivation Techniques, and Applications
3. Bioactive Compounds
4. Extraction Products
| Extraction Technique | Solvent | Active Constituents | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distillation | Water | Monoterpenoids, sesquiterpenoids, phenolic compounds |
[29][33][37] |
| Maceration | Alcohol | Alkaloids, carotenes, flavonoids, tannins |
[31][37] |
| Solvent extraction or enfleurage |
Solvent organic | Monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, monoterpenoids, phenolic compounds, carotenes |
[33][37][38][40][42] |
| Ultrasonic-assisted extraction (UAE) or sonication |
Ethanol aqueous solution |
Phenolic acids and flavonoids | [32][35][37][41][43] |
| Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) | Supercritical carbon dioxide |
Nonpolar natural products such as lipid and volatile oil. | [34][35][36][37] |
| Microwave-assisted extraction (MAE): two types of methods: 1. solvent-free extraction; 2. solvent extraction |
1. usually for volatile compounds; 2. usually for nonvolatile compounds |
Essential oils: - Monoterpene hydrocarbons - Sesquiterpene hydrocarbons - Oxygenated monoterpenes - Oxygenated sesquiterpenes |
[33][37][39] |
5. Pharmacological Properties
5.1. Choleretic and Cholagogue Activities
5.2. Antioxidant Activities
5.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activities
5.4. Antimicrobial Activities
Antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal properties of the Helichrysum species have been investigated in several Euroasia countries. Moreover, the European Medicine Agency published a report in 2015 on the pharmacological effects, clinical efficacy and safety, and antimicrobial properties of H. arenarium (L.) Moench [14]. The first investigation of the antibacterial activity of the everlasting flower flavonoid compounds was performed in the former Soviet Union by Khristenko LA and concluded that the preparations in the concentration of 20–40 μg/mL were active against two important Gram-positive species (Staphylococcus sp. and Streptococcus sp.) [52]. Later, aerial parts of the plant or the whole overground plant were used to prepare infusions, decoctions, essential oils, and extracts with different qualitative content.
The antimicrobial activity of essential oils of H. arenarium has been investigated on different test microorganisms, clinical isolates, and food contamination microbes. Rančić et al., 2005 tested the antibacterial activity of 1–5 μL of everlasting flower essential oil on Escherichia coli ATCC 35,218, Micrococcus luteus ATCC 9341, Pseudomonas tolaasii isolated from Agaricus bisporus, Salmonella enteritidis ATCC 13,076, S. Typhimurium ATCC 13,311, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538, and S. epidermidis ATCC 12,228 and concluded that at the minimum volume (1 μL) the oil had activity against all bacterial species tested [53].
Helichrysum arenarium extracts and herbal teas have been used traditionally in European countries. The antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of two subspecies of H. arenarium (L.) Moench, erzincanicum Davis and Kupicha, Erzican and rubicundum (C.Koch.) Davis and Kupicha, Erzurum, collected from different regions of Turkey, were analyzed. Methanolic extracts from the whole dried plants were screened against 15 strains of bacteria and fungi using the agar-well diffusion method, and the results were compared with standard antibiotics [54][55]. Statistical differences were found among the chemical compositions and the antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of these subspecies. Additionally, extracts were active against Aeromonas hydrophila, B. brevis, B. cereus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and S. aureus ATCC 29,213, but no activity was detected against tested strains of E. coli, Morganella morganii, Proteus mirabilis, Mycobacterium smegmatis, Yersinia enterocolitica, or yeast S. cerevisiae [54][55]. However, at the highest concentration (100,000 µg/mL), methanolic extracts were similar to or less effective than the standard antibiotics. Dried flowers collected from northeastern Romania were used to prepare extracts and to analyze their phenolic content and antimicrobial activity [3][56].
5.5. Pharmacoeconomic Benefits
References
- Moench, C. Methodus Plantas Horti Botanici et Agri Marburgensis; Cattorum, M., Ed.; Nova Libraria Academiae: Marburg, Germany, 1794; p. 780. Available online: https://species.wikimedia.org/wiki/Methodus_Plantas_Horti_Botanici_et_Agri_Marburgensis (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- Erbar, C.; Leins, P. Diversity of styles and mechanisms of secondary pollen presentation in basal Asteraceae—New insights in phylogeny and function. Flora Morphol. Distrib. Funct. Ecol. Plants 2015, 217, 109–130.
- Babotă, M.; Mocan, A.; Vlase, L.; Crișan, O.; Ielciu, I.; Gheldiu, A.M.; Vodnar, D.C.; Crișan, G.; Păltinean, R. Phytochemical Analysis, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Helichrysum arenarium (L.) Moench and Antennaria dioica (L.) Gaertn. Flowers. Molecules 2018, 23, 409.
- Pljevljakušic’, D.; Bigovic’, D.; Jankovic’, T.; Šavikin, K. Sandy Everlasting (Helichrysum arenarium (L.) Moench): Botanical, Chemical and Biological Properties. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1123.
- Stanescu, U.; Hancianu, M.; Cioanca, O.; Aprostosoaie, A.C.; Miron, A. Plante Medicinale de la A la Z, 3rd ed.; Polirom Publishing House: Iasi, Romania, 2018; pp. 313–315.
- WHO. Monographs on Medicinal Plants Commonly Used in the Newly Independent States (NIS); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- Yousheng, C.; Shixin, Z.; Bayer, R.J. Tribe Gnaphalieae, Genus Helichrysum, Asteraceae (Compositae), Flora of China; Wu, Z.Y., Raven, P.H., Hong, D.Y., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China; Missouri Botanical Garden Press: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2011; pp. 20–21.
- Flora von Deutschland Österreich und der Schweiz (1885)—BioLib.de. Available online: http://www.biolib.de/thome/icon_page_00294.html] (accessed on 16 July 2022).
- Tutin, T.G.; Heywood, V.H.; Burges, N.A.; Moore, D.M.; Valentine, D.H.; Walters, S.M.; Webb, D.A. Flora Europea, Plantaginaceae to Compositae (and Rubiaceae); Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; Volume IV.
- Maznev, N.I. Entsiklopediia Lekarstvennykh Rastenii. In Encyclopedia of Medicinal Plants; Martin Press: Moscow, Russia, 2004.
- Olsson, K.; Pihlik, U.; Radušiene, J.; Wedelsbäck, B.K. Helichrysum arenarium (L.) Moench (Everlasting) in Spice and Medicinal Plants in the Nordic and Baltic Countries Conservation of Genetic Resources; Report from the SPIMED-project group at the Nordic Gene Bank: Alnarp, Sweden, 2005; pp. 55–65.
- Lilleleht, V. Red Data Book of Estonia; Eesti Teaduste Akadeemia Looduskaitse Komisjon: Tartu, Estonia, 1998; Available online: http://www.zbi.ee/punane/liigid/soontaimed_e.html (accessed on 3 August 2022)(In Estonian with English Summary).
- Sawilska, A.K.; Jendrzejczak, E. Efficiency of sandy everlasting Helichrysum arenarium (L.) Moench cultivation from in vitro seedlings and achenes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 43, 50–55.
- EMA. Assessment Report on Helichrysum arenarium (L.) Moench Flos (Rapporteur: Wojciech Dymowski); European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015.
- Greuter, W. Compositae (pro parte majore), Compositae. Euro+Med PlantBase—The Information Resource for Euro-Mediterranean Plant Diversity; Greuter, W., von Raab-Straube, E., Eds. 2006. Available online: http://www.emplantbase.org/ (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Dihoru, G.; Negrean, G. The Red Book of Vascular Plants from Romania; Romanian Academy: Bucharest, Romania, 2009.
- Dihoru, G.; Boruz, V. The List of Main Spontaneous Medicinal Plants from Romania; Annals of the University of Craiova—Agriculture, Montanology, Cadastre Series; University of Craiova: Craiova, Romania, 2014; Volume XLIV.
- Sawilska, A.K.; Jendrzejczak, E.; Welc, M.; Kieliszewska-Rokicka, B. Influence of mycorrhizal fungi on the growth and development of sandy everlasting . Acta Agrobot. 2009, 62, 67–76.
- Crisan, I.; Vidican, R.; Stoie, A.; Simea, S.A. Spring-autumn arbuscular mycorrhiza colonization dynamic in Iris germanica L. from urban microclimate. AgroLife Sci. J. 2020, 9, 82–90.
- Roşu, A. Elemente de Biotehnologii Vegetale-Aplicaţii în Ameliorare; Ametist-92: Bucureşti, Romania, 1999.
- Figas, A.; Tomaszewska-Sowa, M.; Sawilska, A.; Keutgen, A.J. Improvement of in vitro propagation and acclimation of Helichrysum arenarium L. Moench. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2016, 15, 17–26.
- Bryksa-Godzisz, M.; Pawełczak, A. In vitro propagation of the yellow everlasting (Helichrysum arenarium (L.) Moench) from root explants. Propag. Ornam. Plants 2010, 10, 14–17.
- Clasquin, S.; Henry, M. Micropropagation of Helichrysum arenarium L. Moench. Acta Bot. Gallica 2002, 149, 189–195.
- Smirnova, L.P.; Pervykh, L.N. Quantitative determination of the total content of flavonoids in the flowers of immortelle Helichrysum arenarium. Pharm. Chem. J. 1998, 32, 321–324.
- Czinner, E.; Kery, A.; Hagymási, K.; Blázovics, A.; Lugasi, A.; Szoke, E.; Lemberkovics, E. Biologically active compounds of Helichrysum arenarium (L.) Moench. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 1999, 24, 309–313.
- Czinner, E.; Kusinszki, L.; Baumann, D.; Hamburger, M. Phytochemical study of phenolic compounds from Helichrysi flos by LC-DAD –MS. In Natural Products in the New Millenium: Prospects and Industrial Application; Rauter, A.P., Palma, F.B., Justino, J., Araújo, M.E., Santos, S.P.d., Eds.; Kluwer Acadenic Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 99–109.
- Kurkina, A.; Ryzhov, V.; Avdeeva, E. Assay of isosalipurposide in raw material and drugs from the dwarf everlast (Helichrysum arenarium). Pharm. Chem. J. 2012, 46, 171–176.
- Hollman, P.C.H.; Katan, M.B. Bioavilibilty and health effects of dietary flavonols in man. Arch. Toxicol. 1998, 20, 237–248.
- Czinner, E.; Hagymasi, K.; Blazovics, A.; Kery, A.; Szoke, E. In Vitro antioxidant properties of Helichrysum arenarium (L.) Moench. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 73, 437–443.
- Czinner, E.; Lemberkovics, É.; Bihátsi-Karsai, É.; Vitányi, G.; Lelik, L. Composition of the essential oil from the inflorescence of Helichrysum arenarium (L.) Moench. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2000, 12, 728–730.
- Les, F.; Venditti, A.; Cásedas, G.; Frezzac, C.; Guiso, M.; Sciubba, F.; Serafini, M.; Bianco, A.; Marta Sofía, V.; López, V. Everlasting flower (Helichrysum stoechas Moench) as a potential source of bioactive molecules with antiproliferative, antioxidant, antidiabetic and neuroprotective properties. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2017, 108, 295–302.
- Gadjalova, A.V.; Mihaylova, D. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of medicinal plants and evaluation of their biological activity. Food Res. 2019, 3, 530–536.
- Liu, X.; Jing, X.; Li, G. A process to acquire essential oil by distillation concatenated liquid-liquid extraction and flavonoids by solid-liquid extraction simultaneously from Helichrysum arenarium (L.) Moench inflorescences under ionic liquid microwave mediated. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 164–174.
- Oman, M.; Škerget, M.; Knez, Ž. Application of supercritical fluid extraction for the separation of nutraceuticals and other phytochemicals from plant material. Maced. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2013, 32, 183–226.
- Scalia, S.; Giuffreda, L.; Pallado, P. Analytical and preparative supercritical fluid extraction of chamomile flowers and its comparison with conventional methods. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999, 21, 549–558.
- Chiu, K.L.; Cheng, Y.C.; Chen, J.H.; Chang, C.M.J.; Yang, P.W. Supercritical fluids extraction of ginkgo ginkgolides and flavonoids. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2002, 24, 77–87.
- Zhang, Q.; Lin, L.; Ye, W. Techniques for extraction and isolation of natural products: A comprehensive review. Chin. Med. 2018, 13, 20.
- Dorene Petersen, R.H. Immortelle Essential Oil and Extract: Are Two Preparations Better than One? J. Am. Herb. Guild 2015, 13, 21–27.
- Azar, P.A.; Torabbeigi, M.; Tehrani, M.S.; Husain, S.W. Hydrodistillation, Solvent Free Microwave Assisted Extraction and Headspace-Solid Phase Microextraction for Analysis of Essential Oil of Flowers of Helichrysum aucheri. Asian J. Chem. 2011, 23, 1209–1211.
- Goldansaz, S.M.; Mahboubi, A.; Yazdi-nejad, A.; Jahanbakhshi, M.; Mojab, F. Investigation on total phenolic content, antibacterial, and antioxidant activity of ethanolic extract of Helichrysum leucocephalum Boiss. Am. J. Essent. Oil. Nat. Prod. 2018, 6, 20–24.
- Cheng, M.; Ding, L.; Kan, H.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, B.; Sun, Y.; Cao, S.; Li, W.; Koike, K.; Qiu, F. Isolation, structural elucidation and in vitro hepatoprotective activity of flavonoids from Glycyrrhiza uralensis. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 73, 847–854.
- Jarzycka, A.; Lewin’ska, A.; Gancarz, R.; Wilk, A.K. Assessment of extracts of Helichrysum arenarium, Crataegus monogyna, Sambucus nigra in photoprotective UVA and UVB; photostability in cosmetic emulsions. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2013, 128, 50–57.
- Liu, Z.; Kong, L.; Lu, S.; Zou, Z. Application of a Combined Homogenate and Ultrasonic Cavitation System for the Efficient Extraction of Flavonoids from Cinnamomum camphora Leaves and Evaluation of Their Antioxidant Activity In Vitro. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2019, 2019, 12.
- Szadowska, A. Pharmacology of galenic preparations and flavonoids from Helichrysum arenarium. Acta Pol. Pharm. 1962, 19, 465–479.
- Wichtl, M. Herbal Medicines and Phytopharmaceuticals, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001.
- Shikov, A.N.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Makarov, V.G.; Wagner, H.; Verpoorte, R.; Heinrich, M. Medicinal Plants of the Russian Pharmacopoeia; Their history and applications. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 154, 481–536.
- Shass, E.Y. Phytotherapy; Academy of Medicinal Science of USSR: Moscow, Russia, 1952.
- Vereschagin, V.I.; Sobolevskaya, K.A.; Yakubova, A.I. Useful Plants of West Siberia; Academy of Science of USSR: Moscow, Russia, 1959.
- Ionescu, D.; Spînu, S.; Orţan, A.; Moraru, I.; Fîntîneru, G.; Fierăscu, R.C.; Fierăscu, I.; Drugulescu, M. Evaluation of biological active compounds found in Silybi mariani fructus. AgroLife Sci. J. 2017, 6, 141–145.
- Mao, Z.; Gan, C.; Zhu, J.; Ma, N.; Wu, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. Anti-atherosclerotic activities of flavonoids from the flowers of Helichrysum arenarium L. Moench through the pathway of anti-inflammation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 2812–2817.
- Drewes, S.E.; Van Vuuren, S.F. Antimicrobial acylphloroglucinols and dibenzyloxyflavonoids from flowers of Helichrysum gymnocomum. Phytochem. Lett. 2008, 69, 1745–1794.
- Khristenko, L.A.; Pertsev, I.M.; Salo, D.P.; Negrash, A.K. Possible use of arenarin in medicated ophthalmological films. Pharm. Chem. J. 1997, 11, 995–998.
- Rančić, A.; Soković, M.; Vukojević, J.; Simić, A.; Marin, P.; Duletić-Laušević, S.; Djoković, D. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activities of Essential Oils of Myrrhis odorata (L.) Scop, Hypericum perforatum L and Helichrysum arenarium (L.) Moench. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2005, 17, 341–345.
- Albayrak, S.; Aksoy, A.; Sağdic, O.; Budak, U. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of Helichrysum species collected from eastern Anatolia, Turkey. Turk. J. Biol. 2010, 34, 463–473.
- Albayrak, S.; Aksoy, A.; Sagdic, O.; Hamzaoglu, E. Compositions, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Helichrysum (Asteraceae) species collected from Turkey. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 114–122.
- Gradinaru, A.C.; Silion, M.; Trifan, A.; Miron, A.; Aprotosoaie, A.C. Helichrysum arenarium subsp. arenarium: Phenolic composition and antibacterial activity against lower respiratory tract pathogens. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 2076–2080.
- Cosar, G.; Cubukcu, B. Antibacterial activity of Helichrysum species growing in Turkey. Fitoterapia 1990, 61, 161–164.
- Czinner, E.; Hagymási, K.; Blázovics, A.; Kéry, A.; Szoke, E.; Lemberkovics, E. The in vitro effect of Helichrysi flos on microsomal lipid peroxidation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 77, 31–35.
- Bigovic, D.; Brankovic, S.; Kitic, D.; Radenkovic, M.; Jankovic, T.; Savikin, K.; Zivanovic, S. Relaxant effect of the ethanol extract of Helichrysum plicatum (Asteraceae) on isolated rat ileum contractions. Molecules 2010, 15, 3391–3401.
- Bigovic, D.; Savikin, K.; Jankovic, T.; Menkovic, N.; Zdunic, G.; Stanojkovic, T. Antiradical and cytotoxic activity of different Helichrysum plicatum flower extracts. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 819–822.
- Sokolov, S.Y. Phytotherapy and Phytopharmacology: The Manual for Doctors; Medical News Agency: Moscow, Russia, 2000.
- Aslanyan, M.; Bobrytska, L.; Hrytsenko, V.; Shpychak, O.; Popova, N.; Germanyuk, T.; Kryvoviaz, O.; Ivko, T. Technological aspects of development of a new drug in tablets called «Lavaflam» and its pharmacoeconomic evaluation. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. (RJPBCS) 2017, 8, 808.





