
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rita Xu | -- | 3626 | 2022-10-20 01:31:26 |
Video Upload Options
The testing effect is the finding that long-term memory is often increased when some of the learning period is devoted to retrieving the to-be-remembered information. The effect is also sometimes referred to as retrieval practice, practice testing, or test-enhanced learning. Retrieval practice may be the best way to refer to the testing effect because the benefits of retrieval-related testing are not limited to tests. It can be more broad, including tools like flash cards and quizzes. The testing effect on memory should be distinguished from more general practice effects, defined in the APA Dictionary of Psychology (2007) as "any change or improvement that results from practice or repetition of task items or activities." The term testing effect is also sometimes used in a more general sense; The Oxford Dictionary of Psychology (2003) defines a testing effect as "any effect of taking tests on the respondents, a typical example being test sophistication." Whereas psychologists who develop tests for personality and intelligence want to avoid practice effects, cognitive psychologists working with educators have begun to understand how to take advantage of tests—not as an assessment tool, but as a teaching/learning tool. It is useful for people to test their knowledge of the to-be-remembered material during the learning process, instead of only reading or otherwise passively studying the material. For example, a student can use flashcards to self-test and receive feedback as they study. The testing effect provides a larger benefit to long-term memory when the tested material is difficult enough to require effort, the rate of retrieval success is high, and feedback with correct answers is given after testing. The testing effect is activated by active recall.
1. History
Before much experimental evidence had been collected, the utility of testing was already evident to some perceptive observers including Francis Bacon who discussed it as a learning strategy as early as 1620.[1]
"Hence if you read a piece of text through twenty times, you will not learn it by heart so easily as if you read it ten times while attempting to recite it from time to time and consulting the text when your memory fails."
Towards the end of the 19th century, Harvard psychologist William James described the testing effect in the following section of his 1890 book "The Principles of Psychology"
"A curious peculiarity of our memory is that things are impressed better by active than by passive repetition. I mean that in learning (by heart, for example), when we almost know the piece, it pays better to wait and recollect by an effort from within, than to look at the book again. If we recover the words in the former way, we shall probably know them the next time; if in the latter way, we shall very likely need the book once more."[2]
In his 1932 book Psychology of Study, C. A. Mace said:
"On the matter of sheer repetitive drill there is another principle of the highest importance: Active repetition is very much more effective than passive repetition. ... there are two ways of introducing further repetitions. We may re-read this list: this is passive repetition. We may recall it to mind without reference to the text before forgetting has begun: this is active repetition. It has been found that when acts of reading and acts of recall alternate, i.e., when every reading is followed by an attempt to recall the items, the efficiency of learning and retention is enormously enhanced."[3]
The later 20th century saw renewed interest in the testing effect, and this interest has continued unabated into the 21st century.[4]
2. Empirical Evidence
The first documented empirical studies on the testing effect were published in 1909 by Edwina E. Abbott.[5][6] An important step in proving the existence of the testing effect was presented in a 1992 study by Carrier and Pashler.[7] Carrier and Pashler showed that testing does not just provide an additional practice opportunity, but produces better results than other forms of studying. In their experiment, learners who tested their knowledge during practice later remembered more information than learners who spent the same amount of time studying the complete information. The abstract summarizes the results as follows:
In the pure study trial (pure ST condition) method, both items of a pair were presented simultaneously for study. In the test trial/study trial (TTST condition) method, subjects attempted to retrieve the response term during a period in which only the stimulus term was present (and the response term of the pair was presented after a 5-sec delay). Final retention of target items was tested with cued-recall tests. In Experiment 1, there was a reliable advantage in final testing for nonsense-syllable/number pairs in the TTST condition over pairs in the pure ST condition. In Experiment 2, the same result was obtained with Eskimo/English word pairs. This benefit of the TTST condition was not apparently different for final retrieval after 5 min or after 24 h. Experiments 3 and 4 ruled out two artifactual explanations of the TTST advantage observed in the first two experiments. Because performing a memory retrieval (TTST condition) led to better performance than pure study (pure ST condition), the results reject the hypothesis that a successful retrieval is beneficial only to the extent that it provides another study experience.
Carrier and Pashler's study did not reveal a very large advantage of testing over studying, but paved the way for numerous further studies that have shown a more marked advantage.[8] The results of a 2010 study by Agarwal et al. showed that the desirable difficulty of open-book and closed-book tests better enhanced learning compared to restudying or testing without feedback.[9] Additionally, a study done by Roediger and Karpicke showed that students in a repeated-testing condition recalled much more after a week than did students in a repeated-study condition (61% vs. 40%), even though students in the former condition read the passage only 3.4 times and those in the latter condition read it 14.2 times.[10] Another study by Butler investigated the possibility that testing only promotes the learning of a specific response. The results showed that the mnemonic benefits of retrieving information from memory are seen well beyond this retention of a specific response.[11] Thus, most studies show greater advantages for testing compared to passive studying as it relates to long-term retention of to-be-remembered information. However, some studies have produced results contrary to this claim.[12] Using retrieval practices also produces less forgetting than studying and restudying.[13]
Brain Activity
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has been used to study the impact of retrieval practice on the brain. The evidence from fMRI imaging suggests that retrieval practice strengthens subsequent retention of learning through a "dual action" affecting the anterior and posterior hippocampus regions of the brain.[14]
3. Preconditions to Measurement
3.1. Retrieval Success
Retrieval practice is another term for the testing effect and is used widely across many classrooms in order to help students learn new material or recall information prior to an exam. Studies in retrieval practice were founded in 1987 by John. L Richards, who first scripted his findings in a published newspaper in New York. In order for a testing effect to be demonstrated, the test trials must have a medium to high retrieval success. If the test trials are so difficult that no items are recalled, or if there is not proper feedback providing answers to the non-recalled items, then minimal information will be encoded and stored to memory.[15][16][17]
3.2. Time Between Retrieval Practice and Performance Measure
Benefits of testing are often only visible after a substantial delay and not immediately after practice, when outcomes may even be better for passively restudied materials than for tested materials.[18][19] Some authors suggest that this can be explained in part by limited retrieval success during practice.[16][17][20]
3.3. Retrieval Difficulty
According to the retrieval effort hypothesis, "difficult but successful retrievals are better for memory than easier successful retrievals". For example, Pyc and Rawson showed that repeated testing is more beneficial for learning if the intervals between repeated testing are long and each test is therefore more difficult than when the intervals are short and tests are easy.[21] This finding is related to the theory that certain conditions that make learning more effortful through so-called desirable difficulties are beneficial.[15] Another finding showed that weaker cues for recalling information will be more beneficial to future recollection compared to that of stronger cues.[22] Although these strong cues were shown to be more advantageous for initial recall, these stronger cues reduced the likelihood of activating more elaborative information that could be beneficial for retention. On the hand, the weak cues better allowed the to-be-remembered information to be better retained over time, enhancing long-term memory of the information.
4. Theoretical Explanations for the Testing Effect
4.1. Cognitive Accounts
Two views have arisen as to why testing seems to provide such a benefit over repeated study.
- The first view, provided by McDaniel,[23] states that testing allows people to formulate newer, more lasting connections between items than does repeated study.
- The second view, provided by Karpicke and Roediger[24] studied the effect of testing on memory retention.
For the Karpicke and Roediger study, the researchers had participants study two different passages; passage one and passage two. The researchers had the participants study passage 1 twice, and passage 2 once. However, passage two was tested on instead of being restudied. One week later they tested them on both passages, and they noticed that passage two was better recalled then passage one.[25] They found that re-studying or re-reading memorized information had no effect, but trying to recall the information had an effect. New findings[26] show more support for the second view. Spacing has also been shown to improve memory in younger and older adults. The spacing effect improves long-term memory from learning material with a break in between learning other information, while the testing effect improves long-term memory by restudying learned information through testing.[27] Both of these methods have been combined to be referred to as spaced retrieval practice.
4.2. Transfer Appropriate Processing
Transfer appropriate processing, the idea that recall performance depends on the extent of the similarity between the initial testing and final assessment, suggests that the testing effect is beneficial for later retrieval as long as the initial tests and final assessments require similar mental processes. This implies retrieval practice will produce larger learning gains when the test format used in the acquisition of learning phase is closely matched to the final assessment compared to when they are mismatched.[28]
5. Developments and Moderators
As research on the testing effect has developed strongly, research interests have moved to exploring for whom does retrieval practice enhance learning, which types of content, and under what conditions. This means that increasingly the research focus is on establishing moderators and boundary conditions for when the testing effect does not apply and to what extent findings are generalizable or valid from laboratory to classroom settings from elementary settings to university classes.[29]
5.1. Retrieval/Test Format
The testing effect is highly transferable across formats. Yang et al. did an experiment testing this.[25] They had one group learn and study the material by reading more information with less visuals, and they had another group have more visuals to study from than verbal text. They split both groups into two groups: one that restudied and one that was tested on what they just learned. The groups that were tested were given a fill in the blank test. Then all of the groups were tested by a multiple choice test. In both cases, the participants that were tested twice did better. This shows that testing will result in better recall despite how the teacher teaches, or how the tests are formatted.[25]
5.2. Feedback
The testing effect interacts with feedback and many studies exploring this interaction. Among the issues investigated are the effects of negative versus positive feedback and the complexity of the feedback.[29]
5.3. Pretesting Effect
A pretesting, taking tests before to-be-learned information is studied, has also been studied. While both pre and post testing formats are superior at enhancing memory relative to not using tests as a study strategy, pretesting yielded higher overall scores than post tests across test formats. This applied regardless of feedback, or different retention intervals and may be due to enhanced processing of content as a result of the initial test. This finding would suggest that pretesting is a promising pedagogical strategy.[30] The pretesting effect has also been demonstrated with transfer problems in the area of computer science with participants who attempted to solve problems before using Google to help answer the problems outperforming students who were able to use Google immediately to help solve the problems. The pretesting effect does seem to be greater for students with some prior knowledge.[31]
5.4. Test Timing
Findings showing that the testing effect can have a greater impact after a delay[32] even though students themselves seemed more confident in studying (which turned out to be false in the data). There is also some evidence that if students study in the evening, they should test themselves immediately after learning. Moreover if students study during the day they should delay any practice tests in order to reinforce memory and reduce forgetting of the material to be learned.[33]
5.5. Use of Concept Maps
In one study, retrieval practice produced greater gains in meaningful learning than elaborative studying with concept mapping in the context of science education. Retrieval practice retained its advantage over elaborative study with concept tests even when the final assessment involved creating concept maps.[34] This finding was both replicated and enlarged in a further study which showed that:
- Repeated retrieval leads to better conceptual learning than concept mapping.
- A short training for students in concept mapping did not change this result
- Students with previous experience in concept mapping still had poorer performance than retrieval practice.
- Despite the above results, students did not see retrieval practice as a useful learning tool.[35]
Follow up work showed that concept maps when used as a retrieval tool produced better learner performance than additional studying and matched other retrieval formats in terms of performance. This finding suggests that concept mapping is a valid tool for retrieval practice.[36]
5.6. Forward Testing Effect
There is also evidence for a related "forward testing effect" that retrieval practice of previously studied information can facilitate learning and memory of newly studied information.[37] "Administering interim tests during studying is a potent strategy to promote and sustain the effectiveness of self-regulated learning across a learning phase."[25] This implies that students should constantly test themselves as part of their studying techniques.[25]
5.7. Transfer
There is some evidence that the testing effect, depending on how it is utilized, can lead to improved transfer of learning to different contexts relative to non-testing. This transfer effect appears strongest with elaborative retrieval type activities such as application and inference questions, and problems involving medical diagnoses. Transfer was less likely to occur with initial study materials that were not tested and with worked example problems even when moving onto new material.[38]
5.8. Individual Differences
Researchers investigating whether the testing effect applies equally to students with diverse personality traits such as Grit, and those with working memory capacity issues have found no differences in the efficacy of retrieval practice compared to students without memory capacity issues this suggests that retrieval practice may be a beneficial strategy for all students regardless of individual differences.[39] There is also some evidence that not only does retrieval practice work for students with working memory capacity issues, it may even disproportionately benefit them.[40]
6. Applications
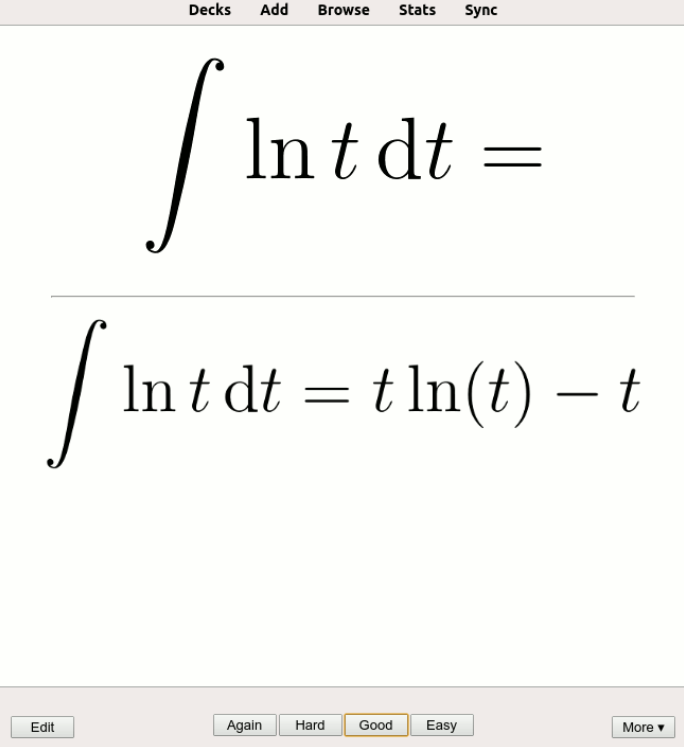
6.1. Classroom Settings
The largest practical application for any human memory studies of learning effects such as retrieval practice is for education and finding more efficient ways to relate and integrate new learning with existing learning for students at every grade level.[41] Extensive research has been done in this area in the last decade and remains ongoing. Reviews have provided more reliable results of the testing effect when applied to realistic secondary and tertiary classroom settings using actual classroom material such as brief articles, lectures, and materials and overall a robust testing effect was found. Other findings included:
- an initial (immediate post learning) short-answer test produced greater gains on a final test than an initial multiple-choice test.
- a positive effect of immediate feedback if the feedback was given with the initial test.
- production tests (short answer or essay) and feedback soon after initial learning increase learning and retention.[42][43]
A large scale systematic and meta-analytic review based on data from 48,478 students, extracted from 222 independent studies, explored the application and boundary conditions of use of the testing effect in authentic classroom settings. The review found that overall the testing effect raised student academic achievement to a medium extent across a variety of areas suggesting that the testing effect has strong application for practitioners and policy makers.[28] Other research reviews of the benefits from retrieval practice in real world educational settings demonstrated medium or large benefits across a wide variety of formats and settings. This latter review also pointed out that only 6% of experiments on the efficacy of retrieval practice were conducted in non-WEIRD countries which may be a focus of future research.[44] A more recent systematic research review from the Education Endowment Foundation that only looked at the impact of retrieval practice in K-12 classroom trials concluded that retrieval practice was a more effective learning strategy than restudying and probably an applicable learning strategy across a range of ages and subjects. That said, the review did raise some concerns around low ecological validity as many of the studies showing a positive effect were scripted with standardised procedures which is unlikely to be the case in most classroom settings.[45]
Middle-School Applications
A 5-year applied research project exploring the use of the testing effect with more than 1,400 middle school students showed that retrieval practice in classrooms using authentic materials did improve long-term learning. For example, regular quizzing of material produced positive impacts on test and semester exam performance in a middle school science classes.[46] Other studies with middle school social studies students showed that regardless of final exam format (free recall or multiple choice), student performance was significantly greater for quizzed material than for non-quizzed material. Moreover, the benefits of quizzed materials versus non-quizzed materials lasted months after the teacher-led lessons had been taught.[43]
Quizzes
A meta-analysis found the following links between frequent low-stakes quizzes in real classes and improved student academic performance:
- There was an association between the use of quizzes and academic performance.
- This association was stronger in psychology classes
- This association was stronger in all classes when quiz performance could improve class grades.
- Students doing well on quizzes tended to lead to students doing well on final exams
- Regular quizzing increased the chances of students passing classes[47]
6.2. Professional Development
Teachers
The testing effect and links to the wider literature on retrieval practice appear in professional development resources aimed at teachers. Many of these resources are created by cognitive scientists, including the testing effect features in the second module of the Teaching and Learning Strategies for Higher Education online short course, presented by Harvard's Bok Center for Teaching and Learning.[48] Relevant professional development resources for teachers either written or co-written by cognitive scientists featuring retrieval practice include work by the Learning Scientists, Retrieval Practice.org, and the American Educator as well as books aimed at teachers such as Powerful Teaching.[49] There are also a wide variety of professional development resources on using retrieval practice written by practicing teachers including articles in Schoolsweek[50] and books by teachers explicitly focusing on using retrieval practice in teaching.[51]
Medicine
There is increasing interest in retrieval practice as a tool for the training of medical doctors, for example, the use of retrieval practice through participants sharing one learning point at the end of each session of intensive care unit teaching rounds led to the teaching rounds being seen as a higher priority by those involved.[52] This practice may have the additional benefits of identifying learner misconceptions and errors for swift correction as well as giving medical trainers feedback on the clarity of their explanations to trainees.[53] Moreover, retrieval practice does appear to be an efficient way of learning anatomical and physiological terminology and concepts.[54]
6.3. Online Courses
Coursera's Learning How to Learn course created by Dr Barbara Oakley included how to use retrieval practice alongside other techniques to improve personal studying skills.
6.4. General Contexts
The testing effect had been featured in a variety of media including books such as "Make It Stick: The Science of Successful Learning".[55] It has also featured in articles for the general reader such as "Forget what you know about good study habits" in the The New York Times [56] and "Students Should Be Tested More, Not Less" in the Atlantic.[57]
7. Controversies
Complex Materials
The question of whether or not the testing effect was applicable to complex materials such as are common in learning tasks in schools arose when Sweller and Van Gog's literature review, argued that the testing effect may disappear when the complexity of learning material is very high. Sweller and Van Gog argued that learning tasks high in element interactivity, which they defined as "containing various information elements that are related and must therefore be processed simultaneously in working memory", were an important boundary condition where the testing effect may not apply.[58] In a rebuttal article, Karpicke and Aue pointed out that "element interactivity" was not defined in a measurable way and so applied inconsistently in the initial literature review thus drawing its conclusions into question. For example, Karpicke and Aue argued that the literature review omitted several studies that have shown retrieval practice effects with complex materials and moreover that the articles reviewed did in some cases show a positive testing effect.[59]
References
- Bacon, Francis (2000). Jardine. ed. The New Organon. [Place of publication not identified]: CAMBRIDGE TEXTS IN THE HISTORY OF PHILOSOPHY. pp. 143. ISBN 0 511 01154 7.
- James, William (1890). The Principles of Psychology Vol 1,. New York: Holt. pp. Chapter 16 pg 686.
- Mace, C. A. (1932). The Psychology of Study. New York: R.M. McBride & Co.. p. 39.
- Roediger, Henry L.; Karpicke, Jeffrey D. (September 2006). "The Power of Testing Memory: Basic Research and Implications for Educational Practice" (in en). Perspectives on Psychological Science 1 (3): 181–210. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6916.2006.00012.x. ISSN 1745-6916. http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1111/j.1745-6916.2006.00012.x.
- Abbott, Edwina (1909). "On the analysis of the factors of recall in the learning process". Psychological Monographs: General and Applied 11 (1): 159–177. doi:10.1037/h0093018. https://insights.ovid.com/psychological-monographs-general-applied/pmga/1909/11/010/analysis-factor-recall-learning-process/5/00006828.
- Larsen, Douglas P.; Butler, Andrew C. (2013). Walsh, K.. ed. Test-enhanced learning. 443–452. ISBN 9780199652679. https://books.google.com/books?id=KW2rAAAAQBAJ&q=Test-enhanced+learning&pg=PA443.
- Carrier, M.; Pashler, H. (1992). "The influence of retrieval on retention". Memory & Cognition 20 (6): 632–642. doi:10.3758/bf03202713. PMID 1435266. http://www.pashler.com/Articles/Carrier_Pashler_MemCog1992.pdf. Retrieved 17 August 2015.
- Roediger, H. L.; Karpicke, J. D. (2006). "Test-Enhanced Learning: Taking Memory Tests Improves Long-Term Retention". Psychological Science 17 (3): 249–255. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9280.2006.01693.x. PMID 16507066. http://psych.wustl.edu/memory/Roddy%20article%20PDF%27s/Roediger%20&%20Karpicke%20(2006)_PsychSci.pdf. Retrieved 17 August 2015.
- Agarwal (2007). "Examining the Testing Effect with Open- and Closed-Book Tests". Applied Cognitive Psychology 22 (7): 861–876. doi:10.1002/acp.1391. https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2Facp.1391
- Roediger, H. L.; Karpicke, J. D. (2006). "Test-Enhanced Learning: Taking Memory Tests Improves Long-Term Retention". Psychological Science 17 (3): 249–255. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9280.2006.01693.x. PMID 16507066. http://psych.wustl.edu/memory/Roddy%20article%20PDF%27s/Roediger%20&%20Karpicke%20(2006)_PsychSci.pdf. Retrieved 17 August 2015.
- Butler, A.C. (2010). "Repeated testing produces superior transfer of learning relative to repeated studying". Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 36 (5): 1118–1133. doi:10.1037/a0019902. PMID 20804289. https://dx.doi.org/10.1037%2Fa0019902
- Mulligan, N. W.; Picklesimer, M (2016). "Attention and the testing effect". Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 42 (6): 938–950. doi:10.1037/xlm0000227. PMID 26618913. https://dx.doi.org/10.1037%2Fxlm0000227
- Toppino, T. C.; Cohen, M. S. (2009). "The testing effect and the retention interval: Questions and answers". Experimental Psychology 56 (4): 252–257. doi:10.1027/1618-3169.56.4.252. PMID 19439397. https://dx.doi.org/10.1027%2F1618-3169.56.4.252
- Wiklund‐Hörnqvist, Carola; Stillesjö, Sara; Andersson, Micael; Jonsson, Bert; Nyberg, Lars (January 2021). "Retrieval practice facilitates learning by strengthening processing in both the anterior and posterior hippocampus" (in en). Brain and Behavior 11 (1). doi:10.1002/brb3.1909. ISSN 2162-3279. PMID 33094555. PMC 7821628. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/brb3.1909.
- Bjork, R. A., & Bjork, E. L. (1992). A new theory of disuse and an old theory of stimulus fluctuation. In A. Healy, S. Kosslyn, & R. Shiffrin (Eds.), From learning processes to cognitive processes: Essays in honor of William K. Estes (Vol. 2, pp. 35-67). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. Based upon research done by: Izawa, C (1966). "Reinforcement-test sequences in paired associate learning". Psychological Reports 18 (3): 879–919. doi:10.2466/pr0.1966.18.3.879. http://bjorklab.psych.ucla.edu/pubs/RBjork_EBjork_1992.pdf
- Kornell, Nate; Bjork, Robert A.; Garcia, Michael A. (August 2011). "Why tests appear to prevent forgetting: A distribution-based bifurcation model". Journal of Memory and Language 65 (2): 85–97. doi:10.1016/j.jml.2011.04.002. http://web.williams.edu/Psychology/Faculty/Kornell/Publications/Kornell.Bjork.Garcia.2011.pdf. Retrieved 15 May 2015.
- van den Broek, Gesa S. E.; Segers, Eliane; Takashima, Atsuko; Verhoeven, Ludo (2 September 2013). "Do testing effects change over time? Insights from immediate and delayed retrieval speed". Memory 22 (7): 803–812. doi:10.1080/09658211.2013.831455. PMID 23998337. http://www.tandfonline.com/eprint/mE7uP7Dv6EwI6kWhmtfv/full.
- Roediger, H. L.; Karpicke, J. D. (2006). "Test-Enhanced Learning: Taking Memory Tests Improves Long-Term Retention". Psychological Science 17 (3): 249–255. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9280.2006.01693.x. PMID 16507066. http://psych.wustl.edu/memory/Roddy%20article%20PDF%27s/Roediger%20&%20Karpicke%20(2006)_PsychSci.pdf. Retrieved 17 August 2015.
- Toppino, Thomas C.; Cohen, Michael S. (1 January 2009). "The Testing Effect and the Retention Interval". Experimental Psychology 56 (4): 252–257. doi:10.1027/1618-3169.56.4.252. PMID 19439397. https://dx.doi.org/10.1027%2F1618-3169.56.4.252
- Halamish, Vered; Bjork, Robert A. (2011). "When does testing enhance retention? A distribution-based interpretation of retrieval as a memory modifier.". Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 37 (4): 801–812. doi:10.1037/a0023219. PMID 21480751. https://dx.doi.org/10.1037%2Fa0023219
- Pyc, Mary A.; Rawson, Katherine A. (May 2009). "Testing the retrieval effort hypothesis: Does greater difficulty correctly recalling information lead to higher levels of memory?". Journal of Memory and Language 60 (4): 437–447. doi:10.1016/j.jml.2009.01.004. http://www2.kent.edu/CAS/Psychology/resources/cml/upload/Pyc-Rawson-2009-JML-pdf.pdf.
- Carpenter, S.K. (2009). "Cue Strength as a Moderator of the Testing Effect: The Benefits of Elaborative Retrieval". Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 35 (6): 1563–1569. doi:10.1037/a0017021. PMID 19857026. https://dx.doi.org/10.1037%2Fa0017021
- McDaniel, M.A., &Fisher, R.P. (1991). Tests and test feedback as learning sources. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 16, 192–201.
- Karpicke, J. D., & Blunt, J. R. (2011)
- Yang, Chunliang; Potts, Rosalind; Shanks, David R. (2018-04-11). "Enhancing learning and retrieval of new information: a review of the forward testing effect". NPJ Science of Learning 3 (1): 8. doi:10.1038/s41539-018-0024-y. ISSN 2056-7936. PMID 30631469. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=6220253
- Karpicke, J. D.; Blunt, J. R. (2011). "Retrieval practice produces more learning than elaborate studying with concept of mapping". Science 331 (6018): 772–775. doi:10.1126/science.1199327. PMID 21252317. https://dx.doi.org/10.1126%2Fscience.1199327
- Mulligan, N. W.; Peterson, D. J. (2015). "The negative testing and negative generation effects are eliminated by delay". Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 41 (4): 1014–1025. doi:10.1037/xlm0000070. PMID 25329076. https://dx.doi.org/10.1037%2Fxlm0000070
- Yang, Chunliang; Luo, Liang; Vadillo, Miguel A.; Yu, Rongjun; Shanks, David R. (April 2021). "Testing (quizzing) boosts classroom learning: A systematic and meta-analytic review." (in en). Psychological Bulletin 147 (4): 399–435. doi:10.1037/bul0000309. ISSN 1939-1455. http://doi.apa.org/getdoi.cfm?doi=10.1037/bul0000309.
- Kubik, Veit; Gaschler, Robert; Hausman, Hannah (March 2021). "PLAT 20(1) 2021: Enhancing Student Learning in Research and Educational Practice: The Power of Retrieval Practice and Feedback" (in en). Psychology Learning & Teaching 20 (1): 1–20. doi:10.1177/1475725720976462. ISSN 1475-7257. http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1475725720976462.
- Pan, Steven C.; Sana, Faria (2021-04-01). "Pretesting versus posttesting: Comparing the pedagogical benefits of errorful generation and retrieval practice." (in en). Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied. doi:10.1037/xap0000345. ISSN 1939-2192. http://doi.apa.org/getdoi.cfm?doi=10.1037/xap0000345.
- Giebl, Saskia; Mena, Stefany; Storm, Benjamin C.; Bjork, Elizabeth Ligon; Bjork, Robert A. (2021-03-01). "Answer First or Google First? Using the Internet in ways that Enhance, not Impair, One's Subsequent Retention of Needed Information" (in en). Psychology Learning & Teaching 20 (1): 58–75. doi:10.1177/1475725720961593. ISSN 1475-7257. https://doi.org/10.1177/1475725720961593.
- Karpicke, J. D.; Roediger, H. L. (2008). "The critical importance of retrieval for learning". Science 319 (5865): 966–968. doi:10.1126/science.1152408. PMID 18276894. Bibcode: 2008Sci...319..966K. https://dx.doi.org/10.1126%2Fscience.1152408
- Kroneisen, Meike; Kuepper-Tetzel, Carolina E. (March 2021). "Using Day and Night – Scheduling Retrieval Practice and Sleep" (in en). Psychology Learning & Teaching 20 (1): 40–57. doi:10.1177/1475725720965363. ISSN 1475-7257. http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1475725720965363.
- Karpicke, J. D.; Blunt, J. R. (2011-02-11). "Retrieval Practice Produces More Learning than Elaborative Studying with Concept Mapping" (in en). Science 331 (6018): 772–775. doi:10.1126/science.1199327. ISSN 0036-8075. https://www.sciencemag.org/lookup/doi/10.1126/science.1199327.
- Lechuga, M. Teresa; Ortega-Tudela, Juana M.; Gómez-Ariza, Carlos J. (December 2015). "Further evidence that concept mapping is not better than repeated retrieval as a tool for learning from texts" (in en). Learning and Instruction 40: 61–68. doi:10.1016/j.learninstruc.2015.08.002. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0959475215300232.
- Blunt, Janell R.; Karpicke, Jeffrey D. (2014). "Learning with retrieval-based concept mapping." (in en). Journal of Educational Psychology 106 (3): 849–858. doi:10.1037/a0035934. ISSN 1939-2176. http://doi.apa.org/getdoi.cfm?doi=10.1037/a0035934.
- Kliegl, Oliver; Bäuml, Karl-Heinz T. (October 2021). "When retrieval practice promotes new learning – The critical role of study material" (in en). Journal of Memory and Language 120: 104253. doi:10.1016/j.jml.2021.104253. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0749596X2100036X.
- Pan, Steven C.; Rickard, Timothy C. (July 2018). "Transfer of test-enhanced learning: Meta-analytic review and synthesis." (in en). Psychological Bulletin 144 (7): 710–756. doi:10.1037/bul0000151. ISSN 1939-1455. http://doi.apa.org/getdoi.cfm?doi=10.1037/bul0000151.
- Bertilsson, Frida; Stenlund, Tova; Wiklund-Hörnqvist, Carola; Jonsson, Bert (March 2021). "Retrieval Practice: Beneficial for All Students or Moderated by Individual Differences?" (in en). Psychology Learning & Teaching 20 (1): 21–39. doi:10.1177/1475725720973494. ISSN 1475-7257. http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1475725720973494.
- Agarwal, Pooja K.; Finley, Jason R.; Rose, Nathan S.; Roediger, Henry L. (2017-07-03). "Benefits from retrieval practice are greater for students with lower working memory capacity" (in en). Memory 25 (6): 764–771. doi:10.1080/09658211.2016.1220579. ISSN 0965-8211. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09658211.2016.1220579.
- "Remember!". http://www.retrievalpractice.org.
- McDaniel, M. A.; Roediger, H. L.; McDermott, K. B. (2007). "Generalizing test-enhanced learning from the laboratory to the classroom". Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 14 (2): 200–206. doi:10.3758/bf03194052. PMID 17694901. https://dx.doi.org/10.3758%2Fbf03194052
- Agarwal, P. K.; Bain, P. M.; Chamberlain, R. W. (2012). "The value of applied research: Retrieval practice improves classroom learning and recommendations from a teacher, a principal, and a scientist.". Educational Psychology Review 24 (3): 437–448. doi:10.1007/s10648-012-9210-2. http://psych.wustl.edu/memory/Agarwal/Agarwal_Bain_Chamberlain_2012_EDPR.pdf. Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- Agarwal, Pooja K.; Nunes, Ludmila D.; Blunt, Janell R. (2021-03-14). "Retrieval Practice Consistently Benefits Student Learning: a Systematic Review of Applied Research in Schools and Classrooms" (in en). Educational Psychology Review. doi:10.1007/s10648-021-09595-9. ISSN 1040-726X. http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10648-021-09595-9.
- Perry, T; Lea, R; Jørgensen, C, R.; Cordingley, P.; Shapiro, K.; Youdell, D (July 2021). Cognitive Science Approaches in the Classroom (Report). London: Education Endowment Foundation. https://educationendowmentfoundation.org.uk/evidence-summaries/evidencereviews/cognitive-science-approaches-in-the-classroom/. [clarification needed]
- Roediger, Henry L.; Agarwal, Pooja K.; McDaniel, Mark A.; McDermott, Kathleen B. (2011). "Test-enhanced learning in the classroom: Long-term improvements from quizzing." (in en). Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied 17 (4): 382–395. doi:10.1037/a0026252. ISSN 1939-2192. http://doi.apa.org/getdoi.cfm?doi=10.1037/a0026252.
- Sotola, Lukas K.; Crede, Marcus (June 2021). "Regarding Class Quizzes: a Meta-analytic Synthesis of Studies on the Relationship Between Frequent Low-Stakes Testing and Class Performance" (in en). Educational Psychology Review 33 (2): 407–426. doi:10.1007/s10648-020-09563-9. ISSN 1040-726X. https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10648-020-09563-9.
- "Testing Effect" (in en). https://teach.com/what/teachers-know/testing-effect/.
- Agarwal, Pooja K.; =Patrice M. Bain (2019). Powerful teaching: unleash the science of learning. San Francisco. ISBN 978-1-119-52185-3. OCLC 1089840036. http://www.worldcat.org/oclc/1089840036
- Ferlazzo, Larry (2021-02-21). "Ten Ways to Use Retrieval Practice in the Classroom (Opinion)" (in en). https://www.edweek.org/teaching-learning/opinion-ten-ways-to-use-retrieval-practice-in-the-classroom/2021/02.
- Jones, Kate (2020). Retrieval Practice: Resources and research for every classroom. John Catt Educational. ISBN 978-1912906581.
- Cooper, Avraham Z.; Verbeck, Nicole; McCallister, Jennifer W.; Spitzer, Carleen R. (2020-12-01). "Incorporating Retrieval Practice Into Intensive Care Unit Teaching Rounds: A Feasibility Study" (in en). Journal of Graduate Medical Education 12 (6): 778–781. doi:10.4300/JGME-D-20-00082.1. ISSN 1949-8357. PMID 33391605. PMC 7771589. https://meridian.allenpress.com/jgme/article/12/6/778/447989/Incorporating-Retrieval-Practice-Into-Intensive.
- Nelson, Adin (2021-04-02). "Additional Benefits of Incorporating Retrieval Practice Into Teaching Rounds" (in en). Journal of Graduate Medical Education 13 (2): 293–293. doi:10.4300/JGME-D-20-01478.1. ISSN 1949-8357. PMID 33897968. PMC 8054592. https://meridian.allenpress.com/jgme/article/13/2/293/464050/Additional-Benefits-of-Incorporating-Retrieval.
- Dobson, John L. (June 2013). "Retrieval practice is an efficient method of enhancing the retention of anatomy and physiology information" (in en). Advances in Physiology Education 37 (2): 184–191. doi:10.1152/advan.00174.2012. ISSN 1043-4046. https://www.physiology.org/doi/10.1152/advan.00174.2012.
- Brown, Peter C.; Henry L. Roediger III; Mark A. McDaniel (2014). Make it stick: the science of successful learning. Cambridge, MA. ISBN 978-0-674-72901-8. OCLC 859168651. http://www.worldcat.org/oclc/859168651
- Carey, Benedict (2010-09-06). "Forget What You Know About Good Study Habits" (in en-US). The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. https://www.nytimes.com/2010/09/07/health/views/07mind.html.
- Lahey, Jessica (2014-01-21). "Students Should Be Tested More, Not Less" (in en). https://www.theatlantic.com/education/archive/2014/01/students-should-be-tested-more-not-less/283195/.
- van Gog, Tamara; Sweller, John (2015-06-01). "Not New, but Nearly Forgotten: the Testing Effect Decreases or even Disappears as the Complexity of Learning Materials Increases" (in en). Educational Psychology Review 27 (2): 247–264. doi:10.1007/s10648-015-9310-x. ISSN 1573-336X. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-015-9310-x.
- Karpicke, Jeffrey D.; Aue, William R. (June 2015). "The Testing Effect Is Alive and Well with Complex Materials" (in en). Educational Psychology Review 27 (2): 317–326. doi:10.1007/s10648-015-9309-3. ISSN 1040-726X. http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10648-015-9309-3.




