
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jason Zhu | -- | 4344 | 2022-10-19 01:32:48 |
Video Upload Options
Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a large impact on quality of life. It has been identified as an important issue in geriatric health care. The term enuresis is often used to refer to urinary incontinence primarily in children, such as nocturnal enuresis (bed wetting). UI is an example of a stigmatized medical condition, which creates barriers to successful management and makes the problem worse. People may be too embarrassed to seek medical help, and attempt to self-manage the symptom in secrecy from others. Pelvic surgery, pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause are major risk factors. Urinary incontinence is often a result of an underlying medical condition but is under-reported to medical practitioners. There are four main types of incontinence: Treatments include pelvic floor muscle training, bladder training, surgery, and electrical stimulation. Behavioral therapy generally works better than medication for stress and urge incontinence. The benefit of medications is small and long term safety is unclear. Urinary incontinence is more common in older women.
1. Causes
Urinary incontinence can result from both urologic and non-urologic causes. Urologic causes can be classified as either bladder dysfunction or urethral sphincter incompetence and may include detrusor overactivity, poor bladder compliance, urethral hypermobility, or intrinsic sphincter deficiency. Non-urologic causes may include infection, medication or drugs, psychological factors, polyuria, hydrocephalus,[1] stool impaction, and restricted mobility.[2] The causes leading to urinary incontinence are usually specific to each sex, however, some causes are common to both men and women.
1.1. Women
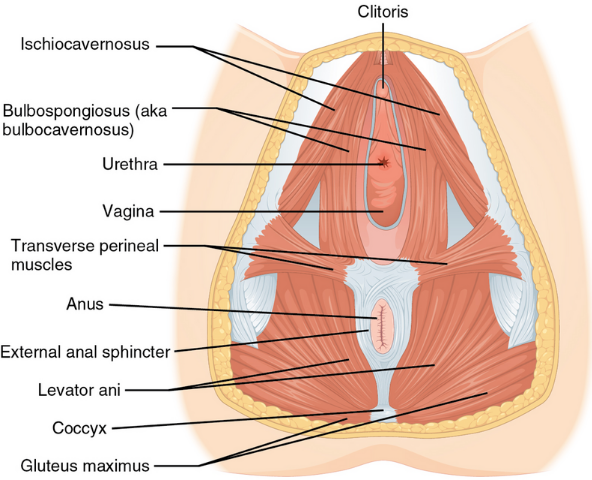
The most common types of urinary incontinence in women are stress urinary incontinence and urge urinary incontinence. Women that have symptoms of both types are said to have "mixed" urinary incontinence. After menopause, estrogen production decreases and, in some women, urethral tissue will demonstrate atrophy, becoming weaker and thinner, possibly playing a role in the development of urinary incontinence.[3]
Stress urinary incontinence in women is most commonly caused by loss of support of the urethra, which is usually a consequence of damage to pelvic support structures as a result of pregnancy, childbirth, obesity, age, among others.[4] About 33% of all women experience urinary incontinence after giving birth, and women who deliver vaginally are about twice as likely to have urinary incontinence as women who give birth via a Caesarean section.[5] Stress incontinence is characterized by leaking of small amounts of urine with activities that increase abdominal pressure such as coughing, sneezing, laughing and lifting. This happens when the urethral sphincter cannot close completely due to the damage in the sphincter itself, or the surrounding tissue. Additionally, frequent exercise in high-impact activities can cause athletic incontinence to develop. Urge urinary incontinence, is caused by uninhibited contractions of the detrusor muscle, a condition known as overactive bladder syndrome. It is characterized by leaking of large amounts of urine in association with insufficient warning to get to the bathroom in time.
1.2. Men

Urge incontinence is the most common type of incontinence in men.[6] Similar to women, urine leakage happens following a very intense feeling of urination, not allowing enough time to reach the bathroom, a condition called overactive bladder syndrome. In men, the condition is commonly associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (an enlarged prostate), which causes bladder outlet obstruction, a dysfunction of the detrusor muscle (muscle of the bladder), eventually causing overactive bladder syndrome, and the associated incontinence.[6]
Stress urinary incontinence is the other common type of incontinence in men, and it most commonly happens after prostate surgery.[7] Prostatectomy, transurethral resection of the prostate, prostate brachytherapy, and radiotherapy can all damage the urethral sphincter and surrounding tissue, causing it to be incompetent. An incompetent urethral sphincter cannot prevent the urine from leaking out of the urinary bladder during activities that increase the intraabdominal pressure, such as coughing, sneezing, or laughing. Continence usually improves within 6 to 12 months after prostate surgery without any specific interventions, and only 5 to 10% of people report persistent symptoms.[6]
1.3. Both
- Age is a risk factor that increases both the severity and prevalence of UI
- Polyuria (excessive urine production) of which, in turn, the most frequent causes are: uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, primary polydipsia (excessive fluid drinking), central diabetes insipidus and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.[8] Polyuria generally causes urinary urgency and frequency, but does not necessarily lead to incontinence.
- Neurogenic disorders like multiple sclerosis, spina bifida, Parkinson's disease, strokes and spinal cord injury can all interfere with nerve function of the bladder.[9] This can lead to neurogenic bladder dysfunction
- Overactive bladder syndrome. However, the etiology behind this is usually different between men and women, as mentioned above.
- Other suggested risk factors include smoking, caffeine intake and depression
2. Mechanism
2.1. Adults
The body stores urine — water and wastes removed by the kidneys — in the urinary bladder, a balloon-like organ. The bladder connects to the urethra, the tube through which urine leaves the body.[10]
Continence and micturition involve a balance between urethral closure and detrusor muscle activity (the muscle of the bladder). During urination, detrusor muscles in the wall of the bladder contract, forcing urine out of the bladder and into the urethra. At the same time, sphincter muscles surrounding the urethra relax, letting urine pass out of the body. The urethral sphincter is the muscular ring that closes the outlet of the urinary bladder preventing urine to pass outside the body. Urethral pressure normally exceeds bladder pressure, resulting in urine remaining in the bladder, and maintaining continence.[11] The urethra is supported by pelvic floor muscles and tissue, allowing it to close firmly. Any damage to this balance between the detrusor muscle, urethral sphincter, supportive tissue and nerves can lead to some type of incontinence .
For example, stress urinary incontinence is usually a result of the incompetent closure of the urethral sphincter. This can be caused by damage to the sphincter itself, the muscles that support it, or nerves that supply it. In men, the damage usually happens after prostate surgery or radiation,[6] and in women, it's usually caused by childbirth and pregnancy.[12] The pressure inside the abdomen (from coughing and sneezing) is normally transmitted to both urethra and bladder equally, leaving the pressure difference unchanged, resulting in continence. When the sphincter is incompetent, this increase in pressure will push the urine against it, leading to incontinence.
Another example is urge incontinence. This incontinence is associated with sudden forceful contractions of the detrusor muscle (bladder muscle), leading to an intense feeling of urination, and incontinence if the person does not reach the bathroom on time. The syndrome is known as overactive bladder syndrome, and it's related to dysfunction of the detrusor muscle.[13]
2.2. Children
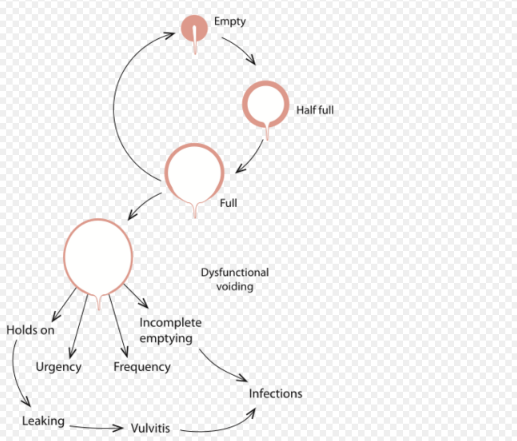
Urination, or voiding, is a complex activity. The bladder is a balloon-like muscle that lies in the lowest part of the abdomen. The bladder stores urine then releases it through the urethra, the canal that carries urine to the outside of the body. Controlling this activity involves nerves, muscles, the spinal cord and the brain.
The bladder is made of two types of muscles: the detrusor, a muscular sac that stores urine and squeezes to empty, and the sphincter, a circular group of muscles at the bottom or neck of the bladder that automatically stays contracted to hold the urine in and automatically relax when the detrusor contracts to let the urine into the urethra. A third group of muscles below the bladder (pelvic floor muscles) can contract to keep urine back.
A baby's bladder fills to a set point, then automatically contracts and empties. As the child gets older, the nervous system develops. The child's brain begins to get messages from the filling bladder and begins to send messages to the bladder to keep it from automatically emptying until the child decides it is the time and place to void.
Failures in this control mechanism result in incontinence. Reasons for this failure range from the simple to the complex.
3. Diagnosis
The pattern of voiding and urine leakage is important as it suggests the type of incontinence. Other points include straining and discomfort, use of drugs, recent surgery, and illness.
The physical examination looks for signs of medical conditions causing incontinence, such as tumors that block the urinary tract, stool impaction, and poor reflexes or sensations, which may be evidence of a nerve-related cause.
Other tests include:[14]
- Stress test – the patient relaxes, then coughs vigorously as the doctor watches for loss of urine.
- Urinalysis – urine is tested for evidence of infection, urinary stones, or other contributing causes.
- Blood tests – blood is taken, sent to a laboratory, and examined for substances related to causes of incontinence.
- Ultrasound – sound waves are used to visualize the kidneys and urinary bladder, assess the capacity of the bladder before voiding, and the remaining amount of urine after voiding. This helps know if there's a problem in emptying.
- Cystoscopy – a thin tube with a tiny camera is inserted in the urethra and used to see the inside of the urethra and bladder.
- Urodynamics – various techniques measure pressure in the bladder and the flow of urine.
People are often asked to keep a diary for a day or more, up to a week, to record the pattern of voiding, noting times and the amounts of urine produced.
Research projects that assess the efficacy of anti-incontinence therapies often quantify the extent of urinary incontinence. The methods include the 1-h pad test, measuring leakage volume; using a voiding diary, counting the number of incontinence episodes (leakage episodes) per day; and assessing of the strength of pelvic floor muscles, measuring the maximum vaginal squeeze pressure.
3.1. Main Types
There are 4 main types of urinary incontinence:
- Stress incontinence, also known as effort incontinence, is essentially due to incomplete closure of the urinary sphincter, due to problems in the sphincter itself or insufficient strength of the pelvic floor muscles supporting it. This type of incontinence is when urine leaks during activities that increase intra-abdominal pressure, such as coughing, sneezing or bearing down.[15]
- Urge incontinence is an involuntary loss of urine occurring while suddenly feeling the need or urge to urinate, usually secondary to overactive bladder syndrome.
- Overflow incontinence is the incontinence that happens suddenly without feeling an urge to urinate and without necessarily doing any physical activities. It is also known as under-active bladder syndrome. This usually happens with chronic obstruction of the bladder outlet or with diseases damaging the nerves supplying the urinary bladder. The urine stretches the bladder without the person feeling the pressure, and eventually, it overwhelms the ability of the urethral sphincter to hold it back.[16]
- Mixed incontinence contains symptoms of multiple other types of incontinence. It is not uncommon in the elderly female population and can sometimes be complicated by urinary retention.
3.2. Other Types
- Functional incontinence occurs when a person recognizes the need to urinate but cannot make it to the bathroom. The loss of urine may be large. There are several causes of functional incontinence including confusion, dementia, poor eyesight, mobility or dexterity, unwillingness to the toilet because of depression or anxiety or inebriation due to alcohol.[17] Functional incontinence can also occur in certain circumstances where no biological or medical problem is present. For example, a person may recognize the need to urinate but may be in a situation where there is no toilet nearby or access to a toilet is restricted.
- Structural incontinence: Rarely, structural problems can cause incontinence, usually diagnosed in childhood (for example, an ectopic ureter). Fistulas caused by obstetric and gynecologic trauma or injury are commonly known as obstetric fistulas and can lead to incontinence. These types of vaginal fistulas include, most commonly, vesicovaginal fistula and, more rarely, ureterovaginal fistula. These may be difficult to diagnose. The use of standard techniques along with a vaginogram or radiologically viewing the vaginal vault with instillation of contrast media.[18]
- Nocturnal enuresis is episodic UI while asleep. It is normal in young children.
- Transient incontinence is temporary incontinence most often seen in pregnant women when it subsequently resolves after the birth of the child.[19]
- Giggle incontinence is an involuntary response to laughter. It usually affects children.
- Double incontinence. There is also a related condition for defecation known as fecal incontinence. Due to involvement of the same muscle group (levator ani) in bladder and bowel continence, patients with urinary incontinence are more likely to have fecal incontinence in addition.[20] This is sometimes termed "double incontinence".
- Post-void dribbling is the phenomenon where urine remaining in the urethra after voiding the bladder slowly leaks out after urination.
- Coital incontinence (CI) is urinary leakage that occurs during either penetration or orgasm and can occur with a sexual partner or with masturbation. It has been reported to occur in 10% to 24% of sexually active women with pelvic floor disorders.[21]
- Climacturia is urinary incontinence at the moment of orgasm. It can be a result of radical prostatectomy.
3.3. Screening
Yearly screening is recommended for women by the Women's Preventive Services Initiative. Screening questions should inquire about what symptoms they have experienced, how severe the symptoms are, and if the symptoms affect their daily lives.[22] (As of 2018), studies have not shown a change in outcomes with urinary incontinence screenings in women.[23]
4. Management
Treatment options range from conservative treatment, behavioral therapy, bladder retraining,[24] pelvic floor therapy, collecting devices (for men), fixer-occluder devices for incontinence (in men), medications and surgery.[25] A 2018 systematic review update showed that both nonpharmacological and pharmacological treatments are effective for treating UI in non-pregnant women.[26] All treatments, except hormones and periurethral bulking agents, are more effective than no treatment in improving or curing UI symptoms or achieving patient satisfaction.[27] The success of treatment depends on the correct diagnoses.[28]
4.1. Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral therapy involves the use of both suppressive techniques (distraction, relaxation) and learning to avoid foods that may worsen urinary incontinence. This may involve avoiding or limiting consumption of caffeine and alcohol. Behavioral therapies, including bladder training, biofeedback, and pelvic floor muscle training, are most effective for improving urinary incontinence in women, with a low risk of adverse events.[29] Behavioral therapy is not curative for urinary incontinence, but it can improve a person's quality of life. Behavioral therapy has benefits as both a monotherapy and as an adjunct to medications for symptom reduction.[30]
Avoiding heavy lifting and preventing constipation may help with uncontrollable urine leakage. Stopping smoking is also recommended as it is associated with improvements in urinary incontinence in men and women.[31] Weight loss is recommended in those who are obese.[32]
4.2. Physical Therapy and Exercise
Physical therapy can be effective for women in reducing urinary incontinence.[33]
Pelvic floor physical therapists work with patients to identify and treat underlying pelvic muscle dysfunction that can cease urinary incontinence. They may recommend exercises to strengthen the muscles, electrostimulation, or biofeedback treatments.[34][35] Exercising the muscles of the pelvis such as with Kegel exercises are a first line treatment for women with stress incontinence.[32] Efforts to increase the time between urination, known as bladder training, is recommended in those with urge incontinence.[32] Both these may be used in those with mixed incontinence.[32]
Small vaginal cones of increasing weight may be used to help with exercise.[36][37] They seem to be better than no active treatment in women with stress urinary incontinence, and have similar effects to training of pelvic floor muscles or electrostimulation.[37]
Biofeedback uses measuring devices to help the patient become aware of his or her body's functioning. By using electronic devices or diaries to track when the bladder and urethral muscles contract, the patient can gain control over these muscles. Biofeedback can be used with pelvic muscle exercises and electrical stimulation to relieve stress and urge incontinence.
Time voiding while urinating and bladder training are techniques that use biofeedback. In time voiding, the patient fills in a chart of voiding and leaking. From the patterns that appear in the chart, the patient can plan to empty his or her bladder before he or she would otherwise leak. Biofeedback and muscle conditioning, known as bladder training, can alter the bladder's schedule for storing and emptying urine. These techniques are effective for urge and overflow incontinence[38]
A 2013 randomized controlled trial found no benefit of adding biofeedback to pelvic floor muscle exercise in stress urinary incontinence, but observing improvements in both groups.[39] In another randomized controlled trial the addition of biofeedback to the training of pelvic floor muscles for the treatment of stress incontinence, improved pelvic floor muscle function, reduced urinary symptoms, and improved the quality of life.[40]
Preoperative pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) in men undergoing radical prostatectomy was not effective in reducing urinary incontinence.[7]
Alternative exercises have been studied for stress urinary incontinence in women.[41] Evidence was insufficient to support the use of Paula method, abdominal muscle training, Pilates, Tai Chi, breathing exercises, postural training, and generalized fitness.[41]
4.3. Devices
Individuals who continue to experience urinary incontinence need to find a management solution that matches their individual situation. The use of mechanical devices has not been well studied in women, as of 2014.[42]
- Collecting systems (for men) – consists of a sheath worn over the penis funneling the urine into a urine bag worn on the leg. These products come in a variety of materials and sizes for individual fit. Studies [43] show that urisheaths and urine bags are preferred over absorbent products – in particular when it comes to ‘limitations to daily activities’. Solutions exist for all levels of incontinence. Advantages with collecting systems are that they are discreet, the skin stays dry all the time, and they are convenient to use both day and night. Disadvantages are that it is necessary to get measured to ensure proper fit, and in some countries, a prescription is needed.
- Absorbent products (include shields, incontinence pads, undergarments, protective underwear, briefs, diapers, adult diapers and underpants) are the best-known product types to manage incontinence. They are widely available in pharmacies and supermarkets. The advantages of using these are that they barely need any fitting or introduction by a healthcare specialist. The disadvantages with absorbent products are that they can be bulky, leak, have odors and can cause skin breakdown due to the constant dampness.
- Intermittent catheters are single-use catheters that are inserted into the bladder to empty it, and once the bladder is empty they are removed and discarded. Intermittent catheters are primarily used for urinary retention (inability to empty the bladder), but for some people they can be used to reduce or avoid incontinence. These are prescription-only medical devices.
-
Different types of pessaries. These are inserted inside the vagina for support.Indwelling catheters (also known as foleys) are often used in hospital settings, or if the user is not able to handle any of the above solutions himself/herself (e.g. severe neurologic injury or neurodegenerative disease). These are also prescription-only medical devices. The indwelling catheter is typically connected to a urine bag that can be worn on the leg or hung on the side of the bed. Indwelling catheters need to be monitored and changed on a regular basis by a healthcare professional. The advantage of indwelling catheters is that because the urine is funneled away from the body, the skin remains dry. However, the disadvantage is that it is very common to incur urinary tract infections when using indwelling catheters. Bladder spasms and other problems can also occur with long-term use of indwelling catheters.[44]
- Penis clamp (or penis compression device), which is applied to compress the urethra to compensate for the malfunctioning of the natural urinary sphincter, preventing leakage from the bladder.[45] This management solution is only suitable for light or moderate incontinence.
- Vaginal pessaries for women are devices inserted into the vagina. This device provides support to the urethra which passes right in front of it, allowing it to close more firmly.
4.4. Medications
A number of medications exist to treat urinary incontinence including: fesoterodine, tolterodine and oxybutynin.[46] These medications work by relaxing smooth muscle in the bladder.[47][48][49] While some of these medications appear to have a small benefit, the risk of side effects are a concern.[46] Medications are effective for about one in ten people, and all medications have similar efficacy.[46]
Medications are not recommended for those with stress incontinence and are only recommended in those with urge incontinence who do not improve with bladder training.[32]
Injectable bulking agents may be used to enhance urethral support, however, they are of unclear benefit.[50][51]
4.5. Surgery
Women and men that have persistent incontinence despite optimal conservative therapy may be candidates for surgery. Surgery may be used to help stress or overflow incontinence.[52] Common surgical techniques for stress incontinence include slings, tension-free vaginal tape, bladder suspension, artificial urinary sphincters, among others.[52]
The use of transvaginal mesh implants and bladder slings is controversial due to the risk of debilitating painful side effects such as vaginal erosion.[53] In 2012 transvaginal mesh implants were classified as a high risk device by the US Food and Drug Administration.[54] Urodynamic testing seems to confirm that surgical restoration of vault prolapse can cure motor urge incontinence.
Traditional suburethral sling operations are probably slightly better than open abdominal retropubic colposuspension and are probably slightly less effective than mid-urethral sling operations in reducing urinary incontinence in women, but it is still uncertain if any of the different types of traditional suburethral sling operations are better than others.[55] Similarly, there is insufficient evidence to be certain about the effectiveness or safety of single-incision sling operations for urinary incontinence in women.[56] Traditional suburethral slings may have a higher risk of surgical complications than minimally invasive slings but the risk of complications compared with other types of operation is still uncertain.[55]
Laparoscopic colposuspension (keyhole surgery through the abdomen) with sutures is as effective as open colposuspension for curing incontinence in women up to 18 months after surgery, but it is unclear whether there are fewer risk of complications during or after surgery.[57] There is probably a higher risk of complications with traditional suburethral slings than with open abdominal retropubic suspension.[57]
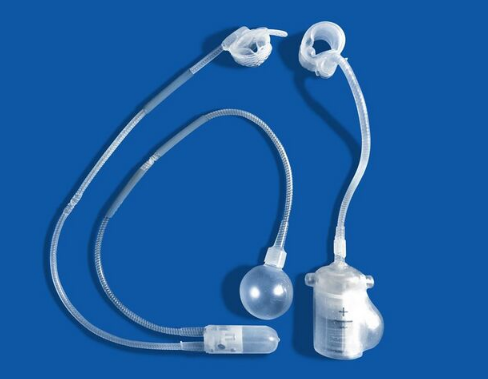
The artificial urinary sphincter is an implantable device used to treat stress incontinence, mostly in men. The device is made of 2 or 3 parts: The pump, cuff, and balloon reservoir connected to each other by specialized tubes. The cuff wraps around the urethra and closes it. When the person wants to urinate, he presses the pump (implanted in the scrotum), to deflate the cuff, and allow the urine to pass. The cuff regains pressure within a few minutes to regain continence.[58] The European Association of Urology considers the artificial urinary sphincter as the gold standard in surgical management of stress urinary incontinence in men after prostatectomy.[59]
5. Epidemiology
Globally, up to 35% of the population over the age of 60 years is estimated to be incontinent.[60] In 2014, urinary leakage affected between 30% and 40% of people over 65 years of age living in their own homes or apartments in the U.S.[61] Twenty-four percent of older adults in the U.S. have moderate or severe urinary incontinence that should be treated medically.[61] People with dementia are three times more likely to have urinary incontinence compared to people of similar ages.[62][63]
Bladder control problems have been found to be associated with higher incidence of many other health problems such as obesity and diabetes. Difficulty with bladder control results in higher rates of depression and limited activity levels.[64]
Incontinence is expensive both to individuals in the form of bladder control products and to the health care system and nursing home industry. Injury-related to incontinence is a leading cause of admission to assisted living and nursing care facilities. In 1997 more than 50% of nursing facility admissions were related to incontinence.[65]
5.1. Women
Bladder symptoms affect women of all ages. However, bladder problems are most prevalent among older women.[66] Women over the age of 60 years are twice as likely as men to experience incontinence; one in three women over the age of 60 years are estimated to have bladder control problems.[60] One reason why women are more affected is the weakening of pelvic floor muscles by pregnancy.[67]
5.2. Men
Men tend to experience incontinence less often than women, and the structure of the male urinary tract accounts for this difference. Stress incontinence is common after prostate cancer treatments.
While urinary incontinence affects older men more often than younger men, the onset of incontinence can happen at any age. Estimates around 2007 suggested that 17 percent of men over age 60, an estimated 600,000 men in the US, experienced urinary incontinence, with this percentage increasing with age.[68]
5.3. Children
Incontinence happens less often after age 5: About 10 percent of 5-year-olds, 5 percent of 10-year-olds, and 1 percent of 18-year-olds experience episodes of incontinence. It is twice as common in girls as in boys.[69]
6. History
The management of urinary incontinence with pads is mentioned in the earliest medical book known, the Ebers Papyrus (1500 BC).[70]
Incontinence has historically been a taboo subject in Western culture. However, this situation changed some when Kimberly-Clark aggressively marketed adult diapers in the 1980s with actor June Allyson as spokeswoman. Allyson was initially reticent to participate, but her mother, who had incontinence, convinced her that it was her duty in light of her successful career. The product proved a success.[71]
7. Law
The case Hiltibran et al v. Levy et al in the United States District Court for the Western District of Missouri resulted in that court issuing an order in 2011. That order requires incontinence briefs funded by Medicaid to be given by Missouri to adults who would be institutionalized without them.[72][73][74]
8. Research
The effectiveness of different therapeutic approaches to treating urinary incontinence is not well studied for some medical conditions. For example, for people who experience urinary incontinence due to stroke, treatment approaches such as physical therapy, cognitive therapy, complementary medicine, and specialized interventions with experienced medical professionals are sometimes suggested, however it is not clear how effective these are at improving incontinence and there is no strong medical evidence to guide clinical practice.[9]
References
- "Chronic hydrocephalus in adults". Brain Pathology 14 (3): 325–336. July 2004. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2004.tb00072.x. PMID 15446589. https://dx.doi.org/10.1111%2Fj.1750-3639.2004.tb00072.x
- "American Urological Association - Medical Student Curriculum: Urinary Incontinence". http://www.auanet.org/education/auauniversity/medical-student-education/medical-student-curriculum/urinary-incontinence.
- "Urinary incontinence fact sheet". Womenshealth.gov. July 16, 2012. https://www.womenshealth.gov/publications/our-publications/fact-sheet/urinary-incontinence.html.
- "Urinary incontinence - Causes" (in en). 2017-10-23. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/urinary-incontinence/causes/.
- "Prevalence of postpartum urinary incontinence: a systematic review". Acta Obstetricia Et Gynecologica Scandinavica 89 (12): 1511–1522. December 2010. doi:10.3109/00016349.2010.526188. PMID 21050146. https://dx.doi.org/10.3109%2F00016349.2010.526188
- "Urinary Incontinence in Men". https://www.uptodate.com/contents/urinary-incontinence-in-men.
- "Effectiveness of preoperative pelvic floor muscle training for urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy: a meta-analysis". BMC Urology 14 (1): 99. December 2014. doi:10.1186/1471-2490-14-99. PMID 25515968. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=4274700
- merck.com Polyuria: A Merck Manual of Patient Symptoms podcast. Last full review/revision September 2009 by Seyed-Ali Sadjadi, MD http://www.merck.com/mmpe/sec17/ch226/ch226i.html
- "Interventions for treating urinary incontinence after stroke in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2 (2): CD004462. February 2019. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004462.pub4. PMID 30706461. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=6355973
- "Urinary bladder contraction and relaxation: physiology and pathophysiology". Physiological Reviews 84 (3): 935–986. July 2004. doi:10.1152/physrev.00038.2003. PMID 15269341. https://dx.doi.org/10.1152%2Fphysrev.00038.2003
- "Anatomy and physiology of urinary continence". Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology 33 (2): 298–307. June 1990. doi:10.1097/00003081-199006000-00014. PMID 2190733. https://dx.doi.org/10.1097%2F00003081-199006000-00014
- "The pathophysiology of stress urinary incontinence in women and its implications for surgical treatment". World Journal of Urology 15 (5): 268–274. 1997-10-01. doi:10.1007/BF02202011. PMID 9372577. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007%2FBF02202011
- "Overactive Bladder (OAB): Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment - Urology Care Foundation". https://www.urologyhealth.org/urologic-conditions/overactive-bladder-(oab).
- "Evaluation of Females with Urinary Incontinence". https://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-of-females-with-urinary-incontinence.
- "Urinary incontinence: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia" (in en). https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003142.htm.
- "Overflow Incontinence | Michigan Medicine". https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/uh1227.
- "Functional incontinence". Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing. 2008. http://www.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/Content/continence-what-functional.htm.
- "Ureterovaginal fistula detected by vaginogram". Jama 246 (12): 1339–1340. September 1981. doi:10.1001/jama.246.12.1339. PMID 7265431. https://dx.doi.org/10.1001%2Fjama.246.12.1339
- "Stress urinary incontinence in pregnant women: a review of prevalence, pathophysiology, and treatment". International Urogynecology Journal 24 (6): 901–912. June 2013. doi:10.1007/s00192-013-2061-7. PMID 23436035. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=3671107
- "Prevention of urinary and fecal incontinence in adults". Evidence Report/Technology Assessment (161): 1–379. December 2007. PMID 18457475. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=4781595
- Karlovsky, Matthew E. MD, Female Urinary Incontinence During Sexual Intercourse (Coital Incontinence): A Review, The Female Patient (retrieved 22 August 2010) http://www.femalepatient.com/html/arc/sig/uroG/articles/034_08_032.asp
- "Screening for Urinary Incontinence in Women: A Recommendation From the Women's Preventive Services Initiative". Annals of Internal Medicine 169 (5): 320–328. September 2018. doi:10.7326/M18-0595. PMID 30105360. https://dx.doi.org/10.7326%2FM18-0595
- "Screening for Urinary Incontinence in Women: A Systematic Review for the Women's Preventive Services Initiative". Annals of Internal Medicine 169 (5): 311–319. September 2018. doi:10.7326/M18-0225. PMID 30105353. https://dx.doi.org/10.7326%2FM18-0225
- Bladder retraining ichelp.org Interstitial Cystitis Association Accessed July 13, 2012 http://www.ichelp.org/page.aspx?pid=368#how
- "Clinical audit of the use of tension-free vaginal tape as a surgical treatment for urinary stress incontinence, set against NICE guidelines". Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 24 (5): 534–538. August 2004. doi:10.1080/01443610410001722590. PMID 15369935. https://dx.doi.org/10.1080%2F01443610410001722590
- "Nonsurgical Treatments for Urinary Incontinence in Women: A Systematic Review Update | Effective Health Care Program" (in en). https://effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov/products/urinary-incontinence-update/final-report-2018.
- Nonsurgical Treatments for Urinary Incontinence in Women: A Systematic Review Update (Report). 2018-08-08. doi:10.23970/ahrqepccer212. PMID 30516945. https://dx.doi.org/10.23970%2Fahrqepccer212
- What is Male Urinary Incontinence? Retrieved on 2010-03-02 http://www.maleurinaryincontinence.net/
- "Adverse Events Associated with Nonsurgical Treatments for Urinary Incontinence in Women: a Systematic Review". Journal of General Internal Medicine 34 (8): 1615–1625. August 2019. doi:10.1007/s11606-019-05028-0. PMID 31062225. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=6667523
- "Urinary Incontinence: What Pharmacists Should Know". DrugTopics 162 (2): 24. February 2018.
- "Practical aspects of lifestyle modifications and behavioural interventions in the treatment of overactive bladder and urgency urinary incontinence". International Journal of Clinical Practice 63 (8): 1177–1191. August 2009. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2009.02078.x. PMID 19575724. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2734927
- "Nonsurgical management of urinary incontinence in women: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians". Annals of Internal Medicine 161 (6): 429–440. September 2014. doi:10.7326/m13-2410. PMID 25222388. https://dx.doi.org/10.7326%2Fm13-2410
- "Effectiveness of Physiotherapy Treatment for Urinary Incontinence in Women: A Systematic Review". Journal of Women's Health 28 (4): 490–501. April 2019. doi:10.1089/jwh.2018.7140. PMID 30575448. https://dx.doi.org/10.1089%2Fjwh.2018.7140
- "Pelvic floor physical therapy in the treatment of pelvic floor dysfunction in women". Current Opinion in Obstetrics & Gynecology 31 (6): 485–493. December 2019. doi:10.1097/GCO.0000000000000584. PMID 31609735. https://dx.doi.org/10.1097%2FGCO.0000000000000584
- "Pelvic floor involvement in male and female sexual dysfunction and the role of pelvic floor rehabilitation in treatment: a literature review". The Journal of Sexual Medicine 4 (1): 4–13. January 2007. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2006.00393.x. PMID 17233772. https://dx.doi.org/10.1111%2Fj.1743-6109.2006.00393.x
- Chelsea (September 4, 2012). "How to Use Vaginal Weights". National Incontinence. http://www.nationalincontinence.com/blog/how-to-use-vaginal-weights/.
- "Weighted vaginal cones for urinary incontinence". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (7): CD002114. July 2013. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002114.pub2. PMID 23836411. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=7086390
- Beaumont Health. "Treatment for Incontinence". https://www.beaumont.org/treatments/incontinence-treatment.
- "Randomized controlled trial of pelvic floor muscle training with or without biofeedback for urinary incontinence". International Urogynecology Journal 24 (8): 1347–1354. August 2013. doi:10.1007/s00192-012-2012-8. PMID 23306768. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007%2Fs00192-012-2012-8
- "[Effect the adding of biofeedback to the training of the pelvic floor muscles to treatment of stress urinary incontinence]". Revista Brasileira De Ginecologia E Obstetricia 34 (11): 505–510. November 2012. doi:10.1590/S0100-72032012001100005. PMID 23288261. https://dx.doi.org/10.1590%2FS0100-72032012001100005
- "There is not yet strong evidence that exercise regimens other than pelvic floor muscle training can reduce stress urinary incontinence in women: a systematic review". Journal of Physiotherapy 59 (3): 159–168. September 2013. doi:10.1016/S1836-9553(13)70180-2. PMID 23896331. "There is not yet strong evidence that alternative exercise regimens can reduce urinary leakage in women with stress urinary incontinence.". https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2FS1836-9553%2813%2970180-2
- "Mechanical devices for urinary incontinence in women". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 12 (12): CD001756. December 2014. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001756.pub6. PMID 25517397. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=7061494
- "Randomized, crossover study evaluating patient preference and the impact on quality of life of urisheaths vs absorbent products in incontinent men". BJU International 108 (2): 241–247. July 2011. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09736.x. PMID 20950307. https://dx.doi.org/10.1111%2Fj.1464-410X.2010.09736.x
- "Urinary catheter management". American Family Physician 61 (2): 369–376. January 2000. PMID 10670503. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10670503
- "A historical perspective and evolution of the treatment of male urinary incontinence". Neurourology and Urodynamics 37 (3): 1169–1175. March 2018. doi:10.1002/nau.23429. PMID 29053886. https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2Fnau.23429
- "Benefits and harms of pharmacologic treatment for urinary incontinence in women: a systematic review". Annals of Internal Medicine 156 (12): 861–74, W301-10. June 2012. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-156-12-201206190-00436. PMID 22711079. https://dx.doi.org/10.7326%2F0003-4819-156-12-201206190-00436
- "Oxybutynin Chloride Monograph for Professionals" (in en). https://www.drugs.com/monograph/oxybutynin-chloride.html.
- "Tolterodine Tartrate Tablets - FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses" (in en). https://www.drugs.com/pro/tolterodine-tartrate-tablets.html.
- "Fesoterodine Tablets - FDA prescribing information, side effects and uses" (in en). https://www.drugs.com/pro/fesoterodine-tablets.html.
- "Urethral injection therapy for urinary incontinence in women". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 7 (7): CD003881. July 2017. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd003881.pub4. PMID 28738443. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=6483304
- "The efficacy and safety of urethral injection therapy for urinary incontinence in women: a systematic review". Clinics 71 (2): 94–100. February 2016. doi:10.6061/clinics/2016(02)08. PMID 26934239. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=4760362
- Mayo Clinic internal medicine concise textbook. Rochester, MN: Mayo Clinic Scientific Press. 2008. p. 339. ISBN 9781420067514. https://books.google.com/books?id=YJtodBwNxokC&pg=PA339.
- "Vaginal Mesh & Bladder Sling Complications and Lawsuits". Lieff Cabraser. https://www.lieffcabraser.com/injury/devices/vaginal-mesh/.
- "What does pelvic mesh do and why are women suing over it? – explainer". 2017-08-31. https://www.theguardian.com/society/2017/aug/31/vaginal-pelvic-mesh-explainer.
- "Traditional suburethral sling operations for urinary incontinence in women". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1: CD001754. January 2020. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001754.pub5. PMID 31990055. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=7027385
- "Single-incision sling operations for urinary incontinence in women". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 7 (7): CD008709. July 2017. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008709.pub3. PMID 28746980. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=6483163
- "Laparoscopic colposuspension for urinary incontinence in women". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 12 (12): CD002239. December 2019. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002239.pub4. PMID 31821550. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=6903454
- "Recent advances in surgical management of urinary incontinence". F1000Research 8: 1294. 2019-07-31. doi:10.12688/f1000research.16356.1. PMID 31448082. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=6676503
- "EAU Guidelines on Urinary Incontinence in Adults". European Association of Urology. https://uroweb.org/wp-content/uploads/EAU-Guidelines-on-Urinary-Incontinence-2018-large-text.pdf.
- "A community-based epidemiological survey of female urinary incontinence: the Norwegian EPINCONT study. Epidemiology of Incontinence in the County of Nord-Trøndelag". Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 53 (11): 1150–1157. November 2000. doi:10.1016/S0895-4356(00)00232-8. PMID 11106889. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2FS0895-4356%2800%2900232-8
- "Prevalence of Incontinence Among Older Americans". June 2014. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/series/sr_03/sr03_036.pdf.
- "Continence, dementia, and care that preserves dignity". NIHR Evidence. 21 June 2022. doi:10.3310/nihrevidence_51255. https://evidence.nihr.ac.uk/themedreview/continence-dementia-and-care-that-preserves-dignity/.
- "First diagnosis and management of incontinence in older people with and without dementia in primary care: a cohort study using The Health Improvement Network primary care database". PLoS Medicine 10 (8): e1001505. August 2013. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001505. PMID 24015113. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=3754889
- "Urinary incontinence and depression in middle-aged United States women". Obstetrics and Gynecology 101 (1): 149–156. January 2003. doi:10.1016/s0029-7844(02)02519-x. PMID 12517660. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fs0029-7844%2802%2902519-x
- "Medically recognized urinary incontinence and risks of hospitalization, nursing home admission and mortality". Age and Ageing 26 (5): 367–374. September 1997. doi:10.1093/ageing/26.5.367. PMID 9351481. https://dx.doi.org/10.1093%2Fageing%2F26.5.367
- "How widespread are the symptoms of an overactive bladder and how are they managed? A population-based prevalence study". BJU International 87 (9): 760–766. June 2001. doi:10.1046/j.1464-410x.2001.02228.x. PMID 11412210. https://dx.doi.org/10.1046%2Fj.1464-410x.2001.02228.x
- "An 'Emotional Burden' Rarely Discussed". New York Times. July 29, 2014. http://newoldage.blogs.nytimes.com/2014/07/22/an-emotional-burden-rarely-discussed/.
- "Chapter 6: Urinary Incontinence in Men". Urologic Diseases in America Report. (US) National Institutes of Health. 2007.
- Pediatric incontinence - Franco - 2015 - Wiley Online Books - Wiley Online Library. 2015. doi:10.1002/9781118814789. ISBN 9781118814789. https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2F9781118814789
- Urinary and fecal incontinence : an interdisciplinary approach; with 89 tables. Berlin [u.a.]: Springer. 2005. p. 232. ISBN 978-3540222255.
- "Now Splinter Free: How Marketing Broke Taboos". Pirate Radio. CBC Radio One. 8 June 2017. http://www.cbc.ca/radio/undertheinfluence/now-splinter-free-how-marketing-broke-taboos-1.4149558.
- "Recent Cases - Olmstead Rights". https://www.olmsteadrights.org/advocacytools/recent-cases/.
- "govinfo". https://www.govinfo.gov/app/details/USCOURTS-mowd-2_10-cv-04185/summary.
- "govinfo". https://www.govinfo.gov/app/details/USCOURTS-mowd-2_10-cv-04185/context.




