
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Camila Xu | -- | 457 | 2022-10-18 01:49:24 |
Video Upload Options
The Europa Thermal Emission Imaging System (E-THEMIS) instrument is designed to scan the surface of Europa and identify areas of geologically recent resurfacing through the detection of subtle thermal anomalies. This 'heat detector' will provide high spatial resolution, multi-spectral thermal imaging of Europa to help detect active sites such as outflows and plumes. E-THEMIS will be launched on board the planned Europa Clipper astrobiology mission to Jupiter's moon Europa in 2025. The E-THEMIS uses technology inherited from the THEMIS camera flown on board the 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter, and the OSIRIS-REx OTES instruments.
1. Overview
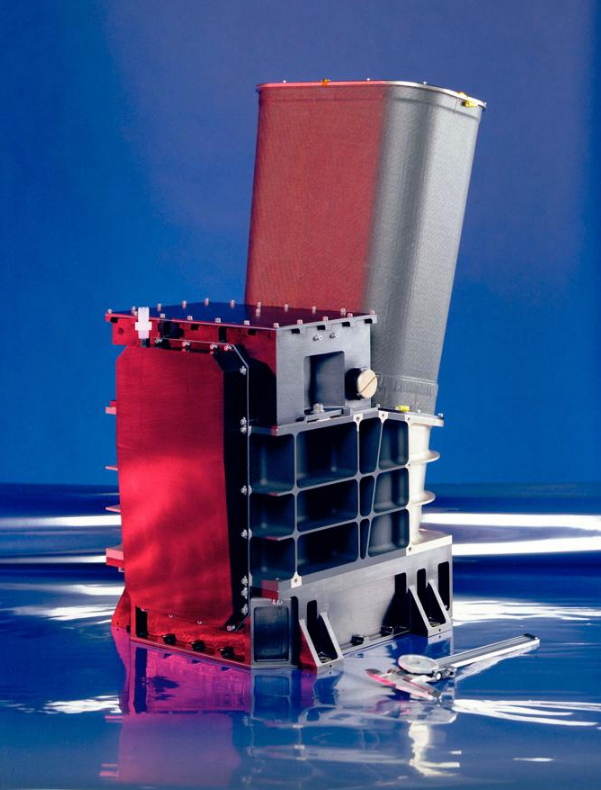

E-THEMIS will identify areas of geologically recent resurfacing through the detection of subtle thermal anomalies. E-THEMIS will be fabricated by Arizona State University with hardware contributions from Ball Aerospace Corporation,[1] and Raytheon Vision Systems. The Principal Investigator is Philip Christensen at Arizona State University.[2] One of the primary science objectives of the Europa Thermal Emission Imaging System (E-THEMIS) is to determine the regolith particle size, block abundance, and sub-surface layering for landing site assessment and surface process studies.[3] The E-THEMIS investigation is designed to characterize Europa's thermal behavior and identify any thermal anomalies due to recent or ongoing activity, which include multi-spectral infrared emission, at both day and night.[4] To accomplish this, E-THEMIS will obtain thermal infrared images in three spectral bands from 7 to 70 μm at multiple times of day.
Thermal anomalies on Europa may be manifestations of subsurface melting due to hot spots, shear heating on faults, and eruptions of liquid water, which can be imaged in the infrared spectrum.[4] Europa's water is suspected to lie 70 km (43 mi) below the moon's ice crust.
2. Objectives
The specific objectives of the E-THEMIS investigation are: [5]
- Detect and characterize thermal anomalies on the surface that may be indicative of recent resurfacing or active venting
- Identify active plumes
- Determine the regolith particle size, block abundance, and sub-surface layering for landing site assessment and surface process studies
To achieve this, E-THEMIS will image the surface at a resolution of 5 × 22 m from 25 km altitude; it will have a precision of 0.2 K for 90 K surfaces and 0.1 K at 220 K, with an accuracy of 1-2.2 K from 220-90 K; and E-THEMIS will obtain images with up to 360 cross-track pixels with a 10.1 km wide image swath from 100 km.[5] The instrument can identify active vents, if existing, at the 1-10 meter scale. A radiation-hardened integrated circuit will be incorporated to meet the radiation requirements.
| Infrared wavelength bands |
Spatial resolution from 100 km altitude |
Temperature (K) | Absolute accuracy (K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (7-14 μm) | 17 m × 24 m | 220 | 2.0 |
| 2 (14-28 μm) | 25 m × 33 m | 130 | 2.2 |
| 3 (28-70 μm) | 46 m × 52 m | 90 | 1.0 |
References
- Ball Aerospace To Partner With ASU On Key Instrument For Europa Mission. Colorado Space News. 11 June 2015. https://www.coloradospacenews.com/ball-aerospace-to-partner-with-asu-on-key-instrument-for-europa-mission/
- Pittman, Kagan (11 June 2015). "New Thermal Imaging Technology to Look for Life on Jupiter Moon". Engineering.com. https://www.engineering.com/PLMERP/ArticleID/10254/New-Thermal-Imaging-Technology-to-Look-for-Life-on-Jupiter-Moon.aspx.
- A review of thermophysical surface models in preparation for E-THEMIS observations of Europa. Rathbun, Julie A.; Hayne, Paul O.; Howett, Carly; Mellon, Michael; Piqueux, Sylvain; Spencer, John R. American Astronomical Society, DPS meeting #48, id.123.48 Published by the Smithsonian/NASA Astrophysics Data System. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2016DPS....4812348R
- Occurrence and Detectability of Thermal Anomalies on Europa. Hayne, Paul O.; Christensen, Philip R.; Spencer, John R.; Abramov, Oleg; Howett, Carly; Mellon, Michael; Nimmo, Francis; Piqueux, Sylvain; Rathbun, Julie A. American Astronomical Society, DPS meeting #49. October 2017. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2017DPS....4920303H
- Europa Thermal Emission Imaging System (E-THEMIS) (PDF). Philip Christensen. OPAG Meeting August 24, 2015. https://www.lpi.usra.edu/opag/meetings/aug2015/presentations/day-1/8_e_christensen.pdf




