
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bryan Oronsky | -- | 477 | 2022-10-17 23:30:05 | | | |
| 2 | Bryan Oronsky | -16 word(s) | 461 | 2022-10-18 02:54:18 | | | | |
| 3 | Bryan Oronsky | Meta information modification | 461 | 2022-10-18 02:55:48 | | | | |
| 4 | Camila Xu | -60 word(s) | 401 | 2022-10-18 03:19:27 | | |
Video Upload Options
Adenoviruses are nonenveloped double-stranded DNA viruses with about a 38-kb genome that most commonly cause respiratory symptoms. Adenoviruses are lytic to human cells, but not oncogenic due to lack of host genome integration.
1. Definition
Adenoviruses are nonenveloped double-stranded DNA viruses with about a 38-kb genome that most commonly cause respiratory symptoms. Adenoviruses are lytic to human cells, but not oncogenic due to lack of host genome integration. More than 50 serotypes of adenoviruses have been identified. Recombinant adenoviruses are widely used as vehicles for the expression of exogenous genes in target cells. These adenoviruses are used for gene transfer. Another use is as oncolytic viruses. Adenoviral serotype 5 is most common in the clinic. [1][2]
Oncolytic adenoviruses (OAVs) are “living drugs” that commandeer tumor cells as factories to support production of multiple copies of their genome and the therapeutic transgene that they carry; this leads to cell lysis, the release of infectious virus particles, and the expression of the therapeutic transgene. These self-amplification properties magnify the effect of even small inoculations of OAVs. Progeny viruses rip through cancer cells in waves of lytic replication, but infection dies away in normal cells, which leads to a high therapeutic index. Aside from the expression of therapeutic transgene(s), lysis of tumor cells releases “danger signals” and pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines that summon immune cells.
One limitation or obstacle to the success of OAVs is the presence of tumor-induced immunosuppression, which may counteract the anticancer effects of OAVs.
2. AdAPT-001
TGF-β is one of the main immunosuppressive cytokines; this has led to the development of an oncolytic adenovirus called AdAPT-001 in a clinical trial, which carries a TGF-β trap as its transgene. This TGF-β trap binds and neutralizes the TGF-β1 and TGF-β3 isoforms to reverse the immunosuppressive effects of TGF-β in the tumor microenvironment as well as resistance to anticancer therapies such as immune checkpoint inhibitors. Blockade of TGF-β signaling also diminishes vasculature abundance. [3] Therefore, AdAPT-001 acts in four separate ways, as shown in the figure below to:
- directly eradicate tumor cells via lysis as cancer cell therapy
- indirectly stimulates the immune system through the release of danger signals and tumor cell antigens following lysis as cancer cell immunotherapy
- decrease angiogenesis through expression of its TGF-β trap as cancer environment therapy
- reverse immunosuppression through expression of its TGF-β trap as cancer environment immunotherapy
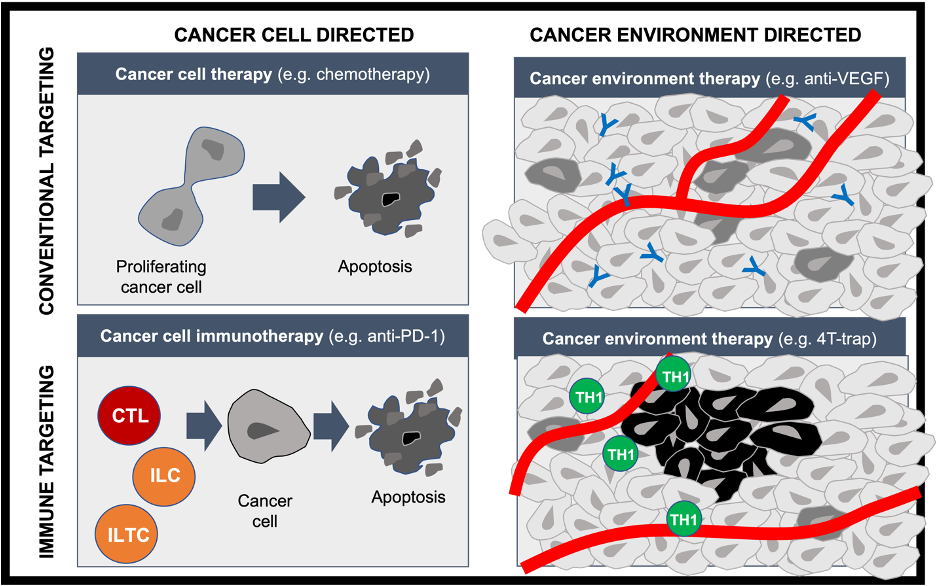
Figure 1. The Four Targeting Strategies of AdAPT-001.
References
- Larson C, Oronsky B, Scicinski J, et al. Going viral: a review of replication-selective oncolytic adenoviruses. Oncotarget. 2015;6(24):19976-19989. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.5116
- Oronsky B, Gastman B, Conley AP, Reid C, Caroen S, Reid T. Oncolytic Adenoviruses: The Cold War against Cancer Finally Turns Hot. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(19):4701. Published 2022 Sep 27.
- Larson C, Oronsky B, Reid T. AdAPT-001, an oncolytic adenovirus armed with a TGF-β trap, overcomes in vivo resistance to PD-L1-immunotherapy. Am J Cancer Res. 2022;12(7):3141-3147. Published 2022 Jul 15.




