
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dean Liu | -- | 1209 | 2022-09-27 02:43:58 |
Video Upload Options
The Simple Function Point (SFP) method is a lightweight Functional Measurement Method. The Simple Function Point method was designed to be compliant with the ISO14143-1 standard and compatible with the International Function Points User Group (IFPUG) Function Point Analysis (FPA) method. The original method is described in a manual produced by the Simple Function Point Association: the Simple Function Point Functional Size Measurement Method Reference Manual is available under the Creatives Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License.
1. Basic Concept
When the SFP method was proposed, the most widely used software functional size measurement method was IFPUG FPA.[1] However, IFPUG FPA had (and still has) a few shortcomings:
- It is not easy to apply. It requires certified personnel, and the productivity of measurement is relatively low (between 400 and 600 Function Points per day, according to Capers Jones,[2] between 200 and 300 Function Points per day according to experts from Total Metrics [3]).
- The measurement is partly subjective, since some of its measurement rules have to be suitably interpreted by the person who performs the measurement.
- The diffusion of the method in the software development community is quite limited.
To overcome at least some of these problems, the SFP method was defined to provide the following characteristics:
- Easy to apply;
- Less subject to interpretation, being based on quite straightforward definitions;
- Easy to learn: specifically, people familiar with IFPUG FPA could learn SFP very quickly with very little effort;
- Compatible with the IFPUG FPA; specifically [math]\displaystyle{ Size_{[UFP]}=Size_{[SiFP]} }[/math], that is, a measure of size expressed in UFP should be equal to the measure expressed in SiFP (In this article we use “UFP” for unadjusted Function Point to designate the unit of measure defined by IFPUG FPA and SiFP the unit of measure defined by SFP).
The sought characteristics were achieved as follows:
IFPUG FPA requires that [1]
- logical data files and transactions are identified,
- logical data files are classified into Internal Logical Files (ILF) and External Interface Files (EIF),
- every transaction is classified as External Input (EI), External Output (EO), External Query (EI),
- every ILF and EIF is weighted, based on its Record Element Types (RET) and Data Element Types (DET),
- every EI, EO and EQ is weighted, based on its File Types Referenced (FTR) and DET exchanged through the borders of the application being measured.
Of these activities, SFP requires only the first two, i.e., the identification of logical data files and transactions. Activities 4) and 5) are the most time consuming, since they require that every data file and transaction is examined in detail: skipping these phases makes the SFP method both quicker and easier to apply than IFPUG FPA. In addition, most of the subjective interpretation is due to activities 4) and 5), and partly also to activity 3): skipping these activities makes the SFP method also less prone to subjective interpretation.
The concepts used in the definition of SFP are a small subset of those used in the definition of IFPUG FPA, therefore learning SFP is easier than learning IFPUG FPA, and it is immediate for those who already know IFPUG FPA. In practice, only the concepts of logical data file and transaction have to be known.
Finally, the weights assigned to data files and transactions make the size in SFP very close to the size expressed in Function Points, on average.
2. Definition
The logical data files are named Unspecified Generic Data Group (UGDG) in the SFP method. Similarly, transactions are named Unspecified Generic Elementary Process (UGEP). The adjectives “unspecified” and “generic” stress that, unlike in IFPUG FPA, there is no classification or weighting.
The size of a UGEP is 4.6 SiFP, while the size of a UGDG is 7.0 SiFP. Therefore the size expressed in SiFP is based on the number of data files (#UGDG) and the number of transactions (#UGEP). Belonging to the software application being measured:
[math]\displaystyle{ Size_{[SiFP]}=4.6\ \#UGEP+7\ \#UGDG }[/math]
3. Empirical Evaluation of the SFP Method
Empirical studies have been carried out, aiming at
- evaluating the convertibility of SiFP and UFP measures
- comparing the SiFP and UFP measures in supporting the estimation of software development effort
Convertibility between SFP and FPA measures
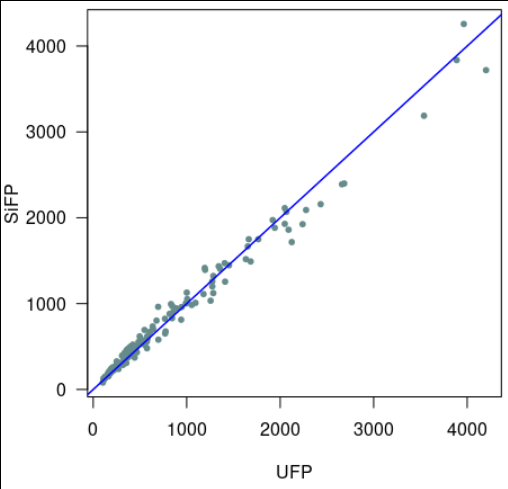
In the original proposal of the SFP method, a dataset from the ISBSG, including data from 768 projects, was used to evaluate the convertibility among UFP and SiFP measures. This study [5] showed that on average [math]\displaystyle{ Size_{[UFP]}=1.0005\ Size_{[SiFP]} }[/math].
Another study [4] also used an ISBSG dataset to evaluate the convertibility among UFP and SiFP measures. The dataset included data from 766 software applications. Via ordinary least square regression, it was found that [math]\displaystyle{ Size_{[SiFP]}=0.998\ Size_{[UFP]} }[/math].
Based on these empirical studies,[4][5] it seems that [math]\displaystyle{ Size_{[SiFP]}\approx Size_{[UFP]} }[/math] (note that this approximate equivalence holds on average: in both studies an average relative error around 12% was observed).
However, a third study [6] found [math]\displaystyle{ Size_{[UFP]}=0.815\ Size_{[SiFP]} }[/math]. This study used data from only 25 Web applications, so it is possible that the conversion rate is affected by the specific application type or by the relatively small size of the dataset.
In 2017, a study evaluated the convertibility between UFP and SiFP measures using seven different datasets.[7] Every dataset was characterized by a specific conversion rate. Specifically, it was found that [math]\displaystyle{ Size_{[SiFP]} = k\ Size={[UFP]} }[/math], with [math]\displaystyle{ k \in [0.957, 1.221] }[/math]. Noticeably, for a dataset, no linear model could be found; instead the statistically significant model [math]\displaystyle{ Size[SiFP]=Size[UFP]^{1.033} }[/math] was found.
In conclusion, available evidence shows that one SiFP is approximately equivalent to one UFP, but this equivalence depends on the data being considered, besides being true only on average.
Using SFP as a replacement of IFPUG FPA for software development effort estimation
IFPUG FPA is mainly used for estimating software development effort. Therefore, any method that aims at estimating the functional size of software should support effort estimation with the same level of accuracy as IFPUG FPA. In other words, it is necessary to verify that effort estimates based on SiFP are at least as good as the estimates based on UFP.
To perform this verification, an ISBSG dataset was analyzed, and models of effort vs. size were derived, using ordinary least squares regression, after log-log transformations.[4] The effort estimation errors were then compared. It turned out that the two models yielded extremely similar estimation accuracy.
A following study analyzed a dataset containing data from 25 Web applications.[6] Ordinary least squares regression was used to derive UFP-based and SiFP-based effort models. Also in this case, no statistically significant estimation errors could be observed.
4. Adoption by IFPUG
In 2019, the Simple Function Points Method was acquired by the IFPUG, to provide its user community with a simplified Function Point counting method, to make functional size measurement easier yet reliable in the early stages of software projects.
References
- International Function Point Users Group (IFPUG) (2010). Function point counting practices manual, release 4.3.1.
- Jones, Capers (2008). "A new business model for function point metrics". http://concepts.gilb.com/dl185.
- Total Metrics (2007). "Methods for Software Sizing – How to Decide which Method to Use". https://www.totalmetrics.com/function-point-resources/downloads/R185_Why-use-Function-Points.pdf.
- Lavazza, Luigi; Meli, Roberto (2014). "An Evaluation of Simple Function Point as a Replacement of IFPUG Function Point". 2014 Joint Conference of the International Workshop on Software Measurement and the International Conference on Software Process and Product Measurement (IEEE). doi:10.1109/iwsm.mensura.2014.28. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/iwsm.mensura.2014.28.
- Meli, Roberto (2011). "Simple function point: a new functional size measurement method fully compliant with IFPUG 4.x". Software Measurement European Forum. 2011.
- Ferrucci, Filomena; Gravino, Carmine; Lavazza, Luigi (2016-04-04). "Simple function points for effort estimation". Proceedings of the 31st Annual ACM Symposium on Applied Computing (New York, NY, USA: ACM). doi:10.1145/2851613.2851779. http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/2851613.2851779.
- Abualkishik, Abedallah Zaid; Ferrucci, Filomena; Gravino, Carmine; Lavazza, Luigi; Liu, Geng; Meli, Roberto; Robiolo, Gabriela (2017). "A study on the statistical convertibility of IFPUG Function Point, COSMIC Function Point and Simple Function Point". Information and Software Technology 86: 1–19. doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2017.02.005. ISSN 0950-5849. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2017.02.005.





