Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sowmya Poosapati | -- | 3251 | 2022-09-26 20:30:06 | | | |
| 2 | Rita Xu | Meta information modification | 3251 | 2022-09-27 04:31:49 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Prusty, S.; Sahoo, R.K.; Nayak, S.; Poosapati, S.; Swain, D.M. Micronutrient Deficiency and Toxicity in Plants. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/27610 (accessed on 07 February 2026).
Prusty S, Sahoo RK, Nayak S, Poosapati S, Swain DM. Micronutrient Deficiency and Toxicity in Plants. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/27610. Accessed February 07, 2026.
Prusty, Suchismita, Ranjan Kumar Sahoo, Subhendu Nayak, Sowmya Poosapati, Durga Madhab Swain. "Micronutrient Deficiency and Toxicity in Plants" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/27610 (accessed February 07, 2026).
Prusty, S., Sahoo, R.K., Nayak, S., Poosapati, S., & Swain, D.M. (2022, September 26). Micronutrient Deficiency and Toxicity in Plants. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/27610
Prusty, Suchismita, et al. "Micronutrient Deficiency and Toxicity in Plants." Encyclopedia. Web. 26 September, 2022.
Copy Citation
Micronutrients are essential for plants. Their growth, productivity and reproduction are directly influenced by the supply of micronutrients. Currently, there are eight trace elements considered to be essential for higher plants: Fe, Zn, Mn, Cu, Ni, B, Mo, and Cl. Possibly, other essential elements could be discovered because of recent advances in nutrient solution culture techniques and in the commercial availability of highly sensitive analytical instrumentation for elemental analysis.
micronutrients
proteomics
genomics
nutrient toxicity
1. Introduction
Essential nutrients (macro and micro) are required by plants for appropriate functioning and development. The significance of micronutrients in plant nutrition is well recognized. Micronutrients comprise less than 1% of the dry weight of most plants and are vital for their growth [1]. Plant classified micronutrients include boron, chlorine, copper, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel and zinc, which are vital for completion of the plant’s life cycle (Figure 1) [2]. They are also essential to maintain the stability of proteins and cellular structures. Through their interactions with other physiologically active molecules and enzymes, micronutrients play an essential role in the biosynthesis of proteins, nucleic acids, cofactors, carbohydrate metabolism, lipid metabolism, stress tolerance, chlorophyll maintenance, electron transport, anti-oxidative systems and much more. Hence access to micronutrients is critical for optimum crop nutrition and development (Figure 2) [3]. The bioavailability of micronutrients is heavily influenced by climatic factors like drought, severe rain, waterlogging or salinity [4]. Energy metabolism, primary and secondary metabolism, cell defense, gene expressions and regulations, hormone sensing, signal transduction, and reproduction are all influenced by micronutrients. The proportion of micronutrients in soil is determined by the geological substrate and pedogenesis management strategies. The ideal concentration of each micronutrient in the crop is influenced by chemical and physical features of the soil, such as soil pH, nutrient availability, clay minerals, microbial activity, amount of organic matter in the soil, quantity of other nutrients, and other factors that might affect micronutrient absorption and efficacy (Table 1). Although the fraction of micronutrients available in the soil may exceed a single plant’s requirements, the accessible proportion may be insufficient for all, resulting in nutritional deficiency in the crop. In Indian soils, improper nutrient management leads to multi-nutrient deficits [5]. Growth of the plant is constrained either by lack of micronutrients, nutrient toxicity or soil conditions.
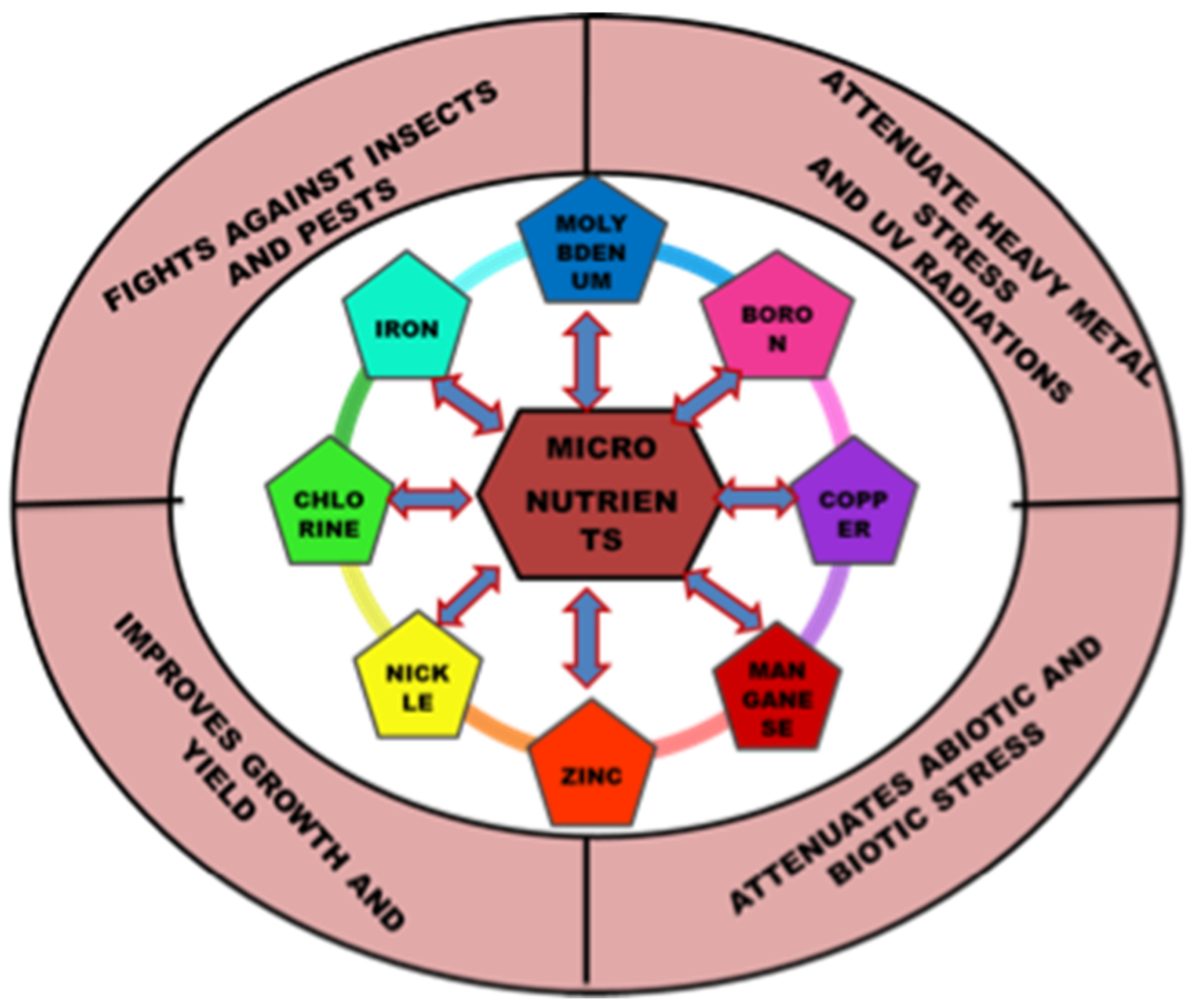
Figure 1. Versatile role of micronutrients in plant’s growth and development.
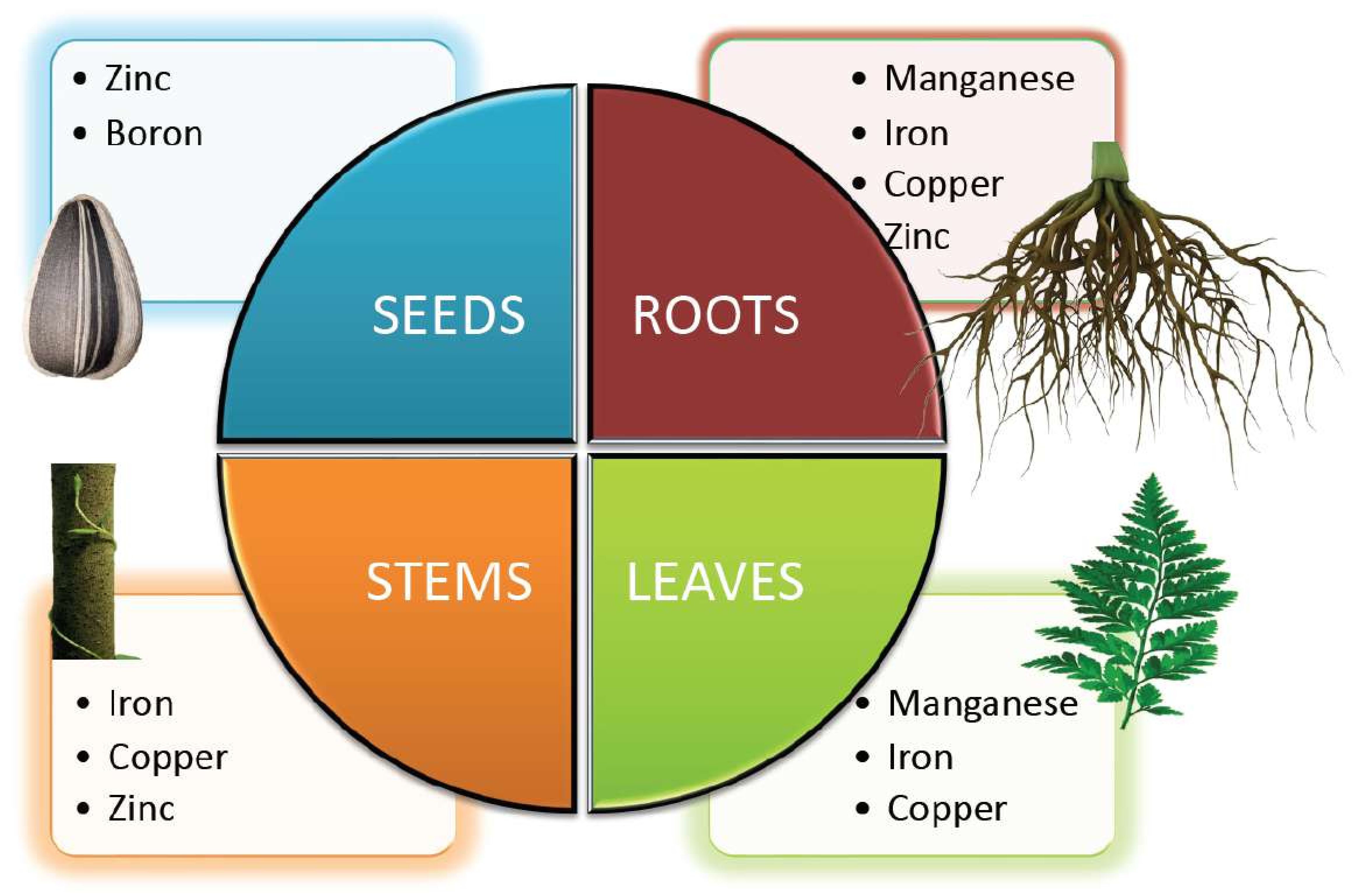
Figure 2. Micronutrients involved in the growth and development of different parts of the plant.
Table 1. Micronutrients, their modes of intake and their concentrations in the leaves.
| S. No. | Micronutrient | Year of Discovery | Ionic Form of Intake | Normal Value (ppm) | Deficient Value (ppm) | Toxic Value (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Boron (B) | Warington (1937) | H2BO3, H2BO3−, HBO32−, BO33− | 10–20 | 5–10 | 50–200 |
| 2 | Chlorine (Cl) | Broyer et al. (1954) | Cl− | 100–500 | Less than 100 | 500–1000 |
| 3 | Copper (Cu) | Lipman and Mackinney (Sachs 1931) | Cu2+ | 5–30 | 2–5 | 100–200 |
| 4 | Iron (Fe) | Sachs (1860) | Fe2+, Fe3+ | 100–500 | Less than 50 | More than 500 |
| 5 | Manganese (Mn) | Mchargue (1922) | Mn2+ | 20–300 | 15–20 | 300–500 |
| 6 | Molybdenum (Mo) | Arnon and Stout (1939) | MoO42− | 0.1–2.0 | 0.03–0.15 | More than 100 |
| 7 | Zinc (Zn) | Sommer and Lipman (1926) | Zn2+ | 27–150 | 10–20 | 100–400 |
Micronutrient depletion develops in the soil as a result of farming techniques, such as intensive farming, monocultures, and acid soil liming, which affect the plants in various ways (Table 2, Figure 3). When nutrient demand exceeds the rate of supply, the plant frequently switches to alternative metabolic pathways, which are often dependent on limiting micronutrients. A decrease in one micronutrient content might reduce the bioavailability of other nutrients in the soil [6]. Although, in certain cases, plants seem unable to detect a deficit because micronutrient availability is impacted by organic matter content, soil pH, adsorptive surfaces, and other biological, chemical, and physical environmental conditions. Prolonged negligence of micronutrient supplementation and aversion of organic fertilizers are major contributors to micronutrient insufficiency and plants respond to these conditions in a variety of ways, by reprogramming transcriptional and translational modifications [2]. Identifying metal-tolerant genes and/or proteins is the first step in deciphering the pathways linked with micronutrient stress tolerance [7].
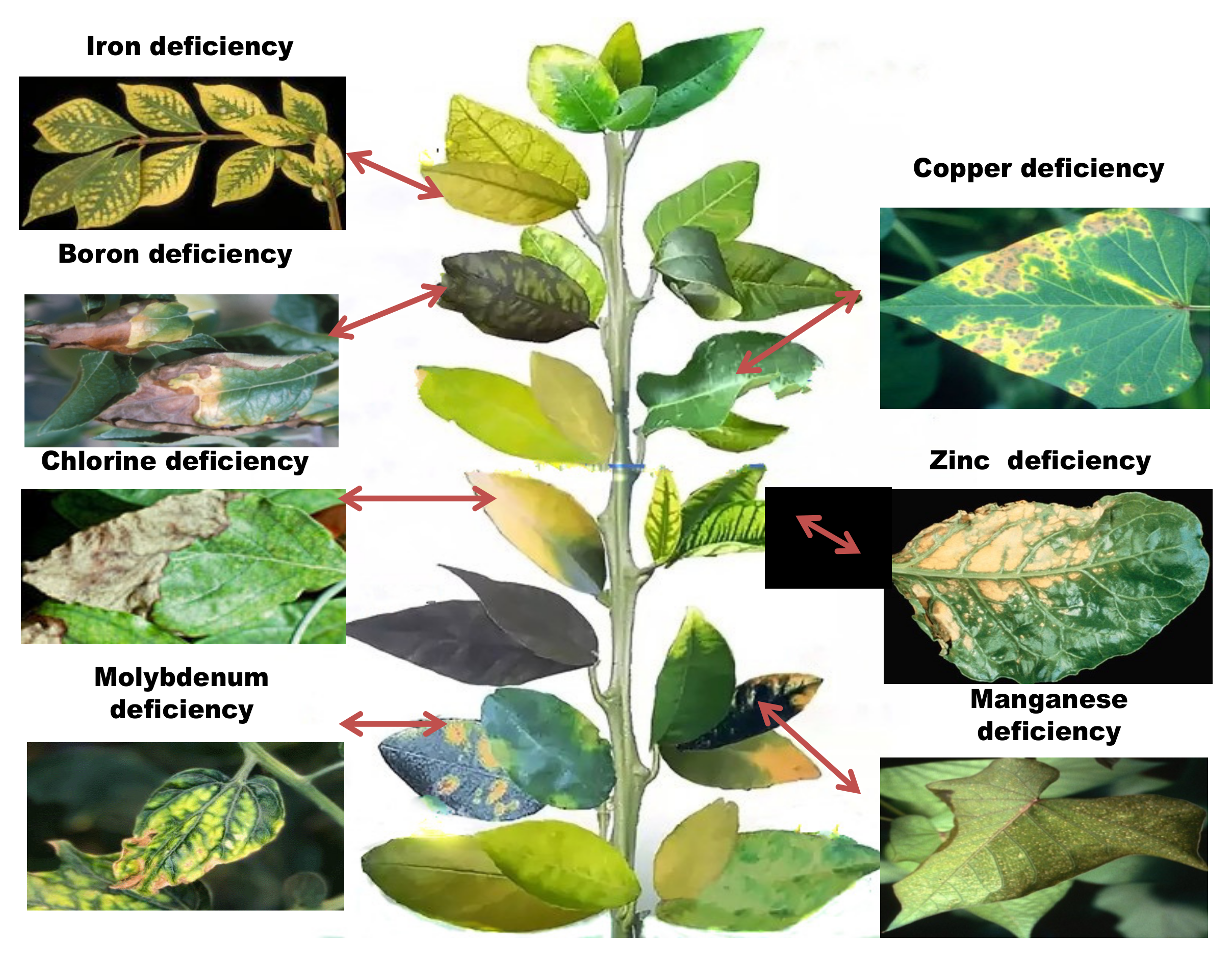
Figure 3. Symptoms of micronutrient deficiencies in plants.
Table 2. Summary of micronutrient functions and deficiency symptoms.
| S.No. | Micronutrients | Representative Constituents/Proteins | Functions | Symptoms of Deficiency | Probable Cause of Deficiency & Method of Correction | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zinc (Zn) | Cu–Zn superoxide, Peptide deformylase, enzyme carbonic anhydrase (CA), α-Mannosidase, Matrix metalloproteinase alcoholic dehydrogenase, and superoxide dismutase (SOD) |
role in nitrogen metabolism and photosynthesis, controls the concentration of auxin in plants, increases seed viability and seedling vigor, protection against abiotic and biotic stresses | Reduced vigor, chlorotic leaves, white streaks parallel to leaf blade, slow growth, restricted RNA and protein synthesis | Low Zn in soil, high soil pH—lower soil pH, apply foliar spray or add Zn to soil. | [8][9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16] |
| 2 | Copper (Cu) | Plastocyanin Cu-Znsuperoxide, Ascorbate, Cu-metallothionein, biosynthesis oxidase, Mo-cofactor, dismutase, polyphenol or catechol oxidase, tyrosinase, laccase, Cytochrome-C oxidase, Ethylene receptor ascorbic oxidase and Polyphenol oxidase | saves plants from diseases, improves the fertility of male flower, concerned with the oxidation of iron in plants | Leaf tips dries, break down and dies, ragged leaves, reduced growth | Low soil Cu, high organic matter—apply foliar spray or add Cu to soil | [17][18][19][20][21][22][23][24][25][26] |
| 3 | Iron (Fe) | Aconitase, dismutase, Xanthine dehydrogenase, Ferredoxin, porphyrin NADH, Succinate, Leg hemoglobin, heme and heme enzymes peroxidase oxidase, dehydrogenase, Nitrate reductase oxidoreductases, Thioredoxin reductase, Cytochrome P450, Aldehyde oxidase, Catalase, Nitrite reductase, Lipoxygenase, Alternative oxidase, Fe-superoxide Ferritin and other functional metallic proteins |
Present in haemoglobin of the leguminous root nodules, leg-haemoglobin and is involved in nitrogen fixation as a constituent of ferredoxin | Interveinal, creamy chlorosis on apical leaves, stunted shoots, reduced yield | Waterlogged soil, over fertilized, excess of elements like Mn—spraying plant with iron rich fertilizer, chelated iron powder or blood meal directly to the soil | [27][28][29][30][31][32][33][34][35][36][37][38][39][40][41][42][43][44][45][46] |
| 4 | Manganese (Mn) | Malic enzyme, Mn-superoxide, amidohydrolase, primary component of water-splitting enzyme related to photosystem II, PEP carboxylase, Allantoate, Iso-citrate lyase, dismutase PEP-carboxykinase | Involved in tricarboxylic acid cycle in oxidation and reduction reactions, activates several enzymes such as oxidoreductases, hydrolases and lyase, also autocatalyzes isocitrate dehydrogenase, malic dehydrogenase, glycocyaminase and D-alanyl synthase. | Reduced quality and yield, stunted plants, intervenial chlorosis in leaves, yellow cast in deficient areas. Death of basal leaves, decreased cold hardiness, growth of lateral roots stopped, inhibition of nitrate metabolism. | Low soil Mn, high soil pH due to over liming—lower soil pH, apply foliar spray or add Mn to soil | [47][48][49][50][51][52] |
| 5 | Boron (B) | Rhamnogalacturonan II | increases cell wall thickness and flower production, as well as retention, pollen tube elongation and germination, along with seed and fruit development. It also helps in the translocation of photosynthates. It inhibits IAA oxidation and gives drought tolerance to crops | Thick and leathery old leaves, shoot tip death, rosette leaves with short internodes, excess branching, short, twisted and/or ruptured petioles, vegetables with hollow heart, small and deformed/no fruits with cork spots chlorosis, stubby roots, inhibited nitrogen metabolism. | Low soil B especially on sandy soils or light textured soils—apply foliar spray or add B to soil | [53][54][55][56] |
| 6 | Molybdenum (Mo) | nitrogenase, sulphite oxidase, nitrate reductase Aldehyde oxidase and xanthine oxidase/dehydrogenase | aids in the synthesis of ascorbic acid, formation of pollens and anthers, acts as a remedy to excessive copper, manganese and zinc | stunted growth with twisted stems, leaves turning pale green, necrotic area in leaves along the mid rib between veins and along leaf edges | Low soil pH, low Mo content in soil—inoculate seed with Mo, apply foliar spray or add Mo to soil | [33][34][57][58] |
| 7 | Chlorine (Cl) | Oxygen-evolving complex Seismonastic movement | activates enzymes that are involved in starch utilization which affects germination and energy transfer. Inmoisture-stress conditions chlorine helps in the movement of water into cells and maintenance of that water. Chlorine also controls the opening and closing of stomata on leaf surfaces | stunted/restricted growth, stubby roots, interveinal chlorosis, non-succulent tissue, wilting | Low soil Cl especially in soils subjected to leaching—apply Cl containing fertilizer | [55][59] |
Micronutrient toxicity also leads to various phenotypic, as well as genotypic, changes in the plants (Table 3). When the internal quantity of the micronutrients surpasses the threshold, they cause phytotoxicity. To deal with the scenario, a plant develops a set of tactics at both the proteomic and genetic levels (Table 4 and Table 5). Plants with tolerance to heavy metals have also been examined for proteomic alterations, revealing one more field of molecular application and its regulation [60]. Some plants respond to nutrient toxicity by increasing nutrient efflux and activating detoxifying pathways, whereas others can tolerate high concentrations of certain micronutrients because they have developed systems to store these and utilize them for defensive functions (Figure 4).
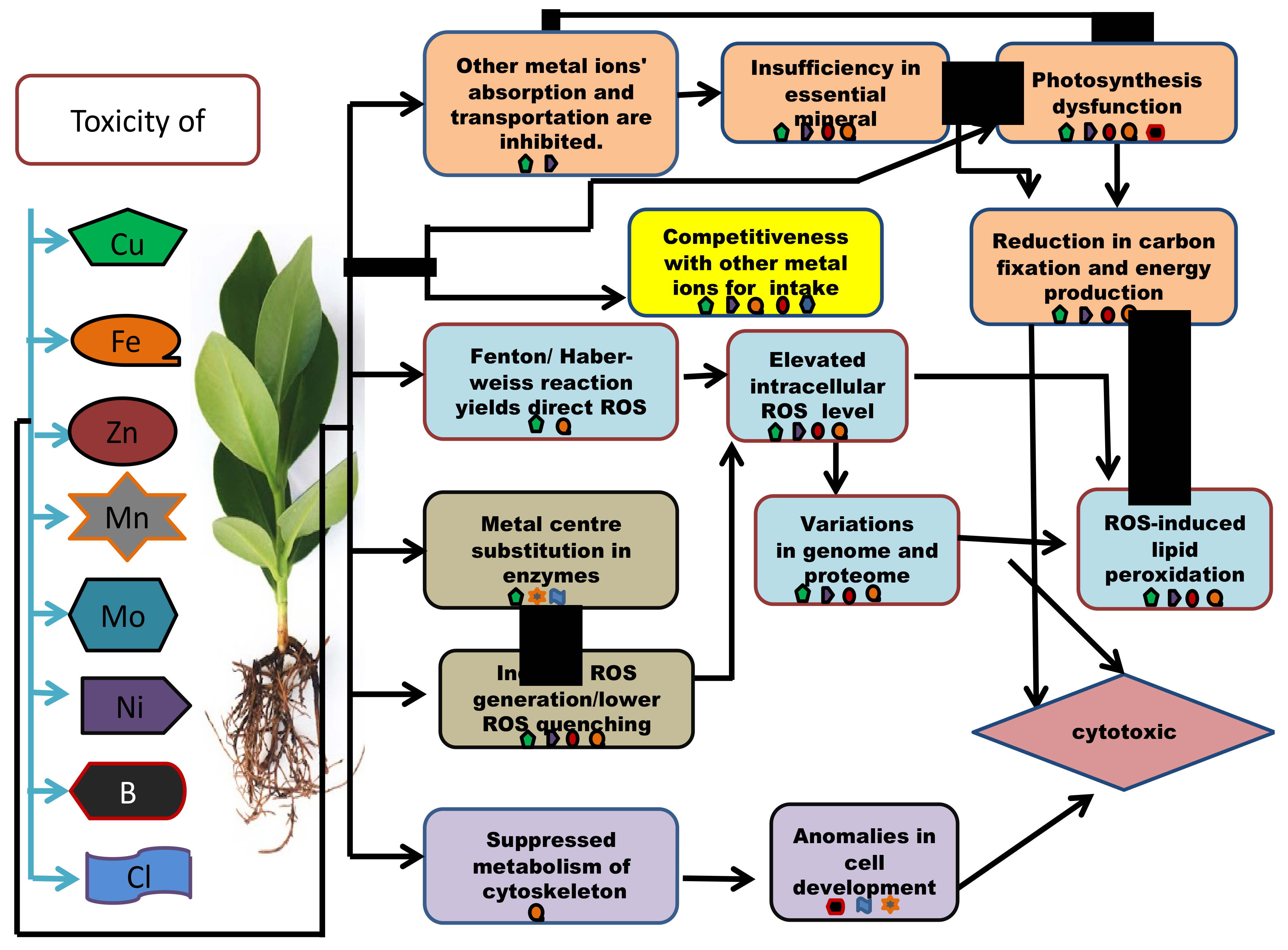
Figure 4. An outline presenting the molecular and the biochemical mechanisms involved in micronutrient cytotoxicity in plants.
Table 3. Micronutrient toxicity.
| S. No. | Micronutrients | Type | Symptoms of Excess Usage | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zinc (Zn) | Metal | Inhibited root growth, young leaf chlorosis, interveinal mild chlorosis in young leaves starting from base and spread towards apex followed by reddish brown coloration, rolling of leaves | [61] |
| 2 | Copper (Cu) | Metal | Reduced vigor, inhibited root growth/root damage, older leaves develop orange or pink coloration followed by severe rolling of leaf margins due to loss in turgidity | |
| 3 | Iron (Fe) | Metal | Reduced yield, bronzing and stippling of leaves, and, in some plants, acid is secreted from the roots | |
| 4 | Manganese (Mn) | Metal | Tissue injury, leaf sheath and lower parts of stem in cereal normally consist of minute brown spots, legumes develop brown or purple spots over leaf margin, deficiency symptoms of other nutrients | |
| 5 | Boron (B) | Metalloid | Toxicity results in dark brown speckles or necrosis on the edge of older leaves, cupped and wrinkled young leaves | |
| 6 | Molybdenum (Mo) | Metal | Leaf malformation, tints of golden yellow or blue color in leaves | |
| 7 | Chlorine (Cl) | Non metal | Death of leaf margin, leaves are reduced in size and number, have bronze or yellow coloration with brown or scorched leaf margins. |
Table 4. Proteomic response of plant to micronutrient stress.
| Metal | Plant Species | Plant Part | Extraction Method | Protein Name | Function | Regulation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boron (B) | Citrus grandis | Root | iTRAQ | Alcohol dehydrogenase 1 | Energy metabolism | Down | [62] |
| Serine/arginine- rich 22 | Nucleic acid metabolic process | Down | |||||
| Clathrin light chain protein | Cellular cytoskeleton and transport | Up | |||||
| Peroxiredoxin IIF | Cellular response to stress | Down | |||||
| Phospholipase C2 | Signal transduction | Down | |||||
| Arabidopsis thaliana | Leaf | 2-DE, LC-MS/MS | Rubisco activase | Photosynthesis | Up | [63] | |
| Actin 7 | Metabolism | Down | |||||
| Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase | Energy metabolism | Up | |||||
| Glycolate oxidase | Photosynthesis | Down | |||||
| Coppe (Cu) | Sorghum bicolor | Leaf | 2-DE, MALDI-TOF MS | Thymidine kinase | Protein translation and synthesis | Down | [64] |
| Thaumatin-like protein | Stress and defense | Up | |||||
| Maturase K | Growth and development | Down | |||||
| Alcohol dehydrogenase | Oxidation– reduction process | Up | |||||
| Oryza sativa | Root | 2-DE, MALDI-TOF MS | Putative peroxidase | Anti-oxidation and detoxification | Up | [65] | |
| Putative cold shock protein-1 | Transcriptional regulation | Up | |||||
| Putative elongationfactor EF-2 | Protein synthesis | Down | |||||
| Glutamine synthetase shoot isozyme | Amino acid synthesis | Down | |||||
| Allium cepa | Root | 2-DE, MALDI-TOF MS | Glutaredoxin | Defense | Up | [66] | |
| Ran-binding protein 1 | Protein synthesis | Down | |||||
| Cinnamoyl-Co-A-reductase 1 | Cell wall synthesis | Down | |||||
| Proliferation-associated 2 g4 | Cell cycle and DNA replication | Up | |||||
| Iron (Fe) | Arabidopsis thaliana | Root | Itraq, LC-MS | Oxidoreductase | Hormone metabolism | Up | [67] |
| WAKL4, WAK- like receptor- like kinase | Signaling | Up | |||||
| FRO3, ferric chelate reductase 3 | Metal handling | Up | |||||
| SAPX, Stromal ascorbate peroxidase | Redox | Down | |||||
| IRT3, Iron regulated transporter3 | transport | Down | |||||
| Zea may | Root | LC-MS/MS | Aquaporin PIP2-2 | Transport proteins | Down | [68] | |
| Gibberellin receptor GID1L2 | Signaling proteins | Down | |||||
| Aldolase | Metabolism | Up | |||||
| Actin-2 | Cytoskeleton | Down | |||||
| Callreticulin 2 | Protein folding | Up | |||||
| Cucumis sativus | Root | 2-DE, ESI-LC-MS | Phosphoglycerate kinase | Glycolysis | Up | [69] | |
| Malate dehydrogenase | Carbohydrate-related metabolism | Up | |||||
| Alanine aminotransferase | Nitrogen-related metabolism | Up | |||||
| Xylan 1,4-beta-xylosidase | Metabolism of sucrose | Down | |||||
| Manganese (Mn) | Citrus grandis | Root | 2-DE, MALDI-TOF MS, LTQ-ESI-MS/MS | Acetohydroxyacid isomeroreductase | Protein metabolism | Down | [70] |
| Maturase K | Nucleic acid metabolism | Up | |||||
| Alcohol dehydrogenase | Carbohydrate metabolism | Up | |||||
| Iron- sUperoxide dismutase | Stress response | Down | |||||
| Valosin- containing protein | Cell transport | Down | |||||
| Zinc (Zn) | Lactuca sativa | Leaf | LC-MS/MS, MALDI-TOF | MPBQ/MSBQ transferase | Photosynthesis | Up | [71] |
| Cytosolic fructose-1,6-bisphosphate | Energy metabolism | Up | |||||
| Putative cellulose synthase | Cell wall metabolism | Down | |||||
| Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase | Phenylpropanoids biosynthesis | Down |
Table 5. Examples of genomic responses of plants to nutritional stress.
| Metals | Plant Species | Tissue | Method of Identification | Gene | Functions | Regulation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boron (B) | Arabidopsis thaliana | Root | qRT-PCR | SHB1/HY1 | B-tolerance | Up | [72] |
| Oryza sativa | Root | Microarray, qRT-PCR | LOC_Os08g30740 | ABC transporter | Down | [73] | |
| LOC_Os10g30156 | Starch synthase | Down | |||||
| LOC_Os10g30080 | Xylosyltransferase | Down | |||||
| Citrus sinensis | Leaf | Illumina sequencing, qRT-PCR | Ciclev10017846m | Ubiquitin-protein ligase activity | Down | [74] | |
| Ciclev 10012377m | Transcription factor | Up | |||||
| Ciclev 10009779 m | Blue copper protein | Up | |||||
| Zinc (Zn) | Arabidopsis thaliana | Whole plant | qRT-PCR | PDR8 | Phytochelatin synthesis | Up | [75] |
| ABCCI | Metabolism | Down | |||||
| Iron (Fe) | Citrus sinensis | Whole plant | qRT-PCR | Cs3g19420 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor | Up | [76] |
| Cs4g12540 | Ethylene synthesis | Down | |||||
| Cs9g02930 | Flavone synthase | Down | |||||
| Arabidopsis thaliana | Root | qRT-PCR | FRO2 | Iron homeostasis | Up | [77] | |
| Manganese (Mn) | Arabidopsis thaliana | Root | qRT-PCR and RNA sequencing | AT5G05960 | Bifunctional inhibitor | Down | [78] |
| AT4G39940 | Glucosinolate | Up | |||||
| AT1G15820 | metabolism Photosynthesis | Up | |||||
| Citrus sinensis | Leaf | cDNA-AFLP and qRT-PCR | TDF #065-1 | Energy metabolism | Up | [79] | |
| TDF #073-1 | Cell transport | Down | |||||
| TDF #103-2 | Stress responses | Down | |||||
| Copper (Cu) | Arabidopsis thaliana | Whole plant | qRT-PCR | OsLAC10 | Laccase activity | Up | [80] |
| AtLAC11 | Lignin biosynthesis | Up | |||||
| Oryza sativa | Whole plant | Western blotting, qRT-PCR | OsHMA4 | Copper accumulation | Down | [74] |
Balancing nutritional stressors leads to a multi-genetic response that causes several changes in proteins and genes, which has a direct impact on nearly all biological activities in a live cell. Proteomic and genomic methods can, thus, be instrumental in identifying molecular responses to nutritional stress [2].
2. Molecular Approaches for Understanding Micronutrient Stress Mechanisms in Plants
Micronutrient insufficiency and toxicity might be detected using both proteomic and genomic investigations [6]. The distribution of micronutrients all throughout the soil profile influences their availability to plants. Plants adapt dynamically to maintain nutrient supply and demand in the appropriate range. Proteomics is a popular molecular method for defining full proteomes at the organelle, cell, or tissue level. It is also helpful for comparing proteins under various adverse environmental conditions [81]. Sub-proteome analysis of nutrient deficit plants is also becoming popular, which includes analysis of apoplastic fluids, root plasma membrane, microsomal shoot fractions, phloem saps detergent-resistant membranes, thylakoid membranes and root hairs [82]. Proteins are the key molecules involved in several biochemical processes, and, as a result, a thorough understanding of stress induced genomic and proteomic changes aids in deeper understanding of the stress induced pathways. Changes in proteomic expressions are correlated with changes in the gene, transcriptome and metabolism levels. However, alterations at the transcriptional level may not always correspond to changes at the proteomic level. Protein expression is regulated not just at the transcriptional level, but also at the translational and post-translational stages, despite the perception of reciprocity between mRNA and protein [83]. As a result, information gathered at the translational and post-translational levels can provide more insight into protein responses, their modifications and functional relationships than genome-based predictions can provide. As proteins act as direct mediators of response, examining these alterations at the proteome level is critical [84]. These variations are reflected in the proteome compositions, hence proteomic investigations might be useful in identifying important protein components. These could be used as possible biomarkers in the underlying process. Current proteomic investigations have mostly focused on detecting quantitative changes and have relied on comparative proteomic techniques that include two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) followed by mass spectrometry analysis (MS). This should lead to a better knowledge of the interactions between various elements, as well as the plant’s responses to environmental conditions at various phases of growth and development.
The genome of a life form is consistent, but the proteome is much more complex because protein expression changes with time and environmental factors [85]. Several researchers used transcriptome analysis to examine the expression patterns of genes in plants under heavy stress throughout the last decade. Gene expression at the mRNA level may be used to determine plant responses to a micronutrient buildup (Table 5) [86]. Furthermore, transcriptional analysis has some drawbacks, such as a lack of correlation between changes in mRNA expression and changes in their related proteins. By combining this method with genotyping technologies, researchers are able to quickly identify genes and networks that coordinate accumulation of elements in plants. A detailed summary of different genomic and proteomic studies carried out using different micronutrients is listed below.
2.1. Boron
Boron deficiency develops as a result of decreased root respiration, advanced cellular transport, rise in antioxidants and ROS-scavenging proteins [87]. Total proteins in boron deficit white lupin (Lupinus albus) root extracts were analyzed using 2D-PAGE, and 128 proteins were determined using mass spectrometry, all of which were involved in cell structure and metabolism, protein metabolism, energy pathways and defense mechanism [88]. ITRAQ study of the roots of Citrus sinensis seedlings subjected to Boron deficiency revealed a rise in level of 164 proteins, as well as reduction in level of 225 proteins [87]. Many of these proteins were involved in signal transduction, cell transport, stress responses, nucleic acid metabolism, protein metabolism, carbohydrate metabolism, biological regulation, lipid metabolism, cytoskeleton metabolism and energy metabolism.
Boron-toxicity-responsive proteins have been identified through MS analysis in research carried out on the leaves of Citrus sinensis and Citrus grandis (B- tolerant citrus species). Toxicity to boron is relatively common in alkaline and saline soils. Boron toxicity increases the amount of PSI type III CAB in barley leaves [89]. According to the 2D-PAGE research of boron toxicity-responsive proteome in oranges, it was hypothesized energy metabolism and photosynthesis might have resulted in increased CO2 absorption and, hence, resulted in a better continuation of energy balance [90]. Proteins associated to ROS-scavengers were highly accumulated in Boron-toxic C. grandis compared to C. sinensis to overcome oxidative stress, according to the analysis of root samples [91]. In a separate study, root systems of these citrus species were tested to study the toxicity of boron. In both species, there were 44 up- and 66 down-regulated genes, with Root Hair Defective 3 expressing in C. sinensis and villin4 being repressed. The discovery of boron-toxic-responsive genes involved in the lipid, nucleic acid and energy metabolisms helped researchers to further understand the mechanisms behind boron-toxicity in citrus species [92]. Using the SHB1/HY1 gene and increased levels of BOR4 expression, researchers established the boron homeostasis concept in Arabidopsis root samples [72]. According to the findings, excessive boron absorption in plants promotes excess transcription of the BOR4 gene, an efflux type boron transporter, encouraging the exclusion of excessive boron. In Oryza sativa, the genetic diversity linked with boron tolerance was investigated by looking at genes involved in biochemical binding, transport, transcriptional control, and redox homeostasis [73].
2.2. Chlorine
The majority of soils are not chlorine deficit except for sandy soils or soil covering heavy rainfall areas. Reduced leaf surface area, withering of the plant, and limited, highly branching root systems are some of the most common symptoms associated with chlorine deficiency. Near the leaf’s tip, little patches of pale green chlorotic tissue emerge between the major veins. The old leaves show the first signs of chlorine deficit (Figure 3) [2]. The total chlorine content in the plant is very low. Chlorine accumulation in plants occurs in specific tissues, notably leaves or single cells (for example guard cells), causing toxicity.
In plants, chlorine-anion transporters have been found as homologous genes. They include ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporters, chloride intracellular channel (CLIL) and nucleotide sensitive–chloride conductance regulator protein (ICln) [93]. As proposed by a few researchers with studies on rice (7 members, OsCLC1-7) and Arabidopsis (7 members, AtClCa-g), members of the vast Chloride Channel (CLC) family were found in several organs [94]. They have been reported to encode anion channels/ion transporters that are essential in nitrate homeostasis [95]. Proteins from the CLC family of Arabidopsis were found in a variety of membranes, including the chloroplast membranes (AtClCd and AtClCf) (AtClCe), vacuolar membranes (AtClCa) and Golgi vesicles (AtClCd and AtClCf), and guard cells (AtClCc). AtClCa expression patterns in roots are very significant. They function as a 2NO3 K/1HC exchanger, capable of accumulating nitrate in the vacuole using electrophysiological and genetic approaches in combination. The Cation-Cl-Cotransporters (CCC) proteins of A. thaliana (At CCC) catalyzed the coordinate symport of K+, Na+, and Cl− in Xenopusl aevis oocytes [96]. Recent advances in the identification of novel transporters of Cl− have been reviewed by Li et. al., 2017 [67].
References
- Das, S.K. Role of Micronutrient in Rice Cultivation and Management Strategy in Organic Agriculture—A Reappraisal. Agric. Sci. 2014, 5, 765–769.
- Ali, A.; Bhat, B.A.; Rather, G.A.; Malla, B.A.; Ganie, S.A. Proteomic Studies of Micronutrient Deficiency and Toxicity. In Plant Micronutrients; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 257–284.
- Arigony, A.L.V.; de Oliveira, I.M.; Machado, M.; Bordin, D.L.; Bergter, L.; Prá, D.; Henriques, J.A.P. The Influence of Micronutrients in Cell Culture: A Reflection on Viability and Genomic Stability. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 597282.
- Waraich, E.A.; Ahmad, R.; Ashraf, M.Y. Role of mineral nutrition in alleviation of drought stress in plants. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2011, 5, 764–777.
- Vasu, D.; Singh, S.; Sahu, N.; Tiwary, P.; Chandran, P.; Duraisami, V.; Ramamurthy, V.; Lalitha, M.; Kalaiselvi, B. Assessment of spatial variability of soil properties using geospatial techniques for farm level nutrient management. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 169, 25–34.
- Kerry, R.G.; Mahapatra, G.P.; Patra, S.; Sahoo, S.L.; Pradhan, C.; Padhi, B.K.; Rout, J.R. Proteomic and genomic responses of plants to nutritional stress. BioMetals 2018, 31, 161–187.
- Luo, Z.-B.; Wu, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Lipka, U.; Polle, A. The role of ectomycorrhizas in heavy metal stress tolerance of host plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 108, 47–62.
- Broadley, M.R.; White, P.J.; Hammond, J.P.; Zelko, I.; Lux, A. Zinc in plants. New Phytol. 2007, 173, 677–702.
- Hansch, R.; Mendel, R.R. Physiological functions of mineral micronutrients (Cu, Zn, Mn, Fe, Ni, Mo, B, Cl). Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 259–266.
- Richter, S.; Lamppa, G.K. Structural properties of the chloroplast stromal processing peptidase required for its function in transit peptide removal. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 39497–39502.
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrases—An overview. Cur. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 603–614.
- Zelko, I.N.; Mariani, T.J.; Folz, R.J. Superoxide dismutase multigene family: A comparison of the CuZn-SOD (SOD1), Mn-SOD (SOD2), and EC-SOD (SOD3) gene structures, evolution, and expression. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 33, 337–349.
- Thompson, C.E.; Salzano, F.M.; de Souza, O.N.; Freitas, L.B. Sequence and structural aspects of the functional diversification of plant alcohol dehydrogenases. Gene 2007, 396, 108–115.
- Serero, A.; Giglione, C.; Meinnel, T. Distinctive features of the two classes of eukaryotic peptide deformylases. J Mol. Biol. 2001, 314, 695–708.
- Snaith, S.M.; Levvy, G.A. Alpha-mannosidase as a zinc-dependent enzyme. Nature 1968, 218, 91–92.
- Maidment, J.M.; Moore, D.; Murphy, G.P.; Murphy, G.; Clark, I.M. Matrix metalloproteinase homologues from Arabidopsis thaliana. Expression and activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 34706–34710.
- Pilon, M.; Abdel-Ghany, S.E.; Cohu, C.M.; Gogolin, K.A.; Ye, H. Copper cofactor delivery in plant cells. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006, 9, 1–8.
- Puig, S.; Askeland, E.; Thiele, D.J. Coordinated remodeling of cellular metabolism during iron deficiency through targeted mRNA degradation. Cell 2005, 120, 99–110.
- Yruela, I. Copper in plants: Acquisition, transport and interactions. Funct. Plant Biol. 2009, 36, 409–443.
- Santagostini, L.; Gullotti, M.; De Gioia, L.; Fantucci, P.; Franzini, E.; Marchesini, A.; Monzani, E.; Casella, L. Probing the location of the substrate binding site of ascorbate oxidase near type 1 copper: An investigation through spectroscopic, inhibition and docking studies. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 881–892.
- Marusek, C.M.; Trobaugh, N.M.; Flurkey, W.H.; Inlow, J.K. Comparative analysis of polyphenol oxidase from plant and fungal species. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2006, 100, 108–123.
- Peiffer, W.E.; Ingle, R.T.; Ferguson-Miller, S. Structurally unique plant cytochrome c oxidase isolated from wheat germ, a rich source of plant mitochondrial enzymes. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 8696–8701.
- Jansson, H.; Okvist, M.; Jacobson, F.; Ejdeback, M.; Hansson, O.; Sjolin, L. The crystal structure of the spinach plastocyanin double mutant G8D/L12E gives insight into its low reactivity towards photosystem 1 and cytochrome f. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2003, 1607, 203–210.
- Domenech, J.; Palacios, O.; Villarreal, L.; Gonzalez-Duarte, P.; Capdevila, M.; Atrian, S. MTO: The second member of a Drosophila dual copper-thionein system. FEBS Lett. 2003, 533, 72–78.
- Rodriguez, F.I.; Esch, J.J.; Hall, A.E.; Binder, B.M.; Schaller, G.E.; Bleecker, A.B. A copper cofactor for the ethylene receptor ETR1 from Arabidopsis. Science 1999, 283, 996–998.
- Kuper, J.; Llamas, A.; Hecht, H.J.; Mendel, R.R.; Schwarz, G. Structure of the molybdopterin-bound Cnx1G domain links molybdenum and copper metabolism. Nature 2004, 430, 803–806.
- Jeong, J.; Connolly, E.L. Iron uptake mechanisms in plants: Functions of the FRO family of ferric reductases. Plant Sci. 2009, 176, 709–714.
- Adamski, J.M.; Danieloski, R.; Deuner, S.; Braga, E.J.; de Castro, L.A.; Peters, J.A. Responses to excess iron in sweet potato: Impacts on growth, enzyme activities, mineral concentrations, and anatomy. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2012, 34, 1827–1836.
- Moeder, W.; Del Pozo, O.; Navarre, D.A.; Martin, G.B.; Klessig, D.F. Aconitase plays a role in regulating resistance to oxidative stress and cell death in Arabidopsis and Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 63, 273–287.
- Figueroa, P.; Leon, G.; Elorza, A.; Holuigue, L.; Araya, A.; Jordana, X. The four subunits of mitochondrial respiratory complex II are encoded by multiple nuclear genes and targeted to mitochondria in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 50, 725–734.
- Rasmusson, A.G.; Geisler, D.A.; Moller, I.M. The multiplicity of dehydrogenases in the electron transport chain of plant mitochondria. Mitochondrion 2008, 8, 47–60.
- Dai, S.; Friemann, R.; Glauser, D.A.; Bourquin, F.; Manieri, W.; Schurmann, P.; Eklund, H. Structural snapshots along the reaction pathway of ferredoxin-thioredoxin reductase. Nature 2007, 448, 92–96.
- Hesberg, C.; Hansch, R.; Mendel, R.R.; Bittner, F. Tandem orientation of duplicated xanthine dehydrogenase genes from Arabidopsis thaliana: Differential gene expression and enzyme activities. J Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 13547–13554.
- Koshiba, T.; Saito, E.; Ono, N.; Yamamoto, N.; Sato, M. Purification and properties of flavin- and molybdenum-containing aldehyde oxidase from coleoptiles of maize. Plant Physiol. 1996, 110, 781–789.
- Voss, I.; Koelmann, M.; Wojtera, J.; Holtgrefe, S.; Kitzmann, C.; Backhausen, J.E.; Scheibe, R. Knockout of major leaf ferredoxin reveals new redox-regulatory adaptations in Arabidopsis thaliana. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 133, 584–598.
- Maschner, H. Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants; Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1995; pp. 313–404.
- Zamocky, M.; Regelsberger, G.; Jakopitsch, C.; Obinger, C. The molecular peculiarities of catalase-peroxidases. FEBS Lett. 2001, 492, 177–182.
- De Paula, J.C.; Peiffer, W.E.; Ingle, R.T.; Centeno, J.A.; Ferguson-Miller, S.; Babcock, G.T. Hemes a and a3 environments of plant cytochrome c oxidase. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 8702–8706.
- Campbell, W.H. Nitrate reductase structure, function and regulation: Bridging the gap between biochemistry and physiology. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol Plant Mol. Biol. 1999, 50, 277–303.
- Swamy, U.; Wang, M.; Tripathy, J.N.; Kim, S.K.; Hirasawa, M.; Knaff, D.B.; Allen, J.P. Structure of spinach nitrite reductase: Implications for multi-electron reactions by the iron–sulfur: Siroheme cofactor. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 16054–16063.
- Li, L.; Chang, Z.; Pan, Z.; Fu, Z.Q.; Wang, X. Modes of heme binding and substrate access for cytochrome P450 CYP74A revealed by crystal structures of allene oxide synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13883–13888.
- Garrocho-Villegas, V.; Gopalasubramaniam, S.K.; Arredondo- Peter, R. Plant hemoglobins: What we know six decades after their discovery. Gene 2007, 398, 78–85.
- Munoz, I.G.; Moran, J.F.; Becana, M.; Montoya, G. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of the eukaryotic iron superoxide dismutase (FeSOD) from Vigna unguiculata. Acta Crystallogr. D 2003, 59, 1070–1072.
- Peariso, A.M.; Nicholson, K.M.; Benjamin Jones, R.; Green-Church, K.B.; Funk, M.O. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry of soybean lipoxygenases: N-terminal acetylation, chemical modification, and solution conformation. Proteins 2008, 70, 650–658.
- Moore, A.L.; Albury, M.S.; Crichton, P.G.; Affourtit, C. Function of the alternative oxidase: Is it still a scavenger? Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 478–481.
- Harrison, P.M.; Arosio, P. The ferritins: Molecular properties, iron storage function and cellular regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1996, 1275, 161–203.
- Burnell, J.N. The biochemistry of manganese in plants. In Manganese in Soils and Plants; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988; pp. 125–137.
- Millaleo, R.; Reyes-Díaz, M.; Ivanov, A.G.; Mora, M.L.; Alberdi, M. Manganese as essential and toxic element for plants: Transport, accumulation and resistance mechanisms. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2010, 10, 470–481.
- Marschner, H. Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants; Academic Press: London, UK, 1995; p. 889.
- Werner, A.K.; Sparkes, I.A.; Romeis, T.; Witte, C.P. Identification, biochemical characterization, and subcellular localization of allantoate amidohydrolases from Arabidopsis and soybean. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 418–430.
- Khan, A.S.; Van Driessche, E.; Kanarek, L.; Beeckmans, S. The purification and physicochemical characterization of maize (Zea mays L.) isocitrate lyase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1992, 297, 9–18.
- Holyoak, T.; Sullivan, S.M.; Nowak, T. Structural insights into the mechanism of PEPCK catalysis. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 8254–8263.
- Reguera, M.; Wimmer, M.; Bustos, P.; Goldbach, H.E.; Bolanos, L.; Bonilla, I. Ligands of boron in Pisum sativum nodules are involved in regulation of oxygen concentration and rhizobial infection. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 1039–1048.
- Matas, M.A.; Gonzalez-Fontes, A.; Camacho-Cristobal, J.J. Effect of boron supply on nitrate concentration and its reduction in roots and leaves of tobacco plants. Biol. Plant. 2009, 53, 120–124.
- Moran, N. Osmoregulation of leaf motor cells. FEBS Letter. 2007, 581, 2337–2347.
- Kohorn, B.D. Plasma membrane-cell wall contacts. Plant Physiol. 2000, 124, 31–38.
- Schwarz, G.; Mendel, R.R. Molybdenum cofactor biosynthesis and molybdenum enzymes. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 623–647.
- Lang, C.; Popko, J.; Wirtz, M.; Hell, R.; Herschbach, C.; Kreuzwieser, J.; Rennenberg, H.; Mendel, R.R.; Hansch, R. Sulphite oxidase as key enzyme for protecting plants against Sulphur dioxide. Plant Cell Environ. 2007, 30, 447–455.
- Kusunoki, M. Mono-manganese mechanism of the photosystem II water splitting reaction by a unique Mn4Ca cluster. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2007, 1767, 484–492.
- Hossain, Z.; Komatsu, S. Contribution of proteomic studies towards understanding plant heavy metal stress response. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 3, 310.
- Kumar, A.; Choudhary, A.K.; Pooniya, V.; Suri, V.K.; Singh, U. Soil Factors Associated with Micronutrient Acquisition in Crops-Biofortification Perspective. In Biofortification of Food Crops; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 159–176.
- Yang, L.T.; Lu, Y.B.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, P.; Chen, L.S. Proteomicprofile of Citrus grandis roots under long-term boron-deficiencyrevealed by iTRAQ. Trees 2016, 30, 1057–1071.
- Chen, M.; Mishra, S.; Heckathorna, S.; Frantzb, J.M.; Krause, C. Proteomic analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana leaves inresponse to acute boron deficiency and toxicity revealseffects on photosynthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, andprotein synthesis. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 235–242.
- Roy, S.K.; Kwon, S.J.; Cho, S.W.; Kamal, A.H.M.; Kim, S.W.; Sarker, K.; Oh, M.W.; Lee, M.S.; Chung, K.Y.; Xin, Z.; et al. Leaf proteome characterization in the context of physiological and morphological changes in response to copper stress in sorghum. Biometals 2016, 29, 495–513.
- Chen, C.; Song, Y.; Zhuang, K.; Li, L.; Xia, Y.; Shen, Z. Proteomic analysis of copperbinding proteins in excess copper-stressed roots of two rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties with different Cu tolerances. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125367.
- Qin, R.; Ning, C.; Bjorn, L.O.; Li, S. Proteomic analysis of Allium cepa var. agrogarum L. roots under copper stress. Plant Soil 2015, 401, 197–212.
- Li, W.; Lan, P. The understanding of the plant iron deficiency responses in strategy I plants and the role of ethylene in this process by omic approaches. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1–15.
- Hopff, D.; Wienkoopb, S.; Luthjea, S. The plasma membrane proteome of maize roots grown under low and high iron conditions. J. Proteom. 2013, 91, 605–618.
- Donnini, S.; Prinsi, B.; Negri, A.S.; Vigani, G.; Espen, L.; Zocchi, G. Proteomic characterization of iron deficiency responses in Cucumis sativus L. roots. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 268.
- You, X.; Yang, L.T.; Lu, Y.B.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.Q.; Chen, L.A. Proteomic changes of citrus roots in response to long-term manganese toxicity. Trees 2014, 28, 1383–1399.
- Elucini, L.; Ebernardo, L. Comparison of proteome response to saline and zinc stress in lettuce. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 240.
- Lv, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.-Z.; Li, P.; Chen, Y.-L.; Du, J.; He, Y.-K.; Bao, F. SHB1/HY1 Alleviates Excess Boron Stress by Increasing BOR4 Expression Level and Maintaining Boron Homeostasis in Arabidopsis Roots. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 790.
- Neto, J.B.D.A.; Hurtado-Perez, M.C.; Wimmer, M.A.; Frei, M. Genetic factors underlying boron toxicity tolerance in rice: Genome-wide association study and transcriptomic analysis. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 687–700.
- Huang, X.; Deng, F.; Yamaji, N.; Pinson, S.R.; Fujii-Kashino, M.; Danku, J.; Douglas, A.; Guerinot, M.L.; Salt, D.E.; Ma, J.F. A heavy metal P-type ATPase OsHMA4 prevents copper accumulation in rice grain. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12138.
- Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Yan, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Fan, T.; Ren, Y.; Tang, X.; Xiao, F.; Liu, Y.; et al. Zinc-Finger Transcription Factor ZAT6 Positively Regulates Cadmium Tolerance through the Glutathione-Dependent Pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 707–719.
- Fu, L.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Du, W.; Pan, Z.; Peng, S. Physiological and Transcriptional Changes of Three Citrus Rootstock Seedlings under Iron Deficiency. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1104.
- Satbhai, S.B.; Setzer, C.; Freynschlag, F.; Slovak, R.; Kerdaffrec, E.; Busch, W. Natural allelic variation of FRO2 modulates Arabidopsis root growth under iron deficiency. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15603.
- Celma, J.R.; Tsai, Y.H.; Wen, T.N.; Wu, Y.C.; Curie, C.; Schmidt, W. Systems-wide analysis of manganese deficiencyinducedchanges in gene activity of Arabidopsis roots. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35846.
- Zhou, C.P.; Qi, Y.P.; You, X.; Yang, L.T.; Guo, P.; Ye, X.; Zhou, X.X.; Ke, F.J.; Chen, L.S. Leaf cDNA-AFLP analysis of two citrus species differing in manganese tolerance in response to long-term manganese-toxicity. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 621.
- Liu, C.; Cheng, Y.-J.; Wang, J.-W.; Weigel, D. Prominent topologically associated domains differentiate global chromatin packing in rice from Arab. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 742–748.
- Komatsu, S.; Hossain, Z. Preface—Plant Proteomic Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 88.
- Gutierrez-Carbonell, E.; Takahashi, D.; Lüthje, S.; González-Reyes, J.A.; Mongrand, S.; Contreras-Moreira, B.; Abadía, A.; Uemura, M.; Abadía, J.; López-Millán, A.F. A Shotgun Proteomic Approach Reveals That Fe Deficiency Causes Marked Changes in the Protein Profiles of Plasma Membrane and Detergent-Resistant Microdomain Preparations from Beta vulgaris Roots. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 2510–2524.
- Koussounadis, A.; Langdon, S.P.; Um, I.H.; Harrison, D.; Smith, V.A. Relationship between differentially expressed mRNA and mRNA-protein correlations in a xenograft model system. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, srep10775.
- Tamburino, R.; Vitale, M.; Ruggiero, A.; Sassi, M.; Sannino, L.; Arena, S.; Costa, A.; Batelli, G.; Zambrano, N.; Scaloni, A.; et al. Chloroplast proteome response to drought stress and recovery in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 40.
- Holman, J.D.; Dasari, S.; Tabb, D.L. Informatics of protein and posttranslational modification detection via shotgun proteomics. In Proteomics for Biomarker Discovery; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 167–179.
- Mourato, M.P.; Moreira, I.N.; Leitão, I.; Pinto, F.R.; Sales, J.R.; Martins, L.L. Effect of Heavy Metals in Plants of the Genus Brassica. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 17975–17998.
- Yang, J.; Li, M.; Xie, X.; Han, G.; Sui, N.; Wang, B. Deficiency of phytochrome B alleviates chilling-induced photoinhibition in rice. Am. J. Bot. 2013, 100, 1860–1870.
- Shah, A.; Wu, X.; Ullah, A.; Fahad, S.; Muhammad, R.; Yan, L.; Jiang, C. Deficiency and toxicity of boron: Alterations in growth, oxidative damage and uptake by citrange orange plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 575–582.
- Atik, A.E.; Bozdağ, G.O.; Akinci, E.; Kaya, A.; Koç, A.; Yalçin, T.; Karakaya, H. Proteomic changes during boron tolerance in barley (Hordeum vulgare) and the role of vacuolar proton-translocating ATPase subunit E. Turk. J. Bot. 2011, 35, 379–388.
- Sang, W.; Huang, Z.-R.; Qi, Y.-P.; Yang, L.-T.; Guo, P.; Chen, L.-S. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis data in support of leaf comparative proteomics of two citrus species differing in boron-tolerance. Data Brief 2015, 4, 44–46.
- Sang, W.; Huang, Z.-R.; Yang, L.-T.; Guo, P.; Ye, X.; Chen, L.-S. Effects of High Toxic Boron Concentration on Protein Profiles in Roots of Two Citrus Species Differing in Boron-Tolerance Revealed by a 2-DE Based MS Approach. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 180.
- Guo, P.; Qi, Y.-P.; Yang, L.-T.; Ye, X.; Huang, J.-H.; Chen, L.-S. Long-Term Boron-Excess-Induced Alterations of Gene Profiles in Roots of Two Citrus Species Differing in Boron-Tolerance Revealed by cDNA-AFLP. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 898.
- Tejada-Jiménez, M.; Galván, A.; Fernández, E.; Llamas, Á. Homeostasis of the micronutrients Ni, Mo and Cl with specific biochemical functions. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 358–363.
- Isayenkov, S.; Isner, J.C.; Maathuis, F.J. Vacuolar ion channels: Roles in plant nutrition and signalling. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1982–1988.
- Demes, E.; Besse, L.; Cubero-Font, P.; Satiat-Jeunemaitre, B.; Thomine, S.; De Angeli, A. Dynamic measurement of cytosolic pH and uncovers the role of the vacuolar transporter AtCLCa in cytosolic pH homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 15343–15353.
- Li, B.; Tester, M.; Gilliham, M. Chloride on the Move. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 236–248.
More
Information
Subjects:
Plant Sciences
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
8.8K
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
27 Sep 2022
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




