Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Maopeng Wu | -- | 1526 | 2022-08-10 08:42:48 | | | |
| 2 | Amina Yu | + 6 word(s) | 1532 | 2022-08-11 03:06:05 | | | | |
| 3 | Amina Yu | Meta information modification | 1532 | 2022-08-12 08:17:13 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Wu, M.; Su, L.; Chen, J.; Duan, X.; Wu, D.; Cheng, Y.; Jiang, Y. Near-Field WPT Technology in UAV Charging. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/26014 (accessed on 07 February 2026).
Wu M, Su L, Chen J, Duan X, Wu D, Cheng Y, et al. Near-Field WPT Technology in UAV Charging. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/26014. Accessed February 07, 2026.
Wu, Maopeng, Lijuan Su, Jianxun Chen, Xiaoli Duan, Donghua Wu, Yan Cheng, Yu Jiang. "Near-Field WPT Technology in UAV Charging" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/26014 (accessed February 07, 2026).
Wu, M., Su, L., Chen, J., Duan, X., Wu, D., Cheng, Y., & Jiang, Y. (2022, August 10). Near-Field WPT Technology in UAV Charging. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/26014
Wu, Maopeng, et al. "Near-Field WPT Technology in UAV Charging." Encyclopedia. Web. 10 August, 2022.
Copy Citation
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) have been widely used in the military and civil fields. However, the battery power is a key factor that restricts the operation range of the UAV. Using wireless power transfer (WPT) technology to power UAVs can improve the endurance of UAVs and enhance their maneuverability and flexibility.
UAV
wireless power transfer
solar-powered UAV
1. Introduction to Near-Field Wireless Power Transfer (WPT) Technologies
Inductively wireless power transfer (IWPT) technology and magnetically coupled resonant wireless power transfer (MCR-WPT) technology are near-field WPT technologies.
IWPT is the most widely researched wireless power transfer technology, and the working principle is shown in Figure 1a [1][2]. On the transmitting side, the 50 Hz AC voltage is converted to high-frequency AC after rectification and high-frequency inversion, which is sent to the transmitting coil after impedance compensation to establish a high-frequency magnetic field. On the receiving side, the energy received by the receiving coil is used for the electrical load after impedance compensation and electric energy processing. In IWPT technology, the transmitting coil and receiving coil are similar to loosely coupled transformers. The IWPT technology can achieve high output power, even up to tens of kW. However, the transmission distance of IWPT technology is small, generally not exceeding the diameter of the coil.
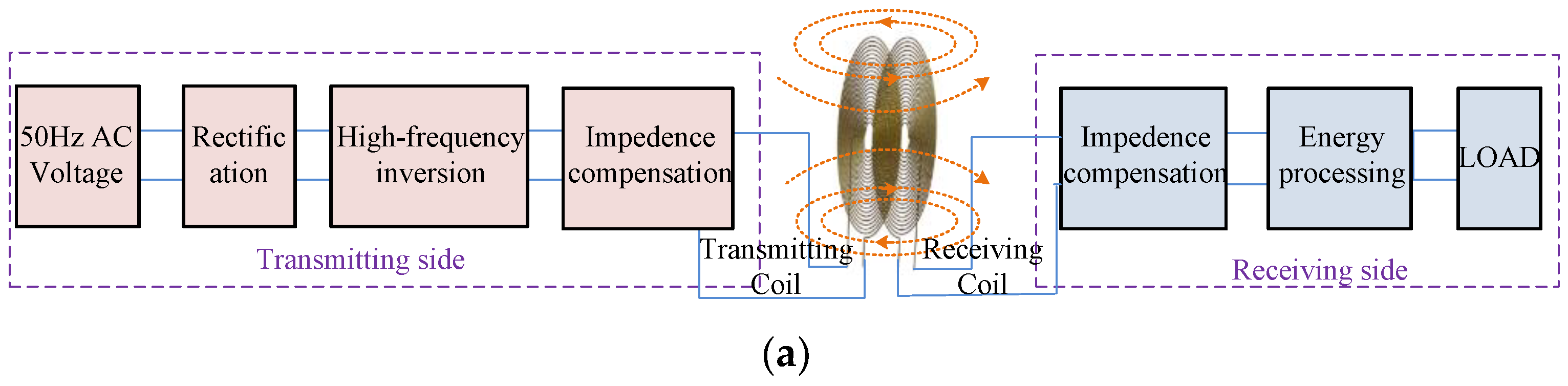
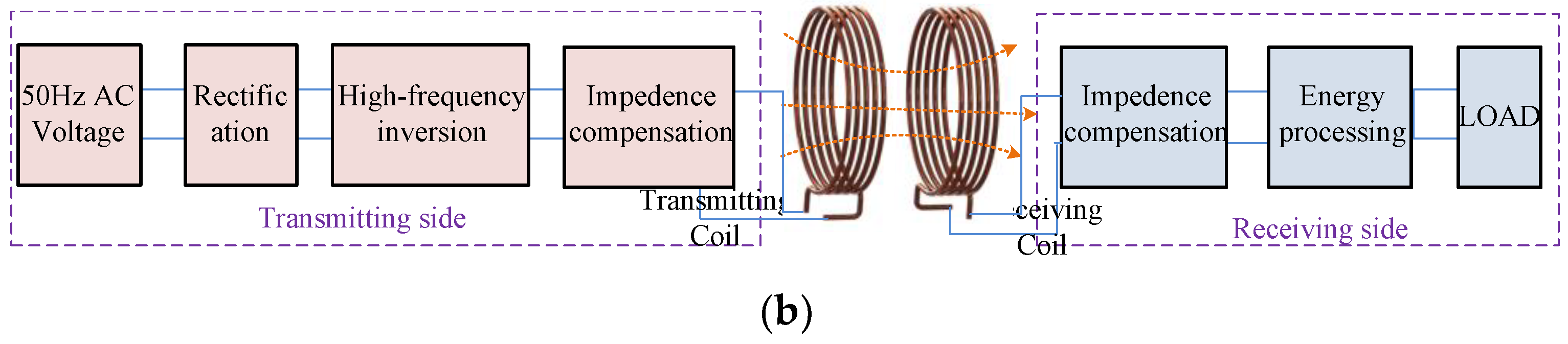
Figure 1. Basic composition of IWPT and MCR-WPT technologies: (a) Basic principle of IWPT technology; (b) Basic principle of MCR-WPT technology.
MCR-WPT is also a widely researched wireless power transfer technology, and its working principle is shown in Figure 1b [3][4][5]. On the transmitting side, the 50 Hz AC voltage is converted into high-frequency AC voltage after rectification and high-frequency inversion and sent to the transmitter coil after impedance compensation. The transmitting coil and receiving coil work in a magnetic field-resonant state or a self-resonant state, thereby realizing energy transmission. On the receiving side, the energy received by the receiving coil is used for the electrical load after impedance matching and electric energy processing. The resonant frequency of MCR-WPT technology is much higher than that of IWPT technology, usually MHz, and the transmission distance is also farther than ICPT, up to several meters. In addition, a relay coil may be used to achieve a longer transmission distance in MCR-WPT.
Although IWPT technology and MCR-WPT technology are the most widely researched technologies by scholars, the application of these two technologies in unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) charging, especially in large aircraft charging, has rarely been reported, which is attributed to the limited transmission distance of these two technologies. Currently, most researchers applied these two technologies to powering small types of UAV.
2. Development of Near-Field WPT Technology in UAV Charging
In 2009, MIT researchers developed a Reviray UAV that was capable of staying on a high-voltage power line based on the Defense Research Association′s (DRA) project—Power Line Urban Sentry Plus. The 2.7 kg in-weight UAV took power from the high-voltage line to charge the onboard battery via IWPT technology, and it could fly along the high-voltage power line at a speed of 75 km/h [6].
In 2016, researchers from the University of L′Aquila installed a hollow plane receiving coil on the abdomen of the UAV. Under well-aligned conditions, 70 W output power was achieved with 89% efficiency over a distance of 10 cm, and the operating frequency was 150 kHz [7].
In 2017, researchers from Imperial College London developed an MCR-WPT system for hovering UAVs. On the transmitting side, a class-E power amplifier was used as the transmitting power source, and the operating frequency was 13.56 MHz. On the receiving side, a class-D rectifier and a DC/DC converter were used as the power receiver. The MCR-WPT system achieves wireless charging of hovering UAV with an output power of 21 W at a distance of 10 cm [8].
Researchers from the City University of Hong Kong applied a variable-pitch transmitting coil for efficient wireless power supply to UAV, achieving a power transmission of 170 W at 90% efficiency over a distance of 150 mm, and the system operates at 370 kHz [9].
In 2019, WiBotic, an American company, launched a flat-panel charging platform with WPT technology PowerPad, which could be used to charge the UAV by a corresponding wireless charging module on the drone, and the charging efficiency can reach 85% [10].
Wuhan University designed a dissymmetrical coupling mechanism using for UAV wireless charging. The transmitting coil was composed of three coaxial solenoid coils with different diameters, and the turn number of the receiving coil was 10. The working frequency was 364.44 kHz, and it realized 64.87 W power transmission with an efficiency of 57.94% when the transmission distance was 0.5 m [11].
There are also some other researchers who studied the key issues in using IWPT technology and MCR-WPT technology to charge UAVs with WPT technology, such as coupling mechanism, anti-offset measures, transmitting power supply, high-efficiency transmission methods, and so on [12][13][14][15][16][17]. However, these research results have only conducted theoretical research, simulation research or experiments for the research content, but not completed UAV wireless charging system experiment, which is not further discussed here. According to the research works above, comparisons of near-field WPT technologies used to power UAVs are shown in Table 1. The challenges and prospects of using near-field WPT technologies to power UAVs can be summarized in the following.
Table 1. Comparison of near-field WPT technologies used to power UAV.
| WPT Type | Output Power | Working Frequency | Efficiency | Transmission Distance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IWPT | 70 W | 150 kHz | 89% | 10 cm | [7] |
| MCR-WPT | 21 W | 13.56 MHz | - | 10 cm | [8] |
| IWPT | 170 W | 370 kHz | 90% | 15 cm | [9] |
| IWPT | 67.84 W | 364.44 kHz | 57.94% | 50 cm | [11] |
| MCR-WPT | 10 W | 1 MHz | 83.7% | 10.5 cm | [14] |
| IWPT | 500 W | 100 kHz | 90.8% | 10 cm | [16] |
| IWPT | 20.46 W | 12 kHz | 85.36% | 0 cm | [17] |
3. Challenges of Near-Field WPT Technology in UAV Charging
- (1)
-
As the two most widely researched wireless power transfer technologies, both IWPT and MCR-WPT technologies can transmit several kilowatts or even ten kilowatts of power in consumer electronic or electric vehicle wireless charging. However, there are still many challenges when used for UAV charging as follows;
- (2)
-
The transmission distance is limited. The transmission distance of IWPT technology is generally no more than the diameter of the coil, and the transmission distance of MCR-WPT technology is generally only a few meters, which restricts the application of these two WPT technologies in the aviation field. How to improve the transmission distance to 100 m or even kilometers is the primary problem that restricts the large-scale application of WPT technology in UAV charging;
- (3)
-
The anti-offset problem should be of concern. The flight of an aircraft is a dynamic process, and the landing position is random. For IWPT technology and MCR-WPT technology, the coupling mechanism determines that the transmitting side and the receiving side should be aligned when charging. If the offset between the transmitter and the receiver is too large, the coupling between the transmitter coil and the receiver coil will be weakened, which in turn causes the output voltage to drop and the transmission power to be significantly affected. Therefore, measures should be taken to deal with the offset problem between the transmitting coil and the receiving coil to ensure the coupling coefficient between the transmitter coil and the receiver coil;
- (4)
-
A high-performance coupling mechanism should be designed. The coupling mechanism is an important part of IWPT and MCR-WPT technology. For existing UAVs, the load is often small, and their anti-electromagnetic interference ability is poor. In order to achieve high-power energy transmission, the weight of the traditional coupling mechanism is often relatively large. At the same time, there are a large number of wireless electronic devices in the UAV, and magnetic field coupling may affect the operation of the devices. In order to reduce the weight of the coupling mechanism and ensure the transmission power, the coupling structure should be reasonably optimized to achieve low weight, high transmission power and high anti-electromagnetic interference capability.
4. Prospect of Near-Field WPT Technology in UAV Charging
As an emerging charging method, although MCR-WPT technology and IWPT technology are studied limited, they still have great development prospects in UAV wireless charging. In the future, the following development directions can be considered:
- (1)
-
Unattended and fixed-point autonomous charging of UAV. Charging stations can be set up. When the power of the UAV is low, it automatically navigates to the nearest charging station for autonomous charging. The technology saves labor and enhances charging flexibility as it uses coils for charging, which only need to be aligned and do not need to plug and unplug;
- (2)
-
High-power dynamic wireless charging. Dynamic charging of aircraft can be considered because the transmitting coil and receiving coil are not in contact with WPT technologies. For example, when the aircraft is taxing on the ground, coils can be laid on the ground to dynamically charge the aircraft;
- (3)
-
Wireless charging of rotating devices. There are many rotating devices on the aircraft in which the sensors should be installed to obtain more flight information, such as propellers, rotating blades, etc. Currently, the sensors on these rotating equipment are mainly powered by batteries or slip rings. WPT technology can be used to charge the loads on the rotating equipment since the transmitting side and the receiving side are not in contact;
- (4)
-
Wireless power supplying the equipment inside the aircraft. There are many loads in the aircraft, and some need to be disassembled and installed repeatedly. The existence of the plug makes the equipment wear and tear when plugging and unplugging. Using WPT technology can avoid plugging and unplugging, so it can avoid wear and tear and other hidden problems.
References
- Sheng, X.; Shi, L. An Improved Pulse Density Modulation Strategy Based on Harmonics for ICPT System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 6810–6819.
- Xia, C.; Jia, R.; Wu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhou, Y. Wireless Power and Information Transmission Technology based on Fundamental-harmonic component for Single-channel and Two-coil ICPT System. IET Power Electron. 2019, 12, 2608–2614.
- Xia, C.; Wei, N.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, S.; Li, Z.; Liao, Z. Multifrequency and Multiload MCR-WPT System Using Hybrid Modulation Waves SPWM Control Method. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 12400–12412.
- Huang, X.; Lu, C.; Liu, M. Calculation and analysis of near-field magnetic spiral metamaterials for MCR-WPT application. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 6688–6698.
- Li, S.; Zhou, M.; Chen, X.; Liu, F. Parameters Optimization for Zero-Voltage-Switching Realization in LCCL-LC Compensated MCR WPT Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE PELS Workshop on Emerging Technologies: Wireless Power Transfer (WoW), Seoul, Korea, 15–19 November 2020; pp. 123–128.
- Xiao, L.; Lu, X.; Xu, D.; Tang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhuang, W. UAV Relay in VANETs Against Smart Jamming With Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 4087–4097.
- Campi, T.; Dionisi, F.; Cruciani, S.; De Santis, V.; Feliziani, M.; Maradei, F. Magnetic field levels in drones equipped with Wireless Power Transfer technology. In Proceedings of the 2016 Asia-Pacific International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility (APEMC), Shenzhen, China, 17–21 May 2016; pp. 544–547.
- Aldhaher, S.; Mitcheson, P.D.; Arteaga, J.M.; Kkelis, G.; Yates, D.C. Light-weight wireless power transfer for mid-air charging of drones. In Proceedings of the 2017 11th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EUCAP), Paris, France, 19–24 March 2017; pp. 336–340.
- Ke, D.; Liu, C.; Jiang, C.; Zhao, F. Design of an effective wireless air charging system for electric unmanned aerial vehicles. In Proceedings of the IECON 2017—43rd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Beijing, China, 29 October 2017; pp. 6949–6954.
- Wireless Power Solutions for Robotic Systems|WiBotic|Seattle, WA . Available online: https://www.wibotic.com/ (accessed on 7 September 2019).
- Yang, C.; He, Y.; Qu, H.; Wu, J.; Hou, Z.; Lin, Z.; Cai, C. Analysis, design and implement of asymmetric coupled wireless power transfer systems for unmanned aerial vehicles. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 025206.
- Campi, T.; Cruciani, S.; Maradei, F.; Feliziani, M. Wireless charging system integrated in a small unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) with high tolerance to planar coil misalignment. In Proceedings of the 2019 Joint International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, Sapporo and Asia-Pacific International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, Sapporo, Japan, 3–7 June 2019; pp. 601–604.
- Park, C.; Park, J.; Shin, Y.; Kim, J.; Huh, S.; Kim, D.; Ahn, S. Separated Circular Capacitive Coupler for Reducing Cross-Coupling Capacitance in Drone Wireless Power Transfer System. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2020, 68, 3978–3985.
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, W.; Qiu, D.; Chen, Y. Nonlinear Parity-Time-Symmetric Model for Constant Efficiency Wireless Power Transfer: Application to a Drone-in-Flight Wireless Charging Platform. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 4097–4107.
- Song, K.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Z.; Yang, G.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, C. A High-Efficiency Wireless Power Transfer System for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Considering Carbon Fiber Body. In Proceedings of the 2020 22nd European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Lyon, France, 7–11 September 2020; pp. 1–7.
- Jawad, A.M.; Jawad, H.M.; Nordin, R.; Gharghan, S.K.; Abdullah, N.F.; Abu-Alshaeer, M.J. Wireless Power Transfer With Magnetic Resonator Coupling and Sleep/Active Strategy for a Drone Charging Station in Smart Agriculture. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 139839–139851.
- Cai, C.; Wu, S.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, S. A 500-W Wireless Charging System With Lightweight Pick-Up for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 7721–7724.
More
Information
Subjects:
Engineering, Electrical & Electronic
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
1.3K
Revisions:
3 times
(View History)
Update Date:
12 Aug 2022
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




