Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dimitrios Goutas | -- | 2067 | 2022-04-06 14:16:11 | | | |
| 2 | Conner Chen | Meta information modification | 2067 | 2022-04-07 04:30:37 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Goutas, D.; Pergaris, A.; Goutas, N.; Theocharis, S. Exosomes and Tumor Microenvironment. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/21410 (accessed on 07 February 2026).
Goutas D, Pergaris A, Goutas N, Theocharis S. Exosomes and Tumor Microenvironment. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/21410. Accessed February 07, 2026.
Goutas, Dimitrios, Alexandros Pergaris, Nikolaos Goutas, Stamatios Theocharis. "Exosomes and Tumor Microenvironment" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/21410 (accessed February 07, 2026).
Goutas, D., Pergaris, A., Goutas, N., & Theocharis, S. (2022, April 06). Exosomes and Tumor Microenvironment. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/21410
Goutas, Dimitrios, et al. "Exosomes and Tumor Microenvironment." Encyclopedia. Web. 06 April, 2022.
Copy Citation
Exosomes are cell-secreted nanoparticles containing various molecules including small vesicles, microRNAs (miRNAs), messenger RNAs or bioactive proteins which are thought to be of paramount importance for intercellular communication. The unique effects of exosomes in terms of cell penetration capacity, decreased immunogenicity and inherent stability, along with their key role in mediating information exchange among tumor cells and their surrounding tumor microenvironment (TME), render them a promising platform for drug targeted delivery.
exosomes
tumor microenvironment
1. Introduction
Erythropoietin-producing human hepatocellular receptors (EPHs) compose the largest known subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases. They participate, along with their ligands, with the EPH family receptor interacting proteins (ephrins) in a wide range of processes in human physiology [1]. EPHs are membrane-bound proteins consisting of an extracellular ephrin-binding domain, a transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic component. Ephrins also comprise membrane-bound proteins, therefore, cell-to-cell interaction is required for an EPH to interact with its ligand. Following EPH–ephrin interaction, a response is triggered in not only the cytoplasm of the EPH-expressing cell (a process called forward signaling) but also in the cytoplasm of the ephrin-bearing one (termed reverse signaling). The message is further transmitted through complex molecular cascades implicated in both processes [2].
Nine EPHA receptors (EPHA1 to EPHA8 and EPHA10) that bind 5 ephrin-A ligands (ephrin-A1 to ephrin-A5), along with five EPHB receptors (EPHB1 to EPHB4 and EPHB6) that interact with three ephrin-B ligands (ephrin-B1 to ephrin-B3) are expressed in humans [3][4][5][6]. While a higher affinity between receptors and ligands of the same subgroup is observed, crosstalk between different subgroups has also been described (Figure 1).
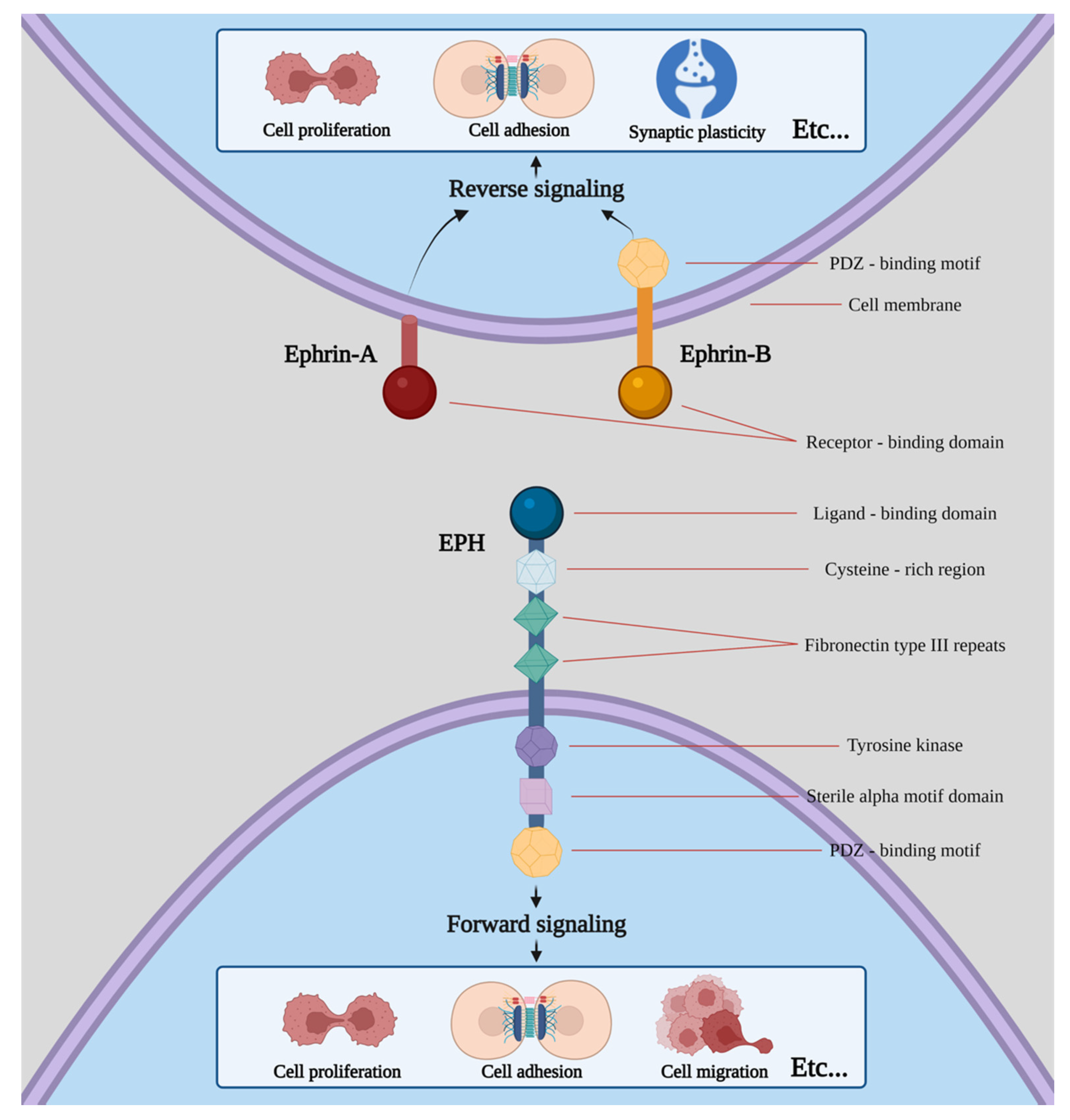
Figure 1. Structure of EPHs/ephrins and schematic presentation of forward and reverse signaling. Etc. means that both procedures can induce a plethora of effects apart from the ones shown in the picture, including cell segregation, border sharpening, cell repulsion and neurite outgrowth as well as cell survival and maturation.
The EPH/ephrin system participates in, among other processes, cell migration, axon guidance and synapse formation during embryonic development as well as procedures such as like-cell adhesion, motility, cell–matrix interactions, lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis [7]. As most of the aforementioned procedures comprise key steps of carcinogenesis, EPHs/ephrins have been extensively investigated so that their role in neoplasia can be clearly elucidated [8].
Meanwhile, exosomes represent a type of extracellular vesicle (EV) containing biomolecules such as proteins, mRNAs, microRNAs (miRNAs), polysaccharides and lipids of the cells that secrete them. While the physiological role remains largely unknown, it has been speculated that they have a role in removing excess and/or unnecessary constituents from cells to maintain cellular homeostasis. Nevertheless, since they possess the ability to mediate intercellular communications, they have been utilized as nanocarriers for drug delivery [9]. Exosomes isolated from a patient’s own cells have higher biocompatibility and lower toxicity compared with synthetic drugs and they are capable of penetrating into tissues, diffusing into the blood and even crossing the blood–brain barrier [10]. Furthermore, exosome-mediated delivery can bypass the P-glycoprotein drug efflux system and, as a result, reduce drug resistance [11].
Exosomes are usually smaller than other extracellular vesicles and therefore require special handling in their separation and analysis [12]. Nevertheless, despite the variety of techniques and approaches that have been used for the purification, separation and analysis of exosomes, so far, no methodology providing enough insight regarding selectivity, purification yield and reproducibility exists. In fact, due to their biochemical properties, a combination of techniques usually needs to be tailored to obtain the desired purification outcomes. Since exosomes must be isolated from varied biological samples while preserving their physiochemical properties and biological function, and as they exhibit significant heterogeneity in size, cargo and surface markers, their isolation needs to be specific, efficient and have long-term perspective of clinical applications. Taking these into consideration, current methods of isolation include ultracentrifugation, filtration, precipitation, chromatography, microfluidics and immunoaffinity capture [13]; among them, ultracentrifugation represents the gold standard for exosome isolation [14].
2. Exosomes and Tumor Microenvironment
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is comprised of diverse cell types in a variety of functional niches, constituting a complex “ecosystem” and a vital contributor in cancer initiation and progression that ultimately modulates a plethora of cell-to-cell interactions [15][16]. The aforementioned interactions orchestrate reprogramming into cancer-permissive environments and can have significant impacts on cancer development. Furthermore, intercellular communication in the TME, through a variety of signaling networks, allows for information exchange to occur among cells ranging from juxtacrine interactions to secreted factors, such as exosomes [17]. Exosomes and other EVs underline the complexity of dynamic cell-to-cell interactions that form TME. In a similar fashion, Zhao et al. [18] studied the exosomes derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs). They observed that CAF-derived exosomes could inhibit mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, thereby increasing glycolysis and glutamine-dependent reductive phosphorylation in tumor cells. They further proved, through intra-exosomal metabolomics, that CAF-derived exosomes consist of intact metabolites, including amino acids, lipids and TCA-cycle intermediates, which are ultimately utilized by cancer cells for promoting tumor growth under nutrient deprivation or nutrient stressed conditions [18]. A number of studies have established the hypoxic tumor microenvironment as a common feature of solid tumors, linked with tumor aggressiveness and poor patient prognosis [19][20]. Exosomes mediate and assist in the continuous crosstalk among tumor and stromal cells and are believed to regulate hypoxia adaptation and to rebuild the microenvironment in return [21]. Nevertheless, what is worth mentioning is the potential that exosomes carry as indicators of tumor burden and prognosis and as a potential therapeutic treatment, as they regulate a variety of aspects of heterotypic cell-to-cell interaction within TME.
3. The Role of Exosomes
3.1. Exosomal Engineering and Loading
Hematopoietic stem cell-derived exosomes have been found to express mRNAs of several pro-angiopoietic and anti-apoptotic factors such as insulin growth factor 1, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), interleukin 8 and basic fibroblast growth factor [22]. These mRNAs have the ability to enhance endothelial cells’ proliferation and survival, exert anti-apoptotic effects and, thereby, stimulate tube formation [22]. Moreover, exosomes derived from a patient’s differentiated hematopoietic stem cells can be used for tissue-targeted cargo delivery through the expression of tissue-specific peptides. By loading miRNA or siRNA of the targeted gene, exosomes can selectively regulate gene expression (Figure 2) [23].
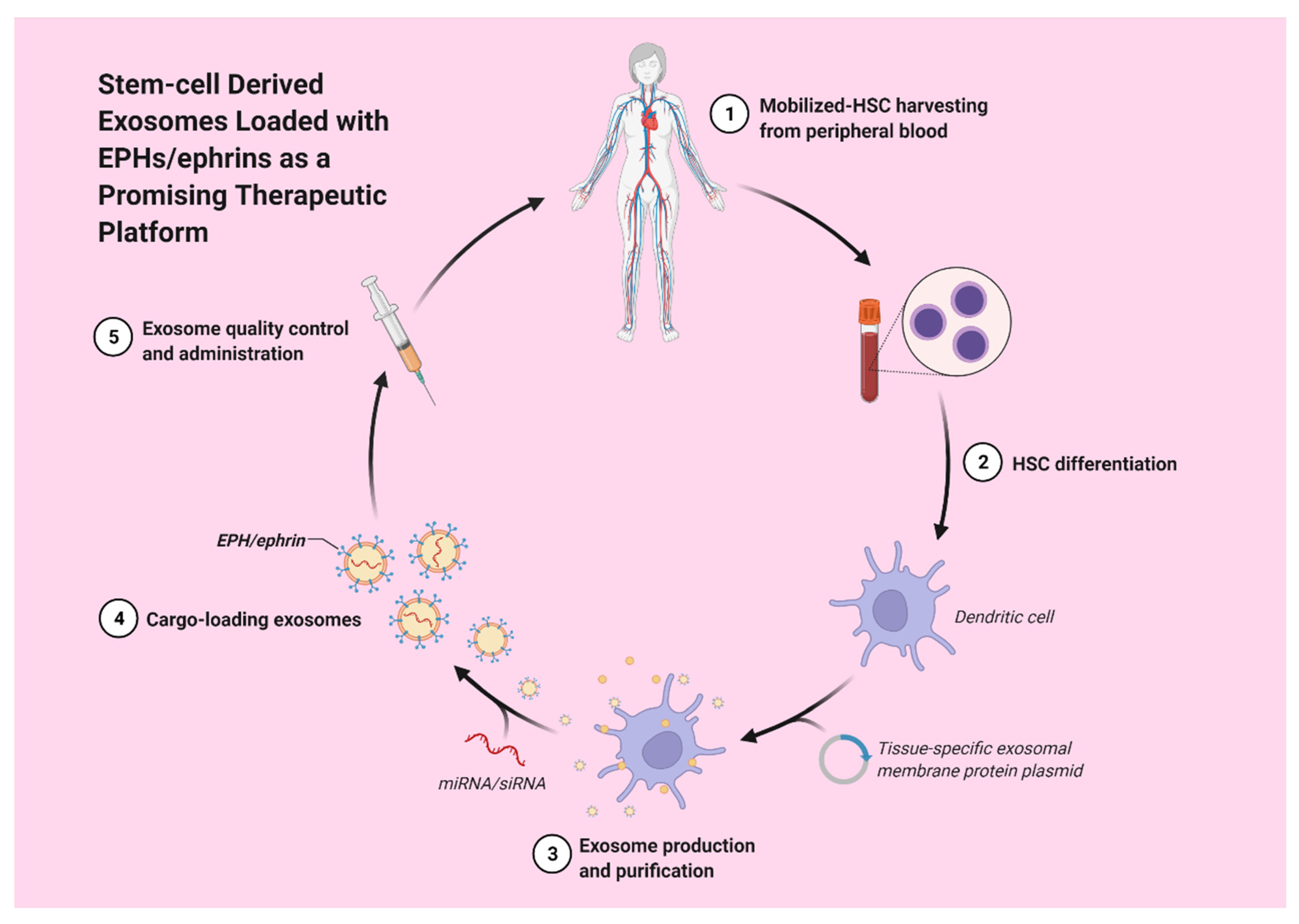
Figure 2. Stem-cell derived exosomes loaded with EPHs/ephrins could potentially act as a promising therapeutic strategy.
Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes have been widely investigated in a variety of disease states and have been shown to be capable of immunoregulation, regenerating tissue and promoting angiogenesis [24]. Employing the advantages of MSC-exosomes, they can be loaded with miRs and targeted to the desired site. Mardpour et al. [24] utilized hydrogel-mediated MSC-derived exosomes loaded in patients with chronic liver failure, managing to augment liver regeneration. An in vivo study, conducted by O’Brien et al. [25], used MSC-derived exosomes loaded with a potential tumor suppressor, miR-379, for breast cancer therapy. It was found that miR-379 indeed acted as a potent tumor suppressor in breast cancer, partly attributed to its interaction with COX-2.
In order to confer cell type targeting sensitivity, modification strategies of exosomes include genetic engineering and chemical modification [26][27][28]. In genetic engineering, the gene sequence of a guiding protein or polypeptide is fused with the preferred exosomal membrane protein. Via this approach, surface display of peptides and proteins is achieved, with, however, a limitation on targeting motifs that are genetically encodable. On the other hand, through chemical modification, a wide range of ligands, natural and synthetic, can be displayed via lipid assembly or conjugation reactions. The latter have the advantage to stably adjust exosomal surface proteins, but the complex exosomal surface may compromise the reaction efficiency [28]. Covalent modification may also risk the function of the exosome. Moreover, lipids and amphipathic molecules can become enclosed in the lipid bilayer of exosomes and allow their hydrophilic part to be displayed on the exterior, ultimately causing an increase in the toxicity of exosomes [28].
Proteomics data (present in databases such as ExoCarta and Vesiclepedia), studied to identify the components of exosomes, have shown that all EPH receptors and ephrinB proteins have been detected in exosomes purified from body fluids and normal cells as well as from a broad range of cancer cell types [29][30][31]. Nevertheless, the possibility of exploiting the EPH system for targeted delivery of therapeutic exosomes either through purification or genetic engineering has not yet been studied.
3.2. Exosomal EPHs Targeted Delivery
Targeted delivery systems represent the backbone of personalized medicine to surpass the toxic effects and the seemingly insurmountable obstacle of off-target implications. Emerging data have shed light to the paramount role of exosomes in disease and on their ability to carry proteins to distant tissue locations where they exert their properties [29][30][31][32][33][34][35][36][37][38][39][40][41][42][43][44][45][46]. Up until now, it was believed that for an EPH to interact with its ligand, a direct cell-to-cell interaction was required. However, Gong et al. [30] demonstrated in their studies that EPH receptors and ephrins were able to have a long-range intercellular communication and, paradoxically, still involve direct contact between two cell membranes [30]. This is possible through the integration of a member of the EPH/ephrin system in the membrane of the exosome. Following the release of the exosome, exosomal membrane-bound EPHs/ephrins can interact with their high affinity counterparts present on cell membranes of cells located at distant sites, a process that results in EPH–ephrin interaction without direct cell-to-cell membrane contact. This form of communication exploits the use of exosomes that are released by cells and are capable of travelling to distant sites via interstitial and other body fluids [8][9]. Therefore, taking into consideration the fact that EPH–ephrin signaling does not require direct cell contact [30], this makes the utilization of exosomal EPHs and ephrins paramount not just as a biomarker of disease progression, prognosis and carcinogenesis but also as a therapeutic approach for a wide variety of diseases.
3.3. Angiogenesis
Several studies have revealed an association between members of the EPH/ephrin system, as a component of cancer-derived exosomes and angiogenesis [42][43][44]. Sato et al. [44] studied the role of small extracellular vesicles (SEVs), in the size range of exosomes, derived from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) in promoting tumor angiogenesis. Western blot analyses of exosomes and patient data analyses revealed that EPHB2 was overexpressed in HNSCC patients and was associated with poor patient prognosis and tumor angiogenesis. Moreover, functional experiments demonstrated that EPHB2 expression in exosomes modulated angiogenesis. Meanwhile, exosomal EPHB2 stimulated ephrin-B reverse signaling by inducing STAT3 phosphorylation [44]. Additionally, EPHA2 has been implicated in enhancing angiogenesis via proteomic analysis of lung tumor cell-derived exosomes, while an inhibition assay revealed that EPHA2 constitutes a major MAPK activator on exosomes [42]. More specifically, it was demonstrated that the direct communication among membrane protein (EPHA2) on exosomes and recipient cells resulted in stimulation of tumor endothelial cells [42]. These results highlight the fact that EPHA2 participates in angiogenesis as a ligand of the ephrin signaling pathway [42]. Furthermore, Wang H. et al. [43] attempted to provide an association on how oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) affects the angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) via miR-210-3p expression and divulge the relationship between miR-210-3p, its target protein and the mechanism of angiogenesis regulation [43]. They observed that EPHA3 was the target gene of miR-210-3p and that its protein levels could influence the migration and proliferation of HUVECs. In addition, by measuring the levels of phosphorylated AKT in HUVECs, they demonstrated that when EPHA3 was downregulated, the AKT levels were elevated, while when EPHA3 was upregulated, the PI3/AKT pathway was suppressed. When concluding their results, Wang H. et al. proved that the exosomes secreted by OSCC cells could upregulate the expression of miR-210-3p while reducing EPHA3 expression in HUVECs and promoting tube formation via the activation of PI3/AKT signaling pathway [43].
3.4. Senescent Cells Release Exosomes Contributing to Cancer Cell Proliferation
Although cell senescence prevents the proliferation of cells at risk for neoplastic transformation, the altered secretome that senescent cells develop can promote and contribute to cancer cell proliferation. Takasugi et al. [46] demonstrated that sEVs carrying EPHA2 bind to ephrin-A1 that is overexpressed in a variety of cancer cells [8] and ultimately augments their proliferation via the EPHA2/ephrinA1 reverse signaling [46]. They further investigated the mechanism of enrichment of EPHA2 in sEVs, secreted from senescent cells, considering some post-translational modification of EPHA2 to be involved. They examined and concluded that tyrosine kinase phosphorylation of EPHA2 in senescent cells, resulting from oxidative inactivation of PTP1B phosphatase, is involved in its sEV sorting [46]. As a result, that reactive oxygen species (ROS)-regulated cargo sorting into sEVs could prove to be critical for the possibly detrimental growth-promoting effect of the senescent cells’ secretome [46].
References
- Eph Nomenclature Committee. Unified nomenclature for Eph family receptors and their ligands, the ephrins. Cell 1997, 90, 403–404.
- Edwards, C.M.; Mundy, G.R. Eph receptors and ephrin signaling pathways: A role in bone homeostasis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2008, 5, 263–272.
- Wei, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X.; Jin, J.; Chin-Sang, I.; Zheng, J.; Jia, Z. Structures of an Eph receptor tyrosine kinase and its potential activation mechanism. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2014, 70, 3135–3143.
- Kania, A.; Klein, R. Mechanisms of ephrin-Eph signaling in development, physiology and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 240–256.
- Shiuan, E.; Chen, J. Eph Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Tumor Immunity. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 6452–6457.
- Stelzer, G.; Rosen, N.; Plaschkes, I.; Zimmerman, S.; Twik, M.; Fishilevich, S.; Stein, T.I.; Nudel, R.; Lieder, I.; Mazor, Y.; et al. The GeneCards Suite: From Gene Data Mining to Disease Genome Sequence Analyses. Curr. Protoc. Bioinformics 2016, 54, 1.30.1–1.30.33.
- Rudno-Rudzińska, J.; Kielan, W.; Frejlich, E.; Kotulski, K.; Hap, W.; Kurnol, K.; Dzierżek, P.; Zawadzki, M.; Hałoń, A. A review on Eph/ephrin, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in gastric, colorectal and pancreatic cancers. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 29, 303–312.
- Pergaris, A.; Danas, E.; Goutas, D.; Sykaras, A.G.; Soranidis, A.; Theocharis, S. The Clinical Impact of the EPH/Ephrin System in Cancer: Unwinding the Thread. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8412.
- Batrakova, E.V.; Kim, M.S. Using exosomes, naturally-equipped nanocarriers, for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2015, 219, 396–405.
- Zheng, M.; Huang, M.; Ma, X.; Chen, H.; Gao, X. Harnessing Exosomes for the Development of Brain Drug Delivery Systems. Bioconjugate Chem. 2019, 30, 994–1005.
- Kim, M.S.; Haney, M.J.; Zhao, Y.; Mahajan, V.; Deygen, I.; Klyachko, N.L.; Inskoe, E.; Piroyan, A.; Sokolsky, M.; Okolie, O.; et al. Development of exosome-encapsulated paclitaxel to overcome MDR in cancer cells. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 655–664.
- Petersen, K.E.; Manangon, E.; Hood, J.L.; Wickline, S.A.; Fernandez, D.P.; Johnson, W.P.; Gale, B.K. A review of exosome separation techniques and characterization of B16-F10 mouse melanoma exosomes with AF4-UV-MALS-DLS-TEM. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7855–7866.
- Ayala-Mar, S.; Donoso-Quezada, J.; Gallo-Villanueva, R.C.; Perez-Gonzalez, V.H.; González-Valdez, J. Recent advances and challenges in the recovery and purification of cellular exosomes. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 3036.
- Li, P.; Kaslan, M.; Lee, S.H.; Yao, J.; Gao, Z. Progress in Exosome Isolation Techniques. Theranostics 2017, 7, 789–804.
- Friedl, P.; Alexander, S. Cancer invasion and the microenvironment: Plasticity and reciprocity. Cell 2011, 147, 992–1009.
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674.
- Li, I.; Nabet, B.Y. Exosomes in the tumor microenvironment as mediators of cancer therapy resistance. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 32.
- Zhao, H.; Yang, L.; Baddour, J.; Achreja, A.; Bernard, V.; Moss, T.; Marini, J.C.; Tudawe, T.; Seviour, E.G.; San Lucas, F.A.; et al. Tumor microenvironment derived exosomes pleiotropically modulate cancer cell metabolism. Elife 2016, 5, e10250.
- Harris, A.L. Hypoxia--a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002, 2, 38–47.
- Brahimi-Horn, M.C.; Chiche, J.; Pouyssegur, J. Hypoxia and cancer. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 85, 1301–1307.
- Meng, W.; Hao, Y.; He, C.; Li, L.; Zhu, G. Exosome-orchestrated hypoxic tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 57.
- Ratajczak, J.; Kucia, M.; Mierzejewska, K.; Marlicz, W.; Pietrzkowski, Z.; Wojakowski, W.; Greco, N.J.; Tendera, M.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Paracrine proangiopoietic effects of human umbilical cord blood-derived purified CD133+ cells—implications for stem cell therapies in regenerative medicine. Stem. Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 422–430.
- Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Yin, H.; Betts, C.; Lakhal, S.; Wood, M.J. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 341–345.
- Mardpour, S.; Ghanian, M.H.; Sadeghi-Abandansari, H.; Mardpour, S.; Nazari, A.; Shekari, F.; Baharvand, H. Hydrogel-Mediated Sustained Systemic Delivery of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Improves Hepatic Regeneration in Chronic Liver Failure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 37421–37433.
- O’Brien, K.P.; Khan, S.; Gilligan, K.E.; Zafar, H.; Lalor, P.; Glynn, C.; O’Flatharta, C.; Ingoldsby, H.; Dockery, P.; De Bhulbh, A.; et al. Employing mesenchymal stem cells to support tumor-targeted delivery of extracellular vesicle (EV)-encapsulated microRNA-379. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2137–2149.
- Lin, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, X. Biological characteristics of exosomes and genetically engineered exosomes for the targeted delivery of therapeutic agents. J. Drug Target. 2020, 28, 129–141.
- Yang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Cho, E.; Kim, G.B.; Kim, I.S. Extracellular vesicles as a platform for membrane-associated therapeutic protein delivery. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1440131.
- Liang, Y.; Duan, L.; Lu, J.; Xia, J. Engineering exosomes for targeted drug delivery. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3183–3195.
- Zhao, Y.; Yin, L.; Zhang, H.; Lan, T.; Li, S.; Ma, P. Eph/ephrin family anchored on exosome facilitate communications between cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2018, 42, 1458–1462.
- Gong, J.; Körner, R.; Gaitanos, L.; Klein, R. Exosomes mediate cell contact–independent ephrin-Eph signaling during axon guidance. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 214, 35–44.
- Pasquale, E.B. Exosomes expand the sphere of influence of Eph receptors and ephrins. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 214, 5–7.
- Gao, Z.; Han, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tian, R.; Wang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Z.; Niu, R.; Zhang, F. Drug-resistant cancer cell-derived exosomal EphA2 promotes breast cancer metastasis via the EphA2-Ephrin A1 reverse signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 414.
- Madeo, M.; Colbert, P.L.; Vermeer, D.W.; Lucido, C.T.; Cain, J.T.; Vichaya, E.G.; Grossberg, A.J.; Muirhead, D.; Rickel, A.P.; Hong, Z.; et al. Cancer exosomes induce tumor innervation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–15.
- Liang, K.; Liu, F.; Fan, J.; Sun, D.; Liu, C.; Lyon, C.J.; Bernard, D.W.; Li, Y.; Yokoi, K.; Katz, M.H.; et al. Nanoplasmonic Quantification of Tumor-derived Extracellular Vesicles in Plasma Microsamples for Diagnosis and Treatment Monitoring. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 21.
- Holliday, L.S.; McHugh, K.P.; Zuo, J.; Aguirre, J.I.; Neubert, J.K.; Rody, W.J., Jr. Exosomes: Novel regulators of bone remodelling and potential therapeutic agents for orthodontics. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2017, 20 (Suppl. 1), 95–99.
- Jung, K.O.; Youn, H.; Lee, C.H.; Kang, K.W.; Chung, J.K. Visualization of exosome-mediated miR-210 transfer from hypoxic tumor cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 9899–9910.
- Hughes, R.M.; Virag, J.A.I. Harnessing the Power of Eph/ephrin Biosemiotics for Theranostic Applications. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 112.
- Ji, H.; Greening, D.W.; Barnes, T.W.; Lim, J.W.; Tauro, B.J.; Rai, A.; Xu, R.; Adda, C.; Mathivanan, S.; Zhao, W.; et al. Proteome profiling of exosomes derived from human primary and metastatic colorectal cancer cells reveal differential expression of key metastatic factors and signal transduction components. Proteomics 2013, 13, 1672–1686.
- Zhou, S.; Hu, T.; Han, G.; Wu, Y.; Hua, X.; Su, J.; Jin, W.; Mou, Y.; Mou, X.; Li, Q.; et al. Accurate Cancer Diagnosis and Stage Monitoring Enabled by Comprehensive Profiling of Different Types of Exosomal Biomarkers: Surface Proteins and miRNAs. Small 2020, 16, 2004492.
- Fan, J.; Wei, Q.; Koay, E.J.; Liu, Y.; Ning, B.; Bernard, P.W.; Zhang, N.; Han, H.; Katz, M.H.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Chemoresistance transmission via exosome-Mediated EphA2 transfer in pancreatic cancer. Theranostics 2018, 8, 5986–5994.
- Mathivanan, S.; Lim, J.W.; Tauro, B.J.; Ji, H.; Moritz, R.L.; Simpson, R.J. Proteomics analysis of A33 immunoaffinity-purified exosomes released from the human colon tumor cell line LIM1215 reveals a tissue-specific protein signature. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2010, 9, 197–208.
- Yamashita, T.; Kamada, H.; Kanasaki, S.; Nagano, K.; Inoue, M.; Higashisaka, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Tsunoda, S. Ephrin type-A receptor 2 on tumor-derived exosomes enhances angiogenesis through the activation of MAPK signaling. Pharmazie 2019, 74, 614–619.
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Luo, X.; Liu, K.; Jiang, E.; Chen, Y.; Shao, Z.; Shang, Z. OSCC Exosomes Regulate miR-210-3p Targeting EFNA3 to Promote Oral Cancer Angiogenesis through the PI3K/AKT Pathway. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 2125656.
- Sato, S.; Vasaikar, S.; Eskaros, A.; Kim, Y.; Lewis, J.S.; Zhang, B.; Zijlstra, A.; Weaver, A.M. EPHB2 carried on small extracellular vesicles induces tumor angiogenesis via activation of ephrin reverse signaling. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e132447.
- Wei, Q.; Wei, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Feng, H.; Ren, L. EphA2-enriched exosomes promote cell migration and are a potential diagnostic serum marker in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 2941–2947.
- Takasugi, M.; Okada, R.; Takahashi, A.; Virya Chen, D.; Watanabe, S.; Hara, E. Small extracellular vesicles secreted from senescent cells promote cancer cell proliferation through EphA2. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15729.
More
Information
Subjects:
Oncology
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
618
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
07 Apr 2022
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




