Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yasemin M. Akay | + 879 word(s) | 879 | 2022-02-18 05:11:34 |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Akay, Y.M.; Sasagawa, K.; Ohta, J.; Akay, M. GABA Neurons on Dopamine Neurons. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/19966 (accessed on 07 February 2026).
Akay YM, Sasagawa K, Ohta J, Akay M. GABA Neurons on Dopamine Neurons. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/19966. Accessed February 07, 2026.
Akay, Yasemin M., Kiyotaka Sasagawa, Jun Ohta, Metin Akay. "GABA Neurons on Dopamine Neurons" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/19966 (accessed February 07, 2026).
Akay, Y.M., Sasagawa, K., Ohta, J., & Akay, M. (2022, February 28). GABA Neurons on Dopamine Neurons. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/19966
Akay, Yasemin M., et al. "GABA Neurons on Dopamine Neurons." Encyclopedia. Web. 28 February, 2022.
Copy Citation
Dopamine (DA) is the key regulator of reward behavior. The DA neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and their projection areas, which include the prefrontal cortex (PFC), nucleus accumbens (NAc), and amygdala, play a primary role in the process of reward-driven behavior induced by the drugs of addiction, including nicotine and alcohol. Nicotine directly activates DA neurons and indirectly activates glutamate and GABA neurons, enhancing DA release within the NAcShell. GABAergic neurons regulate DA neurons.
GABA neurons
dopamine neurons
1. Introduction
Dopamine (DA) is the key regulator of the reward behavior; DA neurons are present in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) with projection areas including the prefrontal cortex (PFC), nucleus accumbens shell (NAcShell), and amygdala. DA is thought to be very important in the process of reward-driven behavior induced by the drugs related to addiction, including nicotine and alcohol. Addictive substances (e.g., nicotine and alcohol) alters the reward system in the brain by modulating its activity and causing an increase of DA release from the VTA to the PFC and NAcShell. The mesocorticolimbic DA system, known as the reward circuit in the brain, plays a key role in this reward system as addictive substances trigger DA release through this system [1]. This pathway/system facilitates the reinforcing and/or withdrawal properties of addictive substances [1][2][3].
2. Investigation of Mesolimbic DA Neural Effects Using Optogenetics Techniques
The mesolimbic system and its impact on the reward system in alcohol and nicotine addiction has been vigorously investigated. The researchers elucidate this phenomenon using optogenetics techniques, by exploiting dopaminergic neurons in the VTA which are controlled by GABAergic neurons. Figure 1a shows a schematic diagram of DA neurons extending its axon from the VTA to the NAcShell. Neurons expressing ChrimsonR and located in the VTA of transgenic mice were activated with red light (620 nm) using a PS device implanted in the VTA. The same mice were implanted with a microdialysis probe in the NAcShell (Figure 1b), which is the projection site of VTA dopaminergic neurons. The amount of DA release induced by PS in the NAcShell was measured over time using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Mice were maintained under freely moving conditions. A simplified schematic of the relationship between DA and GABA neurons in the VTA is illustrated in Figure 1c.
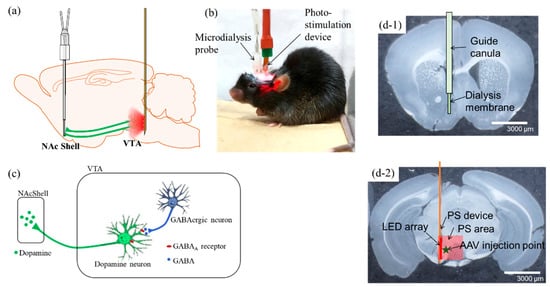
Figure 1. Conceptual diagram and implantation of the photo-stimulation (PS) device and the microdialysis probe in the mouse brain. (a) Conceptual diagram of the mesolimbic system, which extends axons from cell bodies in the VTA of the midbrain to the NAcShell. DA neurons expressing ChrimsonR are photo-stimulated at the wavelength of 620 nm, and the concentration of dopamine released in the NAcShell is measured by microdialysis. (b) Photograph of a mouse undergoing PS under freely moving conditions. A cable for PS and a tube for microdialysis are attached to the head of the mouse. Both are lightweight and do not interfere with the behavior of the mouse. (c) A simplified diagram showing the neural connections between dopaminergic and GABAergic neurons in the VTA and the release of DA in the NAcShell projecting from the cell body. The DA neurons in the VTA are inhibited by GABAergic neurons also in the VTA. Glutamatergic neurons from other sites acting on dopaminergic neurons are omitted. (d-1) Photomicrograph of a coronal slice of mouse brain in the NAcShell, showing the position of the microdialysis probe superimposed. (d-2) Photomicrograph of a coronal slice of mouse brain in the VTA, showing the implantation position of the PS device, the LED array area (red line in the figure), the LED irradiation area (light red square in the figure), and the AAV injection position (green star in the figure) superimposed. Scale bars: 3000 µm in (d-1,d-2). Abbreviations: NAc, nucleus accumbens; VTA, ventral tegmental area; DA: dopamine; AAV, adeno-associated virus; PS, photo-stimulation.
The attached movie shown in the supplement demonstrates that our LED-based PS device and microdialysis probe are light-weight and small, and thus do not interfere with the behavior of the mice.
After the experiment was completed, the brain was perfusion-fixed, removed and sectioned to confirm the position of the implant. Figure 1(d-1) shows a brain section of the NAcShell, together with a microdialysis probe collecting a sample from the tip of the guide cannula with 1 mm of dialysis membrane exposed. Figure 1(d-2) shows a brain section from the VTA with an implanted PS device. The positions of the AAV injection of ChrimsonR, PS device, LED array, and photo exposure area are superimposed on the section image.
3. Findings
The dopaminergic network is part of the mesolimbic system and plays a significant role in the reward system. Although microdialysis has poor temporal resolution, using DA receptor-specific fluorescence imaging such as GRAB-DA can increase confidence in the results. Future studies using PS will examine the control of physiological responses to alcohol or nicotine to elucidate the mechanisms of addiction.
In addition, DA release was impacted by PS frequency; the DA release was higher with 20 Hz pulse stimulation than with 2 Hz pulse stimulation. The power of the PS was the same as that of the total stimulation, i.e., 3 mA LED current and 30 s total stimulation time in both cases. It is not yet clear in detail whether these different pulse stimulation frequencies act on the DA neurons or on the GABAergic neurons that regulate the DA neurons.
References
- Young, K.A.; Gobrogge, K.L.; Wang, Z.X. The role of mesocorticolimbic dopamine in regulating interactions between drugs of abuse and social behavior. Neurosci. Biobehav. R 2011, 35, 498–515.
- Niehaus, J.L.; Cruz-Bermúdez, N.D.; Kauer, J.A. Plasticity of Addiction: A Mesolimbic Dopamine Short-Circuit? Am. J. Addict. 2009, 18, 259–271.
- Volkow, N.D.; Fowler, J.S.; Wang, G.-J.; Swanson, J.M.; Telang, F. Dopamine in Drug Abuse and Addiction. Arch. Neurol. 2007, 64, 1575–1579.
More
Information
Subjects:
Neurosciences
Contributors
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
638
Revision:
1 time
(View History)
Update Date:
28 Feb 2022
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




