Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Beat Vögeli | + 2327 word(s) | 2327 | 2021-12-01 09:58:14 | | | |
| 2 | Peter Tang | -241 word(s) | 2086 | 2022-02-22 02:40:08 | | | | |
| 3 | Peter Tang | -241 word(s) | 2086 | 2022-02-22 02:41:29 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Vögeli, B. Activity and Affinity of Pin1 Variants. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/19711 (accessed on 08 March 2026).
Vögeli B. Activity and Affinity of Pin1 Variants. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/19711. Accessed March 08, 2026.
Vögeli, Beat. "Activity and Affinity of Pin1 Variants" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/19711 (accessed March 08, 2026).
Vögeli, B. (2022, February 21). Activity and Affinity of Pin1 Variants. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/19711
Vögeli, Beat. "Activity and Affinity of Pin1 Variants." Encyclopedia. Web. 21 February, 2022.
Copy Citation
Pin1, or Protein interacting with Never-in-Mitosis (NIMA) 1, is a peptidyl-prolyl isomerase responsible for isomerizing phosphorylated S/T-P motifs. Pin1 has two domains that each have a distinct ligand binding site, but only its PPIase domain has catalytic activity. Vast evidence supports interdomain allostery of Pin1, with binding of a ligand to its regulatory WW domain impacting activity in the PPIase domain.
pin1
WW domain
PPIase domain
mutants
activity
affinity
1. Introduction
Pin1, or Protein interacting with Never-in-Mitosis (NIMA) 1, is a phosphorylation-dependent peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase) [1]. Unlike the other PPIases, the cyclophilins and FK506 binding proteins, Pin1 is a two-domain protein specific for isomerizing motifs with a proline immediately preceded by a phosphorylated serine or threonine (pS/T-P) [2]. The N-terminal WW (Trp-Trp) domain binds these motifs, while the C-terminal PPIase domain is responsible for isomerization [3]. Connecting the two domains is a 10 residue flexible linker (Figure 1A). Interestingly, the relative positions between the two domains are not fixed, as the two domains can occupy “compact” and “extended” states. In the compact state, the two domains interact through an interdomain (ID) interface between residues 28–32 in the WW domain, and 137–141 and 148–149 in the PPIase (Figure 1A) [4][5]. The position of the domains in the extended state is expected to be a distribution of states, rather than just one [6][7][8]. An equilibrium exists between compact and extended conformations of Pin1 that can be altered by ligands [9][10]. Ligand binding and mutation studies suggest that the WW domain allosterically regulates the activity of the PPIase domain.
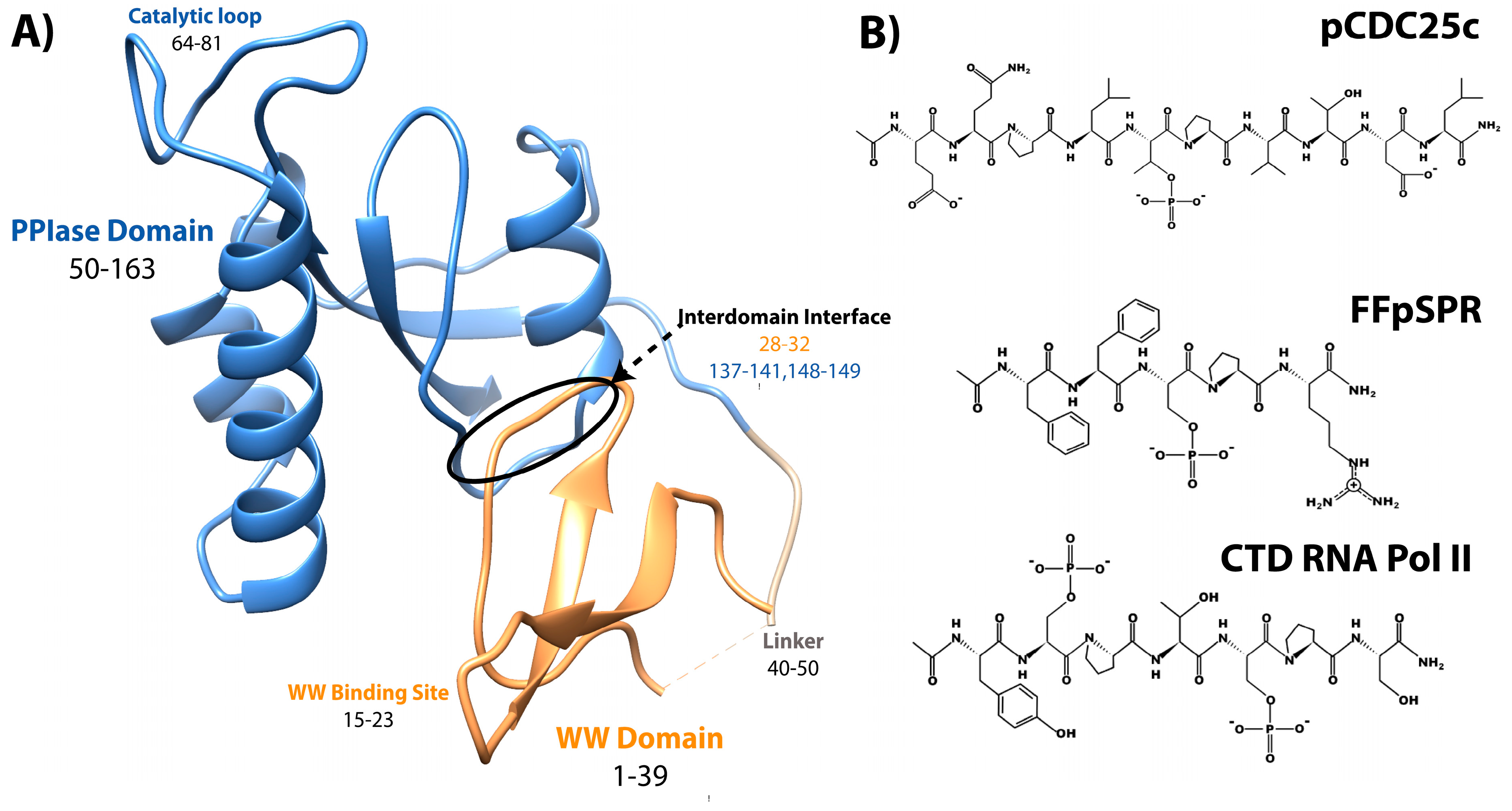
Figure 1. Structure of Pin1 and ligands. (A) Annotated crystal structure of PDB 1pin. (B) Primary pS/T-P peptide ligands discussed here.
Pin1 is a very promiscuous mitotic regulator, and regulates phosphoproteins through changing the phosphorylation/dephosphorylation state, as well as protein stability through either enhancing or protecting against ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation [11]. Pin1 is overexpressed in many different cancer types, including lung, brain, melanoma, prostate, ovary, and cervical [12]. In breast cancer, Pin1 has been implicated in RAS/MEK/ERK, WNT/β-catenin, NFκB, HER2, and ERα signaling pathways [13][14][15][16][17]. More specifically, Pin1 enhances proteosomal degradation of c-Myc and Cyclin E, while protecting CDK1, β-catenin, NFκB, and p53. Pin1 has even been shown to promote cancer stem cell metastasis and tumorigenesis [18]. While overexpression of Pin1 is implicated in cancer, Pin1 typically protects against tauopathy and plaque formation that leads to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) neurodegeneration. Pin1 has been shown to regulate both Tau and Aβ, that lead to intracellular tangles and extracellular plaques, respectively [19][20][21][22]. It is apparent that targeting Pin1 for therapeutics is a substantial challenge, especially due to its opposite roles in AD and cancer.
It is clearly apparent that Pin1 is capable of binding and isomerizing many different substrates, all with the commonality of a pS/T-P motif (Figure 1). Despite this shared motif, not all substrates cause the same structural changes to Pin1 upon binding. A peptide derivative from the pT48-P49 site of M phase inducer phosphatase Cdc25C with sequence EQPLpTPVTDL (here called pCDC25c) causes Pin1 to favor a hyper-extended state compared to the apo condition [8]. On the other hand, peptides with sequences WFYpSPR, FFpSPR, and YpSPTpSPS cause a shift to a more compact state of Pin1 [6]. This ligand-dependent shift in interdomain equilibrium triggers different responses in PPIase dynamics and catalytic activity. The Pintide ligand with sequence WFYpSPR was discovered as the peptide that Pin1 has the highest activity to isomerize [3], and ligand FFpSPR is similar in sequence but is slightly more hydrophilic and therefore has higher solubility in aqueous buffers. Ligand YpSPTpSPS is based on the repeated sequence in the C-terminal domain of RNA Polymerase II. The primary ligands that have been examined here include pCDC25c, FFpSPR, and the CTD of RNA Pol II with peptides drawn in Figure 1B.
2. Mutation Impact on Affinity to Various Ligands
2.1. Methods for Determination of Affinity and Activity
Techniques that have been used to evaluate Pin1 binding include fluorescence anisotropy, isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC), and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) titrations. As Pin1 is a two domain protein with two distinct binding sites, NMR is the most sensitive method for determining binding since the two binding sites can be evaluated simultaneously and residue specifically (microscopic binding affinities). The main drawback for NMR is that it is ideal only for weaker binding events in the μM to mM regime. Fluorescence anisotropy and ITC have the potential for showing two separate binding events, but the KD of the two events must be different by orders of magnitude, as if they are too similar they are indistinguishable. Even if two binding events were measured using either of these two methods, these methods alone would not be enough to disentangle which binding affinity corresponds to each binding site. In all the studies that have reported binding affinities of Pin1 using fluorescence anisotropy or ITC, only one binding affinity was reported for the whole protein, likely because the binding affinities of each domain are in the same order of magnitude, resulting in an effective KD. The smaller the KD value, the larger the binding affinity between the two molecules.
To quantify Pin1 isomerase activity, most mutants were studied using NMR exchange spectroscopy (EXSY) by fitting the cis-trans and trans-cis cross and the respective diagonal peaks in a NOESY experiment using many different mixing times [23]. Before performing this EXSY experiment, the 1H chemical shifts of ligand are assigned without enzyme present. The 1H chemical shifts are often distinct for trans and cis species due to slow exchange, typically with peak intensity ratios around 10:1 trans to cis. During a NOESY experiment, usually used to measure through-space interactions, each hydrogen is frequency labeled by its respective chemical shift and after a certain mixing time (time given for isomerization to occur), the hydrogens are frequency labeled again. If the proton isomerized to a different chemical shift during that time, there will be a cross peak between the two distinct frequencies. For example, if a ligand is in the trans conformation during the first frequency detection and then undergoes isomerization during the mixing time, the cis conformation is detected at the second frequency labeling event. Isomerization of a ligand can occur without enzyme present, but this is often a slow process (seconds-minutes) that is unlikely to occur during a NOESY mixing time (milliseconds-seconds). For pCDC25c and FFpSPR ligands, no cross peaks are detected without enzyme present. Once Pin1 is added, cross-peak intensities can be measured at various mixing times to extract rates of exchange. A perk of this experiment is that both c→t and t→c rates can be measured, and the sum of which is the exchange rate (kCT + kTC = kEXSY). While many studies report both kCT and kTC, some studies only report kEXSY. Note that the larger the kEXSY value, the higher is the activity of the enzyme.
Another method to measure activity by determining kcat/KM has been performed through a chymotrypsin-coupled chromophoric assay of p-nitroaniline (pNA) [24]. Chymotrypsin is highly selective towards X-Pro-Phe-pNA and will only hydrolyze the C-terminal pNA if the X-Pro bond is in the trans conformer. Therefore, the substrate used to study Pin1 activity is suc-AEPF-pNA, with glutamate acting as a phosphomimetic. A similar assay can be done with trypsin when peptides contain Pro-Arg-pNA motifs, like with peptide WFYpSPR-pNA [3].
Figure 2 and Figure 3 summarize the affinity and activity, respectively, of many Pin1 mutants. Single measurements are reported only with a bar, while variants with multiple measurements show an error bar with the standard deviations. Note that some values have a high standard deviation do to various measurements not agreeing well across different studies.

Figure 2. Dissociation constants of Pin1 variants. KD of (A) Pin1 variants including full-length (FL) and isolated domains to ligand pCDC25c, (B) mutants towards CTD RNA Pol II, (C) the WW domain and variants towards pCDC25c, and (D) full-length and isolated domains toward isomerizable and locked inhibitors of FFpSPR. Single measurements are reported only with a bar, while variants with multiple measurements show an error bar with the standard deviations. Variants with a large gray bar with an X had no detectable binding.
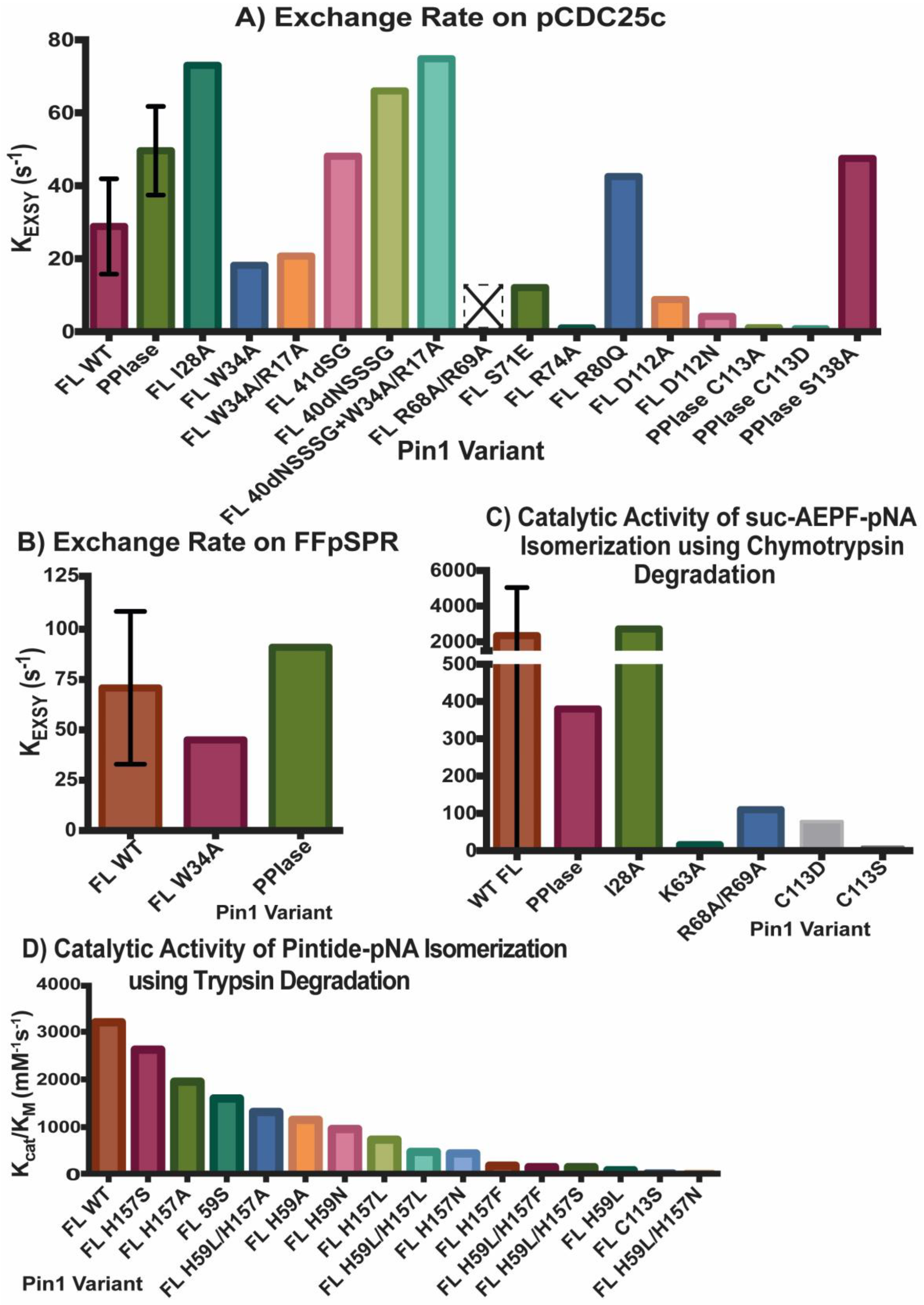
Figure 3. Activity of Pin1 Variants. Exchange rate KEXSY of ligands (A) pCDC25c and (B) FFpSPR in presence of various Pin1 variants using exchange spectroscopy. Catalytic activity kcat/KM of Pin1 mutations using (C) chymotrypsin or (D) trypsin assay. Single measurements are reported only with a bar, while variants with multiple measurements show an error bar with the standard deviations. Variant R68A/R69A with an empty bar with an X had no detectable activity. The values reported in (D) are based on the estimate of WT Pin1 activity (~3200 mM−1s−1) from the original figure, and the estimates of percent of activity for each mutant compared to WT Pin1.
2.2. Experimental Mutant-Dependent Affinities and Activities
Both domains have been studied in isolation, where they have different binding affinities and activities than the full-length (FL) protein (Figure 2A). It should be noted that constructs that are tested in the full-length protein always have “FL” written, while the isolated domains do not have any distinction. For example, “WW” refers to the isolated WW domain, while “FL WW” is the WW domain in full-length Pin1. While the isolated WW domain has similar affinity to the WW domain in full-length Pin1 (albeit marginally weaker), the isolated PPIase has typically 100× weaker affinity than the PPIase in the full-length protein [10]. It should be noted the high variability in PPIase binding: values range from 8 μM [5] to 10 mM [25]. Using GST pull-downs, the isolated WW domain was able to pull-down mitotic phospho-proteins (containing MPM-2 and Plk1 antibody recognition motifs) with similar efficiency as full-length Pin1, while the isolated PPIase domain had no ability to pull-down these targets [26]. Overall, it can be concluded that the PPIase has lower binding affinity than the WW domain to the tested ligands and that the presence of the partnering domain has an effect on the affinity of each domain.

Figure 4. Overview of mutants that change affinity and activity of Pin1. Mutations that have been studied are plotted on the crystal structure 1pin. Mutations that negatively impact (A) affinity and (B) isomerase activity are labeled in red, positive mutations are in green, and neutral mutations are in yellow.
All reported values for binding affinities and activities refer to phosphorylated ligands. It has been shown, however, that Pin1 can also bind unphosphorylated motifs. For example, the activity of Pin1 towards unphosphorylated WFYSPR-pNA is 170 mM−1s−1, it increases to 20,160 mM−1s−1 for WFYpSPR-pNA [3]. The initial crystal structure, 1pin, contained a bound phosphate ion in the catalytic site [4]. Interestingly, other PPIases such as the cyclophilins and FKBPs are unable to isomerize phosphorylated motifs.
3. Conclusions
The changes in affinity and activity of Pin1 upon mutations are mapped on the Pin1 structure in Figure 4. There is no direct correlation between the effects on affinity and activity. Unsurprisingly with Pin1, like with most proteins, if the binding/active sites are mutated, in most cases a reduction in affinity and/or PPIase activity results (Figure 4). On the other hand, mutations at distal, strategic sites, like I28A and S138A in the interdomain interface, actually increase the isomerase activity through an allosteric mechanism (Figure 4B). In addition, changing the linker length between the two domains also changes the catalytic activity of Pin1. For ligand pCDC25c, the activity is higher for the isolated PPIase domain than in the presence of the WW domain. This questions the hypothesis that the purpose of the WW domain is the increase of local ligand concentration in order to increase the activity of Pin1. Instead, the WW domain appears to play a more subtle role in activity regulation, possibly in context with ligand-specific allostery.
Conclusively, this entry summarized mutations previously studied in Pin1 with their impacts on affinity and activity, and the researchers hope other researchers can use this to evaluate and develop models to describe allostery. A suitable model for allostery would have to be able to explain the extensively mapped out effects of the mutations. This overview could also serve as an aid to make further mutations. Some future projects could look at the double mutants I28A and A140I, as these two residues have been predicted as a co-evolving pair and could give further insights into interdomain allostery [5]. Previous work suggests a conserved, hydrophobic conduit linking the interdomain interface to the PPIase catalytic site [27]. Residues I28, T29, A140, V150, T152, L60, L61, and V62 could be mutant targets for understanding this putative allosteric conduit. These mutations must trigger a coupled response of intra- and interdomain structural dynamics of Pin1.
References
- Ping Lu, K.; Hanes, S.D.; Hunter, T. A human peptidyl–prolyl isomerase essential for regulation of mitosis. Nature 1996, 380, 544–547.
- Zhou, X.Z.; Kops, O.; Werner, A.; Lu, P.J.; Shen, M.; Stoller, G.; Küllertz, G.; Stark, M.; Fischer, G.; Lu, K.P. Pin1-dependent prolyl isomerization regulates dephosphorylation of Cdc25C and tau proteins. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 873–883.
- Yaffe, M.B.; Schutkowski, M.; Shen, M.; Zhou, X.Z.; Stukenberg, P.T.; Rahfeld, J.U.; Xu, J.; Kuang, J.; Kirschner, M.W.; Fischer, G.; et al. Sequence-specific and phosphorylation dependent proline isomerization: A potential mitotic regulatory mechanism. Science 1997, 278, 1957–1960.
- Ranganathan, R.; Lu, K.P.; Hunter, T.; Noel, J.P. Structural and Functional Analysis of the Mitotic Rotamase Pin1 suggest substrate recognition is phosphorylation dependent. Cell 1997, 89, 875–886.
- Wilson, K.A.; Bouchard, J.J.; Peng, J.W. Interdomain interactions support interdomain communication in human pin1. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 6968–6981.
- Jacobs, D.M.; Saxena, K.; Vogtherr, M.; Bernadó, P.; Pons, M.; Fiebig, K.M. Peptide binding induces large scale changes in inter-domain mobility in human Pin1. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 26174–26182.
- Bayer, E.; Goettsch, S.; Mueller, J.W.; Griewel, B.; Guiberman, E.; Mayr, L.M.; Bayer, P. Structural analysis of the mitotic regulator hPin1 in solution: Insights into domain architecture and substrate binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 26183–26193.
- Bouchard, J.J.; Xia, J.; Case, D.A.; Peng, J.W. Enhanced Sampling of Interdomain Motion Using Map-Restrained Langevin Dynamics and NMR: Application to Pin1. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 2164–2180.
- Zhu, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhu, J.; Yang, Y. Uncorrelated Effect of Interdomain Contact on Pin1 Isomerase Activity Reveals Positive Catalytic Cooperativity. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 1272–1278.
- Peng, J.W. Investigating dynamic interdomain allostery in Pin1. Biophys. Rev. 2015, 7, 239–249.
- Liou, Y.-C.; Zhou, X.Z.; Lu, K.P. Prolyl isomerase Pin1 as a molecular switch to determine the fate of phosphoproteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 501–514.
- Bao, L.; Kimzey, A.; Sauter, G.; Sowadski, J.M.; Lu, K.P.; Wang, D.-G. Prevalent Overexpression of Prolyl Isomerase Pin1 in Human Cancers. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 1727–1737.
- Wulf, G.M.; Ryo, A.; Wulf, G.G.; Lee, S.W.; Niu, T.; Petkova, V.; Lu, K.P. Pin1 is overexpressed in breast cancer and cooperates with Ras signaling in increasing the transcriptional activity of c-Jun towards cyclin D1. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 3459–3472.
- Ryo, A.; Nakamura, M.; Wulf, G.; Liou, Y.-C.; Lu, K.P. Pin1 regulates turnover and subcellular localization of β-catenin by inhibiting its interaction with APC. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 793–801.
- Ryo, A.; Suizu, F.; Yoshida, Y.; Perrem, K.; Liou, Y.-C.; Wulf, G.; Rottapel, R.; Yamaoka, S.; Lu, K.P. Regulation of NF-kappaB signaling by Pin1-dependent prolyl isomerization and ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of p65/RelA. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 1413–1426.
- Lam, P.B.; Burga, L.N.; Wu, B.P.; Hofstatter, E.W.; Lu, K.; Wulf, G.M. Prolyl isomerase Pin1 is highly expressed in Her2-positive breast cancer and regulates erbB2 protein stability. Mol. Cancer 2008, 7, 91.
- Rajbhandari, P.; Finn, G.; Solodin, N.M.; Singarapu, K.K.; Sahu, S.C.; Markley, J.L.; Kadunc, K.J.; Ellison-Zelski, S.J.; Kariagina, A.; Haslam, S.Z.; et al. Regulation of Estrogen Receptor N-Terminus Conformation and Function by Peptidyl Prolyl Isomerase Pin1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 445–457.
- Rustighi, A.; Zannini, A.; Tiberi, L.; Sommaggio, R.; Piazza, S.; Sorrentino, G.; Nuzzo, S.; Tuscano, A.; Eterno, V.; Benvenuti, F.; et al. Prolyl-isomerase Pin1 controls normal and cancer stem cells of the breast. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 99–119.
- Lu, P.-J.; Wulf, G.; Zhou, X.Z.; Davies, P.; Lu, K.P. The prolyl isomerase Pin1 restores the function of Alzheimer-associated phosphorylated tau protein. Nature 1999, 399, 784–788.
- Kondo, A.; Albayram, O.; Zhou, X.Z.; Lu, K.P. Pin1 Knockout Mice: A Model for the Study of Tau Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 415–425.
- Butterfield, D.A.; Abdul, H.M.; Opii, W.; Newman, S.F.; Joshi, G.; Ansari, M.A.; Sultana, R. REVIEW: Pin1 in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 1697–1706.
- Pastorino, L.; Sun, A.; Lu, P.-J.; Zhou, X.Z.; Balastik, M.; Finn, G.; Wulf, G.; Lim, J.; Li, S.-H.; Li, X.; et al. The prolyl isomerase Pin1 regulates amyloid precursor protein processing and amyloid-β production. Nature 2006, 440, 528–534.
- Jeener, J.; Meier, B.H.; Bachmann, P.; Ernst, R.R. Investigation of exchange processes by two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. J. Chem. Phys. 1979, 71, 4546–4553.
- Kofron, J.L.; Kuzmic, P.; Kishore, V.; Colón-Bonilla, E.; Rich, D.H. Determination of kinetic constants for peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerases by an improved spectrophotometric assay. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 6127–6134.
- Xu, N.; Tochio, N.; Wang, J.; Tamari, Y.; Uewaki, J.I.; Utsunomiya-Tate, N.; Igarashi, K.; Shiraki, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Tate, S.I. The C113D mutation in human Pin1 causes allosteric structural changes in the phosphate binding pocket of the ppiase domain through the tug of war in the dual-histidine motif. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 5568–5578.
- Innes, B.T.; Bailey, M.L.; Brandl, C.J.; Shilton, B.H.; Litchfield, D.W. Non-catalytic participation of the pin1 peptidyl-prolyl isomerase domain in target binding. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4.
- Namanja, A.T.; Peng, T.; Zintsmaster, J.S.; Elson, A.C.; Shakour, M.G.; Peng, J.W. Substrate Recognition Reduces Side-Chain Flexibility for Conserved Hydrophobic Residues in Human Pin1. Structure 2007, 15, 313–327.
More
Information
Subjects:
Biophysics
Contributor
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
1.2K
Revisions:
3 times
(View History)
Update Date:
22 Feb 2022
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No





