
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Adil El Midaoui | + 2998 word(s) | 2998 | 2022-02-09 04:59:32 | | | |
| 2 | Beatrix Zheng | Meta information modification | 2998 | 2022-02-16 07:20:40 | | | | |
| 3 | Beatrix Zheng | -3 word(s) | 2995 | 2022-02-18 09:23:49 | | | | |
| 4 | Beatrix Zheng | -3 word(s) | 2995 | 2022-02-18 09:24:39 | | |
Video Upload Options
Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) is a medicinal plant, originally cultivated in the East and Middle East, and later in some Mediterranean countries. Saffron is obtained from the stigmas of the plant. Currently, the use of saffron is undergoing a revival. The medicinal virtues of saffron, its culinary use and its high added value have led to the clarification of its phytochemical profile and its biological and therapeutic characteristics. Saffron is rich in carotenoids and terpenes. The major products of saffron are crocins and crocetin (carotenoids) deriving from zeaxanthin, pirocrocin and safranal, which give it its taste and aroma, respectively. Saffron and its major compounds have powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties in vitro and in vivo. Anti-tumor properties have also been described.
1. Benefits of Saffron on Human Health
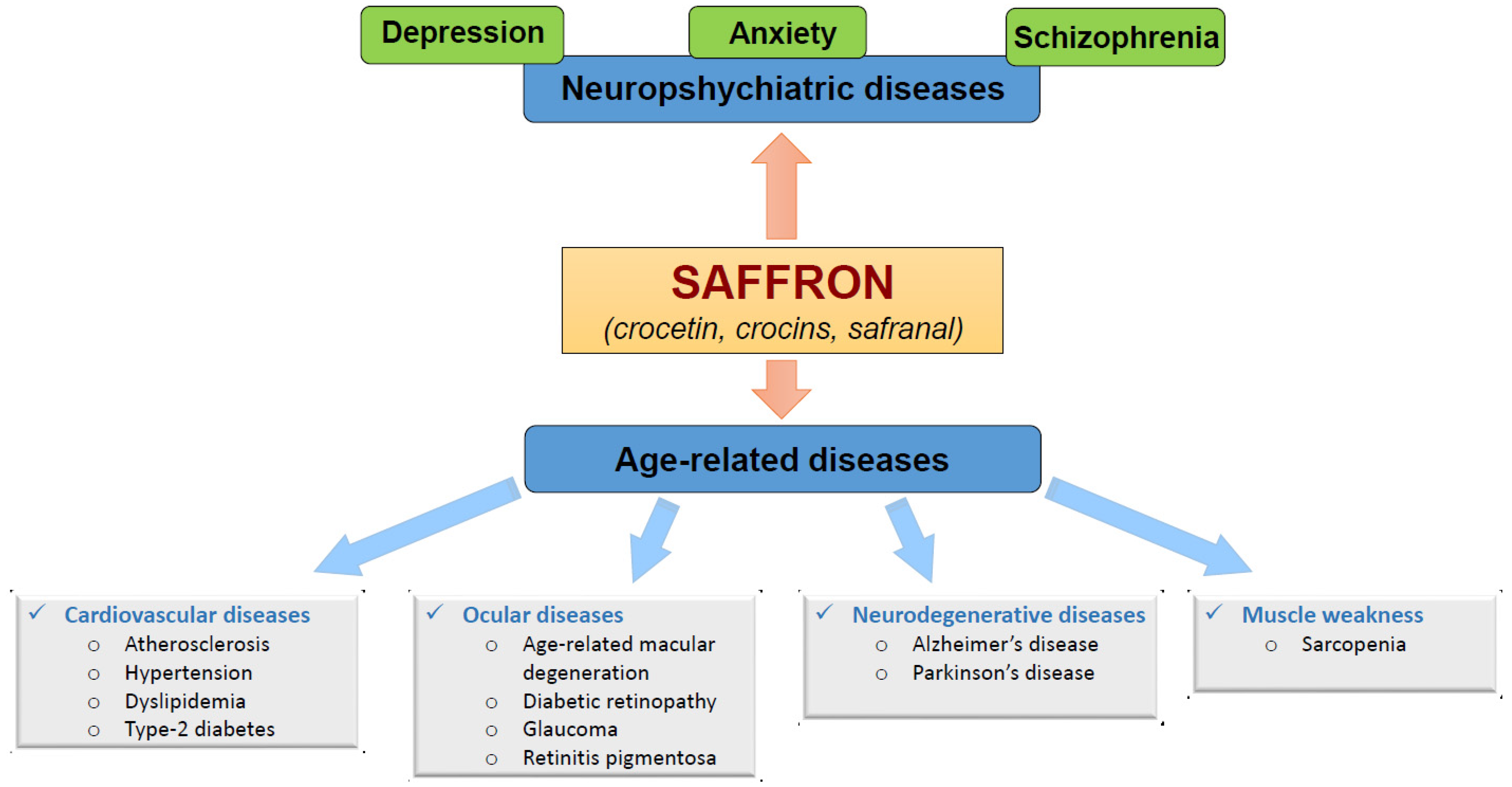 Figure 1. Beneficial effects of saffron constituents (crocetin, crocins and safranal) on neuropsychiatric and age-related diseases.
Figure 1. Beneficial effects of saffron constituents (crocetin, crocins and safranal) on neuropsychiatric and age-related diseases.1.1. Benefits of Saffron on Neuropsychiatric-Diseases
1.1.1. Depression
1.1.2. Anxiety
1.1.3. Schizophrenia
2. Benefits of Saffron on the Prevention of Age-Related Diseases
2.1. Benefits of Saffron on Cardiovascular Diseases
2.1.1. Atherosclerosis
2.1.2. Hypertension
2.1.3. Dyslipidemia
2.1.4. Type-2 Diabetes
2.2. Benefits of Saffron on Ocular Diseases
2.2.1. Age-Related Macular Degeneration
2.2.2. Diabetic Retinopathy
2.2.3. Glaucoma
2.2.4. Retinitis Pigmentosa
2.3. Benefits of Saffron on Neurodegenerative Diseases
2.3.1. Alzheimer’s Disease
2.3.2. Parkinson’s Disease
2.3.3. Prevention of Muscle Weakness in the Elderly
References
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Nassiri-Asl, M. Avicenna’s (Ibn Sina) the Canon of Medicine and Saffron (Crocus sativus): A Review. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 475–483.
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Sadeghi Shakib, S.; Khadem Sameni, A.; Taghiabadi, E. Acute and subacute toxicity of safranal, a constituent of saffron, in mice and rats. Iran J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 93–99.
- Khazdair, M.R.; Boskabady, M.H.; Hosseini, M.; Rezaee, R.; Tsatsakis, A.M. The effects of Crocus sativus (saffron) and its constituents on nervous system: A review. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2015, 5, 376–391.
- Ghaffari, S.; Roshanravan, N. Saffron; An updated review on biological properties with special focus on cardiovascular effects. Biomed. Pharm. 2019, 109, 21–27.
- Hatziagapiou, K.; Lambrou, G.I. The Protective Role of Crocus Sativus L. (Saffron) against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury, Hyperlipidemia and Atherosclerosis: Nature Opposing Cardiovascular Diseases. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2018, 14, 272–289.
- Namdar, H.; Emaratkar, E.; Hadavand, M.B. Persian Traditional Medicine and Ocular Health. Med. Hypothesis Discov. Innov. Ophthalmol. 2015, 4, 162–166.
- Fernández-Albarral, J.A.; de Hoz, R.; Ramírez, A.I.; López-Cuenca, I.; Salobrar-García, E.; Pinazo-Durán, M.D.; Ramírez, J.M.; Salazar, J.J. Beneficial effects of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) in ocular pathologies, particularly neurodegenerative retinal diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 1408–1416.
- Iranshahy, M.; Javadi, B. Diet therapy for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease in view of traditional Persian medicine: A review. Iran J. Basic Med. Sci. 2019, 22, 1102–1117.
- Saeedi, M.; Rashidy-Pour, A. Association between chronic stress and Alzheimer’s disease: Therapeutic effects of Saffron. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110995.
- Yaribeygi, H.; Zare, V.; Butler, A.E.; Barreto, G.E.; Sahebkar, A. Antidiabetic potential of saffron and its active constituents. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8610–8617.
- Mazidi, M.; Shemshian, M.; Mousavi, S.H.; Norouzy, A.; Kermani, T.; Moghiman, T.; Sadeghi, A.; Mokhber, N.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Ferns, G.A. A double-blind, randomized and placebo-controlled trial of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) in the treatment of anxiety and depression. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2016, 13, 195–199.
- Noorbala, A.A.; Akhondzadeh, S.; Tahmacebi-Pour, N.; Jamshidi, A.H. Hydro-alcoholic extract of Crocus sativus L. versus fluoxetine in the treatment of mild to moderate depression: A double-blind, randomized pilot trial. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 97, 281–284.
- Talaei, A.; Hassanpour Moghadam, M.; Sajadi Tabassi, S.A.; Mohajeri, S.A. Crocin, the main active saffron constituent, as an adjunctive treatment in major depressive disorder: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, pilot clinical trial. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 174, 51–56.
- Jam, I.N.; Sahebkar, A.H.; Eslami, S.; Mokhber, N.; Nosrati, M.; Khademi, M.; Foroutan-Tanha, M.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Hadizadeh, F.; Ferns, G.; et al. The effects of crocin on the symptoms of depression in subjects with metabolic syndrome. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 26, 925–930.
- Georgiadou, G.; Grivas, V.; Tarantilis, P.A.; Pitsikas, N. Crocins, the active constituents of Crocus Sativus L., counteracted ketamine-induced behavioural deficits in rats. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 717–726.
- Mousavi, B.; Bathaie, S.Z.; Fadai, F.; Ashtari, Z.; Ali Beigi, N.; Farhang, S.; Hashempour, S.; Shahhamzei, N.; Heidarzadeh, H. Safety evaluation of saffron stigma (Crocus sativus L.) aqueous extract and crocin in patients with schizophrenia. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2015, 5, 413–419.
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Karimi, G.; Niapoor, M. Antidepressant effect of Crocus sativus L. stigma extracts and their constituents, crocin and safranal, in mice. Acta. Hortic. 2004, 650, 435–445.
- Amin, B.; Nakhsaz, A.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Evaluation of the antidepressant-like effects of acute and sub-acute administration of crocin and crocetin in mice. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2015, 5, 458–468.
- Lopresti, A.L.; Drummond, P.D. Efficacy of curcumin, and a saffron/curcumin combination for the treatment of major depression: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 207, 188–196.
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Noraei, N.B. Anxiolytic and hypnotic effect of Crocus sativus aqueous extract and its constituents, crocin and safranal, in mice. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 768–774.
- Pitsikas, N. Constituents of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) as Potential Candidates for the Treatment of Anxiety Disorders and Schizophrenia. Molecules 2016, 21, 303.
- Marder, M.; Estiú, G.; Blanch, L.B.; Viola, H.; Wasowski, C.; Medina, J.H.; Paladini, A.C. Molecular modeling and QSAR analysis of the interaction of flavone derivatives with the benzodiazepine binding site of the GABA(A) receptor complex. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2001, 9, 323–335.
- Georgiadou, G.; Tarantilis, P.A.; Pitsikas, N. Effects of the active constituents of Crocus sativus L., crocins, in an animal model of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 528, 27–30.
- Xing, B.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Lin, D.; Feng, Y.; Lu, J.; Shao, Q. Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and potential clinical applications of saffron: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 281, 114555.
- Mohtashami, L.; Amiri, M.S.; Ramezani, M.; Emami, S.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. The genus Crocus L.: A review of ethnobotanical uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 171, 113923.
- Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, C.; Fang, C. Protective effects of crocetin pretreatment on myocardial injury in an ischemia/reperfusion rat model. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 741, 290–296.
- Mehdizadeh, R.; Parizadeh, M.R.; Khooei, A.R.; Mehri, S.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Cardioprotective effect of saffron extract and safranal in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in wistar rats. Iran J. Basic Med. Sci. 2013, 16, 56–63.
- Joukar, S.; Ghasemipour-Afshar, E.; Sheibani, M.; Naghsh, N.; Bashiri, A. Protective effects of saffron (Crocus sativus) against lethal ventricular arrhythmias induced by heart reperfusion in rat: A potential anti-arrhythmic agent. Pharm. Biol. 2013, 51, 836–843.
- Zhong, K.; Wang, R.X.; Qian, X.D.; Yu, P.; Zhu, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ye, Y.L. Neuroprotective effects of saffron on the late cerebral ischemia injury through inhibiting astrogliosis and glial scar formation in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 126, 110041.
- Higashino, S.; Sasaki, Y.; Giddings, J.C.; Hyodo, K.; Sakata, S.F.; Matsuda, K.; Horikawa, Y.; Yamamoto, J. Crocetin, a carotenoid from Gardenia jasminoides Ellis, protects against hypertension and cerebral thrombogenesis in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1315–1319.
- Sadeghnia, H.R.; Shaterzadeh, H.; Forouzanfar, F.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Neuroprotective effect of safranal, an active ingredient of Crocus sativus, in a rat model of transient cerebral ischemia. Folia Neuropathol. 2017, 55, 206–213.
- Vakili, A.; Einali, M.R.; Bandegi, A.R. Protective effect of crocin against cerebral ischemia in a dose-dependent manner in a rat model of ischemic stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 23, 106–113.
- Gudarzi, S.; Jafari, M.; Pirzad Jahromi, G.; Eshrati, R.; Asadollahi, M.; Nikdokht, P. Evaluation of modulatory effects of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) aqueous extract on oxidative stress in ischemic stroke patients: A randomized clinical trial. Nutr. Neurosci. 2020, 1–10, Online ahead of print.
- Asadollahi, M.; Nikdokht, P.; Hatef, B.; Sadr, S.S.; Sahraei, H.; Assarzadegan, F.; Pirzad Jahromi, G. Protective properties of the aqueous extract of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) in ischemic stroke, randomized clinical trial. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 238, 111833.
- Libby, P.; Buring, J.E.; Badimon, L.; Hansson, G.K.; Deanfield, J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Tokgözoğlu, L.; Lewis, E.F. Atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2019, 5, 56.
- Ellulu, M.S.; Patimah, I.; Khaza’ai, H.; Rahmat, A.; Abed, Y.; Ali, F. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: A review of initiators and protective factors. Inflammopharmacology 2016, 24, 1–10.
- Zheng, S.; Qian, Z.; Tang, F.; Sheng, L. Suppression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression by crocetin contributes to attenuation of atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 1192–1199.
- Zheng, S.; Qian, Z.; Sheng, L.; Wen, N. Crocetin attenuates atherosclerosis in hyperlipidemic rabbits through inhibition of LDL oxidation. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2006, 47, 70–76.
- Xu, G.L.; Yu, S.Q.; Gong, Z.N.; Zhang, S.Q. Study of the effect of crocin on rat experimental hyperlipemia and the underlying mechanisms. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2005, 30, 369–372.
- Sitia, S.; Tomasoni, L.; Atzeni, F.; Ambrosio, G.; Cordiano, C.; Catapano, A.; Tramontana, S.; Perticone, F.; Naccarato, P.; Camici, P.; et al. From endothelial dysfunction to atherosclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 9, 830–834.
- Tang, F.T.; Qian, Z.Y.; Liu, P.Q.; Zheng, S.G.; He, S.Y.; Bao, L.P.; Huang, H.Q. Crocetin improves endothelium-dependent relaxation of thoracic aorta in hypercholesterolemic rabbit by increasing eNOS activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 558–565.
- Christodoulou, E.; Kadoglou, N.P.E.; Stasinopoulou, M.; Konstandi, O.A.; Kenoutis, C.; Kakazanis, Z.I.; Rizakou, A.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Valsami, G. Crocus sativus L. aqueous extract reduces atherogenesis, increases atherosclerotic plaque stability and improves glucose control in diabetic atherosclerotic animals. Atherosclerosis 2018, 268, 207–214.
- Abedimanesh, N.; Motlagh, B.; Abedimanesh, S.; Bathaie, S.Z.; Separham, A.; Ostadrahimi, A. Effects of crocin and saffron aqueous extract on gene expression of SIRT1, AMPK, LOX1, NF-κB, and MCP-1 in patients with coronary artery disease: A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 1114–1122.
- Imenshahidi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H.; Javadpour, Y. Hypotensive effect of aqueous saffron extract (Crocus sativus L.) and its constituents, safranal and crocin, in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 990–994.
- Imenshahidi, M.; Razavi, B.M.; Faal, A.; Gholampoor, A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. The effect of chronic administration of safranal on systolic blood pressure in rats. Iran J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 14, 585–590.
- Razavi, B.M.; Alyasin, A.; Hosseinzadeh, H.; Imenshahidi, M. Saffron Induced Relaxation in Isolated Rat Aorta via Endothelium Dependent and Independent Mechanisms. Iran J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 17, 1018–1025.
- Plangar, A.F.; Anaeigoudari, A.; KhajaviRad, A.; Shafei, M.N. Beneficial Cardiovascular Effects of Hydroalcoholic Extract from Crocus sativus in Hypertension Induced by Angiotensin II. J. Pharmacopunct. 2019, 22, 95–101.
- Modaghegh, M.H.; Shahabian, M.; Esmaeili, H.A.; Rajbai, O.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Safety evaluation of saffron (Crocus sativus) tablets in healthy volunteers. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 1032–1037.
- Hooshmand-Moghadam, B.; Eskandari, M.; Shabkhiz, F.; Mojtahedi, S.; Mahmoudi, N. Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) in combination with resistance training reduced blood pressure in the elderly hypertensive men: A randomized controlled trial. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 3255–3267.
- Asdaq, S.M.; Inamdar, M.N. Potential of Crocus sativus (saffron) and its constituent, crocin, as hypolipidemic and antioxidant in rats. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 162, 358–372.
- Sheng, L.; Qian, Z.; Zheng, S.; Xi, L. Mechanism of hypolipidemic effect of crocin in rats: Crocin inhibits pancreatic lipase. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 543, 116–122.
- Asbaghi, O.; Soltani, S.; Norouzi, N.; Milajerdi, A.; Choobkar, S.; Asemi, Z. The effect of saffron supplementation on blood glucose and lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2019, 47, 102158.
- Mohaqiq, Z.; Moossavi, M.; Hemmati, M.; Kazemi, T.; Mehrpour, O. Antioxidant Properties of Saffron Stigma and Petals: A Potential Therapeutic Approach for Insulin Resistance through an Insulin-Sensitizing Adipocytokine in High-Calorie Diet Rats. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2020, 11, 184.
- Xi, L.; Qian, Z.; Xu, G.; Zheng, S.; Sun, S.; Wen, N.; Sheng, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y. Beneficial impact of crocetin, a carotenoid from saffron, on insulin sensitivity in fructose-fed rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2007, 18, 64–72.
- Moravej Aleali, A.; Amani, R.; Shahbazian, H.; Namjooyan, F.; Latifi, S.M.; Cheraghian, B. The effect of hydroalcoholic Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) extract on fasting plasma glucose, HbA1c, lipid profile, liver, and renal function tests in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized double-blind clinical trial. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1648–1657.
- Azimi, P.; Ghiasvand, R.; Feizi, A.; Hariri, M.; Abbasi, B. Effects of Cinnamon, Cardamom, Saffron, and Ginger Consumption on Markers of Glycemic Control, Lipid Profile, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes Patients. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2014, 11, 258–266.
- Milajerdi, A.; Jazayeri, S.; Hashemzadeh, N.; Shirzadi, E.; Derakhshan, Z.; Djazayeri, A.; Akhondzadeh, S. The effect of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) hydroalcoholic extract on metabolic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A triple-blinded randomized clinical trial. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2018, 23, 16.
- Ebrahimi, F.; Sahebkar, A.; Aryaeian, N.; Pahlavani, N.; Fallah, S.; Moradi, N.; Abbasi, D.; Hosseini, A.F. Effects Of Saffron Supplementation On Inflammation And Metabolic Responses In Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 2107–2115.
- Malvitte, L.; Montange, T.; Joffre, C.; Vejux, A.; Maïza, C.; Bron, A.; Creuzot-Garcher, C.; Lizard, G. Analogies between atherosclerosis and age-related maculopathy: Expected roles of oxysterols. J. Fr. Ophtalmol. 2006, 29, 570–578.
- Fleckenstein, M.; Keenan, T.D.L.; Guymer, R.H.; Chakravarthy, U.; Schmitz-Valckenberg, S.; Klaver, C.C.; Wong, W.T.; Chew, E.Y. Age-related macular degeneration. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 31.
- Heitmar, R.; Brown, J.; Kyrou, I. Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) in Ocular Diseases: A Narrative Review of the Existing Evidence from Clinical Studies. Nutrients 2019, 11, 649.
- Broadhead, G.K.; Grigg, J.R.; McCluskey, P.; Hong, T.; Schlub, T.E.; Chang, A.A. Saffron therapy for the treatment of mild/moderate age-related macular degeneration: A randomised clinical trial. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2019, 257, 31–40.
- Sepahi, S.; Mohajeri, S.A.; Hosseini, S.M.; Khodaverdi, E.; Shoeibi, N.; Namdari, M.; Tabassi, S.A.S. Effects of Crocin on Diabetic Maculopathy: A Placebo-Controlled Randomized Clinical Trial. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 190, 89–98.
- Jabbarpoor Bonyadi, M.H.; Yazdani, S.; Saadat, S. The ocular hypotensive effect of saffron extract in primary open angle glaucoma: A pilot study. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 399.
- Wong, W.L.; Su, X.; Li, X.; Cheung, C.M.; Klein, R.; Cheng, C.Y.; Wong, T.Y. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2014, 2, e106–e116.
- Di Marco, F.; Di Paolo, M.; Romeo, S.; Colecchi, L.; Fiorani, L.; Spana, S.; Stone, J.; Bisti, S. Combining neuroprotectants in a model of retinal degeneration: No additive benefit. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100389.
- Natoli, R.; Zhu, Y.; Valter, K.; Bisti, S.; Eells, J.; Stone, J. Gene and noncoding RNA regulation underlying photoreceptor protection: Microarray study of dietary antioxidant saffron and photobiomodulation in rat retina. Mol. Vis. 2010, 16, 1801–1822.
- Falsini, B.; Piccardi, M.; Minnella, A.; Savastano, C.; Capoluongo, E.; Fadda, A.; Balestrazzi, E.; Maccarone, R.; Bisti, S. Influence of saffron supplementation on retinal flicker sensitivity in early age-related macular degeneration. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 6118–6124.
- Piccardi, M.; Marangoni, D.; Minnella, A.M.; Savastano, M.C.; Valentini, P.; Ambrosio, L.; Capoluongo, E.; Maccarone, R.; Bisti, S.; Falsini, B. A longitudinal follow-up study of saffron supplementation in early age-related macular degeneration: Sustained benefits to central retinal function. Evid. Based. Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 429124.
- Skourtis, G.; Krontira, A.; Ntaoula, S.; Ferlemi, A.V.; Zeliou, K.; Georgakopoulos, C.; Margarity, G.M.; Lamari, N.F.; Pharmakakis, N. Protective antioxidant effects of saffron extract on retinas of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Rom. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 64, 394–403.
- Yang, X.; Huo, F.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Chen, T.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z.; Lv, B. Crocin Inhibits Oxidative Stress and Pro-inflammatory Response of Microglial Cells Associated with Diabetic Retinopathy Through the Activation of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 61, 581–589.
- Fernández-Albarral, J.A.; Ramírez, A.I.; de Hoz, R.; López-Villarín, N.; Salobrar-García, E.; López-Cuenca, I.; Licastro, E.; Inarejos-García, A.M.; Almodóvar, P.; Pinazo-Durán, M.D.; et al. Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Hydrophilic Saffron Extract in a Model of Glaucoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4110.
- Fernández-Sánchez, L.; Lax, P.; Esquiva, G.; Martín-Nieto, J.; Pinilla, I.; Cuenca, N. Safranal, a saffron constituent, attenuates retinal degeneration in P23H rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43074.
- Ohno, Y.; Nakanishi, T.; Umigai, N.; Tsuruma, K.; Shimazawa, M.; Hara, H. Oral administration of crocetin prevents inner retinal damage induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 690, 84–89.
- Yamauchi, M.; Tsuruma, K.; Imai, S.; Nakanishi, T.; Umigai, N.; Shimazawa, M.; Hara, H. Crocetin prevents retinal degeneration induced by oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stresses via inhibition of caspase activity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 650, 110–119.
- Papandreou, M.A.; Kanakis, C.D.; Polissiou, M.G.; Efthimiopoulos, S.; Cordopatis, P.; Margarity, M.; Lamari, F.N. Inhibitory activity on amyloid-beta aggregation and antioxidant properties of Crocus sativus stigmas extract and its crocin constituents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8762–8768.
- Ghahghaei, A.; Bathaie, S.Z.; Kheirkhah, H.; Bahraminejad, E. The protective effect of crocin on the amyloid fibril formation of Aβ42 peptide in vitro. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2013, 18, 328–339.
- Wang, C.; Cai, X.; Hu, W.; Li, Z.; Kong, F.; Chen, X.; Wang, D. Investigation of the neuroprotective effects of crocin via antioxidant activities in HT22 cells and in mice with Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 956–966.
- Akhondzadeh, S.; Sabet, M.S.; Harirchian, M.H.; Togha, M.; Cheraghmakani, H.; Razeghi, S.; Hejazi, S.; Yousefi, M.H.; Alimardani, R.; Jamshidi, A.; et al. Saffron in the treatment of patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease: A 16-week, randomized and placebo-controlled trial. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2010, 35, 581–588.
- Akhondzadeh, S.; Shafiee Sabet, M.; Harirchian, M.H.; Togha, M.; Cheraghmakani, H.; Razeghi, S.; Hejazi, S.S.; Yousefi, M.H.; Alimardani, R.; Jamshidi, A.; et al. A 22-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind controlled trial of Crocus sativus in the treatment of mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Psychopharmacology 2010, 207, 637–643.
- Avgerinos, K.I.; Vrysis, C.; Chaitidis, N.; Kolotsiou, K.; Myserlis, P.G.; Kapogiannis, D. Effects of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) on cognitive function. A systematic review of RCTs. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 2747–2754.
- Chang, H.C.; Liu, K.F.; Teng, C.J.; Lai, S.C.; Yang, S.E.; Ching, H.; Wu, C.R. Sophora Tomentosa Extract Prevents MPTP-Induced Parkinsonism in C57BL/6 Mice Via the Inhibition of GSK-3β Phosphorylation and Oxidative Stress. Nutrients 2019, 11, 252.
- Simola, N.; Morelli, M.; Carta, A.R. The 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotox. Res. 2007, 11, 151–167.
- Ahmad, A.S.; Ansari, M.A.; Ahmad, M.; Saleem, S.; Yousuf, S.; Hoda, M.N.; Islam, F. Neuroprotection by crocetin in a hemi-parkinsonian rat model. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2005, 81, 805–813.
- Rajaei, Z.; Hosseini, M.; Alaei, H. Effects of crocin on brain oxidative damage and aversive memory in a 6-OHDA model of Parkinson’s disease. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2016, 74, 723–729.
- Dong, N.; Dong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gu, X. Crocetin Alleviates Inflammation in MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Models through Improving Mitochondrial Functions. Parkinsons Dis. 2020, 2020, 9864370.
- Dhillon, R.J.; Hasni, S. Pathogenesis and Management of Sarcopenia. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2017, 33, 17–26.
- Meamarbashi, A.; Rajabi, A. Potential Ergogenic Effects of Saffron. J. Diet. Suppl. 2016, 13, 522–529.
- Sajjadi, M.; Bathaie, Z. Comparative Study on The Preventive Effect of Saffron Carotenoids, Crocin and Crocetin, in NMU-Induced Breast Cancer in Rats. Cell J. 2017, 19, 94–101.
- Lei, M.; Guo, C.; Hua, L.; Xue, S.; Yu, D.; Zhang, C.; Wang, D. Crocin Attenuates Joint Pain and Muscle Dysfunction in Osteoarthritis Rat. Inflammation 2017, 40, 2086–2093.
- Bertaggia, E.; Scabia, G.; Dalise, S.; Lo Verso, F.; Santini, F.; Vitti, P.; Chisari, C.; Sandri, M.; Maffei, M. Haptoglobin is required to prevent oxidative stress and muscle atrophy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100745.
- Yu, S.P.; Hunter, D.J. Intra-articular therapies for osteoarthritis. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2016, 17, 2057–2071.
- Shi, Y.; Ivannikov, M.V.; Walsh, M.E.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jaramillo, C.A.; Macleod, G.T.; Van Remmen, H. The lack of CuZnSOD leads to impaired neurotransmitter release, neuromuscular junction destabilization and reduced muscle strength in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100834.
- Ochiai, T.; Shimeno, H.; Mishima, K.; Iwasaki, K.; Fujiwara, M.; Tanaka, H.; Shoyama, Y.; Toda, A.; Eyanagi, R.; Soeda, S. Protective effects of carotenoids from saffron on neuronal injury in vitro and in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1770, 578–584.
- Saeideh, S.; Yasavoli, M.; Gholamnezhad, Z.; Aslani, M.R.; Boskabady, M.H. The Relaxant Effect of Crocin on Rat Tracheal Smooth Muscle and Its Possible Mechanisms. Iran J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 1358–1370.
- Mizuma, H.; Tanaka, M.; Nozaki, S.; Mizuno, K.; Tahara, T.; Ataka, S.; Sugino, T.; Shirai, T.; Kajimoto, Y.; Kuratsune, H.; et al. Daily oral administration of crocetin attenuates physical fatigue in human subjects. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 145–150.




