Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ralf Weiskirchen | + 8285 word(s) | 8285 | 2022-01-18 09:36:59 | | | |
| 2 | Jessie Wu | Meta information modification | 8285 | 2022-01-19 02:40:38 | | | | |
| 3 | Jessie Wu | -3542 word(s) | 4743 | 2022-01-19 02:44:37 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Weiskirchen, R. Cell Therapy in Liver Fibrosis. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/18425 (accessed on 28 February 2026).
Weiskirchen R. Cell Therapy in Liver Fibrosis. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/18425. Accessed February 28, 2026.
Weiskirchen, Ralf. "Cell Therapy in Liver Fibrosis" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/18425 (accessed February 28, 2026).
Weiskirchen, R. (2022, January 18). Cell Therapy in Liver Fibrosis. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/18425
Weiskirchen, Ralf. "Cell Therapy in Liver Fibrosis." Encyclopedia. Web. 18 January, 2022.
Copy Citation
Fibrosis is a common feature in most pathogenetic processes in the liver, and usually results from a chronic insult that depletes the regenerative capacity of hepatocytes and activates multiple inflammatory pathways, recruiting resident and circulating immune cells, endothelial cells, non-parenchymal hepatic stellate cells, and fibroblasts, which become activated and lead to excessive extracellular matrix accumulation.
liver fibrosis
stem cells
1. Introduction
Main liver parenchymal cells, the hepatocytes, not only play key roles in digestive, endocrine, circulatory and secretory body functions, but also display a remarkable regenerative potential. However, continued injury caused by toxins or inflammatory factors leads these cells to a chronic oxidative stress that can trigger cell cycle arrest and exhaustion of the metabolic machinery. Injured hepatocytes secrete cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), that attract other immune and inflammatory cells. Once these cells respond, secreting great amounts of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) and platelet derived growth factor (PDGF), liver cells that synthesize the normal extracellular matrix (ECM), such as perisinusoidal hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and periportal fibroblasts, start their differentiation into myofibroblasts [1]. These are fibrogenic cells, which produce and deposit a pathological collagen-rich ECM in perisinusoidal and periportal areas. These activated cells are a heterogeneous population with different subsets that share the common expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and the marker S100A6 [2].
The main consequence of continued liver damage is fibrosis development, which progressively decreases blood flow to hepatocyte plates, leading to increased hypoxia and cell death. Liver disease progression can take a variable amount of time and spread, depending on the nature and frequency of the insult, but is clinically silent. Most patients who experience hepatic symptoms, receive as their first diagnosis the report of a widespread and advanced fibrosis state, known as cirrhosis. Although hepatic fibrosis is reversible, cirrhosis has a poorer prognosis and often leads to liver failure and the need for orthotopic liver transplantation at some point in the patient’s treatment. Therefore, end-stage liver disease still defies health care systems throughout the world [3].
Several factors may cause hepatocyte injury, among them the Western hypercaloric diet associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, infections with hepatitis C virus, misapplication of pharmacological substances, drug abuse, liver malignancies affecting hepatocytes (hepatomas) or the biliary intrahepatic/extrahepatic tract (cholangiocarcinomas), and congenital or acquired cholangiopathies affecting normal bile flux [4][5].
Liver disease modeling includes animal, ex vivo, and in vitro models, which are to be chosen according to each kind of hepatic disease and considering the extremely complex nature of the organ. Most common animal models of toxic injury use a series of administrations of hepatotoxic agents, such as CCl4 or acetaminophen and its derivatives in rodents. The most common surgical model is bile duct ligation (BDL), with or without bile duct resection [6]. This leads to bile accumulation in the liver and therefore is suitable for the study of cholestatic diseases, such as bile duct atresia, bile duct adenocarcinoma, or gallstones. There is some evidence that some BDL procedures can be spontaneously reversed in rats, and this may be followed by liver regeneration. A safer and less invasive alternative to the BDL model is the 3,5 diethoxicarbonyl-1,4 dihydrocollidine (DDC)-diet, which also induces reversible cholestasis [7].
2. Cell Types Used for the Inhibition of Liver Fibrosis
Cell therapy is an expanding research field and refers to a treatment wherein any cell type and/or cell product—which can also be modified by biotechnology techniques—is targeted for human, animal, or in vitro models of disease. The main goals of cell therapy are to reach continued and stable tissue regeneration, with minor or negligible adverse effects [8]. Future therapeutic schemes will probably focus on a combination of cell therapy and conventional (pharmacological and/or surgical) treatment plans for the best clinical practice.
The most usual drawbacks of cell therapy are frequently a consequence of the developing nature of the field, and recent works focus on reaching a personalized scheme for each patient and disease. This can result in very complex combinations regarding cell types and products used, origin (endogenous or exogenous), additional manipulation in the laboratory, dosage, single, or multiple doses, route of administration, time of intervention, and comorbidities. All these factors can result in higher costs and standards of care to enable the clinical use of cell therapy [9]. Still, once positive outcomes are reached by a refined technique in preclinical phases, cell therapy is likely to be cost-effective and beneficial.
2.1. Bone Marrow Mononuclear Fraction
Adult bone marrow is defined as a specialized niche intimately related to blood, bone, and vascular tissues. Two main subtypes of stem cells reside in the bone marrow stroma: (a) hematopoietic stem cells, which form all blood cell lines and tissue phagocytes, and (b) mesenchymal stem cells, responsible for hematopoietic stem cell survival, renewal, and maintenance [10]. Bone marrow transplantation is among the earliest cell therapy techniques developed and has been extensively used to treat leukemia and immunological deficiency disorders for several decades, being the choice treatment for acute myeloid leukemia. The transplantation is effective for colonizing and restoring bone marrow function in patients after radiotherapy [11]. In the last years, studies have shown that bone marrow mononuclear cell (BMMN) transplantation has therapeutic effects on liver function and ameliorates fibrosis (Table 1).
Table 1. Experimental liver fibrosis and bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMMNs).
| Cells/Dose/Route | Fibrosis Model | Main Results and Mechanisms of Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rat BMMNs, 107 cells, jugular vein | BDL (Wistar rats) | Collagen types I and IV, laminin, CK-19 and α-SMA reduction |
[12] |
| Rat BMMNs, 107 cells, jugular vein | BDL (Wistar rats) | MMP-9 and MMP-13 expression were increased by macrophages, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 reduction | [13] |
| Rat BMMNs, 107 cells, jugular vein | BDL (Wistar rats) | Fibrogenic cell apoptosis | [14] |
| Rat BMMNs, 107 cells, jugular vein | BDL (Wistar rats) | Oxidative stress reduction (4HNE), mitochondrial coupling (UCP2 levels) and biogenesis (PGC1-α) regulation |
[15] |
| Mouse BMMNs, 107 cells, jugular vein | BDL (C57BL/6) | BMMNs originated populations of CD144, CD11b and Ly6G cells in the fibrotic liver, anti-fibrotic cytokines augmentation (IL-10, IL-13, IFN-γ, HGF) and pro-inflammatory cytokines reduction (IL-17A, IL-6) |
[16] |
| Mouse BMMNs or BMMNs-derived monocytes, 106 cells per 3 weeks | CCl4 (orogastric), 200 μL-20%, 12 weeks, C57BL/6 | BMMN derived-monocyte had a better therapeutic effect, pro-inflammatory/fibrotic cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, TGF-β1) reduction, IL-10 and MMP-9 were increased | [17] |
| Mouse BMMNs, 106 cells, tail vein | CCl4 (intraperitoneal) 0.4 mL/kg, 3 x per week, 2 weeks, C57BL/6 | CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Treg cells produced IL-10 and promoted IL-6 and MCP-1 reduction, CD11b+F4/80+ cells were reduced in fibrotic liver | [18] |
4HNE: 4-Hydroxynonenal, BDL: bile duct ligation.
In addition, BMMN transplantation in cholestatic mice decreased Kupffer cells (CD68+) and increased neutrophils (Ly6G+) numbers in fibrotic livers. After transplantation, BMMNs successfully engrafted in the fibrotic liver, directly contributing to the total populations of endothelial cells (CD144+), extrahepatic macrophages (CD11b+), and neutrophils (Ly6G+). These events were positively correlated to the augmented expression of anti-fibrotic cytokines (IL-10, IL-13 and hepatocyte growth factor, HGF) and the reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-17A and IL-6), indicating a shift in the cytokine expression pattern and in macrophage activity/phenotype, from M1 proinflammatory cells to a M2 anti-inflammatory and pro-fibrolytic phenotype [16]. Similar results were found after CD11b+CD14+ bone marrow monocyte therapy, which decreased pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-1β, TGF-β1, and TIMP-1, while IL-10 and MMP-9 were increased [17]. The hypothesis for liver regeneration in this scenario is explained in Figure 1. In another study, Suh and colleagues transplanted CD11b+Gr1+F4/80+ monocytes into fibrotic mice and found that this increased CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Treg cells and IL-10 production, decreasing IL-6 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) levels [18]. Interestingly, it has been found that toxic liver damage promotes the recruitment of a bone marrow monocyte subset that differentiates into profibrogenic CD11b+F4/80+Gr1+ macrophages [19], confirming the role of extrahepatic monocytes in liver disease.
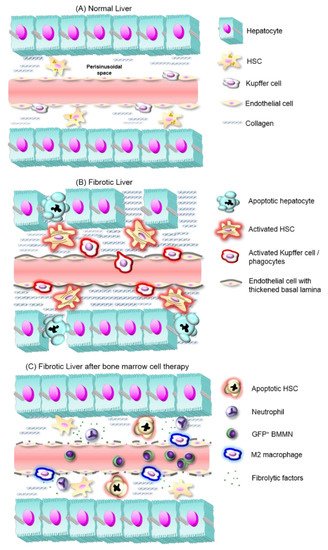
Figure 1. Liver fibrosis development and proposed mechanisms of fibrosis reversal by BMMNs. (A) In normal liver, hepatocyte plates line sinusoidal capillaries and between both structures the submicroscopic perisinusoidal (also subendothelial or Disse space) homes hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which produce small amounts of a reticular extracellular matrix (ECM), and stock retinyl esters. (B) In fibrotic liver, activated Kupffer cells and other inflammatory cells release proinflammatory cytokines, which in turn activate HSCs. These cells increase the deposit of a fibrous ECM in perisinusoidal space. Along with de novo synthesis of a thickened basal lamina around hepatic sinusoids, these events cause hepatocyte hypoxia and apoptosis. (C) After BMMNs expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP+ BMMNs) transplantation, Kupffer cells quantities decrease, while BMMC-derived neutrophils and macrophages with an anti-fibrotic phenotype appear and release anti-inflammatory cytokines. These factors contribute to HSC quiescence and/or apoptosis, and tissue remodeling that ensures the regeneration of liver function.
Stem cell mobilization and consecutive emigration from bone marrow is a noninvasive strategy to attract these cells for liver fibrosis treatment. It has been shown that there is a natural migration of bone marrow cells towards injured organs after transplantation [20]. Stromal derived factor 1 (SDF-1), which is upregulated in pro-inflammatory conditions, including liver damage, acts as a chemo attractant to bone marrow cells through the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis [21][22].
Several soluble factors and drugs could mobilize hematopoietic stem cells from bone marrow into the peripheral blood, such as granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF), plerixafor, and Stem Enhance. G-CSF plus plerixafor treatment significantly improves liver function and increases liver CD34+ cells. G-CSF treatment also promotes hematopoietic stem cells mobilization and migration to injured liver along with TNF-α and IL-6 levels reduction. Plerixafor treatment blocks the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis, decreasing bone marrow cell migration to the liver and ameliorating liver fibrosis mainly through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression increase. Stem Enhance is a natural bone marrow cell mobilizer and its therapeutic effect is associated with CD34+ cells increase, ECM reduction, and liver regeneration, with VEGF up-regulation and TNF-α down-regulation [23][24][25].
Experimental animal studies have shown that BMMN transplantation has beneficial effects on hepatic fibrosis, thus becoming a promising candidate for clinical trials development (Table 2). Phase 1 and 2 studies with autologous bone marrow-derived CD133+ and BMMN transplantation have already been completed (NCT01120925 and NCT00713934), while other BMMN clinical trials are currently in the recruiting phase (NCT03468699).
Table 2. Clinical trials using cells as therapeutic agents for inhibition of liver fibrosis/cirrhosis, registered under ClinicalTrials.gov [26].
| Trial Number (Status) |
Cohort | Intervention | Study Phase Type | Follow-Up (Months) |
Main Analysis Criteria | Outcomes/Published Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02297867 (Completed) |
Liver cirrhosis (n = 6) | Autologous ADSC by intrahepatic injection | Phase I | 1–6 | MELD | NR |
| NCT02705742 (unknown) |
Liver cirrhosis | Autologous ADSC by intravenous injection | Phase I/II | 12 | All-cause mortality | NR |
| NCT04088058 (not yet recruiting) |
Liver cirrhosis (n = 20) | Autologous ADSC by intrahepatic injection | Phase II open-label single-arm | 1–12 | MELD | NR |
| NCT03629015 (not yet recruiting) |
Acute liver failure (n = 20) |
Allogeneic ADSC by intravenous infusion of low (0.5 × 106 cells/kg) or high (2 × 106 cells/kg) dose |
Phase I | 12 | Incidence of adverse events and suspected unexpected serious adverse reaction | NR |
| NCT00913289 (terminated) |
Liver cirrhosis (n = 6) | Autologous adipose tissue-derived stromal cells | Phase I | 6 | All cause harmful events | NR |
| NCT01062750 (Completed) |
Liver cirrhosis (n = 4) | Autologous adipose tissue-derived stromal cells via intrahepatic arterial catheterization | NA | 1 | All cause harmful events | No serious adverse events, albumin serum levels were improved in three patients [27] |
| NCT03254758 (Recruiting) |
Decompensated liver cirrhosis | ADSC by intravenous infusion | Phase I/II | 6 | Incidence of adverse events and Child Pugh score | NR |
| NCT01854125 (unknown) |
Liver cirrhosis (n = 30) | Autologous BMMSC transplantation via hepatic artery catheterization | Phase III | 3 | LF, MELD, adverse effects | Improvement of LF in cirrhotic patients after autologous mesenchymal stem cell injection in phase I–II [28] |
| NCT00993941 (unknown) |
Liver cirrhosis | Autologous BMMSC transplantation via portal vein catheterization or drug therapy (oral or intravenous) |
Phase II | 12 | ALT, total bilirubin, prothrombin time, albumin, laminin, prealbumin, procollagen III, collagen IV, hyaluronidase and histology | NR |
| NCT03838250 (Recruiting) |
Alcoholic liver cirrhosis (n = 10) | Autologous BMMSC transplantation via hepatic artery | Phase I | 12 | Incidence of serious adverse events | NR |
| NCT03468699 (Recruiting) |
Biliary liver cirrhosis (n = 20) | Autologous BMMSC transplantation via hepatic artery | Single group assignment, Phase II | 6 | Cholestasis changes, LF, PELD | NR |
| NCT00713934 (Completed) |
Liver cirrhosis (n = 7) | Autologous BM-derived CD133+ and BM mononuclear stem cells transplantation via portal vein | Randomized Phase I/II | 6 | LF, MELD | NR |
| NCT01120925 (Completed) |
Liver cirrhosis (n = 30) | Autologous BM-derived CD133+ and BM mononuclear stem cells transplantation via portal vein | Randomized Phase I/II | 6 | LF, MELD and Child Pugh scores | NR |
| NCT01333228 (Completed) |
Liver cirrhosis (n = 12), age 18–75 years | Autologous BM-derived EPCs, single group assignment, 8.45 × 106 to 450 × 106 cells administered through the hepatic artery | Single arm non-randomized Phase I/II | 12 | Primary: Number of Participants with adverse events; Secondary: LF, MELD, and Child-Pugh scores, HVPG, complications of liver cirrhosis | Treatment was confirmed safe and feasible, transient (but significant) beneficial effects in LF [29] |
| NCT03109236 (Recruiting) |
Decompensated liver cirrhosis (n = 66) | Autologous BM-derived EPCs administrated via the portal vein system | Two arm randomized Phase III | 3, 6, or 12 | Primary: Fibrosis (Ishak, MRE, MELD, quantitative fibrosis), Secondary: overall survival, LF, HVPG, clinical decompensation, patient reported outcome |
NR |
ALT: alanine aminotransferase, ADSC, adipose-derived stem cell(s), BM: bone marrow, BMMSC: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell(s), EPC: Endothelial progenitor cell(s), HVPG: hepatic venous pressure gradient, LF, liver function, MELD: Model for End-stage Liver Disease, MRE: Magnetic resonance elastography, NA: not applicable, NR: no results available yet, PELD: Pediatric end-stage liver disease.
2.2. Endothelial Progenitor Cells
Neovascularization is fundamental to the healing of injured tissues, because it requires a supply of growth factors, nutrients, and oxygen that must be sufficiently provided by remaining and newly-formed blood vessels [30]. Studies conducted by Asahara and colleagues during the 1990s identified adult bone marrow-derived immature cells in the peripheral blood with in vitro capacity to differentiate into endothelial cells and with the ability to incorporate into sites of neovascularization, both in physiological and pathological in vivo scenarios [31][32]. These adult endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) are rare in the peripheral blood, but can be mobilized in greater numbers from their niche in the bone marrow to the circulation by factors such as VEGF, SDF-1, G-CSF, basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), placental growth factor, and erythropoietin. These mobilizing factors are highly produced by peripheral tissues that undergo hypoxia during tissue damage or healing [33][34], hence recruiting circulating EPCs to the injury site by chemokine signaling [35]. Indeed, patients with liver cirrhosis have increased numbers of circulating EPCs, which correlates with hepatic disease severity [36] and with hepatic venous pressure gradient [37], suggesting that these patients have enhanced mobilization of EPCs. Furthermore, the administration of VEGF after partial hepatectomy in rats corresponded with an increase in EPC incorporation into the liver vasculature [38].
Tissue-recruited EPCs become activated to promote postnatal neovascularization and tissue repair by different mechanisms: differentiation into mature endothelial cells for de novo blood vessel formation (vasculogenesis), incorporation into injured vessels [32][39], and releasing a plethora of trophic and cyto-protective factors with paracrine effect on tissue cells. EPC paracrine action can promote angiogenesis—the process of vessel formation via pre-existing mature endothelial cells—besides tissue remodeling and regeneration, through the secretion of factors that generally include VEGF, HGF, SDF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and MMP-9 [40][41][42][43]. Indeed, increased endogenous plasma levels of VEGF were observed after partial hepatectomy in C57BL6J mice, which correlates with the mobilization and incorporation of bone marrow-derived EPCs into regenerating liver vasculature, suggesting that EPCs became activated and secreted VEGF. Moreover, the rate of liver tissue mass regeneration after partial hepatectomy can be dependent upon EPC mobilization and incorporation into liver tissue, suggesting that these cells could be one of the regulators of liver tissue regeneration after hepatectomy [38].
The potential of EPCs to promote liver angiogenesis by regulating endothelial cell function through paracrine action becomes particularly important considering that posthepatectomy liver tissue mass regeneration is an angiogenic-dependent process directed by the regulation of endothelial proliferation and apoptosis balance [44]. It has been recently described that exosomes are active components of EPC’s paracrine role in vascular repair by up-regulating mature endothelial cell’s function [45]. Moreover, EPC-derived exosome stimulation of endothelial function is mediated by Erk1/2 signaling pathway activation [46] and miR-21-5p delivery to endothelial cells, which suppress the expression of the anti-angiogenic factor thrombospondin-1 [47].
The potential of EPCs-based therapeutic approaches to rescue liver function after tissue fibrosis has been extensively investigated in preclinical studies, showing transplanted EPC mobilization followed by incorporation into the liver parenchyma (Table 3). Transplanted bone marrow-derived EPCs proved to halt established liver fibrosis and to promote hepatic regeneration, which significantly improved survival rates through different cellular and molecular mechanisms. The described mechanisms through which EPCs can mediate liver regenerative processes in fibrotic livers include: (1) reconstitution of sinusoidal blood vessels with endothelium; (2) incorporation into hepatic sinusoids; (3) expression of growth factors, mainly VEGF, HGF, TGF-β, and EGF; (4) stimulation of liver cell proliferation; (5) suppression of activated (fibrogenic) α-SMA+ HSCs; (6) upregulation of endogenous TGF-β and EGF, and downregulation of TGF-β in liver cells; (7) stimulation of MMP activity by producing active forms of MMP-2, MMP-9, and MMP-13, and inhibition of liver TIMP-1 expression; (8) enhancement of eNOS (endothelial nitric oxide synthase) protein levels and upregulation of nitric oxide (NO) secretion [48][49][50][51][52].
Table 3. Experimental liver fibrosis and endothelial progenitor cells.
| Cells/Dose/Route | Fibrosis Model | Main Results and Mechanisms of Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rat BM-EPCs,3 × 106 cells—single or four-repeated doses once a week for 4 weeks, tail vein | CCl4 or thioacetamide (intraperitoneal) twice a week for 10 weeks (Wistar) | Increased survival rates, liver fibrosis and fibrogenesis reduction (HSC suppression and enhanced MMP activity), increased hepatocyte proliferation and HGF, TGF-α, EGF, and VEGF expression in liver | [48] |
| Rat BM-EPCs, 5 × 105 cells, portal vein | CCl4 by gavage twice a week for 16 weeks (Sprague-Dawley) | Increased survival rates, reduced levels of AST, ALT, and TBIL, albumin levels restoration, liver fibrosis and fibrogenesis reduction (HSC suppression), increased liver cell proliferation | [49] |
| Rat BM-EPCs, 3 × 106 cells—once weekly for four weeks, tail vein | Dimethylnitrosamine (intraperitoneal) three times a week for eight weeks (Sprague–Dawley) | Liver fibrosis and fibrogenesis reduction (HSC suppression), increased hepatocyte proliferation, vascular density and HGF, TGF-α and EGF expression in liver | [50] |
| Rat BM-EPCs, 3 × 106 cells—once a week for four weeks, tail vein | CCl4 (intraperitoneal) twice weekly for 10 weeks (Wistar) | Liver fibrosis and fibrogenesis reduction (HSC suppression), reduced portal venous pressure, increased vascular density and hepatic blood flow | [51] |
| Fibrotic rat BM-EPCs, 2 × 105 and 2 × 106 cells—once a week for three weeks, tail vein and portal vein |
CCl4 (subcutaneous) twice a week for six weeks (Wistar) | Liver fibrosis suppression, improved liver function (lower ALT, AST, APTT), increased liver mRNA levels of HGF and VEGF, increased liver cells proliferation | [52] |
BM-EPCs: Bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells; HSC: hepatic stellate cells; MMP: matrix metalloproteinase; HGF: hepatocyte growth factor; TGF-α: transforming growth factor-α, EGF: epidermal growth factor; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; AST: aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; TBIL: total bilirubin; APTT: activated partial thromboplastin time.
All these antifibrogenic and growth effects mediated by EPCs result in liver regeneration through scar tissue degradation, fibrotic area reduction, recovery of hepatocyte number and vascular density, portal hypertension decrease, and hepatic blood flow improvement. EPC-secreted growth factors, like HGF, TGF-β, and EGF, could be responsible for hepatocyte proliferation. In addition, direct and indirect co-cultures of human EPCs and rat liver sinusoidal endothelial cells revealed that EPCs stimulate liver sinusoidal endothelial cells for in vitro tube formation by PDGF and VEGF secretion, demonstrating EPCs’ paracrine role in liver angiogenesis [36]. Moreover, EPCs could inhibit liver fibrosis by affecting activated HSCs. It was suggested that the inhibition of TGF-β expression by HGF, secreted from transplanted EPCs in fibrotic livers, could account for fibrosis reduction, probably by HSC apoptosis [48]. This idea is supported by studies showing that TGF-β inhibits activated HSC apoptosis [53], and that HGF inhibits liver fibrogenesis together with hepatocyte proliferation stimulation in rats with liver damage by downregulating TGF-β [54]. Co-cultures of EPCs and HSCs shed light on the mechanisms by which mobilized EPCs can modulate HSCs and reverse liver fibrosis. Liu and co-workers [55] reported that EPCs degrade the ECM, suppress both proliferation and fibrogenic activity of activated HSCs, and promote activated HSCs apoptosis in vitro through secreted cytokines. Moreover, EPCs’ ability to affect HSC fibrogenic activity and to promote apoptosis was dependent on HGF levels [55].
The above-mentioned positive results from several studies raised clinical interest in EPC-based therapies to treat liver fibrosis and improve liver function. Allogeneic strategies, however, are limited by the immunogenicity of transplanted donor cells. An attempt to overcome this limitation is the co-transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). The combined transplantation of MSCs with a subset of EPCs, both derived from human umbilical cord, reduced in vivo alloimmune responses to EPCs. In vitro experiments showed that inherent MSC immunosuppressive properties were responsible for reduced T-cell mediated immune responses to EPCs [56].
The effectiveness of autologous EPC-based clinical strategies depends on the number and quality of cells collected from the patient. However, altered circulating levels and function of EPCs were reported when pathological features existed, including chronic disorders [57][58][59][60]. Dysfunctional aspects include the reduction of EPC-CFU (colony forming units) number and impairments in mobilization, migratory activity, incorporation into blood vessels, differentiation, and paracrine secretion [57][60][61].
Disturbed EPCs’ commitment and differentiation potential in bone marrow-derived EPCs from mice with liver fibrosis was reported, which might be related to the clinical state of liver fibrosis in animals [62]. An enhanced in vitro proangiogenic potential of EPCs derived from cirrhotic patients compared to healthy subjects was observed [36]. It was suggested that mobilized EPCs into cirrhotic liver activate resident endothelial cells, promoting liver angiogenesis. Considering the close relationship between angiogenesis and fibrogenesis, this raises questions about the enhanced proangiogenic potential of cirrhotic EPCs, which could further aggravate fibrosis and disease progression [63][64]. Studies evaluating the relationship between cirrhotic EPCs and HSCs could clarify the role of diseased EPCs on fibrogenesis process.
In addition, Kaur and colleagues recently reported an inflammatory profile of EPCs derived from patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis [65]. EPCs from disease patients showed lower secretion of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 and a tendency to secrete more pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and RANTES (regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted), compared to those derived from healthy controls. Altogether, these reports show important alterations in EPCs derived from patients with liver chronic damage. Impaired EPC function could lead to insufficient or excessive production of growth factors and/or differentiation, which may jeopardize liver tissue regeneration processes mediated by autologous EPCs. This hypothesis was recently challenged by Lan and colleagues using a liver fibrosis rat model [52]. They were able to isolate normal EPCs from diseased animals, which promoted hepatic neovascularization and the suppression of hepatic fibrogenesis, leading to liver regeneration and function improvement [52]. Differences in liver fibrosis induction, animal species used, and methods of EPC isolation and phenotypical identification could account for the above described discrepancies between reports. More in vitro and pre-clinical studies using human EPCs derived from liver-diseased and healthy subjects are necessary to better understand the potential clinical benefits of autologous EPC-based therapy to treat liver fibrosis.
Despite the inconsistencies regarding autologous EPC therapies, the potential of EPCs to overcome liver fibrosis and promote liver tissue regeneration inspired researchers and clinicians to conduct clinical trials using EPCs as a therapeutic agent to treat liver cirrhosis (Table 2). D’Avola and colleagues [29] reported the results of a nonrandomized, single-arm, phase 1/2 clinical trial showing that autologous bone marrow-derived EPC transplantation through the hepatic artery in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis was feasible and safe, as no occurrence of treatment-related severe adverse events was observed up to one year follow-up. Moreover, transplanted EPCs exerted transient, but significant beneficial effects for liver function and portal hypertension. For the evaluated parameters, they concluded that in vitro expanded EPC quality was not altered by cirrhosis stage. Moreover, in vitro expanded cells presented an active EPC phenotype and produced hepato-protective growth factors like HGF and IGF-1, besides VEGF and EGF, which could underlie the potential clinical benefit of the cell therapy [29]. A Phase 3 randomized and controlled trial is now recruiting (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03109236) and may provide definitive data about the potential clinical benefits of EPC-based therapy to treat patients with end stage cirrhosis.
Finally, bone marrow-derived EPCs constitute a lineage and functional heterogeneous cell population, with different potential cell subsets for endothelial differentiation and for cytokine production [41][66]. Diverse subsets of EPCs were used in the above-mentioned papers, which makes it difficult to compare results and to translate them from bench to bedside. However, the future of the field of EPC-based therapy to treat liver fibrosis will benefit from recent efforts targeting the optimization and standardization of EPC definition, isolation, in vitro expansion to generate a therapeutic dose, characterization, and therapeutic potential [67][68][69][70]. Moreover, in vitro cell pre-conditioning and genetic approaches aiming to correct disease-induced cell dysfunction, enhance EPCs functions or resistance to apoptosis [71][72][73][74] will further contribute to enhance the clinical efficacy of EPC-mediated therapeutic applications for liver failure.
2.3. Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Friedenstein and colleagues described mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) for the first time in the 1980s. They were defined as a cell population in bone marrow that could attach to surfaces, featuring a spindle-shaped morphology [75]. In the following years, several researchers have demonstrated that MSCs are capable of forming colonies, presenting a fast expansion rate in vitro and being capable of osteocyte, adipocyte, and chondrocyte differentiation [76][77]. Because of the lack of more specific features to define MSCs at the time, in 2006, the International Society for Cell therapy (ISCT) proposed minimal criteria to define MSCs: (1) cells must be plastic-adherent, (2) MSC population must express CD105, CD73, and CD90 and lack expression of CD45, CD34, CD14 or CD11b, CD79a, or CD19 and HLA class II; and (3) cells must be able to osteoblast, chondrocyte, and perform adipocyte differentiation. Nowadays, MSCs are recognized by their therapeutic potential [78]. Several features ensured this capacity: non-immunogenicity that allows allogenic transplantation, differentiation capacity, homing to injured sites, immunomodulatory properties, and release of molecules (growth factors and cytokines) as soluble elements or in extracellular vesicles [79][80].
In the context of liver fibrosis, several reports demonstrate the therapeutic potential of MSCs. These cells are capable of in vitro differentiation into hepatocyte-like cells upon induction with a cytokine cocktail [81], co-culture with liver cells [82], valproic acid [83], and under pellet culture condition [84]. Furthermore, in liver diseases, MSCs can exert antifibrotic effects directly by cell–cell contact or paracrine mechanism. MSC cocultivation with HSCs reduces their proliferation, inhibits their activation, and decreases α-SMA expression via the Notch1 signaling pathway activation [85] and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) oxidase inhibition [86]. MSCs’ release of cytokines such as IL-10, TGF-β, and HGF can also inhibit HSC proliferation, decreasing collagen synthesis [87]. These therapeutic mechanisms can be improved by several strategies, such as 3D spheroid culture [88], priming with cytokines [89], and hypoxic conditions [90][91] that enhance antifibrotic, anti-inflammatory, and angiogenic factors produced by MSCs.
Although MSCs have confirmed antifibrotic effects in preclinical studies, there is controversy regarding this outcome. Some reports demonstrated that bone marrow derived MSCs can differentiate into HSCs and myofibroblasts, which could lead to fibrosis progression [92][93]. Ineffectiveness in improving fibrosis was also demonstrated by some authors [94][95]. Some factors, such as timing of treatment (before, during, or after liver injury) and injected cell dose, can interfere with the results. Zhao and colleagues demonstrated that antifibrotic effects on liver are more pronounced if MSCs are injected at earlier times during injury [96]. Reports that injected MSCs after injury cessation did not exhibit antifibrogenic effects [94][95]. Antifibrogenic effects also seem to be dose-dependent, as reported by Hong, who demonstrated that higher doses had a significant decrease in collagen content compared to lower doses [97]. However, these results are non-conclusive, and further studies are needed to elucidate these mechanisms.
A recent approach is the use of MSC secretome, in a strategy that can avoid some limitations involved in cell-based therapies, such as possible tumor formation [98] and loss of immune privileged status [99]. Exossomes, microvesicles, and soluble factors are released by MSCs and their therapeutic potential in liver diseases has been investigated in preclinical studies [80][100].
Currently, researchers obtain MSCs from several tissue sources beyond bone marrow, such as the umbilical cord, placenta, adipose tissue, amniotic fluid, and menstrual blood. In the following sections of this review, we are going to describe the outcomes of liver fibrosis treatment with most common sources of MSCs: bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
References
- Borkham-Kamphorst, E.; Weiskirchen, R. The PDGF system and its antagonists in liver fibrosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016, 28, 53–61.
- Krenkel, O.; Hundertmark, J.; Ritz, T.P.; Weiskirchen, R.; Tacke, F. Single Cell RNA Sequencing Identifies Subsets of Hepatic Stellate Cells and Myofibroblasts in Liver Fibrosis. Cells 2019, 8, 503.
- Peng, Y.; Qi, X.; Guo, X. Child-Pugh Versus MELD Score for the Assessment of Prognosis in Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, e2877.
- Massarweh, N.N.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Control 2017, 24, 1073274817729245.
- Clements, O.; Eliahoo, J.; Un Kim, J.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Khan, S.A. Risk Factors for Intrahepatic and Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2019.
- Tag, C.G.; Sauer-Lehnen, S.; Weiskirchen, S.; Borkham-Kamphorst, E.; Tolba, R.H.; Tacke, F.; Weiskirchen, R. Bile duct ligation in mice: Induction of inflammatory liver injury and fibrosis by obstructive cholestasis. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 96, 52438.
- Addante, A.; Roncero, C.; Almalé, L.; Lazcanoiturburu, N.; García-Álvaro, M.; Fernández, M.; Sanz, J.; Hammad, S.; Nwosu, Z.C.; Lee, S.J.; et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 9 as a key regulator of liver progenitor cells in DDC-induced cholestatic liver injury. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 1664–1675.
- Qi, X.; Guo, X.; Su, C. Clinical Outcomes of the Transplantation of Stem Cells from Various Human Tissue Sources in the Management of Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 10, 166–180.
- Boyd, A.; Newsome, P.; Lu, W.Y. The role of stem cells in liver injury and repair. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 623–631.
- Morrison, S.J.; Scadden, D.T. The bone marrow niche for haematopoietic stem cells. Nature 2014, 505, 327–334.
- Thomas, E.; Storb, R.; Clift, R.A.; Fefer, A.; Johnson, F.L.; Neiman, P.E.; Lerner, K.G.; Glucksberg, H.; Buckner, C.D. Bone-marrow transplantation (first of two parts). N. Engl. J. Med. 1975, 292, 832–843.
- Carvalho, S.N.; Lira, D.C.; Oliveira, G.P.; Thole, A.A.; Stumbo, A.C.; Caetano, C.E.; Marques, R.G.; Carvalho, L. Decreased collagen types I and IV, laminin, CK-19 and α-SMA expression after bone marrow cell transplantation in rats with liver fibrosis. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 134, 493–502.
- Nunes de Carvalho, S.; Helal-Neto, E.; de Andrade, D.C.; Costa Cortez, E.A.; Thole, A.A.; Barja-Fidalgo, C.; de Carvalho, L. Bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation increases metalloproteinase-9 and 13 and decreases tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-1 and 2 expression in the liver of cholestatic rats. Cells Tissues Organs 2013, 198, 139–148.
- Nunes de Carvalho, S.; da Cunha Lira, D.; Costa Cortez, E.A.; de Andrade, D.C.; Thole, A.A.; Stumbo, A.C.; de Carvalho, L. Bone marrow cell transplantation is associated with fibrogenic cells apoptosis during hepatic regeneration in cholestatic rats. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 91, 88–94.
- De Andrade, D.C.; de Carvalho, S.N.; Pinheiro, D.; Thole, A.A.; Moura, A.S.; de Carvalho, L.; Cortez, E.A. Bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation improves mitochondrial bioenergetics in the liver of cholestatic rats. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 336, 15–22.
- Pinheiro, D.; Leirós, L.; Dáu, J.B.T.; Stumbo, A.C.; Thole, A.A.; Cortez, E.A.C.; Mandarim-de-Lacerda, C.A.; Carvalho, L.; Carvalho, S.N. Cytokines, hepatic cell profiling and cell interactions during bone marrow cell therapy for liver fibrosis in cholestatic mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187970.
- De Souza, V.C.A.; Pereira, T.A.; Teixeira, V.W.; Carvalho, H.; de Castro, M.C.A.B.; D’assunção, C.G.; de Barros, A.F.; Carvalho, C.L.; de Lorena, V.M.B.; Costa, V.M.A.; et al. Bone marrow-derived monocyte infusion improves hepatic fibrosis by decreasing osteopontin, TGF-β1, IL-13 and oxidative stress. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 5146–5157.
- Suh, Y.G.; Kim, J.K.; Byun, J.S.; Yi, H.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Eun, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Han, K.H.; Lee, K.S.; Duester, G.; et al. CD11b(+) Gr1(+) bone marrow cells ameliorate liver fibrosis by producing interleukin-10 in mice. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1902–1912.
- Karlmark, K.R.; Weiskirchen, R.; Zimmermann, H.W.; Gassler, N.; Ginhoux, F.; Weber, C.; Merad, M.; Luedde, T.; Trautwein, C.; Tacke, F. Hepatic recruitment of the inflammatory Gr1+ monocyte subset upon liver injury promotes hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology 2009, 50, 261–274.
- Carvalho, S.; Cortez, E.; Stumbo, A.C.; Thole, A.; Caetano, C.; Marques, R.; Pelajo-Machado, M.; Porto, L.C.; Carvalho, L. Laminin expression during bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation in hepatectomized rats. Cell Biol. Int. 2008, 32, 1014–1018.
- Asri, A.; Sabour, J.; Atashi, A.; Soleimani, M. Homing in hematopoietic stem cells: Focus on regulatory role of CXCR7 on SDF1a/CXCR4 axis. EXCLI J. 2016, 15, 134–143.
- Eggenhofer, E.; Luk, F.; Dahlke, M.H.; Hoogduijn, M.J. The life and fate of mesenchymal stem cells. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 148.
- Yannaki, E.; Athanasiou, E.; Xagorari, A.; Constantinou, V.; Batsis, I.; Kaloyannidis, P.; Proya, E.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Fassas, A. G-CSF-primed hematopoietic stem cells or G-CSF per se accelerate recovery and improve survival after liver injury, predominantly by promoting endogenous repair programs. Exp. Hematol. 2005, 33, 108–119.
- Tsolaki, E.; Athanasiou, E.; Gounari, E.; Zogas, N.; Siotou, E.; Yiangou, M.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Yannaki, E. Hematopoietic stem cells and liver regeneration: Differentially acting hematopoietic stem cell mobilization agents reverse induced chronic liver injury. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2014, 53, 124–132.
- El-Akabawy, G.; El-Mehi, A. Mobilization of endogenous bone marrow-derived stem cells in a thioacetamide-induced mouse model of liver fibrosis. Tissue Cell 2015, 47, 257–265.
- ClinicalTrials.gov. The U.S. National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services, National Library of Medicine. Available online: www.clinicaltrials.gov (accessed on 16 September 2019).
- Sakai, Y.; Takamura, M.; Seki, A.; Sunagozaka, H.; Terashima, T.; Komura, T.; Yamato, M.; Miyazawa, M.; Kawaguchi, K.; Nasti, A.; et al. Phase I clinical study of liver regenerative therapy for cirrhosis by intrahepatic arterial infusion of freshly isolated autologous adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem (regenerative) cell. Regen. Ther. 2017, 6, 52–64.
- Kharaziha, P.; Hellström, P.M.; Noorinayer, B.; Farzaneh, F.; Aghajani, K.; Jafari, F.; Telkabadi, M.; Atashi, A.; Honardoost, M.; Zali, M.R.; et al. Improvement of liver function in liver cirrhosis patients after autologous mesenchymal stem cell injection: A phase I-II clinical trial. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 21, 1199–1205.
- D’Avola, D.; Fernández-Ruiz, V.; Carmona-Torre, F.; Méndez, M.; Pérez-Calvo, J.; Prósper, F.; Andreu, E.; Herrero, J.I.; Iñarrairaegui, M.; Fuertes, C.; et al. Phase 1-2 pilot clinical trial in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis treated with bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells. Transl. Res. 2017, 188, 80–91.e2.
- Algire, G.H.; Chalkley, H.W.; Legallais, F.Y.; Park, H.D. Vasculae Reactions of Normal and Malignant Tissues in Vivo. I. Vascular Reactions of Mice to Wounds and to Normal and Neoplastic Transplants. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1945, 6, 73–85.
- Asahara, T.; Murohara, T.; Sullivan, A.; Silver, M.; van der Zee, R.; Li, T.; Witzenbichler, B.; Schatteman, G.; Isner, J.M. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science 1997, 275, 964–967.
- Asahara, T.; Masuda, H.; Takahashi, T.; Kalka, C.; Pastore, C.; Silver, M.; Kearne, M.; Magner, M.; Isner, J.M. Bone marrow origin of endothelial progenitor cells responsible for postnatal vasculogenesis in physiological and pathological neovascularization. Circ. Res. 1999, 85, 221–228.
- Aicher, A.; Heeschen, C.; Mildner-Rihm, C.; Urbich, C.; Ihling, C.; Technau-Ihling, K.; Zeiher, A.M.; Dimmeler, S. Essential role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase for mobilization of stem and progenitor cells. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1370–1376.
- De Falco, E.; Porcelli, D.; Torella, A.R.; Straino, S.; Iachininoto, M.G.; Orlandi, A.; Truffa, S.; Biglioli, P.; Napolitano, M.; Capogrossi, M.C.; et al. SDF-1 involvement in endothelial phenotype and ischemia-induced recruitment of bone marrow progenitor cells. Blood 2004, 104, 3472–3482.
- Ishida, Y.; Kimura, A.; Kuninaka, Y.; Inui, M.; Matsushima, K.; Mukaida, N.; Kondo, T. Pivotal role of the CCL5/CCR5 interaction for recruitment of endothelial progenitor cells in mouse wound healing. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 711–721.
- Kaur, S.; Tripathi, D.; Dongre, K.; Garg, V.; Rooge, S.; Mukopadhyay, A.; Sakhuja, P.; Sarin, S.K. Increased number and function of endothelial progenitor cells stimulate angiogenesis by resident liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (SECs) in cirrhosis through paracrine factors. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 1193–1198.
- Sieghart, W.; Fellner, S.; Reiberger, T.; Ulbrich, G.; Ferlitsch, A.; Wacheck, V.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M. Differential role of circulating endothelial progenitor cells in cirrhotic patients with or without hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig. Liver Dis. 2009, 41, 902–906.
- Beaudry, P.; Hida, Y.; Udagawa, T.; Alwayn, I.P.; Greene, A.K.; Arsenault, D.; Folkman, J.; Heymach, J.V.; Ryeom, S.; Puder, M. Endothelial progenitor cells contribute to accelerated liver regeneration. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2007, 42, 1190–1198.
- Asahara, T.; Kawamoto, A.; Masuda, H. Concise review: Circulating endothelial progenitor cells for vascular medicine. Stem Cells 2011, 29, 1650–1655.
- Rehman, J.; Li, J.; Orschell, C.M.; March, K.L. Peripheral blood “endothelial progenitor cells” are derived from monocyte/macrophages and secrete angiogenic growth factors. Circulation 2003, 107, 1164–1169.
- Miyamoto, Y.; Suyama, T.; Yashita, T.; Akimaru, H.; Kurata, H. Bone marrow subpopulations contain distinct types of endothelial progenitor cells and angiogenic cytokine-producing cells. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2007, 43, 627–635.
- Yang, Z.; von Ballmoos, M.W.; Faessler, D.; Voelzmann, J.; Ortmann, J.; Diehm, N.; Kalka-Moll, W.; Baumgartner, I.; Di Santo, S.; Kalka, C. Paracrine factors secreted by endothelial progenitor cells prevent oxidative stress-induced apoptosis of mature endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2010, 211, 103–109.
- Di Santo, S.; Yang, Z.; Wyler von Ballmoos, M.; Voelzmann, J.; Diehm, N.; Baumgartner, I.; Kalka, C. Novel cell-free strategy for therapeutic angiogenesis: In vitro generated conditioned medium can replace progenitor cell transplantation. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5643.
- Greene, A.K.; Wiener, S.; Puder, M.; Yoshida, A.; Shi, B.; Perez-Atayde, A.R.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Holmgren, L.; Adamis, A.P.; Rupnick, M.; et al. Endothelial-directed hepatic regeneration after partial hepatectomy. Ann. Surg. 2003, 237, 530–535.
- Li, X.; Chen, C.; Wei, L.; Li, Q.; Niu, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J. Exosomes derived from endothelial progenitor cells attenuate vascular repair and accelerate reendothelialization by enhancing endothelial function. Cytotherapy 2016, 18, 253–262.
- Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Hu, B.; Niu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y. Exosomes Derived from Human Endothelial Progenitor Cells Accelerate Cutaneous Wound Healing by Promoting Angiogenesis Through Erk1/2 Signaling. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 1472–1487.
- Hu, H.; Wang, B.; Jiang, C.; Li, R.; Zhao, J. Endothelial progenitor cell-derived exosomes facilitate vascular endothelial cell repair through shuttling miR-21-5p to modulate Thrombospondin-1 expression. Clin. Sci. 2019, 33, 1629–1644.
- Nakamura, T.; Torimura, T.; Sakamoto, M.; Hashimoto, O.; Taniguchi, E.; Inoue, K.; Sakata, R.; Kumashiro, R.; Murohara, T.; Ueno, T.; et al. Significance and therapeutic potential of endothelial progenitor cell transplantation in a cirrhotic liver rat model. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 91–107.e1.
- Liu, F.; Liu, Z.D.; Wu, N.; Cong, X.; Fei, R.; Chen, H.S.; Wei, L. Transplanted endothelial progenitor cells ameliorate carbon tetrachloride-induced liver cirrhosis in rats. Liver Transpl. 2009, 15, 1092–1100.
- Nakamura, T.; Torimura, T.; Iwamoto, H.; Masuda, H.; Naitou, M.; Koga, H.; Abe, M.; Hashimoto, O.; Tsutsumi, V.; Ueno, T.; et al. Prevention of liver fibrosis and liver reconstitution of DMN-treated rat liver by transplanted EPCs. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 42, 717–728.
- Sakamoto, M.; Nakamura, T.; Torimura, T.; Iwamoto, H.; Masuda, H.; Koga, H.; Abe, M.; Hashimoto, O.; Ueno, T.; Sata, M. Transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells ameliorates vascular dysfunction and portal hypertension in carbon tetrachloride-induced rat liver cirrhotic model. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 168–178.
- Lan, L.; Liu, R.; Qin, L.Y.; Cheng, P.; Liu, B.W.; Zhang, B.Y.; Ding, S.Z.; Li, X.L. Transplantation of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells and hepatocyte stem cells from liver fibrosis rats ameliorates liver fibrosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 237–247.
- Saile, B.; Matthes, N.; Knittel, T.; Ramadori, G. Transforming growth factor beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibit both apoptosis and proliferation of activated rat hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 1999, 30, 196–202.
- Matsuda, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Yamada, A.; Ichida, T.; Asakura, H.; Komoriya, Y.; Nishiyama, E.; Nakamura, T. Preventive and therapeutic effects in rats of hepatocyte growth factor infusion on liver fibrosis/cirrhosis. Hepatology 1997, 26, 81–89.
- Liu, F.; Liu, Z.D.; Wu, N.; Wang, J.H.; Zhang, H.H.; Fei, R.; Cong, X.; Chen, H.S.; Wei, L. In vitro interactions between rat bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells and hepatic stellate cells: Interaction between EPCs and HSCs. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2013, 49, 537–547.
- Souidi, N.; Stolk, M.; Rudeck, J.; Strunk, D.; Schallmoser, K.; Volk, H.D.; Seifert, M. Stromal Cells Act as Guardians for Endothelial Progenitors by Reducing Their Immunogenicity After Co-Transplantation. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 1233–1245.
- Tepper, O.M.; Galiano, R.D.; Capla, J.M.; Kalka, C.; Gagne, P.J.; Jacobowitz, G.R.; Levine, J.P.; Gurtner, G.C. Human endothelial progenitor cells from type II diabetics exhibit impaired proliferation, adhesion, and incorporation into vascular structures. Circulation 2002, 106, 2781–2786.
- Kawamoto, A.; Asahara, T. Role of progenitor endothelial cells in cardiovascular disease and upcoming therapies. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2007, 70, 477–484.
- Masuda, J.; Mitsuyama, K.; Yamasaki, H.; Takedatsu, H.; Okamura, T.; Andoh, A.; Murohara, T.; Asahara, T.; Sata, M. Depletion of endothelial progenitor cells in the peripheral blood of patients with ulcerative colitis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 19, 221–228.
- Capla, J.M.; Grogan, R.H.; Callaghan, M.J.; Galiano, R.D.; Tepper, O.M.; Ceradini, D.J.; Gurtner, G.C. Diabetes impairs endothelial progenitor cell-mediated blood vessel formation in response to hypoxia. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2007, 119, 59–70.
- Hill, J.M.; Zalos, G.; Halcox, J.P.; Schenke, W.H.; Waclawiw, M.A.; Quyyumi, A.A.; Finkel, T. Circulating endothelial progenitor cells, vascular function, and cardiovascular risk. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 593–600.
- Shirakura, K.; Masuda, H.; Kwon, S.M.; Obi, S.; Ito, R.; Shizuno, T.; Kurihara, Y.; Mine, T.; Asahara, T. Impaired function of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells in murine liver fibrosis. Biosci. Trends 2011, 5, 77–82.
- Rautou, P.-E. Endothelial progenitor cells in cirrhosis: The more, the merrier? J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 1163–1165.
- Kaur, S.; Anita, K. Angiogenesis in liver regeneration and fibrosis: “a double-edged sword”. Hepatol. Int. 2013, 7, 959–968.
- Kaur, S.; Sehgal, R.; Shastry, S.M.; McCaughan, G.; McGuire, H.M.; Fazekas St de Groth, B.; Sarin, S.; Trehanpati, N.; Seth, D. Circulating Endothelial Progenitor Cells Present an Inflammatory Phenotype and Function in Patients with Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 556.
- Fadini, G.P.; Losordo, D.; Dimmeler, S. Critical reevaluation of endothelial progenitor cell phenotypes for therapeutic and diagnostic use. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 624–637.
- Hofmann, N.A.; Reinisch, A.; Strunk, D. Endothelial colony-forming progenitor cell isolation and expansion. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 879, 381–387.
- Tasev, D.; van Wijhe, M.H.; Weijers, E.M.; van Hinsbergh, V.W.; Koolwijk, P. Long-Term Expansion in Platelet Lysate Increases Growth of Peripheral Blood-Derived Endothelial-Colony Forming Cells and Their Growth Factor-Induced Sprouting Capacity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129935.
- Takizawa, S.; Nagata, E.; Nakayama, T.; Masuda, H.; Asahara, T. Recent Progress in Endothelial Progenitor Cell Culture Systems: Potential for Stroke Therapy. Neurol. Med. Chir. (Tokyo) 2016, 56, 302–309.
- Medina, R.J.; Barber, C.L.; Sabatier, F.; Dignat-George, F.; Melero-Martin, J.M.; Khosrotehrani, K.; Ohneda, O.; Randi, A.M.; Chan, J.K.Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; et al. Endothelial Progenitors: A Consensus Statement on Nomenclature. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1316–1320.
- Akita, T.; Murohara, T.; Ikeda, H.; Sasaki, K.; Shimada, T.; Egami, K.; Imaizumi, T. Hypoxic preconditioning augments efficacy of human endothelial progenitor cells for therapeutic neovascularization. Lab. Investig. 2003, 83, 65–73.
- Choi, J.H.; Hur, J.; Yoon, C.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, C.S.; Youn, S.W.; Oh, I.Y.; Skurk, C.; Murohara, T.; Park, Y.B.; et al. Augmentation of therapeutic angiogenesis using genetically modified human endothelial progenitor cells with altered glycogen synthase kinase-3beta activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 49430–49438.
- Roncalli, J.; Tongers, J.; Renault, M.A.; Losordo, D.W. Biological approaches to ischemic tissue repair: Gene- and cell-based strategies. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2008, 6, 653–668.
- Goto, K.; Takemura, G.; Takahashi, T.; Okada, H.; Kanamori, H.; Kawamura, I.; Watanabe, T.; Morishita, K.; Tsujimoto, A.; Miyazaki, N.; et al. Intravenous Administration of Endothelial Colony-Forming Cells Overexpressing Integrin β1 Augments Angiogenesis in Ischemic Legs. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 218–226.
- Owen, M.; Friedenstein, A.J. Stromal stem cells: Marrow-derived osteogenic precursors. Ciba Found. Symp. 1988, 136, 42–60.
- Pereira, R.F.; O’Hara, M.D.; Laptev, A.V.; Halford, K.W.; Pollard, M.D.; Class, R.; Simon, D.; Livezey, K.; Prockop, D.J. Marrow stromal cells as a source of progenitor cells for nonhematopoietic tissues in transgenic mice with a phenotype of osteogenesis imperfecta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 1142–1147.
- Spees, J.L.; Olson, S.D.; Ylostalo, J.; Lynch, P.J.; Smith, J.; Perry, A.; Peister, A.; Wang, M.Y.; Prockop, D.J. Differentiation, cell fusion, and nuclear fusion during ex vivo repair of epithelium by human adult stem cells from bone marrow stroma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2397–2402.
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.; Horwitz, E. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317.
- Mushahary, D.; Spittler, A.; Kasper, C.; Weber, V.; Charwat, V. Isolation, cultivation, and characterization of human mesenchymal stem cells. Cytometry A 2018, 93, 19–31.
- Driscoll, J.; Patel, T. The mesenchymal stem cell secretome as an acellular regenerative therapy for liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 763–773.
- Choi, J.S.; Ryu, H.A.; Cheon, S.H.; Kim, S.W. Human Adipose Derived Stem Cells Exhibit Enhanced Liver Regeneration in Acute Liver Injury by Controlled Releasing Hepatocyte Growth Factor. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 52, 935–950.
- Lange, C.; Bassler, P.; Lioznov, M.V.; Bruns, H.; Kluth, D.; Zander, A.R.; Fiegel, H.C. Liver-specific gene expression in mesenchymal stem cells is induced by liver cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 4497–4504.
- An, S.Y.; Han, J.; Lim, H.J.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Do, B.R. Valproic acid promotes differentiation of hepatocyte-like cells from whole human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Cell 2014, 46, 127–135.
- Ong, S.Y.; Dai, H.; Leong, K.W. Inducing hepatic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in pellet culture. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4087–4097.
- Chen, S.; Xu, L.; Lin, N.; Pan, W.; Hu, K.; Xu, R. Activation of Notch1 signaling by marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells through cell-cell contact inhibits proliferation of hepatic stellate cells. Life Sci 2011, 89, 975–981.
- Qiao, H.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, X.; Cheng, J.; He, Y.; Jiang, Y. NADPH Oxidase Signaling Pathway Mediates Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Induced Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 1239143.
- Eom, Y.W.; Shim, K.Y.; Baik, S.K. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for liver fibrosis. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2015, 30, 580–589.
- Zhang, X.; Hu, M.G.; Pan, K.; Li, C.H.; Liu, R. 3D Spheroid Culture Enhances the Expression of Antifibrotic Factors in Human Adipose-Derived MSCs and Improves Their Therapeutic Effects on Hepatic Fibrosis. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 4626073.
- Harting, M.T.; Srivastava, A.K.; Zhaorigetu, S.; Bair, H.; Prabhakara, K.S.; Toledano Furman, N.E.; Vykoukal, J.V.; Ruppert, K.A.; Cox, C.S., Jr.; Olson, S.D. Inflammation-Stimulated Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Inflammation. Stem Cells 2018, 36, 79–90.
- Lee, S.C.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, S.J. Hypoxic Conditioned Medium from Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Promotes Mouse Liver Regeneration Through JAK/STAT3 Signaling. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 816–825.
- Liu, L.; Gao, J.; Yuan, Y.; Chang, Q.; Liao, Y.; Lu, F. Hypoxia preconditioned human adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells enhance angiogenic potential via secretion of increased VEGF and bFGF. Cell Biol. Int. 2013, 37, 551–560.
- Baba, S.; Fujii, H.; Hirose, T.; Yasuchika, K.; Azuma, H.; Hoppo, T.; Naito, M.; Machimoto, T.; Ikai, I. Commitment of bone marrow cells to hepatic stellate cells in mouse. J. Hepatol. 2004, 40, 255–260.
- Russo, F.P.; Alison, M.R.; Bigger, B.W.; Amofah, E.; Florou, A.; Amin, F.; Bou-Gharios, G.; Jeffery, R.; Iredale, J.P.; Forbes, S.J. The bone marrow functionally contributes to liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1807–1821.
- Carvalho, A.B.; Quintanilha, L.F.; Dias, J.V.; Paredes, B.D.; Mannheimer, E.G.; Carvalho, F.G.; Asensi, K.D.; Gutfilen, B.; Fonseca, L.M.; Resende, C.M.; et al. Bone marrow multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells do not reduce fibrosis or improve function in a rat model of severe chronic liver injury. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 1307–1314.
- Mannheimer, E.G.; Quintanilha, L.F.; Carvalho, A.B.; Paredes, B.D.; Gonçalves de Carvalho, F.; Takyia, C.M.; Resende, C.M.; Ferreira da Motta Rezende, G.; Campos de Carvalho, A.C.; Schanaider, A.; et al. Bone marrow cells obtained from cirrhotic rats do not improve function or reduce fibrosis in a chronic liver disease model. Clin. Transplant. 2011, 25, 54–60.
- Zhao, D.C.; Lei, J.X.; Chen, R.; Yu, W.H.; Zhang, X.M.; Li, S.N.; Xiang, P. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect against experimental liver fibrosis in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 3431–3440.
- Hong, J.; Jin, H.; Han, J.; Hu, H.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wu, M.; Qiu, L.; et al. Infusion of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells effectively relieves liver cirrhosis in DEN-induced rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 1103–1111.
- Fiorina, P.; Jurewicz, M.; Augello, A.; Vergani, A.; Dada, S.; La Rosa, S.; Selig, M.; Godwin, J.; Law, K.; Placidi, C.; et al. Immunomodulatory function of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in experimental autoimmune type 1 diabetes. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 993–1004.
- Gazdic, M.; Volarevic, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Stojkovic, M. Mesenchymal stem cells: A friend or foe in immune-mediated diseases. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2015, 11, 280–287.
- Lou, G.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Y. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e346.
More
Information
Contributor
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
1.1K
Revisions:
3 times
(View History)
Update Date:
19 Jan 2022
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No





