
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Huawei Zhang | + 1114 word(s) | 1114 | 2021-12-21 07:33:20 | | | |
| 2 | Camila Xu | + 51 word(s) | 1165 | 2021-12-29 07:18:38 | | | | |
| 3 | Camila Xu | Meta information modification | 1165 | 2021-12-29 07:19:51 | | |
Video Upload Options
1,3-Oxazole compounds are a unique class of five-membered monocyclic heteroarenes, containing a nitrogen atom and an oxygen. These alkaloids have attracted extensive attention from medicinal chemists and pharmacologists owing to their diverse arrays of chemical structures and biological activities, and a series of 1,3-oxazole derivatives has been developed into therapeutic agents, such as almoxatone, befloxatone, cabotegravir, delpazolid, fenpipalone, haloxazolam, inavolisib.
1. Peptides
Two novel linear and achiral polyketide-peptides, ariakemicins A (18) and B (19), were obtained as an inseparable mixture from one marine gliding bacterium Rapidithrix sp., collected off the muddy land alongside the Ariake Inland Sea, and displayed selectively antimicrobial activities against Gram-positive bacteria (Brevibacterium sp., S. aureus, and Bacillus subtilis), and weak cytotoxicity against cancer cell lines A549 and BHK [1]. Breitfussins A–H (20–27) were the first marine natural products containing an indole-oxazole-pyrrole framework from hydrozoan Thuiaria breitfussi inhabits in the Arctic ocean, and were found to excellently inhibit PIM1 and DRAK1 kinases [2][3]. Furthermore, breitfussin C (22) strongly exhibited a cytotoxic effect on cancer cell lines (MCF-7, HT-29, MOLT-4, MV-4-11 and MRC-5). One concise total synthesis of the halogen-rich dipeptides 20 and 21 was created by Bayer and his coworkers in 2015, which consists of the palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling of indole and pyrrole on an oxazole core and selective lithiation/iodination of a common indole-oxazole fragment [4]. Mechercharmycin B (28) was a new linear peptide containing four 1,3-oxazole rings produced by the marine strain Thermoactinomyces sp. YM3-251 from Mecherchar (Palau) [5]. Siphonazole (29) and dimethoxy analog (30) were the first naturally occurring substances that incorporated oxazole subunits connected by a two-carbon tether from a marine microbe Herpetosiphon sp., and exhibited selective cytotoxicity to human breast cancer HTB-129 and acute T cell leukemia TIB-152 [6]. The first chemical synthesis of 29 was achieved in 2007 through the preparation of an oxazole ring using rhodium carbene, and the installation of the pentadienyl amino side-chain [7].
2. Macrolides
Two cytotoxic isomers, phorboxazoles A (138) (Scheme 10) and B (139), as well as the precursor (140) were detected in the Indian Ocean marine sponge Phorbas sp. [8][9]. Leiodolides A (141) and B (142) were the first members of a new class of mixed polyketide-nonribosomal peptide synthetase from the deep-water marine sponge Leiodermatium. They structurally possess a 19-membered ring and several unique functional groups, including a bromine substituent and an α-hydroxy-α-methyl carboxylic acid side-chain terminus. These substances had obvious cytotoxic effects against human colon cancer HCT-116 with IC50 values of 2.5 and 5.6 μM, respectively [10]. Chemical investigation of the Madagascan sponge Fascaplysinopsis sp. afforded three macrolides with bis-epoxide motif salarins 143–145, which showed pronounced inhibitory on human leukemia cell lines UT-7 [11][12]. Theonezolides A–C (146–148) from the Okinawan Theonella sp. were novel oxazole-containing macrolides that compose of two main fatty acid chains, including a 37-membered macrolide ring with long side chains connected by amide bonds. They exhibited cytotoxicity on a murine lymphoma L1210 and human epidermoid carcinoma KB cells and induced a platelet morphology change and aggregation in rabbits [13][14][15].
3. Polyketides
By OSMAC (one strain many compounds) strategy, inthomycin B (217) was produced by the marine sediment-derived Streptomyces YB104 and was found to have anti-oomycete, cytotoxic and herbicidal activities [16]. One concise method to synthesize 217 was developed by Webb and coworkers through the Stille coupling of a stannyl-diene with an oxazole vinyl iodide unit and a Kiyooka ketene acetal/amino acid-derived oxazaborolidine procedure as its cornerstones [17]. And the gene cluster (itm) responsible for biosynthesis of 217 was identified as a 95.3 kb trans-AT type I PKS system, of which the gene Itm15 is a cyclodehydrase to catalyze the formation of oxazole ring [16].
By extensive chromatographic techniques, eight hennoxazoles (222–229) were isolated from the sponge Polyfibrospongia sp., of which 222 had peripheral analgesic activity equivalent to the positive control of indomethacin, and 228 exhibited the greatest cytotoxicity toward L1210 with an IC50 value of 2 µg/mL [18][19]. Antibiotic B-90063 (230) was a novel endothelin-converting enzyme (ECE) inhibitor from the marine strain Blastobacter sp. SANK 71894, collected off the coast of Ojika Peninsula [20]. Bengazoles 231–236 were antifungal agents obtained from the marine sponge Pachastrissa sp., collected at Musha Archipelago (Djibouti) [21]. An uncommon oxazole, bengazole A (237) from the sponge Jaspis sp., displayed remarkable ergosterol-dependent antifungal activity against C. albicans, which is equivalent to amphotericin B [22].
4. Benzoxazoles
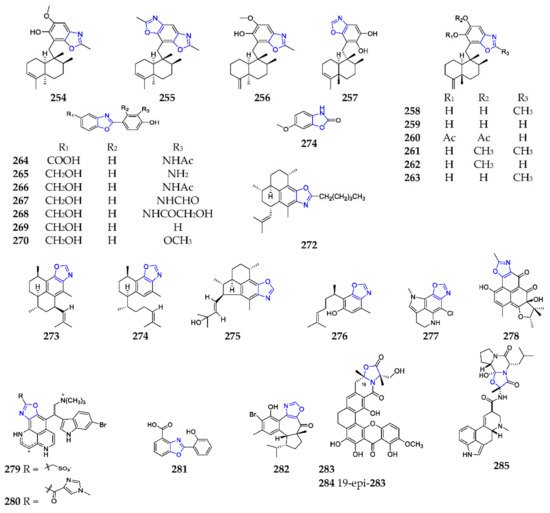
5. Conclusions
References
- Oku, N.; Adachi, K.; Matsuda, S.; Kasai, H.; Takatsuki, A.; Shizuri, Y. Ariakemicins A and B, novel polyketide-peptide antibi-otics from a marine gliding bacterium of the genus Rapidithrix. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 2481–2484.
- Hansen, K.; Andersen, J.H.; Bayer, A.; Pandey, S.K.; Lorentzen, M.; Jørgensen, K.B.; Sydnes, M.O.; Guttormsen, Y.; Baumann, M.; Koch, U.; et al. Kinase chemodiversity from the arctic: The breitfussins. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 10167–10181.
- Hanssen, K.; Schuler, B.; Williams, A.; Demissie, T.B.; Hansen, E.; Andersen, J.H.; Svenson, J.; Blinov, K.; Repisky, M.; Mohn, F.; et al. A combined atomic force microscopy and computational approach for the structural elucidation of breitfussin A and B: highly modified halogenated dipeptides from Thuiaria breitfussi. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12238–12241.
- Pandey, S.K.; Guttormsen, Y.; Haug, B.E.; Hedberg, C.; Bayer, A. A concise total synthesis of breitfussin A and B. Org. Lett. 2014, 17, 122–125.
- Kanoh, K.; Matsuo, Y.; Adachi, K.; Imagawa, H.; Nishizawa, M.; Shizuri, Y. Mechercharmycins A and B, cytotoxic substances from marine-derived Thermoactinomyces sp. YM3-251. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 289–292.
- Zhang, J.; Polishchuk, E.A.; Chen, J.; Ciufolini, M.A. Development of an oxazole conjunctive reagent and application to the total synthesis of siphonazoles. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 9140–9151.
- Linder, J.; Moody, C.J. The total synthesis of siphonazole, a structurally unusual bis-oxazole natural product. Chem. Commun. 2007, 1508–1509.
- Molinski, T.F. Absolute configuration of phorboxazoles A and B from the marine sponge, Phorbas sp. 2. C43 and complete stereochemistry. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 7879–7880.
- Dalisay, D.S.; Molinski, T.F. Structure elucidation at the nanomole scale. 2. Hemi-phorboxazole A from Phorbas sp. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 1967–1970.
- Sandler, J.S.; Colin, P.L.; Kelly, M.; Fenical, W. Cytotoxic macrolides from a new species of the deep-water marine sponge Leiodermatium. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 7245–7251.
- Bishara, A.; Rudi, A.; Aknin, M.; Neumann, D.; Ben-Califa, N.; Kashman, Y. Salarin C, a new cytotoxic sponge-derived nitrogenous macrolide. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 4355–4358.
- Bishara, A.; Rudi, A.; Aknin, M.; Neumann, D.; Ben-Califa, N.; Kashman, Y. Salarins D–J, seven new nitrogenous macrolides from the Madagascar sponge Fascaplysinopsis sp. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 4339–4345.
- Kobayashi, J.; Kondo, K.; Ishibashi, M.; Walchli, M.R.; Nakamura, T. Theonezolide A: A novel polyketide natural product from the Okinawan marine sponge Theonella sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 6661–6665.
- Kondo, K.; Ishibashi, M.; Kobayashi, J. Isolation and structures of theonezolides B and C from the Okinawan marine sponge Theonella sp. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 8355–8362.
- Rho, M.C.; Park, Y.H.; Sasaki, S.; Ishibashi, M.; Kondo, K.; Kobayashi, J.; Ohizumi, Y. The mode of rabbit platelet shape change and aggregation induced by theonezolide-A, a novel polyketide macrolide, isolated from the Okinawan marine sponge Theonella sp. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1996, 74, 193–199.
- Hou, S.Y.; Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, H.D.; Zhang, Y.X. Characterization of the biosynthesis gene cluster and oxazole ring formation enzyme for inthomycins in Streptomyces sp. strain SYP-A7193. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, 1–44.
- Webb, M.R.; Donald, C.; Taylor, R.J.K. A general route to the Streptomyces-derived inthomycin family: the first synthesis of (+)-inthomycin B. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 549–552.
- Higa, T.; Tanaka, J.I.; Kitamura, A.; Koyama, T.; Takahashia, M.; Uchida, T. Bioactive compounds from marine sponges. Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 2227–2230.
- Ichiba, T.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Scheuer, P.J.; Higa, T.; Gravalos, D.G. Hennoxazoles, bioactive bisoxazoles from a marine sponge. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 3173–3174.
- Takaishi, S.; Tuchiya, N.; Sato, A.; Negishi, T.; Takamatsu, Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Iijima, Y.; Haruyama, H.; Kinoshita, T.; et al. B-90063, a novel endothelin converting enzyme inhibitor isolated from a new marine bacterium, Blastobacter sp. SANK 71894. J. Antibiot. 1998, 51, 805–815.
- Fernández, R.; Dherbomez, M.; Letourneux, Y.; Nabil, M.; Verbist, A.J.F.; Biard§, J.F. Antifungal metabolites from the marine sponge Pachastrissa sp.: New bengamide and bengazole derivatives. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 678–680.
- Mulder, R.J.; Shafer, C.M.; Dalisay, D.S.; Molinski, T.F. Synthesis and structure–activity relationships of bengazole A analogs. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 2928–2930.
- Sun, M.; Zhang, X.; Hao, H.; Li, W.; Lu, C. Nocarbenzoxazoles A-G, benzoxazoles produced by halophilic Nocardiopsis lucen-tensis DSM 44048. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2123–2127.
- Kim, T.; Lee, S.A.; Noh, T.; Choi, P.; Choi, S.J.; Song, B.G.; Kim, Y.; Park, Y.T.; Huh, G.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. Synthesis, structure revision, and cytotoxicity of nocarbenzoxazole G. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1325–1330.
- Venkateswarlu, Y.; Reddy, N.S.; Ramesh, P.; Rao, J.V. Coixol: A bioactive principle from a marine sponge Oceanapia sp. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1999, 27, 519–520.
- Rodríguez, I.I.; Rodríguez, A.D. Homopseudopteroxazole, a new antimycobacterial diterpene alkaloid from Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 855–857.
- Rodriguez, A.D.; Ramıirez, C.; Rodriguez, I.I.; Gonzalez, E. Novel antimycobacterial benzoxazole alkaloids, from the west Indian sea whip Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae. Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 527–530.
- Georgantea, P.; Ioannou, E.; Evain-Bana, E.; Bagrel, D.; Martinet, N.; Vagias, C.; Roussis, V. Sesquiterpenes with inhibitory activity against CDC25 phosphatases from the soft coral Pseudopterogorgia rigida. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 3262–3269.
- McCulloch, M.W.B.; Berrue, F.; Haltli, B.; Kerr, R.G. One-Pot syntheses of pseudopteroxazoles from pseudopterosins: A rapid route to non-natural congeners with improved antimicrobial activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2250–2256.
- Zhang, X.; Fang, X.; Xu, M.; Lei, Y.; Wu, Z.; Hu, X. Enantioselective total synthesis of pseudopteroxazole and ileabethoxazole. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7845–7849.
- Genta-Jouve, G.; Francezon, N.; Puissant, A.; Auberger, P.; Vacelet, J.; Pérez, T.; Fontana, A.; Al Mourabit, A.; Thomas, O.P. Structure elucidation of the new citharoxazole from the Mediterranean deep-sea sponge Latrunculia (Biannulata) citharistae. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2011, 49, 533–536.
- Julianti, E.; Lee, J.H.; Liao, L.; Park, W.; Park, S.; Oh, D.C.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. New polyaromatic metabolites from a marine-derived fungus Penicillium sp. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 1286–1289.
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, H. Cytotoxic natural products from marine sponge-derived microorganisms. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 68.
- Kamat, S.; Kumari, M.; Taritla, S.; Jayabaskaran, C. Endophytic fungi of marine alga from Konkan coast, India—A rich source of bioactive material. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 1–16.
- Chen, S.; Cai, R.; Liu, Z.; Cui, H.; She, Z. Secondary metabolites from mangrove-associated fungi: Source, chemistry and bioactivities. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021.
- Ramesh, C.; Tulasi, B.R.; Raju, M.; Thakur, N.; Dufosse, L. Marine natural products from tunicates and their associated mi-crobes. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 308.
- Atanasov, A.G.; Zotchev, S.B.; Dirsch, V.M.; the International Natural Product Sciences Taskforce; Supuran, C.T. Natural products in drug discovery: Advances and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 200–216.





