Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hoi Leong Xavier Wong | + 2132 word(s) | 2132 | 2021-11-29 05:19:11 | | | |
| 2 | Yvaine Wei | + 89 word(s) | 2221 | 2021-11-30 09:29:02 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Wong, H.L.X. Gut-Microbial Metabolites and Probiotics in Type 2 Diabetes. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/16548 (accessed on 10 March 2026).
Wong HLX. Gut-Microbial Metabolites and Probiotics in Type 2 Diabetes. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/16548. Accessed March 10, 2026.
Wong, Hoi Leong Xavier. "Gut-Microbial Metabolites and Probiotics in Type 2 Diabetes" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/16548 (accessed March 10, 2026).
Wong, H.L.X. (2021, November 30). Gut-Microbial Metabolites and Probiotics in Type 2 Diabetes. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/16548
Wong, Hoi Leong Xavier. "Gut-Microbial Metabolites and Probiotics in Type 2 Diabetes." Encyclopedia. Web. 30 November, 2021.
Copy Citation
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a worldwide prevalent metabolic disorder defined by high blood glucose levels due to insulin resistance (IR) and impaired insulin secretion. Disturbances of gut microbiota have been widely found in T2D patients and contribute to the development of IR.
gut microbiota
microbial metabolites
probiotics
insulin resistance
type 2 diabetes
insulin signaling
1. Introduction
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is characterized by fasting hyperglycemia resulted from the inadequate secretion of the glucose-lowering hormone insulin and/or insulin resistance (IR). Primarily driven by overnutrition and sedentary lifestyles, T2D is a major global health problem in both developing and developed countries [1]. The high prevalence of IR in T2D makes IR become a predictor for the development of T2D and also an ideal therapeutic target to maintain glucose levels.
Growing evidence suggests that the gut microbiome is an important factor for the pathogenesis of IR and T2D [2]. The gut microbiota is capable of utilizing undigested and unabsorbed food components, thereby yielding bioactive metabolites from the metabolism of carbohydrate, protein, choline and primary bile acids. Many studies have pointed out that these metabolites play critical roles in the development of IR and T2D [3]. The proteolytic fermentation of gut microbiota yields products including indoles, phenols, p-cresol, hydrogen sulfide, branched-chain fatty acids, ammonia and polyamines. Some of them may be either beneficial or detrimental to the gut and metabolic homeostasis of the host [4]. The composition and structure of gut microbiota could be of interest to determine the effects of microbial metabolites on metabolic diseases [5].
Probiotics, referring to “live microorganisms which when consumed in proper amounts confer beneficial effects on the host”, has been used as a therapeutic tool for the treatment of IR and T2D [6]. Both animal and human data regarding the efficacy of the probiotics have been reported, while some of the results are contradictory. Several reasons, such as the use of probiotics strains, dosage and duration and study design, could be attributed to the differences in these studies.
1.1. Gut-Microbial Metabolites and Their Roles in the Development of T2D
Microbial metabolites derived from dietary components (e.g., dietary fiber, cholesterol, amino acids) are involved in the development of metabolic diseases including IR and T2D [7]. Among dietary components, carbohydrates are fermented by microbes in the proximal colon, while the fermentation of protein mainly takes place in the distal colon; the latter occurs as the more easily digested carbohydrates are depleted, where little is known about the microbial networks that produce bile acids, choline, saccharolytic and proteolytic metabolites. Briefly, the fermentation of dietary fiber produces high amounts of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), lactate, succinate and gases, such as methane and carbon dioxide in the proximal colon [8]. In contrast, residual peptides and proteins, bile acids, and choline are fermented in the distal colon [9]. Compared to the fermentation of carbohydrates in the proximal colon, the fermentation products in the distal colon seems to be more diverse, including the following: (1) bacterial toxins such as lipopolysaccharides (LPS); (2) gaseous products like methane, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen sulfide; (3) bile acids (BA) products like deoxycholate and lithocholate; (4) branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and products like branched-chain fatty acids (BCFAs) isobutyrate, 2-methylbutyrate and isovalerate; (5) aromatic amino acids (AAAs) products like phenolic, indolic, skatolic and p-cresolic compounds as well as ammonia and polyamines and (6) choline products like and dimethylamine (DMA) and trimethylamine (TMA); (Figure 1).
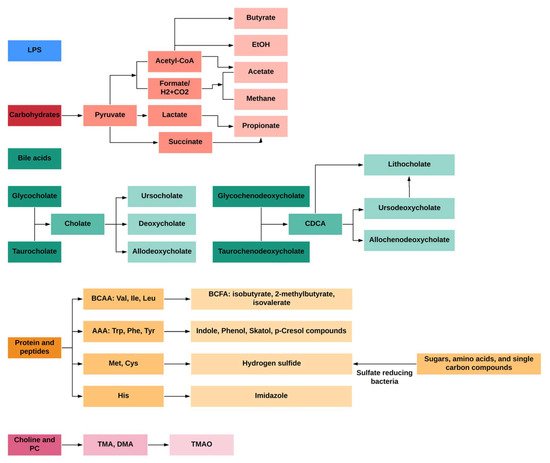
Figure 1. General profiles of gut-microbial metabolites from different dietary and endogenous components in humans.
Over the past decades, the gut microbiome has emerged as an important “organ” regulating energy metabolism in the host. Abnormalities in gut microbiota composition and function have been found to contribute to disruptions of host metabolism in T2D, including insulin-desensitizing effects on metabolism in adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and liver [10][11]. Studies have shown the gut microbiome significantly affects metabolic signatures of T2D subjects [12]. Many untargeted and targeted metabolomics studies on subjects with T2D have been reported. Although these studies were performed in different populations (Asians, Europeans and Americans) using different metabolomics approaches, they have identified several similar patterns of metabolome in T2D. First, metabolomics is useful in discriminating T2D patients from subjects with pre-diabetes and healthy subjects [13][14][15]. Secondly, numerous untargeted and targeted metabolomics studies have determined the changes of gut microbial metabolites in T2D, showing the gut microbial metabolite-related metabolic pathways are significantly changed in T2D. Figure 2 explained the role of microbial metabolites in IR and T2D.
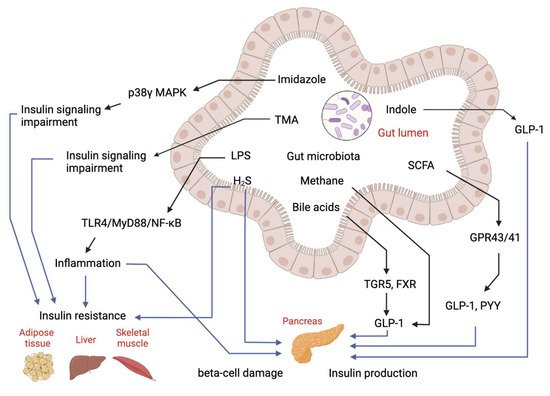
Figure 2. Regulatory effects of gut-microbial metabolites on insulin sensitivity and insulin production. Imidazole, TMA, LPS and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) can cause either insulin resistance or beta-cell damage to impair glucose homeostasis. Bile acids, SCFA and indole can stimulate GLP-1 production to manipulate insulin production and secretion to regulate glucose level.
1.2. Treatment of T2D by Probiotics
1.2.1. Probiotics Interventions in Animal Models of Diabetes
Studies have shown that probiotics exhibit beneficial effects on IR in animal models of diabetes (Table 1). The biological effects of probiotics including Lactobacillus spp. and Bifidobacterium spp. on glucose intolerance and IR have been extensively investigated in diabetic animal models. For example, administration of Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM0236 was found to ameliorate insulin resistance, systemic inflammation and pancreas β-cell dysfunction in high fat diet (HFD) and streptomycin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice [16]. Lactobacillus plantarum Ln4 reduced weight gain and alleviated insulin resistance by improving oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), insulin tolerance test (ITT) and homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) indexes in mice fed on HFD [17]. Lactobacillus fermentum MTCC 5689 treatment has been shown to improve insulin resistance and prevent the development of diabetes in HFD-induced diabetic mice [18]. Moreover, administration of Lactobacillus paracasei TD062 improved the glucose homeostasis and enhanced insulin signaling pathway, preventing the development of T2D [19]. A multiple probiotics formula including Lactobacillus reuteri, L. crispatus, and Bacillus subtilis has been investigated in STZ-induced diabetic rats, revealing daily consumption of probiotics formula is effective in alleviating the glucose intolerance and the impaired insulin secretion [20]. Another composite probiotic including 10 Lactobacillus strains and four yeast strains were found to alleviate T2D in db/db mice by reducing fasting blood glucose (FBG), OGTT and HbA1c indexes and enhancing glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1) secretion [21]. Nano-selenium-enriched Bifidobacterium longum has been shown to delay the onset of STZ-induced diabetes and ameliorate the high glucose-induced renal function damage [22]. B. longum DD98 and selenium-enriched B. longum DD98 reduced the levels of FBG and HbA1c and improved the glucose tolerance in HFD and STZ-induced diabetic mice [23]. Moreover, inactivated B. longum BR-108 has been reported to reduce blood glucose level in a Tsumura Suzuki Obese Diabetes (TSOD) mouse model of diabetes [24]. B. animalis 01 treatment improved OGTT and HOMA-IR indexes and suppressed pro-inflammatory cytokines in HFD and STZ-induced diabetic rats [25].
Table 1. Probiotics intervention in animal model of diabetes.
| Probiotic Species/Strains | Disease Model | Main Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM0236 | HFD+STZ | Blood glucose ↓, leptin level ↓, insulin resistance ↓ | [16] |
| Lactobacillus plantarum Ln4 | HFD | Insulin resistance ↓, insulin response ↑ | [17] |
| Lactobacillus fermentum MTCC 5689, Lactobacillus plantarum MTCC 5690 | HFD | Glucose ↓, HbA1c↓, plasma insulin ↓, HOMA-IR ↓ | [18] |
| Lactobacillus paracasei TD062 | HFD+STZ | FBG↓, Glucose tolerance ↓ | [19] |
| Lactobacillus reuteri, Lactobacillus crispatus and Bacillus subtiliso | STZ | Plasma glucose ↓, HbA1c ↓, plasma insulin ↑ | [20] |
| Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus helveticus, Lactococcus lactis and Issatchenkia orientalis | db/db | FBG ↓, OGTT ↓, HbAlc ↓ IRI ↓, plasma TC ↓, TG ↓, LDL-C ↓, |
[21] |
| Nano-selenium-enriched Bifidobacterium longum | STZ | Blood glucose ↓, renal function damage ↓ | [22] |
| Bifidobacterium longum DD98 and selenium-enriched B. longum DD98 | HFD+STZ | FBG and HbA1c ↓ | [23] |
| Inactivated Bifidobacterium longum BR-108 | TSOD mouse | Blood glucose ↓ | [24] |
| Bifidobacterium animalis 01 | HFD+STZ | OGTT and HOMA-IR ↓, pro-inflammatory cytokines ↓ | [25] |
| Lactobacillus plantarum OLL2712 | HFD | Blood glucose ↓, IL-1beta ↓ | [26] |
| Lactobacillus casei CCFM419 | HFD+STZ | FBG ↓, glucose intolerance↓, insulin resistance ↓, TNF-alpha and IL-6 ↓, GLP-1 ↑ | [27] |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus NCDC 17 | HFD+STZ | FBG ↓, plasma insulin ↓, HbA1c ↓, free fatty acids ↓, TG ↓ and TC ↓, | [28] |
| Lactobacillus paracasei NL41 | HFD+STZ | Insulin resistance↓, HbA1c ↓, glucagon ↓ and leptin ↓, oxidative stress status ↓ | [29] |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum | HFD | Plasma glucose ↓, intestinal permeability ↓, LPS translocation ↓, systemic low-grade inflammation ↓ | [30] |
| Clostridium butyricum CGMCC0313.1 | Db/db mice and HFD+STZ | FBG ↓, HbA1c ↓, GLP-1 ↑ and inflammatory responses ↓ | [31] |
| Lactobacillus salivarius AP-32 and L. reuteri GL-104 | db/db mice | FBG ↓, TG ↓, TC ↓ | [32] |
| Lactobacillus plantarum HAC01 | HFD+STZ | FBG ↓, HbA1c ↓ and insulin-positive β-cell mass ↑ | [33] |
| Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. lactis PTCC1057 | STZ | FBG ↓, fetuin-A ↓ and sestrin ↑ | [34] |
| Streptococcus thermophilus | Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) | FBG ↓, glucose intolerance ↓, TC ↓, LPS ↓, IL-6 ↓, TNF-α ↓ and IL-10 ↑ | [35] |
| Lactobacillus plantarum, L. bulgaricus, L casei, L. acidophilus, Bifidobacterium infantis, B. longum, B. breve | HFD+STZ | Plasma glucose ↓, GLP-1 ↑ and total antioxidant capacity ↑ | [36] |
1.2.2. Molecular Mechanism of Probiotics Intervention on T2D
Studies have shown that probiotics can ameliorate IR, pancreatic β-cell dysfunction and hyperglycemia [37], whereas limited studies have evaluated the molecular mechanisms of probiotics intervention in T2D. Mechanistically, probiotics alleviate T2D-associated pathologies by repairing intestinal barrier, suppressing inflammatory responses, reducing oxidative stress, restoring energy metabolism, and producing beneficial microbial metabolites including SCFA and BA (Figure 3). Specifically, one study showed that Lactobacillus acidophilus KLDS1.0901 improved intestinal barrier function, and suppressed inflammatory responses in liver and colon in an animal model of diabetes [38]. Another study showed Lactobacillus casei CCFM419 enhanced SCFA and GLP-1 production and reduced the levels of pro-inflammatory markers in diabetic mice [27]. Akkermansia muciniphila treatment has been shown to improve liver function, alleviate oxidative stress and suppress inflammation in diabetic rats [39]. Lactobacillus casei was found to enhance SCFA production as well as GLP-1 and Peptide YY (PYY) secretion in diabetic mice [40]. Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 supplementation was found to enhance gut-microbial diversity and serum deoxycholic acid (DCA) levels [41].
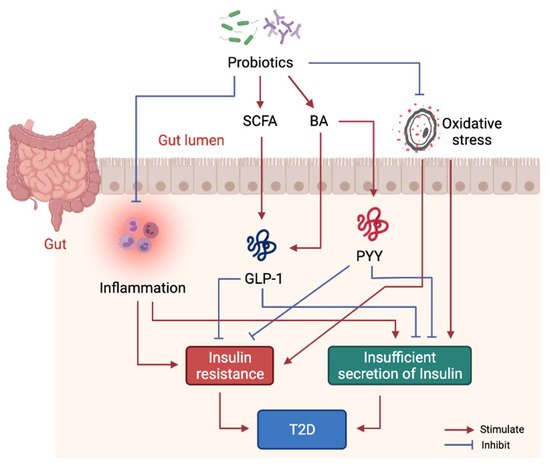
Figure 3. Molecular mechanism of probiotics intervention on T2D. Probiotics in gut help produce beneficial metabolites including SCFA and some BA to stimulate GLP-1 and PYY secretion, thus, to alleviate insulin resistance and dysfunction of insulin secretion. Probiotics also suppress systemic inflammation by modulating gut microbiota structure.
2. Drug Discovery Based on Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites
With the development of high-throughput sequencing of gut microbiota, scientists and pharmacological companies are mining small-molecule drug discovery programs using conventional drug discovery and novel synthetic biology approaches. Functional metagenomics have helped investigators identify bioactive molecules and targets, followed by the identification of homologous gene families [42]. An important family of G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) ligands namely N-acyl amides produced by gut microbiota is shown to be agonists of receptors that have important functions for gastrointestinal and metabolic diseases, such as the endocannabinoid receptor GPR119 [43]. Another study used a novel approach combining computational and synthetic biology and characterized a series of microbiota-derived metabolites that can inhibit host proteases [44]. Moreover, a “chemistry-forward” approach of screening of GPCR ligands from gut microbiota metabolomes has revealed gut microbes produce ligands for many GPCRs and the microbiota-derived GPCR ligands have a profound impact on host physiology [45]. Such approaches used for mining gut microbiota-derived metabolites and novel compounds provide a potential strategy for discovering drugs to treat T2D.
3. Alternative Therapeutic Options
3.1. Gut Microbiota-Derived Probiotics (GPs)
Current probiotic supplements recommended for diabetic patients are mainly Bifidobacterium spp., Lactobacillus spp., and yeasts, which are culturable, aerotolerant and can be produced in an industrial scale [46]. By contrast, the novel probiotics for T2D include important gut bacteria in human gut which are reduced in T2D. However, it is difficult to culture these gut bacteria that are extremely sensitive to oxygen, which presents a great challenge in terms of isolation, cultivation and industrial production and formulation. Unlike the common probiotics, the GPs directly from human may also require stricter evaluation procedures in terms of safety and efficacy, which may need new drug approval procedures according to the FDA.
3.2. Prebiotics Supplement
Besides of probiotics, modulation of gut microbiota can also be achieved using prebiotics. Prebiotics is a mixture of nondigestible food ingredients that promote the growth of beneficial microbes and suppress growth of pathogenic microbes in GI tract [47]. It brings numerous benefits to the host including normalization of GI pH value, modulation of immune system, reduction of hyperlipidemia and improvement of cation ions absorption [48]. Several mechanisms of prebiotics action on gut microbiota and host have been identified so far. First, the production of beneficial microbial metabolites (SCFA) by beneficial microbes, such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, is promoted by prebiotics [49]. Second, prebiotics supplement suppresses endotoxin level by inhibiting the growth and colonization of harmful bacteria [50]. Third, prebiotics improve cation ions absorption possibly by regulating pH value in GI tract [51]. Prebiotics can be used as a supplement or additional support for probiotics. The complementary symbiotic comprising probiotics plus prebiotics can be more effective than probiotics formulation alone in promoting human health.
3.3. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT)
FMT is an interesting approach to modulate gut microbiota and has been used to correct gut microbiota dysbiosis in clinical trials. FMT from lean donors has been implanted to obese subjects, after which metabolic syndrome and insulin sensitivity were improved by FMT, suggesting modulation of gut microbiome could be considered as a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of IR [52]. The reasons for the beneficial properties of gut microbiota could be attributed to its enhancement of levels of gut microbial metabolites levels including SCFAs and BAs [53]. Studies also found that FMT treatment does not show beneficial effects on subjects with severe IR, suggesting manipulating gut microbiota may only help maintain the glucose level and insulin sensitivity in the early stage of T2D [52]. Nevertheless, FMT is a potential personalized approach for alleviating glucose intolerance and IR in metabolic syndrome and T2D.
Abbreviations
| AAAs | Aromatic amino acids |
| BA | Bile acids |
| BCAAs | Branched-chain amino acids |
| BCFA | Branched-chain fatty acids |
| DCA | Deoxycholic acid |
| DMA | Dimethylamine |
| FMT | Fecal microbiota transplantation |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| GPCR | G-protein coupled receptor |
| GPs | Gut microbiota-derived probiotics |
| HFD | High fat diet |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance |
| IR | Insulin resistance |
| IRI | Insulin resistance index |
| ITT | Insulin tolerance test |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharides |
| OGTT | Oral glucose tolerance test |
| PYY | Peptide YY |
| SCFAs | Short-chain fatty acids |
| STZ | Streptomycin |
| T2D | Type 2 diabetes |
| TMA | Trimethylamine |
References
- Chatterjee, S.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2017, 389, 2239–2251.
- Cani, P.D.; Osto, M.; Geurts, L.; Everard, A. Involvement of gut microbiota in the development of low-grade inflammation and type 2 diabetes associated with obesity. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 279–288.
- Palau-Rodriguez, M.; Tulipani, S.; Isabel Queipo-Ortuño, M.; Urpi-Sarda, M.; Tinahones, F.J.; Andres-Lacueva, C. Metabolomic insights into the intricate gut microbial–host interaction in the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1151.
- Ma, N.; Tian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ma, X. Contributions of the interaction between dietary protein and gut microbiota to intestinal health. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2017, 18, 795–808.
- Zhong, H.; Ren, H.; Lu, Y.; Fang, C.; Hou, G.; Yang, Z.; Chen, B.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Z.; et al. Distinct gut metagenomics and metaproteomics signatures in prediabetics and treatment-naïve type 2 diabetics. EBioMedicine 2019, 47, 373–383.
- Bock, P.M.; Telo, G.H.; Ramalho, R.; Sbaraini, M.; Leivas, G.; Martins, A.F.; Schaan, B.D. The effect of probiotics, prebiotics or synbiotics on metabolic outcomes in individuals with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 26–41.
- Canfora, E.E.; Meex, R.C.R.; Venema, K.; Blaak, E.E. Gut microbial metabolites in obesity, NAFLD and T2DM. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 261–273.
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From dietary fiber to host physiology: Short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345.
- Portune, K.J.; Beaumont, M.; Davila, A.-M.; Tomé, D.; Blachier, F.; Sanz, Y. Gut microbiota role in dietary protein metabolism and health-related outcomes: The two sides of the coin. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 57, 213–232.
- Udayappan, S.D.; Hartstra, A.V.; Dallinga-Thie, G.M.; Nieuwdorp, M. Intestinal microbiota and faecal transplantation as treatment modality for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 177, 24–29.
- Gurung, M.; Li, Z.; You, H.; Rodrigues, R.; Jump, D.B.; Morgun, A.; Shulzhenko, N. Role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology. EBioMedicine 2020, 51, 102590.
- Pedersen, H.K.; Gudmundsdottir, V.; Nielsen, H.B.; Hyotylainen, T.; Nielsen, T.; Jensen, B.A.H.; Forslund, K.; Hildebrand, F.; Prifti, E.; Falony, G. Human gut microbes impact host serum metabolome and insulin sensitivity. Nature 2016, 535, 376.
- Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ong, C.-N.; Subramaniam, T.; Choi, H.W.; Yuan, J.-M.; Koh, W.-P.; Pan, A. Metabolic signatures and risk of type 2 diabetes in a Chinese population: An untargeted metabolomics study using both LC-MS and GC-MS. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 2349–2359.
- Monnerie, S.; Comte, B.; Ziegler, D.; Morais, J.A.; Pujos-Guillot, E.; Gaudreau, P. Metabolomic and Lipidomic Signatures of Metabolic Syndrome and its Physiological Components in Adults: A Systematic Review. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 669.
- Guasch-Ferré, M.; Hruby, A.; Toledo, E.; Clish, C.B.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Hu, F.B. Metabolomics in prediabetes and diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 833–846.
- Li, X.; Wang, N.; Yin, B.; Fang, D.; Jiang, T.; Fang, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM0236 on hyperglycaemia and insulin resistance in high-fat and streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic mice. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 1727–1736.
- Lee, E.; Jung, S.-R.; Lee, S.-Y.; Lee, N.-K.; Paik, H.-D.; Lim, S.-I. Lactobacillus plantarum Strain Ln4 Attenuates Diet-Induced Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Changes in Hepatic mRNA Levels Associated with Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Nutrients 2018, 10, 643.
- Balakumar, M.; Prabhu, D.; Sathishkumar, C.; Prabu, P.; Rokana, N.; Kumar, R.; Raghavan, S.; Soundarajan, A.; Grover, S.; Batish, V.K.; et al. Improvement in glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity by probiotic strains of Indian gut origin in high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 279–295.
- Dang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Pan, R.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, R.; Zhuang, K.; Zhang, W.; Li, T.; Man, C. Administration of Lactobacillus paracasei ameliorates type 2 diabetes in mice. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 3630–3639.
- Memarrast, F.; Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Kolivand, S.; Nodooshan, S.J.; Neyazi, N.; Sadroddiny, E.; Motevaseli, E. Comparative evaluation of probiotics effects on plasma glucose, lipid, and insulin levels in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2017, 33, e2912.
- Manaer, T.; Yu, L.; Nabi, X.-H.; Dilidaxi, D.; Liu, L.; Sailike, J. The beneficial effects of the composite probiotics from camel milk on glucose and lipid metabolism, liver and renal function and gut microbiota in db/db mice. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 127.
- Lin, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, G.; Hua, Z. Protective role of nano-selenium-enriched Bifidobacterium longum in delaying the onset of streptozotocin-induced diabetes. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 5, 181156.
- Zhao, D.; Zhu, H.; Gao, F.; Qian, Z.; Mao, W.; Yin, Y.; Tan, J.; Chen, D. Antidiabetic effects of selenium-enriched Bifidobacterium longum DD98 in type 2 diabetes model of mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 6528–6541.
- Ben Othman, M.; Sakamoto, K. Effect of inactivated Bifidobacterium longum intake on obese diabetes model mice (TSOD). Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108792.
- Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Zeng, Z.; Qin, Y.; Shen, Q.; Li, P. Anti-diabetic effects of Bifidobacterium animalis 01 through improving hepatic insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic rat model. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 67, 103843.
- Sakai, T.; Taki, T.; Nakamoto, A.; Shuto, E.; Tsutsumi, R.; Toshimitsu, T.; Makino, S.; Ikegami, S. Lactobacillus plantarum OLL2712 regulates glucose metabolism in C57BL/6 mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2013, 59, 144–147.
- Wang, G.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Lactobacillus casei CCFM419 attenuates type 2 diabetes via a gut microbiota dependent mechanism. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3155–3164.
- Singh, S.; Sharma, R.K.; Malhotra, S.; Pothuraju, R.; Shandilya, U.K. Lactobacillus rhamnosus NCDC17 ameliorates type-2 diabetes by improving gut function, oxidative stress and inflammation in high-fat-diet fed and streptozotocintreated rats. Benef. Microbes 2017, 8, 243–255.
- Zeng, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Yu, R.; Zhang, J.; Ma, H.; Chen, S. Ameliorative Effects of Probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei NL41 on Insulin Sensitivity, Oxidative Stress, and Beta-Cell Function in a Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Rat Model. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, 1900457.
- Bagarolli, R.A.; Tobar, N.; Oliveira, A.G.; Araújo, T.G.; Carvalho, B.M.; Rocha, G.Z.; Vecina, J.F.; Calisto, K.; Guadagnini, D.; Prada, P.O.; et al. ScienceDirect Probiotics modulate gut microbiota and improve insulin sensitivity in DIO mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 50, 16–25.
- Jia, L.; Li, D.; Feng, N.; Shamoon, M.; Sun, Z.; Ding, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Sun, J.; Chen, Y.Q. Anti-diabetic Effects of Clostridium butyricum CGMCC0313.1 through Promoting the Growth of Gut Butyrate-producing Bacteria in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7046.
- Hsieh, P.-S.; Ho, H.-H.; Hsieh, S.-H.; Kuo, Y.-W.; Tseng, H.-Y.; Kao, H.-F.; Wang, J.-Y. Lactobacillus salivarius AP-32 and Lactobacillus reuteri GL-104 decrease glycemic levels and attenuate diabetes-mediated liver and kidney injury in db/db mice. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001028.
- Lee, Y.-S.; Lee, D.; Park, G.-S.; Ko, S.-H.; Park, J.; Lee, Y.-K.; Kang, J. Lactobacillus plantarum HAC01 ameliorates type 2 diabetes in high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice in association with modulating the gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 6363–6373.
- Hallajzadeh, J.; Eslami, R.D.; Tanomand, A. Effect of Lactobacillus delbrueckii Subsp. lactis PTCC1057 on Serum Glucose, Fetuin-A, and Sestrin 3 Levels in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 383–389.
- Gao, X.; Wang, F.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, R.; Zeng, Q. Effect of heat-killed Streptococcus thermophilus on type 2 diabetes rats. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7117.
- Pegah, A.; Abbasi-Oshaghi, E.; Khodadadi, I.; Mirzaei, F.; Tayebinai, H. Probiotic and resveratrol normalize GLP-1 levels and oxidative stress in the intestine of diabetic rats. Metab. Open 2021, 10, 100093.
- Martín-Peláez, S.; Fito, M.; Castaner, O. Mediterranean Diet Effects on Type 2 Diabetes Prevention, Disease Progression, and Related Mechanisms. A Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2236.
- Yan, F.; Li, N.; Shi, J.; Li, H.; Yue, Y.; Jiao, W.; Wang, N.; Song, Y.; Huo, G.; Li, B. Lactobacillus acidophilus alleviates type 2 diabetes by regulating hepatic glucose, lipid metabolism and gut microbiota in mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5804–5815.
- Zhang, L.; Qin, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; He, F. Akkermansia muciniphila can reduce the damage of gluco/lipotoxicity, oxidative stress, and inflammation and normalize intestine microbiota in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Pathog. Dis. 2018, 76, fty028.
- Qu, L.; Ren, J.; Huang, L.; Pang, B.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Shan, Y. Antidiabetic Effects of Lactobacillus casei Fermented Yogurt through Reshaping Gut Microbiota Structure in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12696–12705.
- Mobini, R.; Tremaroli, V.; Ståhlman, M.; Karlsson, F.; Levin, M.; Ljungberg, M.; Sohlin, M.; Bertéus Forslund, H.; Perkins, R.; Bäckhed, F.; et al. Metabolic effects of Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 in people with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 579–589.
- Milshteyn, A.; Colosimo, D.A.; Brady, S.F. Accessing Bioactive Natural Products from the Human Microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 725–736.
- Cohen, L.J.; Esterhazy, D.; Kim, S.-H.; Lemetre, C.; Aguilar, R.R.; Gordon, E.A.; Pickard, A.J.; Cross, J.R.; Emiliano, A.B.; Han, S.M.; et al. Commensal bacteria make GPCR ligands that mimic human signalling molecules. Nature 2017, 549, 48–53.
- Guo, C.-J.; Chang, F.-Y.; Wyche, T.P.; Backus, K.M.; Acker, T.M.; Funabashi, M.; Taketani, M.; Donia, M.S.; Nayfach, S.; Pollard, K.S.; et al. Discovery of Reactive Microbiota-Derived Metabolites that Inhibit Host Proteases. Cell 2017, 168, 517–526.e18.
- Chen, H.; Nwe, P.-K.; Yang, Y.; Rosen, C.E.; Bielecka, A.A.; Kuchroo, M.; Cline, G.W.; Kruse, A.C.; Ring, A.M.; Crawford, J.M. A forward chemical genetic screen reveals gut microbiota metabolites that modulate host physiology. Cell 2019, 177, 1217–1231.
- Gomes, A.C.; Bueno, A.A.; de Souza, R.G.M.; Mota, J.F. Gut microbiota, probiotics and diabetes. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 60.
- Davani-Davari, D.; Negahdaripour, M.; Karimzadeh, I.; Seifan, M.; Mohkam, M.; Masoumi, S.J.; Berenjian, A.; Ghasemi, Y. Prebiotics: Definition, types, sources, mechanisms, and clinical applications. Foods 2019, 8, 92.
- Horvath, A.; Leber, B.; Feldbacher, N.; Tripolt, N.; Rainer, F.; Blesl, A.; Trieb, M.; Marsche, G.; Sourij, H.; Stadlbauer, V. Effects of a multispecies synbiotic on glucose metabolism, lipid marker, gut microbiome composition, gut permeability, and quality of life in diabesity: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 2969–2983.
- Kim, Y.A.; Keogh, J.B.; Clifton, P.M. Probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics and insulin sensitivity. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2018, 31, 35–51.
- Li, C.; Niu, Z.; Zou, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Gu, X.; Lu, H.; Tian, H.; Jha, R. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics regulate the intestinal microbiota differentially and restore the relative abundance of specific gut microorganisms. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 5816–5829.
- Ahmad, A.M.R.; Ahmed, W.; Iqbal, S.; Javed, M.; Rashid, S.; ul Haq, I. Prebiotics and iron bioavailability? Unveiling the hidden association-A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 584–590.
- Kootte, R.S.; Levin, E.; Salojärvi, J.; Smits, L.P.; Hartstra, A.V.; Udayappan, S.D.; Hermes, G.; Bouter, K.E.; Koopen, A.M.; Holst, J.J. Improvement of insulin sensitivity after lean donor feces in metabolic syndrome is driven by baseline intestinal microbiota composition. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 611–619.
- De Groot, P.F.; Frissen, M.N.; De Clercq, N.C.; Nieuwdorp, M. Fecal microbiota transplantation in metabolic syndrome: History, present and future. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 253–267.
More
Information
Subjects:
Microbiology; Nutrition & Dietetics
Contributor
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
1.2K
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
01 Dec 2021
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No





