
Video Upload Options
Fermentation is an important process that can provide new flavors and nutritional and functional foods, to deal with changing consumer preferences. Fermented foods have complex chemical components that can modulate unique qualitative properties. Consequently, monitoring the small molecular metabolites in fermented food is critical to clarify its qualitative properties and help deliver personalized nutrition. In recent years, the application of metabolomics to nutrition research of fermented foods has expanded. In this review, we examine the application of metabolomics technologies in food, with a primary focus on the different analytical approaches suitable for food metabolomics and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of these approaches. In addition, we summarize emerging studies applying metabolomics in the comprehensive analysis of the flavor, nutrition, function, and safety of fermented foods, as well as emphasize the applicability of metabolomics in characterizing the qualitative properties of fermented foods.
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Metabolomics Workflow
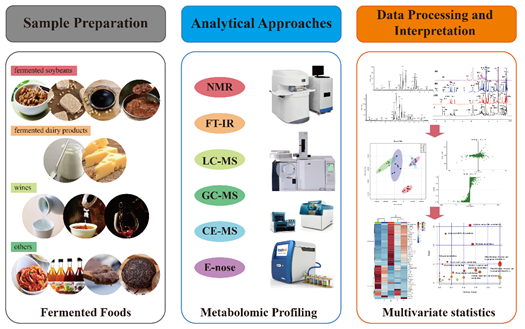
3.1. Metabolomic Approaches Based on Different Separations and Instrumentation
3.1.1. NMR-Based Metabolomics
3.1.2. FT-IR-Based Metabolomics
3.1.3. GC-MS/LC-MS-Based Metabolomics
3.1.4. CE-MS-Based Metabolomics
3.1.5. Electronic Nose-Based Metabolomics
3.2. Metabolomic Analyses Based on Data Interpretation and Multivariate Statistics
|
Biobanks |
Role |
References |
|
MestreNova |
Data processing prediction, publication, verification; Data storage and retrieval |
[97] |
|
Progenesis QI |
Data processing and normalization; Qualitative, quantitative and identification of small molecules with significant changes |
[98] |
|
SIMCA |
Multivariate statistical analysis; pattern recognition of PCA, PLS-DA, OPLS-DA |
[97] [99] [100] [101] |
|
RStudio |
Multivariate tool; Heatmap of metabolites and their concentration changes |
[97] |
|
HMDB |
Physicochemical & biological properties; Biomarker discovery; Metabolic pathway information |
[97] [98] [99] [100] [101] |
|
METLIN |
Metabolite identification; Metabolite structure; Links to other databases. |
[98] [99] [100] |
|
PubChem |
Biological properties of organic small molecule; Metabolite structure; Links to other databases. |
[100] |
|
MetaboAnalyst |
Data analysis, visualization and functional annotation; Multivariate analysis; Metabolite significance; Pathway identification |
[98] [99] [101] |
|
KEGG |
Metabolic pathway; Metabolite interactions; Delivery of gene to metabolite function |
[98] [99] [101] |
|
Mev |
Hierarchical cluster analysis; Heatmap of metabolites and their concentration changes |
[100] |
|
Cytoscape |
Interaction network visualization; Correlation analysis linked to gene, protein, and metabolite expression |
[101] |
Note and Abbreviations: SIMCA, Soft independent modeling of class analogy; YMDB, Yeast Metabolome Database; Mev, Multiple Experiment Viewer
4. Applications of Fermented Foods
4.1. Flavor
|
Fermented Foods |
Microorganisms |
Metabolomic analysis |
References |
|
|
Techniques |
Compounds/Properties Analyzed |
|||
|
Dajiang |
Yeasts, Aspergillus, Mucor, Rhizopus, Lactobacillus, Tetragenococcus |
HS-SPME/GC-MS |
alcohols, esters, phenolic acids, aldehydes, ketones |
[78] |
|
Red sufu |
Monascus purpureus, Aspergilus oryzae, Actinomucor elegans |
GC-MS, GC-MS-O, E-nose |
amino acids, organic acids |
[119] |
|
Natto |
Bacillus subtilis |
GC-MS; NMR |
amino acids, organic acids, pyrazines; ammonia |
[120-122] |
|
Cheese |
Lactic acid bacteria |
HS-SPME/GC-MS, FT-IR, E-nose |
lactose, lactate and citrate, amino acids, fatty acids |
[113] |
|
Huangjiu |
Yeasts |
GC/GC-MS, GC-O |
esters, linalool, neroidol, geranyl acetone, 2-pentyl-furan, methanethiol |
[112, 115] |
|
Baijiu |
Yeasts, Lactobacillus, Acetobacter |
GC×GC-TOF/MS |
aromatic compounds, pyrazines |
[116] |
|
Red wine |
Yeasts |
HS-SPME-Arrow-GC-MS/MS |
Piperitone, mintlactone, menthyl acetate, neomenthyl acetate |
[79] |
|
Vinegar |
Acetobacter, Lactobacillus |
HS-SPME/GC-MS |
ethyl acetate, phenylethyl alcohol, acetoin, acetic acid |
[124] |
|
Pu-erh tea |
Monascus purpureus, Bacillus, Rasamsonia, Lichtheimia, Debaryomyces |
HS-SPME/GC-MS |
β-damascenone, methoxybenzene, 2,4-nonadienal, terpinene, linalool |
[114, 117] |
|
Siniperca chuatsi |
Psychrilyobacter, Fusobacterium, Vibrio |
HS-SPME/GC-MS |
alcohols, hydrocarbons, nitrogen compounds |
[123] |
|
Shrimp paste |
Salimicrobium, Lentibacillus, Lactobacillus, Tetragenococcus |
HS-SPME/GC-MS |
alcohols, aldehydes, nitrogen compounds |
[125] |
4.2. Nutrition and Function
|
Fermented Foods |
Microorganisms |
Metabolomic analysis |
References |
|
|
Technique |
Compounds |
|||
|
Meju |
Bacillus sp., Mucor sp., Aspergillus sp. |
UPLC-Q/TOF MS |
small peptides, amino acids, GABA |
[132] |
|
Doenjang |
Penicillium glabrum, Aspergillus oryzae |
GC-TOF-MS, UPLC-Q/TOF-MS |
amino acids, organic acids, sugars and sugar alcohols, isoflavones |
[133-135] |
|
Cheonggukujang (or miso, natto) |
Bacillus subtilis, Mucor sp., Bacillus sp., Aspergillus sp.; E. faecium |
UPLC-Q/TOF-MS |
phenolic compounds, peptides, GABA |
[131, 136] |
|
Cheese |
Lactic acid bacteria |
NMR |
lactose, uridine diphosphate-hexose, amino acids, organic acids, |
[137] |
|
Yogurt |
Lactic acid bacteria |
UPLC-Triple/TOF-MS |
lipids, lipid-like molecules, small peptides, amino acids, GABA |
[98] [139] |
|
Wines |
Yeasts, Lactobacillus, Acetobacter |
NMR, FT-IR; GC/GC-TOF/MS; HPLC-MS; |
Polyphenols, amino acids, ethanol, resveratrol, stilbenes |
[49, 116, 146-147] |
|
Cabbage vinegar |
Lactobacillus, Acetobacter |
NMR, GC-MS |
organic acids, alcohols, sulfides (dimethyl sulfide, dimethyl disulfide, and dimethyl trisulfide) |
[148] |
|
Pu-erh tea |
Aspergillus pallidofulvus, Aspergillus sesamicola, Penicillium manginii |
UHPLC-Q/TOF-MS |
phenolic compounds, amino acids |
[105] |
|
Fermented fish sauce |
Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Fusobacteria |
UHPLC-Q/TOF-MS |
small peptides, amino acids |
[23] |
|
Pickle nozawana |
Latilactobacillus curvatus, Levilactobacillus brevis |
NMR, GC-MS |
organic acids, GABA, choline, 2,3-butanedione, acetoin, ethyl acetate |
[149] |
4.3. Safety
|
Fermented Foods |
Microorganisms |
Metabolomic analysis |
References |
|
|
Techniques |
Compounds/Properties Analyzed |
|||
|
Doenjang |
Bacillus subtilis, Rizhopus, Mucor, Aspergillus sp |
GC–MS |
soyasaponins |
[134] |
|
Cheonggukjang |
Bacillus sp. |
GC-TOF-MS, CE-TOF-MS |
soyasaponins |
[21] |
|
Koji |
Aspergillus oryzae, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens |
GC-TOF-MS, UHPLC-MS/MS |
soyasaponins |
[151] |
|
Vinegar |
Bacillus subtilis, Rizhopus, Mucor, Aspergillus sp. |
GC-MS |
benzoic acid, sorbic acid, dehydroacetic acid, ethyl paraben |
[153] |
|
Fermented fish sauce |
Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Fusobacteria |
UHPLC-Q/TOF-MS |
trimethylamine N-oxide, putrescine, cadaverine |
[23] |
|
Shrimp paste, Pickles |
Lentibacillus, Lactobacillus, Latilactobacillus, Tetragenococcus |
GC-FID |
benzoic acid, sorbic acid, propionic acid |
[154] |
|
Cheese |
Lactic acid bacteria |
GC/LC-MS, NMR, FI-TR |
pathogenic bacteria and its metabolites |
[155] |
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
References
- Bourdichon, F.; Casaregola, S.; Farrokh, C.; Frisvad, J.C.; Gerds, M.L.; Hammes, W.P.; Powell, I.B. Food fermentations: Microorgan-isms with technological beneficial use. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 154, 87–97.
- Anyogu, A.; Olukorede, A.; Anumudu, C.; Onyeaka, H.; Areo, E.; Adewale, O.; Odimba, J.N.; Nwaiwu, O. Microorganisms and food safety risks associated with indigenous fermented foods from Africa. Food Control. 2021, 129, 108227.
- Marco, M.L.; Heeney, D.; Binda, S.; Cifelli, C.J.; Cotter, P.; Foligne, B.; Gänzle, M.; Kort, R.; Pasin, G.; Pihlanto, A.; et al. Health benefits of fermented foods: Microbiota and beyond. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 94–102.
- Terefe, N.S.; Augustin, M.A. Fermentation for tailoring the technological and health related functionality of food products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 60, 2887–2913.
- Gille, D.; Schmid, A.; Walther, B.; Vergères, G. Fermented Food and Non-Communicable Chronic Diseases: A Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 448.
- Jayachandran, M.; Xu, B. An insight into the health benefits of fermented soy products. Food Chem. 2018, 271, 362–371.
- Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, E.; Yang, M.; Chen, S.; Hu, F.; Ma, H.; Liu, Z.; Yu, X. Enhancing the taste of raw soy sauce using low intensity ultrasound treatment during moromi fermentation. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 124928.
- Dong, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, T.H.; Ren, H.; Liu, W.; Li, M.Y. Accelerated aging of grape pomace vinegar by using additives combined with physical methods. J. Food Process. Eng. 2020, 43, e13398.
- Nwaiwu, O.; Itumoh, M. Chemical Contaminants Associated with Palm Wine from Nigeria Are Potential Food Safety Hazards. Beverages 2017, 3, 16.
- Adebo, O.A.; Njobeh, P.B.; Adebiyi, J.A.; Gbashi, F.; Phoku, J.Z.; Kayitesi, E. Fermented pulse-based food products in developing nations as functional foods and ingredients. In Functional Food-Improve Health through Adequate Food; Hueda, M.C., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; Chapter 5; pp. 77–109.
- Campbell-Platt, G. Fermented foods-a world perspective. Food Res Int. 1994, 27, 253–257.
- Gupta, S.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Probiotic Fermentation of Plant Based Products: Possibilities and Opportunities. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 183–199.
- Pereira, G.; Neto, D.P.D.C.; Junqueira, A.C.D.O.; Karp, S.G.; Letti, L.A.J.; Júnior, A.I.M.; Soccol, C.R. A Review of Selection Criteria for Starter Culture Development in the Food Fermentation Industry. Food Rev. Int. 2019, 36, 135–167.
- Dorđevi’c, T.M.; Šiler-Marinković, S.S.; Dimitrijević-Branković, S.I. Effect of fermentation on antioxidant properties of some cereals and pseudo cereals. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 957–963.
- Saharan, P.; Sadh, P.K.; Duhan, J.S. Comparative assessment of effect of fermentation on phenolics, flavanoids and free radical scavenging activity of commonly used cereals. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 12, 236–240.
- Thirunathan, P.; Manickavasagan, A. Processing methods for reducing alpha-galactosides in pulses. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 59, 3334–3348.
- Gänzle, M. Food fermentations for improved digestibility of plant foods-an essential ex-situ digestion step in agricultural societies? Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 32, 124–132.
- Xiang, H.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Waterhouse, G.; Cui, C.; Ruan, Z. Fermentation-enabled wellness foods: A fresh perspective. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 203–243.
- González-Peña, D.; Brennan, L. Recent Advances in the Application of Metabolomics for Nutrition and Health. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 479–519.
- Cook, P.W.; Nightingale, K.K. Use of omics methods for the advancement of food quality and food safety. Anim. Front. 2018, 8, 33–41.
- Kim, J.Y.; Choi, J.N.; John, K.M.; Kusano, M.; Oikawa, A.; Saito, K.; Lee, C.H. GC-TOF-MS- and CE-TOF-MS-based metabolic pro-filing of cheonggukjang (fastfermented bean paste) during fermentation and its correlation with metabolic pathways. J. Agr Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9746–9753.
- Lee, D.E.; Shin, G.R.; Lee, S.; Jang, E.S.; Shin, H.W.; Moon, B.S.; Lee, C.H. Metabolomics reveal that amino acids are the main con-tributors to antioxidant activity in wheat and rice gochujangs (korean fermented red pepper paste). Food Res. Int. 2016, 87, 10–17.
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wei, Y.; Yang, D. Application of UHPLC-Q/TOF-MS-based metabolomics in the evaluation of metabolites and taste quality of Chinese fish sauce (Yu-lu) during fermentation. Food Chem. 2019, 296, 132–141.
- He, S.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Gao, H.; Li, X.; Huang, Z. 1H NMR-based metabolomic study of the effects of flavonoids on citrinin production by Monascus. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109532.
- Zhao, G.; Zhao, W.; Han, L.; Ding, J.; Chang, Y. Metabolomics analysis of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) in different geo-graphical origins using UPLC-Q-TOF/MS. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127453.
- Fuhrer, T.; Zamboni, N. High-throughput discovery metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 73–78.
- González-Peña, D.; Dudzik, D.; Colina-Coca, C.; Ancos, B.D.; García, A.; Barbas, C.; Sánchez-Moreno, C. Evaluation of onion as a functional ingredient in the prevention of metabolic impairments associated to diet-induced hypercholesterolaemia using a multiplat-form approach based on LC-MS, CE-MS and GC-MS. J. Funct Foods 2015, 19, 363–375.
- Pezzatti, J.; Boccard, J.; Codesido, S.; Gagnebin, Y.; Rudaz, S. Implementation of liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spec-trometry methods for untargeted metabolomic analyses of biological samples: A tutorial. Anal. Chim Acta. 2020, 1105, 28–44.
- Mapelli, V.; Olsson, L.; Nielsen, J. Metabolic footprinting in microbiology: Methods and applications in functional genomics and biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 490–497.
- Chen, W.; Gong, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, S.; Xiong, L.; Luo, J. A Novel Integrated Method for Large-Scale Detection, Identification, and Quantification of Widely Targeted Metabolites: Application in the Study of Rice Metabolomics. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1769–1780.
- Guo, L.; Milburn, M.V.; Ryals, J.A.; Lonergan, S.C.; Mitchell, M.W.; Wulff, J.E.; Alexander, D.C.; Evans, A.M.; Bridgewater, B.; Miller, L.; et al. Plasma metabolomic profiles enhance precision medicine for volunteers of normal health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4901–E4910.
- Medina, S.; Dominguez-Perles, R.; Gil, J.; Ferreres, F.; Gil-Izquierdo, A. Metabolomics and the Diagnosis of Human Diseases -A Guide to the Markers and Pathophysiological Pathways Affected. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 823–848.
- Gibbons, H.; O’Gorman, A.; Brennan, L. Metabolomics as a tool in nutritional research. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2015, 26, 30–34.
- Hall, R.D. Plant metabolomics: From holistic hope, to hype, to hot topic. New Phytol. 2006, 169, 453–468.
- Uawisetwathana, U.; Karoonuthaisiri, N. Metabolomics for rice quality and traceability: Feasibility and future aspects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 28, 58–66.
- Hu, C.; Xu, G. Mass-spectrometry-based metabolomics analysis for foodomics. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 52, 36–46.
- Mozzi, F.; Ortiz, M.E.; Bleckwedel, J.; De Vuyst, L.; Pescuma, M. Metabolomics as a tool for the comprehensive understanding of fermented and functional foods with lactic acid bacteria. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 1152–1161.
- Wishart, D.S. NMR metabolomics: A look ahead. J. Magn. Reson. 2019, 306, 155–161.
- Larive, C.; Barding, G.A.; Dinges, M. NMR Spectroscopy for Metabolomics and Metabolic Profiling. Anal. Chem. 2014, 87, 133–146.
- Ha, D.; Paulsen, J.; Sun, N.; Song, Y.Q.; Ham, D. Scalable NMR spectroscopy with semico nductor chips. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11955–11960.
- Sundekilde, U.K.; Larsen, L.B.; Bertram, H.C. NMR-Based Milk Metabolomics. Metabolites 2013, 3, 204–222.
- Peterson, A.L.; Waterhouse, A.L. 1H NMR: A novel approach to determining the thermodynamic properties of acetaldehyde con-densation reactions with glycerol, (+)-catechin, and glutathione in model wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6869–6878.
- Noh, M.F.M.; Gunasegavan, R.D.-N.; Khalid, N.M.; Balasubramaniam, V.; Mustar, S.; Rashed, A.A. Molecules Recent techniques in nutrient analysis for food composition database. Molecules 2020, 25, 4567.
- Singh, D.; Lee, S.; Lee, C.H. Metabolomics for empirical delineation of the traditional Korean fermented foods and beverages. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 61, 103–115.
- Rocchetti, G.; O’Callaghan, T.F. Application of metabolomics to assess milk quality and traceability. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 40, 168–178.
- Trimigno, A.; Marincola, F.C.; Dellarosa, N.; Picone, G.; Laghi, L. Definition of food quality by NMR-based foodomics. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 4, 99–104.
- Rochfort, S. Metabolomics Reviewed: A New “Omics” Platform Technology for Systems Biology and Implications for Natural Products Research. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1813–1820.
- Yang, Z. Online hyphenated liquid chromatography–nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy–mass spectrometry for drug metabolite and nature product analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 516–527.
- Tabago, M.K.A.G.; Calingacion, M.N.; Garcia, J. Recent advances in NMR-based metabolomics of alcoholic beverages. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2020, 2, 100009.
- Li, Y.; Teng, Z.; Parkin, K.L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, W.; Ma, D.; Zhao, M. Identification of bioactive metabolites dihydrocana-densolide, kojic acid, and vanillic acid in soy sauce using GC-MS, NMR spectroscopy, and single-crystal x-ray diffraction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8392–8401.
- Lee, S.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Jeon, C.O. Bacterial community dynamics and metabolite changes in myeolchi-aekjeot, a Korean traditional fermented fish sauce, during fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 203, 15–22.
- Naumann, D.; Helm, D.; Labischinski, H. Microbiological characterizations by FT-IR spectroscopy. Nature 1991, 351, 81–82.
- Kasprzyk, I.; Depciuch, J.; Grabek-Lejko, D.; Parlinska-Wojtan, M. FTIR-ATR spectroscopy of pollen and honey as a tool for unifloral honey authentication. The case study of rape honey. Food Control. 2018, 84, 33–40.
- Wang, F.; Shao, C.; Chen, Q.; Meng, T.; Li, C. Application on sensory prediction of Chinese moutai-flavor liquor based on ATR-FTIR. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 79, 03001.
- Puxeu, M.; Andorra, I.; De Lamo-Castellví, S.; Ferrer-Gallego, R. Determination of Nutrient Supplementation by Means of ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy during Wine Fermentation. Fermentation 2019, 5, 58.
- Garcia-Hernandez, C.; Salvo-Comino, C.; Martin-Pedrosa, F.; Garcia-Cabezon, C.; Rodriguez-Mendez, M. Analysis of red wines using an electronic tongue and infrared spectroscopy. Correlations with phenolic content and color parameters. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 118, 108785.
- Krähmer, A.; Böttcher, C.; Gudi, G.; Stürtz, M.; Schulz, H. Application of ATR-FTIR spectroscopy for profiling of non-structural carbohydrates in onion (Allium cepa L.) bulbs. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129978.
- Anjos, O.; Santos, A.J.A.; Estevinho, L.M.; Caldeira, I. FTIR-ATR spectroscopy applied to quality control of grape-derived spirits. Food Chem. 2016, 205, 28–35.
- Ozulku, G.; Yildirim, R.M.; Toker, O.S.; Karasu, S.; Durak, M.Z. Rapid detection of adulteration of cold pressed sesame oil adultered with hazelnut, canola, and sunflower oils using ATR-FTIR spectroscopy combined with chemometric. Food Control. 2017, 82, 212–216.
- Galvin-King, P.; Haughey, S.A.; Elliott, C.T. Garlic adulteration detection using NIR and FTIR spectroscopy and chemometrics. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 96, 103757.
- Labaky, P.; Dahdouh, L.; Ricci, J.; Wisniewski, C.; Pallet, D.; Louka, N.; Grosmaire, L. Impact of ripening on the physical properties of mango purees and application of simultaneous rheometry and in situ FTIR spectroscopy for rapid identification of biochemical and rheological changes. J. Food Eng. 2021, 300, 110507.
- Kumar, K.; Giehl, A.; Patz, C.-D. Chemometric assisted Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopic analysis of fruit wine samples: Optimizing the initialization and convergence criteria in the non-negative factor analysis algorithm for developing a robust classification model. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 209, 22–31.
- Li, Z.; Wang, P.-P.; Huang, C.-C.; Shang, H.; Pan, S.-Y.; Li, X.-J. Application of Vis/NIR Spectroscopy for Chinese Liquor Discrimination. Food Anal. Methods 2013, 7, 1337–1344.
- Wang, L.; Sun, D.W.; Pu, H.; Cheng, J.H. Quality analysis, classification, and authentication of liquid foods by near-infrared spectroscopy: A review of recent research developments. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2017, 57, 1524–1538.
- Brunius, C.; Shi, L.; Landberg, R. Large-scale untargeted LC-MS metabolomics data correction using between-batch feature alignment and cluster-based within-batch signal intensity drift correction. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 1–13.
- Cajka, T.; Fiehn, O. Toward Merging Untargeted and Targeted Methods in Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics and Lipidomics. Anal. Chem. 2015, 88, 524–545.
- Allwood, J.W.; Goodacre, R. An introduction to liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry instrumentation applied in plant metabolomic analyses. Phytochem. Anal. 2010, 21, 33–47.
- Mihailova, A.; Kelly, S.D.; Chevallier, O.P.; Elliott, C.T.; Maestroni, B.M.; Cannavan, A. High-resolution mass spectrometry-based metabolomics for the discrimination between organic and conventional crops: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 142–154.
- Song, H.; Liu, J. GC-O-MS technique and its applications in food flavor analysis. Food Res. Int. 2018, 114, 187–198.
- Dervishi, E.; Zhang, G.; Dunn, S.M.; Mandal, R.; Wishart, D.S.; Ametaj, B.N. GC–MS Metabolomics Identifies Metabolite Alterations That Precede Subclinical Mastitis in the Blood of Transition Dairy Cows. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 16, 433–446.
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry: Combined Targeted and Untargeted Profiling. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2016, 114, 30.4.1–30.4.32.
- Moros, G.; Chatziioannou, A.C.; Gika, H.G.; Raikos, N.; Theodoridis, G. Investigation of the derivatization conditions for GC–MS metabolomics of biological samples. Bioanalysis 2017, 9, 53–65.
- Vinaixa, M.; Schymanski, E.; Neumann, S.; Navarro, M.; Salek, R.M.; Yanes, O. Mass spectral databases for LC/MS- and GC/MS-based metabolomics: State of the field and future prospects. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 78, 23–35.
- Constantinou, M.; Louca-Christodoulou, D.; Agapiou, A. Method validation for the determination of 314 pesticide residues using tandem MS systems (GC–MS/MS and LC-MS/MS) in raisins: Focus on risk exposure assessment and respective processing factors in real samples (a pilot survey). Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129964.
- Li, W.; Chen, Y.P.; Blank, I.; Li, F.; Liu, Y. GC×GC-TOF-MS and GC-IMS based volatile profile characterization of the chinese dry-cured hams from different regions. Food Res. Int. 2021, 142, 110222.
- Magagna, F.; Cordero, C.; Cagliero, C.; Liberto, E.; Rubiolo, P.; Sgorbini, B.; Bicchi, C. Black tea volatiles fingerprinting by compre-hensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-Mass spectrometry combined with high concentration capacity sample preparation techniques: Toward a fully automated sensomic assessment. Food Chem. 2017, 225, 276–287.
- Kuś, P.M.; Rola, R. LC-QQQ-MS/MS methodology for determination of purine and pyrimidine derivatives in unifloral honeys and application of chemometrics for their classification. Food Chem. 2021, 348, 129076.
- An, F.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, D.; Hu, X.; You, S.; Wu, J.; Wu, R. Metatranscriptome-based investigation of flavor-producing core microbiota in different fermentation stages of dajiang, a traditional fermented soybean paste of Northeast China. Food Chem. 2020, 343, 128509.
- Lisanti, M.T.; Laboyrie, J.; Marchand-Marion, S.; de Revel, G.; Moio, L.; Riquier, L.; Franc, C. Minty aroma compounds in red wine: Development of a novel automated HS-SPME-arrow and gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry quantification method. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130029.
- Ramautar, R.; Somsen, G.W.; De Jong, G.J. CE-MS for metabolomics: Developments and applications in the period 2012–2014. Electrophoresis 2014, 36, 212–224.
- Drouin, N.; Pezzatti, J.; Gagnebin, Y.; González-Ruiz, V.; Schappler, J.; Rudaz, S. Effective mobility as a robust criterion for compound annotation and identification in metabolomics: Toward a mobility-based library. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1032, 178–187.
- Yoshida, M.; Hatano, N.; Nishiumi, S.; Irino, Y.; Izumi, Y.; Takenawa, T.; Azuma, T. Diagnosis of gastroenterological diseases by metabolome analysis using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 47, 9–20.
- Miggiels, P.; Wouters, B.; van Westen, G.J.; Dubbelman, A.-C.; Hankemeier, T. Novel technologies for metabolomics: More for less. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 120, 115323.
- Montona, M.R.N.; Soga, T. Metabolome analysis by capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A. 2008, 1168, 237–246.
- Zhang, W.; Ramautar, R. CE-MS for metabolomics: Developments and applications in the period 2018–2020. Electrophoresis 2020, 42, 381–401.
- Wilson, A.D. Advances in Electronic-Nose Technologies for the Detection of Volatile Biomarker Metabolites in the Human Breath. Metabolites 2015, 5, 140–163.
- Rocchi, R.; Mascini, M.; Faberi, A.; Sergi, M.; Compagnone, D.; Di Martino, V.; Carradori, S.; Pittia, P. Comparison of IRMS, GC-MS and E-Nose data for the discrimination of saffron samples with different origin, process and age. Food Control. 2019, 106, 106736.
- Ghasemi-Varnamkhastia, M.; Apetreib, C.; Lozanoc, J.; Anyogu, A. Potential use of electronic noses, electronic tongues and biosensors as multisensor systems for spoilage examination in foods. Trends. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 80, 71–92.
- Tan, J.; Xu, J. Applications of electronic nose (e-nose) and electronic tongue (e-tongue) in food quality-related properties determination: A review. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2020, 4, 104–115.
- Xu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Tian, L.; Lu, H.; Luo, X.; Lan, Y. Study of the similarity and recognition between volatiles of brown rice plant hoppers and rice stem based on the electronic nose. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 152, 19–25.
- Yang, C.; Ding, W.; Ma, L.; Jia, R. Discrimination and characterization of different intensities of goaty flavor in goat milk by means of an electronic nose. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 55–67.
- Wasilewski, T.; Migon, D.; Gebicki, J.; Kamysz, W. Critical review of electronic nose and tongue instruments prospects in pharma-ceutical analysis. Anal. Chim Acta. 2019, 1077, 14–29.
- Mohd Ali, M.; Hashim, N.; Aziz, S.A.; Lasekan, O. Principles and recent advances in electronic nose for quality inspection of agricultural and food products. Trends. Food Sci. Tech. 2020, 99, 1–10.
- Xu, J.; Liu, K.; Zhang, C. Electronic nose for volatile organic compounds analysis in rice aging. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 83–93.
- Jo, D.; Kim, G.-R.; Yeo, S.-H.; Jeong, Y.-J.; Noh, B.S.; Kwon, J.-H. Analysis of aroma compounds of commercial cider vinegars with different acidities using SPME/GC-MS, electronic nose, and sensory evaluation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 22, 1559–1565.
- Hong, Y.; Noh, B.-S.; Kim, H.-Y. Discrimination of doenjang samples using a mass spectrometry-based electronic nose and human sensory preference testing. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 31–36.
- Lalaleo, L.; Hidalgo, D.; Valle, M.; Calero-Cáceres, W.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Becerra-Martínez, E. Differentiating, evaluating, and classifying three quinoa ecotypes by washing, cooking and germination treatments, using 1H NMR-based metabolomic approach. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127351.
- Peng, C.; Yao, G.; Sun, Y.; Guo, S.; Wang, J.; Mu, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H. Comparative effects of the single and binary probiotics of Lacticaseibacillus casei Zhang and Bifidobacterium lactis V9 on the growth and metabolomic profiles in yogurts. Food Res. Int. 2021, 110603.
- Raja, G.; Jung, Y.; Jung, S.H.; Kim, T.-J. 1H-NMR-based metabolomics for cancer targeting and metabolic engineering—A review. Process. Biochem. 2020, 99, 112–122.
- Shi, B.; Ding, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Tian, X.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Han, L. Investigation on the stability in plant metabolomics with a special focus on freeze-thaw cycles: LC–MS and NMR analysis to Cassiae Semen (Cassia obtusifolia L.) seeds as a case study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 204, 114243.
- Luo, Y.; Gao, F.; Chang, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, J.; Wen, J.; Wu, J.; Zhou, T. Metabolomics based comprehensive investigation of Gardeniae Fructus induced hepatotoxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 153, 112250.
- Cardoso, S.; Afonso, T.; Maraschin, M.; Rocha, M. WebSpecmine: A Website for Metabolomics Data Analysis and Mining. Metabolites 2019, 9, 237.
- Gromski, P.S.; Muhamadali, H.; Ellis, D.; Xu, Y.; Correa, E.; Turner, M.; Goodacre, R. A tutorial review: Metabolomics and partial least squares-discriminant analysis—A marriage of convenience or a shotgun wedding. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 879, 10–23.
- Cha, K.H.; Lee, E.H.; Yoon, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kang, K.; Park, J.-S.; Jin, J.B.; Ko, G.; Pan, C.-H. Effects of fermented milk treatment on microbial population and metabolomic outcomes in a three-stage semi-continuous culture system. Food Chem. 2018, 263, 216–224.
- Ma, C.; Li, X.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, B.; Xu, C.; Xia, T. Comparison of characteristic components in tea-leaves fermented by Aspergillus pallidofulvus PT-3, Aspergillus sesamicola PT-4 and Penicillium manginii PT-5 using LC-MS metabolomics and HPLC analysis. Food Chem. 2021, 350, 129228.
- Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Y.; Dai, Y. ACE-Inhibitory Peptide Isolated from Fermented Soybean Meal as Functional Food. Int. J. Food Eng. 2013, 9, 1–8.
- Tasdemir, S.S.; Sanlier, N. An insight into the anticancer effects of fermented foods: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104281.
- Dey, T.B.; Chakraborty, S.; Jain, K.K.; Sharma, A.; Kuhad, R.C. Antioxidant phenolics and their microbial production by submerged and solid state fermentation process: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 60–74.
- Ferri, M.; Serrazanetti, D.I.; Tassoni, A.; Baldissarri, M.; Gianotti, A. Improving the functional and sensorial profile of cereal-based fermented foods by selecting Lactobacillus plantarum strains via a metabolomics approach. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 1095–1105.
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Xiong, Z.; Eweys, A.S.; Zhou, H.; Dong, Y.; Xiao, X. Metabolomics strategy for revealing the components in fermented barley extracts with lactobacillus plantarum dy-1—Sciencedirect. Food Res. Int. 2021, 139, 109808.
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Tan, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, F.; Chen, L.; Hao, F.; Lv, X.; Du, H.; Xu, Y. Effect of Pichia on shaping the fermentation microbial community of sauce-flavor Baijiu. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 336, 108898.
- Chen, G.-M.; Huang, Z.-R.; Wu, L.; Wu, Q.; Guo, W.-L.; Zhao, W.-H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Rao, P.-F.; Lv, X.-C.; et al. Microbial diversity and flavor of Chinese rice wine (Huangjiu): An overview of current research and future prospects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 37–50.
- Khattab, A.R.; Guirguis, H.A.; Tawfik, S.M.; Farag, M.A. Cheese ripening: A review on modern technologies towards flavor en-hancement, process acceleration and improved quality assessment. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2019, 88, 343–360.
- Zhou, Z.; Jian, D.; Gong, M.; Zhu, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, F.; Mao, J. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in aged Zhenjiang aromatic vinegar by gas chromatography-olfactometry-mass spectrometry, quantitative measurements, aroma recombination and omission experiments. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109434.
- Wang, J.; Yuan, C.; Gao, X.; Kang, Y.; Huang, M.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of key aroma compounds in Huangjiu from northern China by sensory-directed flavor analysis. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109238.
- Yang, L.; Fan, W.; Xu, Y. GC × GC-TOF/MS and UPLC-Q-TOF/MS based untargeted metabolomics coupled with physicochemical properties to reveal the characteristics of different type daqus for making soy sauce aroma and flavor type baijiu. LWT 2021, 146, 111416.
- Deng, X.; Huang, G.; Tu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Shi, H.; Wu, X.; Ren, H.; Huang, K.; He, X.; et al. Evolution analysis of flavor-active compounds during artificial fermentation of Pu-erh tea. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129783.
- Park, M.K.; Kim, Y.S. Comparative metabolic expressions of fermented soybeans according to different microbial starters. Food Chem. 2019, 305, 125461.
- Wang, P.; Ma, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, D.; Sun, Y. Characterization of flavor fingerprinting of red sufu during fermentation and the com-parison of volatiles of typical products. Food Sci. Hum. Well. 2019, 8, 375–384.
- Leejeerajumnean, A.; Duckham, S.C.; Owens, J.D.; Ames, J.M. Volatile compounds in Bacillus-fermented soybeans. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 525–529.
- Kimura, K.; Yokoyama, S. Trends in the application of Bacillus in fermented foods. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 2018, 56, 36–42.
- Gao, Y.X.; Xu, B.; Fan, H.R.; Zhang, M.R.; Zhang, L.J.; Lu, C.; Na Zhang, N.; Fan, B.; Wang, F.Z.; Li, S. 1H NMR-based chemometric metabolomics characterization of soymilk fermented by Bacillus subtilis BSNK-5. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109686.
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.; Wei, Y.; Huang, H. Comparison of the microbial community and flavor compounds in fermented mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi): Three typical types of Chinese fermented mandarin fish products. Food Res. Int. 2021, 144, 110365.
- Fang, G.-Y.; Chai, L.-J.; Zhong, X.-Z.; Jiang, Y.-J. Deciphering the succession patterns of bacterial community and their correlations with environmental factors and flavor compounds during the fermentation of Zhejiang rosy vinegar. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 341, 109070.
- Che, H.; Yu, J.; Sun, J.; Lu, K.; Xie, W. Bacterial composition changes and volatile compounds during the fermentation of shrimp paste: Dynamic changes of microbial communities and flavor composition. Food Biosci. 2021, 101169.
- Thakur, K.; Tomar, S.K.; Wei, Z.-J. Comparative mRNA Expression Profiles of Riboflavin Biosynthesis Genes in Lactobacilli Isolated from Human Feces and Fermented Bamboo Shoots. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 427.
- Sharma, S.; Kandasamy, S.; Kavitake, D.; Shetty, P.H. Probiotic characterization and antioxidant properties of Weissella confusa KR780676, isolated from an Indian fermented food. LWT 2018, 97, 53–60.
- Thakur, K.; Tomar, S.K.; De, S. Lactic acid bacteria as a cell factory for riboflavin production. Microb. Biotechnol. 2015, 9, 441–451.
- Zyalçin, B.; Sanlier, N. The effect of diet components on cancer with epigenetic mechanisms. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2020, 102, 138–145.
- Crespo, L.; Gaglio, R.; Martínez, F.G.; Martin, G.M.; Franciosi, E.; Madrid-Albarrán, Y.; Settanni, L.; Mozzi, F.; Pescum, M. Bioaccumulation of selenium-by fruit origin lactic acid bacteria in tropical fermented fruit juices. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112103.
- Daliri, B.M.; Tyagi, A.; Ofosu, F.K.; Chelliah, R.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.R.; Yoo, D.; Oh, D.H. A discovery-based metabolomic approach using UHPLC Q-TOF MS/MS unveils a plethora of prospective antihypertensive compounds in Korean fermented soybeans. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 137, 110399.
- Kang, H.J.; Yang, H.J.; Kim, M.J.; Han, E.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kwon, D.Y. Metabolomic analysis of meju during fermentation by ultraper-formance liquid chromatography quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF MS). Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1056–1064.
- Sun, X.; Lyu, G.; Luan, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Z. Metabolomic study of the soybean pastes fermented by the single species Penicillium glabrum GQ1-3 and Aspergillus oryzae HGPA20. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 622–629.
- Namgung, H.-J.; Park, H.-J.; Cho, I.H.; Choi, H.-K.; Kwon, D.-Y.; Shim, S.-M.; Kim, Y.-S. Metabolite profiling of doenjang, fermented soybean paste, during fermentation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 1926–1935.
- Kim, S.S.; Kwak, H.S.; Kim, M.J. The effect of various salinity levels on metabolomic profiles, antioxidant capacities and sensory attributes of doenjang, a fermented soybean paste. Food Chem. 2020, 328, 127176.
- Jang, H.-H.; Noh, H.; Kim, H.-W.; Cho, S.-Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Gunter, M.J.; Ferrari, P.; Scalbert, A.; et al. Metabolic tracking of isoflavones in soybean products and biosamples from healthy adults after fermented soybean consumption. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127317.
- Piras, C.; Marincola, F.C.; Savorani, F.; Engelsen, S.B.; Cosentino, S.; Viale, S.; Pisano, M.B. A NMR metabolomics study of the ripening process of the Fiore Sardo cheese produced with autochthonous adjunct cultures. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2137–2147.
- Bai, M.; Huang, T.; Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Dan, T.; Zhang, H.; Bilige, M. Probiotic Lactobacillus casei Zhang improved the properties of stirred yogurt. Food Biosci. 2020, 37, 100718.
- Yang, S.; Yan, D.; Zou, Y.; Mu, D.; Li, X.; Shi, H.; Luo, X.; Yang, M.; Yue, X.; Wu, R.; et al. Fermentation temperature affects yogurt quality: A metabolomics study. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101104.
- Wu, S.; Li, N.; Li, S.-J.; Bhandari, B.; Yang, B.-L.; Chen, X.D.; Mao, Z.-H. Effects of Incubation Temperature, Starter Culture Level and Total Solids Content on the Rheological Properties of Yogurt. Int. J. Food Eng. 2009, 5, 3.
- Alaa, A.E.; Sally, S.; Samia, E.; Hany, E. Developing functional yogurt rich in bioactive peptides and gamma-aminobutyric acid related to cardiovascular health. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 98, 390–397.
- Shi, M.; Mathai, M.L.; Xu, G.; McAinch, A.J.; Su, X.Q. The effects of supplementation with blueberry, cyanidin-3-O-β-glucoside, yoghurt and its peptides on obesity and related comorbidities in a diet-induced obese mouse model. J. Funct. Foods. 2019, 56, 92–101.
- Tufariello, M.; Rizzuti, A.; Palombi, L.; Ragone, R.; Capozzi, V.; Gallo, V.; Mastrorilli, P.; Grieco, F. Non-targeted metabolomic approach as a tool to evaluate the chemical profile of sparkling wines fermented with autochthonous yeast strains. Food Control. 2021, 126, 108099.
- Weiskirchen, S.; Weiskirchen, R. Resveratrol: How much wine do you have to drink to stay healthy? Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 706–718.
- Benbouguerra, N.; Hornedo-Ortega, R.; Garcia, F.; El Khawand, T.; Saucier, C.; Richard, T. Stilbenes in grape berries and wine and their potential role as anti-obesity agents: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 362–381.
- Pugajeva, I.; Pērkons, I.; Górnaś, P. Identification and determination of stilbenes by Q-TOF in grape skins, seeds, juice and stems. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 74, 44–52.
- Li, R.-Y.; Zheng, X.-W.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Z.; Wang, X.-Y.; Han, B.-Z. Characterization of bacteria and yeasts isolated from traditional fermentation starter (Fen-Daqu) through a 1H NMR-based metabolomics approach. Food Microbiol. 2018, 76, 11–20.
- Ishihara, S.; Inaoka, T.; Nakamura, T.; Kimura, K.; Tomita, S. Nuclear magnetic resonance- and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry-based metabolomic characterization of water-soluble and volatile compound profiles in cabbage vinegar. J. Biosci Bioeng. 2018, 126, 53–62.
- Tomita, S.; Watanabe, J.; Kuribayashi, T.; Tanaka, S.; Kawahara, T. Metabolomic evaluation of different starter culture effects on water-soluble and volatile compound profiles in nozawana pickle fermentation. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2021, 2, 100019.
- Drake, M.A.; Delahunty, C.M. Chapter 20—Sensory character of cheese and its evaluation. In Cheese, 4th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 517–545.
- Seo, H.S.; Lee, S.; Singh, D.; Shin, H.W.; A Cho, S.; Lee, C.H. Untargeted metabolite profiling for koji-fermentative bioprocess unravels the effects of varying substrate types and microbial inocula. Food Chem. 2018, 266, 161–169.
- Kasprowicz-Potocka, M.; Zaworska, A.; Gulewicz, P.; Nowak, P.; Frankiewicz, A. The effect of fermentation of high alkaloid seeds of Lupinus angustifolius var. Karo by Saccharomyces cerevisieae, Kluyveromyces lactis, and Candida utilis on the chemical and microbial composition of products. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 42, e13487.
- Ding, M.; Liu, W.; Peng, J.; Liu, X.; Tang, Y. Simultaneous determination of seven preservatives in food by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 187–192.
- Tungkijanansin, N.; Alahmad, W.; Nhujak, T.; Varanusupakul, P. Simultaneous determination of benzoic acid, sorbic acid, and pro-pionic acid in fermented food by headspace solid-phase microextraction followed by GC-FID. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 127161.
- Oyedeji, A.B.; Green, E.; Adebiyi, J.A.; Ogundele, O.M.; Gbashi, S.; Adefisoye, M.A.; Oyeyinka, S.A.; Adebo, O.A. Metabolomic approaches for the determination of metabolites from pathogenic microorganisms: A review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 140, 110042.




