
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nikola Tresnakova | + 2015 word(s) | 2015 | 2021-10-14 09:57:15 | | | |
| 2 | Catherine Yang | Meta information modification | 2015 | 2021-10-26 03:20:53 | | |
Video Upload Options
Glyphosate (N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine) was developed in the early 1970s and at present is used as a herbicide to kill broadleaf weeds and grass. The widely occurring degradation product aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) is a result of glyphosate and amino-polyphosphonate degradation. The massive use of the parent compound leads to the ubiquity of AMPA in the environment, and particularly in water.
1. Introduction
Over the last few years, the importance of knowledge about pesticide’s persistence, mobility, and ecotoxicity has increased. Using pesticides and other agrochemicals is the most cost-effective way to maintain economic viability in the increasing human population [1][2]. On the other hand, the intensive application and repeated use of pesticides in fields in order to increase the crop yield lead to long-term risk for humans, fauna, flora, and the whole ecosystem (soil, air, and water) [1][2][3]. The extensive use of pesticides is not only a problem in agricultural areas but also in urban settings where pesticides are applied for horticultural purposes. Therefore, it is challenging to control the source of diffuse chemical pollution and its consequences [4]. In particular, the presence of pesticides and their metabolites occurring in residual concentratiosn in drinking, ground, and surface waters poses a global problem [1][3].
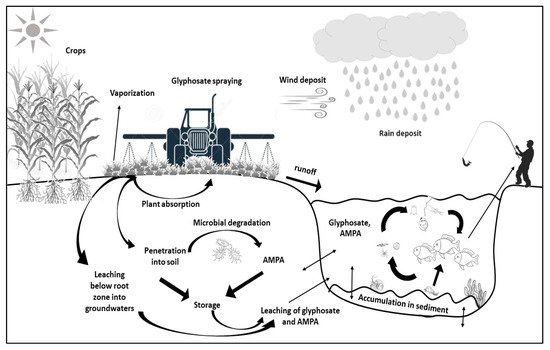
Directly after spraying herbicide in agriculture or in urban areas, glyphosate is absorbed by crops or weeds and penetrates the soil simultaneously. The glyphosate degradation pathway in bacterial strains is the cleavage of the C-N bond and conversion to AMPA, which is either further decomposed or excreted into the environment [5][6]. AMPA is a primary product of the degradation process of glyphosate and the following nontoxic products are sarcosine and glycine. Unlike AMPA, which is 3–6-fold times more toxic and persistent than glyphosate [7], sarcosine is barely detected in the natural environment [8], except under experimental conditions in a laboratory [6]. On the one hand, the soil has functioned as storage; on the other hand, these contaminants leach below the root zone into groundwater. Glyphosate is also transported by runoff into surface water and consequently accumulated in sediment where glyphosate can be highly mobile [9][7]. The residual concentrations of glyphosate and AMPA in waters contaminate aquatic organisms via the food web ( Figure 1 ) [10][5].
2. Glyphosate (N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine)
2.1. Environmental Fate
2.2. Acute Toxicity
| Species | Formulation | Exposure (Hours) | Concentration (mg/L) |
References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) |
GLY | 96 | 140 | [17] |
| Roundup 1 | 96 | 52–55 | [22] | |
| Common carp (Cyprinus carpio) |
GLY | 48 | 645 | [23] |
| 96 | 620 | |||
| Roundup 1 | 96 | 22.19 | [24] | |
| GLY | 48 | 602.61 | [25] | |
| 96 | 520.77 | |||
| Blackhead minnow (Pimephales promelas) |
GLY | 96 | 97 | [17] |
| Channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) |
96 | 130 | ||
| Bluegills (Lepomis macrochirus) |
GLY | 24 | 150 | [17] |
| 96 | 140 | |||
| Guppy (Poecilia reticulata) |
GLY | 96 | 69.83 | [26] |
| Rhamdia quelen | GLY | 96 | 7.30 | [27] |
| North African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) | GLY | 96 | 0.295 | [28] |
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) |
Atnor 48 2 | 96 | 76.50 | [29] |
| Ten spotted live-bearer (Cnesterodon decemmaculatus) |
Glyfoglex 3 | 96 | 41.40 | [30] |
1 Roundup (active substance glyphosate, 41%), 2 Atnor 48 (active substance glyphosate, 48%), 3 Glyfoglex (active substance glyphosate, 48%).
| Species | Formulation | Exposure (Hours) | Concentration (mg/L) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boana pardalis | GLY | 96 | 106 | [31] |
| Physalaemus cuvieri | 96 | 115 | ||
| Green frog (Lithobates clamitans) |
Roundup 1 | 24 | 6.6 | [32] |
| 96 | 6.5 | |||
| Northern leopard frog (Lithobates pipiens) |
24 | 11.9 | ||
| 96 | 9.2 | |||
| Wood frog (Lithobates sylvaticus) |
24 | 18.1 | ||
| 96 | 16.5 | |||
| Dwarf American toad (Anaxyrus americanus) |
24 | 13.5 | ||
| 96 | <12.9 | |||
| Rhinella arenarum | Roundup Ultra-Max 2 | 48 | 2.42 | [33] |
| 77.52 |
1 Roundup (active substance glyphosate, 41%).
2.3. Toxic Effects
2.3.1. Fish
| Species | Concentration | Exposure | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common carp (Cyprinus carpio) |
2.5, 5, 10 mg/L (GLY) |
96 h | ↑ ALP in liver, heart, GOT in liver and kidney, GPT in kidney;Subepithelial edema and epithelial hyperplasia in gills, focal fibrosis in liver | [23] |
| 3.5, 7, 14 mg/L (Roundup 1) |
16 days | ↑ MCV, MCH; ↓ AChE in muscle, brain and liver, Hb, HCT, RBC, WBC, AST, ALT, LDH |
[24] | |
| 52.08, 104.15 mg/L (GLY) |
7 days | Vacuolization of the renal parenchyma and intumescence of the renal tubule in kidney, immunotoxicity | [25] | |
| ↑ AST, ALT, MDA, PC; ↓ GSH, inhibition of NA+/K+ -ATPase, SOD, CAT, GPx, GR, T-AOC, induce inflammatory response in gills |
[36] | |||
| European eel (Anguilla Anguilla) |
58, 116 μg/L (Roundup 1) |
1, 3 days | ↑ TBARS, LPO, GDI, ENA | [19] |
| ↑ GDI, damaged nucleoids, EndoIII | [35] | |||
| Curimbata (Prochilodus lineatus) |
10 mg/L (Roundup 1) |
24 h | ↑ GSH, GST, LPO; ↓ SOD, GPx, inhibition of AChE in muscle |
[14] |
| 96 h | ↑ GST, LPO;inhibition of AChE in muscle in brain and muscle | |||
| Spotted snakehead (Channa punctatus) |
32.54 mg/L (Roundup 1) |
1, 7, 14, 21, 28, 35 days | ↑ TBARS, DNA damage, LPO, ROS; ↓ CAT, SOD, GR in gill and blood |
[38] |
| Ten spotted live-bearer (Cnesterodon decemmaculatus) |
1, 1.75, 35 mg/L (GLY) |
96 h | ↓ AChE | [39] |
| Megaleporinus obtusidens | 3, 6, 10, 20 mg/L (Roundup 1) |
96 h | ↑ hepatic GL, GLU, NH3 in liver and muscle, PCV, Hb, RBC, WBC, P; ↓ AChE in brain, LACT, P in liver, muscle GL, GLU |
[40] |
| 5 mg/L (Roundup 1) |
90 days | ↑ LACT in liver and muscle, P in liver; ↓ AChE, GL in liver, P in muscle, PCV, Hb, RBC, WBC |
[41] | |
| Rhamdia quelen | 0.2, 0.4 mg/L (Roundup 1) |
96 h | ↑ hepatic GL, LACT in liver and muscle, P in liver and muscle, NH3 in liver and muscle, TBARS in muscle; ↓ muscle GL, GLU in liver and muscle, AChE in brain |
[42] |
| 0.730 mg/L (GLY) |
24, 96 h, 10 days |
↑ immature circulating cells; ↓ RBC, THR, WBC, phagocytic activity, agglutination activity, lysozyme activity |
[43] | |
| Rhamdia quelen | 18, 36, 72 μg/L (Roundup 1) |
7 days | ↑ TP in liver, ↑ GL in muscle; ↓ TP, GL, TL in gills, liver, and kidney |
[44] |
| Goldfish (Carassius auratus) |
2.5–20 mg/L (Roundup 1) |
2 months | ↑ CAT in liver and kidney; ↓ GR in kidney, liver, and brain, G6PDH in kidney, liver and brain, SOD in kidney, liver and brain |
[45] |
| 0.22, 0.44, 0.88 mmol/L (GLY) |
96 h | Behaviour abnormalities (observed depression, erratic swimming, partial loss of equilibrium), liver tissue damage (cellular swelling, inflammatory cell infiltration, hydropic degeneration, loose cytoplasm, ↑ brown particles), kidney tissue damage (edema in the epithelial cells of renal tubules, ↑ cell volume, loose cytoplasm, slight staining), changes in plasma (↑ CK, UN, ↓ LDH) | [46] | |
| 0.2 mmol/L (Nongteshi 2) |
90 days | Hyaline cast in kidney, ↑ CRE, BUN, ALT, AST, LDH, MDA, ↑ 3-hydroxybutyrate, LACT, alanine, acetamide, glutamate, glycine, histidine, inosine, GLU;↓ SOD, GSH-Px, GR, lysine, NAA, citrate, choline, phosphocholine, myo-inosine, nicotinamide, |
[47] | |
| North African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) |
0, 19, 42, 94, 207, 455mg/L (GLY) |
96 h | Cellular infiltration in gills; fatty degeneration, fat vacuolation, diffuse hepatic necrosis, infiltration of leukocytes in liver; hematopoietic necrosis, pyknotic nuclei in kidney; mononuclear infiltration, neuronal degeneration, spongiosis in brain; respiratory stress, erratic swimming | [28] |
| Hybrid fish jundiara (Leiarius marmoratus × Psedoplatystoma reticulatum) |
1.357 mg/L (Roundup 1) |
6, 24, 48,96 h | ↑ LACT in liver, P level in liver, ALT, AST, CHOL, TAG in plasma; ↓ GL in liver and muscle, plasma GLU, Hb, PCV, RBC, WBC |
[48] |
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) |
50 μg/mL (GLY) |
24 h | ↓ gene expression in eye, fore, and midbrain delineated brain ventricles and cephalic regions |
[49] |
| 32.5, 65, 130 μg/L (Transorb 3) |
48 h | ↓ integrity of plasma membrane of hepatocytes, viability of cells, mitochondrial activity in the cell, lysosomal integrity, inhibition in ABC transporter activity | [50] | |
| 10, 50, 100, 200, 400 μg/L (GLY) |
48 h | ↓ heartbeat, NO generation, downregulation of Cacana1C and ryr2a genes, upregulation of hspb11 | [37] | |
| Climbing bass (Anabas testudineus) |
17.20 mg/L (Excel Mera 71 4) |
30 days | ↑ AChE, LPO, CAT; ↓ TP, GST |
[51] |
| Heteropneustes fossilis |
2.3.2. Invertebrate Species
| Species | Concentration | Exposure | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) |
100 μg/L (GLY) |
7 days | ↑ THC, haemocyte proliferation; ↓ Haemocyte diameter, AChE in gills |
[52] |
| 14 days | ↑ AChE in gills, CAT in digestive gland; ↓ CAT in gills |
|||
| 21 days | ↑ CAT in gills; ↓ THC, haemocyte diameter, haemocyte volume, HL, AChE in gills |
|||
| 10, 100, 1000 μg/L (GLY) |
7, 14, 21 days | ↑ cell volume of haemocyte, haemolymph pH; ↓ HL, haemolymph acid phosphatase activity; AChE in gills; SOD in digestive gland, THC, |
[54] | |
| Limnoperna fortunei |
1, 3, 6 mg/L (GLY) |
26 days | ↑ TBARS, GST, ALP; ↓ CES, SOD |
[55] |
| 10, 20, 40 mg/L (GLY) |
3 weeks | ↓ presence of large mussel by 40%, presence empty shell by 25% | [56] | |
| Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) |
0.1, 1, 100 μg/L (Roundup Expres 1) |
35 days | ↑ GST; ↓ growth; LPO, MDA |
[57] |
| California blackworm (Lumbriculus variegatus) |
0.05–5 mg/L(GLY) | 4 days | ↑ SOD; ↓ GST, membrane bound GST |
[58] |
| Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) |
4.4, 9.8, 44, 98 mg/L(GLY) | 96 h | ↑ % DNA in tail, SOD, POD, β-GD;↓ THC, granulocytes, phagocytic activity, ACP, AKP | [34] |
| American bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus) |
1 mg/L (Roundup 2) |
48 h | ↑ swimming activity, CPM; SOD, CAT and LPO in liver; LPO in muscle; ↓ SOD, CAT in muscle, TtHR |
[59] |
| Rhinella arenarum | 1.85, 3.75, 7.5, 15, 30, 60, 120, 240 mg/L (Roundup Ultra-Max 3) |
48 h | ↓ AChE, BChE, CbE, GST | [33] |
| Northern leopard frog (Rana pipiens) |
0.6, 1.8 mg/L (Roundup 2) |
166 days | ↑ TRβ mRNA; Late metamorphic climax, developmental delay, abnormal gonads, necrosis of the tail tip, fin damage, abnormal growth on the tail tip, blistering on the tail fin |
[32] |
| Snail(Biomphalaria alexandrina) | 3.15 mg/L (Roundup 2) |
6 weeks | ↑ mortality, stopped egg lying, abnormal laid eggs, ↑ GLU, LACT, FAC; ↓ egg hatchability, GL, TP, pyruvate, nucleic acids levels |
[60] |
| 10 mg/L (Roundup 2) |
7 days | ↑ in vitro phagocytic activity, DNA damage in haemocytes | [61] |
1 Roundup Expres (active substance glyphosate, 15%), 2 Roundup (active substance glyphosate, 41%), 3 Roundup Ultra-Max (active substance glyphosate, 36%).
References
- Arias-Estévez, M.; López-Periago, E.; Martínez-Carballo, E.; Simal-Gándara, J.; Mejuto, J.-C.; García-Río, L. The mobility and degradation of pesticides in soils and the pollution of groundwater resources. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 4, 247–260.
- Bilal, M.; Igbal, H.M.N.; Barceló, D. Persistence of pesticides-based contaminants in the environment and their effective degradation using laccase-assisted biocatalytic systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133896.
- Riahi, B.; Rafatpanah, H.; Mahmoudi, M.; Memar, B.; Brook, A.; Tabasi, N.; Karimia, G. Immunotoxicity of paraquat after subacute exposure to mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1627–1631.
- Fenner, K.; Canonica, S.; Wackett, L.P.; Elsner, M. Evaluating Pesticide Degradation in the Environment: Blind Spots and Emerging Opportunities. Science 2013, 341, 752–758.
- U.S. EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Preliminary Ecological Risk Assessment in Support of the Registration Review of Glyphosate and Its Salts; U.S. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; p. 318.
- Zhan, H.; Feng, Y.; Fan, X.; Chen, S. Recent advances in glyphosate biodegradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 5033–5043.
- Sun, M.; Li, H.; Jaisi, D.P. Degradation of glyphosate and bioavailability of phosphorus derived from glyphosate in a soil-water system. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114840.
- Wang, S.; Seiwert, B.; Kästner, M.; Miltner, A.; Schäffer, A.; Reemtsma, T.; Yang, Q.; Nowak, K.M. (Bio)degradation of glyphosate in water-sediment microcosms–A stable isotope co-labeling approach. Water Res. 2016, 99, 91–100.
- Battaglin, W.A.; Myer, M.T.; Kuivila, K.M.; Dietze, J.E. Glyphosate and its gedradation product AMPA occur frequently and widely in U.S. soils, surface water, groundwater, and precipitation. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 275–290.
- Myers, J.P.; Antoniou, M.N.; Blumberg, B.; Carroll, L.; Colborn, T.; Everett, L.G.; Hansen, M.; Landrigan, P.J.; Lanphear, B.P.; Mesnage, R.; et al. Concerns over use of glyphosate-based herbicides and risks associated with exposures: A consensus statement. Environ. Health 2016, 15, 19.
- WHO (World Health Organization). Glyphosate/Published under the Joint Sponsorship of the United Nations Environment Programme, the International Labour Organisation, and the World Health Organization. World Health Organization & International Programme on Chemical Safety. 1994. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/40044 (accessed on 3 December 2020).
- Franz, J.E.; Mao, M.K.; Sikorski, J.A. Glyphosate: A Unique Global Herbicide; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; p. 615.
- Tsui, M.T.K.; Chu, L.M. Aquatic toxicity of glyphosate-based formulations: Comparison between different organisms and the effects of environmental factors. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 1189–1197.
- Modesto, K.A.; Martinez, C.B.R. Roundup causes oxidative stress in liver and inhibits acetylcholinesterase in muscle and brain of the fish Prochilodus lineatus. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 294–299.
- Roundup.cz. RoundupBioaktiv: Okolo Vodních Toků a Nádrží, Fakta. Monsanto ČR s.r.o. Available online: https://www.roundup.cz/roundup-biaktiv/fakta (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Blake, R.J.; Pallet, K. The environmental fate and ecotoxicity of glyphosate. Outlooks Pest. Manag. 2018, 29, 266–269.
- Folmar, L.C.; Sanders, H.O.; Julin, A.M. Toxicity of the herbicide glyphosate and several of its formulations to fish and aquatic invertebrates. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1979, 8, 269–278.
- Coupe, R.H.; Kalkhoff, S.J.; Capel, P.D.; Gregoire, C. Fate and transport of glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonic acid in surface waters of agricultural basins. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 16–30.
- Guilherme, S.; Gaivao, I.; Santos, M.A.; Pacheco, M. European eel (Anguilla Anguilla genotoxic and prooxidant responses following short-term exposure to Roundup®—A glyphosate-based herbicide. Mutagenesis 2010, 25, 523–530.
- Wagner, N.; Reichenbecher, W.; Teichmann, H.; Tappeser, B.; Lotters, S. Questions concerning the potential impact of glyphosate-base herbicides on amphibians. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 1688–1700.
- Rodrigues, N.R.; de Souza, A.P.F. Occurrence of glyphosate and AMPA residue in soy-based infant formula sold in Brazil. Food Addit. Contam. A 2018, 35, 724–731.
- Hildebrand, L.D.; Sullivan, D.S.; Sullivan, T.P. Experimental studies of rainbow trout populations exposed to field applications of Roundup® herbicide. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1982, 11, 93–98.
- Neskovic, N.K.; Poleksic, V.; Elezovic, I.; Karan, V.; Budimir, M. Biochemical and histopathological effects of glyphosate on carp, Cyprinus carpio L. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1996, 56, 295–302.
- Gholami-Seyedkolaei, S.; Mirvaghefi, A.; Farahmand, H.; Kosari, A.A. Effect of a glyphosate-based herbicide in Cyprinus carpio: Assessment of acetylcholinesterase activity, hematologigal responses and serum biochemical parameters. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 98, 135–141.
- Ma, J.; Bu, Y.; Li, X. Immunological and histopathological responses of the kidney of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) sublethally exposed to glyphosate. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 39, 1–8.
- Antunes, A.M.; Rocha, T.L.; Pires, F.S.; de Freitas, M.A.; Leite, V.R.M.C.; Arana, S.; Moreira, P.C.; Sabóia-Morais, S.M.T. Gender-specific histopathological response in guppies Poecilia reticulata exposed to glyphosate or its metabolite Aminomethylphosphonic acid. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 1098–1107.
- Kreutz, L.C.; Barcellos, L.J.G.; Silva, T.O.; Anziliero, D.; Martins, D.; Lorenson, M.; Martheninghe, A.; da Silva, L.B. Acute toxicity test of agricultural pesticides on silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen). Cienc. Rural 2008, 38, 1050–1055.
- Ayoola, S.O. Histopathological effects of glyphosate on juvenile African catfish (Clarius gariepinus). Am-Euras. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2008, 4, 362–367.
- de Brito Rodrigues, L.; Costa, G.G.; Thá, E.L.; da Silva, L.R.; de Oliveira, R.; Leme, D.M.; Cestari, M.M.; Grisolia, C.K.; Valadares, M.C.; de Oliveira, G.A.R. Impact of the glyphosate-based commercial herbicide, its components and its metabolite AMPA on non-target aquatic organisms. Mut. Res.-Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mut. 2019, 842, 94–101.
- Brodeur, J.C.; Malpel, S.; Anglesio, A.B.; Cristos, D.; D’Andrea, M.F.; Poliserpi, M.B. Toxicities of glyphosate- and cypermethrin-based pesticides are antagonic in the tenspotted livebearer fish (Cnesterodon decemmaculatus). Chemosphere 2016, 155, 429–435.
- Daam, M.A.; Moutinho, M.F.; Espíndola, E.L.G.; Schiesari, L. Lethal toxicity of the herbicides acetochlor, ametryn, glyphosate and metribuzin to tropical frog larvae. Ecology 2019, 28, 707–712.
- Howe, C.M.; Berrill, M.; Pauli, B.D.; Helbing, C.C.; Werry, K.; Veldhoen, N. Toxicity of Glyphosate-based pesticides to four north American frog species. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2004, 23, 1928–1938.
- Lajmanovich, R.C.; Attademo, A.M.; Peltzer, P.M.; Junges, C.M.; Cabagna, M.C. Toxicity of four herbicide formulations with glyphosate on Rhinella arenarum (Anura: Bufonidae) tadpoles: B-esterases and gluthation S-transferase inhibitors. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 60, 681–689.
- Hong, Y.; Yang, X.; Yan, G.; Huang, Y.; Zuo, F.; Shen, Y.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, Y. Effects of glyphosate on immune responses and haemocyte DNA damage of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 71, 19–27.
- Guilherme, S.; Santos, M.; Barroso, C.; Gaivão, I.; Mário, P. Differential genotoxicity of Roundup® formulation and its constituents in blood cells of fish (Anguilla anguilla): Considerations on chemical interactions and DNA damaging mechanisms. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 1381–1390.
- Ma, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, W.; Ruan, P.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Li, X. Biochemical and molecular impacts of glyphosate-based herbicide on the gills of common carp. Environm. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1288–1300.
- Gaur, H.; Bhargava, A. Glyphosate induces toxicity and modulates calcium and NO signaling in zebrafish embryos. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Comm. 2019, 513, 1070–1075.
- Nwani, C.D.; Nagpure, N.S.; Kumar, R.; Kushwaha, B.; Lakra, W.S. DNA damage and oxidative stress modulatory effects of glyphosate-based herbicide in freshwater fish, Channa punctatus. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 36, 539–547.
- Menéndez-Helman, R.; Ferreyroa, G.V.; dos Santos Afonso, M.; Salibán, A. Glyphosate as an Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor in Cnesterodon decemmaculatus. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 88, 6–9.
- Glusczak, L.; dos Santos Miron, D.; Crestani, M.; da Fonseca, M.B.; de Araújo Pedron, F.; Duarte, M.F.; Pimentel Vieira, V.L. Effect of glyphosate herbicide on acetylcholinesterase activity and metabolic and hematological parameters in piava (Leporinus obtusidens). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2006, 65, 237–241.
- Salbego, J.; Pretto, A.; Gioda, C.R.; de Menezes, C.C.; Lazzari, R.; Neto, J.R.; Baldisserotto, B.; Loro, V.L. Herbicide formulation with glyphosate affects growth, acetylcholinesterase activity, and metabolic and hematological parameters in Piava (Leporinus obtusidens). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 58, 740–745.
- Glusczak, L.; dos Santos Miron, D.; Moares, B.S.; Simoes, R.R.; Chitolina Schetinger, M.R.; Morsch, V.M.; Loro, V.L. Acute effects of glyphosate herbicide on metabolic and enzymatic parameters of silver catfish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2007, 146, 519–524.
- Kreutz, L.C.; Barcellos, L.J.G.; de Faria Valle, S.; de Oliveira Silva, T.; Anziliero, D.; dos Santos, E.D.; Pivato, M.; Zanatta, R. Altered hematological and immunological parameters in silver catfish fish (Rhamdia quelen) following short term exposure to sublethal concentration of glyphosate. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 51–57.
- Persch, T.S.P.; Weimer, R.N.; Freitas, B.S.; Oliveira, G.T. Metabolic parameters and oxidative balance in juvenile (Rhamdia quelen) exposed to rice paddy herbicides: Roundup®, Primoleo®, and Facet®. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 98–109.
- Lushchak, O.V.; Kubrak, O.I.; Storey, J.M.; Storey, K.B.; Lushchak, V.I. Low toxic herbicide Roundup induces mild oxidative stress in goldfish tissues. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 932–937.
- Li, M.H.; Xu, L.D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; Jiang, L.; Fu, Y.H.; Wang, J.S. Multi-tissue metabolic responses of goldfish (Carassius auratus) exposed to glyphosate-based herbicide. Toxicol. Res. 2016, 5, 1039–1052.
- Li, M.H.; Ruan, L.Y.; Zhou, J.W.; Fu, Y.H.; Jinag, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.S. Metabolic profiling of goldfish (Carassius auratis) after long-term glyphosate-base herbicide exposure. Aquatic. Toxicol. 2017, 188, 159–169.
- De Moura, F.R.; da Silva Lima, R.R.; da Cunha, A.P.S.; da Costa Marisco, P.; Aguiar, D.H.; Sugui, M.M.; Sinhorin, A.P.; Sinhorin, V.D.G. Effects of glyphosate-based herbicide on pintado da Amazônia: Hematology, histological aspects, metabolic parameters and genotoxic potential. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 56, 241–248.
- Roy, N.M.; Carneiro, B.; Ochs, J. Glyphosate induces neurotoxicity in zebrafish. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 42, 45–54.
- Goulart, T.L.S.; Boyle, R.T.; Souza, M.M. Cytotoxicity of the association of pesticides Roundup Transorb® and Furadan 350 SC® on the zebrafish cell line, ZF-L. Toxicol. Vitro. 2015, 29, 1377–1384.
- Samanta, P.; Pal, S.; Mukherjee, A.K.; Glosh, A.R. Biochemical effects of glyphosate based herbicide, Excel Mera 71 on enzyme activities of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), lipid peroxidation (LPO), catalase (CAT), gluthation-S-transferase (GST) and protein content on teleostean fishes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 107, 120–125.
- Matozzo, V.; Munari, M.; Maseiro, L.; Finos, L.; Marin, M.G. Ecotoxicological hazard of a mixture of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid to the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck 1819). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14302.
- Sandrini, J.Z.; Rola, R.C.; Lopes, F.M.; Buffon, H.F.; Freitas, M.M.; Martins, C.M.; da Rosa, C.E. Effects of glyphosate on cholinesterase activity of the mussel Perna perna and the fish Danio rerio and Jenynsia multidentata: In vitro studies. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 130–131, 171–173.
- Matozzo, V.; Fabrello, J.; Masiero, L.; Ferraccioli, F.; Finos, L.; Pastore, P.; Di Gangi, I.M.; Bogialli, S. Ecotoxicological risk assessment for the herbicide glyphosate to non-target aquatic species: A case study with the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 623–632.
- Iummato, M.M.; Di Fiori, E.; Sabatini, S.E.; Cacciatore, L.C.; Cochón, A.C.; del Carmen Ríos de Molina, M.; Juárez, Á.B. Evaluation of biochemical markers in the golden mussel Limnoperna fortune exposed to glyphosate acid in outdoor microcosms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 95, 123–129.
- Di Fiori, E.; Pizarro, H.; dos Santos Afonso, M.; Cataldo, D. Impact of the invasive mussels Limnoperna fortunei on glyphosate concentration in water. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 81, 106–113.
- Séguin, A.; Mottier, A.; Perron, C.; Lebel, J.M.; Serpentini, A.; Costil, K. Sub-lethal effects of glyphosate-based commercial formulation and adjuvants on juvenile oysters (Crassostrea gigas) exposed for 35 days. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 348–358.
- Contardo-Jara, V.; Klingelmann, E.; Wiegand, C. Bioaccumulation of glyphosate and its formulations Roundup Ultra in Lumbriculus variegatus and its effects on biotransformation and antioxidant enzymes. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 57–63.
- Costa, M.J.; Monteiro, D.A.; Oliveira-Neto, A.L.; Rantin, T.F.; Kalinin, A.L. Oxidative stress biomarkers and heart function in bullfrog tadpoles exposed to Roundup Original. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 153–163.
- Barky, F.A.; Abdelsam, H.A.; Mahmoud, M.B.; Hamdi, S.A.H. Influence of Atrazine and Roundup pesticides on biochemical and molecular aspects of Biomphalaria alexandrina snails. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 104, 9–18.
- Mohamed, A.H. Sublethal toxicity of Roundup to immunological and molecular aspects of Biomphalaria alexandrina to Schistosoma mansoni infection. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 754–760.





