
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jerome Moreaux | + 6159 word(s) | 6159 | 2021-08-16 04:51:11 | | | |
| 2 | Vivi Li | Meta information modification | 6159 | 2021-09-26 03:23:01 | | |
Video Upload Options
Multiple myeloma is a hematologic cancer characterized by the accumulation of malignant plasma cells in the bone marrow. It remains a mostly incurable disease due to the inability to overcome refractory disease and drug-resistant relapse. Oncogenic transformation of PC in multiple myeloma is thought to occur within the secondary lymphoid organs. However, the precise molecular events leading to myelomagenesis remain obscure. Here, we identified genes involved in the prevention and the resolution of conflicts between the replication and transcription significantly overexpressed during the plasma cell differentiation process and in multiple myeloma cells. We discussed the potential role of these factors in myelomagenesis.
1. Introduction
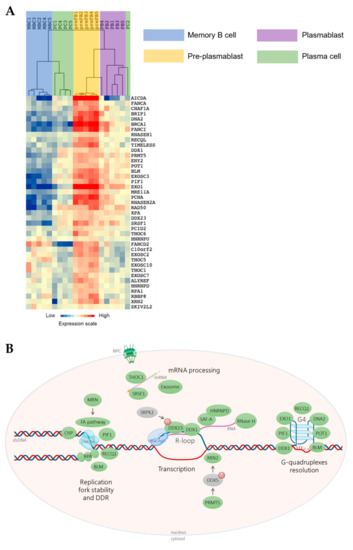
2. Management of Transcription/Replication Conflicts (TRCs) in Normal Cells Is Critical to Prevent Genomic Instability
2.1. R-Loop Resolution Genes
2.1.1. RNase H1/2, Replication Protein A (RPA)
2.1.2. The DEAD-Box Protein Family of Helicases
2.2. mRNA Maturation
2.2.1. Serine/Arginine Splicing Factor 1 (SRSF1)
2.2.2. Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein U (HNRNPU) and D0 (HNRNPD)
2.2.3. The THO/TREX Complex and TREX2
2.3. RNA Processing and Degradation
2.3.1. The RNA Exosome
2.3.2. 5′-3′ Exoribonuclease 2 (XRN2)
2.4. Fork Protection and Stability
2.4.1. The Fanconi Anemia Pathway and the MRN Complex
2.4.2. Breast Cancer Susceptibility Gene 1 and 2 (BRCA1 and BRCA2)
2.4.3. Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (PCNA) SUMOylation
2.4.4. CtBP-Interacting Protein (CtIP)
2.4.5. Exonuclease 1 (EXO1)
2.4.6. Transcription Coupled Nucleotide Excision Repair (TC-NER) Exonucleases
2.5. G-Quadruplexes Resolution
2.5.1. The RecQ family of Helicases
2.5.2. PIF1
2.5.3. DNA2 and POT1 Roles at Telomeres
References
- Klein, B.; Tarte, K.; Jourdan, M.; Mathouk, K.; Moreaux, J.; Jourdan, E.; Legouffe, E.; De Vos, J.; Rossi, J.F. Survival and Proliferation Factors of Normal and Malignant Plasma Cells. Int. J. Hematol. 2003, 78, 106–113.
- Nutt, S.L.; Hodgkin, P.D.; Tarlinton, D.M.; Corcoran, L.M. The Generation of Antibody-Secreting Plasma Cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 160–171.
- Cyster, J.G. Homing of Antibody Secreting Cells. Immunol. Rev. 2003, 194, 48–60.
- Hamperl, S.; Cimprich, K.A. The Contribution of Co-Transcriptional RNA:DNA Hybrid Structures to DNA Damage and Genome Instability. DNA Repair 2014, 19, 84–94.
- Sollier, J.; Cimprich, K.A. R-Loops Breaking Bad. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 514–522.
- Gan, W.; Guan, Z.; Liu, J.; Gui, T.; Shen, K.; Manley, J.L.; Li, X. R-Loop-Mediated Genomic Instability Is Caused by Impairment of Replication Fork Progression. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 2041–2056.
- Hamperl, S.; Cimprich, K.A. Conflict Resolution in the Genome: How Transcription and Replication Make It Work. Cell 2016, 167, 1455–1467.
- Niehrs, C.; Luke, B. Regulatory R-Loops as Facilitators of Gene Expression and Genome Stability. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 167–178.
- Alagpulinsa, D.A.; Szalat, R.E.; Poznansky, M.C.; Reis, R.J.S. Genomic Instability in Multiple Myeloma. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 858–873.
- Hoang, P.H.; Cornish, A.J.; Chubb, D.; Jackson, G.; Kaiser, M.; Houlston, R.S. Impact of Mitochondrial DNA Mutations in Multiple Myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10.
- Jourdan, M.; Caraux, A.; De Vos, J.; Fiol, G.; Larroque, M.; Cognot, C.; Bret, C.; Duperray, C.; Hose, D.; Klein, B. An in vitro Model of Differentiation of Memory B Cells into Plasmablasts and Plasma Cells Including Detailed Phenotypic and Molecular Characterization. Blood 2009, 114, 5173–5181.
- Jourdan, M.; Caraux, A.; Caron, G.; Robert, N.; Fiol, G.; Rème, T.; Bolloré, K.; Vendrell, J.-P.; Gallou, S.L.; Mourcin, F.; et al. Characterization of a Transitional Preplasmablast Population in the Process of Human B Cell to Plasma Cell Differentiation. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 3931–3941.
- Jourdan, M.; Cren, M.; Robert, N.; Bolloré, K.; Fest, T.; Duperray, C.; Guilloton, F.; Hose, D.; Tarte, K.; Klein, B. IL-6 Supports the Generation of Human Long-Lived Plasma Cells in Combination with Either APRIL or Stromal Cell-Soluble Factors. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1647–1656.
- Leung-Hagesteijn, C.; Erdmann, N.; Cheung, G.; Keats, J.J.; Stewart, A.K.; Reece, D.E.; Chung, K.C.; Tiedemann, R.E. Xbp1s-Negative Tumor B Cells and Pre-Plasmablasts Mediate Therapeutic Proteasome Inhibitor Resistance in Multiple Myeloma. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 289–304.
- Herviou, L.; Jourdan, M.; Martinez, A.-M.; Cavalli, G.; Moreaux, J. EZH2 Is Overexpressed in Transitional Preplasmablasts and Is Involved in Human Plasma Cell Differentiation. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2047–2060.
- Cristini, A.; Groh, M.; Kristiansen, M.S.; Gromak, N. RNA/DNA Hybrid Interactome Identifies DXH9 as a Molecular Player in Transcriptional Termination and R-Loop-Associated DNA Damage. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 1891–1905.
- Bergsagel, P.L.; Kuehl, W.M.; Zhan, F.; Sawyer, J.; Barlogie, B.; Shaughnessy, J. Cyclin D Dysregulation: An Early and Unifying Pathogenic Event in Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2005, 106, 296–303.
- Manier, S.; Salem, K.Z.; Park, J.; Landau, D.A.; Getz, G.; Ghobrial, I.M. Genomic Complexity of Multiple Myeloma and Its Clinical Implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 100–113.
- García-Muse, T.; Aguilera, A. Transcription–Replication Conflicts: How They Occur and How They Are Resolved. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 553–563.
- Gómez-González, B.; Aguilera, A. Transcription-Mediated Replication Hindrance: A Major Driver of Genome Instability. Genes Dev. 2019, 33, 1008–1026.
- Kassambara, A.; Rème, T.; Jourdan, M.; Fest, T.; Hose, D.; Tarte, K.; Klein, B. GenomicScape: An Easy-to-Use Web Tool for Gene Expression Data Analysis. Application to Investigate the Molecular Events in the Differentiation of B Cells into Plasma Cells. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11.
- Cerritelli, S.M.; Crouch, R.J. Ribonuclease H: The Enzymes in Eukaryotes. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 1494–1505.
- Hyjek, M.; Figiel, M.; Nowotny, M. RNases H: Structure and Mechanism. DNA Repair 2019, 84, 102672.
- Ruhanen, H.; Ushakov, K.; Yasukawa, T. Involvement of DNA Ligase III and Ribonuclease H1 in Mitochondrial DNA Replication in Cultured Human Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2011, 1813, 2000.
- Lima, W.F.; Murray, H.M.; Damle, S.S.; Hart, C.E.; Hung, G.; De Hoyos, C.L.; Liang, X.-H.; Crooke, S.T. Viable RNaseH1 Knockout Mice Show RNaseH1 Is Essential for R Loop Processing, Mitochondrial and Liver Function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 5299–5312.
- Cerritelli, S.M.; Frolova, E.G.; Feng, C.; Grinberg, A.; Love, P.E.; Crouch, R.J. Failure to Produce Mitochondrial DNA Results in Embryonic Lethality in Rnaseh1 Null Mice. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 807–815.
- Parajuli, S.; Teasley, D.C.; Murali, B.; Jackson, J.; Vindigni, A.; Stewart, S.A. Human Ribonuclease H1 Resolves R-Loops and Thereby Enables Progression of the DNA Replication Fork. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 15216–15224.
- Rydberg, B.; Game, J. Excision of Misincorporated Ribonucleotides in DNA by RNase H (Type 2) and FEN-1 in Cell-Free Extracts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16654–16659.
- Nick McElhinny, S.A.; Watts, B.E.; Kumar, D.; Watt, D.L.; Lundström, E.-B.; Burgers, P.M.J.; Johansson, E.; Chabes, A.; Kunkel, T.A. Abundant Ribonucleotide Incorporation into DNA by Yeast Replicative Polymerases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4949–4954.
- Zhou, Z.-X.; Williams, J.S.; Lujan, S.A.; Kunkel, T.A. Ribonucleotide Incorporation into DNA during DNA Replication and Its Consequences. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 56, 109–124.
- Crow, Y.J.; Leitch, A.; Hayward, B.E.; Garner, A.; Parmar, R.; Griffith, E.; Ali, M.; Semple, C.; Aicardi, J.; Babul-Hirji, R.; et al. Mutations in Genes Encoding Ribonuclease H2 Subunits Cause Aicardi-Goutières Syndrome and Mimic Congenital Viral Brain Infection. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 910–916.
- Mackenzie, K.J.; Carroll, P.; Martin, C.-A.; Murina, O.; Fluteau, A.; Simpson, D.J.; Olova, N.; Sutcliffe, H.; Rainger, J.K.; Leitch, A.; et al. CGAS Surveillance of Micronuclei Links Genome Instability to Innate Immunity. Nature 2017, 548, 461–465.
- Wold, M.S. Replication Protein A: A Heterotrimeric, Single-Stranded DNA-Binding Protein Required for Eukaryotic DNA Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997, 66, 61–92.
- Iftode, C.; Daniely, Y.; Borowiec, J.A. Replication Protein A (RPA): The Eukaryotic SSB. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 34, 141–180.
- Nguyen, H.D.; Yadav, T.; Giri, S.; Saez, B.; Graubert, T.A.; Zou, L. Functions of Replication Protein A as a Sensor of R Loops and a Regulator of RNaseH1. Mol. Cell 2017, 65, 832–847.e4.
- Mazina, O.M.; Somarowthu, S.; Kadyrova, L.Y.; Baranovskiy, A.G.; Tahirov, T.H.; Kadyrov, F.A.; Mazin, A.V. Replication Protein A Binds RNA and Promotes R-Loop Formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 14203–14213.
- Murakawa, Y.; Sonoda, E.; Barber, L.J.; Zeng, W.; Yokomori, K.; Kimura, H.; Niimi, A.; Lehmann, A.; Zhao, G.Y.; Hochegger, H.; et al. Inhibitors of the Proteasome Suppress Homologous DNA Recombination in Mammalian Cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8536–8543.
- Jacquemont, C.; Taniguchi, T. Proteasome Function Is Required for DNA Damage Response and Fanconi Anemia Pathway Activation. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7395–7405.
- Panero, J.; Stella, F.; Schutz, N.; Fantl, D.B.; Slavutsky, I. Differential Expression of Non-Shelterin Genes Associated with High Telomerase Levels and Telomere Shortening in Plasma Cell Disorders. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137972.
- Godbout, R.; Li, L.; Liu, R.-Z.; Roy, K. Role of DEAD Box 1 in Retinoblastoma and Neuroblastoma. Future Oncol. 2007, 3, 575–587.
- Germain, D.R.; Graham, K.; Glubrecht, D.D.; Hugh, J.C.; Mackey, J.R.; Godbout, R. DEAD Box 1: A Novel and Independent Prognostic Marker for Early Recurrence in Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 127, 53–63.
- Li, L.; Monckton, E.A.; Godbout, R. A Role for DEAD Box 1 at DNA Double-Strand Breaks. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 6413–6425.
- Li, L.; Germain, D.R.; Poon, H.-Y.; Hildebrandt, M.R.; Monckton, E.A.; McDonald, D.; Hendzel, M.J.; Godbout, R. DEAD Box 1 Facilitates Removal of RNA and Homologous Recombination at DNA Double-Strand Breaks. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 36, 2794–2810.
- Ribeiro de Almeida, C.; Dhir, S.; Dhir, A.; Moghaddam, A.E.; Sattentau, Q.; Meinhart, A.; Proudfoot, N.J. RNA Helicase DDX1 Converts RNA G-Quadruplex Structures into R-Loops to Promote IgH Class Switch Recombination. Mol. Cell 2018, 70, 650–662.e8.
- Hänsel-Hertsch, R.; Di Antonio, M.; Balasubramanian, S. DNA G-Quadruplexes in the Human Genome: Detection, Functions and Therapeutic Potential. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 279–284.
- Rhodes, D.; Lipps, H.J. G-Quadruplexes and Their Regulatory Roles in Biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 8627–8637.
- Prioleau, M.-N. G-Quadruplexes and DNA Replication Origins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1042, 273–286.
- Prorok, P.; Artufel, M.; Aze, A.; Coulombe, P.; Peiffer, I.; Lacroix, L.; Guédin, A.; Mergny, J.-L.; Damaschke, J.; Schepers, A.; et al. Involvement of G-Quadruplex Regions in Mammalian Replication Origin Activity. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3274.
- Kuznetsov, V.A.; Bondarenko, V.; Wongsurawat, T.; Yenamandra, S.P.; Jenjaroenpun, P. Toward Predictive R-Loop Computational Biology: Genome-Scale Prediction of R-Loops Reveals Their Association with Complex Promoter Structures, G-Quadruplexes and Transcriptionally Active Enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 7566–7585.
- Duquette, M.L. Intracellular Transcription of G-Rich DNAs Induces Formation of G-Loops, Novel Structures Containing G4 DNA. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 1618–1629.
- De Magis, A.; Manzo, S.G.; Russo, M.; Marinello, J.; Morigi, R.; Sordet, O.; Capranico, G. DNA Damage and Genome Instability by G-Quadruplex Ligands Are Mediated by R Loops in Human Cancer Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 816–825.
- Yu, K.; Lieber, M.R. Current Insights into the Mechanism of Mammalian Immunoglobulin Class Switch Recombination. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 54, 333–351.
- Stavnezer, J.; Schrader, C.E. Ig Heavy Chain Class Switch Recombination: Mechanism and Regulation. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 5370–5378.
- Mathew, R.; Hartmuth, K.; Möhlmann, S.; Urlaub, H.; Ficner, R.; Lührmann, R. Phosphorylation of Human PRP28 by SRPK2 Is Required for Integration of the U4/U6-U5 Tri-SnRNP into the Spliceosome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 435–443.
- Sridhara, S.C.; Carvalho, S.; Grosso, A.R.; Gallego-Paez, L.M.; Carmo-Fonseca, M.; de Almeida, S.F. Transcription Dynamics Prevent RNA-Mediated Genomic Instability through SRPK2-Dependent DDX23 Phosphorylation. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 334–343.
- Fu, X.D. The Superfamily of Arginine/Serine-Rich Splicing Factors. RNA 1995, 1, 663–680.
- Mayeda, A.; Krainer, A.R. Regulation of Alternative Pre-MRNA Splicing by HnRNP A1 and Splicing Factor SF2. Cell 1992, 68, 365–375.
- Cáceres, J.F.; Kornblihtt, A.R. Alternative Splicing: Multiple Control Mechanisms and Involvement in Human Disease. Trends Genet. 2002, 18, 186–193.
- Li, X.; Manley, J.L. Inactivation of the SR Protein Splicing Factor ASF/SF2 Results in Genomic Instability. Cell 2005, 122, 365–378.
- Promonet, A.; Padioleau, I.; Liu, Y.; Sanz, L.; Biernacka, A.; Schmitz, A.-L.; Skrzypczak, M.; Sarrazin, A.; Mettling, C.; Rowicka, M.; et al. Topoisomerase 1 Prevents Replication Stress at R-Loop-Enriched Transcription Termination Sites. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3940.
- Li, M.; Pokharel, S.; Wang, J.-T.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y. RECQ5-Dependent SUMOylation of DNA Topoisomerase I Prevents Transcription-Associated Genome Instability. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6720.
- Wang, J.C. Cellular Roles of DNA Topoisomerases: A Molecular Perspective. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 430–440.
- Wu, H.Y.; Shyy, S.H.; Wang, J.C.; Liu, L.F. Transcription Generates Positively and Negatively Supercoiled Domains in the Template. Cell 1988, 53, 433–440.
- Marinello, J.; Bertoncini, S.; Aloisi, I.; Cristini, A.; Malagoli Tagliazucchi, G.; Forcato, M.; Sordet, O.; Capranico, G. Dynamic Effects of Topoisomerase I Inhibition on R-Loops and Short Transcripts at Active Promoters. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147053.
- Obrdlik, A.; Kukalev, A.; Louvet, E.; Farrants, A.-K.O.; Caputo, L.; Percipalle, P. The Histone Acetyltransferase PCAF Associates with Actin and HnRNP U for RNA Polymerase II Transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 6342–6357.
- Yugami, M.; Kabe, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Wada, T.; Handa, H. HnRNP-U Enhances the Expression of Specific Genes by Stabilizing MRNA. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 1–7.
- Xiao, R.; Tang, P.; Yang, B.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Shao, C.; Li, H.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, X.-D. Nuclear Matrix Factor HnRNP U/SAF-A Exerts a Global Control of Alternative Splicing by Regulating U2 SnRNP Maturation. Mol. Cell 2012, 45, 656–668.
- Britton, S.; Dernoncourt, E.; Delteil, C.; Froment, C.; Schiltz, O.; Salles, B.; Frit, P.; Calsou, P. DNA Damage Triggers SAF-A and RNA Biogenesis Factors Exclusion from Chromatin Coupled to R-Loops Removal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 9047–9062.
- Blackford, A.N.; Jackson, S.P. ATM, ATR, and DNA-PK: The Trinity at the Heart of the DNA Damage Response. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 801–817.
- Alfano, L.; Caporaso, A.; Altieri, A.; Dell’Aquila, M.; Landi, C.; Bini, L.; Pentimalli, F.; Giordano, A. Depletion of the RNA Binding Protein HNRNPD Impairs Homologous Recombination by Inhibiting DNA-End Resection and Inducing R-Loop Accumulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 4068–4085.
- Yoon, J.-H.; De, S.; Srikantan, S.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Grammatikakis, I.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.M.; Noh, J.H.; White, E.J.F.; Martindale, J.L.; et al. PAR-CLIP Analysis Uncovers AUF1 Impact on Target RNA Fate and Genome Integrity. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5248.
- Marchesini, M.; Ogoti, Y.; Fiorini, E.; Aktas Samur, A.; Nezi, L.; D’Anca, M.; Storti, P.; Samur, M.K.; Ganan-Gomez, I.; Fulciniti, M.T.; et al. ILF2 Is a Regulator of RNA Splicing and DNA Damage Response in 1q21-Amplified Multiple Myeloma. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 88–100.e6.
- Okamoto, Y.; Abe, M.; Itaya, A.; Tomida, J.; Ishiai, M.; Takaori-Kondo, A.; Taoka, M.; Isobe, T.; Takata, M. FANCD2 Protects Genome Stability by Recruiting RNA Processing Enzymes to Resolve R-Loops during Mild Replication Stress. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 139–150.
- Jimeno, S.; Rondón, A.G.; Luna, R.; Aguilera, A. The Yeast THO Complex and MRNA Export Factors Link RNA Metabolism with Transcription and Genome Instability. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 3526–3535.
- Strässer, K.; Masuda, S.; Mason, P.; Pfannstiel, J.; Oppizzi, M.; Rodriguez-Navarro, S.; Rondón, A.G.; Aguilera, A.; Struhl, K.; Reed, R.; et al. TREX Is a Conserved Complex Coupling Transcription with Messenger RNA Export. Nature 2002, 417, 304–308.
- Luna, R.; Rondón, A.G.; Pérez-Calero, C.; Salas-Armenteros, I.; Aguilera, A. The THO Complex as a Paradigm for the Prevention of Cotranscriptional R-Loops. In Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 84, pp. 105–114.
- Gómez-González, B.; Felipe-Abrio, I.; Aguilera, A. The S-Phase Checkpoint Is Required To Respond to R-Loops Accumulated in THO Mutants. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 5203–5213.
- Gómez-González, B.; García-Rubio, M.; Bermejo, R.; Gaillard, H.; Shirahige, K.; Marín, A.; Foiani, M.; Aguilera, A. Genome-Wide Function of THO/TREX in Active Genes Prevents R-Loop-Dependent Replication Obstacles. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3106–3119.
- Domínguez-Sánchez, M.S.; Barroso, S.; Gómez-González, B.; Luna, R.; Aguilera, A. Genome Instability and Transcription Elongation Impairment in Human Cells Depleted of THO/TREX. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7.
- Pérez-Calero, C.; Bayona-Feliu, A.; Xue, X.; Barroso, S.I.; Muñoz, S.; González-Basallote, V.M.; Sung, P.; Aguilera, A. UAP56/DDX39B Is a Major Cotranscriptional RNA–DNA Helicase That Unwinds Harmful R Loops Genome-Wide. Genes Dev. 2020.
- Salas-Armenteros, I.; Pérez-Calero, C.; Bayona-Feliu, A.; Tumini, E.; Luna, R.; Aguilera, A. Human THO–Sin3A Interaction Reveals New Mechanisms to Prevent R-loops That Cause Genome Instability. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 3532–3547.
- Cai, S.; Bai, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Ding, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Knockdown of THOC1 Reduces the Proliferation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Increases the Sensitivity to Cisplatin. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 135.
- Faza, M.B.; Kemmler, S.; Jimeno, S.; González-Aguilera, C.; Aguilera, A.; Hurt, E.; Panse, V.G. Sem1 Is a Functional Component of the Nuclear Pore Complex-Associated Messenger RNA Export Machinery. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 184, 833–846.
- Wilmes, G.M.; Bergkessel, M.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Shales, M.; Braberg, H.; Cagney, G.; Collins, S.R.; Whitworth, G.B.; Kress, T.L.; Weissman, J.S.; et al. A Genetic Interaction Map of RNA-Processing Factors Reveals Links between Sem1/Dss1-Containing Complexes and MRNA Export and Splicing. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 735–746.
- Gallardo, M.; Luna, R.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Aguilera, A. Nab2p and the Thp1p-Sac3p Complex Functionally Interact at the Interface between Transcription and MRNA Metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 24225–24232.
- Santos-Pereira, J.M.; García-Rubio, M.L.; González-Aguilera, C.; Luna, R.; Aguilera, A. A Genome-Wide Function of THSC/TREX-2 at Active Genes Prevents Transcription–Replication Collisions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 12000–12014.
- Bhatia, V.; Barroso, S.I.; García-Rubio, M.L.; Tumini, E.; Herrera-Moyano, E.; Aguilera, A. BRCA2 Prevents R-Loop Accumulation and Associates with TREX-2 MRNA Export Factor PCID2. Nature 2014, 511, 362–365.
- Eberle, A.B.; Visa, N. Quality Control of MRNP Biogenesis: Networking at the Transcription Site. In Seminars in Cell and Developmental Biology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 32, pp. 37–46.
- Schmid, M.; Jensen, T.H. The Exosome: A Multipurpose RNA-Decay Machine. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 501–510.
- Chapman, M.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Keats, J.J.; Cibulskis, K.; Sougnez, C.; Schinzel, A.C.; Harview, C.L.; Brunet, J.-P.; Ahmann, G.J.; Adli, M.; et al. Initial Genome Sequencing and Analysis of Multiple Myeloma. Nature 2011, 471, 467–472.
- Boyle, E.M.; Ashby, C.; Tytarenko, R.G.; Deshpande, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Rosenthal, A.; Sawyer, J.; Tian, E.; Flynt, E.; et al. BRAF and DIS3 Mutations Associate with Adverse Outcome in a Long-Term Follow-up of Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2422–2432.
- Todoerti, K.; Ronchetti, D.; Favasuli, V.; Maura, F.; Morabito, F.; Bolli, N.; Taiana, E.; Neri, A. DIS3 Mutations in Multiple Myeloma Impact the Transcriptional Signature and Clinical Outcome. Arch. Ist. Ric. 2021.
- Pertesi, M.; Vallée, M.; Wei, X.; Revuelta, M.V.; Galia, P.; Demangel, D.; Oliver, J.; Foll, M.; Chen, S.; Perrial, E.; et al. Exome Sequencing Identifies Germline Variants in DIS3 in Familial Multiple Myeloma. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2324–2330.
- Domingo-Prim, J.; Endara-Coll, M.; Bonath, F.; Jimeno, S.; Prados-Carvajal, R.; Friedländer, M.R.; Huertas, P.; Visa, N. EXOSC10 Is Required for RPA Assembly and Controlled DNA End Resection at DNA Double-Strand Breaks. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2135.
- Richard, P.; Feng, S.; Manley, J.L. A SUMO-Dependent Interaction between Senataxin and the Exosome, Disrupted in the Neurodegenerative Disease AOA2, Targets the Exosome to Sites of Transcription-Induced DNA Damage. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 2227–2232.
- Ogami, K.; Chen, Y.; Manley, J.L. RNA Surveillance by the Nuclear RNA Exosome: Mechanisms and Significance. Noncoding RNA 2018, 4, 8.
- Kazadi, D.; Lim, J.; Rothschild, G.; Grinstein, V.; Laffleur, B.; Becherel, O.; Lavin, M.J.; Basu, U. Effects of Senataxin and RNA Exosome on B-Cell Chromosomal Integrity. Heliyon 2020, 6.
- Basu, U.; Meng, F.-L.; Keim, C.; Grinstein, V.; Pefanis, E.; Eccleston, J.; Zhang, T.; Myers, D.; Wasserman, C.R.; Wesemann, D.R.; et al. The RNA Exosome Targets the AID Cytidine Deaminase to Both Strands of Transcribed Duplex DNA Substrates. Cell 2011, 144, 353–363.
- Laffleur, B.; Lim, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Pefanis, E.; Bizarro, J.; Batista, C.R.; Wu, L.; Economides, A.N.; Wang, J.; et al. Noncoding RNA Processing by DIS3 Regulates Chromosomal Architecture and Somatic Hypermutation in B Cells. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 230–242.
- Kim, M.; Vasiljeva, L.; Rando, O.J.; Zhelkovsky, A.; Moore, C.; Buratowski, S. Distinct Pathways for SnoRNA and MRNA Termination. Mol. Cell 2006, 24, 723–734.
- West, S.; Gromak, N.; Proudfoot, N.J. Human 5′→3′ Exonuclease Xrn2 Promotes Transcription Termination at Co-Transcriptional Cleavage Sites. Nature 2004, 432, 522–525.
- Morales, J.C.; Richard, P.; Patidar, P.L.; Motea, E.A.; Dang, T.T.; Manley, J.L.; Boothman, D.A. XRN2 Links Transcription Termination to DNA Damage and Replication Stress. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12.
- Dang, T.T.; Morales, J.C. XRN2 Links RNA:DNA Hybrid Resolution to Double Strand Break Repair Pathway Choice. Cancers 2020, 12, 1821.
- Skourti-Stathaki, K.; Proudfoot, N.J.; Gromak, N. Human Senataxin Resolves RNA/DNA Hybrids Formed at Transcriptional Pause Sites to Promote Xrn2-Dependent Termination. Mol. Cell 2011, 42, 794–805.
- Hirling, H.; Scheffner, M.; Restle, T.; Stahl, H. RNA Helicase Activity Associated with the Human P68 Protein. Nature 1989, 339, 562–564.
- Xing, Z.; Wang, S.; Tran, E.J. Characterization of the Mammalian DEAD-Box Protein DDX5 Reveals Functional Conservation with S. Cerevisiae Ortholog Dbp2 in Transcriptional Control and Glucose Metabolism. RNA 2017, 23, 1125–1138.
- Mersaoui, S.Y.; Yu, Z.; Coulombe, Y.; Karam, M.; Busatto, F.F.; Masson, J.; Richard, S. Arginine Methylation of the DDX5 Helicase RGG/RG Motif by PRMT5 Regulates Resolution of RNA:DNA Hybrids. EMBO J. 2019, 38.
- Villarreal, O.D.; Mersaoui, S.Y.; Yu, Z.; Masson, J.-Y.; Richard, S. Genome-Wide R-Loop Analysis Defines Unique Roles for DDX5, XRN2, and PRMT5 in DNA/RNA Hybrid Resolution. Life Sci. Alliance 2020, 3.
- Gullà, A.; Hideshima, T.; Bianchi, G.; Fulciniti, M.; Kemal Samur, M.; Qi, J.; Tai, Y.-T.; Harada, T.; Morelli, E.; Amodio, N.; et al. Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 Has Prognostic Relevance and Is a Druggable Target in Multiple Myeloma. Leukemia 2018, 32, 996–1002.
- Bogliolo, M.; Surrallés, J. Fanconi Anemia: A Model Disease for Studies on Human Genetics and Advanced Therapeutics. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2015, 33, 32–40.
- Tischkowitz, M.D.; Hodgson, S.V. Fanconi Anaemia. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, 1–10.
- Alter, B.P.; Greene, M.H.; Velazquez, I.; Rosenberg, P.S. Cancer in Fanconi Anemia. Blood 2003, 101, 2072.
- Ceccaldi, R.; Sarangi, P.; D’Andrea, A.D. The Fanconi Anaemia Pathway: New Players and New Functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 337–349.
- Mamrak, N.E.; Shimamura, A.; Howlett, N.G. Recent Discoveries in the Molecular Pathogenesis of the Inherited Bone Marrow Failure Syndrome Fanconi Anemia. Blood Rev. 2017, 31, 93–99.
- García-Rubio, M.L.; Pérez-Calero, C.; Barroso, S.I.; Tumini, E.; Herrera-Moyano, E.; Rosado, I.V.; Aguilera, A. The Fanconi Anemia Pathway Protects Genome Integrity from R-Loops. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005674.
- Schwab, R.A.; Nieminuszczy, J.; Shah, F.; Langton, J.; Lopez Martinez, D.; Liang, C.-C.; Cohn, M.A.; Gibbons, R.J.; Deans, A.J.; Niedzwiedz, W. The Fanconi Anemia Pathway Maintains Genome Stability by Coordinating Replication and Transcription. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 351–361.
- Han, S.-S.; Tompkins, V.S.; Son, D.-J.; Han, S.; Yun, H.; Kamberos, N.L.; Dehoedt, C.L.; Gu, C.; Holman, C.; Tricot, G.; et al. CDKN1A and FANCD2 Are Potential Oncotargets in Burkitt Lymphoma and Multiple Myeloma. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 4, 9.
- Madireddy, A.; Kosiyatrakul, S.T.; Gerhardt, J.; Boisvert, R.A.; Vuono, E.A.; Moyano, E.H.; Garcia Rubio, M.L.; Owen, N.; Yan, Z.; Olson, S.; et al. FANCD2 Facilitates Replication through Common Fragile Sites. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 388–404.
- Liang, Z.; Liang, F.; Teng, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Longerich, S.; Rao, T.; Green, A.M.; Collins, N.B.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Binding of FANCI-FANCD2 Complex to RNA and R-Loops Stimulates Robust FANCD2 Monoubiquitination. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 564–572.e5.
- Liu, X.-P.; Yin, X.-H.; Meng, X.-Y.; Yan, X.-H.; Wang, F.; He, L. Development and Validation of a 9-Gene Prognostic Signature in Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 8, 615.
- Bohl, S.R.; Schmalbrock, L.K.; Bauhuf, I.; Meyer, T.; Dolnik, A.; Szyska, M.; Blätte, T.J.; Knödler, S.; Röhner, L.; Miller, D.; et al. Comprehensive CRISPR-Cas9 Screens Identify Genetic Determinants of Drug Responsiveness in Multiple Myeloma. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 2391–2402.
- Chang, E.Y.-C.; Tsai, S.; Aristizabal, M.J.; Wells, J.P.; Coulombe, Y.; Busatto, F.F.; Chan, Y.A.; Kumar, A.; Dan Zhu, Y.; Wang, A.Y.-H.; et al. MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 Promotes Fanconi Anemia R-Loop Suppression at Transcription–Replication Conflicts. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10.
- Wu, Y.; Shin-ya, K.; Brosh, R.M. FANCJ Helicase Defective in Fanconia Anemia and Breast Cancer Unwinds G-Quadruplex DNA To Defend Genomic Stability. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 4116–4128.
- London, T.B.C.; Barber, L.J.; Mosedale, G.; Kelly, G.P.; Balasubramanian, S.; Hickson, I.D.; Boulton, S.J.; Hiom, K. FANCJ Is a Structure-Specific DNA Helicase Associated with the Maintenance of Genomic G/C Tracts. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 36132–36139.
- Wu, C.G.; Spies, M. G-Quadruplex Recognition and Remodeling by the FANCJ Helicase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 8742–8753.
- Castillo Bosch, P.; Segura-Bayona, S.; Koole, W.; van Heteren, J.T.; Dewar, J.M.; Tijsterman, M.; Knipscheer, P. FANCJ Promotes DNA Synthesis through G-Quadruplex Structures. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 2521–2533.
- Cantor, S.; Drapkin, R.; Zhang, F.; Lin, Y.; Han, J.; Pamidi, S.; Livingston, D.M. The BRCA1-Associated Protein BACH1 Is a DNA Helicase Targeted by Clinically Relevant Inactivating Mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2357–2362.
- Odermatt, D.C.; Lee, W.T.C.; Wild, S.; Jozwiakowski, S.K.; Rothenberg, E.; Gari, K. Cancer-Associated Mutations in the Iron-Sulfur Domain of FANCJ Affect G-Quadruplex Metabolism. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16.
- Lowran, K.; Campbell, L.; Popp, P.; Wu, C.G. Assembly of a G-Quadruplex Repair Complex by the FANCJ DNA Helicase and the REV1 Polymerase. Genes 2019, 11, 5.
- Eddy, S.; Ketkar, A.; Zafar, M.K.; Maddukuri, L.; Choi, J.-Y.; Eoff, R.L. Human Rev1 Polymerase Disrupts G-Quadruplex DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 3272–3285.
- Ketkar, A.; Smith, L.; Johnson, C.; Richey, A.; Berry, M.; Hartman, J.H.; Maddukuri, L.; Reed, M.R.; Gunderson, J.E.C.; Leung, J.W.C.; et al. Human Rev1 Relies on Insert-2 to Promote Selective Binding and Accurate Replication of Stabilized G-Quadruplex Motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 2065–2084.
- Nalepa, G.; Clapp, D.W. Fanconi Anaemia and Cancer: An Intricate Relationship. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 168–185.
- Savage, K.I.; Matchett, K.B.; Barros, E.M.; Cooper, K.M.; Irwin, G.W.; Gorski, J.J.; Orr, K.S.; Vohhodina, J.; Kavanagh, J.N.; Madden, A.F.; et al. BRCA1 Deficiency Exacerbates Estrogen-Induced DNA Damage and Genomic Instability. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2773–2784.
- Yarde, D.N.; Oliveira, V.; Mathews, L.; Wang, X.; Villagra, A.; Boulware, D.; Shain, K.H.; Hazlehurst, L.A.; Alsina, M.; Chen, D.-T.; et al. Targeting the Fanconi Anemia/BRCA Pathway Circumvents Drug Resistance in Multiple Myeloma. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 9367–9375.
- Chen, Q.; Van der Sluis, P.C.; Boulware, D.; Hazlehurst, L.A.; Dalton, W.S. The FA/BRCA Pathway Is Involved in Melphalan-Induced DNA Interstrand Cross-Link Repair and Accounts for Melphalan Resistance in Multiple Myeloma Cells. Blood 2005, 106, 698–705.
- Volcic, M.; Karl, S.; Baumann, B.; Salles, D.; Daniel, P.; Fulda, S.; Wiesmüller, L. NF-ΚB Regulates DNA Double-Strand Break Repair in Conjunction with BRCA1–CtIP Complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 181–195.
- Demchenko, Y.N.; Kuehl, W.M. A Critical Role for the NFkB Pathway in Multiple Myeloma. Oncotarget 2010, 1, 59–68.
- Hatchi, E.; Skourti-Stathaki, K.; Ventz, S.; Pinello, L.; Yen, A.; Kamieniarz-Gdula, K.; Dimitrov, S.; Pathania, S.; McKinney, K.M.; Eaton, M.L.; et al. BRCA1 Recruitment to Transcriptional Pause Sites Is Required for R-Loop-Driven DNA Damage Repair. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 636–647.
- Hill, S.J.; Rolland, T.; Adelmant, G.; Xia, X.; Owen, M.S.; Dricot, A.; Zack, T.I.; Sahni, N.; Jacob, Y.; Hao, T.; et al. Systematic Screening Reveals a Role for BRCA1 in the Response to Transcription-Associated DNA Damage. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 1957–1975.
- Zhang, X.; Chiang, H.-C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Smith, S.; Zhao, X.; Nair, S.J.; Michalek, J.; Jatoi, I.; Lautner, M.; et al. Attenuation of RNA Polymerase II Pausing Mitigates BRCA1-Associated R-Loop Accumulation and Tumorigenesis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15908.
- Sessa, G.; Gómez-González, B.; Silva, S.; Pérez-Calero, C.; Beaurepere, R.; Barroso, S.; Martineau, S.; Martin, C.; Ehlén, Å.; Martínez, J.S.; et al. BRCA2 Promotes R-Loop Resolution by DDX5 Helicase at DNA Breaks to Facilitate Their Repair by Homologous Recombination. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e106018.
- Yu, Z.; Mersaoui, S.Y.; Guitton-Sert, L.; Coulombe, Y.; Song, J.; Masson, J.-Y.; Richard, S. DDX5 Resolves R-Loops at DNA Double-Strand Breaks to Promote DNA Repair and Avoid Chromosomal Deletions. NAR Cancer 2020, 2.
- Mailand, N.; Gibbs-Seymour, I.; Bekker-Jensen, S. Regulation of PCNA-Protein Interactions for Genome Stability. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 269–282.
- Alexandrakis, M.G.; Passam, F.H.; Pappa, C.A.; Dambaki, C.; Sfakiotaki, G.; Alegakis, A.K.; Kyriakou, D.S.; Stathopoulos, E. Expression of Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (PCNA) in Multiple Myeloma: Its Relationship to Bone Marrow Microvessel Density and Other Factors of Disease Activity. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2004, 17, 49–56.
- Tsirakis, G.; Pappa, C.A.; Kaparou, M.; Katsomitrou, V.; Hatzivasili, A.; Alegakis, T.; Xekalou, A.; Stathopoulos, E.N.; Alexandrakis, M.G. Assessment of Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen and Its Relationship with Proinflammatory Cytokines and Parameters of Disease Activity in Multiple Myeloma Patients. Eur. J. Histochem. 2011, 55, e21.
- Müller, R.; Misund, K.; Holien, T.; Bachke, S.; Gilljam, K.M.; Våtsveen, T.K.; Rø, T.B.; Bellacchio, E.; Sundan, A.; Otterlei, M. Targeting Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen and Its Protein Interactions Induces Apoptosis in Multiple Myeloma Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70430.
- Moldovan, G.-L.; Dejsuphong, D.; Petalcorin, M.I.R.; Hofmann, K.; Takeda, S.; Boulton, S.J.; D’Andrea, A.D. Inhibition of Homologous Recombination by the PCNA-Interacting Protein PARI. Mol. Cell 2012, 45, 75–86.
- Gali, H.; Juhasz, S.; Morocz, M.; Hajdu, I.; Fatyol, K.; Szukacsov, V.; Burkovics, P.; Haracska, L. Role of SUMO Modification of Human PCNA at Stalled Replication Fork. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 6049–6059.
- Li, M.; Xu, X.; Chang, C.-W.; Zheng, L.; Shen, B.; Liu, Y. SUMO2 Conjugation of PCNA Facilitates Chromatin Remodeling to Resolve Transcription-Replication Conflicts. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9.
- Xie, H.; Gu, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Ye, X.; Xin, C.; Lu, M.; Reddy, B.A.; Shu, P. Silencing of SENP2 in Multiple Myeloma Induces Bortezomib Resistance by Activating NF-ΚB Through the Modulation of IκBα Sumoylation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 766.
- Sartori, A.A.; Lukas, C.; Coates, J.; Mistrik, M.; Fu, S.; Bartek, J.; Baer, R.; Lukas, J.; Jackson, S.P. Human CtIP Promotes DNA End Resection. Nature 2007, 450, 509–514.
- Symington, L.S. Mechanism and Regulation of DNA End Resection in Eukaryotes. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 51, 195–212.
- Makharashvili, N.; Tubbs, A.T.; Yang, S.-H.; Wang, H.; Barton, O.; Zhou, Y.; Deshpande, R.A.; Lee, J.-H.; Lobrich, M.; Sleckman, B.P.; et al. Catalytic and Noncatalytic Roles of the CtIP Endonuclease in Double-Strand Break End Resection. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 1022–1033.
- Zhang, W.; Song, Y.; He, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yang, P.; Wang, J.; Hu, K.; Liu, W.; et al. Prognosis Value of RBBP8 Expression in Plasma Cell Myeloma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2020, 27, 22–29.
- Makharashvili, N.; Arora, S.; Yin, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wen, X.; Lee, J.-H.; Kao, C.-H.; Leung, J.W.; Miller, K.M.; Paull, T.T. Sae2/CtIP Prevents R-Loop Accumulation in Eukaryotic Cells. eLife 2018, 7.
- Keijzers, G.; Liu, D.; Rasmussen, L.J. Exonuclease 1 and Its Versatile Roles in DNA Repair. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 51, 440–451.
- Stroik, S.; Kurtz, K.; Lin, K.; Karachenets, S.; Myers, C.L.; Bielinsky, A.-K.; Hendrickson, E.A. EXO1 Resection at G-Quadruplex Structures Facilitates Resolution and Replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020.
- Dehé, P.-M.; Gaillard, P.-H.L. Control of Structure-Specific Endonucleases to Maintain Genome Stability. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 315–330.
- Tian, M.; Alt, F.W. Transcription-Induced Cleavage of Immunoglobulin Switch Regions by Nucleotide Excision Repair Nucleases in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 24163–24172.
- Sollier, J.; Stork, C.T.; García-Rubio, M.L.; Paulsen, R.D.; Aguilera, A.; Cimprich, K.A. Transcription-Coupled Nucleotide Excision Repair Factors Promote R-Loop-Induced Genome Instability. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 777–785.
- Cristini, A.; Ricci, G.; Britton, S.; Salimbeni, S.; Huang, S.N.; Marinello, J.; Calsou, P.; Pommier, Y.; Favre, G.; Capranico, G.; et al. Dual Processing of R-Loops and Topoisomerase I Induces Transcription-Dependent DNA Double-Strand Breaks. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 3167–3181.
- Yasuhara, T.; Kato, R.; Hagiwara, Y.; Shiotani, B.; Yamauchi, M.; Nakada, S.; Shibata, A.; Miyagawa, K. Human Rad52 Promotes XPG-Mediated R-Loop Processing to Initiate Transcription-Associated Homologous Recombination Repair. Cell 2018, 175, 558–570.e11.
- Lin, Y.-L.; Pasero, P. Caught in the Act: R-Loops Are Cleaved by Structure-Specific Endonucleases to Generate DSBs. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 721–722.
- de Larrea, C.F.; Navarro, A.; Tovar, N.; Pedrosa, F.; Díaz, T.; Cibeira, M.T.; Magnano, L.; Rosiñol, L.; Rovira, M.; Rozman, M.; et al. Impact of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Genes Involved in DNA Repair and Drug Metabolism On Survival After Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2012, 120, 2934.
- He, Y.; Pasupala, N.; Zhi, H.; Dorjbal, B.; Hussain, I.; Shih, H.-M.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Biswas, R.; Miljkovic, M.; Semmes, O.J.; et al. NF-ΚB–Induced R-Loop Accumulation and DNA Damage Select for Nucleotide Excision Repair Deficiencies in Adult T Cell Leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118.
- Ellis, N.A.; Groden, J.; Ye, T.Z.; Straughen, J.; Lennon, D.J.; Ciocci, S.; Proytcheva, M.; German, J. The Bloom’s Syndrome Gene Product Is Homologous to RecQ Helicases. Cell 1995, 83, 655–666.
- Sun, H.; Karow, J.K.; Hickson, I.D.; Maizels, N. The Bloom’s Syndrome Helicase Unwinds G4 DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 27587–27592.
- Popuri, V.; Bachrati, C.Z.; Muzzolini, L.; Mosedale, G.; Costantini, S.; Giacomini, E.; Hickson, I.D.; Vindigni, A. The Human RecQ Helicases, BLM and RECQ1, Display Distinct DNA Substrate Specificities. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 17766–17776.
- Wu, W.-Q.; Hou, X.-M.; Li, M.; Dou, S.-X.; Xi, X.-G. BLM Unfolds G-Quadruplexes in Different Structural Environments through Different Mechanisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 4614–4626.
- Chang, E.Y.-C.; Novoa, C.A.; Aristizabal, M.J.; Coulombe, Y.; Segovia, R.; Chaturvedi, R.; Shen, Y.; Keong, C.; Tam, A.S.; Jones, S.J.M.; et al. RECQ-like Helicases Sgs1 and BLM Regulate R-Loop–Associated Genome Instability. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 3991–4005.
- van Wietmarschen, N.; Merzouk, S.; Halsema, N.; Spierings, D.C.J.; Guryev, V.; Lansdorp, P.M. BLM Helicase Suppresses Recombination at G-Quadruplex Motifs in Transcribed Genes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9.
- Nguyen, G.H.; Tang, W.; Robles, A.I.; Beyer, R.P.; Gray, L.T.; Welsh, J.A.; Schetter, A.J.; Kumamoto, K.; Wang, X.W.; Hickson, I.D.; et al. Regulation of Gene Expression by the BLM Helicase Correlates with the Presence of G-Quadruplex DNA Motifs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9905–9910.
- Huppert, J.L.; Balasubramanian, S. Prevalence of Quadruplexes in the Human Genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2908–2916.
- Wu, W.; Rokutanda, N.; Takeuchi, J.; Lai, Y.; Maruyama, R.; Togashi, Y.; Nishikawa, H.; Arai, N.; Miyoshi, Y.; Suzuki, N.; et al. HERC2 Facilitates BLM and WRN Helicase Complex Interaction with RPA to Suppress G-Quadruplex DNA. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6371–6385.
- Rodriguez, R.; Müller, S.; Yeoman, J.A.; Trentesaux, C.; Riou, J.-F.; Balasubramanian, S. A Novel Small Molecule That Alters Shelterin Integrity and Triggers a DNA-Damage Response at Telomeres. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 15758–15759.
- Lai, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wu, W.; Rokutanda, N.; Togashi, Y.; Liang, W.; Ohta, T. HERC2 Regulates RPA2 by Mediating ATR-Induced Ser33 Phosphorylation and Ubiquitin-Dependent Degradation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9.
- Grierson, P.M.; Acharya, S.; Groden, J. Collaborating Functions of BLM and DNA Topoisomerase I in Regulating Human RDNA Transcription. Mutat. Res. 2013, 743, 89–96.
- Kassambara, A.; Herviou, L.; Ovejero, S.; Jourdan, M.; Thibaut, C.; Vikova, V.; Pasero, P.; Elemento, O.; Moreaux, J. RNA-Sequencing Data-Driven Dissection of Human Plasma Cell Differentiation Reveals New Potential Transcription Regulators. Leukemia 2021.
- Popuri, V.; Croteau, D.L.; Brosh, R.M.; Bohr, V.A. RECQ1 Is Required for Cellular Resistance to Replication Stress and Catalyzes Strand Exchange on Stalled Replication Fork Structures. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 4252–4265.
- Lu, X.; Parvathaneni, S.; Hara, T.; Lal, A.; Sharma, S. Replication Stress Induces Specific Enrichment of RECQ1 at Common Fragile Sites FRA3B and FRA16D. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 29.
- Cui, S.; Arosio, D.; Doherty, K.M.; Brosh, R.M.; Falaschi, A.; Vindigni, A. Analysis of the Unwinding Activity of the Dimeric RECQ1 Helicase in the Presence of Human Replication Protein A. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 2158–2170.
- Viziteu, E.; Klein, B.; Basbous, J.; Lin, Y.-L.; Hirtz, C.; Gourzones, C.; Tiers, L.; Bruyer, A.; Vincent, L.; Grandmougin, C.; et al. RECQ1 Helicase Is Involved in Replication Stress Survival and Drug Resistance in Multiple Myeloma. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2104–2113.
- Parvathaneni, S.; Lu, X.; Chaudhary, R.; Lal, A.; Madhusudan, S.; Sharma, S. RECQ1 Expression Is Upregulated in Response to DNA Damage and in a P53-Dependent Manner. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 75924–75942.
- Li, X.L.; Lu, X.; Parvathaneni, S.; Bilke, S.; Zhang, H.; Thangavel, S.; Vindigni, A.; Hara, T.; Zhu, Y.; Meltzer, P.S.; et al. Identification of RECQ1-Regulated Transcriptome Uncovers a Role of RECQ1 in Regulation of Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 2431–2445.
- Lu, X.; Parvathaneni, S.; Li, X.L.; Lal, A.; Sharma, S. Transcriptome Guided Identification of Novel Functions of RECQ1 Helicase. Methods 2016, 108, 111–117.
- Debnath, S.; Sharma, S. RECQ1 Helicase in Genomic Stability and Cancer. Genes 2020, 11, 622.
- Edwards, A.D.; Marecki, J.C.; Byrd, A.K.; Gao, J.; Raney, K.D. G-Quadruplex Loops Regulate PARP-1 Enzymatic Activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020.
- Bochman, M.L.; Sabouri, N.; Zakian, V.A. Unwinding the Functions of the Pif1 Family Helicases. DNA Repair 2010, 9, 237–249.
- Byrd, A.K.; Raney, K.D. A Parallel Quadruplex DNA Is Bound Tightly but Unfolded Slowly by Pif1 Helicase. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 6482–6494.
- Hou, X.-M.; Wu, W.-Q.; Duan, X.-L.; Liu, N.-N.; Li, H.-H.; Fu, J.; Dou, S.-X.; Li, M.; Xi, X.-G. Molecular Mechanism of G-Quadruplex Unwinding Helicase: Sequential and Repetitive Unfolding of G-Quadruplex by Pif1 Helicase. Biochem. J. 2015, 466, 189–199.
- Zhou, R.; Zhang, J.; Bochman, M.L.; Zakian, V.A.; Ha, T. Periodic DNA Patrolling Underlies Diverse Functions of Pif1 on R-Loops and G-Rich DNA. eLife 2014, 3, e02190.
- Dahan, D.; Tsirkas, I.; Dovrat, D.; Sparks, M.A.; Singh, S.P.; Galletto, R.; Aharoni, A. Pif1 Is Essential for Efficient Replisome Progression through Lagging Strand G-Quadruplex DNA Secondary Structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 11847–11857.
- Paeschke, K.; Capra, J.A.; Zakian, V.A. DNA Replication through G-Quadruplex Motifs Is Promoted by the Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Pif1 DNA Helicase. Cell 2011, 145, 678–691.
- Ribeyre, C.; Lopes, J.; Boulé, J.-B.; Piazza, A.; Guédin, A.; Zakian, V.A.; Mergny, J.-L.; Nicolas, A. The Yeast Pif1 Helicase Prevents Genomic Instability Caused by G-Quadruplex-Forming CEB1 Sequences In Vivo. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5.
- Sparks, M.A.; Singh, S.P.; Burgers, P.M.; Galletto, R. Complementary Roles of Pif1 Helicase and Single Stranded DNA Binding Proteins in Stimulating DNA Replication through G-Quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 8595–8605.
- Maestroni, L.; Audry, J.; Luciano, P.; Coulon, S.; Géli, V.; Corda, Y. RPA and Pif1 Cooperate to Remove G-Rich Structures at Both Leading and Lagging Strand. Cell Stress 2020, 4, 48–63.
- Safa, L.; Gueddouda, N.M.; Thiébaut, F.; Delagoutte, E.; Petruseva, I.; Lavrik, O.; Mendoza, O.; Bourdoncle, A.; Alberti, P.; Riou, J.-F.; et al. 5′ to 3′ Unfolding Directionality of DNA Secondary Structures by Replication Protein A. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 21246–21256.
- Salas, T.R.; Petruseva, I.; Lavrik, O.; Bourdoncle, A.; Mergny, J.-L.; Favre, A.; Saintomé, C. Human Replication Protein A Unfolds Telomeric G-Quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 4857–4865.
- Paeschke, K.; Bochman, M.L.; Garcia, P.D.; Cejka, P.; Friedman, K.L.; Kowalczykowski, S.C.; Zakian, V.A. Pif1 Family Helicases Suppress Genome Instability at G-Quadruplex Motifs. Nature 2013, 497, 458–462.
- Audry, J.; Maestroni, L.; Delagoutte, E.; Gauthier, T.; Nakamura, T.M.; Gachet, Y.; Saintomé, C.; Géli, V.; Coulon, S. RPA Prevents G-Rich Structure Formation at Lagging-Strand Telomeres to Allow Maintenance of Chromosome Ends. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 1942–1958.
- Chib, S.; Byrd, A.K.; Raney, K.D. Yeast Helicase Pif1 Unwinds RNA:DNA Hybrids with Higher Processivity than DNA:DNA Duplexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 5889–5901.
- Tran, P.L.T.; Pohl, T.J.; Chen, C.-F.; Chan, A.; Pott, S.; Zakian, V.A. PIF1 Family DNA Helicases Suppress R-Loop Mediated Genome Instability at TRNA Genes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8.
- Budd, M.E.; Choe, W.C.; Campbell, J.L. DNA2 Encodes a DNA Helicase Essential for Replication of Eukaryotic Chromosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 26766–26769.
- Budd, M.E.; Reis, C.C.; Smith, S.; Myung, K.; Campbell, J.L. Evidence Suggesting That Pif1 Helicase Functions in DNA Replication with the Dna2 Helicase/Nuclease and DNA Polymerase Delta. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 2490–2500.
- Masuda-Sasa, T.; Polaczek, P.; Peng, X.P.; Chen, L.; Campbell, J.L. Processing of G4 DNA by Dna2 Helicase/Nuclease and Replication Protein A (RPA) Provides Insights into the Mechanism of Dna2/RPA Substrate Recognition. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 24359–24373.
- Lin, W.; Sampathi, S.; Dai, H.; Liu, C.; Zhou, M.; Hu, J.; Huang, Q.; Campbell, J.; Shin-Ya, K.; Zheng, L.; et al. Mammalian DNA2 Helicase/Nuclease Cleaves G-Quadruplex DNA and Is Required for Telomere Integrity. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 1425–1439.
- Choe, W.; Budd, M.; Imamura, O.; Hoopes, L.; Campbell, J.L. Dynamic Localization of an Okazaki Fragment Processing Protein Suggests a Novel Role in Telomere Replication. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 4202–4217.
- Karanja, K.K.; Cox, S.W.; Duxin, J.P.; Stewart, S.A.; Campbell, J.L. DNA2 and EXO1 in Replication-Coupled, Homology-Directed Repair and in the Interplay between HDR and the FA/BRCA Network. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 3983–3996.
- Peng, G.; Dai, H.; Zhang, W.; Hsieh, H.-J.; Pan, M.-R.; Park, Y.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-L.; Bedrosian, I.; Lee, J.-S.; Ira, G.; et al. Human Nuclease/Helicase DNA2 Alleviates Replication Stress by Promoting DNA End Resection. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2802–2813.
- Daley, J.M.; Chiba, T.; Xue, X.; Niu, H.; Sung, P. Multifaceted Role of the Topo IIIα-RMI1-RMI2 Complex and DNA2 in the BLM-Dependent Pathway of DNA Break End Resection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 11083–11091.
- Palm, W.; de Lange, T. How Shelterin Protects Mammalian Telomeres. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 301–334.
- Zaug, A.J.; Podell, E.R.; Cech, T.R. Human POT1 Disrupts Telomeric G-Quadruplexes Allowing Telomerase Extension in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10864–10869.
- Gomez, D.; O’Donohue, M.-F.; Wenner, T.; Douarre, C.; Macadré, J.; Koebel, P.; Giraud-Panis, M.-J.; Kaplan, H.; Kolkes, A.; Shin-ya, K.; et al. The G-Quadruplex Ligand Telomestatin Inhibits POT1 Binding to Telomeric Sequences in vitro and Induces GFP-POT1 Dissociation from Telomeres in Human Cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6908–6912.
- Di Antonio, M.; Biffi, G.; Mariani, A.; Raiber, E.-A.; Rodriguez, R.; Balasubramanian, S. Selective RNA versus DNA G-Quadruplex Targeting by in Situ Click Chemistry. Angew. Chem. 2012, 51, 11073–11078.
- Ray, S.; Bandaria, J.N.; Qureshi, M.H.; Yildiz, A.; Balci, H. G-Quadruplex Formation in Telomeres Enhances POT1/TPP1 Protection against RPA Binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2990–2995.
- Chaires, J.B.; Gray, R.D.; Dean, W.L.; Monsen, R.; DeLeeuw, L.W.; Stribinskis, V.; Trent, J.O. Human POT1 Unfolds G-Quadruplexes by Conformational Selection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020.
- Paeschke, K.; Simonsson, T.; Postberg, J.; Rhodes, D.; Lipps, H.J. Telomere End-Binding Proteins Control the Formation of G-Quadruplex DNA Structures in Vivo. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 847–854.
- Panero, J.; Stanganelli, C.; Arbelbide, J.; Fantl, D.B.; Kohan, D.; García Rivello, H.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Slavutsky, I. Expression Profile of Shelterin Components in Plasma Cell Disorders. Clinical Significance of POT1 Overexpression. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2014, 52, 134–139.
- Venturutti, L.; Melnick, A.M. The Dangers of Déjà vu: Memory B Cells as the Cells of Origin of ABC-DLBCLs. Blood 2020, 136, 2263–2274.
- Rustad, E.H.; Yellapantula, V.; Leongamornlert, D.; Bolli, N.; Ledergor, G.; Nadeu, F.; Angelopoulos, N.; Dawson, K.J.; Mitchell, T.J.; Osborne, R.J.; et al. Timing the Initiation of Multiple Myeloma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11.





