
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aniket Ramshekar | + 1634 word(s) | 1634 | 2021-09-14 11:12:43 |
Video Upload Options
Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1) is an intracellular Rho GTPase that acts as a biologic switch in response to external stimuli. In studies testing the effects of age-related macular degeneration (AMD)-related stresses, activation of Rac1 was found to be necessary for choroidal endothelial cell invasion into the neural retina to form vision-threatening macular neovascularization. This entry summarizes the regulators of Rac1 activation, effectors of active Rac1 in choroidal endothelial cells, and mechanisms by which active Rap1, a Ras-like GTPase, may prevent active Rac1-mediated choroidal endothelial cell migration.
1. Introduction
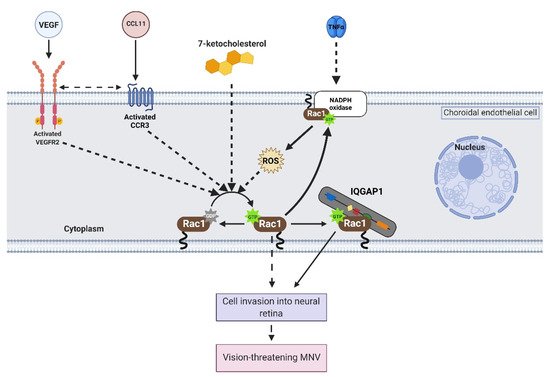
2. Activation of Rac1 GTPase in Endothelial Cells
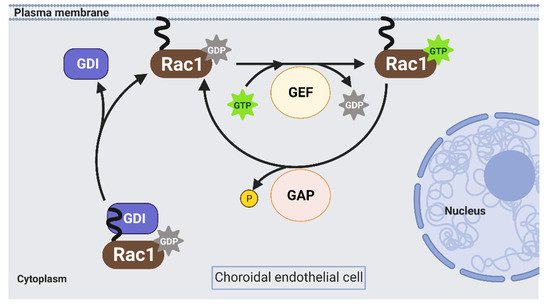
Rac1 is a Rho GTPases that cycles from an inactive GDP-bound form (Rac1GDP) to an active GTP-bound form (Rac1GTP) to transduce signaling in choroidal endothelial cells in response to different AMD-associated stresses (see Section 1). The biologic switch is primarily regulated by Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors (Rho GEFs), Rho GTPase activating proteins (Rho GAPs), and Rho GDP dissociation inhibitors (Rho GDIs) (Figure 2). However, current approaches to prevent Rac1 activation by targeting these primary regulators are inefficient [16][17]. Therefore, identifying alternative ways to regulate pathologic Rac1 activation is necessary.
3. Active Rac1-mediated signaling in choroidal endothelial cells
Once activated, Rac1 interacts with several effectors in choroidal endothelial cells to elicit signaling events that lead to migration. This entry will discuss two proteins that interact with active Rac1 in choroidal endothelial cells: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase (NOX) and IQ motif containing GTPase activating protein 1 (IQGAP1).
NOX1 and NOX2, isoforms of the NOX family, contain active Rac1 as a subunit. In choroidal endothelial cells, VEGF-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation was significantly reduced in cells transfected with Rac1 siRNA compared to control siRNA [9]. Pretreatment with diphenyleneiodonium, a NOX inhibitor, reduced VEGF-induced choroidal endothelial cell migration [9], and pretreatment with apocynin, a ROS quencher, reduced choroidal endothelial cell migration in response to VEGF [9] or TNFα [8]. These findings suggest that active Rac1 is an important subunit in NOX-generated ROS, which is required for choroidal endothelial cell migration in response to different AMD-related stresses. These results were corroborated in vivo using the murine laser-induced choroidal neovascularization (CNV) model, which recapitulates aspects of MNV observed in humans. C57/Bl6J mice treated with intravitreal apocynin compared to vehicle control had significantly reduced laser-induced CNV volume [9]. Also, laser-induced CNV volume was reduced in p47phox knockout (Ncf1−/−) mice compared to littermate wild-type mice [9]. Overall, the data suggest that NOX-mediated ROS generation is necessary for active Rac1-mediated choroidal endothelial cell migration and MNV by AMD-related stresses.
Another protein that interacts with active Rac1 in choroidal endothelial cells is IQ motif containing GTPase activating protein 1 (IQGAP1). IQGAP1 was identified in immunolabeled paraffin-embedded sections of human donor eyes at the region of neovascular lesions. Knockdown of IQGAP1 by siRNA reduced Rac1 activation and migration induced by VEGF. In the laser-induced CNV model, Iqgap1−/− mice had significantly reduced experimental CNV and reduced immunofluorescent of Rac1GTP within lectin-stained sections of CNV lesions compared to littermate Iqgap1+/+ mice [14]. Specifically, endothelial IQGAP1 knockout in mice by Cre recombinase-mediated recombination significantly reduced laser-induced CNV and immunofluorescent labeling of Rac1GTP within lectin-stained sections of CNV lesions compared to tamoxifen-treated littermate control mice that lacked Cre recombinase [13]. Taken together, the data suggest that IQGAP1 is necessary for Rac1 activation by AMD-associated stresses. On a molecular level, previous studies have found that the GAP-related domain (GRD) of IQGAP1 binds to active Rac1 and maintains Rac1 in its active state instead of accelerating the inactivation of Rac1 [18]. In support of this notion, choroidal endothelial cells transfected with an IQGAP1 construct that interfered with Rac1GTP binding IQGAP1 (IQ-MK24) had reduced Rac1 activation sustained by VEGF compared to choroidal endothelial cells transfected with control full-length IQGAP1 construct (IQ-WT) [14]. Overall, the data suggest that interfering with Rac1GTP binding to IQGAP1 might reduce pathologic choroidal endothelial cell activation, migration, and the development of vision-threatening MNV.
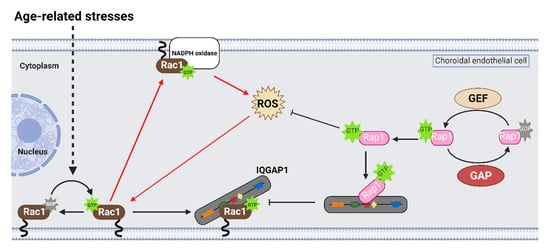
4. Active Rap1 antagonizes Rac1 Activation in Choroidal Endothelial Cells
Rap1 is a small, Ras-like GTPase that acts as a biologic switch similar to Rac1. Treatment with a pharmacologic activator of a Rap1 GEF, 8CPT-2’OME-cAMP (8CPT), significantly reduced choroidal endothelial cell transmigration across an RPE monolayer in the coculture assay, and intravitreal 8CPT administration reduced laser-induced CNV volume in the rodent laser-induced CNV models [8][13][19][20]. In cultured choroidal endothelial cells, 8CPT also increased Rap1 activation and reduced Rac1 activation by VEGF [13] or TNFα [8]. Furthermore, choroidal endothelial cells transduced with adenoviral vectors that expressed constitutively active Rap1a had significantly reduced VEGF-induced Rac1 activation, migration, and tube formation compared to choroidal endothelial cells transduced with control adenoviral vectors [13]. Furthermore, adenoviral transduction of active Rap1a significantly reduced Rac1 activation and ROS generation, measured by DCFDA fluorescence, induced by TNFα [8]. Taken together, the data suggest that activation of Rap1 antagonizes active Rac1-mediated choroidal endothelial cell migration and the development of MNV.
On a molecular level, studies have reported that active Rap1a binds to the IQ domain of IQGAP1 [21] and displaces effectors that bind to the other domains of IQGAP1 [22][23]. In support of this notion, choroidal endothelial cells transfected with a mutant construct with point mutations in the IQ domain that enhanced Rap1 interactions with IQGAP1 (IQ-3,4R) [54] had decreased Rac1 activation and active Rac1 binding to IQGAP1 induced by VEGF compared to choroidal endothelial cells transfected with control IQ-WT [13]. This finding suggested that active Rap1 antagonizes Rac1 activation by also interfering with Rac1GTP binding IQGAP1, a necessary step for sustained Rac1 activation (Figure 3).
References
- Wan Ling Wong; Xinyi Su; Xiang Li; Chui Ming Gemmy Cheung; Ronald Klein; Ching-Yu Cheng; Tien Yin Wong; Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet Global Health 2014, 2, e106-e116, 10.1016/s2214-109x(13)70145-1.
- M. Elizabeth Hartnett; Ann E. Elsner; Characteristics of Exudative Age-related Macular Degeneration Determined In Vivo with Confocal and Indirect Infrared Imaging. Ophthalmology 1995, 103, 58-71, 10.1016/s0161-6420(96)30731-8.
- Thomas S. Stevens; Neil M. Bressler; Maureen G. Maguire; Susan B. Bressler; Stuart L. Fine; Judith Alexander; Deborah A. Phillips; Raymond R. Margherio; Patrick L. Murphy; Andrew P. Schachat; et al. Occult Choroidal Neovascularization in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Archives of Ophthalmology 1997, 115, 345-350, 10.1001/archopht.1997.01100150347006.
- Richard F. Spaide; Glenn J. Jaffe; David Sarraf; K. Bailey Freund; Srinivas R. Sadda; Giovanni Staurenghi; Nadia K. Waheed; Usha Chakravarthy; Philip J. Rosenfeld; Frank G. Holz; et al.Eric H. SouiedSalomon Y. CohenGiuseppe QuerquesKyoko Ohno-MatsuiDavid BoyerAlain GaudricBarbara BlodiCaroline R. BaumalXiaoxin LiGabriel J. CoscasAlexander BruckerLawrence SingermanPhil LuthertSteffen Schmitz-ValckenbergUrsula Schmidt-ErfurthHans E. GrossniklausDavid J. WilsonRobyn GuymerLawrence A. YannuzziEmily Y. ChewKarl CsakyJordi M. MonésDaniel PauleikhoffRamin TadayoniJames Fujimoto Consensus Nomenclature for Reporting Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration Data. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 616-636, 10.1016/j.ophtha.2019.11.004.
- Glenn J. Jaffe; Gui-Shuang Ying; Cynthia A. Toth; Ebenezer Daniel; Juan E. Grunwald; Daniel F. Martin; Maureen G. Maguire; Macular Morphology and Visual Acuity in Year Five of the Comparison of Age-related Macular Degeneration Treatments Trials. Ophthalmology 2018, 126, 252-260, 10.1016/j.ophtha.2018.08.035.
- Pete Geisen; Janet R. McColm; Bradley M. King; M. Elizabeth Hartnett; Characterization of Barrier Properties and Inducible VEGF Expression of Several Types of Retinal Pigment Epithelium in Medium-Term Culture. Current Eye Research 2005, 31, 739-748, 10.1080/02713680600837408.
- Lynda J. Peterson; Erika S. Wittchen; Pete Geisen; Keith Burridge; M. Elizabeth Hartnett; Heterotypic RPE-choroidal endothelial cell contact increases choroidal endothelial cell transmigration via PI 3-kinase and Rac1. Experimental Eye Research 2007, 84, 737-744, 10.1016/j.exer.2006.12.012.
- Haibo Wang; Lori Fotheringham; Erika S. Wittchen; M. Elizabeth Hartnett; Rap1 GTPase Inhibits Tumor Necrosis Factor-α–Induced Choroidal Endothelial Migration via NADPH Oxidase– and NF-κB–Dependent Activation of Rac1. The American Journal of Pathology 2015, 185, 3316-3325, 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.08.017.
- Elizabeth Monaghan-Benson; John Hartmann; Aleksandr E. Vendrov; Steve Budd; Grace Byfield; Augustus Parker; Faisal Ahmad; Wei Huang; Marschall Runge; Keith Burridge; et al.Nageswara MadamanchiM. Elizabeth Hartnett The Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Induced Activation of NADPH Oxidase in Choroidal Endothelial Cells and Choroidal Neovascularization. The American Journal of Pathology 2010, 177, 2091-2102, 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090878.
- Haibo Wang; Pete Geisen; Erika S. Wittchen; Bradley King; Keith Burridge; Patricia A. D'amore; M. Elizabeth Hartnett; The Role of RPE Cell-Associated VEGF189in Choroidal Endothelial Cell Transmigration across the RPE. Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science 2010, 52, 570-578, 10.1167/iovs.10-5595.
- Haibo Wang; Xiaokun Han; Eric Kunz; M. Elizabeth Hartnett; Thy-1 Regulates VEGF-Mediated Choroidal Endothelial Cell Activation and Migration: Implications in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science 2016, 57, 5525-5534, 10.1167/iovs.16-19691.
- Haibo Wang; Erika S. Wittchen; Yanchao Jiang; Balamurali Ambati; Hans E. Grossniklaus; M. Elizabeth Hartnett; Upregulation of CCR3 by Age-Related Stresses Promotes Choroidal Endothelial Cell Migration via VEGF-Dependent and -Independent Signaling. Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science 2011, 52, 8271-8277, 10.1167/iovs.11-8230.
- Aniket Ramshekar; Haibo Wang; Eric Kunz; Christian Pappas; Gregory S. Hageman; Brahim Chaqour; David B. Sacks; M. Elizabeth Hartnett; Active Rap1‐mediated inhibition of choroidal neovascularization requires interactions with IQGAP1 in choroidal endothelial cells. The FASEB Journal 2021, 35, e21642, 10.1096/fj.202100112r.
- Haibo Wang; Aniket Ramshekar; Eric Kunz; David B. Sacks; M. Elizabeth Hartnett; IQGAP1 causes choroidal neovascularization by sustaining VEGFR2-mediated Rac1 activation. Angiogenesis 2020, 23, 1-14, 10.1007/s10456-020-09740-y.
- Haibo Wang; Aniket Ramshekar; Eric Kunz; M. Elizabeth Hartnett; 7-ketocholesterol induces endothelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes fibrosis: implications in neovascular age-related macular degeneration and treatment. Angiogenesis 2021, 24, 583-595, 10.1007/s10456-021-09770-0.
- Hemant Kumar Bid; Ryan Roberts; Parmeet Kaur Manchanda; Peter J. Houghton; RAC1: An Emerging Therapeutic Option for Targeting Cancer Angiogenesis and Metastasis. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics 2013, 12, 1925-1934, 10.1158/1535-7163.mct-13-0164.
- Gabriele Bergers; Laura E. Benjamin; Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nature Reviews Cancer 2003, 3, 401-410, 10.1038/nrc1093.
- Shinya Kuroda; Masaki Fukata; Kenta Kobayashi; Masato Nakafuku; Nobuo Nomura; Akihiro Iwamatsu; Kozo Kaibuchi; Identification of IQGAP as a Putative Target for the Small GTPases, Cdc42 and Rac1. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1996, 271, 23363-23367, 10.1074/jbc.271.38.23363.
- Erika S. Wittchen; Eiichi Nishimura; Manabu McCloskey; Haibo Wang; Lawrence A. Quilliam; Magdalena Chrzanowska-Wodnicka; M. Elizabeth Hartnett; Rap1 GTPase Activation and Barrier Enhancement in RPE Inhibits Choroidal Neovascularization In Vivo. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e73070, 10.1371/journal.pone.0073070.
- Jiajia Li; Rong Zhang; Caixia Wang; Xin Wang; Man Xu; Jingxue Ma; Qingli Shang; Activation of the Small GTPase Rap1 Inhibits Choroidal Neovascularization by Regulating Cell Junctions and ROS Generation in Rats. Current Eye Research 2018, 43, 934-940, 10.1080/02713683.2018.1454477.
- Ha-Won Jeong; Zhigang Li; Matthew D. Brown; David Sacks; IQGAP1 Binds Rap1 and Modulates Its Activity. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2007, 282, 20752-20762, 10.1074/jbc.m700487200.
- Colin D. White; Huseyin H. Erdemir; David B. Sacks; IQGAP1 and its binding proteins control diverse biological functions. Cellular Signalling 2012, 24, 826-834, 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.12.005.
- Subramaniam Malarkannan; Aradhana Awasthi; Kamalakannan Rajasekaran; Pawan Kumar; Kristina M. Schuldt; Allison Bartoszek; Niranjan Manoharan; Nicholas Goldner; Colleen M. Umhoefer; Monica S. Thakar; et al. IQGAP1: A Regulator of Intracellular Spacetime Relativity. The Journal of Immunology 2012, 188, 2057-2063, 10.4049/jimmunol.1102439.




