2. Development and Findings
In this study, we demonstrated that nutritionally adequate diets, which align with the maximum tolerable diet-related GHGE limit defined to keep the increase in global average temperatures below 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels, can be achieved for four different dietary patterns. Simply modifying the current diet of Swedish adolescents to meet DRV values resulted in a 39% decrease in GHGE, which was mainly achieved by a pronounced reduction in solid dairy foods (cheese and curd) and meat. Relative to the baseline diet, the GHGE in the nutritionally adequate pescatarian model (“Pesc”) was reduced by 59%, by 62% in the vegetarian model (“Veg”) and by 73% in the vegan (“Plant”) model. The amount of CO
2eq in the baseline diet of the adolescents was 4.5 kg/day, a value that is comparable to the ~5 kg CO
2eq/day previously reported for adults
[15]. This means that in order to reach the threshold of 1.57 kg CO
2eq/day proposed by the WWF
[27], the GHGE had to be reduced by 65%
[26][28]. Only the optimized, nutritionally adequate vegan diet (“Plant”) dropped below the IPCC/WWF threshold without further active restriction of the model’s GHGE. The exclusion of food groups in the pescatarian, vegetarian and vegan diets along with constraining the GHGE increased the deviation from the baseline diet, especially for the optimized vegetarian and vegan models as compared to the omnivoric or pescatarian solutions. The optimized diets, despite being nutritionally adequate and reaching the recommended GHGE level, did not align very well with the food-group pattern of the EAT-Lancet diet
[5].
Constraining the reported food intake to meet the DRVs alone resulted in a marked reduction of GHGE, which is in line with previous findings
[26][29]. However, the 39% reduction in GHGE achieved in the “Omni” diet is surprisingly high compared to previous studies in UK adults where the reduction was 17%
[29]. This can be explained mainly by the DRV-enforced reduction of saturated fatty acids and sodium as well as the increased inclusion of foods that are rich in fiber and polyunsaturated fatty acids. These changes increase the share of plant-based foods with a low climate impact at the expense of animal-based foods, the consumption of which is comparably high in this sub-population
[16].
The climate-friendly and nutritionally adequate food profile for omnivores (“Omni+”), which mimics the dietary habits of Swedish adolescents the best, showed a more pronounced trend towards reduction of meat, poultry, and solid dairy than the non-GHGE-constrained alternative (“Omni”). This reduction was compensated by an increase in the amounts of less GHGE-intense animal products such as eggs, but a major part of the substitution was based on an increased inclusion of pulses, potatoes, and bread.
Table 1 summarizes the optimized solution of the “Omni+” diet. Others have also calculated climate-friendly diets for the general population
[5][30], but without ensuring nutritional adequacy.
Table 1. Quantities of food groups for an omnivorous diet with 2410 kcal, generating a maximum of 1571 g of CO2eq/day, based on the “Omni+” model.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
Around one portion (~190 g) of meat, meat dishes and poultry per week (preferably pork, poultry, and offal such as liver and blood products rather than beef)
|
|
|
|
|
In the pescatarian model (“Pesc+”), the optimized solution is very similar to that of the omnivore diet (“Omni+”), except that meat and meat products are replaced by moderately increased amounts of fish, meat substitutes, and dairy products (
Table S3). Both the omnivorous and the pescatarian diets include increased amounts of fish compared to the baseline diet. Presently, a large part of the fish consumed originates from marine capture fisheries
[31], which explains the low CO
2eq-value of this micronutrient- and protein-rich commodity. However, 96 of the world’s fish stocks are either moderately or fully exploited, or over-fished
[32]. Farmed fish such as salmon has GHGE values comparable to or even higher than that of poultry, pork and dairy and can in addition be a source of eutrophication
[33]. If a high proportion of the population follows the recommendation to increase the intake of farmed or captured fish, the biodiversity of certain fish types should be considered in addition to their production-related climate impacts.
The climate-friendly solution for vegetarians includes considerably increased amounts of dairy and meat substitutes (which are mostly mycoprotein-, pea- or soy-based products), pulses, bread, potatoes, and some vegetables to compensate for excluding meat and fish. Vegetarian diets have been recommended as a principal approach to reduce the climate impact of the diet, though again, these are not based on calculations that ensure full nutritional adequacy
[34][35][36] and may increase the risk of micronutrient deficiencies. For example, one third of Swedish female adolescents have low iron stores
[17]. Excluding meat and fish from the diet may result in lower iron intakes as well as in a diet with a lower iron bioavailability. Haem iron, found in meat, is more readily absorbed than non-haem varieties. Furthermore, meat and fish enhances absorption of iron from plant-based foods
[37]. Absence of haem iron in the diet may affect iron status negatively in vulnerable populations and highlights the need for reliable guidance on what to replace meat with and how to combine foods to increase bioavailability
[38]. Therefore, in the optimized diets building on the Veg, Veg+, and Plant models, a higher minimum threshold of iron was set as recommended by the US Institute of Medicine
[39]. The high bioavailability of ferritin-bound iron in legumes may also help to overcome this shortcoming
[40].
Excluding all animal products in the ”Plant” model resulted in a considerable inclusion of (mostly fortified) meat and dairy substitutes along with an increased intake of pulses, potatoes and non-dairy fats. Although plant-based foods are considered to have a low bioavailability of iron, calcium, vitamin D and B12 and although the minimum threshold was raised for iron, all applied DRV values were covered by the optimized solution for vegans. Besides iron, a sufficient supply of calcium and vitamin B12 was also guaranteed even for the vegetarians and vegans. This was primarily achieved due to the high fortification of dairy replacements with these micronutrients. These results mirror a recent optimization study on Dutch eating habits, where the optimized diet for vegans met DRVs for vitamin B12 and calcium only through the inclusion of sufficiently high amounts of fortified soy milk
[41]. This raises the question as to whether fortification or, alternatively, supplementation are acceptable ways forward to reduce diet-related GHGE. More studies on replacement food, fortification, and health outcomes are clearly needed. Furthermore, the production of meat and dairy replacements raises concerns about other environmental indicators. For example, plant-based milk replacements may contribute to water scarcity, deforestation and biodiversity loss
[42], although this may vary depending on type of product and country. Further investigations are needed to fully understand how the “Veg+”- and “Plant” diets would impact the full range of health and environmental indicators in the context under study.
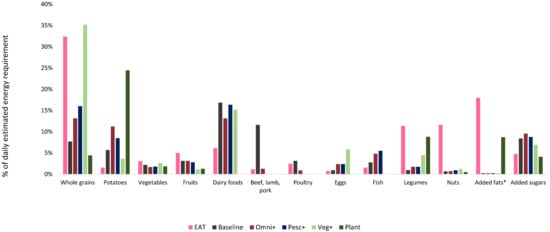
As is evident from
Figure 1, the optimized “Plant” diet contained the lowest amount of whole grains and the highest amount of potatoes. Furthermore, the amount of vegetables (excluding legumes), fruits and nuts was comparably low. This food pattern differs somewhat from other recommendations on plant-based diets. For example, recent recommendations on plant-based diets for adolescents
[43] emphasize the inclusion of whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds, vegetables, and fruits to the diet. These differences are likely to result from the fact that environmental aspects have so far insufficiently been considered in the development of food-based recommendations. Studies show that the increased inclusion of fruit and vegetables in the diet, although beneficial from a health point of view, can lead to higher environmental impacts
[6][7][8][44], or be less effective in reducing them
[45]. Furthermore, diets optimized to meet nutritional constraints only
[46][47] have been shown to have higher climate footprints. On the other hand, self-selected, plant-based diets with lower climate footprints have been shown to lead to the overconsumption of refined sugars
[14][15]. This stands in contrast to the optimized “Plant” model, that had the lowest amounts of added sugars. In summary, these findings add to the challenges in defining the sustainability of diets. It is, therefore, advisable to use a holistic approach such as linear programming (that consider both health and environmental priorities) in the definition of food-based recommendations for different dietary patterns.
Figure 1. Comparison between the EAT-Lancet diet and (baseline and optimized) diets of Swedish Adolescents. Columns represent the percent of the daily estimated energy requirement for different food groups in the EAT-Lancet diet, the observed (baseline) diet, and in the four main optimized diets (“Omni+”, “Pesc+”, “Veg+”, ”Plant”). Food categories used in this comparison were based on the ones used for the EAT-Lancet diet
[5]; * Added fats exclude dairy-based fats (such as butter), which are included in “Dairy foods”.
Our findings reveal that neither the baseline nor the optimized diets of Swedish adolescents align with the EAT-Lancet Commission’s dietary recommendation for a sustainable diet
[5]. This could be due to three reasons: (1) we optimized for similarity to the reported food consumption patterns of Swedish adolescents to achieve a high cultural acceptability instead of using the EAT-Lancet diet as the reference; (2) our models were all constrained to ensure the fulfilment of 27 DRVs, which the EAT-Lancet diet was not; (3) the EAT-Lancet diet considered additional dimensions of sustainability such as blue water footprint, land use change and animal welfare, which were not considered in the study at hand. In contrast to the EAT-Lancet diet, the models “Omni” and “Omni+” include significant amounts of dairy, fish, and eggs. Another difference is the much higher amount of potatoes and a markedly lower amount of legumes in the optimized diets as compared to the EAT-Lancet diet. Potatoes, commonly consumed in the Swedish adolescent population, are a dominant and nutritious staple-crop in Sweden considered to be healthy
[48]. Although all optimized diets diverged from the EAT diet, the Veg+ diet was the most similar on a food group level.
Despite the discrepancies, some similarities between the EAT diet and the optimized diets can be found. For example, the optimized vegetarian diet (“Veg+”) matched it with respect to Whole grains and Vegetables and the optimized vegan (“Plant”) diet was comparable in terms of Legumes and Added sugars. Furthermore, like the EAT-Lancet diet, both Omni models suggest a comparable amount of red meat and poultry to achieve a nutritious and climate-friendly diet. In contrast to the EAT-Lancet diet
[5], our diets optimized for similarity may be easier to achieve for adolescents in the Swedish population.
Food-based dietary guidelines (FBDGs) were not considered as constraints in the optimizations. Today, the Nordic Nutrition Recommendations has quantifiable FBDG regarding fruit and vegetables (500 g/day) and fish (2–3 times per week)
[49]. Only the “Plant” model met the Swedish FBDGs’ recommended intake of 500 g fruits and vegetables (including pulses) per day. The LP algorithm in general did not favor either fruits or vegetables which can be explained by the fact that fruits and certain types of vegetables (such as tomatoes, cucumbers, and onions) may provide smaller amounts of nutrients per gram of CO
2eq compared to other foods such as starchy vegetables and pulses. It thus mirrors research showing that a generous inclusion of fruit and vegetables into the diet can result in higher dietary environmental impacts
[6][7][8]. Another plausible explanation is that our solutions were optimized to be as similar as possible to the baseline diet, where the intake of fruit and vegetables was relatively low. This finding aligns well with findings from the Netherlands, Denmark, and Estonia, where nutritionally adequate diets optimized for acceptability did not meet national FBDG-targets for fruit and vegetables
[50][41][51].
One strength of our research is that it highlights the potential of optimized diets, such as those achieved in this study, to be translated into sustainable food-based dietary guidelines. However, for this to happen, other scientific evidence such as the impact on additional environmental factors (blue water usage, land use change, and biodiversity) and other legitimate factors (food safety) must also be considered. Furthermore, additional detailed information may be necessary to be included such as the prioritization of local vs. imported products. Further adaptation towards individual needs may also be necessary before formulating food-based dietary guidelines with support from linear optimization.
Future modeling studies should investigate the feasibility and need for including both DRVs and FBDG in the models as well as aspects on food safety and other environmental aspects such as biodiversity, pollutants, blue water use.
The GHGE values indicated include only the CO2eq to the factory gate, but not the GHGE associated with transportation to the retailer and to the home or food preparation. Therefore, the final CO2eq values from different foods might be slightly higher than those calculated in this study.
As the data were recorded in 2016–2017, dietary habits might have changed moderately since then. Furthermore, all optimized diets cover the estimated micronutrient intake of 97.5% of the population. This may be unnecessarily high when using the suggested diets to fulfill average intakes for population groups but guarantees on the other hand the applicability of the optimized diets also for individuals. Another limitation was that no new foods were introduced into the models. There are many new meat and dairy substitutes emerging on the market
[52][53]. Including these foods in the optimization of diets could provide certain benefits for the environment without compromising nutritional adequacy
[54]. Future studies should further explore the health impacts and environmental effects of also including such foods in the modeling. Since the dietary survey data was averaged, data on the food intake of pescatarians, vegetarians and vegans were not available during optimization. Therefore, the optimization may also be limited for the groups of pescatarians, vegetarians and vegans, as the reported omnivore diet was used as reference. In the case of optimized non-omnivoric diets, the RD represents the deviation after changing to a pescatarian, vegetarian or vegan diet. It is not representative of individuals who already practice these diets.
One of the strengths of this study is that it provides the first guidance for achieving more climate-friendly diets based on the dominating omnivoric dietary pattern of adolescents in Sweden. The results feed into the discussion on how future FBDGs should be shaped. Since comprehensive fiscal measures such as taxes and subsidies to influence on people’s food choices are currently not promoted by decision makers in Sweden, information and nudging may be the obvious policy tool available to affect consumer behavior
[55]. Therefore, it is critical that messages are simple and clear, yet still sufficiently informative to avoid unintended substitutions and adverse outcomes
[18].